The Child Behavior Checklist as a Screening Instrument for PTSD in Refugee Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Assessment
2.2. Psychometric Testing and Statistical Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analysis
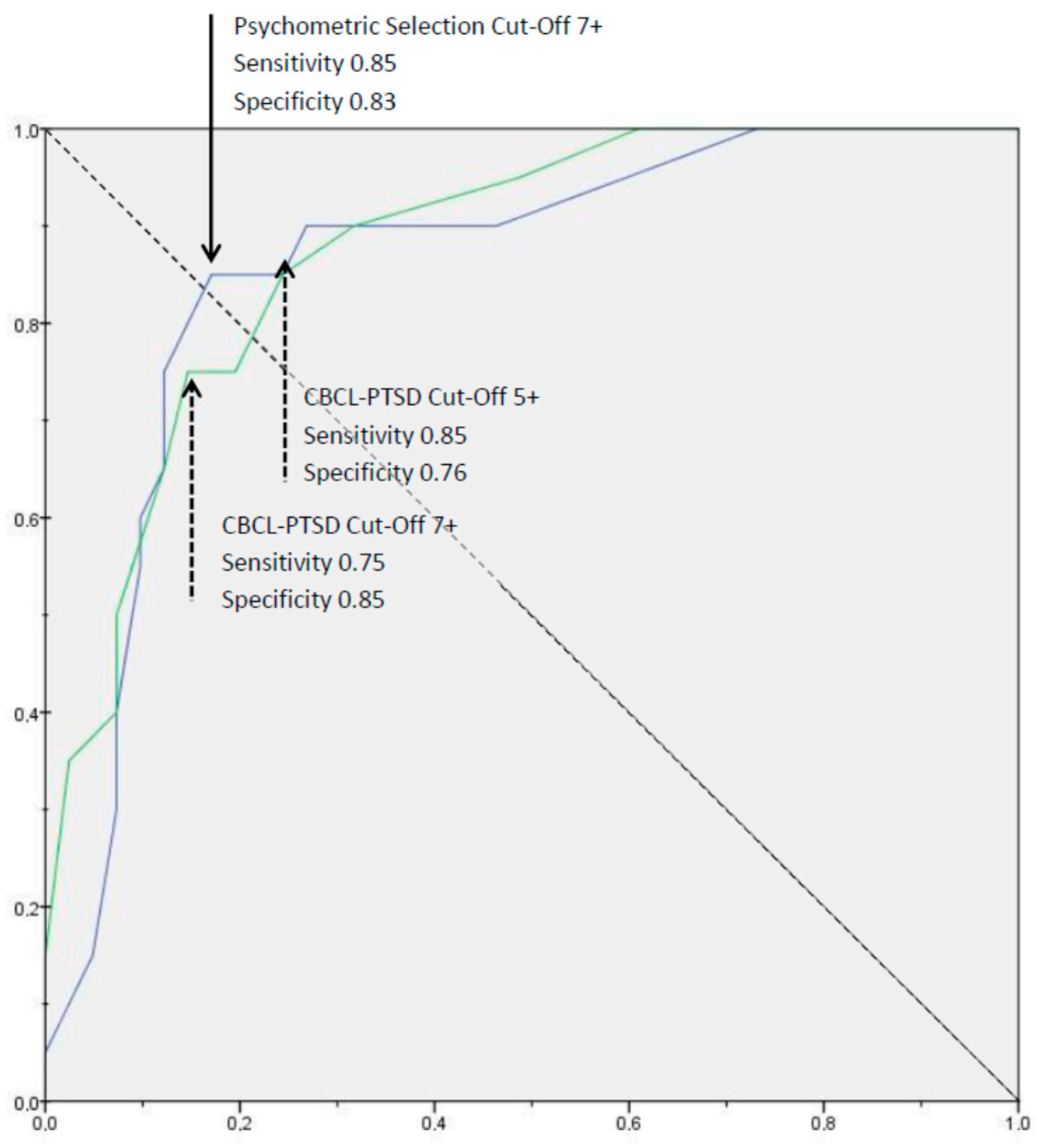
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Test Results
3.2.1. Item-Frequencies and Item/Criterion-Item/Total Correlations
3.2.2. Internal Consistency and Proposed Cut-Offs
4. Discussion
Strengths & Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberer, M.; Wendeborn, M.; Löscher, T.; Seilmaier, M. Spectrum of diseases occurring in refugees and asylum seekers: Data from three different medical institutions in the Munich area from 2014 and 2015. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2016, 141, e8–e15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Berlaer, G.; Carbonell, F.B.; Manantsoa, S.; de Béthune, X.; Buyl, R.; Debacker, M.; Hubloue, I. A refugee camp in the centre of Europe: Clinical characteristics of asylum seekers arriving in Brussels. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e013963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpak, G.; Unal, A.; Bulbul, F.; Sagaltici, E.; Bez, Y.; Altindag, A.; Dalkilic, A.; Savas, H.A. Post-traumatic stress disorder among Syrian refugees in Turkey: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2015, 19, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazel, M.; Wheeler, J.; Danesh, J. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7000 refugees resettled in western countries: A systematic review. Lancet 2005, 365, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slone, M.; Mann, S. Effects of War, Terrorism and Armed Conflict on Young Children: A Systematic Review. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2016, 47, 950–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soykoek, S.; Mall, V.; Nehring, I.; Henningsen, P.; Aberl, S. Post-traumatic stress disorder in Syrian children of a German refugee camp. Lancet 2017, 389, 903–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutermann, J.; Schreiber, F.; Matulis, S.; Schwartzkopff, L.; Deppe, J.; Steil, R. Psychological Treatments for Symptoms of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 19, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morina, N.; Koerssen, R.; Pollet, T.V. Interventions for children and adolescents with posttraumatic stress disorder: A meta-analysis of comparative outcome studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 47, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AACAP. Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 49, 414–430. [Google Scholar]
- Gadeberg, A.; Montgomery, E.; Frederiksen, H.; Norredam, M. Assessing trauma and mental health in refugee children and youth: A systematic review of validated screening and measurement tools. Eur. J. Public Health 2017, 27, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foa, E.B.; Johnson, K.M.; Feeny, N.C.; Treadwell, K.R.H. The child PTSD Symptom Scale: A preliminary examination of its psychometric properties. J. Clin. Child. Psychol. 2001, 30, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, A.M.; Brymer, M.J.; Decker, K.B.; Pynoos, R.S. The UCLA PTSD Reaction Index. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2004, 6, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagay, S.; Düllmann, S.; Hermans, E.; Repic, N.; Hiller, R.; Senf, W. Das Essener Trauma-Inventar für Kinder und Jugendliche (ETI-KJ). 2007. Available online: https://www.uni-due.de/rke-pp/essenertraumainventareti.php (accessed on 15 May 2017).
- Levendosky, A.A.; Huth-Bocks, A.C.; Semel, M.A.; Shapiro, D.L. Trauma symptoms in preschool-age children exposed to domestic violence. J. Interpers. Violence 2002, 17, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehon, C.; Scheeringa, M.S. Screening for Preschool Posttraumatic Stress Disorder with the Child Behavior Checklist. J. Pediatric. Psychol. 2006, 31, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, V.V.; Gentile, C.; Wolfe, D.A. The Impact of Sexual Abuse on Children: A PTSD Formulation. Behav. Ther. 1989, 20, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, K.J.; McLeer, S.V. PTSD scale of the Child Behavior Checklist: Concurrent and discriminant validity with non-clinic-referred sexually abused children. J. Trauma. Stress 2000, 13, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, N.; Stewart, J. The MacArthur Scale of Subjective Social Status. 2007. Available online: http://www.macses.ucsf.edu/research/psychosocial/subjective.php (accessed on 15 May 2017).
