Nucleated Red Blood Cells: Could They Be Indicator Markers of Illness Severity for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables’ Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
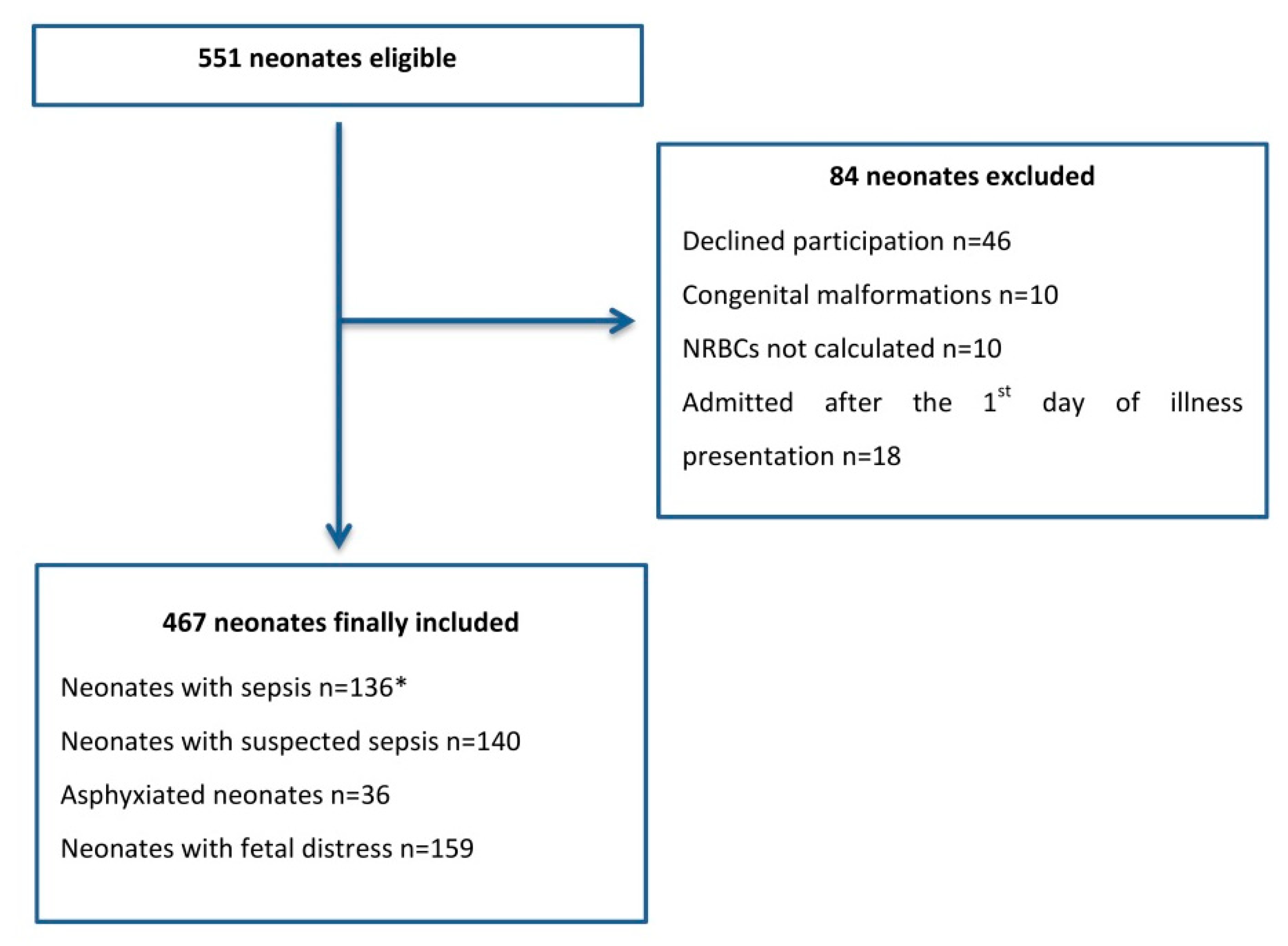
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorling, J.S.; Field, D.J.; Manktelow, B. Neonatal disease severity scoring systems. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005, 90, F11–F16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, D.K.; Corcoran, J.D.; Escobar, G.J.; Lee, S.K. SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II: Simplified newborn illness severity and mortality risk scores. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janota, J.; Stranák, Z.; Statecná, B.; Dohnalová, A.; Sípek, A.; Simák, J. Characterization of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in very low birthweight infants: A new sequential scoring system. Shock 2001, 15, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, G.; Tucker, J.; Tarnow-Mordi, W. CRIB II: An update of the clinical risk index for babies score. Lancet 2003, 361, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.; Dwivedi, R.; Gohiya, P.; Hegde, D. Nucleated red blood cell in cord blood as a marker of perinatal asphyxia. J. Clin. Neonatol. 2013, 2, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulay, A.T.; Buhimschi, I.A.; Zhao, G.; Luo, G.; Abdel-Razeq, S.; Cackovic, M.; Rosenberg, V.A.; Pettker, C.M.; Thung, S.F.; Bahtiyar, M.O.; et al. Nucleated red blood cells are a direct response to mediators of inflammation in newborns with early-onset neonatal sepsis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 198, 426.e1–426.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskabadi, H.; Zakerihamidi, M.; Sadeghian, M.H.; Avan, A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Ferns, G.A. Nucleated red blood cells count as a prognostic biomarker in predicting the complications of asphyxia in neonates. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 30, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Farahbakhsh, N.; Shastri, S.; Sharma, P. Biomarkers for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: A literature review. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 1646–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, V. Effective Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Neonatal Sepsis. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2014, 3, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Islam, M.N.; Mollah, A.H.; Hoque, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Nazir, F.; Ahsan, M.M. Status of liver enzymes in babies with perinatal asphyxia. Mymensingh Med. J. 2011, 20, 446–449. [Google Scholar]
