Intussusception and COVID-19 in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aim of the Study
2. Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Inclusion–Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics and Quality
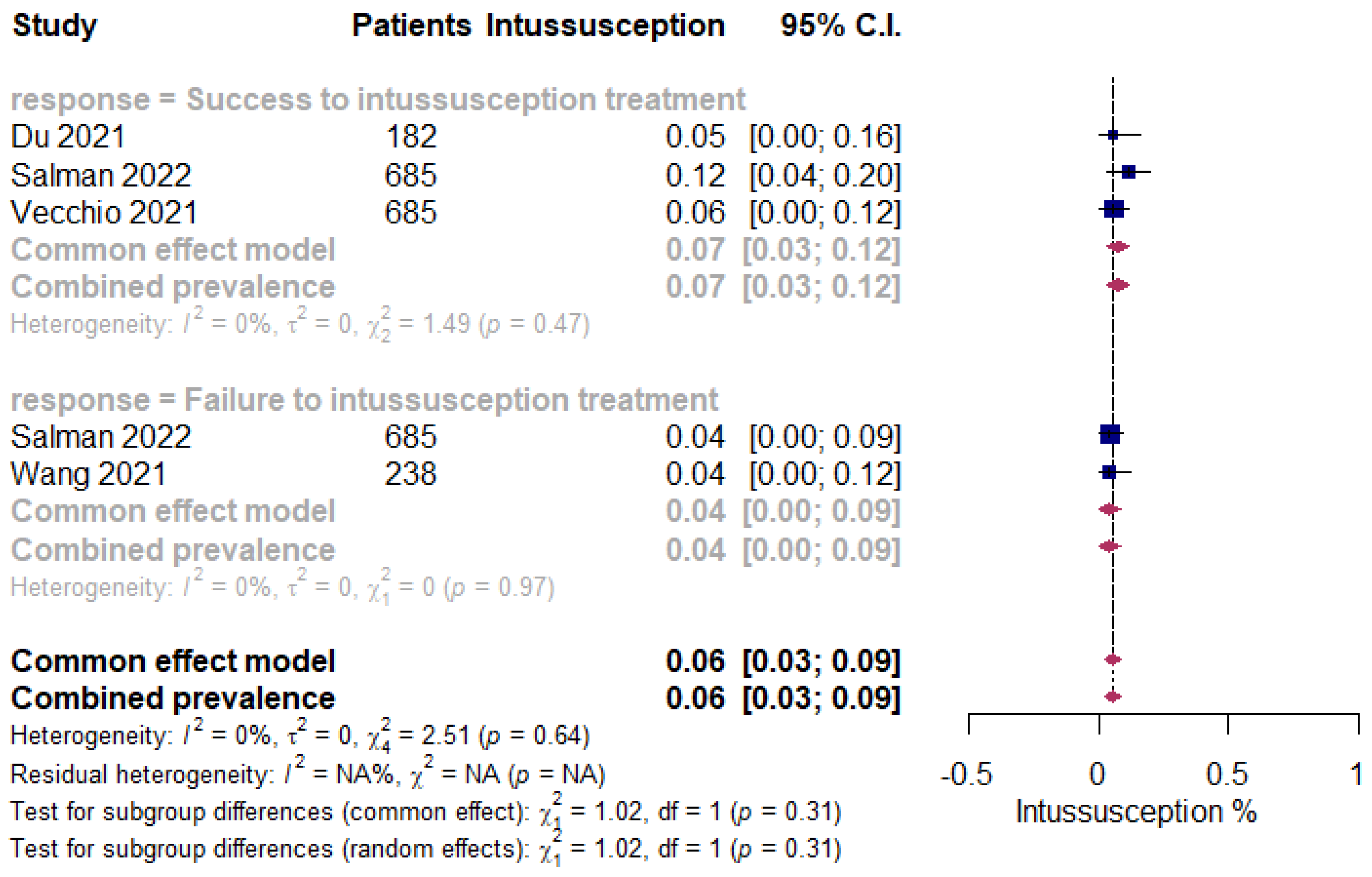
3.2. Meta-Analysis of ISN in Pediatric Patients following COVID-19 Infection
3.3. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of ISN Pediatric Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.4. Treatment Outcome and Predictors of Mortality in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with ISN
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rubenstein, S.; Grew, E.; Clouser, K.; Kwok, A.; Veerapandiyan, A.; Kornitzer, J.; Pecor, K.; Ming, X. COVID-19 in Pediatric Inpatients: A Multi-Center Observational Study of Factors Associated with Negative Short-Term Outcomes. Children 2021, 8, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Garrett, S.; Sun, J. Gastrointestinal symptoms, pathophysiology, and treatment in COVID-19. Genes Dis. 2021, 8, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-G.; Cui, H.-R.; Tang, H.-B.; Deng, X.-L. Gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal nucleic acid testing of children with 2019 coronavirus disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazuaye-Ekwuyasi, E.A.; Camacho, A.C.; Rios, F.S.; Torck, A.; Choi, W.J.; Aigbivbalu, E.E.; Mehdi, M.Q.; Shelton, K.J.; Radhakrishnan, G.L.; Radhakrishnan, R.S. Intussusception in a child with COVID-19 in the USA. Emerg. Radiol. 2020, 27, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Rong, Z.; Li, W. Clinical characteristics of 5 COVID-19 cases with non-respiratory symptoms as the first manifestation in children. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrinioti, H.; MacDonald, A.; Lu, X.; Wallace, S.; Mathew, J.; Zhang, F.; Shao, J.; Bretherton, J.; Tariq, M.; Eyre, E. Intussusception in two children with SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2020, 9, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajalakshmi, L.; Satish, S.; Nandhini, G.; Ezhilarasi, S. Unusual presentation of COVID-19 as intussusception. Indian J. Pract. Pediatr. 2020, 22, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, A.; Friedheim, A.; Parsh, B. Intussusception: Treatment and nursing considerations. Nursing 2022, 52, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClaran, J.K.; Buriko, Y. Intussusception. In Small Animal Surgical Emergencies, 2nd ed.; Aronson, L.R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, A.; Rubin, D.C. Small Intestine: Anatomy and Structural Anomalies; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw, C.J.; Johnson, P. Intussusception. Surgery 2022, 40, 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.S.; Byun, Y.-H.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Ryu, J.-M.; Lee, J.-Y. Decreased incidence of pediatric Intussusception during COVID-19. Children 2021, 8, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, M.P. Gastrointestinal. Fundamentals of Pediatric Imaging; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 95–138. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharyya, S.; Pareek, D.; Acharyya, K.; Bhaduri, B. Serosal Hematoma Acting as a Lead Point for Acute Intussusception in an Infant with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Indian J. Pediatr. 2022, 89, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwalla, S.K.; Jalan, A. Intussusception as a Manifestation of COVID-19. IJHSR 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athamnah, M.N.; Masade, S.; Hamdallah, H.; Banikhaled, N.; Shatnawi, W.; Elmughrabi, M.; Azzam, H.S.A. COVID-19 presenting as intussusception in infants: A case report with literature review. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 66, 101779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellazzi, M.L.; Corsello, A.; Cerrato, L.; Carnevali, A.; Morandi, A.; Leva, E.; Agostoni, C.V.; Marchisio, P. Intussusception in an Infant With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report and a Review of the Literature. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 693348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Ruiz, R.; Ponce-de-León-Lovatón, P.; Delgado-Seminario, P.; Urrunaga-Pastor, D. Spontaneous resolution of intussusception after COVID-19 infection found at laparoscopy in a 6-year-old. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2022, 81, 102273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.J.; Cao, Y.Y.; Akdis, M.; Huang, P.Q.; Chen, H.W.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.H.; Akdis, C.A. Clinical characteristics of 182 pediatric COVID-19 patients with different severities and allergic status. Allergy 2021, 76, 510–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadgyas, B.; Garai, G.I.; Schnur, J.; Kiss, V.I.; Vass, V.; Mátyus, E.; Balázs, G.; Cserni, T. COVID-19-Related Intestinal Ischemia in A 7-Year Old Boy. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. Rep. 2022, 10, e107–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Zaldaña, J. Intususcepción en niño con COVID-19. Revista Méd. 2021, 160, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrón, N.; Figueroa, L.M. Intussusception and COVID-19, successful mechanic reduction, case report. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2021, 8, 2333794X211019693. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, J.Y.; Ahern, B.J. A lethargic child with COVID-19 infection. J. Am. Acad. PAS 2022, 35, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Hartman, L.; Navarro, Y.J.S.; Rossini, C.J.; Burdett, C.; Pennell, C. Pediatric Covid-19 mesenteric lymphoid hyperplasia associated intussusception: A case report and literature review. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 73, 101988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiva, T.; Luschen, C.; Yu, Z.; Liebe, H.; Golubkova, A.; Hunter, C.J. COVID-19–Related Intussusception: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Surg. Infect. 2022, 23, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castaño, I.; Calabuig-Barbero, E.; Gonzálvez-Piñera, J.; López-Ayala, J.M. COVID-19 Infection Is a Diagnostic Challenge in Infants With Ileocecal Intussusception. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2020, 36, e368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado-Martínez, I.; Arreaga-Gutiérrez, F.J.; Pedraza-Peña, A.N. Intussusception and SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 67, 101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazzam, Z.; Salim, A.; Ashraf, A.; Jehan, F.; Arshad, M. Intussusception in an infant as a manifestation of COVID-19. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 59, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, C.; Bollettini, T.; Mercedes, R.; Papparella, A.; Nobile, S.; Cobellis, G. COVID-19 can cause severe intussusception in infants: Case report and literature review. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorno, J.F.; Giraldo, M.; Marín, A.F.; Figueroa, L.M. Novel Coronavirus Infection in an Infant with Intussusception. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2021, 8, 2333794X211012978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmani, C.; Hulse, T. Beware of the jolly toddler who has not read the right textbooks. