Rhabdomyosarcoma and Extraosseous Ewing Sarcoma
Abstract
1. Rhabdomyosarcoma
2. Tumor Biology, Histology and Molecular Diagnosis
3. Presentation
4. Assessment
5. Lymph Node Evaluation
6. Staging
7. Clinical Group
8. Risk Group Stratification
9. Treatment
9.1. Medical Treatment
9.2. Radiotherapy (RT)
9.3. Primary Surgical Resection
9.4. Pre-Treatment Re-Excision
9.5. Delayed Primary Excision (DPE)
10. Metastatic Disease and Recurrent RMS
11. Outcomes
12. Extraosseous Ewing Sarcoma
13. Tumor Biology and Histology
14. Assessment
15. Medical Treatment
16. Local Control Therapy
17. Outcomes
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dasgupta, R.; Fuchs, J.; Rodeberg, D. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 25, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognjanovic, S.; Linabery, A.M.; Charbonneau, B.; Ross, J.A. Trends in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma incidence and survival in the United States, 1975–2005. Cancer 2009, 115, 4218–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.W.; Young, J.L.; Novakovic, B. Childhood cancer. Cancer 1995, 75 (Suppl. 1), 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeberg, D.; Paidas, C. Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 15, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, E.A.; Kassira, N.; Cheung, M.C.; Koniaris, L.G.; Neville, H.L.; Sola, J.E. Rhabdomyosarcoma in children: A SEER population based study. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 170, e243–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varan, A.; Şen, H.; Aydın, B.; Yalçın, B.; Kutluk, T.; Akyüz, C. Neurofibromatosis type 1 and malignancy in childhood. Clin. Genet. 2016, 89, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebulla, C.M.; Kleinerman, R.A.; Alegret, A.; Kulak, A.; Dubovy, S.R.; Hess, D.J. Rapid appearance of rhabdomyosarcoma after radiation and chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: A clinicopathologic correlation. Retin. Cases Brief Rep. 2009, 3, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, H.; Danysh, H.E.; Scheurer, M.E.; Okcu, M.F.; Skapek, S.X.; Hawkins, D.S. The Role of Childhood Infections and Immunizations on Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taulli, R.; Scuoppo, C.; Bersani, F.; Accornero, P.; Forni, P.E.; Miretti, S. Validation of met as a therapeutic target in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4742–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnowski, M.; Grymula, K.; Liu, R.; Tarnowska, J.; Drukala, J.; Ratajczak, J. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is secreted by rhabdomyosarcoma cells, modulates tumor metastasis by binding to CXCR4 and CXCR7 receptors and inhibits recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1328–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Timares, L.; Heilpern, C.; Weng, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, H. Targeting wild-type and mutant p53 with small molecule CP-31398 blocks the growth of rhabdomyosarcoma by inducing reactive oxygen species-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6566–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Hurlburt, W.; Greer, A.; Reeves, K.A.; Hillerman, S.; Chang, H. Differential mechanisms of acquired resistance to insulin-like growth factor-i receptor antibody therapy or to a small-molecule inhibitor, BMS-754807, in a human rhabdomyosarcoma model. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7221–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, S.; McDowell, H.P.; Vigne, S.D.; Kokai, G.; Uccini, S.; Tartaglia, M. RAS signaling dysregulation in human embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, D.M.; Qualman, S.J.; Teot, L.; Barr, F.G.; Morotti, R.; Sorensen, P.H. Correlation between histology and PAX/FKHR fusion status in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, D.M.; Barr, F.G. Classification of rhabdomyosarcoma and its molecular basis. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2013, 20, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davicioni, E.; Anderson, M.J.; Finckenstein, F.G.; Lynch, J.C.; Qualman, S.J.; Shimada, H. Molecular classification of rhabdomyosarcoma--genotypic and phenotypic determinants of diagnosis: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davicioni, E.; Anderson, J.R.; Buckley, J.D.; Meyer, W.H.; Triche, T.J. Gene expression profiling for survival prediction in pediatric rhabdomyosarcomas: A report from the children’s oncology group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, D.; Missiaglia, E.; de Reyniès, A.; Pierron, G.; Thuille, B.; Palenzuela, G. Fusion gene-negative alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is clinically and molecularly indistinguishable from embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missiaglia, E.; Williamson, D.; Chisholm, J.; Wirapati, P.; Pierron, G.; Petel, F. PAX3/FOXO1 fusion gene status is the key prognostic molecular marker in rhabdomyosarcoma and significantly improves current risk stratification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, C.M.; Domaschenz, R.; Amagase, Y.; Williamson, D.; Missiaglia, E.; Shipley, J. HES6 enhances the motility of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.A.; Anderson, J.R.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Barr, F.G.; Skapek, S.X.; Hawkins, D.S. Histology, Fusion Status, and Outcome in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma with Low-Risk Clinical Features: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raney, R.B.; Anderson, J.R.; Barr, F.G.; Donaldson, S.S.; Pappo, A.S.; Qualman, S.J. Rhabdomyosarcoma and undifferentiated sarcoma in the first two decades of life: A selective review of intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study group experience and rationale for Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study, V. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2001, 23, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangle, P.P.; Correa, A.; Tennyson, L.; Gayed, B.; Reyes-Múgica, M.; Ost, M. Current management of paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma. Urol. Oncol. 2016, 34, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzinski, E.R.; Anderson, J.R.; Chi, Y.Y.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Astbury, C.; Barr, F.G. Histology, fusion status, and outcome in metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzinski, E.R.; Teot, L.A.; Anderson, J.R.; Moore, J.; Bridge, J.A.; Barr, F.G. Dense pattern of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, a lesion easily confused with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 140, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, B.K.; Kim, A.; Peña, M.T.; Dong, T.A.; Rossi, C.; Murnick, J.G. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and neck in children: Review and update. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.W.; Esiashvili, N.; George, B.A.; Katzenstein, H.M.; Olson, T.A.; Rapkin, L.B. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy with use of cone-down boost for pediatric head-and-neck rhabdomyosarcoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, E.S.; Anderson, J.R.; Ojimba, J.I.; Lobe, T.E.; Paidas, C.; Andrassy, R.J. Controversies in the management of paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma: Is staging retroperitoneal lymph node dissection necessary for adolescents with resected paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma? Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2001, 10, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walterhouse, D.O.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Hall, D.; Ferrari, A.; De Salvo, G.L.; Koscielniak, E. Demographic and Treatment Variables Influencing Outcome for Localized Paratesticular Rhabdomyosarcoma: Results From a Pooled Analysis of North American and European Cooperative Groups. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakely, M.L.; Andrassy, R.J.; Raney, R.B.; Anderson, J.R.; Wiener, E.S.; Rodeberg, D.A. Prognostic factors and surgical treatment guidelines for children with rhabdomyosarcoma of the perineum or anus: A report of Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Studies I through, I.V.; 1972 through 1997. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2003, 38, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, J.; Dantonello, T.M.; Blumenstock, G.; Kosztyla, D.; Klingebiel, T.; Leuschner, I. Treatment and outcome of patients suffering from perineal/perianal rhabdomyosarcoma: Results from the CWS trials--retrospective clinical study. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, H.L.; Andrassy, R.J.; Lobe, T.E.; Bagwell, C.E.; Anderson, J.R.; Womer, R.B. Preoperative staging, prognostic factors, and outcome for extremity rhabdomyosarcoma: A preliminary report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV (1991–1997). J. Pediatr. Surg. 2000, 35, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sambeeck, S.J.; Mavinkurve-Groothuis, A.M.; Flucke, U.; Dors, N. Sarcoma botryoides in an infant. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, A.R.; Lyden, E.R.; Anderson, J.R.; Hawkins, D.S.; Spunt, S.L.; Walterhouse, D.O. Histologic and clinical characteristics can guide staging evaluations for children and adolescents with rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3226–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Shandal, V.; Shamim, S.A.; Halanaik, D.; Malhotra, A. Clinical applications of PET and PET/CT in pediatric malignancies. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2010, 10, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, R.J.; Bui, C.; Hutchinson, R.J.; Yanik, G.A.; Castle, V.P.; Frey, K.A. FDG PET imaging of childhood sarcomas. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 54, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodeberg, D.A.; Garcia-Henriquez, N.; Lyden, E.R.; Davicioni, E.; Parham, D.M.; Skapek, S.X. Prognostic significance and tumor biology of regional lymph node disease in patients with rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, E.S.; Lawrence, W.; Hays, D.; Lobe, T.E.; Andrassy, R.; Donaldson, S. Retroperitoneal node biopsy in paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1994, 29, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobeck, I.; Dupree, P.; Karns, R.; Rodeberg, D.; von Allmen, D.; Dasgupta, R. Quality assessment of lymph node sampling in rhabdomyosarcoma: A surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) program study. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, T.H.; Wolden, S.L.