Anthropometric and Physiologic Parameters in Cleft Neonates: A Hospital-Based Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Demographics
3.2. Comparison among Cleft and Non-Cleft Neonates
3.3. Comparison of Each Type of Cleft
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Implication
4.2. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mossey, P.A.; Little, J.; Munger, R.G.; Dixon, M.J.; Shaw, W.C. Cleft lip and palate. Lancet 2009, 374, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Reports, Human Genetics Programme: Management of Noncommunicable Diseases: International Collaborative Research on Craniofacial Anomalies. In Global Strategies Towards Reducing the Health Care Burden of Craniofacial Anomalies; Mossey, P.A., Munger, R., Murray, J.C., Shaw, W.C., Eds.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; ISBN 92 4 159038 6. [Google Scholar]
- Mossey, P.; Little, J. Addressing the challenges of cleft lip and palate research in India. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2009, 42, S9–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.G.; Reddy, R.R.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Prasad, R.; Ettema, A.M.; Sailer, H.F.; Bergé, S.J. Incidence of cleft Lip and palate in the state of Andhra Pradesh, South India. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2010, 43, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J. Strengthening the reporting of ob-servational studies in epidemiology (STROBE): Explantion and elaboration. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 805–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, B.L.; Dahl, E.; Kreiborg, S. Longitudinal study of body height, radius length and skeletal maturity in Danish boys with cleft lip and palate. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1983, 91, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh Ismail, L.; Knight, H.E.; Ohuma, E.O.; Hoch, L.; Chumlea, W.C.; International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium for the 21st Century. Anthropometric standardisation and quality control protocols for the construction of new, international, fetal and newborn growth standards: The INTERGROWTH-21st Project. BJOG 2013, 120 (Suppl. S2), 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, A.; Rao, K.S.; Sharma, S.M.; Shetty, V. Modified Presurgical Nasoalveolar Molding in the Infants with Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate: A Stepwise Approach. