A 10-Week Program of Combined Hippotherapy and Scroth’s Exercises Improves Balance and Postural Asymmetries in Adolescence Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Controlled Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
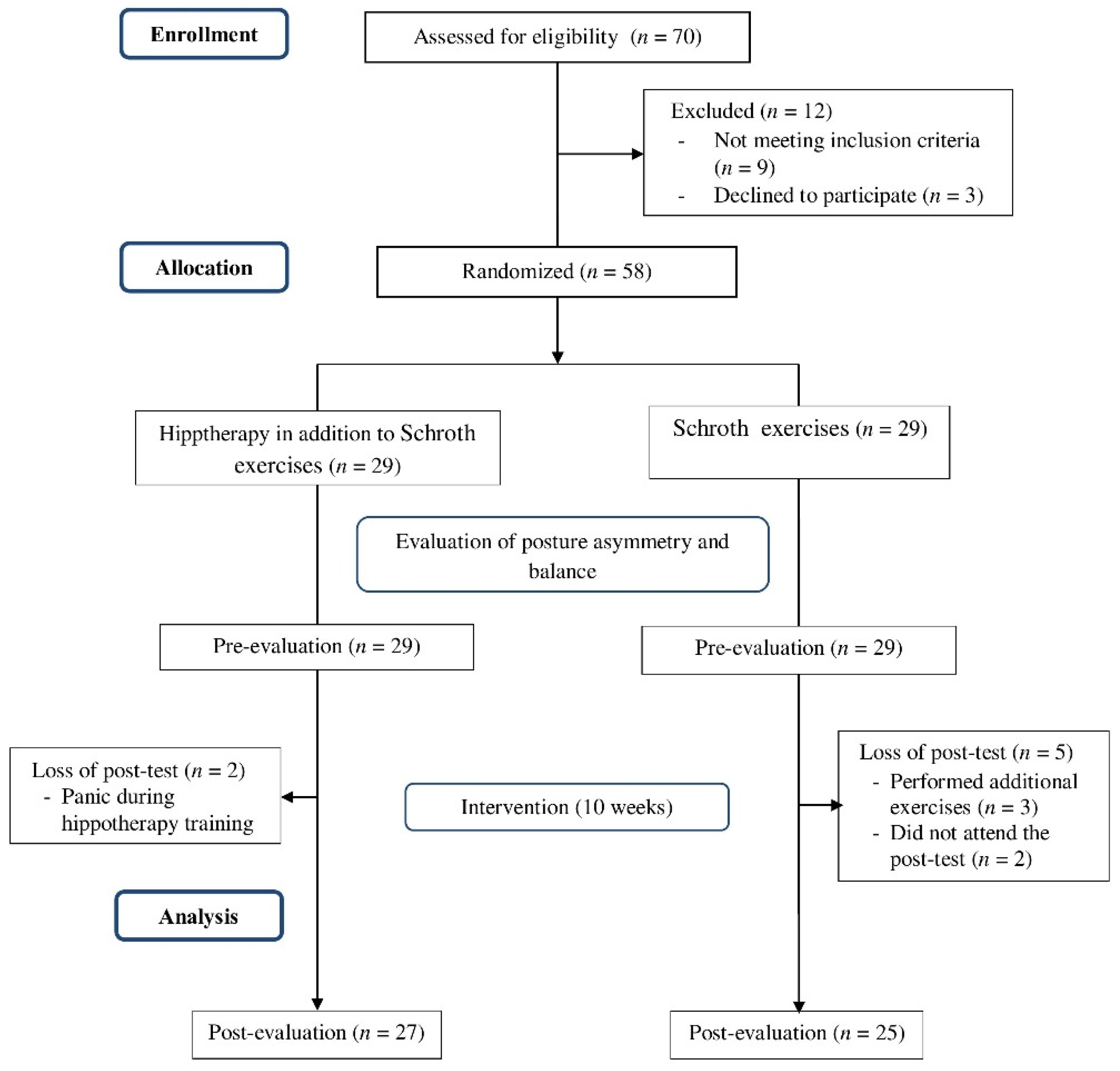
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
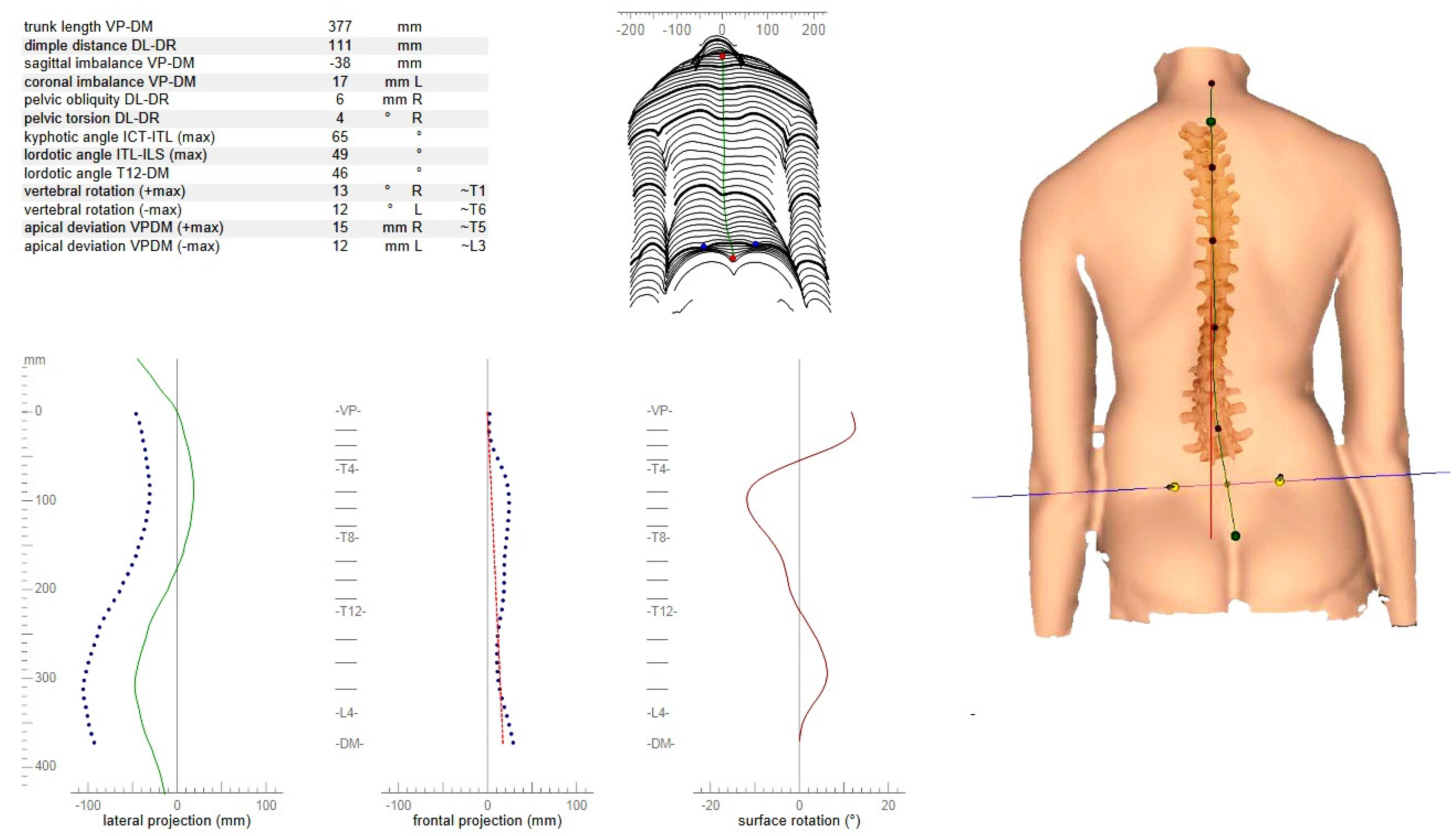
2.2. Assessment Procedure
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Canavese, F. Idiopathic scoliosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouwenhoven, J.-W.M.; Castelein, R.M. The Pathogenesis of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Review of the Literature. Spine 2008, 33, 2898–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Chau, W.W.; Chan, Y.-L.; Cheng, J. Relative anterior spinal overgrowth in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Results of disproportionate endochondral membranous bone growth. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2003, 85, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavese, F.; Dimeglio, A.; Bonnel, F.; Corradin, M.; Pereira, B.; Marcoul, A.; Charles, Y.P. Thoracic cage volume and dimen-sion assessment by optoelectronic molding in normal children and adolescents during growth. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2019, 41, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, C.; Björk, R.; Ortengren, R.; Andersson, G.B.J. Electromyography of the paravertebral muscles in idiopathic scoliosis: Measurements of amplitude and spectral changes under load. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1984, 55, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, H.; Zateri, C.; Ozkan, A.K.; Kayalar, G.; Berk, H. Prevalence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Turkey: An epidemiological study. Spine J. 2020, 20, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penha, P.J.; Ramos, N.L.J.P.; de Carvalho, B.K.G.; Andrade, R.M.; Schmitt, A.C.B.; João, S.M.A. Prevalence of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Spine 2018, 43, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.M.; Newton, R.A.; Lamb, R.L.; Nogi, J. A Study of Postural Equilibrium in Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1984, 4, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, F.-C.; Wang, N.-H.; Hong, C.-Z. Impact of Visual and Somatosensory Deprivation on Dynamic Balance in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2010, 35, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorič, M.; Pečak, F.; Trontelj, J.V.; Dimitrijevic, M.R. Postural Control in Scoliosis: A Statokinesimetric Study in Patients with Scoliosis due to Neuromuscular Disorders and in Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981, 52, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, P.R.; Geis, C.C.; Moroz, A.; O’Neill, B.J.; Bogey, R. Stroke and neurodegenerative disorders. 4. neurodegenerative disorders. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’beirne, J.; Goldberg, C.; Dowling, F.E.; Fogarty, E.E. Equilibrial Dysfunction in Scoliosis???Cause or Effect? J. Spinal Disord. 