Associations between Language at 2 Years and Literacy Skills at 7 Years in Preterm Children Born at Very Early Gestational Age and/or with Very Low Birth Weight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
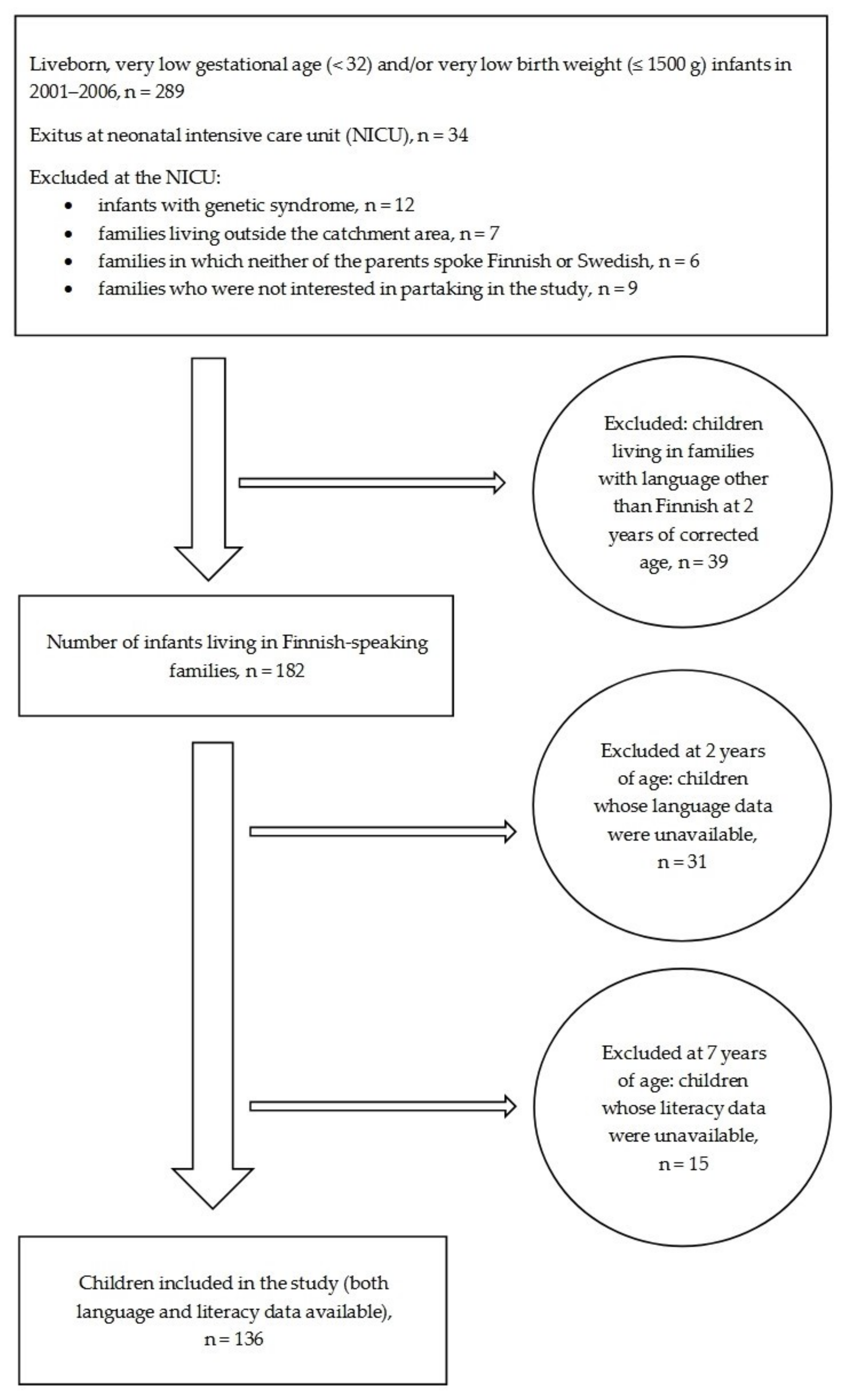
2.1. Participants
2.2. Assessment at 2 Years of Corrected Age
2.3. Assessment at 7 Years
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Data Description
3.2. Associations between Language Development at 2 years of Corrected Age and Literacy Skills at 7 Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Reading Precursors | Reading | Writing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | |
| Gestational age | 0.01 | −0.87 to 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.02 | −0.53 to 0.65 | 0.81 | −0.04 | −0.78 to 0.52 | 0.73 |
| Reading difficulties | |||||||||
| Mothers | 0.08 | −2.67 to 3.90 | 0.38 | 0.06 | −0.85 to 3.43 | 0.45 | 0.13 | −0.58 to 4.12 | 0.22 |
| Fathers | −0.10 | −6.62 to 1.95 | 0.25 | −0.02 | −3.21 to 2.36 | 0.80 | −0.04 | −3.75 to 2.38 | 0.66 |
| Paternal education | 0.06 | −1.36 to 3.45 | 0.47 | 0.19 | 0.38 to 3.51 | 0.029 | 0.12 | −0.50 to 2.94 | 0.26 |
| Lexicon size | 0.38 | 0.01 to 0.19 | <0.001 | 0.39 | 0.01 to 0.15 | <0.001 | 0.34 | 0.005 to 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Fit statistics | |||||||||
| F | 4.2 | 5.3 | 3.3 | ||||||
| P for F | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.12 | ||||||
| ΔR2 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| Reading Precursors | Reading | Writing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | |
| Gestational age | 0.005 | −0.90 to 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.02 | −0.54 to 0.67 | 0.62 | −0.04 | −0.80 to 0.51 | 0.66 |
| Reading difficulties | |||||||||
| Mothers | 0.03 | −2.80 to 3.80 | 0.77 | 0.09 | −1.02 to 3.33 | 0.63 | 0.12 | −0.66 to 4.03 | 0.16 |
| Fathers | −0.10 | −6.70 to 1.90 | 0.27 | −0.03 | −3.32 to 2.37 | 0.72 | −0.04 | −3.80 to 2.32 | 0.63 |
| Paternal education | 0.05 | −1.80 to 3.04 | 0.61 | 0.17 | 0.02 to 3.22 | 0.04 | 0.09 | −0.82 to 2.62 | 0.30 |
| M3L | 0.34 | 0.30 to 0.91 | <0.001 | 0.38 | 0.26 to 0.67 | <0.001 | 0.36 | 0.24 to 0.68 | <0.001 |
| Fit statistics | |||||||||
| F | 3.4 | 5.6 | 4.1 | ||||||
| P for F | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.002 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.16 | ||||||
| ΔR2 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
| Reading Precursors | Reading | Writing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | |
| Gestational age | 0.01 | −0.86 to 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.02 | −0.52 to 0.68 | 0.80 | −0.03 | −0.79 to 0.53 | 0.70 |
| Reading difficulties | |||||||||
| Mothers | 0.04 | −2.61 to 4.15 | 0.65 | 0.11 | −0.72 to 3.65 | 0.38 | 0.14 | −0.40 to 4.34 | 0.10 |
| Fathers | −0.09 | −6.64 to 2.13 | 0.31 | −0.02 | −3.19 to 2.48 | 0.81 | −0.04 | −0.370 to 2.50 | 0.68 |
| Paternal education | 0.06 | −1.60 to 3.32 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.20 to 3.38 | 0.03 | 0.11 | −0.70 to 2.80 | 0.22 |
| ELS | 0.29 | 0.14 to 0.59 | 0.002 | 0.38 | 0.19 to 0.48 | <0.001 | 0.35 | 0.16 to 0.47 | <0.001 |