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2011, 10, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, D.; Goyal, R.; Puri, T. Presurgical Nasoalveolar Moulding—An Adjunct to Facilitate Surgical Repair in Infants with Cleft Lip and Palate. Mod. Plast. Surg. 2013, 3, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshak, B.; Assif, D.; Pilo, R. A controlled putty-wash impression technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1990, 64, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, B.H.; Shetye, P.R. Presurgical nasoalveolar moulding treatment in cleft lip and palate patients. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2009, 42, S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seckel, N.G.; Van Der Tweel, I.; Elema, G.A.; Specken, T.F. Landmark Positioning on Maxilla of Cleft Lip and Palate Infant—A Reality? Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1995, 32, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Ohishi, M.; Tashiro, H. Longitudinal Study on the Changes of Maxillary Arch Dimensions in Japanese Children with Cleft Lip and/or Palate: Infancy to 4 Years of Age. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1995, 32, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Ismail, L.C.; Victora, C.G.; Ohuma, E.O.; Bertino, E.; Altman, D.G.; Lambert, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Carvalho, M.; Jaffer, Y.A.; et al. International standards for newborn weight, length, and head circumference by gestational age and sex: The Newborn Cross-Sectional Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Lancet 2014, 384, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, I.L.; Nackashi, J.A.; Borgo, H.C.; Martinelli, A.P.M.C.; Pegoraro-Krook, M.I.; Williams, W.N.; Dutka, J.; Seagle, M.B.; Souza, T.V.; Garla, L.A.; et al. Longitudinal study of growth of children with unilateral cleft-lip palate from birth to two years of age. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2009, 46, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, E.J.; Mayro, R.F.; Whitaker, L.A.; Pasquariello, P.S.; LaRossa, D.; Randall, P. General Body Growth in Children with Clefts of the Lip, Palate, and Craniofacial Structure. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1987, 21, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix-Schollaart, B.; Hoeksma, J.B.; Prahl-Andersen, B. Growth Comparison between Children with Cleft Lip and/or Palate and Controls. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1992, 29, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, M.L.; Jerome, J.T. Linear growth characteristics of children with cleft lip and palate. J. Pediatr. 1997, 131, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.K.; McWilliams, B.J. Weight gain in children with cleft palate from birth to two years. Cleft Palate J. 1988, 25, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, P.A.; Shapiro, L.R.; Soley, R.L.; Turet, S.E. Linear Growth Patterns in Patients With Cleft Lip or Palate or Both. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1983, 137, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudman, D.; Davis, G.T.; Priest, J.H.; Patterson, J.H.; Kutner, M.H.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Bethel, R.A. Prevalence of growth hormone deficiency in children with cleft lip or palate. J. Pediatr. 1978, 93, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranalli, D.N.; Mazaheri, M. Height-weight growth of cleft children, birth to six years. Cleft Palate J. 1975, 12, 400–404. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.; Svensson, H.; Källén, B. Birth weight, body length, and cranial circumference in newborns with cleft lip or palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1998, 35, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supplement, D.; Candotto, V.; Oberti, L.; Gabrione, F.; Greco, G.; Rossi, D.; Romano, M.; Mummolo, S. Current concepts on cleft lip and palate etiology. J Biol. Regul. Homeost Agents 2019, 33, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Markus, A.; Smith, W.; Delaire, J. Facial balance in cleft lip and palate I. Normal development and cleft palate. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1992, 30, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, B.Z.F.; Fernandes, V.M.; Carrara, C.F.C.; Machado, M.A.A.M.; Garib, D.; Oliveira, T.M. Evaluation of the intercanine distance in newborns with cleft lip and palate using 3D digital casts. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2013, 21, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harila, V.; Ylikontiola, L.P.; Palola, R.; Sándor, G.K. Maxillary arch dimensions in cleft infants in Northern Finland. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2013, 71, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, L.