- Hadzimuratovic, E.; Skokic, F.; Hadzimuratovic, A.; Nazdrajic, A.; Mujic, M.; Hadzimuratovic, A. Acute renal failure in term newborn following perinatal asphyxia. Sanamed 2017, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Christensen, R.D.; Henry, E.; Andres, R.L.; Bennett, S.T. Reference ranges for blood concentrations of nucleated red blood cells in neonates. Neonatology 2011, 99, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachon, A.; Segbers, E.; Holland-Letz, T.; Kempf, R.; Hering, S.; Krieg, M. Nucleated red blood cells in the blood of medical intensive care patients indicate increased mortality risk: A prospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menk, M.; Giebelhäuser, L.; Vorderwülbecke, G.; Gassner, M.; Graw, J.A.; Weiss, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Wernecke, K.-D.; Weber-Carstens, S. Nucleated red blood cells as predictors of mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): An observational study. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer, C.; Schmugge, M.; Frey, B. Prognostic value of nucleated red blood cells in critically ill children. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2014, 144, w13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschat, A.A.; Gungor, S.; Kush, M.L.; Berg, C.; Gembruch, U.; Harman, C.R. Nucleated red blood cell counts in the first week of life: A critical appraisal of relationships with perinatal outcome in preterm growth-restricted neonates. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 197, 286.e281–286.e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boskabadi, H.; Maamouri, G.; Sadeghian, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Heidarzade, M.; Shakeri, M.-T.; Ferns, G. Early Diagnosis of Perinatal Asphyxia by Nucleated Red Blood Cell Count: A Case-control Study. Arch. Iran. Med. 2010, 13, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, R.D.; Lambert, D.K.; Richards, D.S. Estimating the nucleated red blood cell ‘emergence time’ in neonates. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walti, H.; Couchard, M.; Relier, J.P. Neonatal diagnosis of respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. Suppl. 