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 58, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, P.; Karimi, A.; Tabatabaie, S.R.; Khalili, M.; Sayyari, A. Protein losing enteropathy and pneumatosis intestinalis in a child with COVID 19 infection. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 64, 101667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, R.; Sher, A.C.; Sammer, M.B.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Shah, S.R.; Seghers, V.J. Ileocolic intussusception in pediatric SARS-CoV-2 patients: Experience at a tertiary pediatric center. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2022, 38, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.K.; Macdonald, A.; Jobson, M.; Bretherton, J.; Mehmood, T. Pediatric Intussusception During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2021, 37, 340–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scottoni, F.; Giobbe, G.G.; Zambaiti, E.; Khalaf, S.; Sebire, N.J.; Curry, J.; Coppi, P.D.; Gennari, F. Intussusception and COVID-19 in Infants: Evidence for an Etiopathologic Correlation. Pediatrics 2022, 149, e2021054644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkhi, H.; Dooki, M.E.; Hadipour, A.; Hosseinpour, S.; Abdavi, P.; Mohammadi, M. A Rare Case of Intussusception in A COVID-19 Positive Patient with Nephrotic Syndrome. J. Babol Univ. Med. Sci. 2022, 24, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, K.; Gurien, L.; Maxson, R.; Stephenson, M.K. Recurrent Intussusception as a Manifestation of COVID-19. Surgery 2021, 3, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, G.A.; Skertich, N.J.; Jones, K.B.; Williams, M.; Gulack, B.C.; Shah, A.N. An Infant with COVID-19-Associated Intussusception. Am. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swyden, S.; Damanakis, H.; Cooper, A.; Velasquez, J.; James, J. Intussusception in the setting of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection following rotavirus vaccination. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Phys. Open 2022, 3, e12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.D.; Cheung, C.; Archambeau, B.; Dong, F.; Neeki, M.M. Pediatric Intussusception Following COVID-19 Infection: A Rare Presentation. Cureus 2022, 14, e23488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, A.L.; Garazzino, S.; Smarrazzo, A.; Venturini, E.; Poeta, M.; Berlese, P.; Denina, M.; Meini, A.; Bosis, S.; Galli, L. Factors associated with severe gastrointestinal diagnoses in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection or multisystem inflammatory syndrome. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2139974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Tang, F.; Luo, W.; Fang, J.; Qi, C.; Sun, H.; Xiao, H.; Peng, X.; Shao, J. Be aware of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with COVID-19. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 36, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçınkaya, R.; Polat, M.; Şen, Z.S.; Üner, Ç.; Öz, F.N.; Tanır, G. Transient Ileo-Ileal Intussusception as a Manifestation of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 57, 1546–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Ott. Ott. Hosp. Res. Inst. 2011, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bazerbachi, F.; Sawas, T.; Vargas, E.J.; Prokop, L.J.; Chari, S.T.; Gleeson, F.C.; Levy, M.J.; Martin, J.; Petersen, B.T.; Pearson, R.K. Metal stents versus plastic stents for the management of pancreatic walled-off necrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 30–42.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaolong, X.; Yang, W.; Qi, W.; Yiyang, Z.; Bo, X. Risk factors for failure of hydrostatic reduction of intussusception in pediatric patients: A retrospective study. Medicine 2019, 98, e13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.-L.; Hu, Z.-C.; Tan, Y.-L.; Sheng, M.; Wang, J. Risk factors for recurrent intussusception in children: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e018604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Kacker, R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: An update. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2007, 28, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statist. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabishi, A.S.; Aljarad, Z.; Shebli, B.; Masri, A.H.; Anadani, R.; Shabouk, M.B.; Trissi, M. A rare case of bowel intussusception due to adenocarcinomatous polyp in a 14 year-old child: Case report. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, A.; Ferrone, L.; Squarcina, M. Are COVID-19 Containment Measures Equally Effective in Different World Regions? Università degli Studi di Firenze: Florence, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, P.; Furceri, D.; Ostry, J.D.; Tawk, N. The Effect of Containment Measures on the COVID-19 Pandemic. 2020. Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2020/08/07/The-Effect-of-Containment-Measures-on-the-COVID-19-Pandemic-49572 (accessed on 13 October 2022).
- Lee, S.Y.; Sasaki, S.; Kurokawa, H.; Ohtake, F. The school education, ritual customs, and reciprocity associated with self-regulating hand hygiene practices during COVID-19 in Japan. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barathy, C.; Kittu, D.; Babji, S.; Pothapregada, S.; Rakesh, C. Adherence to Home Treatment Guidelines Among Pediatric Home Treated COVID-19 Patients in Puducherry. Indian Pediatr. 2022, 59, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betsch, C.; Korn, L.; Felgendreff, L.; Eitze, S.; Thaiss, H. School opening during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: Public acceptance of wearing fabric masks in class. Public Health Pract. 2021, 2, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickells, G.E.; Figueroa, J.; West, K.W.; Wood, A.; McElhanon, B.O. Adherence to Masking Requirement During the COVID -19 Pandemic by Early Elementary School Children. J. Sch. Health 2021, 91, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueggemann, A.B.; van Rensburg, M.J.J.; Shaw, D.; McCarthy, N.D.; Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.; van der Linden, M.P.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Bennett, D.E.; Borrow, R. Changes in the incidence of invasive disease due to Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningitidis during the COVID-19 pandemic in 26 countries and territories in the Invasive Respiratory Infection Surveillance Initiative: A prospective analysis of surveillance data. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e360–e370. [Google Scholar]
- Buettcher, M.; Baer, G.; Bonhoeffer, J.; Schaad, U.B.; Heininger, U. Three-year surveillance of intussusception in children in Switzerland. Pediatrics 2007, 120, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bines, J.E.; Liem, N.T.; Justice, F.A.; Son, T.N.; Kirkwood, C.D.; de Campo, M.; Barnett, P.; Bishop, R.F.; Robins-Browne, R.; Carlin, J.B. Risk factors for intussusception in infants in Vietnam and Australia: Adenovirus implicated, but not rotavirus. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 452–460.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.; Ramsay, M.; Waight, P. Rotavirus vaccination and intussusception. Lancet 1999, 354, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudville, I.C.; Phua, K.B.; Quak, S.H.; Lee, B.W.; Han, H.H.; Verstraeten, T.; Bock, H.L. The epidemiology of paediatric intussusception in Singapore: 1997 to 2004. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2006, 35, 674. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.; Kim, J.; Jung, J.Y.; Ham, E.M.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, H.; Kim, D.K.; Kwak, Y.H. The epidemiology of childhood intussusception in South Korea: An observational study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpabalwani, E.M.; Bvulani, B.; Simwaka, J.; Chitambala, P.; Matapo, B.; Tate, J.; Parashar, U.; Mwenda, J. Age distribution and mortality associated with intussusception in children under two years of age in nine sentinel surveillance hospitals in Zambia, 2007–2018. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 1), 6. [Google Scholar]