1989, 2, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, P.; Chavet, P.; Barbier, F.; Gatto, L.; Labelle, H.; Sadeghi, H. Effect of Body Morphology on Standing Balance in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 83, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, M.; Toulotte, C.; Gatto, L.; Rivard, C.-H.; Teasdale, N.; Simoneau, M.; Allard, P. Postural imbalance in non-treated adolescent idiopathic scoliosis at different periods of progression. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 18, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Q.; Wang, J.-L.; Tsuang, Y.-H.; Liao, T.-L.; Huang, P.-I.; Hang, Y.-S. The postural stability control and gait pattern of idiopathic scoliosis adolescents. Clin. Biomech. 1998, 13, S52–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalleau, G.; Allard, M.S.; Beaulieu, M.; Rivard, C.-H.; Allard, P. Free moment contribution to quiet standing in able-bodied and scoliotic girls. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Chau, W.W.; Hui-Chan, C.W.Y.; Cheung, C.S.K.; Tsang, W.W.N.; Cheng, J.C.Y. Balance Control in Adolescents With Idiopathic Scoliosis and Disturbed Somatosensory Function. Spine 2006, 31, E437–E440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, M.-L.; Allard, P.; Hinse, S.; Le Blanc, R.; Caron, O.; Labelle, H.; Sadeghi, H. Relations Between Standing Stability and Body Posture Parameters in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2002, 27, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlstrand, T.; Örtengren, R.; Nachemson, A. Postural Equilibrium in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1978, 49, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneau, M.; Mercier, P.; Blouin, J.; Allard, P.; Teasdale, N. Altered sensory-weighting mechanisms is observed in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneau, M.; Richer, N.; Mercier, P.; Allard, P.; Teasdale, N. Sensory deprivation and balance control in idiopathic scoliosis adolescent. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 170, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauchard, G.C.; Lascombes, P.; Kuhnast, M.; Perrin, P.P. Influence of Different Types of Progressive Idiopathic Scoliosis on Static and Dynamic Postural Control. Spine 2001, 26, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haumont, T.; Gauchard, G.C.; Lascombes, P.; Perrin, P.P. Postural Instability in Early-Stage Idiopathic Scoliosis in Adolescent Girls. Spine 2011, 36, E847–E854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurtleff, T.L.; Standeven, J.W.; Engsberg, J.R. Changes in Dynamic Trunk/Head Stability and Functional Reach After Hippotherapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinotti, F.; Correia, N.; Christofoletti, G.; Borges, G. Use of hippotherapy in gait training for hemiparetic post-stroke. Arq. Neuro. Psiquiatr. 2010, 68, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janura, M.; Svoboda, Z.; Cabell, L.; Dvoráková, T.; Jelen, K. Effect of repeated therapeutic horse riding sessions on the trunk movement of the rider. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2015, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Stergiou, A.; Tzoufi, M.; Ntzani, E.; Varvarousis, D.; Beris, A.; Ploumis, A. Therapeutic Effects of Horseback Riding Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Lasa, S.; Ferriero, G.; Valero, R.; Gomez-Muñiz, F.; Rabini, A.; Varela, E. Effect of therapeutic horseback riding on balance and gait of people with multiple sclerosis. G Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2012, 33, 462–467. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.-Y. Effects of mechanical horseback riding on the balance ability of the elderly. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 2499–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, T.; Oh, S.; Yoon, B. Equine Exercise in Younger and Older Adults: Simulated Versus Real Horseback Riding. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2017, 125, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, W.; McGibbon, N.H.; Grant, K.L. Improvements in Muscle Symmetry in Children with Cerebral Palsy after Equine-Assisted Therapy (Hippotherapy). J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2003, 9, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, M.; Ihara, M.; Doumura, M. Effect of therapeutic riding on functional scoliosis as observed by roentgenography. Pediatr. Int. 2012, 54, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, B.A.; Rigby, B.R. Human pelvis motions when walking and when riding a therapeutic horse. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 39, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabard-Fougère, A.; Bonnefoy-Mazure, A.; Hanquinet, S.; Lascombes, P.F.M.; Armand, S.; Dayer, R.O.P. Validity and Reliability of Spine Rasterstereography in Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2017, 42, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankerl, P.; Keller, A.K.; Häberle, L.; Stumptner, T.; Pfaff, G.; Uder, M.; Forst, R. Effects on posture by different neuromuscular afferent stimulations and proprioceptive insoles: Rasterstereographic evaluation. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2016, 40, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, K.M.; Guzman, J. Evaluation of Static and Dynamic Postural Balance in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2013, 25, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Basatiny, H.M.Y.; Abdel-Aziem, A.A. Effect of backward walking training on postural balance in children with hemiparetic cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled study. Clin. Rehabil. 2014, 29, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, F.; Urak, Ö.; Akkaya, N. Evaluation of balance in young adults with idiopathic scoliosis. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 65, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliere, C.; Collado-Mateo, D.; Villafaina, S.; Duque-Fonseca, P.; Parraça, J.A. Benefits of Hippotherapy and Horse Riding Simulation Exercise on Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review. PM&R 2018, 10, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Parent, E.C.; Hill, D.L.; Hedden, D.M.; Moreau, M.J.; Southon, S.C. Patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis perceive positive improvements regardless of change in the Cobb angle—Results from a randomized controlled trial comparing a 6-month Schroth intervention added to standard care and standard care alone. SOSORT 2018 Award winner. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, H.