| Fit statistics | |||||||||
| F | 2.5 | 5.5 | 3.7 | ||||||
| P for F | 0.04 | <0.001 | 0.004 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.14 | ||||||
| ΔR2 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.10 |
References
- Foster-Cohen, S.; Edgin, J.O.; Champion, P.R.; Woodward, E.J. Early delayed language development in very preterm infants: Evidence from the MacArthur-Bates CDI. J. Child Lang. 2007, 34, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansavini, A.; Guarini, A.; Justice, L.M.; Savini, S.; Broccoli, S.; Alessandroni, R.; Faldella, G. Does preterm birth increase a child’s risk for language impairment? Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolt, S.; Matomäki, J.; Lind, A.; Lapinleimu, H.; Haataja, L.; Lehtonen, L. The prevalence and predictive value of weak language skills in children with very low birth weight—A longitudinal study. Acta Paediatr 2014, 103, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twilhaar, E.S.; de Kieviet, J.F.; Aarnoudse-Moens, C.S.H.; van Elburg, R.M.; Oosterlaan, J. Academic performance of children born preterm: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 103, F322–F330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munck, P.; Niemi, P.; Väliaho, A.; Lapinleimu, H.; Lehtonen, L.; Haataja, L. Prereading skills of very-low-birth-weight prematurely born Finnish children. Child Neuropsychol. 2012, 18, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarini, A.; Bonifacci, B.; Tobia, V.; Alessandroni, R.; Faldella, G.; Sansavini, A. The profile of very preterm children on academic achievement. A cross-population comparison with children with specific learning disorders. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 87, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanko, O.; Niemi, P.; Munck, P.; Matomäki, J.; Turunen, T.; Nurmi, J.-E.; Lehtonen, L.; Haataja, L.; Rautava, P. Reading and math abilities of Finnish school beginners born very preterm or with very low birth weight. Learn Individ. Differ. 2017, 54, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noort-van der Spek, I.; Franken, M.-C.; Weisglas-Kuperus, N. Language Functions in Preterm-Born Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovachy, V.N.; Adams, J.N.; Tamaresis, J.S.; Feldman, H.M. Reading abilities in school-aged preterm children: A review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-N.-N.; Spencer-Smith, M.; Zannino, D.; Burnett, A.; Scratch, S.E.; Pascoe, L.; Ellis, R.; Cheong, J.; Thompson, D.; Inder, T.; et al. Developmental trajectory of language from 2 to 13 years in children born very preterm. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnick, D.L.; Bornstein, M.H.; Eryigit-Madzwamuse, S.; Wolke, D. Long-Term Stability of Language Performance in Very Preterm, Moderate-Late Preterm, and Term Children. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkaluk, M.