- Mandeville, K.; Chien, M.; Willyerd, F.A.; Mandell, G.; Hostetler, M.A.; Bulloch, B. Intussusception: Clinical presentations and imaging characteristics. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2012, 28, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice-Townsend, S.; Chen, C.; Barnes, J.N.; Rangel, S.J. Variation in practice patterns and resource utilization surrounding management of intussusception at freestanding Children’s Hospitals. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 48, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkovitz, L.A.; Kolbe, A.B.; Orth, R.C.; Mahood, N.F.; Thapa, P.; Hull, N.C.; Thacker, P.G.; Moir, C. Pediatric ileocolic intussusception: New observations and unexpected implications. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 49, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsicovetere, P.; Ivatury, S.J.; White, B.; Holubar, S.D. Intestinal Intussusception: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2016, 30, 030–039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, P.; Yagnik, P.J.; Saikumar, P.; Parmar, N.; Dave, M.; Amponsah, J.K.; Bhatt, N.S.; Sharma, M.; Thakkar, B.; Donda, K.; et al. Surgery and Resource Utilization Trends for Pediatric Intussusception From 2005 Through 2014. Cureus 2020, 12, e10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, L.; Cortina-Borja, M.; El Bashir, H.; Sutcliffe, A.G.; Marven, S.; Cameron, J.C.; Lynn, R.; Taylor, B. Intussusception incidence among infants in the UK and Republic of Ireland: A pre-rotavirus vaccine prospective surveillance study. Vaccine 2013, 31, 4098–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muhsen, K.; Kassem, E.; Efraim, S.; Goren, S.; Cohen, D.; Ephros, M. Incidence and risk factors for intussusception among children in northern Israel from 1992 to 2009: A retrospective study. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraja, R.M.; Oo, Y.M.; Ljuhar, D.; Pacilli, M.; Win, N.N.; Stevens, S.; Aye, A.; Nestel, D. Long-Term Impact of a Low-Cost Paediatric Intussusception Air Enema Reduction Simulation-Based Education Programme in a Low-Middle Income Country. World J. Surg. 2021, 46, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose, A.; Keita, A.M.; Tapia, M.D.; O Sow, S.; Mast, T.C.; Kotloff, K.L. Incidence of Intussusception in Bamako, Mali, Before and After the Introduction of Rotavirus Vaccine. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalya, P.L.; Kayange, N.M.; Chandika, A.B. Childhood intussusceptions at a tertiary care hospital in northwestern Tanzania: A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in resource-limited setting. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2014, 40, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gou, Z.-H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.-X.; Xiang, B. How Does the COVID-19 Pandemic Affect Pediatric Patients with Intussusception Treated by Ultrasound-Guided Hydrostatic Enema Reduction? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-Y.; Su, Y.-T.; Ko, P.-J.; Chen, Y.-L.; Shih, H.-H.; Tsai, C.-C. Chronic Nocturnal Abdominal Pain as the Presentation of Inverted Meckel Diverticulum: A Case Report. Children 2022, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, S.C.; Lopez, M.E.; Zhang, W.; Brandt, M.L.; Wesson, D.E.; Lee, T.C.; Rodriguez, J.R. Risk factors for surgery in pediatric intussusception in the era of pneumatic reduction. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 48, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.-I.; Seo, J.-M.; Jung, S.-M. Factors Associated with Failure of Pneumatic Reduction in Children with Ileocolic Intussusception. Children 2021, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundoyin, O.O.; Olulana, D.I.; Lawal, T.A. Childhood intussusception: Impact of delay in presentation in a developing country. Afr. J. Paediatr. Surg. 2016, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ro, Y.S.; Kwon, H.; Suh, D.; Moon, S. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Emergency Care Utilization and Outcomes in Pediatric Patients with Intussusception. Children 2022, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbone, I.; Tagliaferri, F.; Carboni, E.; Crotti, B.; Ruggiero, J.; Monzani, A.; Bonetti, L.; Soliani, M.; Bellone, S.; Cavalli, C.; et al. Changing Admission Patterns in Pediatric Emergency Departments during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Italy Were Due to Reductions in Inappropriate Accesses. Children 2021, 8, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.D.; Turner, C.G.; Kamran, S.C.; Yu, A.Y.; Ferrari, L.; Zurakowski, D.; Fauza, D.O. Pediatric Postoperative Intussusception in the Minimally Invasive Surgery Era: A 13-Year, Single Center Experience. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 216, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntoulia, A.; Tharakan, S.J.; Reid, J.R.; Mahboubi, S. Failed Intussusception Reduction in Children: Correlation Between Radiologic, Surgical, and Pathologic Findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 207, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, E.; Parashar, U.D.; Tate, J.E. Associations of Intussusception With Adenovirus, Rotavirus, and Other Pathogens: A Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, E.; Kabir, F.; Trang, N.V.; Rayamajhi, A.; Satter, S.M.; Liu, J.; Yousafzai, M.T.; Anh, D.D.; Basnet, A.T.; Flora, M.S. Infectious etiologies of intussusception among children < 2 years old in 4 Asian countries. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, S.; Cegolon, L.; Khafaei, M.; Gholami, N.; Zhao, S.; Khalesi, N.; Moosavian, H.; Fathi, S.; Izadi, M.; Ghadian, A. Gastrointestinal cancers, ACE-2/TMPRSS2 expression and susceptibility to COVID-19. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Wei, G.; Huang, R.; Livanos, A.; Jha, D.; Levescot, A.; Irizar, H.; Kosoy, R.; Cording, S. Intestinal inflammation modulates the expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and potentially overlaps with the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2–related disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 287–301.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, E.A.; Pigg, N.; Courtier, J.; Zapala, M.A.; MacKenzie, J.D.; Phelps, A.S. Intussusception: Past, present and future. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 47, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopystecka, A.; Kopeć, I.; Mitek-Palusińska, J.; Woźniak, M.M. Intestinal intussusceptions in children population. J. Educ. Health Sport 2022, 12, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, S.; Karpelowsky, J.; Webster, A.C.; McGee, R.G. Management for intussusception in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD006476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.G.; Kavanagh, R.G.; Leidhin, C.N.; Cullinan, N.M.; Lavelle, L.P.; Malone, D.E. Comparative effectiveness of imaging modalities for the diagnosis and treatment of intussusception: A critically appraised topic. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Martore, M.; Firnberg, M.T.; Kohn, M.A.; Kornblith, A.E.; Gottlieb, M. Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care ultrasonography for intussusception in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 58, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, T.; Penninga, L.; Reurings, J.C.; Berry, M.C.J. Intussusception in Children: A Clinical Review. Acta Chir. Belg. 2015, 115, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Carson, W.K.; Chintanaboina, J.K.; Prajapati, D.N. Colocolonic intussusception identified during endoscopy: An incidental diagnosis. Laryngo Rhino Otologie 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, M.A.; Polites, S.F.; Alzghari, M.; Onkendi, E.O.; Grotz, T.E.; Zielinski, M.D. Intussusception in adults and the role of evolving computed tomography technology. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 209, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doo, J.W.; Kim, S.C. Sedative reduction method for children with intussusception. Medicine 2020, 99, e18956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, J.; Singhavejsakul, J.; Ukarapol, N.; Laohapensang, M.; Wakhanrittee, J.; Patumanond, J. Enema reduction of intussusception: The success rate of hydrostatic and pneumatic reduction. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; Xiang, B. A randomized trial of pneumatic reduction versus hydrostatic reduction for intussusception in pediatric patients. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 1464–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niramis, R.; Watanatittan, S.; Kruatrachue, A.; Anuntkosol, M.; Buranakitjaroen, V.; Rattanasuwan, T.; Wongtapradit, L.; Tongsin, A. Management of recurrent intussusception: Nonoperative or operative reduction? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2010, 45, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley-Quon, L.I.; Arthur, L.G.; Williams, R.F.; Goldin, A.B.; Peter, S.D.S.; Beres, A.L.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Renaud, E.J.; Ricca, R.; Slidell, M.B.; et al. Management of intussusception in children: A systematic review. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 56, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, J.E.; Zuckerbraun, N.S.; Nworgu, C.R.; Mollen, K.P.; Furtado, A.D.; Manole, M.D. Management and Outcome of Pediatric Patients With Transient Small Bowel–Small Bowel Intussusception. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2021, 37, e110–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindyck, T.; Parashar, U.; Mwenda, J.M.; Tadesse, A.; Armah, G.; Omore, R.; Ngwira, B.; Jani, B.; Mpabalwani, E.M.; Mbuwayesango, B.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Increased Mortality From Intussusception in African Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Jiang, B.; Parashar, U.; Nguyen, T.; Bines, J.; Patel, M.M. Childhood Intussusception: A Literature Review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Curns, A.T.; Patel, M.M.; Parashar, U.D. Trends in Intussusception-Associated Deaths among US Infants from 1979-2007. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A. Health care systems in low-and middle-income countries. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.C.; Wehrmeister, F.C.; Barros, A.J.; Victora, C.G. Gender bias in careseeking practices in 57 low–and middle–income countries. J. Glob. Health 2017, 7, 010418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, Y.; Hu, C.; Wan, K.; Hu, P.; Wang, R.; Luo, J.; Li, T.; Ping, R.; Hu, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19: A major mechanism of morbidity and mortality. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 41, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
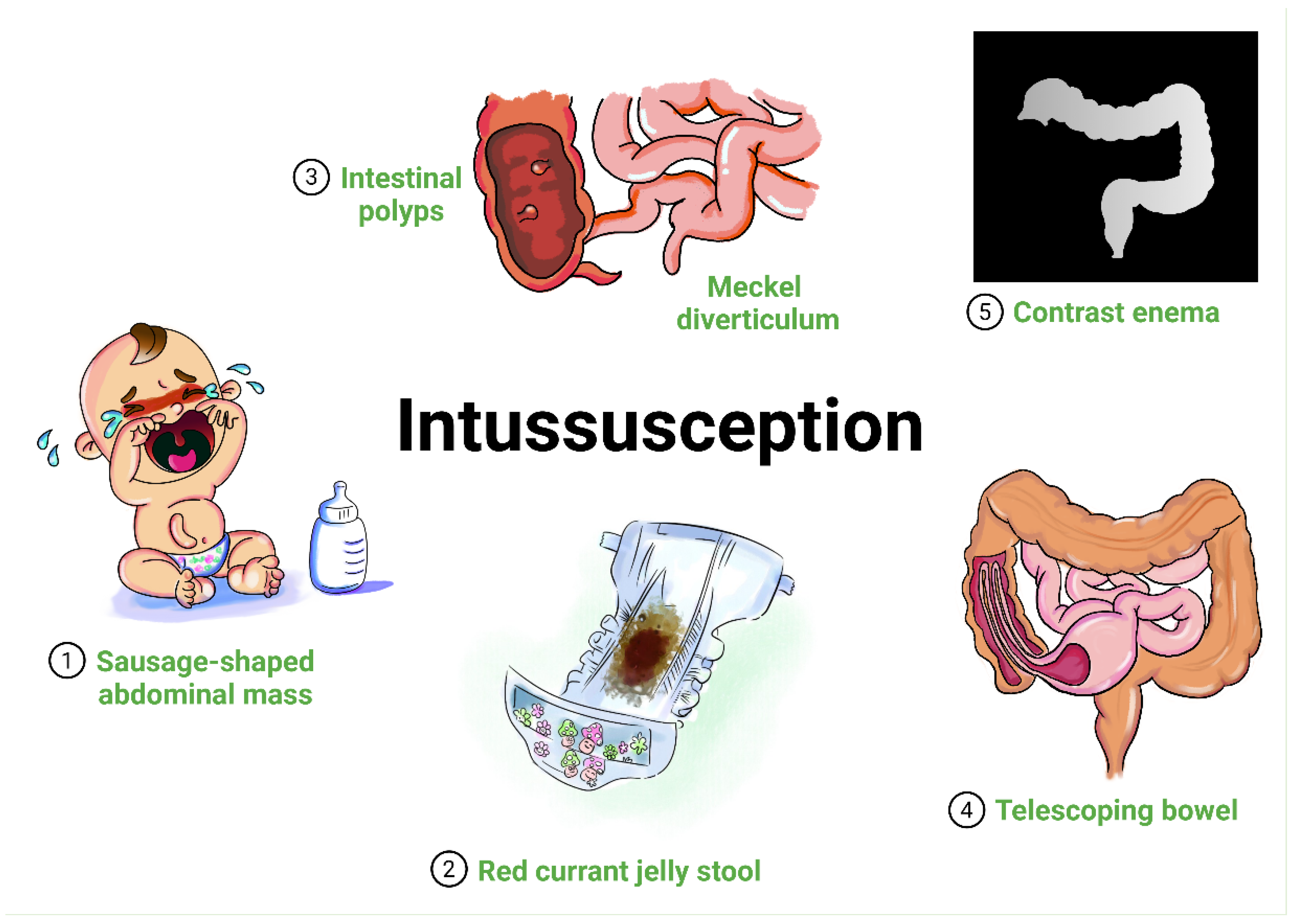
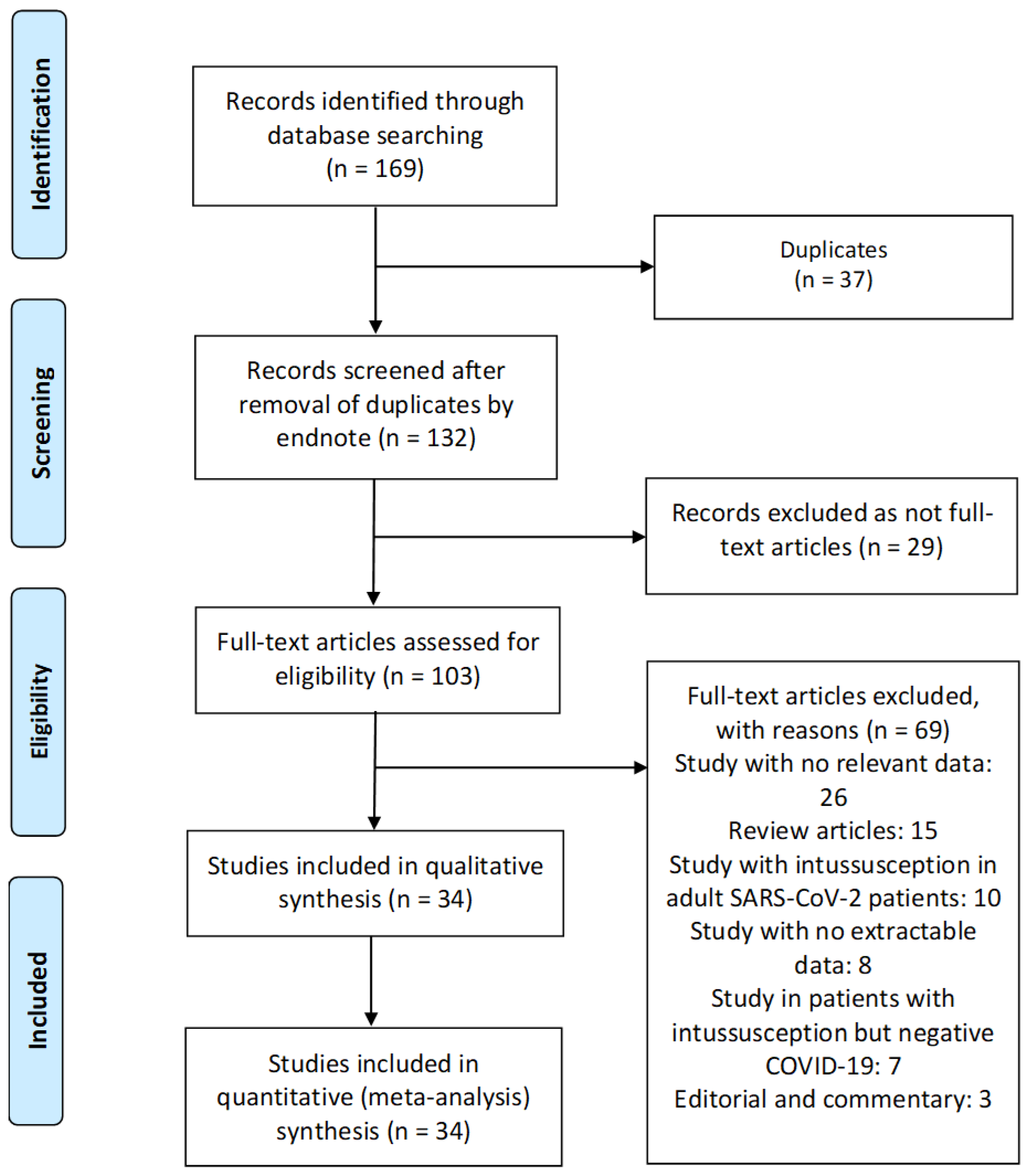
| Author, Year, Study Location | Study Design, Setting | Age (Months) a | Male, n (%) | Ethnicity | Comorbidities, n | Number of Patients (n = 1828) | Number of SARS-CoV-2 Patients with ISN (n = 64, 3.5%) | ISN Classification by Location AND Symptoms from ISN, n | Laboratory Findings | Imaging | Admitted to ICU, n | Mechanical Ventilation, n | ARDS, n | Treatment, n; If Failure to Pneumatic, Hydrostatic or Surgical Reduction Occurred; If ISN Was Recurrent | Assessment of Study Risk of Bias (Tool Used, Finding); Treatment Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acharyya et al., 2022 [15], India | Retrospective case report, single center | 4 | 1 (100) | 1 Indian | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Abdominal distension 1 Blood in stool 1 Large hematoma in the serous layer of the intestine | 1 Raised procalcitonin 1 High D-dimer 1 High prothrombin time 1 High NT-proBNP | 1 Acute ISN 1 Multiple air fluid levels | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Surgical reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 survived |
| Agarwalla and Jalan 2022 [16], India | Retrospective case report, single center | 10 | 1 (100) | 1 Indian | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileo-ileal ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Crying 1 Vomiting 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Drowsiness 1 Low BP 1 Pallor 1 Tachycardia 1 Low oxygen saturation 1 Cold extremities 1 Peripheral pulses 1 Autonomic dysfunction 1 Irregular heartbeat 1 Ectopic beats | 1 Low Hb 1 High CRP 1 High ferritin 1 High D-dimer 1 High LDH | 1 Acute ISN | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 Surgical reduction of the ISN 1 Dopamine 1 IV fluids 1 Oxygen supplementation 1 Inotropes 1 Antibiotics 1 Steroids 1 Anticoagulant 1 NGT feeding 1 Removal of surgical drain 1 Dressing No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Athamnah et al., 2021 [17], Jordan | Retrospective case report, single center | 2.5 | 1 (100) | 1 Arab | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Fever 1 Vomiting 1 Dehydration 1 Blood in stool 1 Abdominal distension 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Bilious discharge from the NGT 1 Red currant jelly stools | 1 Not reported | 1 Distal small bowel obstruction and decreased gas in the colon 1 Acute ISN (target sign) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN 1 IV fluids 1 Antibiotics No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Bazuaye-Ekwuyasi et al., 2020 [4], United States | Retrospective case report, single center | 9 | 1 (100) | 1 Hispanic | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Vomiting 1 Abdominal pain 1 Anorexia 1 Blood in stool 1 Dehydration | 1 Ketonuria 1 Proteinuria 1 Decreased lymphocytes | 1 Acute ISN 1 Colon cutoff sign of ISN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Cai et al., 2020 [5], China | Retrospective case-series, single center | 10 | 0 (0) | 1 Asian | 1 No medical history | 5 | 1 | 1 Location was not reported AND 1 Crying 1 Restlessness 1 Vomiting 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Apathy 1 Drowsiness 1 Convulsions 1 Septic shock 1 Multiple organ dysfunction 1 Abdominal distension 1 Blood in stool 1 Coffee dreg-like gastric contents | 1 Leukopenia 1 Decreased lymphocytes 1 Thrombocytopenia 1 High CRP 1 Raised procalcitonin 1 High D-dimer 1 High prothrombin time 1 High APTT 1 High ferritin 1 High interleukin-6 1 High interleukin-10 1 Hypoalbuminemia 1 Hyponatremia 1 Hypocalcemia 1 Reduced number of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ T lymphocytes and CD16 + CD56 natural killer cells | 1 Acute ISN 1 Large amount of abdominal dropsy 1 Necrosis of the proximal ileus of the small intestine | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 Steroids 1 IVIG 1 Interferon 1 Antivirals 1 Antibiotics 1 Oxygen supplementation 1 CRRT 1 Plasma exchange 1 Surgical resection of necrotic intestine 1 Dopamine 1 Dobutamine No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Died |
