Mortality and Comorbidities in Extremely Low Birth Weight Thai Infants: A Nationwide Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
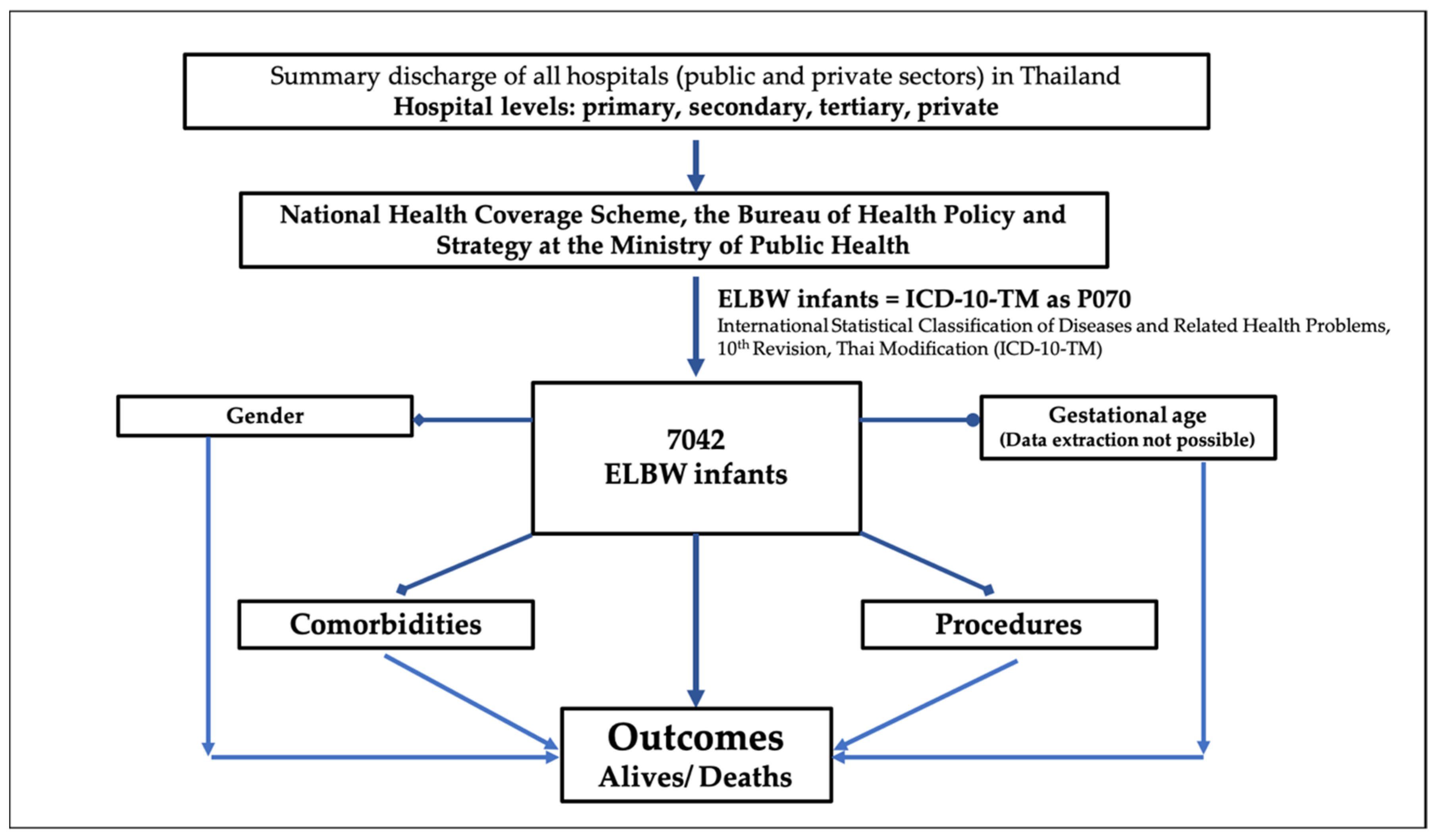
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ELBW | extremely low birth weight; |
| RDS | respiratory distress syndrome; |
| BPD | bronchopulmonary dysplasia; |
| PPHN | persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn; |
| IVH | intraventricular hemorrhage; |
| NEC | necrotizing enterocolitis; |
| PDA | patent ductus arteriosus; |
| ROP | retinopathy of prematurity; |
| CPR | cardiopulmonary resuscitation; |
| ICD | intercostal drainage; |
| PRC | packed red cell. |
References
- Kiatchoosakun, P.; Jirapradittha, J.; Areemitr, R.; Sutra, S.; Thepsuthammarat, K. Current Challenges in Reducing Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality in Thailand. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2012, 95 (Suppl. S7), S17–S23. [Google Scholar]
- Oestergaard, M.Z.; Inoue, M.; Yoshida, S.; Mahanani, W.R.; Gore, F.M.; Cousens, S.; Lawn, J.E.; Mathers, C.D.; United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation and the Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group. Neonatal Mortality Levels for 193 Countries in 2009 with Trends since 1990: A Systematic Analysis of Progress, Projections, and Priorities. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, J.E.; Cousens, S.; Zupan, J.; Lancet Neonatal Survival Steering Team. 4 Million Neonatal Deaths: When? Where? Why? Lancet Lond. Engl. 2005, 365, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, L.; Alexander, M.; You, D.; Alkema, L.; UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. National, Regional, and Global Levels and Trends in Neonatal Mortality between 1990 and 2017, with Scenario-Based Projections to 2030: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e710–e720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuin, C.S.; Khor, G.L.; Liabsuetrakul, T.; Achadi, E.L.; Htay, T.T.; Firestone, R.; Bhutta, Z.A. Maternal, Neonatal, and Child Health in Southeast Asia: Towards Greater Regional Collaboration. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2011, 377, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysavy, M.A.; Horbar, J.D.; Bell, E.F.; Li, L.; Greenberg, L.T.; Tyson, J.E.; Patel, R.M.; Carlo, W.A.; Younge, N.E.; Green, C.E.; et al. Assessment of an Updated Neonatal Research Network Extremely Preterm Birth Outcome Model in the Vermont Oxford Network. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e196294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbar, J.D.; Carpenter, J.H.; Badger, G.J.; Kenny, M.J.; Soll, R.F.; Morrow, K.A.; Buzas, J.S. Mortality and Neonatal Morbidity among Infants 501 to 1500 Grams from 2000 to 2009. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.I.; Bell, E.F.; Walsh, M.C.; Carlo, W.A.; Shankaran, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Sánchez, P.J.; Van Meurs, K.P.; Wyckoff, M.; et al. Trends in Care Practices, Morbidity, and Mortality of Extremely Preterm Neonates, 1993–2012. JAMA 2015, 314, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabashi, K.; Horiuchi, T.; Kusuda, S.; Kabe, K.; Itani, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Fujimura, M.; Matsuo, M. Mortality Rates for Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants Born in Japan in 2005. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Kanda, E.; Konno, J.; Mitani, M.; Makino, Y.; Matsui, H. Survival Rate of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants and Its Risk Factors: Case-Control Study in Japan. ISRN Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 2013, 873563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommiska, V.; Heinonen, K.; Lehtonen, L.; Renlund, M.; Saarela, T.; Tammela, O.; Virtanen, M.; Fellman, V. No Improvement in Outcome of Nationwide Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant Populations between 1996–1997 and 1999–2000. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayama, T.; Lee, S.K.; Mori, R.; Kusuda, S.; Fujimura, M.; Ye, X.Y.; Shah, P.S.; Canadian Neonatal Network; Neonatal Research Network of Japan. Comparison of Mortality and Morbidity of Very Low Birth Weight Infants between Canada and Japan. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e957–e965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohr, B.R.; Wright, L.L.; Dusick, A.M.; Perritt, R.; Poole, W.K.; Tyson, J.E.; Steichen, J.J.; Bauer, C.R.; Wilson-Costello, D.E.; Mayes, L.C.; et al. Center Differences and Outcomes of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, T.; Anand, P.; Verma, A.; Saksena, M.; Sankar, M.J.; Thukral, A.; Agarwal, R.; Deorari, A.; Paul, V.K. Outcome of Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) Infants from a Birth Cohort (2013–2018) in a Tertiary Care Unit in North India. J. Perinatol. Off. J. Calif. Perinat. Assoc. 2020, 40, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.-H.; Feng, Z.-S.; Lin, X.-J.; Cui, Q.-L.; Han, S.-S.; Jin, Y.; Liu, G.-S.; Yang, C.-Z.; Ye, X.-T.; Dai, Y.-H.; et al. Short Term Outcomes of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants from a Multicenter Cohort Study in Guangdong of China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marete, I.; Ekhaguere, O.; Bann, C.M.; Bucher, S.L.; Nyongesa, P.; Patel, A.B.; Hibberd, P.L.; Saleem, S.; Goldenberg, R.L.; Goudar, S.S.; et al. Regional Trends in Birth Weight in Low- and Middle-Income Countries 2013–2018. Reprod. Health 2020, 17, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piriyapokin, N.; Chuthapisith, J.; Emrat, K.; Nuntnarumit, P. Outcomes of Preterm Infants Born with Marginal Viability in a University Hospital in Thailand. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 56, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanvitan, P.; Ruangnapa, K.; Janjindamai, W.; Disaneevate, S. Outcomes of Very Low Birth Weight Infants in Songklanagarind Hospital. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2010, 93, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Sritipsukho, S.; Suarod, T.; Sritipsukho, P. Survival and Outcome of Very Low Birth Weight Infants Born in a University Hospital with Level II NICU. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2007, 90, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Number of Total Livebirths and Livebirths in Hospital and Percentage of Livebirths in Hospital per Total Livebirths by Region and Province, 2015—2019; Ministry of Public Health: Nonthaburi, Thailand, 2020; p. 32.