-L.; Rousseau, J.; Benhammou, V.; Datin-Dorrière, V.; Flamant, C.; Gire, C.; Kern, S.; Pierrat, V.; Kaminski, M.; Marret, S. Association of Language Skills with Other Developmental Domains in Extremely, Very, and Moderately Preterm Children: EPIPAGE 2 Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2019, 208, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenson, L.; Marchman, V.A.; Thal, D.J.; Dale, P.S.; Reznick, J.S.; Bates, E. MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventories. In User’s Guide and Technical Manual, 2nd ed.; Paul H. Brookes Publisihing Co.: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guarini, A.; Sansavini, A.; Fabbri, C.; Savini, S.; Alessandroni, R.; Faldella, G.; Karmiloff-Smith, A. Long-term effects of preterm birth on language and literacy at eight years. J. Child Lang. 2010, 37, 865–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wocadlo, C.; Rieger, I. Phonology, rapid naming and academic achievement in very preterm children at eight years of age. Early Hum. Dev. 2007, 83, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochers, L.R.; Bruckert, L.; Travis, K.E.; Dodson, C.K.; Loe, I.M.; Marchman, V.A.; Feldman, H.M. Predicting text reading skills at age 8 years in children born preterm and at term. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 130, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, V.E.; Samudragupta, B.; Austin, N.C.; Levin, K.J.; Woodward, L.J. Identifying Very Preterm Children at Educational Risk Using a School Readiness Framework. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e825–e832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holopainen, L.; Ahonen, T.; Lyytinen, H. Predicting Delay in Reading Achievement in a Highly Transparent Language. J. Learn. Disabil. 2001, 34, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, P.; Nurmi, J.-E.; Lyyra, A.-L.; Lerkkanen, M.-K.; Lepola, J.; Poskiparta, E.; Poikkeus, A.-M. Task avoidance, number skills and parental learning difficulties as predictors of poor response to instruction. J. Learn. Disabil. 2011, 44, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torppa, M.; Lyytinen, P.; Erskine, J.; Eklund, K.; Lyytinen, H. Language Development, Literacy Skills, and Predictive Connections to Reading in Finnish Children with and Without Familial Risk for Dyslexia. J. Learn. Disabil. 2010, 43, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyytinen, P.; Lyytinen, H. Growth and predictive relations of vocabulary and inflectional morphology in children with and without familial risk for dyslexia. Appl. Psycholinguist. 2004, 25, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PIPARI. Development and Functioning of very Low Birth Weight Infants from Infancy to School Age. Available online: https://sites.utu.fi/pipari/en/ (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Setänen, S.; Lehtonen, L.; Lapinleimu, H.; Haataja, L. Lessons learnt about the long-term neurodevelopment in very preterm born children in the PIPARI Study. Lääketieteellinen Aikakausk Duodecim 2018, 134, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bayley, N. Bayley Scales of Infant Development, 2nd ed.; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lyytinen, P. Varhaisen Kommunikaation ja Kielen Kehityksen Arviointimenetelmä, The adapted Finnish long-form version of the MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventories; Niilo