1989, 3, 22s–26s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sokou, R.; Giallouros, G.; Konstantinidi, A.; Pantavou, K.; Nikolopoulos, G.; Bonovas, S.; Lytras, T.; Kyriakou, E.; Lambadaridis, I.; Gounaris, A.; et al. Thromboelastometry for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis-associated coagulopathy: An observational study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinidi, A.; Sokou, R.; Tsantes, A.G.; Parastatidou, S.; Bonovas, S.; Kouskouni, E.; Gounaris, A.K.; Tsantes, A.E.; Iacovidou, N. Thromboelastometry variables in neonates with perinatal hypoxia. Semin Thromb Hemost 2020, 46, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, M.; Giannoni, E.; Kuester, H.; Turner, M.A.; van den Hoogen, A.; Bliss, J.M.; Koenig, J.M.; Keij, F.M.; Mazela, J.; Finnegan, R.; et al. Challenges in developing a consensus definition of neonatal sepsis. Pediatr. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, J.; Walker, W.A. Necrotizing enterocolitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, A.; Smith, L.E.H.; Dammann, O. Retinopathy of prematurity. Lancet 2013, 382, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer-Larocque, I.; Soraisham, A.; Stritzke, A.; Al Awad, E.; Thomas, S.; Murthy, P.; Kamaluddeen, M.; Scott, J.N.; Mohammad, K. Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Risk Factors and Association With Patent Ductus Arteriosus Treatment in Extremely Preterm Neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, N.; Ahmed, M. Pathophysiology of periventricular leukomalacia: What we learned from animal models. Neural. Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 1795–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitz, W.E. Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghartey, K.; Coletta, J.; Lizarraga, L.; Murphy, E.; Ananth, C.V.; Gyamfi-Bannerman, C. Neonatal respiratory morbidity in the early term delivery. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 207, 292.e291–292.e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankins, G.D.V. Neonatal Organ System Injury in Acute Birth Asphyxia Sufficient to Result in Neonatal Encephalopathy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 101, 203–204. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldız, E.P.; Ekici, B.; Tatlı, B. Neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: An update on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aufieri, R.; Picone, S.; Paolillo, P. Multiple organ failure in the newborn. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetinkaya, M.; Köksal, N.; Özkan, H. A New Scoring System for Evaluation of Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome in Premature Infants. Am. J. Crit. Care Publ. Am. Assoc. Crit. Care Nurses 2012, 21, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purtle, S.W.; Horkan, C.M.; Moromizato, T.; Gibbons, F.K.; Christopher, K.B. Nucleated red blood cells, critical illness survivors and postdischarge outcomes: A cohort study. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.E.; Marques, M.B.; Reddy, V.V.B.; Gangaraju, R. Three neglected numbers in the CBC: The RDW, MPV, and NRBC count. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2019, 86, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghinasab, J.; Boskabadi, H.; Sadeghian, M. Investigation of Changes in Nucleated Red Blood Cells in Neonatal Infection. Iran. J. Neonatol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanodia, P.; Bhatta, N.; Shah, G.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, S. Nucleated Red Blood Cell in Cord Blood as a Marker of Perinatal Asphyxia. J. Nepal Paediatr. Soc. 2016, 35, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.; Brettin, K.; Feldman, H.; Leeman, K. Association of Nucleated Red Blood Cell Count with Mortality among Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Descriptive Statistics | Value |
|---|---|
| Population (n) | 467 |
| Gender (Male) | 300 (64.2%) |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 35.3 ± 4.3 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2452.4 ± 976.9 |
| Delivery mode (Caesarian session) | 312 (66.8%) |
| Maternal diseases * | 176 (42.1%) |
| All Study Neonates n = 467 | Term Neonates n = 248 | Preterm Neonates n = 219 | Terms vs. Preterms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | ||||
| Gestational age (weeks) | 35.3 ± 4.3 | 38.7 ± 1.2 | 31.5 ± 3.2 | 0.000 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2452.4 ± 976.9 | 3147 ± 554 | 1665 ± 722 | 0.000 |
| Death | 45 (9.6%) | 23 (9.3%) | 22 (10%) | 0.875 |
| Respiratory Distress Syndrome | 244 (52.6%) | 88 (35.5%) | 156 (71.2%) | 0.000 |
| Intrauterine Growth Retardation | 56 (12.0%) | 24 (9.7%) | 32 (14.6%) | 0.117 |
| Sepsis | 136 (29.1%) | 52 (21%) | 84 (38.4%) | 0.000 |
| Infection | 140 (30.0%) | 67 (27%) | 73 (33.3%) | 0.157 |
| Perinatal hypoxia | 195 (41.8%) | 136 (54.8%) | 59 (27%) | 0.000 |
| Perinatal asphyxia | 36 (7.7%) | 31 (12.5%) | 5 (2.3%) | 0.000 |
| Fetal distress | 159 (34%) | 105 (42.3%) | 54 (24.7%) | 0.000 |
| Acute Kidney Injury | 75 (16.1%) | 37 (14.9%) | 38 (17.4%) | 0.528 |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy | 78 (16.7%) | 36 (14.5%) | 42 (19.2%) | 0.174 |
| Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome | 82 (17.6%) | 45 (18.1%) | 37 (16.9%) | 0.808 |
| Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | 70 (15%) | - | 70 (32%) | - |
| Mild | 19 (0.04%) | 19 (8.7%) | ||
| Moderate | 14 (0.03%) | 14 (6.4%) | ||
| Severe | 56 (12%) | 56 (25.5%) | ||
| Retinopathy of Prematurity | 77 (16.5%) | - | 77 (35.1%) | - |
| Laser treatment | 29 (0.06%) | 29 (13.2%) | ||
| No treatment | 48 (10.3%) | 48 (22%) | ||
| Patent Ductus Arteriosus | 24 (5.1%) | - | 24 (11%) | - |
| Pharmacological treatment | 16 (0.03%) | 16 (7.3%) | ||
| Surgical ligation | 5 (0.01%) | 5 (2.3%) | ||
| Conservative treatment | 3 (0.006%) | 3 (1.4%) | ||
| Periventricular Leukomalacia | 71 (15.2%) | - | 71 (32.4%) | - |
| Intra-Ventricular Hemorrhage ≥ grade 2 | 61 (13%) | - | 61 (27.8%) | - |
| Necrotizing Enterocolitis | 15 (0.03%) | - | 15 (6.8%) | - |
| Survivors (n = 422) | Non-Survivors (n = 45) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | p Value |
| Gestational_Age (weeks) | 37 (32–39) | 37 (32–40) | 0.1089 |
| Birth_Weight (g) | 2640 (1490–3230) | 2550 (1420–3300) | 0.9921 |
| Base Deficit (mmol/L) | 3.4 (1.5–5.5) | 4.2 (1.1–12) | 0.1617 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.6 (2.3–2.8) | 2.3 (2.1–2.5) | 0.0001 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 41.2 (37–45.9) | 35.1 (33–41.2) | 0.0000 |
| WBC (/mL) | 13,045 (9680–17,930) | 14,600 (9030–20,430) | 0.5954 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 61 (47.3–72) | 55 (40–75.1) | 0.7930 |
| NRBC (%) | 0.4 (0–2.3) | 1.6 (0–7.9) | 0.1649 |
| PLT (/mL) | 229,500 (120,000–297,000) | 57,000 (13,000–169,000) | 0.0000 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 13.4 (3.4–40.2) | 49.1 (7.2–85.2) | 0.0010 |
| SGOT (IU/L) | 55 (33–83) | 89 (54–235.5) | 0.0000 |
| SGPT (IU/L) | 18 (12–30) | 43 (23–141) | 0.0000 |
| T_BIL (mg/dL) | 6 (3.8–9) | 8.2 (3.9–25.4) | 0.0053 |
| D_BIL (mg/dL) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.9 (0.3–17) | 0.0000 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 27.5 (19–47) | 57 (35–92) | 0.0000 |
| Cr (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.4–0.8) | 0.7 (0.5–1.2) | 0.0105 |
| Modified NEOMOD score | 2 (1–4) | 8 (5–10) | 0.0000 |
| SNAPPE score | 9 (2–17) | 19 (13–36) | 0.0000 |
| TOLLNER score | 0.1 (0–3.5) | 10 (0–13.5) | 0.0019 |
| Morbidity | OR and 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Kidney Injury | 28.65 (13.5–60.79) | <0.0001 |
| Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | 0.3 (0.09–1) | 0.0377 |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy | 10.88 (5.6–21.15) | <0.0001 |
| Intrauterine Growth Retardation | 1.4 (0.59–3.31) | 0.4388 |
| Multi-organ Dysfunction Syndrome | 32.7 (14.81–72.19) | <0.0001 |
| Necrotizing Enterocolitis | 2.82 (0.89–8.97) | 0.0670 |
| Patent Ductus Arteriosus | 4.36 (1.7–11.16) | 0.0009 |
| Perinatal Hypoxia | 2.27 (1.21–4.25) | 0.0090 |
| Periventricular Leucomalakia | 14.52 (7.35–28.66) | <0.0001 |
| Respiratory Distress Syndrome | 5.61 (2.45–12.85) | <0.0001 |
| Sepsis | 2.58 (1.39–4.82) | 0.0021 |
| AUC | 95% CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
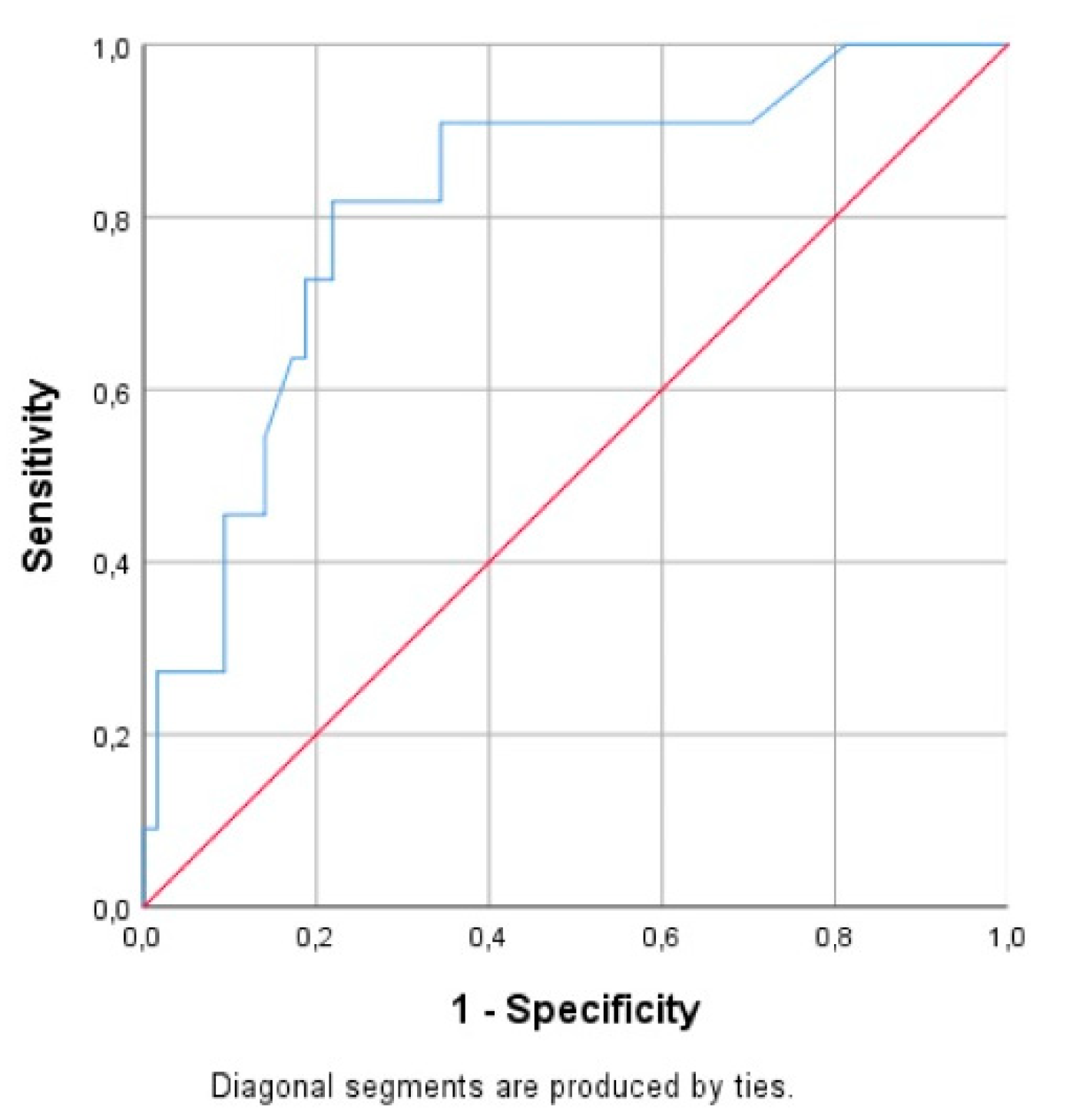
| Sepsis diagnosis | 0.615 | 0.559–0.671 | 0.000 |
| Hypoxia diagnosis | 0.710 | 0.660–0.759 | 0.000 |
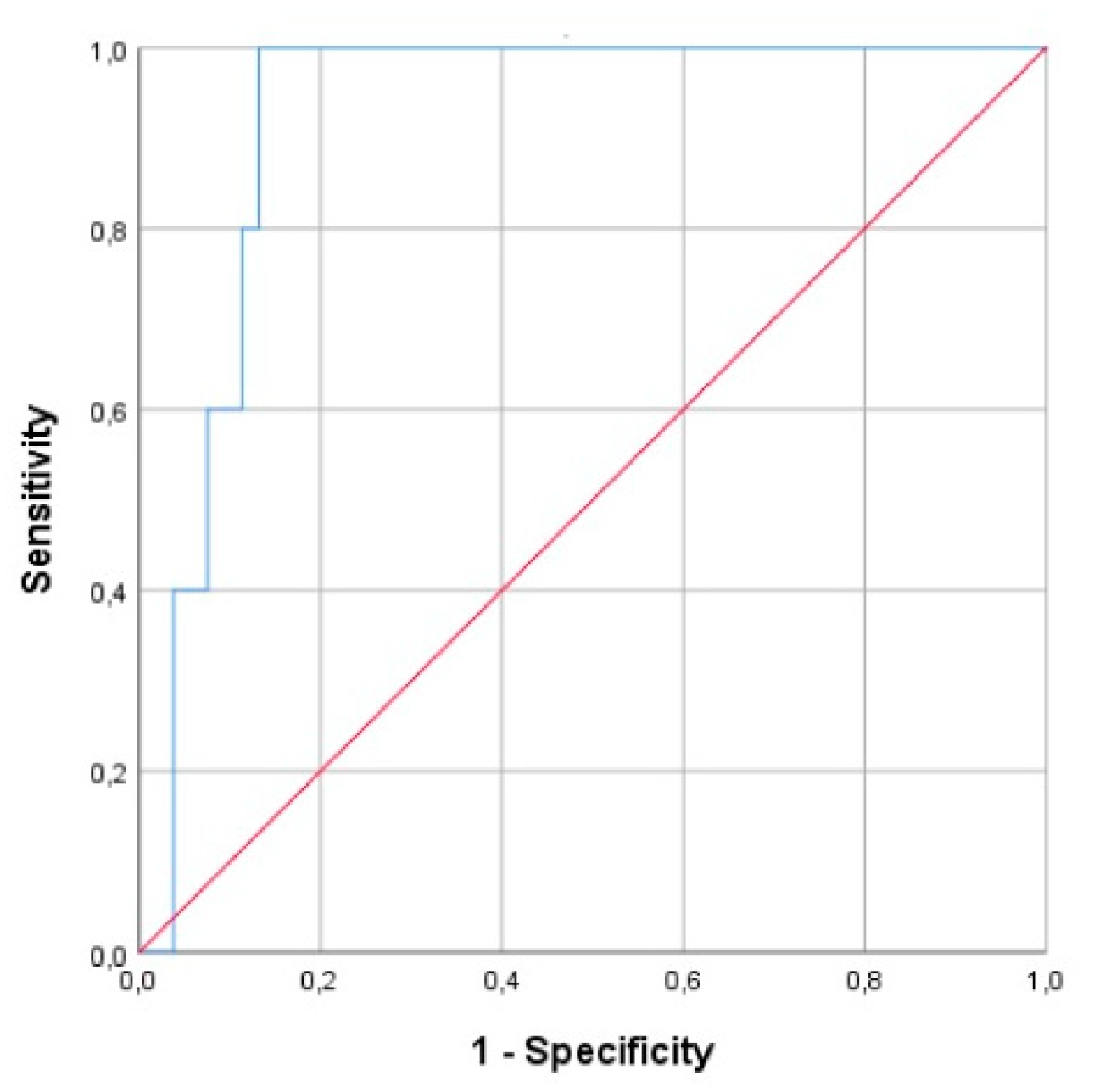
| Mortality prognosis in all neonates | 0.565 | 0.461–0.670 | 0.000 |
| Mortality prognosis in septic neonates | 0.760 | 0.631–0.888 | 0.001 |
| Mortality prognosis in asphyxiated neonates | 0.671 | 0.465–0.876 | 0.145 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokou, R.; Ioakeimidis, G.; Lampridou, M.; Pouliakis, A.; Tsantes, A.G.; Tsantes, A.E.; Iacovidou, N.; Konstantinidi, A. Nucleated Red Blood Cells: Could They Be Indicator Markers of Illness Severity for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients? Children 2020, 7, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110197
Sokou R, Ioakeimidis G, Lampridou M, Pouliakis A, Tsantes AG, Tsantes AE, Iacovidou N, Konstantinidi A. Nucleated Red Blood Cells: Could They Be Indicator Markers of Illness Severity for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients? Children. 2020; 7(11):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110197
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokou, Rozeta, Georgios Ioakeimidis, Maria Lampridou, Abraham Pouliakis, Andreas G. Tsantes, Argyrios E. Tsantes, Nicoletta Iacovidou, and Aikaterini Konstantinidi. 2020. "Nucleated Red Blood Cells: Could They Be Indicator Markers of Illness Severity for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients?" Children 7, no. 11: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110197
APA StyleSokou, R., Ioakeimidis, G., Lampridou, M., Pouliakis, A., Tsantes, A. G., Tsantes, A. E., Iacovidou, N., & Konstantinidi, A. (2020). Nucleated Red Blood Cells: Could They Be Indicator Markers of Illness Severity for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients? Children, 7(11), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110197









