Combined Single Nucleotide Variants of ORAI1 and BLK in a Child with Refractory Kawasaki Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
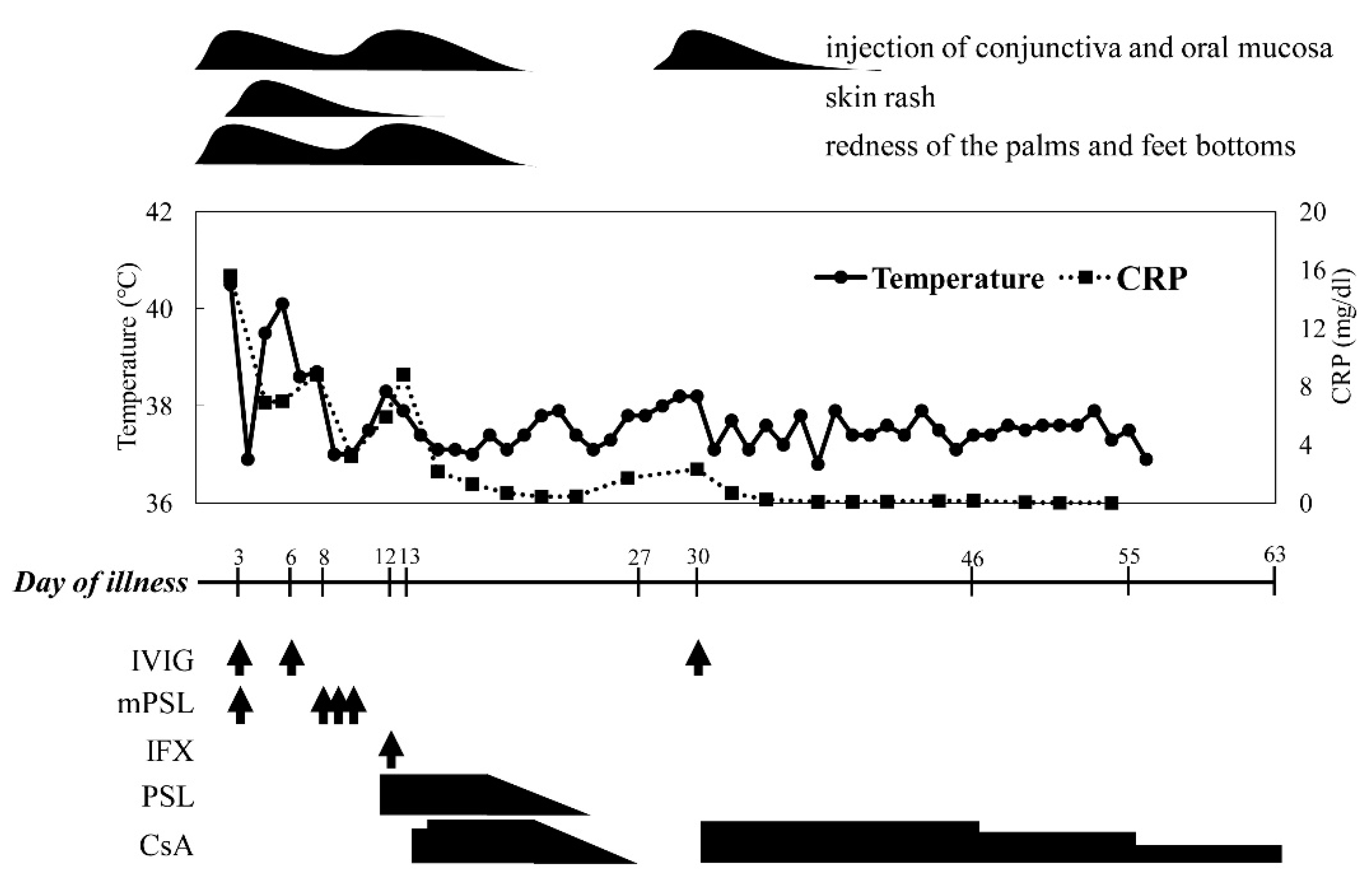
2. Case Presentation
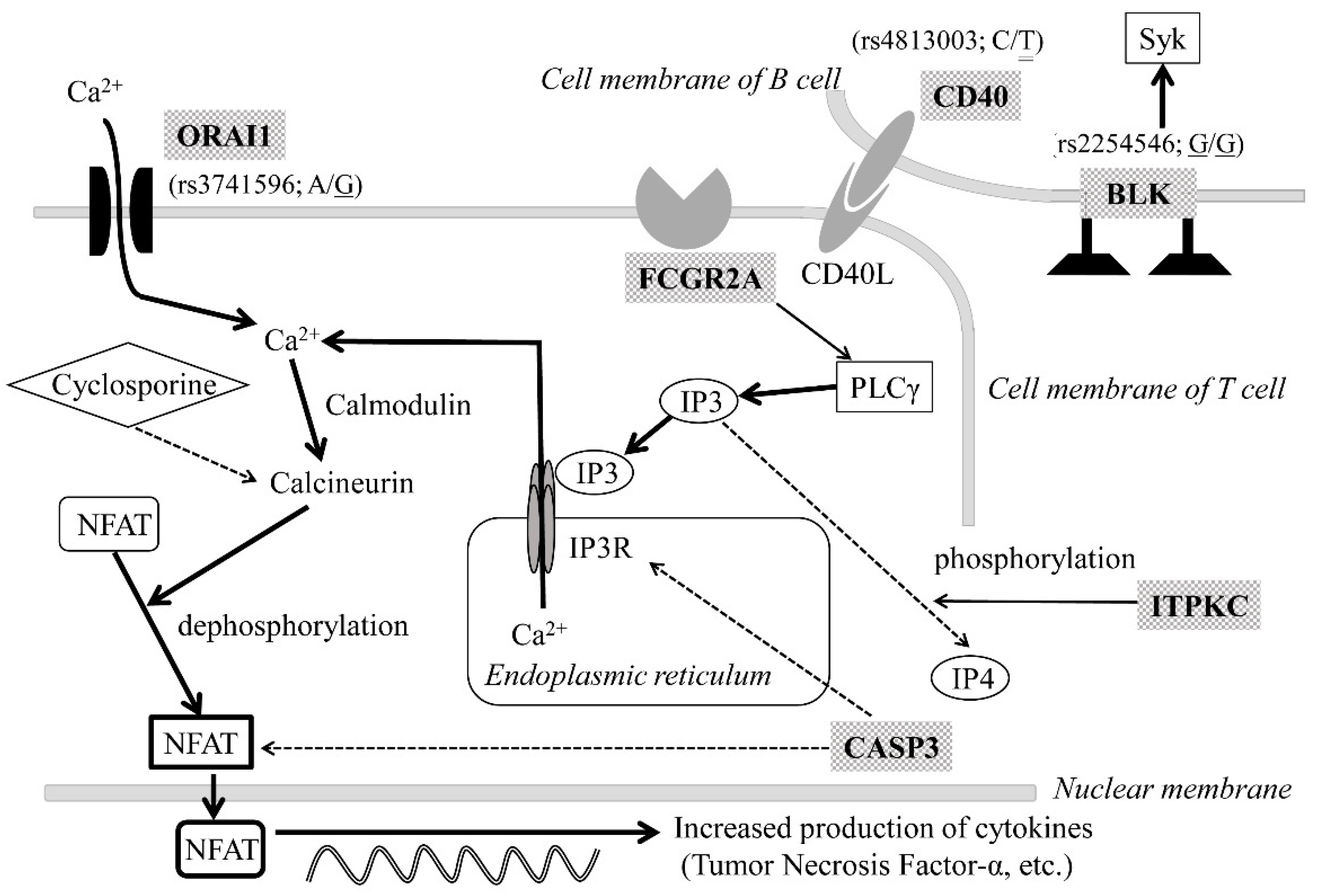
3. Genetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, 927–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onouchi, Y. Genetics of Kawasaki disease: What we know and don’t know. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumrah, R.; Vignesh, P.; Rawat, A.; Singh, S. Immunogenetics of Kawasaki disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 59, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onouchi, Y.; Fukazawa, R.; Yamamura, K.; Suzuki, H.; Kakimoto, N.; Suenaga, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Hamada, H.; Honda, T.; Yasukawa, K.; et al. Variations in ORAI1 gene associated with Kawasaki disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashigawa, M.; Nakamura, T.; Hattori, T.; Yoshino, A.; Ito, M.; Ichimi, R. Combination of prednisolone and cyclosporin A as third-line therapy for refractory Kawasaki disease: A case study. Minerva Pediatr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Chang, J.S.; Chang, L.Y.; Huang, L.M.; Chen, M.R.; Liang, C.D.; Chi, H.; Huang, F.Y.; Lee, M.L.; et al. Two new susceptibility loci for Kawasaki disease identified through genome-wide association analysis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Zhong, R.; Shen, N.; Lu, X.Z.; Ke, J.T.; Duan, J.Y.; Qi, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; et al. Systematic confirmation study of GWAS-identified genetic variants for Kawasaki disease in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.R.; Chang, T.Y.; Chiu, N.C.; Chi, H.; Yang, K.D.; Chang, L.; Huang, D.T.N.; Huang, F.Y.; Lien, Y.P.; Lin, W.S.; et al. Validation of genome-wide associated variants for Kawasaki disease in a Taiwanese case-control sample. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Akagawa, S.; Akagawa, Y.; Kimata, T.; Tsuji, S. Our evolving understanding of Kawasaki disease pathogenesis: Role of the gut microbiota. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, A.; Le, C.K.; Poupart, S.; Autmizguine, J.; Meloche-Dumas, L.; Turgeon, J.; Fournier, A.; Dahdah, N. Profile of resistance to IVIG treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease and concomitant infection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeotti, C.; Kaveri, S.V.; Cimaz, R.; Koné-Paut, I.; Bayry, J. Predisposing factors, pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention of Kawasaki disease. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 13, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.P.; Huang, Y.S.; Hsu, Y.W.; Yang, K.D.; Chien, H.C.; Yu, H.R.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, C.L.; Chang, W.C.; Kuo, H.C. TARC/CCL17 gene polymorphisms and expression associated with susceptibility and coronary artery aneurysm formation in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuo, H.C.; Hsu, Y.W.; Wu, M.S.; Chien, S.C.; Liu, S.F.; Chang, W.C. Intravenous immunoglobulin, pharmacogenomics, and Kawasaki disease. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, J.; Ebata, R.; Jibiki, T.; Yasukawa, K.; Saito, H.; Terai, M. Elevated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor levels predict treatment failure in patients with Kawasaki disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, M.L.; Manlhiot, C.; Latino, G.A.; Collins, T.H.; Chahal, N.; Yeung, R.S.M.; McCrindle, B.W. Variability in response to intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of Kawasaki disease. J. Pediatr. 2016, 179, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, D.; Valentini, P.; Rizzo, D.; Leo, A.; Rosa, G.D.; Onesimo, R.; Nisco, A.D.; Angelone, D.F.; Compagnone, A.; Delogu, A.B. Responsiveness to intravenous immunoglobulins and occurrence of coronary artery abnormalities in a single-center cohort of Italian patients with Kawasaki syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 30, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C.; Hsu, Y.W.; Wu, C.M.; Chen, S.H.; Hung, K.S.; Chang, W.P.; Yang, K.D.; Hsieh, K.S.; Chen, W.C.; Onouchi, Y.; et al. A replication study for association of ITPKC and CASP3 two-locus analysis in IVIGSimunresponsiveness and coronary artery lesion in Kawasaki disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiha, K.; Mashimo, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Hamada, H.; Hata, A.; Hara, T.; Tanaka, T.; Ito, K.; Onouchi, Y. Japan Kawasaki Disease Genome Consortium. Investigation of novel variations of ORAI1 gene and their association with Kawasaki disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, R.M.; Laky, K.; Hayes, S.M. Unexpected role for the B cell-specific Src family kinase B lymphoid