-J.; Wong, F.-H.; Chen, Y.-R.; Lin, W.-Y.; Ko, E.W.-C. Palatal Surface Area Measurement: Comparisons among Different Cleft Types. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2003, 50, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Filho, O.G.; Ramos, A.L.; Abdo, R.C. The influence of unilateral cleft lip and palate on maxillary dental arch morphology. Angle Orthod. 1992, 62, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brief, J.; Behle, J.; Stellzig-Eisenhauer, A.; Hassfeld, S. Precision of Landmark Positioning on Digitized Models from Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2005, 43, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvann, T.A.; Hermann, N.V.; Ersbøll, B.K.; Kreiborg, S.; Berkowitz, S. Palatal Surface Area of Maxillary Plaster Casts—A Comparison between Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Measurements. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2007, 44, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.E., Jr.; Hathaway, R.; Daskalogiannakis, J.; Mercado, A.; Russell, K.; Cohen, M.; Semb, G.; Shaw, W. The Americleft study: An inter-center study of treatment outcomes for patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate part 1. Principles and study design. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2011, 48, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenarts, C.; Bartzela, T.; Bronkhorst, E.; Semb, G.; Shaw, W.; Katsaros, C.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A. Photographs of dental casts or digital models: Rating dental arch relationships in bilateral cleft lip and palate. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschulz, J.; Schaefer, I.; Scheer, M.; Christ, H.; Braumann, B. Maxillary reaction patterns identified by three-dimensional analysis of casts from infants with unilateral cleft lip and palate. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2013, 74, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, J.; McIntyre, G. Dental Arch Relationships on Three-Dimensional Digital Study Models and Conventional Plaster Study Models for Patients with Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2012, 49, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, P.K.; Kharbanda, O.P. Intraoral 3D Scanning in Cleft Care. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2017, 54, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, P.; Gribel, B.F.; Abhinav, B.A.; Arora, A.; Raghavan, S. OrthoAligner “NAM”: A Case Series of Presurgical Infant Orthopedics (PSIO) Using Clear Aligners. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2019, 57, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