-R. The Method of Katharina Schroth—History, Principles and Current Development. Scoliosis 2011, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biery, M.J.; Kauffman, N. The Effects of Therapeutic Horseback Riding on Balance. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 1989, 6, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldmann, T.; Vilimek, M. Kinematics of human spine during hippotherapy. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 15, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi, R.; Masuda, K.; Uchiyama, H.; Ohta, M. A possible mechanism of horseback riding on dynamic trunk alignment. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.R.; Lee, N.G.; Cha, H.J.; Sung, O.Y.; You, S.; Joshua, H.; Oh, J.H.; Bang, H.S. The effect of robo-horseback riding therapy on spinal alignment and associated muscle size in MRI for a child with neuromuscular scoliosis: An experimenter-blind study. Neurorehabilitation 2011, 29, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, S.-G.; Hwangbo, G. The effects of horse-riding simulator exercise and Kendall exercise on the forward head posture. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 1125–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbar, M.; Salekzamani, Y.; Jahanjou, F.; Eslamian, F.; Niroumand, A.; Dolatkhah, N. Effect of hippotherapy simulator on pain, disability and range of motion of the spinal column in subjects with mechanical low back pain: A randomized single-blind clinical trial. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2018, 31, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-H.; Kim, S.-E.; Lee, M.-G.; Jin, J.-J.; Hong, J.; Choi, Y.-T.; Kim, M.-H.; Jee, Y.-S. The effect of horse simulator riding on visual analogue scale, body composition and trunk strength in the patients with chronic low back pain. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2014, 68, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, T.B.; Silva, N.A.; Costa, J.N.; Pereira, M.M.; Safons, M.P. Effect of equine-assisted therapy on the postural balance of the elderly. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2011, 15, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homnick, D.N.; Henning, K.M.; Swain, C.V.; Homnick, T.D. Effect of Therapeutic Horseback Riding on Balance in Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Balance Deficits. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2013, 19, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda-García, S.; Iricibar, A.; Planas, A.; Prat-Subirana, J.A.; Angulo-Barroso, R.M. Comparative Effects of Horse Exercise Versus Traditional Exercise Programs on Gait, Muscle Strength, and Body Balance in Healthy Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handzel, T.M. Core training for improved performance. NSCA’S Perform. Train. J. 2014, 2, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs, A.; Thompson, K.; French, D.; Hodgson, D.; Spears, I. Peak and average rectified EMG measures: Which method of data reduction should be used for assessing core training exercises? J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2011, 21, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, D.G.; Drinkwater, E.J.; Willardson, J.M.; Cowley, P.M. The use of instability to train the core musculature. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 35, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, H.; Terada, K.; Mullineaux, D.R.; Lanovaz, J.; Kato, K. Electromyographic analysis of the rider’s muscles at trot. Equine Comp. Exerc. Physiol. 2004, 1, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Looze, M.; Groen, H.; Horemans, H.; Kingma, I.; van Dieen, J. Abdominal muscles contribute in a minor way to peak spinal compression in lifting. J. Biomech. 1999, 32, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGibbon, N.H.; Benda, W.; Duncan, B.R.; Silkwood-Sherer, D. Immediate and Long-Term Effects of Hippotherapy on Symmetry of Adductor Muscle Activity and Functional Ability in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Parent, E.C.; Moez, E.K.; Hedden, D.M.; Hill, D.L.; Moreau, M.; Lou, E.; Watkins, E.M.; Southon, S.C. Schroth Physiotherapeutic Scoliosis-Specific Exercises Added to the Standard of Care Lead to Better Cobb Angle Outcomes in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis—An Assessor and Statistician Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuru, T.; Yeldan, I.; Dereli, E.E.; Özdinçler, A.R.; Dikici, F.; Çolak, I. The efficacy of three-dimensional Schroth exercises in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomised controlled clinical trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2015, 30, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Parent, E.C.; Hedden, D.M.; Moreau, M.; Hill, D.; Lou, E. Effect of Schroth exercises on curve characteristics and clinical outcomes in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial. J. Physiother. 2014, 60, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsaris, G.; Loukos, A.; Valavanis, J.; Vassiliou, M.; Behrakis, P.K. The immediate effect of a Boston brace on lung volumes and pulmonary compliance in mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 1999, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yagci, G.; Demirkiran, G.; Yakut, Y. In-brace alterations of pulmonary functions in adolescents wearing a brace for idiopathic scoliosis. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2019, 43, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Aulisa, A.G.; Czaprowski, D.; Schreiber, S.; De Mauroy, J.C.; Diers, H.; Grivas, T.B.; Knott, P.; Kotwicki, T.; et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, B.S.; Bernstein, R.M.; D’Amato, C.R.; Thompson, G.H. Standardization of criteria for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis brace studies: SRS Committee on Bracing and Nonoperative Management. Spine 2005, 30, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, F.; Vescio, A.; Caldaci, A.; Vancheri, A.; Di Maria, C.; Sapienza, M.; Testa, G.; Pavone, V. Immediate Effects of Sforzesco® Bracing on Respiratory Function in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Health 2021, 9, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Groups | Experimental Group, n = 27 | Control Group B, n = 25 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 14.74 ± 1.79 | 15.04 ± 1.81 | 0.552 a |
| Height, cm | 157.22 ± 6.88 | 158.00 ± 7.27 | 0.693 a |
| Weight, kg | 48.99 ± 5.15 | 50.54 ± 5.28 | 0.289 a |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 19.77 ± 1.02 | 20.21 ± 1.05 | 0.133 a |