- Subramaniam, P.; Ho, J.J.; Davis, P.G. Prophylactic Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Preventing Morbidity and Mortality in Very Preterm Infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 14, CD001243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.J.; Ternberg, J.L.; Feigin, R.D.; Keating, J.P.; Marshall, R.; Barton, L.; Brotherton, T. Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Therapeutic Decisions Based upon Clinical Staging. Ann. Surg. 1978, 187, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papile, L.A.; Burstein, J.; Burstein, R.; Koffler, H. Incidence and Evolution of Subependymal and Intraventricular Hemorrhage: A Study of Infants with Birth Weights Less than 1,500 Gm. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffel, C.; Kistler, K.D.; Sarda, S.P. Global Incidence of Intraventricular Hemorrhage among Extremely Preterm Infants: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Perinat. Med. 2021, 49, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierson, W.M.; American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Ophthalmology; American Academy of Ophthalmology; American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus; American Association of Certified Orthoptists; Chiang, M.F.; Good, W.; Phelps, D.; Reynolds, J.; Robbins, S.L.; et al. Screening Examination of Premature Infants for Retinopathy of Prematurity. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20183061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Bhatia, J. Total Parenteral Nutrition for the Very Low Birth Weight Infant. Semin. Fetal. Neonatal Med. 2017, 22, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirardello, S.; Dusi, E.; Cortinovis, I.; Villa, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Agosti, M.; Milani, S.; Mosca, F. Effects of Red Blood Cell Transfusions on the Risk of Developing Complications or Death: An Observational Study of a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Am. J. Perinatol. 2017, 34, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, A.K.; Yang, J.; Harrison, A.; Pelausa, E.; Shah, P.S. Canadian Neonatal Network Temporal Changes in Blood Product Usage in Preterm Neonates Born at Less than 30 Weeks’ Gestation in Canada. Transfusion 2015, 55, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.; Lee, H.C.; Escobedo, M.B.; Hoover, A.V.; Kamath-Rayne, B.D.; Kapadia, V.S.; Magid, D.J.; Niermeyer, S.; Schmölzer, G.M.; Szyld, E.; et al. Part 5: Neonatal Resuscitation: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2020, 142, S524–S550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, D.G.; Carnielli, V.; Greisen, G.; Hallman, M.; Ozek, E.; Te Pas, A.; Plavka, R.; Roehr, C.C.; Saugstad, O.D.; Simeoni, U.; et al. European Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Respiratory Distress Syndrome—2019 Update. Neonatology 2019, 115, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimba, E.M.; Ballot, D. Survival of Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants. S. Afr. J. Child Health 2013, 7, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Das, J.K.; Bahl, R.; Lawn, J.E.; Salam, R.A.; Paul, V.K.; Sankar, M.J.; Sankar, J.M.; Blencowe, H.; Rizvi, A.; et al. Can Available Interventions End Preventable Deaths in Mothers, Newborn Babies, and Stillbirths, and at What Cost? Lancet Lond. Engl. 2014, 384, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassi, Z.S.; Bhutta, Z.A. Community-Based Intervention Packages for Reducing Maternal and Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality and Improving Neonatal Outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 23, CD007754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasswell, S.M.; Barfield, W.D.; Rochat, R.W.; Blackmon, L. Perinatal Regionalization for Very Low-Birth-Weight and Very Preterm Infants: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2010, 304, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total live births | 736,352 | 704,058 | 702,755 | 666,109 | 618,193 | 587,368 | 4,014,835 |
| ELBW | 1211 | 1204 | 1268 | 1206 | 1175 | 978 | 7042 |