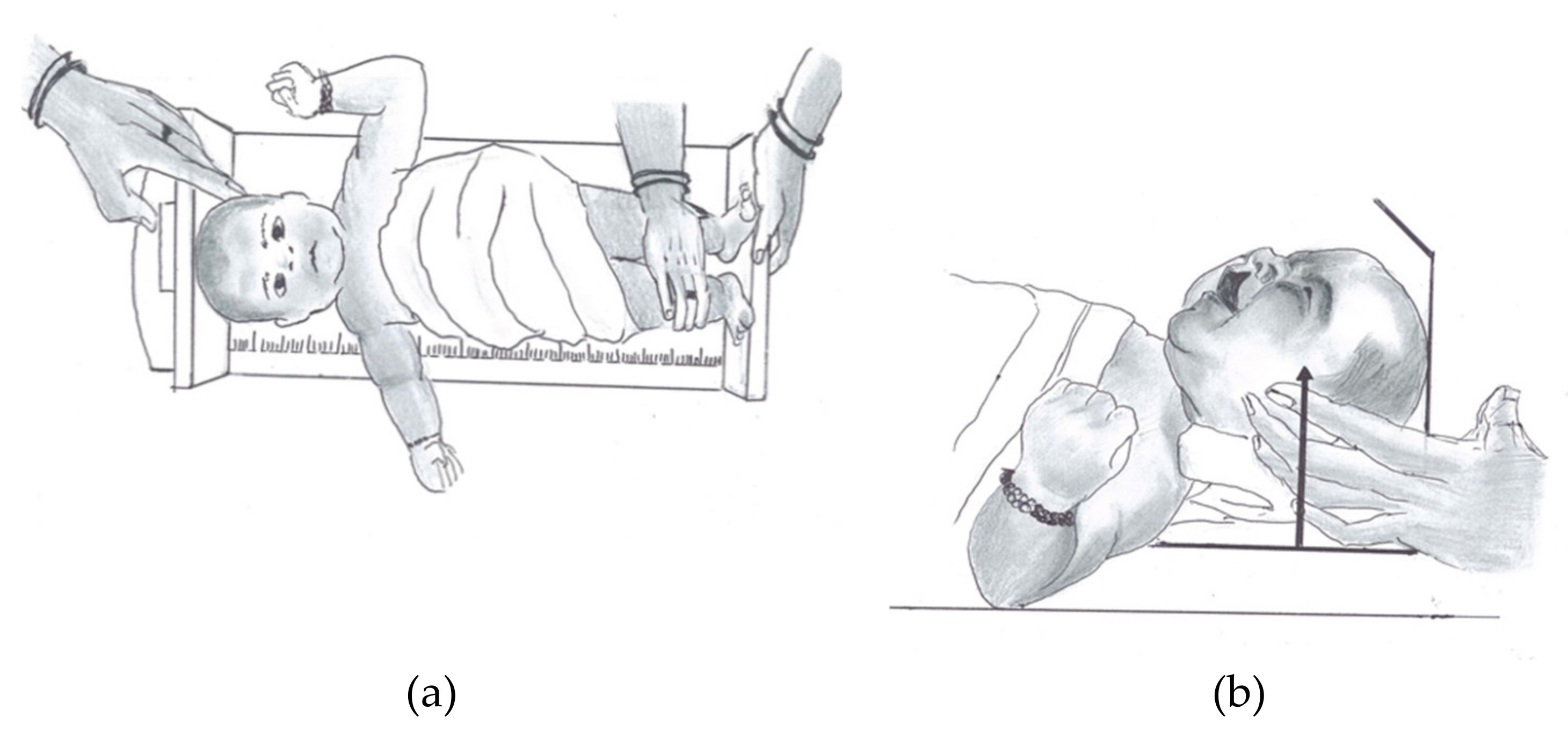
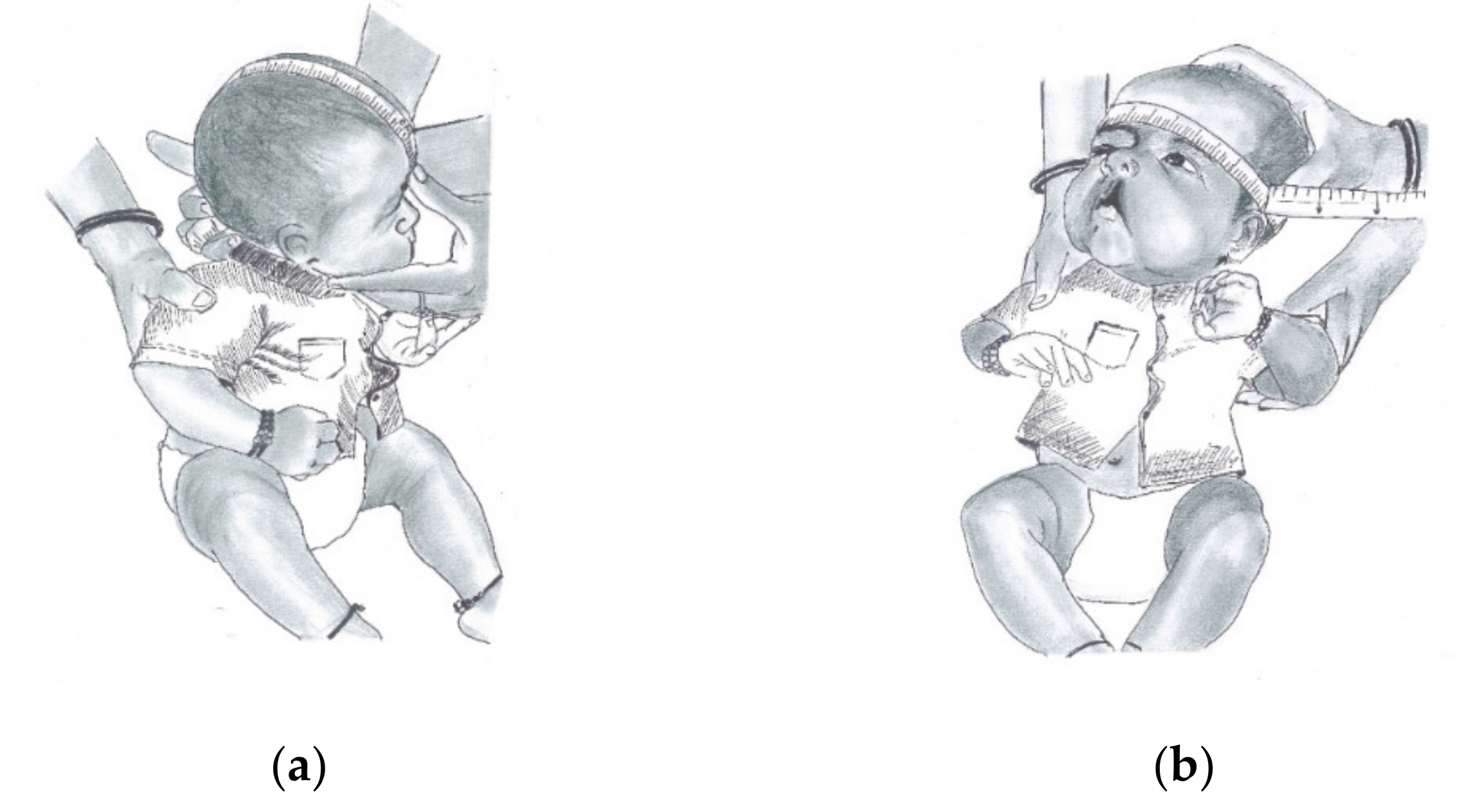
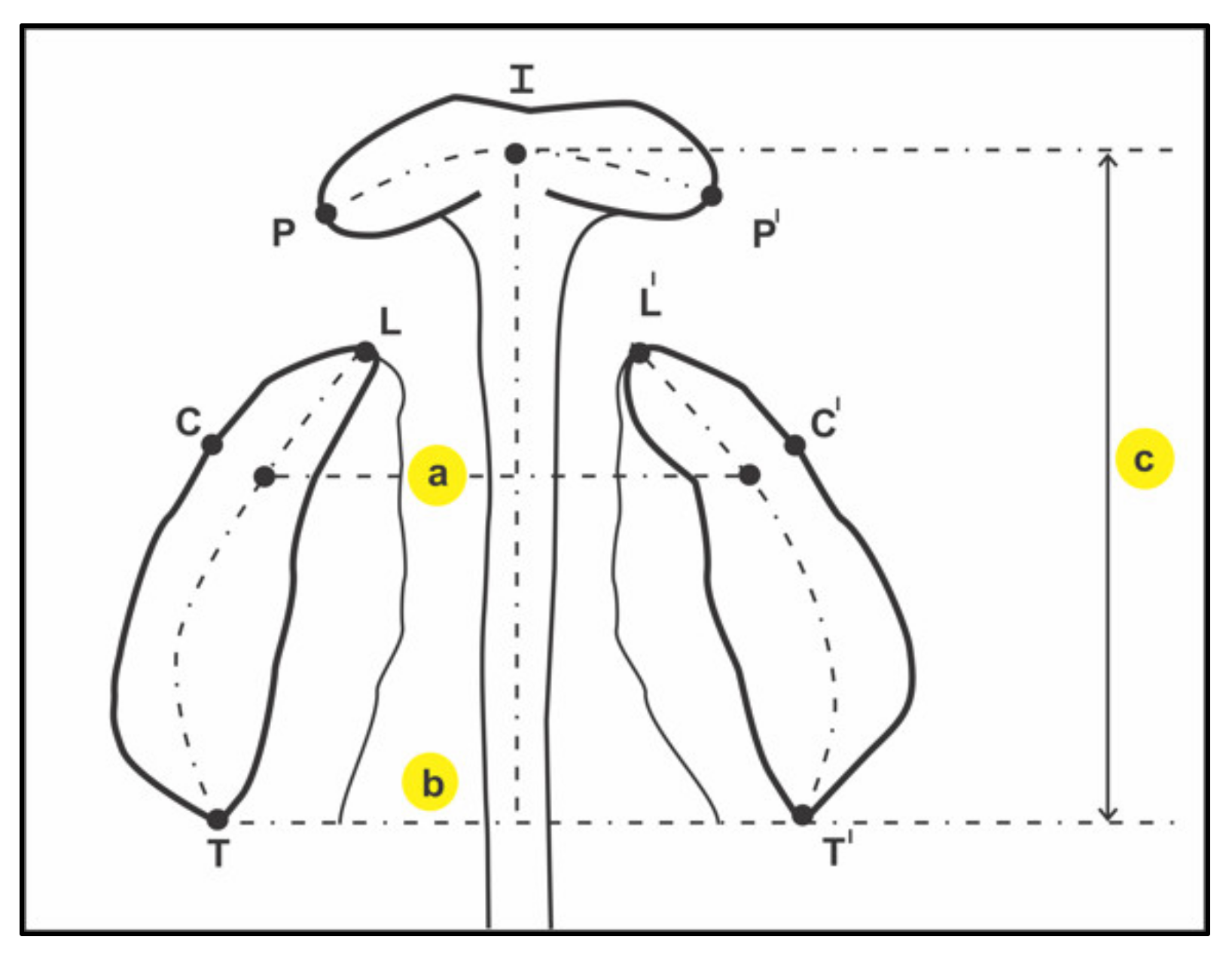
| S. No. | Variables | Units | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Head Length (HL) | cm | The maximum length of the head in sagittal plane; measured from glabella, anteriorly to the most prominent point of the head posteriorly. |
| 2 | Head Circumference (HC) | cm | The distance recorded from glabella, anteriorly to the most prominent point of the head posteriorly in transverse plane where the measuring tape is anchored and loop around head transversely. |
| 3 | Inter-canine width (ICW) | mm | The distance between the canine points C-C′. The canine point is the landmark at intersection of the groove of the lateral labial frenum and the crest of the ridge. (C-C′) |
| 4 | Inter-tuberosity width (ITW) | mm | The distance between the tuberosity points T-T′. The tuberosity point is the landmark at intersection maxillary tuberosity and the crest of the ridge outlined on the cast. (T-T′) |
| 5 | Arch Length (AL) | mm | A compound measurement. (I-TT′) The perpendicular distance from incisal point to the T-T′ plane. |
| 6 | Arch Circumference (AC) | mm | A compound measurement. For UCLP: T-C-I-P+ L-C′-T′ For BCLP: T-C-L + P-I-P′ + L′-C′-T′ For ICP and Controls: T-C-I-C′-T′ |
| Variables | Cleft Neonates | Non Cleft Neonates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCLP (22) | ICP (10) | BLCP (12) | Total (44) | |||
| Age Mean ± SD | 21 ± 1.34 | 18 ± 1.11 | 23 ± 1.12 | 48 ± 1.17 | 36 ± 2.89 | |
| Sex | Female | 11 (52.4%) | 6 (28.6%) | 4 (19.0%) | 21 | 22 (50%) |
| n (%) | Male | 11 (47.8%) | 4 (17.4%) | 8 (34.8%) | 23 | 22 (50%) |
| Origin n (%) | Gujarati | 22 (50.0%) | 10 (22.8%) | 12 (27.2%) | 44 | 44 (100%) |
| Others | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Variables | Group | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth Weight kg | Cleft | 44 | 2.4693 | 0.53060 | 0.07999 | 0.0001 * |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 2.9355 | 0.41032 | 0.06186 | ||