| Castellazzi et al., 2021 [18], Italy | Retrospective case report, single center | 10 | 0 (0) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Irritability 1 Anorexia 1 Crying 1 Vomiting 1 Rectal blood 1 Spiking colicky pain | 1 High CRP | 1 Acute ISN 1 Increased thickness of the intestinal wall and accompanying mesentery 1 Enlarged lymph nodes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN 1 Antibiotics 1 IV fluids 1 Surgical reduction of the ISN 1 Laparotomy 1 Ileocecopexy Yes failure (hydrostatic, n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Díaz-Ruiz et al., 2022 [19], Peru | Retrospective case report, single center | 72 | 1 (100) | 1 Hispanic | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Liquid stools with mucus and no blood 1 Anorexia 1 Chills 1 Vomiting 1 Nausea | 1 High CRP 1 High leukocytes | 1 Acute ISN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Surgical reduction of the ISN 1 Laparotomy 1 Appendectomy 1 Analgesics No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Du et al., 2021 [20], China | Retrospective cohort, single center | 10 | 0 (0) | 1 Asian | 1 No medical history | 182 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Nausea 1 Vomiting 1 Multiple organ dysfunction 1 Intestinal necrosis 1 Septic shock 1 DIC | 1 High CRP 1 High LDH 1 High BUN | 1 Acute ISN | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 Interferon 1 Antibiotics 1 Oxygen supplementation No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (NOS, 7) 1 Died |
| Fadgyas et al., 2022 [21], Hungary | Retrospective case report, single center | 90 | 1 (100) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 Left-sided renal agenesis 1 Developmental delay 1 Meningism | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Headache 1 Vomiting 1 Facial petechiae 1 Dehydration 1 Abdominal pain 1 Low BP | 1 High CRP 1 High WBCs 1 High neutrophils 1 High D-dimer 1 Raised liver enzymes 1 Raised bilirubin 1 High troponin | 1 Enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes 1 Acute ISN 1 Very dilated, fluid- and gas-filled small bowel loops 1 Meckel’s diverticulum 1 Bowel obstruction | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 Antibiotics 1 Analgesics 1 IV fluids 1 Oxygen supplementation 1 Laparotomy 1 Surgical resection 1 Anastomosis No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| García et al., 2021 [22], Guatemala | Retrospective case report, single center | 6 | 1 (100) | 1 Hispanic | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Irritability 1 Vomiting 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Pallor 1 Abdominal pain | 1 Low Hb 1 High D-dimer 1 High CRP 1 High ferritin | 1 Acute ISN 1 Dilation of intestinal loops 1 Poor gas distribution | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Antibiotics 1 Analgesics 1 Surgical resection 1 Oxygen supplementation 1 Total parenteral nutrition No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Guerrón and Figueroa 2021 [23], Colombia | Retrospective case report, single center | 5 | 1 (100) | 1 Hispanic | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Vomiting 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Absence of bowel sounds 1 Anorexia | 1 Not reported | 1 Acute ISN 1 Significant colonic parietal thickening | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Hyun et al., 2022 [24], United States | Retrospective case report, single center | 20 | 0 (0) | 1 Hispanic | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Weakness 1 Lethargy 1 Abdominal pain 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Increased fussiness 1 Crying 1 Facial cyanosis 1 Cold extremities 1 Perception of a firm and painful mass 1 Low oxygen saturation | 1 High WBCs 1 High neutrophils 1 High monocytes 1 Hypokalemia 1 High LDH | 1 Acute ISN 1 Concentric rings of the bowel 1 Enlarged lymph nodes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Analgesics 1 Oxygen supplementation 1 IV fluids 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Khan et al., 2021 [25], United States | Retrospective case report, single center | 2 | 1 (100) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Vomiting 1 Diarrhea 1 Blood in stool 1 Abdominal distension 1 Red currant jelly stools | 1 Not reported | 1 Acute ISN 1 Enlarged lymph nodes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Leiva et al., 2022 [26], United States | Retrospective case reports, single center | 7 and 9 | 1 (50) | 2 Whites (Caucasians) | 1 No medical history | 2 | 2 | 2 Ileocolic ISN AND 2 Abdominal pain 2 Irritability 1 Vomiting 2 Blood in stool | 1 Not reported | 2 Acute ISN 1 Hypertrophied lymph nodes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 Hydrostatic reductions of the ISN 2 Surgical reductions of the ISN 2 Laparotomy Yes failure (hydrostatic, n = 2) No recurrence (n = 2) | (Modified NOS, high) 2 Survived |
| Makrinioti et al., 2020 [6], United Kingdom | Retrospective case reports, multicenter | 10 and 10 | 0 (0) | 1 White (Caucasian) and 1 Asian | 2 No medical history | 2 | 2 | 2 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Crying 2 Vomiting 2 Red currant jelly stools 1 Abdominal distension 1 Absence of bowel sounds 1 Peritonitis 1 Ascites 1 Swelling of the small intestinal wall 1 Lethargy 1 DIC | 2 High CRP | 1 Acute ISN | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 Pneumatic reductions of the ISN 1 Laparotomy 1 Defunctioning ileostomy 1 Antibiotics 1 Inotropes 1 Surgical reduction of the ISN 1 Ladd’s procedure No failure (n = 1) Yes failure (pneumatic, n = 1) No recurrence (n = 2) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived 1 Died |
| Martínez-Castaño et al., 2020 [27], Spain | Retrospective case report, single center | 6 | 1 (100) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Vomiting 1 Abdominal cramps 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Anemia | 1 Low Hb 1 High CRP 1 High WBCs | 1 Acute ISN (target sign) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Mercado-Martínez et al., 2021 [28], Mexico | Retrospective case reports, multicenter | 8 and 7 | 1 (50) | 2 Hispanics | 2 No medical history | 2 | 2 | 2 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Crying 2 Vomiting 2 Red currant jelly stools 2 Irritability 1 Pallor 1 Tachycardia 1 Abdominal distension 1 Decreased peristalsis 1 Painful on deep palpation in mesogastrium 1 Perception of a firm and painful mass 2 Rectal mucus and blood | 1 High CRP 1 High D-dimer 1 Anemia 1 Low Hb | 2 Acute ISN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 Surgical reductions of the ISN 1 Rockey–Davis incision for manual reduction 1 Anticoagulant No failure (n = 2) No recurrence (n = 2) | (Modified NOS, high) 2 Survived |
