Study on Nutritional Knowledge, Attitude and Behavior of Chinese School Football Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Tools
2.3. Survey Process
2.4. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
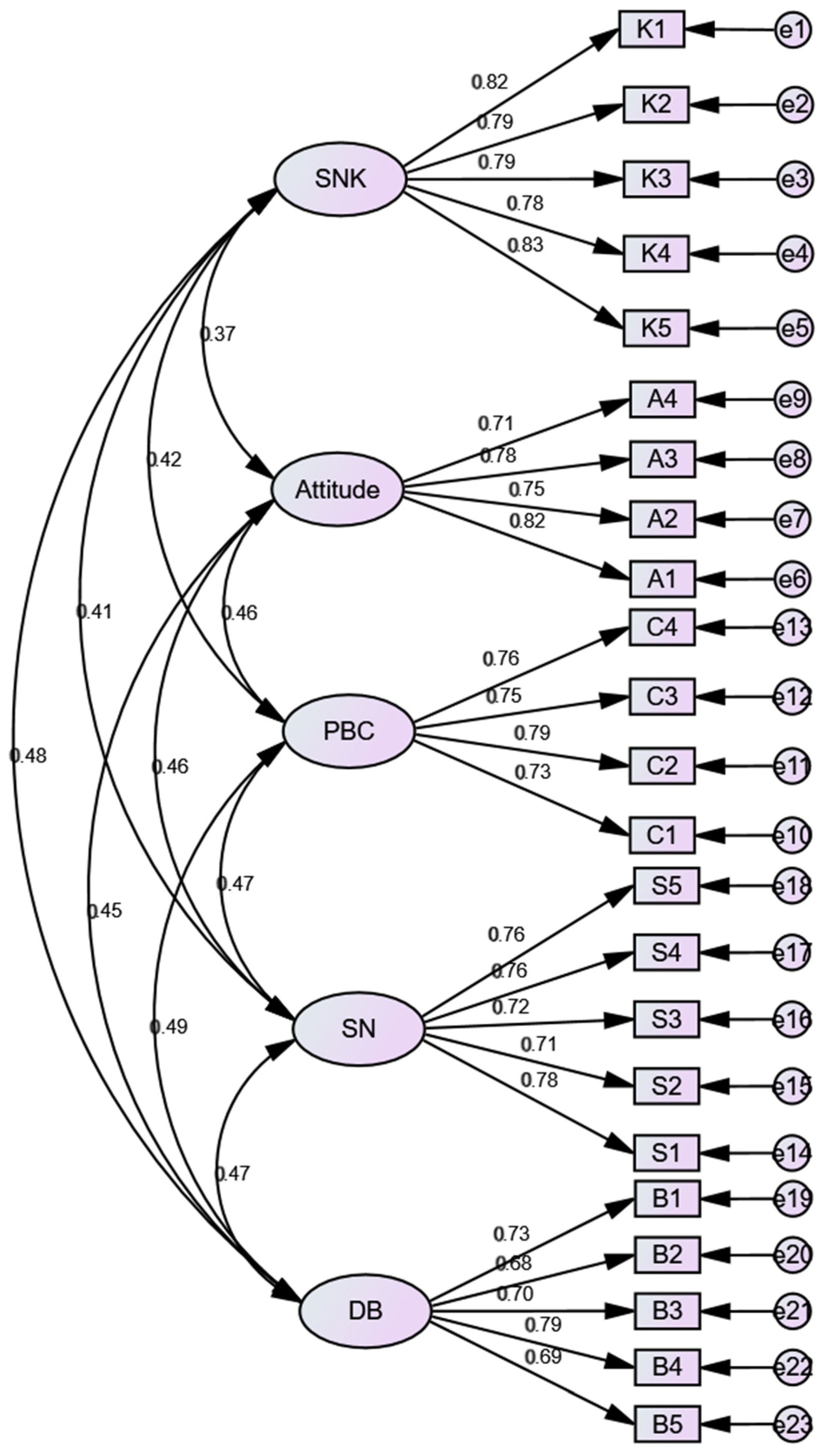
3.1. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
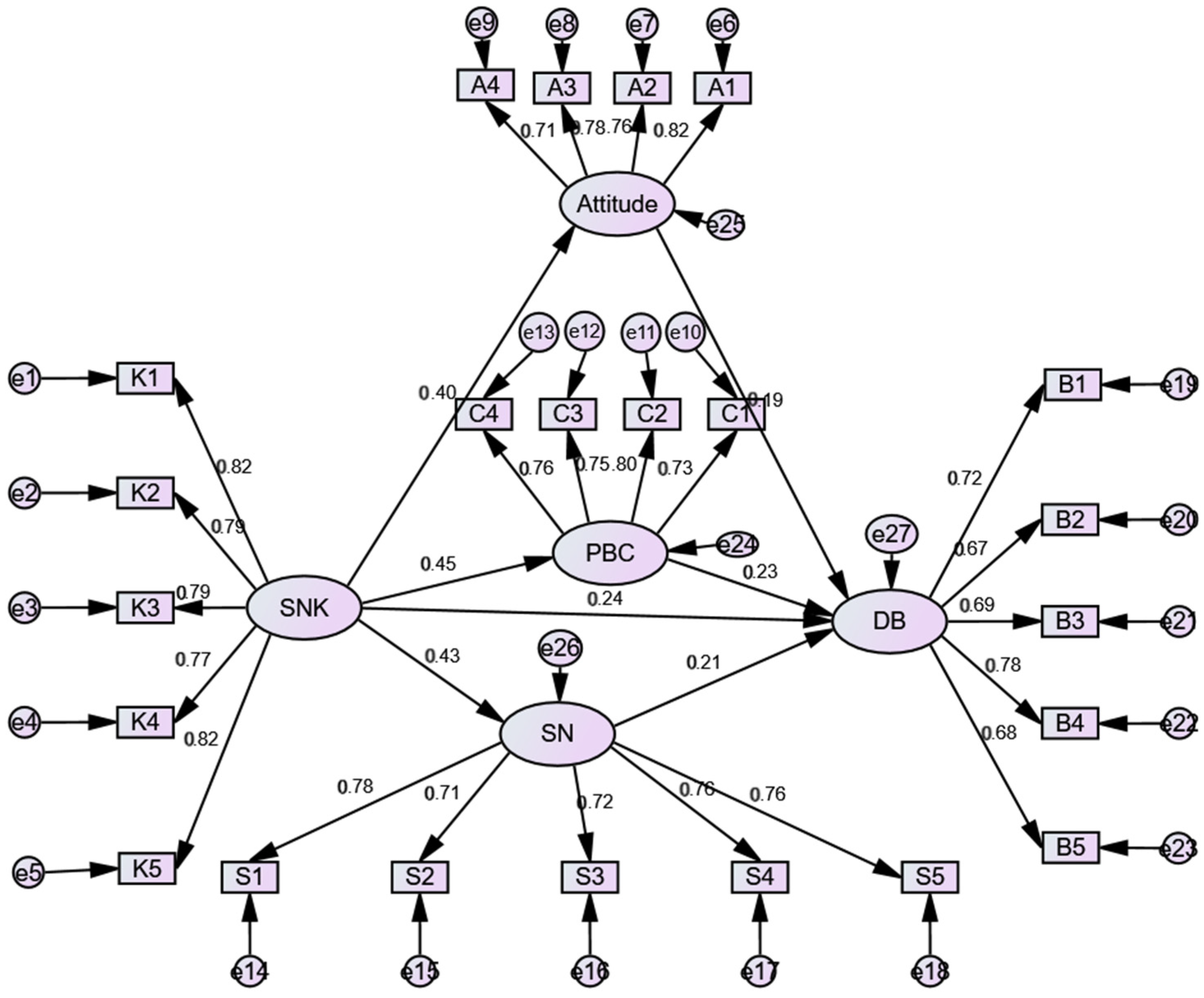
3.2. Structural Equation Model
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Sports nutrition knowledge can affect the attitude toward sports nutrition (H1).
- (2)
- Sports nutrition knowledge can affect dietary behavior (H2).
- (3)
- Sports nutrition knowledge can affect subjective norms (H3).
- (4)
- Sports nutrition knowledge can affect perceived behavioral control (H4).
- (5)
- Subjective norms can affect dietary behavior (H5).