Mäki–Instituutti: Jyväskylä, Finland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Poskiparta, E. Miten Ehkäisen Oppilaitteni Luku- ja Kirjoitusvaikeuden Syntymisen? Kielellisen Tietoisuuden Kehittäminen 1. Luokalla Ryhmämuotoisena Erityisopetuksena; Developing linquistic awareness in Grade 1; University of Turku, Centre for Learning Research: Turku, Finland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lerkkanen, M.K.; Poikkeus, A.M.; Ketonen, R. ARMI–Luku- ja Kirjoitustaidon Arviointimateriaali 1. Luokalle; ARMI–A tool for assessing reading and writing skills in Grade 1; WSOY: Helsinki, Finland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tape, T.G. The Area under an ROC Curve. Available online: http://gim.unmc.edu/dxtests/ROC3.htm (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Setänen, S.; Haataja, L.; Parkkola, R.; Lind, A.; Lehtonen, L. Predictive value of neonatal brain MRI on the neurodevelopmental outcome of preterm infants by 5 years of age. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pereira, M.; Martínez-López, Z.; Maneiro, L. Longitudinal relationships between reading abilities, phonological awareness, language abilities and executive functions: Comparison of low risk preterm and full-term children. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Pascoe, L.; Scratch, S.; Doyle, L.W.; Anderson, P.; Roberts, G. A simple screen performed at school entry can predict academic under-achievement at age seven in children born very preterm. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2016, 52, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, A.; Korhonen, T.; Munck, P.; Parkkola, R.; Lehtonen, L.; Haataja, L. Factors affecting the cognitive profile of 11-year-old children born very preterm. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescorla, L. Do late-talking toddlers turn out to have reading difficulties a decade later? Ann. Dyslexia 2000, 50, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescorla, L. Age 17 Language and reading outcomes in late-talking toddlers: Support for dimensional perspective on language delay. J. Speech Lang. Hear 2009, 52, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.L.; Frost, S.J.; Mencl, W.E.; Fulbright, R.K.; Landi, N.; Grigorenko, E.; Jacobsen, L.; Pugh, K.R. Early and late talkers: School-age language, literacy and neurolinguistics differences. Brain 2010, 133, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Children Born VP/VLBW | Controls |
|---|---|---|
| (n = 136) | (n = 137) | |
| n (%) | n (%) | |
| Gestational age (weeks); M (SD), (min., max) | 28.9 (2.7) (23.0, 35.9) | 40.2 (1.2) (37.1, 42.3) |
| Birth weight (grams); M (SD) (min., max) | 1116 (303) (400, 1820) | 3663 (442) (2830, 4980) |
| Small for gestational age a, | 39 (29) | 0 |
| Prenatal corticosteroids | 129 (95) | – |
| Multiple birth | 49 (36) | 0 |
| Male | 83 (61) | 67 (49) |
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia | 22 (8) | – |
| Laser-treated retinopathy of prematurity | 4/127 d (3), | – |
| Neurodevelopmental impairment | 13 (10) | 0 |
| Mental Developmental Index <70 | 3/134 d (2) | 0 |
| Cerebral palsy | 9 (7) | 0 |