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Hawkins, D.S.; Brown, K.L.; Anderson, J.R. Regional nodal involvement and patterns of spread along in-transit pathways in children with rhabdomyosarcoma of the extremity: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walterhouse, D.O.; Pappo, A.S.; Meza, J.L.; Breneman, J.C.; Hayes-Jordan, A.A.; Parham, D.M. Shorter-duration therapy using vincristine, dactinomycin, and lower-dose cyclophosphamide with or without radiotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed low-risk rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3547–3552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, D.S.; Anderson, J.R.; Mascarenhas, L.; McCowage, G.B.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Wolden, S.L. Vincristine, dactinomycin, cyclophosphamide (VAC) versus VAC/V plus irinotecan (VI) for intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma (IRRMS): A report from the Children’s Oncology Group Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee. 32. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walterhouse, D.O.; Pappo, A.S.; Meza, J.L.; Breneman, J.C.; Hayes-Jordan, A.; Parham, D.M. Reduction of cyclophosphamide dose for patients with subset 2 low-risk rhabdomyosarcoma is associated with an increased risk of recurrence: A report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 2017, 123, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.S.; Gupta, A.A.; Rudzinski, E.R. What is new in the biology and treatment of pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma? Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2014, 26, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, A.M.; Stafman, L.L.; Garner, E.F.; Mruthyunjayappa, S.; Stewart, J.E.; Friedman, G.K. Effect of Repeat Dosing of Engineered Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus on Preclinical Models of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, G.; Jenney, M.; Bergeron, C.; Gallego Melcón, S.; Ferrari, A.; Oberlin, O. Addition of dose-intensified doxorubicin to standard chemotherapy for rhabdomyosarcoma (EpSSG RMS 2005): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; ClinicalTrials.gov [internet]. Combination Chemotherapy with or without Temsirolimus in Treating Patients with Intermediate Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma. National Cancer Institute: Rockville, MD, USA, October 2015; Identifier NCT02567435. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT02567435 (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Bisogno, G.; De Salvo, G.L.; Bergeron, C.; Jenney, M.; Merks, J.H.; Minard-Colin, V. Maintenance low-dose chemotherapy in patients with high-risk (HR) rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS): A report from the European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group (EpSSG). 36. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.T.; Pappo, A.S.; Wu, J.; Indelicato, D.J.; Krasin, M.J. Excessive Treatment Failures in Patients With Parameningeal Rhabdomyosarcoma With Reduced-dose Cyclophosphamide and Delayed Radiotherapy. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 40, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharam, M.D.; Hanfelt, J.J.; Tefft, M.C.; Johnston, J.; Ensign, L.G.; Breneman, J. Radiation therapy for rhabdomyosarcoma: Local failure risk for Clinical Group III patients on Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study, I.I. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 38, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egas-Bejar, D.; Huh, W.W. Rhabdomyosarcoma in adolescent and young adult patients: Current perspectives. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2014, 5, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paulino, A.C.; Simon, J.H.; Zhen, W.; Wen, B.C. Long-term effects in children treated with radiotherapy for head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, M.; Murayama, S.; Akimoto, T.; Demizu, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Ishida, Y. Long-term follow-up after proton beam therapy for pediatric tumors: A Japanese national survey. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, J.A.; Kayton, M.L.; Chi, Y.Y.; Hawkins, D.S.; Tian, J.; Breneman, J. Treatment Approach and Outcomes in Infants with Localized Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladra, M.M.; Szymonifka, J.D.; Mahajan, A.; Friedmann, A.M.; Yong Yeap, B.; Goebel, C.P. Preliminary results of a phase II trial of proton radiotherapy for pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3762–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakely, M.L.; Lobe, T.E.; Anderson, J.R.; Donaldson, S.S.; Andrassy, R.J.; Parham, D.M. Does debulking improve survival rate in advanced-stage retroperitoneal embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma? J. Pediatr. Surg. 1999, 34, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeberg, D.A.; Paidas, C.N.; Lobe, T.L.; Brown, K.; Andrassy, R.J.; Crist, W.M. Surgical Principles for Children/Adolescents With Newly Diagnosed Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee of the Children’s Oncology Group. Sarcoma 2002, 6, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, A.R.; Anderson, J.R.; Lyden, E.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Wolden, S.L.; Kao, S.C. Early response as assessed by anatomic imaging does not predict failure-free survival among patients with Group III rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeberg, D.A.; Wharam, M.D.; Lyden, E.R.; Stoner, J.A.; Brown, K.; Wolden, S.L. Delayed primary excision with subsequent modification of radiotherapy dose for intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwisscha van Scheltinga, C.E.; Spronk, P.; van Rosmalen, J.; Wijnen, M.H.; Heij, H.A.; van Baren, R. Diagnosis and treatment of lymph node metastases in pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma in the Netherlands: A retrospective analysis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2014, 49, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes-Jordan, A.; Doherty, D.K.; West, S.D.; Raney, R.B.; Blakely, M.L.; Cox, C.S. Outcome after surgical resection of recurrent rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruchel, S.; Pappo, A.; Krailo, M.; Baker, K.S.; Wu, B.; Villaluna, D. A phase 2 trial of trabectedin in children with recurrent rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma and non-rhabdomyosarcoma soft tissue sarcomas: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Anderson, J.R.; Qualman, S.J.; Crist, W.M.; Paidas, C.N.; Teot, L.A. Which patients with microscopic disease and rhabdomyosarcoma experience relapse after therapy? A report from the soft tissue sarcoma committee of the children’s oncology group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 4058–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharam, M.D.; Meza, J.; Anderson, J.; Breneman, J.C.; Donaldson, S.S.; Fitzgerald, T.J. Failure pattern and factors predictive of local failure in rhabdomyosarcoma: A report of group III patients on the third Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, S.; Zanetti, I.; Orbach, D.; Ranchère, D.; Shipley, J.; Zin, A. Fusion status in patients with lymph node-positive (N1) alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a powerful