- Nehring, I.; Schlag, E.; Qirjako, E.; Büyükyaglioglu, C.; Mall, V.; Sattel, H.; Sack, M.; Henningsen, P.; Aberl, S. Health State of Syrian Children and Their Parents in a German Refugee Camp. J. Refug. Stud. 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnewehr, S.; Schneider, S.; Margraf, J. Kinder-DIPS: Diagnostisches Interview bei Psychischen Störungen im Kindes- und Jugendalter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Irblich, A.G.D.; Landhold, M.A. Posttraumatische Belastungsstörungen bei Säuglingen und Kleinkindern [Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Infants and Toddlers]. Praxis der Kinderpsychologie und Kinderpsychiatrie 2008, 57, 247–263. [Google Scholar]
- Scheeringa, M.S.; Zeanah, C.H. PTSD Semi-Structured Interview and Observation Record for Infants and Young Children; T.U.H.S.C. Department of Psychiatry and Neurology: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Achenbach, T.M. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist 4-18 and 1991 Profile; University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry: Burlington, VT, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Döpfner, M.U.A. Elternfragebogen Über das Verhalten von Kindern und Jugendlichen: Deutsche Beabeitung der Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL/4-18). 1998. Available online: www.testzentrale.de (accessed on 1 June 2013).
- Achenbach, T.M.; Rescorla, L.A. Chapter 9 Reliability, Internal Consistency, Cross-Informant Agreement, and Stability in Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms and Profiles; University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families: Burlington, VT, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.A.; Watson, D. Constructing validity: Basic issues in objective scale development. Psychol. Assess. 1995, 7, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienert, G.A.; Raatz, U. Testaufbau und Testanalyse; Beltz PVU: Weinheim, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Moosbrugger, H.; Kelava, A. (Eds.) Deskriptivstatistische Evaluation von Items (Itemanalyse) und Testwertverteilungen, in Testtheorie und Fragebogenkonstruktion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Upadhye, S.; Worster, A. Understanding receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. CJEM 2006, 8, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeer, S.V.; Callaghan, M.; Henry, D.; Wallen, J. Psychiatric disorders in sexually abused children. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1994, 33, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbaran, B.; Erermis, S.; Bukusoglu, N.; Bildik, T.; Tamar, M.; Ercan, E.S.; Aydin, C.; Cetin, S.K. Social and emotional outcomes of child sexual abuse: A clinical sample in Turkey. J. Interpers Violence 2009, 24, 1478–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, T.; Maerker, A. Komplexe posttraumatische Belastungsstörung nach ICD-11. Psychotherapeut 2015, 60, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PTSD (n = 20) | No PTSD (n = 41) | |
|---|---|---|
| Children 4–14 years | ||
| Age (years (SD)) | 8.2 (2.5) | 9.3 (2.9) |
| Boys (n) | 12 | 24 |
| Religion (n) | ||
| Islam | 19 | 39 |
| Other | 1 | 2 |
| In Germany since, months (SD) | 1.1 (1.1) | 1.1 (1.0) |
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Interview partner (n = 38) | |
| mother | 27 (71.1) |
| father | 11 (28.9) |
| Country of birth | |
| Syria | 35 (92.1) |
| other (Iraq, Jordan, Libya) | 3 (7.9) |
| Religion | |
| Islam | 36 (94.7) |
| other | 2 (5.3) |
| Mother tongue | |
| Arabic | 30 (78.9) |