| Birth Length cm | Cleft | 44 | 45.080 | 6.1351 | 0.9249 | 0.337 |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 46.029 | 2.2322 | 0.3365 | ||
| Head Length cm | Cleft | 44 | 19.148 | 4.5820 | 0.6908 | 0.011 * |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 20.988 | 1.0134 | 0.1528 | ||
| Head Circumference cm | Cleft | 44 | 30.848 | 5.0974 | 0.7685 | 0.007 * |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 33.042 | 1.4385 | 0.2169 | ||
| ICW mm | Cleft | 44 | 28.6534 | 4.97135 | 0.74946 | <0.0001 * |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 21.7686 | 1.21610 | 0.18333 | ||
| ITW mm | Cleft | 44 | 31.0927 | 4.86118 | 0.73285 | <0.0001 * |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 27.3818 | 1.04641 | 0.15775 | ||
| Arch Length mm | Cleft | 44 | 27.4307 | 7.12700 | 1.07444 | <0.0001 * |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 18.9145 | 0.66602 | 0.10041 | ||
| Arch Circumference mm | Cleft | 44 | 63.273 | 13.0836 | 1.9724 | <0.0001 * |
| Non-Cleft | 44 | 68.023 | 1.6352 | 0.2465 |
| Variable | Cleft Type | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval for Mean | Minimum | Maximum | p Value | POST HOC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||||||
| Birth Weight kg | UCLP | 22 | 2.4295 | 0.54416 | 0.11602 | 2.1883 | 2.6708 | 1.40 | 3.50 | 0.525 | - |
| ICP | 10 | 2.3800 | 0.66466 | 0.21019 | 1.9045 | 2.8555 | 1.40 | 3.50 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 2.6167 | 0.37376 | 0.10790 | 2.3792 | 2.8541 | 2.30 | 3.40 | |||
| Birth Length cm | UCLP | 22 | 43.000 | 6.8522 | 1.4609 | 39.962 | 46.038 | 20.0 | 54.0 | 0.018 * | 3 > 1, 2 |
| ICP | 10 | 44.850 | 4.3910 | 1.3885 | 41.709 | 47.991 | 38.0 | 53.0 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 49.083 | 3.9418 | 1.1379 | 46.579 | 51.588 | 44.0 | 55.0 | |||
| Head Length cm | UCLP | 22 | 17.705 | 2.5850 | 0.5511 | 16.558 | 18.851 | 9.0 | 24.0 | 0.019 * | 2 > 1, 3 |
| ICP | 10 | 22.500 | 7.7172 | 2.4404 | 16.979 | 28.021 | 15.0 | 33.5 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 19.000 | 2.4863 | 0.7177 | 17.420 | 20.580 | 17.0 | 24.0 | |||
| Head circumference cm | UCLP | 22 | 31.695 | 4.3515 | 0.9277 | 29.766 | 33.625 | 14.0 | 36.0 | 0.038 * | 2 < 3, 1 |
| ICP | 10 | 27.300 | 6.9290 | 2.1911 | 22.343 | 32.257 | 16.0 | 32.0 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 32.250 | 3.3337 | 0.9624 | 30.132 | 34.368 | 26.0 | 36.0 | |||