| Hearing impairment (threshold >40) | 4 (3) | 0 |
| Visual impairment | 0 | 0 |
| Brain pathology, MRI at term age b | – | |
| Normal finding or minor abnormality | 94/135 d (69) | – |
| Major abnormality | 41/135 d (30) | – |
| Maternal education c | ||
| High | 64/127 d (47) | 43 (31) |
| Intermediate | 52/127 d (38) | 70 (51) |
| Low | 11/127 d (8) | 24 (18) |
| Paternal education c | ||
| High | 36/126 d (27) | 36 (26) |
| Intermediatel | 80 (59) | 72 (53) |
| Low | 10 (7) | 29 (21) |
| VP/VLBW Children | Controls | Group Comparison for the Mean | VP/VLBW Children | Controls | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Mean (SD) (min, max) | Mean (SD) (min, max) | 95% CI | p | Weak skills n (%) | Weak skills n (%) |
| Language at 2 years | ||||||
| Lexicon size | 236 (159) (4, 574) | 281 (164) (9, 581) | 5.87 to 82.76 | 0.017 | 21 (15%) | 6 (4%) |
| M3L | 5 (3) (1, 14) | 6 (4) (1, 21) | 0.02 to 1.61 | 0.036 | 26 (21%) | 18 (14%) |
| ELS | 9 (5) (0, 15) | 11 (5) (0, 15) | 0.86 to 3.31 | <0.001 | 21 (17%) | 13 (10%) |
| Literacy skills at 7 years | ||||||
| Reading precursors | 30 (8) (3, 38) | 33 (6) (11, 38) | 1.08 to 4.56 | 0.002 | 27 (20%) | 13 (10%) |
| Reading | 4 (4) (0, 10) | 6 (4) (0, 10) | 0.55 to 2.57 | 0.003 | 49 (36%) | 25 (18%) |
| Writing | 3 (4) (0, 13) | 4 (4) (0, 13) | 0.70 to 2.65 | 0.001 | 64 (48%) | 45 (33%) |
| VP/VLBW children without NDI | ||||||
| Language at 2 years | ||||||
| Lexicon size | 247 (155) (4, 574) | −5.08 to 73.1 | 0.087 | 16 (13%) | ||
| M3L | 5 (3) (1, 14) | −0.20 to 1.43 | 0.138 | 20 (18%) | ||
| ELS | 9 (5) (0, 15) | 0.57 to 3.05 | 0.004 | 17 (15%) | ||
| Literacy skills at 7 years | ||||||
| Reading precursors | 31 (8) (4, 38) | 0.64 to 4.06 | 0.007 | 23 (19%) | ||
| Reading | 4 (4) (0, 10) | 0.42 to 2.50 | 0.006 | 36 (44%) | ||
| Writing | 3 (4) (0, 13) | 0.59 to 2.60 | 0.002 | 60 (49%) |
| 7 y | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reading Precursors | Reading Skills | Writing Skills | |
| 2 y | |||
| Children born VP/VLBW | |||
| Lexicon size | 0.37 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.33 ** |
| M3L | 0.43 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.31 ** |
| ELS | 0.36 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.29 ** |
| Children born VP/VLBW without NDI | |||
| Lexicon size | 0.33 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.34 ** |
| M3L | 0.39 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.32 ** |
| ELS | 0.30 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.31 ** |
| Controls | |||
| Lexicon size | 0.32 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.32 ** |
| M3L | 0.34 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.36 ** |
| ELS | 0.29 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.33 ** |
| Weak Reading Precursors at 7 years | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children born VP/VLBW | Children without NDI | Controls | ||||
| Measured at 2 years | n (%) | p | n (%) | p | n (%) | p |
| Lexicon size | 0.001 | 0.039 | 0.101 | |||
| Weak | 10 (48%) | 6 (38%) | 2 (33%) | |||
| Normal | 17 (15%) | 17 (16%) | 11 (8%) | |||