| Moazzam et al., 2020 [29], Pakistan | Retrospective case report, single center | 4 | 1 (100) | 1 Pakistani | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Crying 1 Drawing up of the legs towards the abdomen 1 Anorexia 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Pallor 1 Irritability 1 Sausage-shaped lump 1 Anemia | 1 High D-dimer 1 Low Hb | 1 Acute ISN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN 1 Antibiotics 1 Analgesics No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Noviello et al., 2021 [30], Italy | Retrospective case report, single center | 7 | 1 (100) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Anorexia 1 Diarrhea 1 Vomiting 1 Sleepiness 1 Pallor 1 Lethargy 1 Dehydration 1 Red currant jelly stools | 1 High D-dimer | 1 Acute ISN 1 Alternating rings of low and high echogenicity 1 “Pseudokidney” sign | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN 1 Laparotomy 1 Surgical resection 1 Anastomosis Yes failure (hydrostatic, n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Osorno et al., 2021 [31], Colombia | Retrospective case report, single center | 8 | 1 (100) | 1 Hispanic | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Perception of a firm and painful mass 1 Metabolic acidosis 1 Peritonitis | 1 Not reported | 1 Acute ISN 1 Ischemia of distal ileum and right colon | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 Laparotomy 1 Surgical resection 1 Ileostomy 1 Fistula No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Ponmani and Hulse 2022 [32], United Kingdom | Retrospective case report, single center | 18 | 0 (0) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Constipation 1 Abdominal pain | 1 High CRP | 1 Acute ISN 1 Doughnut-shaped mass | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 survived |
| Rajalakshmi et al., 2020 [7], India | Retrospective case report, single center | 8 | 1 (100) | 1 Indian | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Vomiting 1 Lethargy 1 Dehydration 1 Perception of a firm and painful mass | 1 Low Hb 1 Low hematocrit | 1 Acute ISN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 IV fluids 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Rohani et al., 2021 [33], Iran | Retrospective case report, single center | 72 | 1 (100) | 1 Persian | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Location was not reported AND 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Abdominal pain 1 Vomiting 1 Diarrhea 1 Abdominal distension | 1 Leukopenia 1 Decreased lymphocytes 1 High calprotectin 1 Hypoalbuminemia 1 Hypocalcemia 1 Hypophosphatemia 1 Hypomagnesaemia 1 Raised liver enzymes | 1 Multifocal small bowel loops intussusceptum 1 Pneumatosis intestinalis in ascending colon 1 Dilatation in colon caliber 1 Necrotizing enterocolitis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Oral rehydration solution 1 Ondansetron 1 Total parenteral nutrition 1 Antibiotics No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Salman et al., 2022 [34], United States | Retrospective cohort, single center | Median (IQR), 36 (3-216) | 19 (79.2) | 4 Whites (Caucasians) 6 Hispanics 1 Asian | 11 Not reported | 685 | 24 | 8 Small bowel ISN and 3 ileocolic ISN AND 7 Vomiting 5 Abdominal pain 2 Blood in stool 4 Red currant jelly stools | 11 Not reported | 11 Abnormal imaging 3 Acute ISN | 11 Not reported | 11 Not reported | 11 Not reported | 3 Pneumatic reductions of the ISN 4 Surgical reductions of the ISN No failure (n = 8) Yes failure (pneumatic, n = 3) No recurrence (n = 11) | (NOS, 7) 11 Survived |
| Saxena et al., 2021 [35], United Kingdom | Retrospective case report, single center | 10 | 0 (0) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Location was not reported AND 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Vomiting | 1 Not reported | 1 Acute ISN 1 Waugh syndrome (ISN with malrotation) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN 1 Surgical reduction of the ISN 1 Ladd’s procedure Yes failure (pneumatic, n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Scottoni et al., 2022 [36], Italy | Retrospective case reports, multicenter | 1 and 5.5 | 1 (50) | 2 Whites (Caucasians) | 1 No medical history 1 Hyperinsulinism | 2 | 2 | 2 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Constipation 2 Vomiting 2 Lethargy 1 Dehydration 2 Blood in stool 1 Anorexia | 2 Not reported | 2 Acute ISN 1 Enlarged lymph nodes 1 Necrosis of the terminal ileum to the splenic flexure | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN 1 Laparotomy 1 Removal of lymph node 1 Hemicolectomy 1 Anastomosis 1 Noradrenaline No failure (n = 1) Yes failure (pneumatic, n = 1) No recurrence (n = 2) | (Modified NOS, high) 2 Survived |
| Sorkhi et al., 2022 [37], Iran | Retrospective case report, single center | 132 | 1 (100) | 1 Persian | 1 Nephrotic syndrome 1 Long use of steroid (15 years) | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Vomiting 1 Nausea 1 Weakness 1 Anorexia 1 Myalgia 1 Pallor 1 Dehydration | 1 High leukocytes 1 Hypernatremia 1 Hypokalemia | 1 Acute ISN 1 Meckel’s diverticulum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Steroids 1 Enalapril 1 Pantoprazole 1 Antibiotics 1 IV fluids 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN 1 Diverticulectomy No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, moderate) 1 Survived |
| Stephenson et al., 2021 [38], United States | Retrospective case report, single center | 6 | 1 (100) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Vomiting 1 Irritability 1 Red currant jelly stools | 1 Not reported | 1 Acute ISN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Pneumatic reduction of the ISN Yes failure (pneumatic, n = 1) Yes recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Sullivan et al., 2021 [39], United States | Retrospective case report, single center | 7 | 1 (100) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileal-ileal ISN and 1 ileocolic ISN AND 1 Abdominal pain 1 Crying 1 Fist clenching 1 Grimacing | 1 Not reported | 1 Acute ISN 1 Ileocolic ISN (Target sign) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN Yes failure (hydrostatic, n = 1) Yes recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Swyden et al., 2022 [40], United States | Retrospective case report, single center | 4 | 1 (100) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileocolic ISN AND 1 Blood in stool 1 Anorexia 1 Red currant jelly stools 1 Tachycardia 1 Lethargy 1 Metabolic acidosis | 1 Thrombocytosis 1 High leukocytes 1 Hypochloremia 1 Raised procalcitonin | 1 Acute ISN 1 Doughnut-shaped mass 1 Pneumoperitoneum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 IV fluids 1 Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN 1 Laparotomy Yes failure (hydrostatic, n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, high) 1 Survived |
| Tran et al., 2022 [41], United States | Retrospective case report, single center | 8 | 0 (0) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Location was not reported AND 1 Blood in stool 1 Rash 1 Diarrhea 1 Metabolic acidosis | 1 High leukocytes 1 High CRP | 1 Acute ISN (target sign) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 No treatment for ISN (follow-up and bowel rest) No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (Modified NOS, moderate) 1 Survived |