| Per 1000 live births | 1.64 | 1.71 | 1.80 | 1.81 | 1.90 | 1.67 | 1.75 |
| Male | 586 (48.4%) | 597 (49.6%) | 639 (50.4%) | 605 (50.2%) | 622 (52.9%) | 492 (50.3%) | 3541 (50.3%) |
| Female | 625 (51.6%) | 607 (50.4%) | 629 (49.6%) | 601 (49.8%) | 553 (47.1%) | 486 (49.7%) | 3501 (49.7%) |
| Hospital level | |||||||
| Primary | 42 | 31 | 29 | 31 | 25 | 27 | 185 (2.6%) |
| Secondary | 332 | 334 | 383 | 479 | 331 | 285 | 2044 (29.0%) |
| Tertiary | 798 | 798 | 799 | 760 | 792 | 640 | 4587 (65.1%) |
| Private | 39 | 41 | 57 | 36 | 27 | 26 | 226 (3.2%) |
| Comorbidities | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| P220 respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) | 4982 | 70.7 |
| P590-9 neonatal jaundice | 4694 | 66.7 |
| P360-9 sepsis | 4253 | 60.4 |
| Q250 patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) | 2630 | 37.3 |
| P271 bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) | 2285 | 32.4 |
| P612 anemia of prematurity | 2164 | 30.7 |
| P230-9 congenital pneumonia | 1845 | 26.2 |
| P520-9 intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), all grades | 1492 | 21.2 |
| P210 severe asphyxia | 1438 | 20.4 |
| P704 hypoglycemia | 1410 | 20.0 |
| P77 necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) | 1353 | 19.2 |
| H351 ROP P708, R73 hyperglycemia P250-8 pulmonary interstitial emphysema and air leak | 1179 488 695 | 16.7 6.9 9.9 |
| P260-9 pulmonary hemorrhage | 665 | 9.4 |
| P293 persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) P742, E870, E871disturbance of sodium balance of newborn | 358 1647 | 5.1 23.4 |
| Procedures | ||
| Respiratory support | ||
| 9390 non- invasive respiratory support | 1236 | 17.6 |
| 9671 mechanical ventilation <96 h | 1467 | 20.8 |
| 9672 mechanical ventilation >96 h | 4339 | 61.6 |
| 3891-3 arterial and/or venous catheterization | 5440 | 77.2 |
| 9904 blood transfusion | 4934 | 70.0 |
| 9915 parenteral nutrition | 3686 | 52.3 |
| 9960 cardiopulmonary resuscitation | 832 | 11.8 |
| 3404 intercostal drainage Gastrointestinal tract surgery 4502-3, 451-6 intestinal resection 460-6 related to stoma creation 459, 4673-9, 4693-4 intestinal anastomosis 450, 5411 exploratory laparotomy 5491 percutaneous abdominal drainage 3885 PDA ligation | 468 179 84 98 47 5 63 333 | 6.6 2.5 1.2 1.4 0.7 0.1 0.9 4.7 |
| Variables | Alive N (%) | Death N (%) | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 4445 (63.1) | 2597 (36.9) | |||
| Sex | <0.001 | ||||
| -Female (Ref.) | 2364 (67.5) | 1137 (32.5) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Male | 2081 (58.8) | 1460 (41.2) | 1.36 (1.26, 1.47) | 1.28 (1.19, 1.39) | |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| P210 severe asphyxia | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 3737 (66.7) | 1867 (33.3) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 708 (49.2) | 730 (50.8) | 1.66 (1.52, 1.81) | 1.34 (1.22, 1.46) | |
| P220 RDS | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 1494 (72.5) | 566 (27.5) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 2951 (59.2) | 2031 (40.8) | 1.36 (1.24, 1.49) | 1.45 (1.31, 1.59) | |
| P230-9 congenital pneumonia | 0.089 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 3182 (61.2) | 2015 (38.8) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 1263 (68.5) | 582 (31.5) | 0.63 (0.57, 0.69) | 0.92 (0.83, 1.01) | |
| P250-8 air leak | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4208 (66.3) | 2139 (33.7) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 237 (34.1) | 458 (65.9) | 2.04 (1.84, 2.26) | 1.48 (1.29, 1.70) | |
| P260-9 pulmonary hemorrhage | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4193 (65.8) | 2184 (34.3) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 252 (37.9) | 413 (62.1) | 2.04 (1.84, 2.27) | 1.95 (1.75, 2.18) | |
| P271 BPD | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 2373 (49.9) | 2384 (50.1) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 2072 (90.7) | 213 (9.3) | 0.10 (0.08, 0.11) | 0.13 (0.11, 0.15) | |
| P293 PPHN | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4324 (64.7) | 2360 (35.3) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 121 (33.8) | 237 (66.2) | 1.88 (1.64, 2.15) | 1.80 (1.57, 2.07) | |
