Epilepsy in Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Is there a real association between epilepsy and autism?
- If we suggest a link between epilepsy and autism, will this contribute to solving the etiology of autism?
- Does a particular therapeutic approach to the epilepsy of autistic patients exist and is it the same for all autistic children?
- Could achieving therapeutic control of the epilepsy, i.e., making patients seizure-free, improve autistic behavior and/or intellectual disability (ID)?
- Does the treatment of epileptiform EEG abnormalities improve autistic behavior and cognitive functions, and should epileptiform EEG abnormalities be treated?
2. Patients and Methods
Statistical Methods
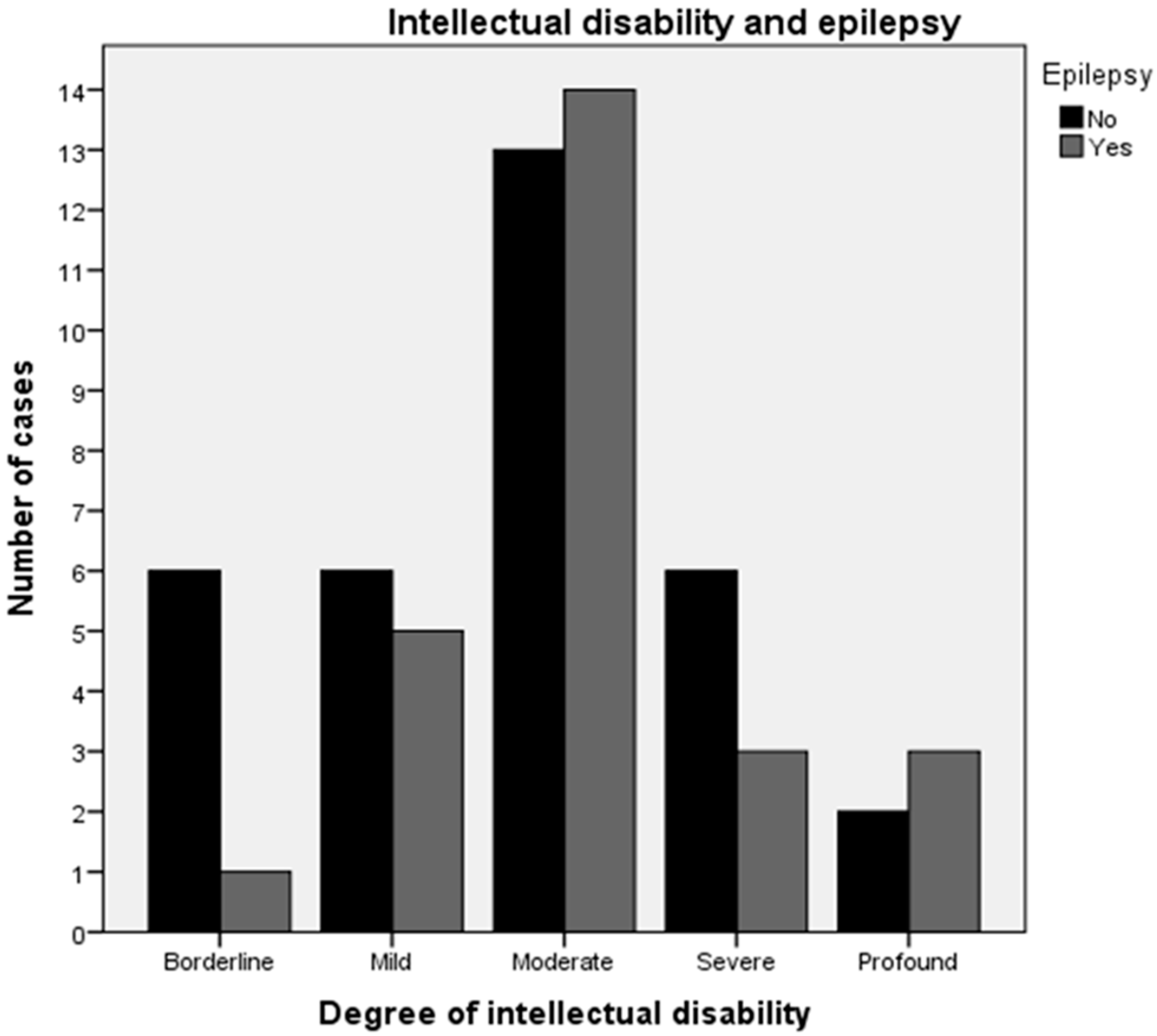
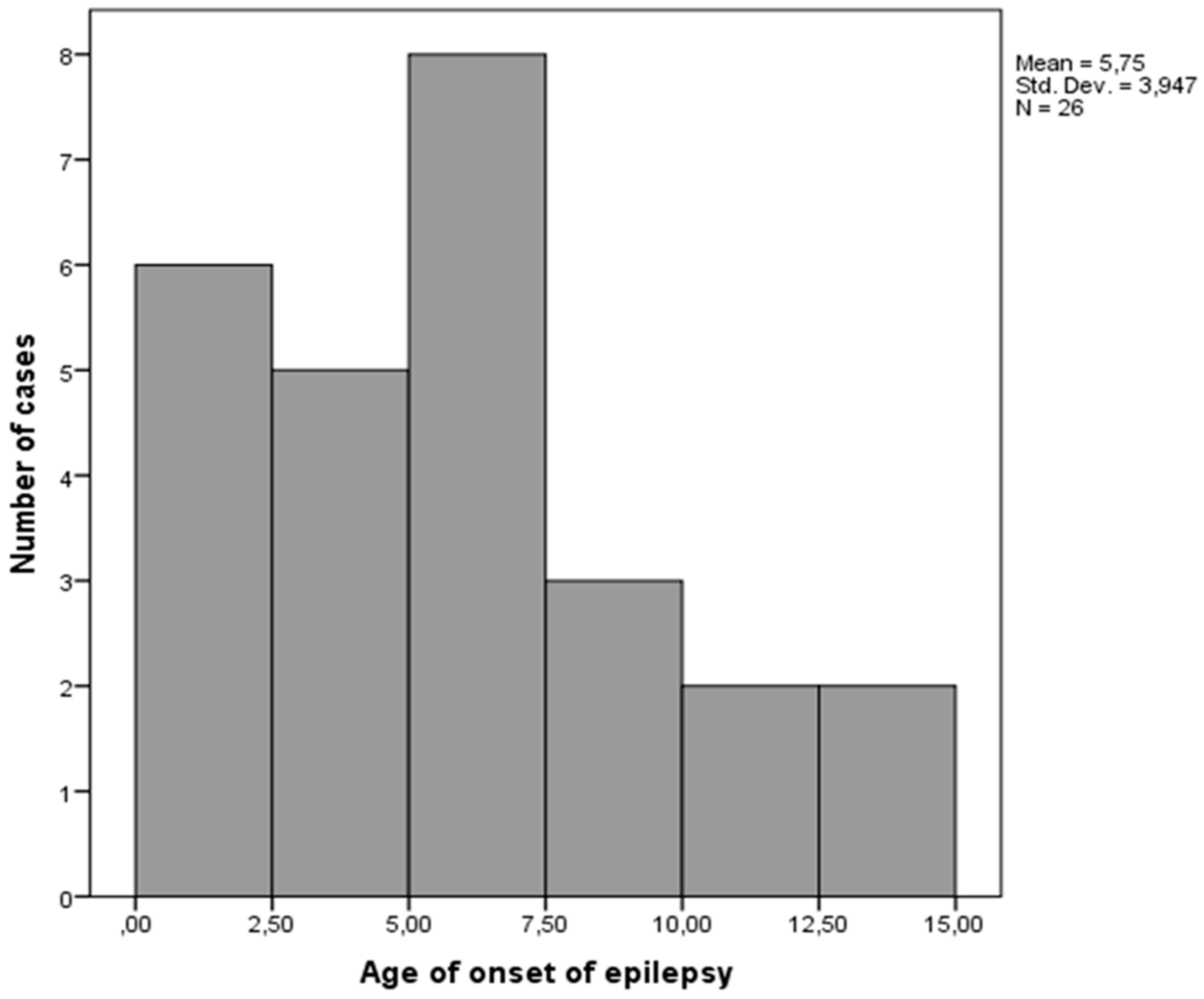
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aaberg, K.M.; Gunnes, N.; Bakken, I.J.; Lund Soraas, C.; Berntsen, A.; Magnus, P.; Lossius, M.I.; Stoltenberg, C.; Chin, R.; Suren, P. Incidence and Prevalence of Childhood Epilepsy: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Pediatrics 2017, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, S.J.; Schneider, M.T. The role of epilepsy and epileptiform EEGs in autism spectrum disorders. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchman, R.; Rapin, I. Epilepsy in autism. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiet, C.; Gourfinkel-An, I.; Bouzamondo, A.; Tordjman, S.; Baulac, M.; Lechat, P.; Mottron, L.; Cohen, D. Epilepsy in autism is associated with intellectual disability and gender: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokiranta, E.; Sourander, A.; Suominen, A.; Timonen-Soivio, L.; Brown, A.S.; Sillanpaa, M. Epilepsy among children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders: A population-based study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 2547–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscidi, E.W.; Triche, E.W.; Pescosolido, M.F.; McLean, R.L.; Joseph, R.M.; Spence, S.J.; Morrow, E.M. Clinical characteristics of children with autism spectrum disorder and co-occurring epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, H. Autism and epilepsy: A retrospective follow-up study. Brain Dev. 2007, 29, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, S.; Gillberg, I.C.; Billstedt, E.; Gillberg, C.; Olsson, I. Epilepsy in young adults with autism: A prospective population-based follow-up study of 120 individuals diagnosed in childhood. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.W.; Holmes, G.L. Epilepsy and Autism. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a022749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.P. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zwaigenbaum, L.; Bauman, M.L.; Stone, W.L.; Yirmiya, N.; Estes, A.; Hansen, R.L.; McPartland, J.C.; Natowicz, M.R.; Choueiri, R.; Fein, D.; et al. Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder: Recommendations for Practice and Research. Pediatrics 2015, 136 (Suppl. 1), S10–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaigenbaum, L.; Penner, M. Autism spectrum disorder: Advances in diagnosis and evaluation. BMJ 2018, 361, k1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, Y.; Provenzano, G.; Casarosa, S. Neurobiological bases of autism-epilepsy comorbidity: A focus on excitation/inhibition imbalance. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxbaum, J.; Hof, P. The Neuroscience of Autism Spectrum Disorders; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 113–144. [Google Scholar]
- Inui, T.; Kumagaya, S.; Myowa-Yamakoshi, M. Neurodevelopmental Hypothesis about the Etiology of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson, J.; Goldin, R. Comorbidity and autism: Trends, topics and future directions. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2013, 7, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabis, L.V.; Pomeroy, J. An etiologic classification of autism spectrum disorders. Isr. Med. Association J. IMAJ 2014, 16, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Betancur, C.; Coleman, M. Etiological Heterogeneity in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Role of Rare Variants; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 113–144. [Google Scholar]
- Jeste, S.S.; Tuchman, R. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Epilepsy: Two Sides of the Same Coin? J. Child Neurol. 2015, 30, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Sahin, M. Autism spectrum disorder and epileptic encephalopathy: Common causes, many questions. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2017, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Pasquier, L.; Cohen, D.; Fradin, M.; Canitano, R.; Damaj, L.; Odent, S.; Tordjman, S. Role of Genetics in the Etiology of Autistic Spectrum Disorder: Towards a Hierarchical Diagnostic Strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eeghen, A.M.; Pulsifer, M.B.; Merker, V.L.; Neumeyer, A.M.; van Eeghen, E.E.; Thibert, R.L.; Cole, A.J.; Leigh, F.A.; Plotkin, S.R.; Thiele, E.A. Understanding relationships between autism, intelligence, and epilepsy: A cross-disorder approach. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, A.O. Genetic causes of syndromic and non-syndromic autism. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchman, R. CSWS-related autistic regression versus autistic regression without CSWS. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. 7), 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; D‘Souza, C.; French, J.A.; Haut, S.R.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshe, S.L.; et al. Instruction manual for the ILAE 2017 operational classification of seizure types. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmar, F.R.; Nelson, D.S. Seizure disorders in autism. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1990, 29, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, M.; Maeda, T.; Sasaki, K.; Ishii, K.; Hamasaki, Y. Frequent association of autism spectrum disorder in patients with childhood onset epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, I.; Steffenburg, S.; Gillberg, C. Epilepsy in autism and autisticlike conditions. A population-based study. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Al Baradie, R. Epileptic encephalopathies: An overview. Epilepsy Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 403592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J., Jr. ILAE classification of epilepsy syndromes. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 70 (Suppl. 1), S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabbout, R.; Dulac, O. Epileptic encephalopathies: A brief overview. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. Publ. Am. Electroencephalogr. Soc. 2003, 20, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.; Gillberg, C. The Biology of the Autistic Syndromes; Praeger: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Saemundsen, E.; Ludvigsson, P.; Rafnsson, V. Autism spectrum disorders in children with a history of infantile spasms: A population-based study. J. Child Neurol. 2007, 22, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkvens, J.J.; Veugen, I.; Veendrick-Meekes, M.J.; Snoeijen-Schouwenaars, F.M.; Schelhaas, H.J.; Willemsen, M.H.; Tan, I.Y.; Aldenkamp, A.P. Autism and behavior in adult patients with Dravet syndrome (DS). Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 47, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosander, C.; Hallbook, T. Dravet syndrome in Sweden: A population-based study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVicar, K.A.; Ballaban-Gil, K.; Rapin, I.; Moshe, S.L.; Shinnar, S. Epileptiform EEG abnormalities in children with language regression. Neurology 2005, 65, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballaban-Gil, K.; Tuchman, R. Epilepsy and epileptiform EEG: association with autism and language disorders. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2000, 6, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Fernandez, I.; Loddenkemper, T.; Galanopoulou, A.S.; Moshe, S.L. Should epileptiform discharges be treated? Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, G.L. EEG abnormalities as a biomarker for cognitive comorbidities in pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Epilepsia 2013, 54 (Suppl. 2), 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronen, G.M.; Richards, J.E.; Cunningham, C.; Secord, M.; Rosenbloom, D. Can sodium valproate improve learning in children with epileptiform bursts but without clinical seizures? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2000, 42, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez Fernandez, I.; Peters, J.M.; An, S.; Bergin, A.M.; Takeoka, M.; Rotenberg, A.; Kothare, S.V.; Riviello, J.J., Jr.; Loddenkemper, T. Long-term response to high-dose diazepam treatment in continuous spikes and waves during sleep. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 49, 163–170.e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.T.; Plioplys, S.; Tuchman, R. Risk and correlates of autism spectrum disorder in children with epilepsy: A community-based study. J. Child Neurol. 2011, 26, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.F.; Roberts, W.; Daraksan, M.; Dupuis, A.; McCabe, J.; Wood, H.; Snead, O.C., 3rd; Weiss, S.K. The prevalence of autistic spectrum disorder in children surveyed in a tertiary care epilepsy clinic. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1970–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Rossignol, D.; Casanova, M.F.; Brown, G.L.; Martin, V.; Edelson, S.; Coben, R.; Lewine, J.; Slattery, J.C.; Lau, C.; et al. A review of traditional and novel treatments for seizures in autism spectrum disorder: Findings from a systematic review and expert panel. Front. Public Health 2013, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruining, H.; Passtoors, L.; Goriounova, N.; Jansen, F.; Hakvoort, B.; de Jonge, M.; Poil, S.S. Paradoxical Benzodiazepine Response: A Rationale for Bumetanide in Neurodevelopmental Disorders? Pediatrics 2015, 136, e539–e543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; de Vries, P.J.; Schonig, K.; Rossner, V.; Waltereit, R. mTOR inhibitor reverses autistic-like social deficit behaviours in adult rats with both Tsc2 haploinsufficiency and developmental status epilepticus. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 267, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, M.; Ikeda, H.; Kagitani-Shimono, K.; Yoshinaga, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Aoki, M.; Endo, M.; Yonemura, M.; Kubota, M. Everolimus for epilepsy and autism spectrum disorder in tuberous sclerosis complex: EXIST-3 substudy in Japan. Brain Dev. 2019, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Tai, C.; Westenbroek, R.E.; Yu, F.H.; Cheah, C.S.; Potter, G.B.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Scheuer, T.; de la Iglesia, H.O.; Catterall, W.A. Autistic-like behaviour in Scn1a+/- mice and rescue by enhanced GABA-mediated neurotransmission. Nature 2012, 489, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braat, S.; Kooy, R.F. The GABAA Receptor as a Therapeutic Target for Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Neuron 2015, 86, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippman-Bell, J.J.; Rakhade, S.N.; Klein, P.M.; Obeid, M.; Jackson, M.C.; Joseph, A.; Jensen, F.E. AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX attenuates later-life epileptic seizures and autistic-like social deficits following neonatal seizures. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of Seizures | N = 26 | % |