| Vecchio et al., 2021 [42], Italy | Retrospective cohort, multicenter | 4 Not reported | 4 Not reported | 4 Whites (Caucasians) | 4 Not reported | 685 | 4 | 1 Ileal ISN and 3 ileocolic ISN AND 4 Abdominal pain 4 Vomiting 4 Red currant jelly stools | 4 Not reported | 4 Not reported | 4 Not reported | 4 Not reported | 4 Not reported | 2 Surgical reductions of the ISN 1 Removal of solid mass Failure was not reported (n = 4) Recurrence was not reported (n = 4) | (NOS, 8) 4 Not reported |
| Wang et al., 2021 [43], China | Retrospective cohort, single center | 10 | 0 (0) | 1 Asian | 1 No medical history | 238 | 1 | 1 Location was not reported AND 1 Blood in stool 1 Vomiting 1 Diarrhea 1 Oliguria 1 Acute kidney injury (stage 3) | 1 Raised procalcitonin 1 High CRP 1 High interleukin-6 1 High D-dimer 1 High LDH 1 High BUN 1 High serum creatinine 1 Low estimated glomerular filtration rate 1 Proteinuria 1 Hematuria | 1 Acute ISN 1 Intestinal necrosis | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 Surgical reduction of the ISN 1 Antibiotics 1 Antivirals 1 Steroids 1 IVIG 1 CRRT 1 Plasma exchange Yes failure (surgical, n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (NOS, 7) 1 Died |
| Yalçınkaya et al., 2021 [44], Turkey | Retrospective cohort, single center | 72 | 0 (0) | 1 White (Caucasian) | 1 No medical history | 1 | 1 | 1 Ileo-ileal ISN AND 1 Diarrhea 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Abdominal pain 1 Conjunctivitis 1 Tachycardia 1 Abdominal tenderness 1 Blood in stool 1 Mitral regurgitation 1 Left ventricular systolic dysfunction | 1 High CRP 1 Raised ESR 1 Raised procalcitonin 1 High interleukin-6 1 High ferritin 1 High fibrinogen 1 Decreased lymphocytes | 1 Acute ISN 1 Fluid retention in the ileal and colonic walls | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 IVIG 1 Steroids 1 No treatment for ISN (follow-up and bowel rest) No failure (n = 1) No recurrence (n = 1) | (NOS, 7) 1 Survived |
| Variable | Findings a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 64) | Survived (n = 43) | Died (n = 4) | p-Value b | |
| Age | ||||
| Less than 1 month | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 * |
| 1 month to less than 1 year | 32 (50) | 28 (65.1) | 4 (100) | |
| 1 year to less than 3 years | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| 3 years to less than 6 years | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| 6 years to less than 12 years | 7 (10.9) | 7 (16.3) | 0 | |
| 12 years to 18 years | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 41 (64.1) | 41 (95.3) | 0 | 0.000 * |
| Female | 18 (28.1) | 14 (32.5) | 4 (100) | |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| White (Caucasian) | 25 (39.1) | 25 (58.1) | 0 | 0.000 * |
| Hispanic | 13 (20.3) | 13 (30.2) | 0 | |
| Asian | 5 (7.8) | 1 (2.3) | 4 (100) | |
| Persian | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Indian | 3 (4.7) | 3 (7) | 0 | |
| Arab | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| Pakistani | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| ISN classification by location | ||||
| Ileocolic | 34 (53.1) | 32 (74.4) | 2 (50) | 0.001 * |
| Ileo-ileal | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| Location was not reported | 5 (7.8) | 3 (7) | 2 (50) | |
| Imaging | ||||
| Acute ISN | 37 (57.8) | 33 (76.7) | 4 (100) | 0.237 |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | 6 (9.4) | 6 (13.9) | 0 | |
| Target sign | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| Imaging findings were not reported | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| Intestinal necrosis | 4 (6.2) | 2 (4.6) | 2 (50) | |
| Doughnut-shaped mass | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Meckel’s diverticulum | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Symptoms from ISN | ||||
| Vomiting | 36 (56.2) | 32 (74.4) | 4 (100) | 0.179 |
| Abdominal pain | 29 (45.3) | 29 (67.4) | 0 | |
| Red currant jelly stools | 25 (39.1) | 23 (53.5) | 2 (50) | |
| Blood in stool | 15 (23.4) | 13 (30.2) | 2 (50) | |
| Anorexia | 9 (14.1) | 9 (20.9) | 0 | |
| Irritability | 8 (12.5) | 8 (18.6) | 0 | |
| Abdominal tenderness | 8 (12.5) | 8 (18.6) | 0 | |
| Dehydration | 7 (10.9) | 7 (16.3) | 0 | |
| Pallor | 6 (9.4) | 6 (13.9) | 0 | |
| Crying | 8 (12.5) | 6 (13.9) | 2 (50) | |
| Lethargy | 7 (10.9) | 6 (13.9) | 1 (25) | |
| Abdominal distension | 7 (10.9) | 5 (11.6) | 2 (50) | |
| Diarrhea | 6 (9.4) | 5 (11.6) | 1 (25) | |
| Tachycardia | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| Perception of a firm and painful mass | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| Rectal mucus and blood | 3 (4.7) | 3 (7) | 0 | |
| Metabolic acidosis | 3 (4.7) | 3 (7) | 0 | |
| Low BP | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Anemia | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Weakness | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Nausea | 3 (4.7) | 2 (4.6) | 1 (25) | |
| Cold extremities | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Constipation | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| DIC | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| Septic shock | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| Multiple organ dysfunction | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| Peritonitis | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Drowsiness | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Absence of bowel sounds | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Laboratory findings | ||||
| Laboratory results were not reported | 25 (39.1) | 25 (58.1) | 0 | 0.063 |
| High CRP | 14 (21.9) | 10 (23.2) | 4 (100) | |
| High D-dimer | 9 (14.1) | 7 (16.3) | 2 (50) | |
| Low Hb | 6 (9.4) | 6 (13.9) | 0 | |
| Raised procalcitonin | 5 (7.8) | 3 (7) | 2 (50) | |
| High leukocytes | 4 (6.2) | 4 (9.3) | 0 | |
| Decreased lymphocytes | 4 (6.2) | 3 (7) | 1 (25) | |
| High ferritin | 4 (6.2) | 3 (7) | 1 (25) | |
| High LDH | 4 (6.2) | 2 (4.6) | 2 (50) | |
| High WBCs | 3 (4.7) | 3 (7) | 0 | |
| High interleukin-6 | 3 (4.7) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (50) | |
| High neutrophils | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Raised liver enzymes | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Hypokalemia | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| High BUN | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| Proteinuria | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| High prothrombin time | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Leukopenia | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Hypocalcemia | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| No medical history | 32 (50) | 28 (65.1) | 4 (100) | 0.036 * |
| Not reported | 15 (23.4) | 15 (34.9) | 0 | |
| Left-sided renal agenesis | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| Developmental delay | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| Meningism | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| Hyperinsulinism | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| Nephrotic syndrome | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| Long use of steroid (15 years) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.3) | 0 | |
| Treatment | ||||
| Surgical reduction of the ISN | 17 (26.6) | 15 (34.9) | 2 (50) | 0.051 |
| Pneumatic reduction of the ISN | 13 (20.2) | 11 (25.6) | 2 (50) | |
| Antibiotics | 12 (18.7) | 8 (18.6) | 4 (100) | |