- (6)
- Perceived behavioral control could affect dietary behavior (H6).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, K. The dilemma of school sports governance in China in the context of deepening the integration of sports and education and the path selection. J. Tianjin Inst. Phys. Educ. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Kong, N.-X.; Gong, H.-P.; Hu, Y.-J. A new direction for the integration of sports and education: Youth health promotion and sports reserve talent training. Sport Sci. 2020, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y. On the connotation concept and implementation path of integration of sports and education in the new era. J. Tianjin Inst. Phys. Educ. 2020, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, H. Exploring the basic issues of deepening the development of school football in the context of “integration of sports and education. Sport Res. Educ. 2021, 36, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, Z. The optimization path of Chinese youth football tournament system in the context of integration of sports and education. J. Shanghai Inst. Phys. Educ. 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Notice of Action Plan for the Construction of the Eight Major Systems of National Youth Campus Football. 2020. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-09/27/content_5547544.htm (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Peng, Q.; Skinner, J.; Houlihan, B. An analysis of the Chinese Football Reform of 2015: Why then and not earlier? Int. J. Sport Policy Politics 2019, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, T.; Gilbourne, D. Science and football: A review of applied research in the football codes. J. Sport. Sci. 2003, 21, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, C.A.; Jonnalagadda, S.S.; Skinner, R. Nutrition knowledge of collegiate athletes in a Division I National Collegiate Athletic Association institution. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2002, 102, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbrow, B.; McCormack, J.; Burke, L.M.; Cox, G.R.; Fallon, K.; Hislop, M.; Logan, R.; Marino, N.; Sawyer, S.M.; Shaw, G. Sports Dietitians Australia position statement: Sports nutrition for the adolescent athlete. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 24, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmansyah, A.; Prasetya, M.R.A. The nutrition needs of adolescent athletes: A systematic review. J. SPORTIF J. Penelit. Pembelajaran 2021, 7, 400–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenhead, K.L.; Slater, G. A review of factors influencing athletes’ food choices. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiar, M.; Masud-ur-Rahman, M.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Sultana, N.; Rahman, S.S. Determinants of nutrition knowledge, attitude and practices of adolescent sports trainee: A cross-sectional study in Bangladesh. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, S.; O’Connor, H.; Michael, S.; Gifford, J.; Naughton, G. Nutrition knowledge in athletes: A systematic review. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luszczynska, A.; Sutton, S. Attitudes and expectations. In ABC of Behavior Change; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2005; pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, B.; Batchelor, P.; Treasure, E.; Watt, R. Essential Dental Public Health; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, K.; Comerford, T.; Deavin, N.; Walton, K. Characteristics of successful primary school-based experiential nutrition programmes: A systematic literature review. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 4642–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessen, J.P.; Bates, S.; Sherlock, K.; Seeparsand, F.; Wright, R. Designing interventions to improve tooth brushing. Int. Dent. J. 2008, 58, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. From Intentions to Actions: A Theory of Planned Behavior. In Action Control from Cognition to Behavior; Kuhl, J., Beckmann, J., Eds.; Action Control. SSSP Springer Series in Social Psychology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 11–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. EBOOK: Attitudes, Personality and Behaviour; McGraw-Hill Education: Maidenhead, UK, 2005; pp. 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bandura, A.; Walters, R.H. Social Learning Theory; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1977; Volume 1, pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tolvanen, M.; Lahti, S.; Miettunen, J.; Hausen, H. Relationship between oral health-related knowledge, attitudes and behavior among 15–16-year-old adolescents—A structural equation modeling approach. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2012, 70, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, C.J.H.; Burns, S.F.; Kawabata, M. Developing Nutrition Knowledge and Attitude Measures for Athletes with the Knowledge–Attitude–Behavior Model. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, K.Z.; Fan, S.; Gao, H. Changing Chinese diets to achieve a win-win solution for health and the environment. China World Econ. 2021, 29, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Hunter, J.E. Attitude-behavior relations: A meta-analysis of attitudinal relevance and topic. J. Commun. 1993, 43, 101–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior: Frequently asked questions. Hum. Behav. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 2, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N. Factor analysis as a tool for survey analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2021, 9, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, M.S. Application of Structural Equation Modeling in Educational Research and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, R.O.; Hancock, G.R. Structural equation modeling. In The Reviewer’s Guide to Quantitative Methods in the Social Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 445–456. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Lin, B. Principles and Applications of Structural Equation Modeling; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Rönkkö, M.; Cho, E. An updated guideline for assessing discriminant validity. Organ. Res. Methods 2022, 25, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Structural equation modeling. In Models and Methods for Management Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 363–381. [Google Scholar]
- Javadi, M.H.M.; Dolatabadi, H.R.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Poursaeedi, A.; Asadollahi, A.R. An analysis of factors affecting on online shopping behavior of consumers. Int. J. Mark. Stud. 2012, 4, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contento, I.R. Nutrition education: Linking research, theory, and practice. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, T.L.; Zimmerman, B.J. Social Learning and Cognition; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, B.; Dinsdale, A.; Jones, B.; Till, K. The training of short distance sprint performance in football code athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 1179–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Num |
|---|---|
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | 5 |
| Attitude | 4 |
| Perceived behavioral control | 4 |
| Subjective norms | 5 |
| Dietary behavior | 5 |
| Total | 23 |
| Effective samples | 279 |
| Factor | Manifest Variable | Coef. | Std. Error | CR | p | Standard Loading (Std. Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | K1 | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.825 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | K2 | 0.915 | 0.062 | 14.858 | 0.000 | 0.789 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | K3 | 0.941 | 0.063 | 14.849 | 0.000 | 0.788 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | K4 | 0.927 | 0.064 | 14.531 | 0.000 | 0.776 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | K5 | 0.990 | 0.062 | 15.851 | 0.000 | 0.827 |
| Attitude | A1 | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.821 |
| Attitude | A2 | 0.913 | 0.071 | 12.940 | 0.000 | 0.752 |
| Attitude | A3 | 0.939 | 0.070 | 13.434 | 0.000 | 0.778 |
| Attitude | A4 | 0.862 | 0.071 | 12.080 | 0.000 | 0.708 |
| Perceived behavioral control | C1 | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.733 |
| Perceived behavioral control | C2 | 1.110 | 0.092 | 12.103 | 0.000 | 0.793 |
| Perceived behavioral control | C3 | 1.060 | 0.092 | 11.522 | 0.000 | 0.750 |
| Perceived behavioral control | C4 | 1.028 | 0.088 | 11.649 | 0.000 | 0.759 |
| Subjective norms | S1 | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.776 |
| Subjective norms | S2 | 0.900 | 0.076 | 11.781 | 0.000 | 0.711 |
| Subjective norms | S3 | 0.925 | 0.077 | 11.983 | 0.000 | 0.723 |
| Subjective norms | S4 | 0.981 | 0.077 | 12.698 | 0.000 | 0.762 |
| Subjective norms | S5 | 1.004 | 0.079 | 12.633 | 0.000 | 0.759 |
| Dietary behavior | B1 | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.732 |
| Dietary behavior | B2 | 0.957 | 0.091 | 10.565 | 0.000 | 0.683 |
| Dietary behavior | B3 | 0.954 | 0.088 | 10.850 | 0.000 | 0.702 |
| Dietary behavior | B4 | 1.124 | 0.093 | 12.093 | 0.000 | 0.790 |
| Dietary behavior | B5 | 0.915 | 0.086 | 10.628 | 0.000 | 0.687 |