predictor of prognosis: Experience of the European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group (EpSSG). Cancer 2018, 124, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes-Jordan, A.; Green, H.; Lin, H.; Owusu-Agyemang, P.; Mejia, R.; Okhuysen-Cawley, R. Cytoreductive surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) for children, adolescents, and young adults: The first 50 cases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, P.; Milano, M.T.; Constine, L.S.; Travis, L.B. Long-term cause-specific mortality in survivors of adolescent and young adult bone and soft tissue sarcoma: A population-based study of 28,844 patients. Cancer 2014, 120, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, H.; Colineau, X.; Acalet, L.; Tourrette, J.H.; Civatte, M.; Fesselet, J. Ewing’s sarcoma of the soft tissues: Apropos of 3 cases and review of the literature. J. Radiol. 1999, 80, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Applebaum, M.A.; Worch, J.; Matthay, K.K.; Goldsby, R.; Neuhaus, J.; West, D.C. Clinical features and outcomes in patients with extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.C.; Kandel, R.A.; Bell, R.S.; Mathews, R.E.; Ghazarian, D.M. Extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma in a 77-year-old woman. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2001, 125, 1358–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Galyfos, G.; Karantzikos, G.A.; Kavouras, N.; Sianou, A.; Palogos, K.; Filis, K. Extraosseous Ewing Sarcoma: Diagnosis, Prognosis and Optimal Management. Indian J. Surg. 2016, 78, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geens, L.; Robays, J.V.; Geert, V.; der Speeten, K.V. An Unusual Location of Extraosseous Ewing’s Sarcoma. Case Rep. Oncol. 2013, 6, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, A.R.; Reddy AV, S.; Killampalli, L.K.; Rajinikanth, M. Extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma of the maxillary sinus: A very rare entity. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2018, 39, 380–384. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, H.; Heinen, R.C.; van der Pal, H.J.; Merks, J.H. Extra-osseous Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 26, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, J.L.; Osuna, D.; Herrero, D.; de Alava, E.; Madoz-Gúrpide, J. Advances in Ewing’s sarcoma research: Where are we now and what lies ahead? Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7140–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folpe, A.L.; Goldblum, J.R.; Rubin, B.P.; Shehata, B.M.; Liu, W.; Dei Tos, A.P. Morphologic and immunophenotypic diversity in Ewing family tumors: A study of 66 genetically confirmed cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arvand, A.; Denny, C.T. Biology of EWS/ETS fusions in Ewing’s family tumors. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5747–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Stamenkovic, I. The cancer stem cell paradigm in Ewing’s sarcoma: What can we learn about these rare cells from a rare tumor? Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2011, 11, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Suvà, D.; Cironi, L.; Provero, P.; Tercier, S. EWS-FLI-1 expression triggers a Ewing’s sarcoma initiation program in primary human mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Iwakuma, T.; Harimaya, K.; Sato, H.; Iwamoto, Y. EWS-Fli1 antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits proliferation of human Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorthi, A.; Romero, J.C.; Loranc, E.; Cao, L.; Lawrence, L.A.; Goodale, E. EWS-FLI1 increases transcription to cause R-loops and block BRCA1 repair in Ewing sarcoma. Nature 2018, 555, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Dickman, P.; Parham, D. Pathobiologic markers of the ewing sarcoma family of tumors: State of the art and prediction of behaviour. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 856190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llombart-Bosch, A.; Machado, I.; Navarro, S.; Bertoni, F.; Bacchini, P.; Alberghini, M. Histological heterogeneity of Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET: An immunohistochemical analysis of 415 genetically confirmed cases with clinical support. Virchows Arch. 2009, 455, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, N.; Tjoe, J. Immunohistochemical profile of monoclonal antibody O13: Antibody that recognizes glycoprotein p30/32MIC2 and is useful in diagnosing Ewing’s sarcoma and peripheral neuroepithelioma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1994, 18, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italiano, A.; Di Mauro, I.; Rapp, J.; Pierron, G.; Auger, N.; Alberti, L. Clinical effect of molecular methods in sarcoma diagnosis (GENSARC): A prospective, multicentre, observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, A.; Arekapudi, S.; DeMattia, F.; Abu-Isa, E.; Kraut, M. High-grade undifferentiated small round cell sarcoma with t(4;19)(q35;q13.1) CIC-DUX4 fusion: Emerging entities of soft tissue tumors with unique histopathologic features--a case report and literature review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2015, 16, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- O’Keeffe, F.; Lorigan, J.G.; Wallace, S. Radiological features of extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma. Br. J. Radiol. 1990, 63, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, A.C.; Panicker, N.; Sarawagi, S.; Anwekar, S.; Kharat, A.T. Fine needle aspiration cytology diagnosis of paravertebral extraosseus Ewing’s sarcoma. J. Cytol. 2010, 27, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie-Large, M.; James, S.L.; Tiessen, L.; Davies, A.M.; Grimer, R.J. Imaging strategy for detecting lung metastases at presentation in patients with soft tissue sarcomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 1841–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Galindo, C.; Liu, T.; Krasin, M.J.; Wu, J.; Billups, C.A.; Daw, N.C. Analysis of prognostic factors in ewing sarcoma family of tumors: Review of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital studies. Cancer 2007, 110, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karski, E.E.; Matthay, K.K.; Neuhaus, J.M.; Goldsby, R.E.; Dubois, S.G. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with Ewing sarcoma over 40 years of age at diagnosis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Ewing Sarcoma Version 1.2019. Available online: www.nccn.org (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Womer, R.B.; West, D.C.; Krailo, M.D.; Dickman, P.S.; Pawel, B.R.; Grier, H.E. Randomized controlled trial of interval-compressed chemotherapy for the treatment of localized Ewing sarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4148–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, G.; Balladelli, A.; Forni, C.; Ferrari, S.; Longhi, A.; Bacchini, P. Adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for Ewing sarcoma family tumors in patients aged between 40 and 60: Report of 35 cases and comparison of results with 586 younger patients treated with the same protocols in the same years. Cancer 2007, 109, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castex, M.P.; Rubie, H.; Stevens, M.C.; Escribano, C.C.; de Gauzy, J.S.; Gomez-Brouchet, A. Extraosseous localized ewing tumors: Improved outcome with anthracyclines—The French society of pediatric oncology and international society of pediatric oncology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamberger, R.C.