| P360-9 sepsis | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 1710 (61.3) | 1079 (38.7) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 2735 (64.3) | 1518 (35.7) | 0.71 (0.66, 0.77) | 0.82 (0.75, 0.89) | |
| P77 NEC | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 3454 (60.7) | 2235 (39.3) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 991 (73.2) | 362 (26.8) | 0.51 (0.46, 0.57) | 0.73 (0.65, 0.81) | |
| Q250 PDA | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 2561 (58.1) | 1851 (42.0) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 1884 (71.6) | 746 (28.4) | 0.49 (0.45, 0.53) | 0.72 (0.65, 0.78) | |
| P708, R73 hyperglycemia | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4207 (64.2) | 2347 (35.8) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 238 (48.8) | 250 (51.2) | 1.53 (1.35, 1.75) | 1.42 (1.24, 1.62) | |
| P742, E870, E871 disturbance of sodium balance | 0.079 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 3325 (61.6) | 2070 (38.4) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 1120 (68.0) | 527 (32.0) | 0.66 (0.60, 0.72) | 0.91 (0.83, 1.01) | |
| Procedures | |||||
| 9390 non-invasive respiratory support (Ref.) | 989 (80.0) | 247 (20.0) | 1 | 1 | <0.001 |
| 9671 mechanical ventilation < 96 h | 475 (32.4) | 992 (67.6) | 5.04 (4.39, 5.80) | 3.71 (3.20, 4.30) | |
| 9672 mechanical ventilation > 96 h | 2981 (68.7) | 1358 (31.3) | 1.02 (0.89, 1.17) | 1.35 (1.16, 1.57) | |
| 9960 CPR | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4257 (68.6) | 1953 (31.5) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 188 (22.6) | 644 (77.4) | 3.39 (3.10, 3.70) | 2.18 (1.98, 2.40) | |
| 3404 ICD | 0.008 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4289 (65.2) | 2285 (34.8) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 156 (33.3) | 312 (66.7) | 2.01 (1.79, 2.27) | 1.24 (1.06, 1.45) | |
| 9904 PRC transfusion | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 1153 (54.7) | 955 (45.3) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 3292 (66.7) | 1642 (33.3) | 0.42 (0.39, 0.46) | 0.62 (0.56, 0.67) | |
| 9915 parenteral nutrition | <0.001 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 1883 (56.1) | 1473 (43.9) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 2562 (69.5) | 1124 (30.5) | 0.49 (0.46, 0.53) | 0.69 (0.64, 0.75) | |
| Gastrointestinal tract surgery | 0.008 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4349 (63.4) | 2514 (36.6) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 96 (53.6) | 83 (46.4) | 0.92 (0.74, 1.15) | 1.37 (1.08, 1.72) | |
| 3885 PDA ligation | 0.002 | ||||
| -No (Ref.) | 4171 (62.2) | 2538 (37.8) | 1 | 1 | |
| -Yes | 274 (82.3) | 59 (17.7) | 0.31 (0.24, 0.40) | 0.64 (0.49, 0.84) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiatchoosakun, P.; Jirapradittha, J.; Paopongsawan, P.; Techasatian, L.; Lumbiganon, P.; Thepsuthammarat, K.; Sutra, S. Mortality and Comorbidities in Extremely Low Birth Weight Thai Infants: A Nationwide Data Analysis. Children 2022, 9, 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121825
Kiatchoosakun P, Jirapradittha J, Paopongsawan P, Techasatian L, Lumbiganon P, Thepsuthammarat K, Sutra S. Mortality and Comorbidities in Extremely Low Birth Weight Thai Infants: A Nationwide Data Analysis. Children. 2022; 9(12):1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121825
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiatchoosakun, Pakaphan, Junya Jirapradittha, Pongsatorn Paopongsawan, Leelawadee Techasatian, Pagakrong Lumbiganon, Kaewjai Thepsuthammarat, and Sumitr Sutra. 2022. "Mortality and Comorbidities in Extremely Low Birth Weight Thai Infants: A Nationwide Data Analysis" Children 9, no. 12: 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121825
APA StyleKiatchoosakun, P., Jirapradittha, J., Paopongsawan, P., Techasatian, L., Lumbiganon, P., Thepsuthammarat, K., & Sutra, S. (2022). Mortality and Comorbidities in Extremely Low Birth Weight Thai Infants: A Nationwide Data Analysis. Children, 9(12), 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121825