| M3L | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.058 | |||
| Weak | 13 (50%) | 9 (45%) | 4 (22%) | |||
| Normal | 11 (11%) | 11 (12%) | 8 (7%) | |||
| ELS | 0.037 | 0.169 | 0.325 | |||
| Weak | 7 (33%) | 5 (29%) | 2 (15%) | |||
| Normal | 16 (15%) | 15 (15%) | 10 (8%) | |||
| Weak reading skills at 7 years | ||||||
| Lexicon size | 0.007 | 0.068 | 0.301 | |||
| Weak | 13 (62%) | 9 (56%) | 2 (33%) | |||
| Normal | 36 (31%) | 35 (33%) | 23 (18%) | |||
| M3L | 0.009 | 0.058 | 0.013 | |||
| Weak | 14 (54%) | 10 (50%) | 7 (39%) | |||
| Normal | 27 (27%) | 26 (28%) | 17 (15%) | |||
| ELS | 0.08 | 0.101 | 0.253 | |||
| Weak | 11 (51%) | 9 (53%) | 4 (31%) | |||
| Normal | 34 (32%) | 32 (32%) | 20 (16%) | |||
| Lexicon size | 0.019 | 0.027 | 0.019 | |||
| Weak | 14 (74%) | 12 (75%) | 5 (83%) | |||
| Normal | 50 (44%) | 48 (45%) | 40 (31%) | |||
| M3L | 0.005 | 0.004 | <0.001 | |||
| Weak | 17 (71%) | 15 (75%) | 14 (78%) | |||
| Normal | 39 (39%) | 37 (40%) | 28 (24%) | |||
| ELS | 0.028 | 0.019 | 0.268 | |||
| Weak | 14 (70%) | 13 (77%) | 6 (46%) | |||
| Normal | 46 (44%) | 44 (44%) | 38 (31%) |
| Reading Precursors | Reading | Writing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | |
| Gestational age | −0.05 | −0.66 to 0.38 | 0.589 | 0.04 | −0.20 to 0.32 | 0.642 | 0.03 | −0.20 to 0.27 | 0.764 |
| Reading difficulties | |||||||||
| Mothers | 0.15 | −0.40 to 9.50 | 0.071 | 0.10 | −0.93 to 4.01 | 0.223 | 0.07 | −1.29 to 3.25 | 0.462 |
| Fathers | −0.07 | −5.63 to 2.39 | 0.432 | −0.02 | −2.28 to 1.73 | 0.791 | −0.07 | −2.73 to 0.95 | 0.412 |
| Paternal education | 0.25 | 1.47 to 7.56 | 0.004 | 0.31 | 1.42 to 4.46 | <0.001 | 0.20 | 0.26 to 3.05 | 0.024 |
| Lexicon size | 0.31 | 0.01 to 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.32 | 0.004 to 0.01 | <0.001 | 0.30 | 0.002 to 0.01 | 0.001 |
| Fit statistics | |||||||||
| F | 7.0 | 9.0 | 5.0 | ||||||
| P for F | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.17 | ||||||
| ΔR2 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.13 |
| Reading Precursors | Reading | Writing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | |
| Gestational age | −0.06 | −0.72 to 0.34 | 0.484 | 0.03 | −0.22 to 0.32 | 0.711 | 0.03 | −0.21 to 0.29 | 0.762 |
| Reading difficulties | |||||||||
| Mothers | 0.12 | −1.47 to 8.67 | 0.163 | 0.08 | −1.35 to 3.82 | 0.351 | 0.07 | −1.49 to 3.30 | 0.472 |
| Fathers | −0.06 | −5.51 to 2.63 | 0.491 | −0.02 | −2.28 to 1.87 | 0.842 | −0.08 | −2.78 to 1.07 | 0.294 |
| Paternal education | 0.25 | 1.50 to 7.66 | 0.004 | 0.32 | 1.44 to 4.57 | <0.001 | 0.21 | 0.27 to 3.18 | 0.021 |
| M3L | 0.37 | 0.57 to 1.54 | <0.001 | 0.35 | 0.25 to 0.75 | <0.001 | 0.26 | 0.08 to 0.55 | 0.008 |
| Fit statistics | |||||||||
| F | 8.0 | 8.5 | 4.0 | ||||||
| P for F | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.16 | ||||||
| ΔR2 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.12 |
| Reading Precursors | Reading | Writing | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | b | 95% CI | p | |
| Gestational age | −0.01 | −0.58 to 0.50 | 0.901 | 0.07 | −0.15 to 0.39 | 0.401 | 0.06 | −0.17 to 0.33 | 0.531 |
| Reading difficulties | |||||||||