| Factor | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | 0.642 | 0.900 |
| Attitude | 0.586 | 0.850 |
| Perceived behavioral control | 0.576 | 0.844 |
| Subjective norms | 0.557 | 0.863 |
| Dietary behavior | 0.518 | 0.843 |
| Sports Nutrition Knowledge | Attitude | Perceived Behavioral Control | Subjective Norms | Dietary Behavior | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sports nutrition knowledge | 0.801 | ||||
| Attitude | 0.320 | 0.766 | |||
| Perceived behavioral control | 0.364 | 0.389 | 0.759 | ||
| Subjective norms | 0.355 | 0.388 | 0.401 | 0.747 | |
| Dietary behavior | 0.419 | 0.372 | 0.415 | 0.407 | 0.720 |
| Index | X2 | df | p | X2/df | GFI | RMSEA | RMR | CFI | NFI | NNFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Judgment standard | - | - | >0.05 | <3 | >0.9 | <0.10 | <0.05 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 |
| 257.729 | 220 | 0.041 | 1.171 | 0.929 | 0.025 | 0.030 | 0.988 | 0.923 | 0.986 |
| X | → | Y | SE | z (CR) | p | Regression Coefficients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | Attitude | 0.062 | 5.908 | 0.000 | 0.401 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | Perceived behavioral control | 0.053 | 6.395 | 0.000 | 0.451 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | Subjective norms | 0.057 | 6.377 | 0.000 | 0.434 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | Dietary behavior | 0.059 | 2.858 | 0.004 | 0.236 |
| Attitude | → | Dietary behavior | 0.054 | 2.742 | 0.006 | 0.187 |
| Perceived behavioral control | → | Dietary behavior | 0.069 | 3.203 | 0.001 | 0.231 |
| Subjective norms | → | Dietary behavior | 0.060 | 2.998 | 0.003 | 0.209 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | K2 | 0.062 | 14.903 | 0.000 | 0.790 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | K1 | - | - | - | 0.824 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | K5 | 0.063 | 15.739 | 0.000 | 0.823 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | K4 | 0.064 | 14.417 | 0.000 | 0.771 |
| Sport Nutrition Knowledge | → | K3 | 0.063 | 14.809 | 0.000 | 0.787 |
| Attitude | → | A4 | 0.073 | 11.964 | 0.000 | 0.710 |
| Attitude | → | A3 | 0.072 | 13.170 | 0.000 | 0.776 |
| Attitude | → | A2 | 0.072 | 12.847 | 0.000 | 0.758 |
| Attitude | → | A1 | - | - | - | 0.816 |
| Perceived behavioral control | → | C4 | 0.090 | 11.498 | 0.000 | 0.759 |
| Perceived behavioral control | → | C3 | 0.094 | 11.337 | 0.000 | 0.747 |
| Perceived behavioral control | → | C2 | 0.094 | 11.993 | 0.000 | 0.800 |
| Perceived behavioral control | → | C1 | - | - | - | 0.728 |
| Subjective norms | → | S5 | 0.079 | 12.630 | 0.000 | 0.757 |
| Subjective norms | → | S4 | 0.076 | 12.652 | 0.000 | 0.758 |
| Subjective norms | → | S3 | 0.076 | 11.965 | 0.000 | 0.720 |
| Subjective norms | → | S2 | 0.076 | 11.832 | 0.000 | 0.713 |
| Subjective norms | → | S1 | - | - | - | 0.782 |
| Dietary behavior | → | B5 | 0.089 | 10.310 | 0.000 | 0.678 |
| Dietary behavior | → | B4 | 0.096 | 11.719 | 0.000 | 0.783 |
| Dietary behavior | → | B3 | 0.091 | 10.526 | 0.000 | 0.693 |
| Dietary behavior | → | B2 | 0.093 | 10.250 | 0.000 | 0.674 |
| Dietary behavior | → | B1 | - | - | - | 0.724 |
| Index | X2 | df | p | X2/df | GFI | RMSEA | RMR | CFI | NFI | NNFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Judgment standard | - | - | >0.05 | <3 | >0.9 | <0.10 | <0.05 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 |
| 322.694 | 223 | 0.000 | 1.447 | 0.909 | 0.040 | 0.066 | 0.968 | 0.903 | 0.963 | |
| Index | TLI | AGFI | IFI | PGFI | PNFI | SRMR | RMSEA 90%CI | |||
| Judgment standard | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 | <0.1 | ||||
| 0.963 | 0.887 | 0.968 | 0.734 | 0.796 | 0.086 | 0.030 ~ 0.049 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, D. Study on Nutritional Knowledge, Attitude and Behavior of Chinese School Football Players. Children 2022, 9, 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121910
Chen Y, Sun Y, Liu Z, Hu D. Study on Nutritional Knowledge, Attitude and Behavior of Chinese School Football Players. Children. 2022; 9(12):1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121910
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yao, Yingshuang Sun, Zhiyun Liu, and Donglin Hu. 2022. "Study on Nutritional Knowledge, Attitude and Behavior of Chinese School Football Players" Children 9, no. 12: 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121910
APA StyleChen, Y., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., & Hu, D. (2022). Study on Nutritional Knowledge, Attitude and Behavior of Chinese School Football Players. Children, 9(12), 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121910