|---|---|---|
| Focal with or without secondary generalization | 14 | 53.4 |
| Generalized tonic-clonic | 5 | 19.2 |
| Absences | 2 | 7.7 |
| Polymorphic seizures | 4 | 15.4 |
| Preceding infantile spasms | 3 | 11.5 |
| Relationship | Chi-Square | df | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID*Epilepsy | 2.035 | 1 | 0.154 |
| ID*Type of seizures | 4.167 | 4 | 0.384 |
| ID*Sleep-EEG | 2.513 | 4 | 0.642 |
| ID*Age of onset of epilepsy | 0.264 | 1 | 0.607 |
| ID*Frequency of seizures | 2.189 | 1 | 0.139 |
| ID*Awake-EEG | 2.640 | 4 | 0.620 |
| ID*Therapeutic response | 0.124 | 1 | 0.725 |
| ID degree*Epilepsy | 3.200 | 3 | 0.362 |
| ID degree*Type of seizures | 10.069 | 12 | 0.610 |
| ID degree*Age of onset of epilepsy | 0.582 | 3 | 0.901 |
| ID degree*Frequency of seizures | 4.391 | 3 | 0.222 |
| ID degree*Sleep-EEG | 8.370 | 12 | 0.756 |
| MR degree*Awake-EEG | 11.467 | 12 | 0.489 |
| ID degree*Therapeutic response | 3.427 | 3 | 0.330 |
| Intelligence*Epilepsy | 0.198 | 1 | 0.656 |
| Intelligence*Type of seizures | 1.688 | 4 | 0.793 |
| Intelligence*Sleep-EEG | 1.328 | 4 | 0.857 |
| Intelligence*Awake-EEG | 5.137 | 4 | 0.274 |
| Intelligence*Therapeutic response | 0.116 | 1 | 0.733 |
| Correlation | Spearman’s Rho | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligence*Age of onset of seizures | 0.180 | 0.368 |
| Intelligence*Frequency of seizures | −0.505 * | 0.033 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacheva, I.; Ivanov, I.; Yordanova, R.; Gaberova, K.; Galabova, F.; Panova, M.; Petkova, A.; Timova, E.; Sotkova, I. Epilepsy in Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder. Children 2019, 6, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020015
Pacheva I, Ivanov I, Yordanova R, Gaberova K, Galabova F, Panova M, Petkova A, Timova E, Sotkova I. Epilepsy in Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder. Children. 2019; 6(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020015
Chicago/Turabian StylePacheva, Iliyana, Ivan Ivanov, Ralitsa Yordanova, Katerina Gaberova, Fani Galabova, Margarita Panova, Aneliya Petkova, Elena Timova, and Iglika Sotkova. 2019. "Epilepsy in Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder" Children 6, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020015
APA StylePacheva, I., Ivanov, I., Yordanova, R., Gaberova, K., Galabova, F., Panova, M., Petkova, A., Timova, E., & Sotkova, I. (2019). Epilepsy in Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder. Children, 6(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020015