kinase in the development of IL-17-producing γδ T cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6518–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compeer, E.B.; Janssen, W.; van Royen-Kerkhof, A.; van Gijn, M.; van Montfrans, J.M.; Boes, M. Dysfunctional BLK in common variable immunodeficiency perturbs B-cell proliferation and ability to elicit antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell help. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10759–10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simpfendorfer, K.R.; Armstead, B.E.; Shih, A.; Li, W.; Curran, M.; Manjarrez-Orduño, N.; Lee, A.T.; Diamond, B.; Gregersen, P.K. Autoimmune disease-associated haplotypes of BLK exhibit lowered thresholds for B cell activation and expansion of Ig class-switched B cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2866–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Geng, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The elevated serum levels of calcineurin and nuclear factor of activated T-cells 1 in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2020, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Geng, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, C.; et al. The role of Ca2+/NFAT in dysfunction and inflammation of human coronary endothelial cells induced by sera from patients with Kawasaki disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, H.; Suzuki, H.; Onouchi, Y.; Ebata, R.; Terai, M.; Fuse, S.; Okajima, Y.; Kurotobi, S.; Hirai, K.; Soga, T.; et al. Efficacy of primary treatment with immunoglobulin plus ciclosporin for prevention of coronary artery abnormalities in patients with Kawasaki disease predicted to be at increased risk of non-response to intravenous immunoglobulin (KAICA): A randomised controlled, open-label, blinded-endpoints, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Day of Illness | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 30 | 84 | |
| White Blood Cell (/μL) | 13,500 | 37,600 | 37,300 | 29,100 | 13,600 | 10,800 |
| Neutrophil (/μL) | 10,700 | 21,400 | 18,500 | 11,800 | 5000 | 5000 |
| Platelet Cell (×109/L) | 297 | 667 | 808 | 815 | 485 | 369 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 42 | 26 | 28 | 27 | 37 | NA (g) |
| CRP (a) (mg/L) | 156.0 | 32.2 | 59.1 | 88.1 | 23.1 | NA (g) |
| NT-pro-BNP (b) (pg/mL) | 4560.0 | 1406.5 | 633.5 | 514.7 | 328.1 | NA (g) |