| Hydrostatic reduction of the ISN | 11 (17.2) | 11 (25.6) | 0 | |
| Laparotomy | 10 (15.6) | 9 (20.9) | 1 (25) | |
| IV fluids | 8 (12.5) | 8 (18.6) | 0 | |
| Oxygen supplementation | 6 (9.4) | 4 (9.3) | 2 (50) | |
| Analgesics | 5 (7.8) | 5 (11.6) | 0 | |
| Surgical resection | 5 (7.8) | 4 (9.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Steroids | 5 (7.8) | 3 (7) | 2 (50) | |
| Anastomosis | 3 (4.7) | 3 (7) | 0 | |
| Anticoagulant | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Total parenteral nutrition | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| No. treatment for ISN (follow-up and bowel rest) | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| CRRT | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| Plasma exchange | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| Interferon | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| Antivirals | 2 (3.1) | 0 | 2 (50) | |
| IVIG | 3 (4.7) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (50) | |
| Ladd’s procedure | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Inotropes | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| Dopamine | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (25) | |
| ISN was recurrent | ||||
| No | 45 (70.3) | 41 (95.3) | 4 (100) | 0.140 |
| Yes | 2 (3.1) | 2 (4.6) | 0 | |
| Failure to ISN treatment | ||||
| No failure | 25 (39.1) | 23 (53.5) | 2 (50) | 0.002 * |
| Pneumatic reduction (yes) | 7 (10.9) | 6 (13.9) | 1 (25) | |
| Hydrostatic reduction (yes) | 6 (9.4) | 6 (13.9) | 0 | |
| Surgical reduction (yes) | 1 (1.5) | 0 | 1 (25) | |
| Complications and treatment outcomes | ||||
| Patient was admitted to ICU | 9 (14.1) | 5 (11.6) | 4 (100) | 0.000 * |
| Patient was intubated and on mechanical ventilation during the ICU stay | 6 (9.4) | 2 (4.6) | 4 (100) | 0.000 * |
| Patient experienced ARDS | 6 (9.4) | 2 (4.6) | 4 (100) | 0.000 * |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis OR (95% CI) for Death | Multivariate Analysis OR (95% CI) for Death | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (1 month to <1 year) | 0.42 (0.1–0.33) | 0.04 * | 0.1 (0.13–0.25) | 0.52 |
| Gender (Female) | 0.74 (0.36–0.52) | <0.001 * | 1.13 (0.31–0.79) | 0.045 * |
| Location (Asia) | 0.36 (0.26–0.45) | <0.001 * | 0.38 (0.28–0.48) | <0.001 * |
| ISN symptom (abdominal pain) | 0.14 (0.43–0.71) | 0.62 | 0.19 (0.13–0.3) | 0.41 |
| ISN symptom (blood in stool) | 0.14 (0.41–0.7) | 0.61 | 0.32 (0.11–0.31) | 0.34 |
| ISN symptom (constipation) | 0.5 (0.15–1.15) | 0.13 | 0.7 (0.22–0.45) | 0.36 |
| ISN symptom (crying) | 0.13 (0.44–0.69) | 0.66 | NA | NA |
| ISN symptom (diarrhea) | 0.17 (0.41–0.74) | 0.57 | NA | NA |
| ISN symptom (DIC) | 1 (0.35–1.65) | 0.003 * | 1.31 (0.47–0.97) | 0.42 |
| ISN symptom (drowsiness) | 0.5 (0.21–1.15) | 0.13 | 0.68 (0.2–0.41) | 0.33 |
| ISN symptom (lethargy) | 0.33 (0.24–0.91) | 0.25 | NA | NA |
| ISN symptom (multiple organ failure) | 1 (0.35–1.65) | 0.003 * | 1.31 (0.47–0.97) | 0.42 |
| ISN symptom (nausea) | 0.33 (0.28–0.95) | 0.29 | 0.41 (0.22–0.47) | 0.43 |
| ISN symptom (peritonitis) | 0.5 (0.15–1.15) | 0.13 | 0.7 (0.22–0.45) | 0.36 |
| ISN symptom (red currant jelly stools) | 0.04 (0.5–0.58) | 0.88 | 0.32 (0.51–0.87) | 0.32 |
| ISN symptom (vomiting) | 0.11 (0.43–0.66) | 0.68 | 0.39 (0.24–0.68) | 0.75 |
| Laboratory finding (decreased lymphocytes) | 0.25 (0.77–1.27) | 0.62 | 1.01 (0.74–0.75) | 0.22 |
| Laboratory finding (high bloods urea nitrogen) | 1 (0.12–2.12) | 0.08 | 0.86 (0.33–0.56) | 0.48 |
| Laboratory finding (high C reactive protein) | 0.31 (0.64–1.25) | 0.52 | 0.71 (0.2–0.68) | 0.47 |
| Laboratory finding (high D-dimer) | 0.22 (0.74–1.18) | 0.64 | 0.48 (0.24–0.71) | 0.55 |
| Laboratory finding (high ferritin) | 0.25 (0.77–1.27) | 0.62 | 0.38 (0.27–0.4) | 0.48 |
| Laboratory finding (high interleukin-6) | 0.67 (0.38–1.72) | 0.21 | 0.6 (0.38–0.74) | 0.64 |
| Laboratory finding (high lactate dehydrogenase) | 0.5 (0.52–1.52) | 0.33 | NA | NA |
| Laboratory finding (high prothrombin time) | 0.5 (0.62–1.62) | 0.37 | NA | NA |
| Laboratory finding (hypocalcemia) | 0.5 (0.62–1.62) | 0.37 | 0.21 (0.1–0.35) | 0.49 |
| Laboratory finding (leukopenia) | 0.5 (0.62–1.62) | 0.37 | NA | NA |
| Laboratory finding (proteinuria) | 0.5 (0.62–1.62) | 0.37 | NA | NA |
| Failure to ISN reduction (pneumatic or surgical) (yes) | 0.16 (0.06–0.27) | 0.002 * | 0.11 (0.05–0.21) | 0.036 * |
| Recurrent ISN (yes) | 0.17 (0.09–0.43) | 0.21 | 0.34 (0.19–0.29) | 0.51 |
| Intensive care unit admission (yes) | 0.53 (0.45–0.6) | <0.001 * | 0.71 (0.83–1.18) | 0.03 * |
| Mechanically ventilated (yes) | 0.84 (0.79–0.9) | <0.001 * | 0.68 (0.51–1.41) | 0.01 * |
| Suffered from ARDS (yes) | 0.75 (0.68–0.81) | <0.001 * | 0.88 (0.93–1.88) | 0.01 * |
| Treatment (antibiotics = yes) | 0.31 (0.02–0.59) | 0.03 * | 0.29 (0.01–0.03) | 0.06 |
| Treatment (antivirals = yes) | 1 (0.61–1.39) | <0.001 * | 0.78 (0.93–1.22) | 0.77 |
| Treatment (CRRT = yes) | 1 (0.55–1.45) | <0.001 * | 0.64 (0.31–0.45) | 0.63 |
| Treatment (dopamine = yes) | 0.5 (0.05–0.95) | 0.03 * | NA | NA |
| Treatment (inotropes = yes) | 0.5 (0.05–0.95) | 0.03 * | NA | NA |
| Treatment (interferon = yes) | 1 (0.55–1.45) | <0.001 * | 0.64 (0.31–0.45) | 0.63 |
| Treatment (IVIG = yes) | 0.75 (0.39–1.11) | <0.001 * | 0.78 (0.48–1.49) | 0.27 |
| Treatment (Ladd’s procedure = yes) | 0.5 (0.05–0.95) | 0.03 * | NA | NA |
| Treatment (oxygen supplementation = yes) | 0.33 (0.61–1.39) | 0.04 * | 0.19 (0.17–0.34) | 0.23 |
| Treatment (plasma exchange = yes) | 1 (0.55–1.45) | <0.001 * | 0.64 (0.31–0.45) | 0.63 |
| Treatment (pneumatic reduction of ISN = yes) | 0.03 (0.23–0.28) | 0.83 | 0.13 (0.16–0.45) | 0.61 |
| Treatment (surgical reduction of ISN = yes) | 0.09 (0.16–0.34) | 0.47 | NA | NA |
| Treatment (steroids = yes) | 0.5 (0.17–0.83) | <0.001 * | 0.21 (0.14–0.58) | 0.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhumaid, S.; Al Alawi, Z.; Alnaim, A.A.; Al Ghamdi, M.A.; Alabdulqader, M.; Al Noaim, K.; Rabaan, A.A.; Al mutared, K.M.; Al Dossary, N.; Alsuliman, M.; et al. Intussusception and COVID-19 in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Children 2022, 9, 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111745
Alhumaid S, Al Alawi Z, Alnaim AA, Al Ghamdi MA, Alabdulqader M, Al Noaim K, Rabaan AA, Al mutared KM, Al Dossary N, Alsuliman M, et al. Intussusception and COVID-19 in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Children. 2022; 9(11):1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111745
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhumaid, Saad, Zainab Al Alawi, Abdulrahman A. Alnaim, Mohammed A. Al Ghamdi, Muneera Alabdulqader, Khalid Al Noaim, Ali A. Rabaan, Koblan M. Al mutared, Nourah Al Dossary, Murtadha Alsuliman, and et al. 2022. "Intussusception and COVID-19 in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Children 9, no. 11: 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111745
APA StyleAlhumaid, S., Al Alawi, Z., Alnaim, A. A., Al Ghamdi, M. A., Alabdulqader, M., Al Noaim, K., Rabaan, A. A., Al mutared, K. M., Al Dossary, N., Alsuliman, M., Almatawah, Y. A., AlOmran, A. T., Al HajjiMohammed, S. M., Alfarhan, D. R., Al Suwaiq, H. A., Al mutarid, M. M., Alkolib, M. J., Mohapatra, R. K., & Al Mutair, A. (2022). Intussusception and COVID-19 in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Children, 9(11), 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9111745