| ICW mm | UCLP | 22 | 30.8782 | 5.44867 | 1.16166 | 28.4624 | 33.2940 | 18.00 | 38.00 | <0.0001 * | 1 > 3 > 2 |
| ICP | 10 | 23.6920 | 2.12724 | 0.67269 | 22.1703 | 25.2137 | 20.88 | 26.00 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 28.7092 | 1.98762 | 0.57378 | 27.4463 | 29.9720 | 25.07 | 32.52 | |||
| ITW mm | UCLP | 22 | 32.0845 | 5.56885 | 1.18728 | 29.6155 | 34.5536 | 20.00 | 41.60 | <0.0001 * | 3, 1 > 2 |
| ICP | 10 | 26.5050 | 1.72657 | 0.54599 | 25.2699 | 27.7401 | 24.00 | 29.00 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 33.0975 | 2.29046 | 0.66120 | 31.6422 | 34.5528 | 27.82 | 35.68 | |||
| Arch Length mm | UCLP | 22 | 24.6123 | 2.61028 | 0.55651 | 23.4549 | 25.7696 | 18.00 | 30.00 | <0.0001 * | 3 < 1, 2 |
| ICP | 10 | 21.7470 | 2.71107 | 0.85732 | 19.8076 | 23.6864 | 18.00 | 28.00 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 37.3342 | 5.22381 | 1.50798 | 34.0151 | 40.6532 | 33.00 | 48.27 | |||
| Arch Circumference mm | UCLP | 22 | 58.545 | 8.3764 | 1.7859 | 54.832 | 62.259 | 47.0 | 77.0 | <0.0001 * | 1, 2 < 3 |
| ICP | 10 | 53.300 | 6.7831 | 2.1450 | 48.448 | 58.152 | 46.0 | 68.0 | |||
| BCLP | 12 | 60.750 | 0.9653 | 0.2787 | 60.137 | 61.363 | 60.0 | 62.0 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verma, S.; Mehta, F.; Mishra, S.; Mohamed, R.N.; Parekh, H.K.A.; Sokhi, R.K.; Nagarajappa, A.K.; Alam, M.K. Anthropometric and Physiologic Parameters in Cleft Neonates: A Hospital-Based Study. Children 2021, 8, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100893
Verma S, Mehta F, Mishra S, Mohamed RN, Parekh HKA, Sokhi RK, Nagarajappa AK, Alam MK. Anthropometric and Physiologic Parameters in Cleft Neonates: A Hospital-Based Study. Children. 2021; 8(10):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100893
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerma, Swati, Falguni Mehta, SukhDev Mishra, Roshan Noor Mohamed, Harshik Kumar A. Parekh, Ramandeep Kaur Sokhi, Anil Kumar Nagarajappa, and Mohammad Khursheed Alam. 2021. "Anthropometric and Physiologic Parameters in Cleft Neonates: A Hospital-Based Study" Children 8, no. 10: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100893
APA StyleVerma, S., Mehta, F., Mishra, S., Mohamed, R. N., Parekh, H. K. A., Sokhi, R. K., Nagarajappa, A. K., & Alam, M. K. (2021). Anthropometric and Physiologic Parameters in Cleft Neonates: A Hospital-Based Study. Children, 8(10), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100893