| AST (c) (U/L) | 174 | 29 | 27 | 26 | 30 | NA (g) |
| ALT (d) (U/L) | 106 | 33 | 23 | 23 | 10 | NA (g) |
| Diameter of LAD (e) (mm) | 1.5 [0.6] | 2.9 [6.0] | 3.6 [9.2] | 4.8 [14.8] | 6.3 [21.8] | 6.0 [20.2] |
| Diameter of RCA (f) (mm) | 1.5 [0.4] | 4.0 [8.2] | 4.0 [8.2] | 5.6 [13.7] | 9.9 [28.2] | 8.5 [23.3] |
| ORAI1 | CD40 | BLK | FCGR2A | CASP3 | ITPKC | HLA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs868908978 | rs4813003 | rs2254546 | rs10401344 | rs113420705 | rs28493229 | rs2857151 |
| rs141919534 | rs4810485 | rs2736340 | rs17713068 | |||
| rs782675422 | rs6074022 | rs13277113 | rs2233152 | |||
| rs543433737 | rs3746821 | rs2618476 | es10403040 | |||
| rs781980977 | rs1569723 | rs12680762 | rs1801274 | |||
| rs3741595 | rs1883832 | rs2736340 | ||||
| rs782238081 | rs1569723 | rs6993775 | ||||
| rs3741596 | rs4813003 | rs1382566 | ||||
| rs782308800 | rs199581355 | |||||
| rs782722476 | ||||||
| rs377456337 | ||||||
| rs200214435 | ||||||
| rs3741597 | ||||||
| rs781789915 | ||||||
| rs3825174 | ||||||
| rs3825175 | ||||||
| rs555170508 | ||||||
| rs375464035 | ||||||
| rs12313273 | ||||||
| rs6486789 | ||||||
| rs117324670 | ||||||
| rs7484839 | ||||||
| rs7486943 | ||||||
| rs712853 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanda, S.; Fujii, Y.; Hori, S.-i.; Ohmachi, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Higasa, K.; Kaneko, K. Combined Single Nucleotide Variants of ORAI1 and BLK in a Child with Refractory Kawasaki Disease. Children 2021, 8, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060433
Kanda S, Fujii Y, Hori S-i, Ohmachi T, Yoshimura K, Higasa K, Kaneko K. Combined Single Nucleotide Variants of ORAI1 and BLK in a Child with Refractory Kawasaki Disease. Children. 2021; 8(6):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060433
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanda, Saki, Yoshimitsu Fujii, Shin-ichiro Hori, Taichi Ohmachi, Ken Yoshimura, Koichiro Higasa, and Kazunari Kaneko. 2021. "Combined Single Nucleotide Variants of ORAI1 and BLK in a Child with Refractory Kawasaki Disease" Children 8, no. 6: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060433
APA StyleKanda, S., Fujii, Y., Hori, S.-i., Ohmachi, T., Yoshimura, K., Higasa, K., & Kaneko, K. (2021). Combined Single Nucleotide Variants of ORAI1 and BLK in a Child with Refractory Kawasaki Disease. Children, 8(6), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060433