| Mothers | 0.18 | 0.24 to 10.48 | 0.039 | 0.13 | −0.58 to 4.56 | 0.132 | 0.11 | −0.98 to 3.72 | 0.253 |
| Fathers | −0.06 | 0.5.75 to 2.71 | 0.501 | −0.02 | −2.33 to 1.91 | 0.824 | −0.08 | −2.80 to 1.08 | 0.384 |
| Paternal education | 0.20 | 0.46 to 7.10 | 0.029 | 0.27 | 0.88 to 4.19 | 0.003 | 0.18 | −0.09 to 2.93 | 0.069 |
| ELS | 0.26 | 0.13 to 0.72 | 0.005 | 0.28 | 0.08 to 0.38 | 0.002 | 0.21 | 0.01 to 0.28 | 0.029 |
| Fit statistics | |||||||||
| F | 6.0 | 7.0 | 3.4 | ||||||
| P for F | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.007 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.14 | ||||||
| ΔR2 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.10 |
| AUC Value of Lexicon Size | 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children born VP/VLBW | |||
| Reading precursors | 0.70 | 0.58 to 0.83 | 0.001 |
| Reading | 0.72 | 0.63 to 0.81 | <0.001 |
| Writing | 0.72 | 0.64 to 0.80 | <0.001 |
| Controls | |||
| Reading precursors | 0.65 | 0.50 to 0.80 | 0.081 |
| Reading | 0.67 | 0.56 to 0.78 | 0.009 |
| Writing | 0.69 | 0.60 to 0.78 | <0.001 |
| Children born VP/VLBW | |||
| Reading precursors | 0.77 | 0.66 to 0.89 | <0.001 |
| Reading | 0.74 | 0.65 to 0.83 | <0.001 |
| Writing | 0.73 | 0.64 to 0.82 | <0.001 |
| Controls | |||
| Reading precursors | 0.73 | 0.58 to 0.87 | 0.009 |
| Reading | 0.65 | 0.51 to 0.78 | 0.029 |
| Writing | 0.73 | 0.64 to 0.82 | <0.001 |
| Children born VP/VLBW | |||
| Reading precursors | 0.72 | 0.61 to 0.82 | 0.001 |
| Reading | 0.71 | 0.62 to 0.80 | <0.001 |
| Writing | 0.74 | 0.65 to 0.83 | <0.001 |
| Controls | |||
| Reading precursors | 0.62 | 0.44 to 0.80 | 0.182 |
| Reading | 0.64 | 0.52 to 0.77 | 0.029 |
| Writing | 0.71 | 0.62 to 0.80 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joensuu, E.; Munck, P.; Setänen, S.; Lipsanen, J.; Huhtala, M.; Lapinleimu, H.; Stolt, S.K.J. Associations between Language at 2 Years and Literacy Skills at 7 Years in Preterm Children Born at Very Early Gestational Age and/or with Very Low Birth Weight. Children 2021, 8, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060510
Joensuu E, Munck P, Setänen S, Lipsanen J, Huhtala M, Lapinleimu H, Stolt SKJ. Associations between Language at 2 Years and Literacy Skills at 7 Years in Preterm Children Born at Very Early Gestational Age and/or with Very Low Birth Weight. Children. 2021; 8(6):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060510
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoensuu, Eveliina, Petriina Munck, Sirkku Setänen, Jari Lipsanen, Mira Huhtala, Helena Lapinleimu, and Suvi K. J. Stolt. 2021. "Associations between Language at 2 Years and Literacy Skills at 7 Years in Preterm Children Born at Very Early Gestational Age and/or with Very Low Birth Weight" Children 8, no. 6: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060510
APA StyleJoensuu, E., Munck, P., Setänen, S., Lipsanen, J., Huhtala, M., Lapinleimu, H., & Stolt, S. K. J. (2021). Associations between Language at 2 Years and Literacy Skills at 7 Years in Preterm Children Born at Very Early Gestational Age and/or with Very Low Birth Weight. Children, 8(6), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060510