| Kurdish | 5 (13.2) |
| other | 3 (7.9) |
| Communication (language) problems in Germany 1 | 29 (76.3) |
| Feels socially isolated 2 | 17 (44.7) |
| Community-based subjective sociodemographic status in Germany above the median 3 | 19 (51.3) |
| Society-based subjective sociodemographic status in Germany above the median 3 | 12 (35.3) |
| CBCL Item Selections | Coincidence of Item with PTSD Diagnosis 1 | Occurrence/Frequency 2 [%] | Item—Total Correlation 1 (CBCL-PTSD-Scale) | Item—Total Correlation 1 (Psycho-Metrically Guided Item Selection) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequent Behaviors, Well Associated with a PTSD-Diagnosis Overlapping Items of both Item Selections | ||||
| Unhappy, sad. or depressed a | 0.60 | 47.5 | 0.762 | 0.766 |
| Nightmares a | 0.48 | 41.0 | 0.597 | 0.702 |
| Cannot concentrate, cannot pay attention for long a | 0.45 | 23.0 | 0.483 | 0.552 |
| Sudden changes in mood or feelings a | 0.45 | 19.7 | 0.537 | 0.554 |
| Trouble sleeping a | 0.42 | 36.1 | 0.522 | 0.588 |
| Too fearful, anxious a | 0.39 | 37.7 | 0.451 | 0.507 |
| Stubborn, sullen/irritable a | 0.38 | 34.4 | 0.451 | 0.468 |
| Fears certain places, animals, situations other than school a | 0.37 | 35.0 | 0.467 | 0.412 |
| Nervous, high-strung, or tense a | 0.33 | 25.0 | 0.455 | 0.480 |
| Clings to adults or too dependent a | 0.22 | 35.0 | 0.381 | 0.394 |
| Argues a lot a | 0.20 | 45.9 | 0.257 | 0.274 |
| Rare/Unassociated Behaviors Additional Items of CBCL-PTSD Subscale | ||||
| Withdrawn, does not get involved with others | 0.36 | 9.8 | 0.337 | – |
| Stomachaches and cramps | 0.25 | 13.1 | 0.203 | – |
| Feels others are out to get him/her | 0.25 | 13.1 | 0.305 | – |
| Cannot get his/her mind off certain thoughts, obsessions | 0.25 | 13.1 | 0.367 | – |
| Feels too guilty | 0.12 | 9.8 | 0.258 | – |
| Vomiting and throwing up | 0.07 | 3.3 | 0.061 | – |
| Secretive and keeps things to self | 0.03 | 27.9 | 0.249 | – |
| Headaches | 0.01 | 5.0 | 0.140 | – |
| Nausea and feels sick | −0.04 | 6.7 | 0.000 | – |
| Additional Psychometrically Suitable Items (Psychometrically Guided Item Selection) | ||||
| Disobedient at home | 0.41 | 32.8 | – | 0.561 |
| Impulsive or acts without thinking | 0.32 | 21.3 | – | 0.590 |
| Cries a lot | 0.30 | 39.3 | – | 0.649 |
| Too shy or timid | 0.28 | 36.1 | – | 0.371 |
| Does not get along with others | 0.28 | 23.3 | – | 0.383 |
| Worries | 0.27 | 29.7 | – | 0.653 |
| Can’t sit still, restless, or hyperactive | 0.22 | 26.2 | – | 0.373 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nehring, I.; Sattel, H.; Al-Hallak, M.; Sack, M.; Henningsen, P.; Mall, V.; Aberl, S. The Child Behavior Checklist as a Screening Instrument for PTSD in Refugee Children. Children 2021, 8, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060521
Nehring I, Sattel H, Al-Hallak M, Sack M, Henningsen P, Mall V, Aberl S. The Child Behavior Checklist as a Screening Instrument for PTSD in Refugee Children. Children. 2021; 8(6):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060521
Chicago/Turabian StyleNehring, Ina, Heribert Sattel, Maesa Al-Hallak, Martin Sack, Peter Henningsen, Volker Mall, and Sigrid Aberl. 2021. "The Child Behavior Checklist as a Screening Instrument for PTSD in Refugee Children" Children 8, no. 6: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060521
APA StyleNehring, I., Sattel, H., Al-Hallak, M., Sack, M., Henningsen, P., Mall, V., & Aberl, S. (2021). The Child Behavior Checklist as a Screening Instrument for PTSD in Refugee Children. Children, 8(6), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060521