| Cobb angle, degree | 18.59 ± 2.66 | 19.32 ± 2.69 | 0.332 a |
| Gender, male/female | 8/19 | 7/18 | 0.897 b |
| Variables | Experimental Group, n = 27 | Control Group, n = 25 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scoliotic angle, degrees | Pre | 24.09 ± 5.50 | 25.06 ± 5.24 | 0.520 |
| Post | 18.41 ± 5.42 | 22.32 ± 4.73 | 0.008 * | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | ||
| Kyphotic angle, degrees | Pre | 49.26 ± 6.19 | 50.32 ± 5.76 | 0.526 |
| Post | 44.26 ± 5.47 | 48.00 ± 5.45 | 0.017 * | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | ||
| Pelvic obliquity, degrees | Pre | 4.91 ± 1.46 | 4.99 ± 1.38 | 0.838 |
| Post | 2.37 ± 1.05 | 3.08 ± 0.90 | 0.012 * | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | ||
| Pelvic torsion, degrees | Pre | 1.92 ± 0.82 | 1.95 ± 0.81 | 0.897 |
| Post | 1.07 ± 0.55 | 1.51 ± 0.70 | 0.013 * | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | ||
| Vertical rotation (RMS), degrees | Pre | 4.09 ± 1.49 | 4.30 ± 1.35 | 0.602 |
| Post | 2.51 ± 1.14 | 3.34 ± 1.12 | 0.011 * | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | ||
| Variables | Experimental Group, n = 27 | Control Group, n = 25 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall stability index | Pre | 0.39 ± 0.11 | 0.41 ± 0.12 | 0.632 |
| Post | 0.32 ± 0.10 | 0.39 ± 0.11 | 0.024 * | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | ||
| Anteroposterior stability index | Pre | 0.28 ± 0.11 | 0.29 ± 0.12 | 0.746 |
| Post | 0.21 ± 0.10 | 0.28 ± 0.11 | 0.033* | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | ||
| Mediolateral stability index | Pre | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.25 ± 0.12 | 0.751 |
| Post | 0.18 ± 0.09 | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.041 * | |
| p-value | 0.001 * | 0.012 * | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel-aziem, A.A.; Abdelraouf, O.R.; Ghally, S.A.; Dahlawi, H.A.; Radwan, R.E. A 10-Week Program of Combined Hippotherapy and Scroth’s Exercises Improves Balance and Postural Asymmetries in Adolescence Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Children 2022, 9, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010023
Abdel-aziem AA, Abdelraouf OR, Ghally SA, Dahlawi HA, Radwan RE. A 10-Week Program of Combined Hippotherapy and Scroth’s Exercises Improves Balance and Postural Asymmetries in Adolescence Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Children. 2022; 9(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel-aziem, Amr A., Osama R. Abdelraouf, Shahesta A. Ghally, Haytham A. Dahlawi, and Rafik E. Radwan. 2022. "A 10-Week Program of Combined Hippotherapy and Scroth’s Exercises Improves Balance and Postural Asymmetries in Adolescence Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Controlled Study" Children 9, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010023
APA StyleAbdel-aziem, A. A., Abdelraouf, O. R., Ghally, S. A., Dahlawi, H. A., & Radwan, R. E. (2022). A 10-Week Program of Combined Hippotherapy and Scroth’s Exercises Improves Balance and Postural Asymmetries in Adolescence Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Children, 9(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9010023