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Gebhardt, M.C.; Neff, J.R.; Tarbell, N.J.; Marcus, K.C. Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the chest wall: Impact of initial versus delayed resection on tumor margins, survival, and use of radiation therapy. Ann. Surg. 2003, 238, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, H.E.; Krailo, M.D.; Tarbell, N.J.; Link, M.P.; Fryer, C.J.; Pritchard, D.J. Addition of ifosfamide and etoposide to standard chemotherapy for Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor of bone. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasin, M.J.; Davidoff, A.M.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Billups, C.A.; Fuller, C.E.; Neel, M.D. Definitive surgery and multiagent systemic therapy for patients with localized Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: Local outcome and prognostic factors. Cancer 2005, 104, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.T.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Extraskeletal Ewing sarcomas in late adolescence and adults: A study of 37 patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 2967–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Domínguez, D.J.; Hontecillas-Prieto, L.; Rodríguez-Núñez, P.; Pascual-Pasto, G.; Vila-Ubach, M.; García-Mejías, R. The combination of epigenetic drugs SAHA and HCI-2509 synergistically inhibits EWS-FLI1 and tumor growth in Ewing sarcoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31397–31410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, H.D.; Beekman, J.F.; Kingry, R.L. Extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma: Prolonged survival with recurrence after operation. South. Med. J. 1980, 73, 1294–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.S.; Laskar, S.; Kembhavi, S.; Talole, S.; Chinnaswamy, G.; Vora, T. Extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma in children and adolescents: Impact of narrow but negative surgical margin. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2013, 29, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamuth, N.J.; Womer, R.B. Ewing’s sarcoma. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasin, M.J.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Billups, C.A.; Davidoff, A.M.; Neel, M.D.; Merchant, T.E. Definitive irradiation in multidisciplinary management of localized Ewing sarcoma family of tumors in pediatric patients: Outcome and prognostic factors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cash, T.; McIlvaine, E.; Krailo, M.D.; Lessnick, S.L.; Lawlor, E.R.; Laack, N. Comparison of clinical features and outcomes in patients with extraskeletal versus skeletal localized Ewing sarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hoang, B.H.; Ziogas, A.; Zell, J.A. Analysis of prognostic factors in Ewing sarcoma using a population-based cancer registry. Cancer 2010, 116, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
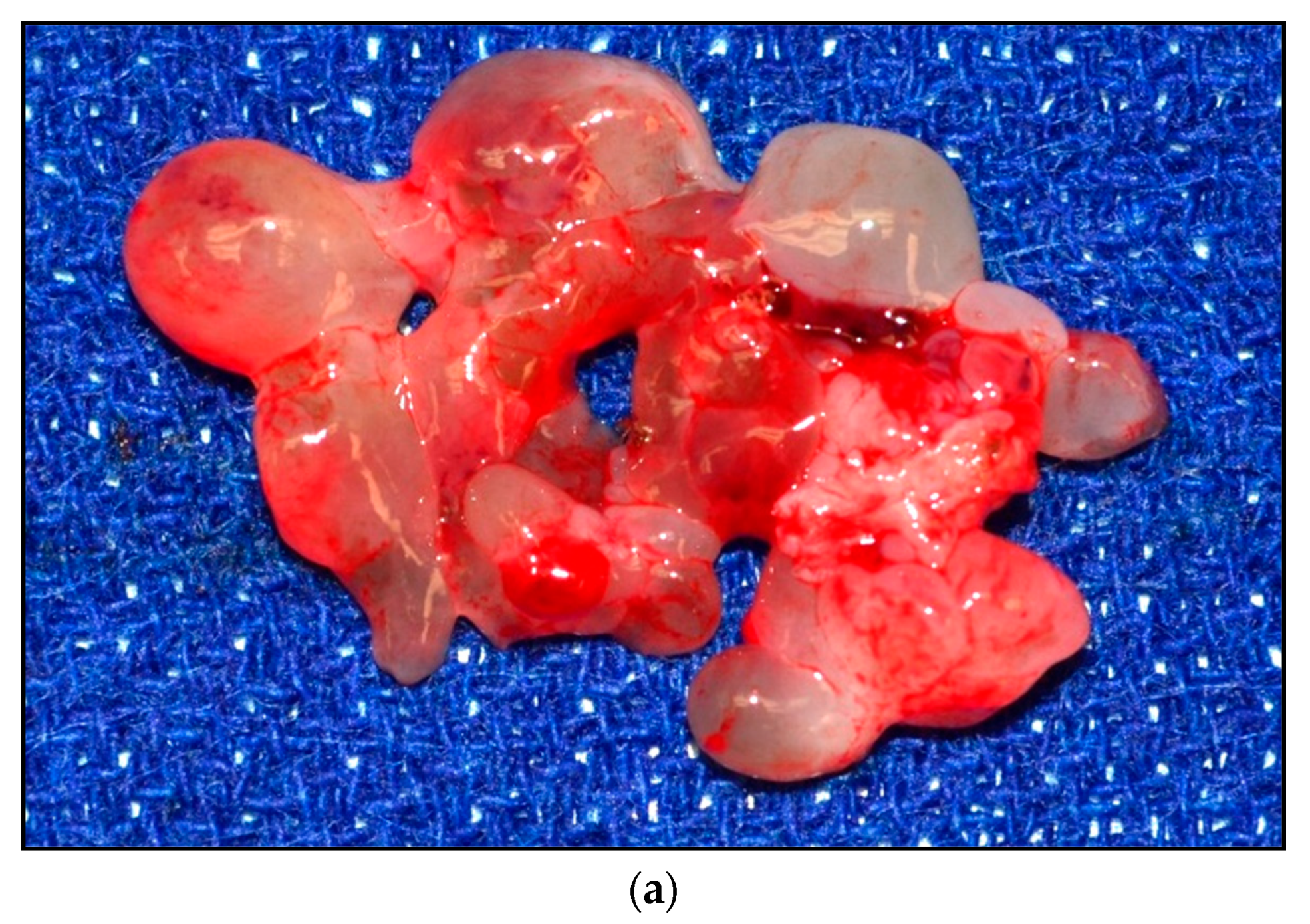
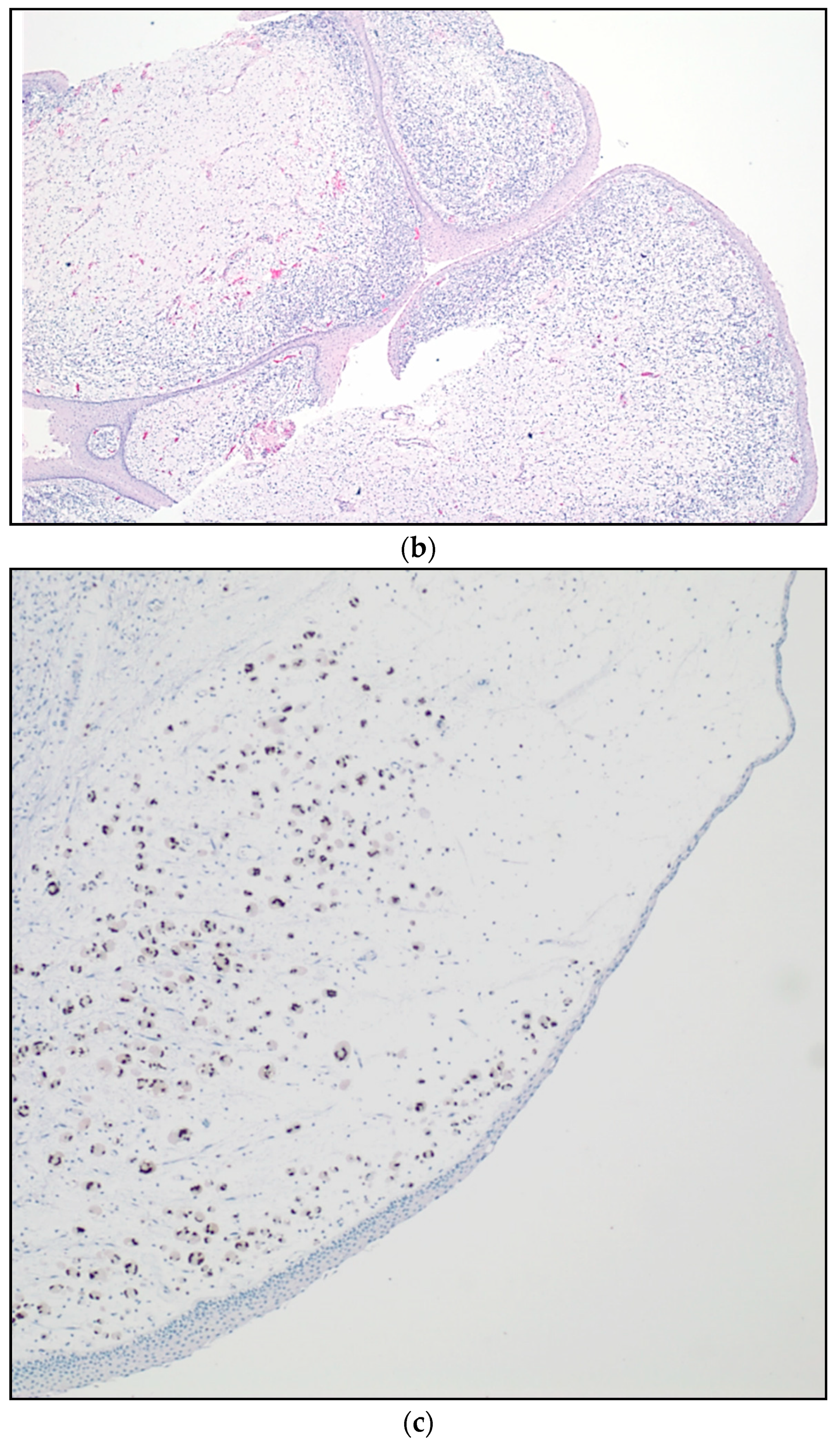
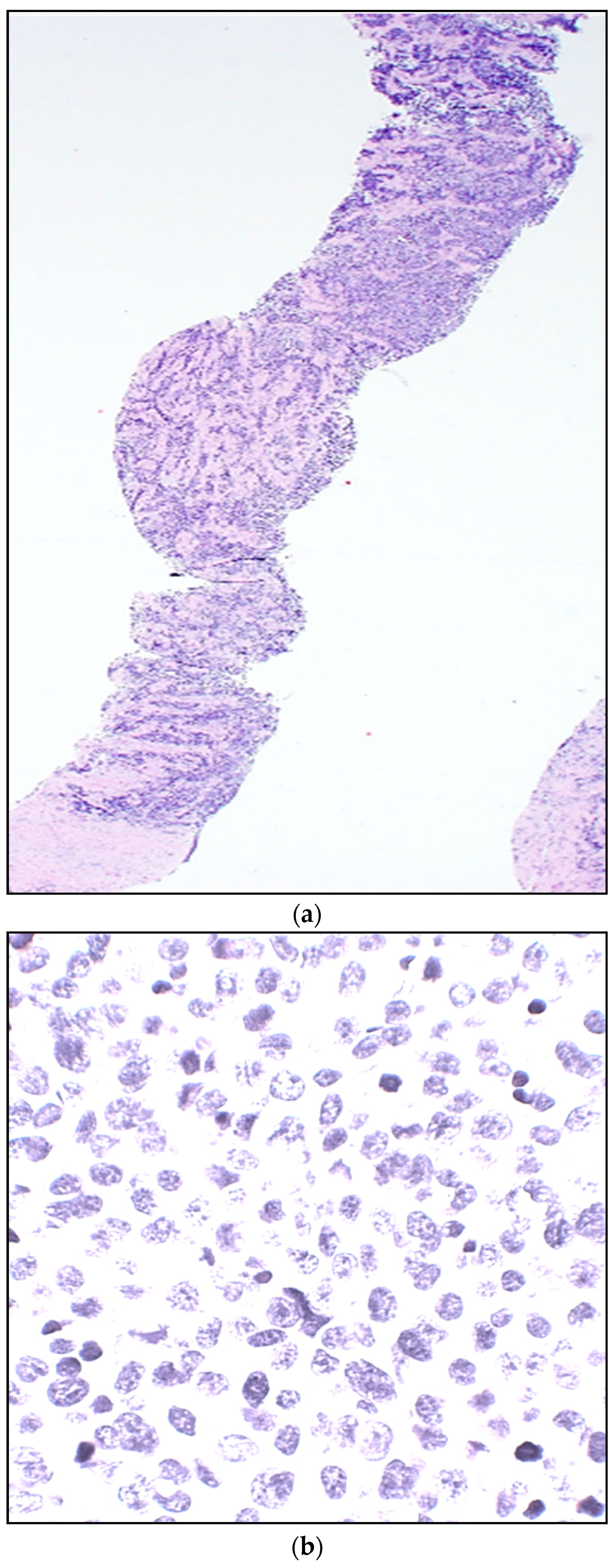
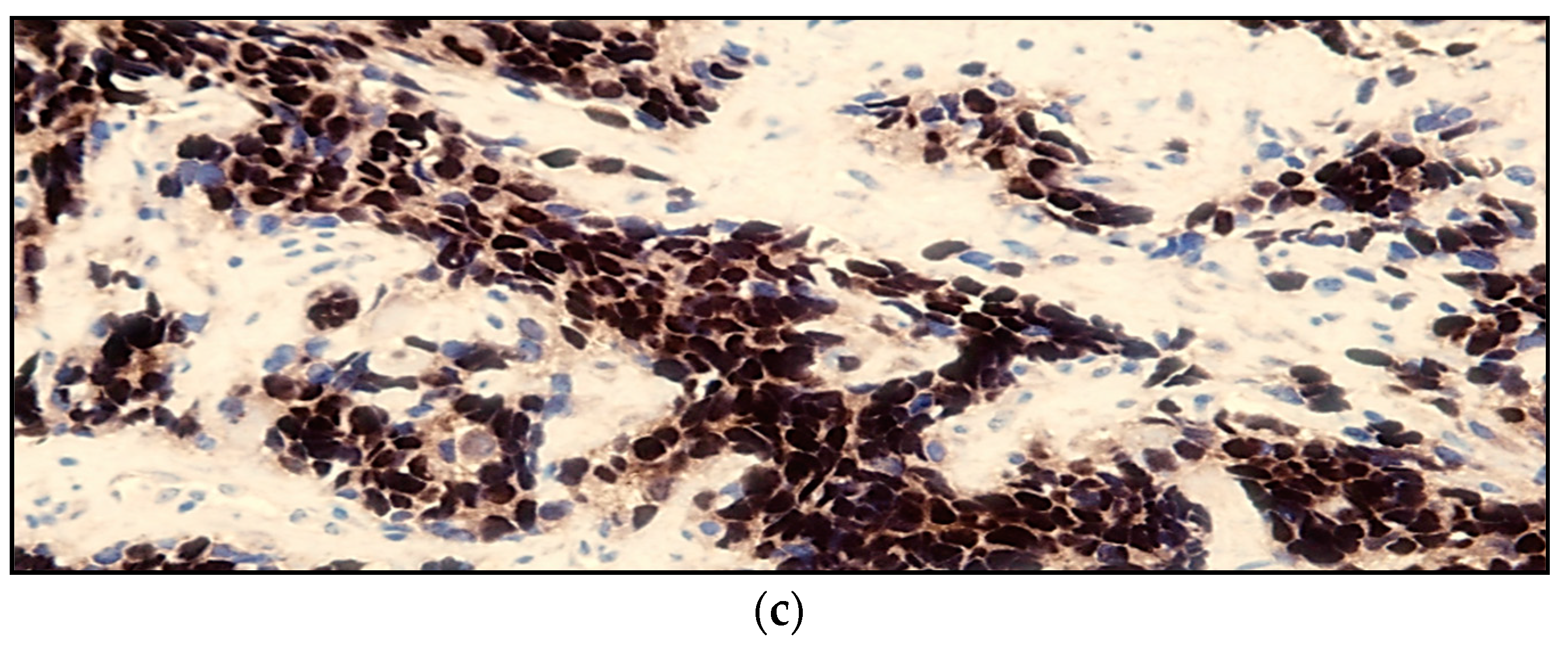
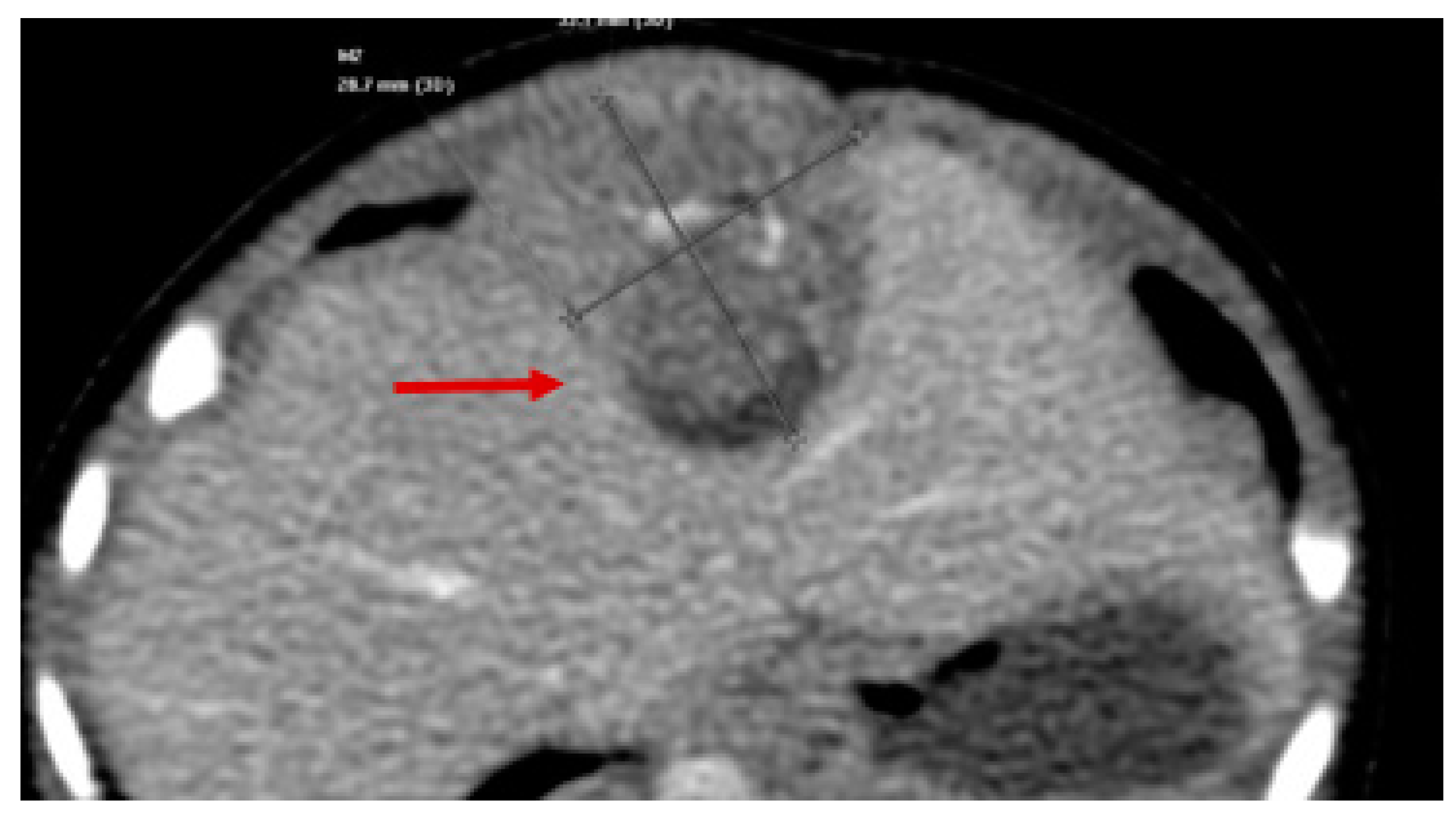
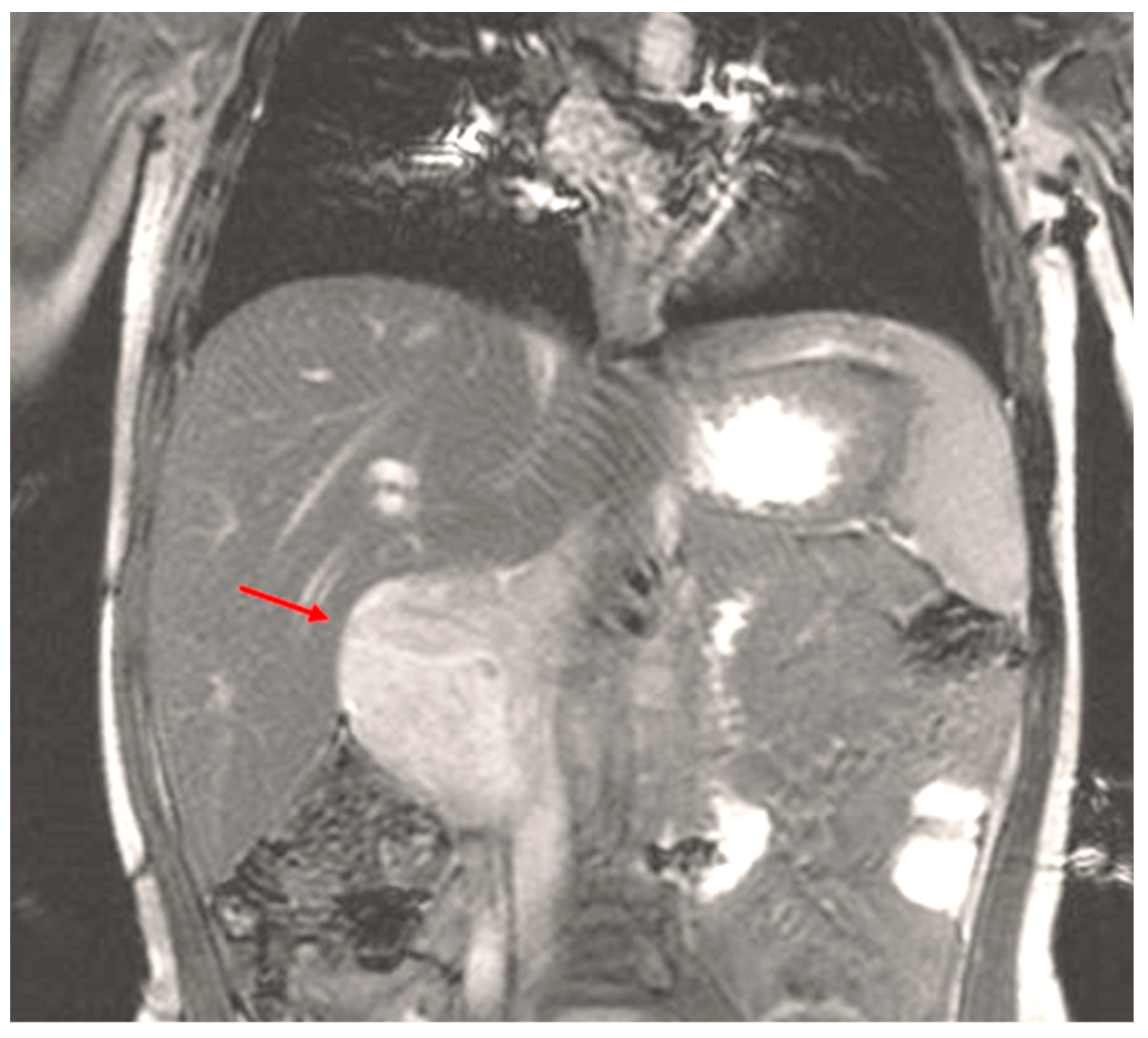
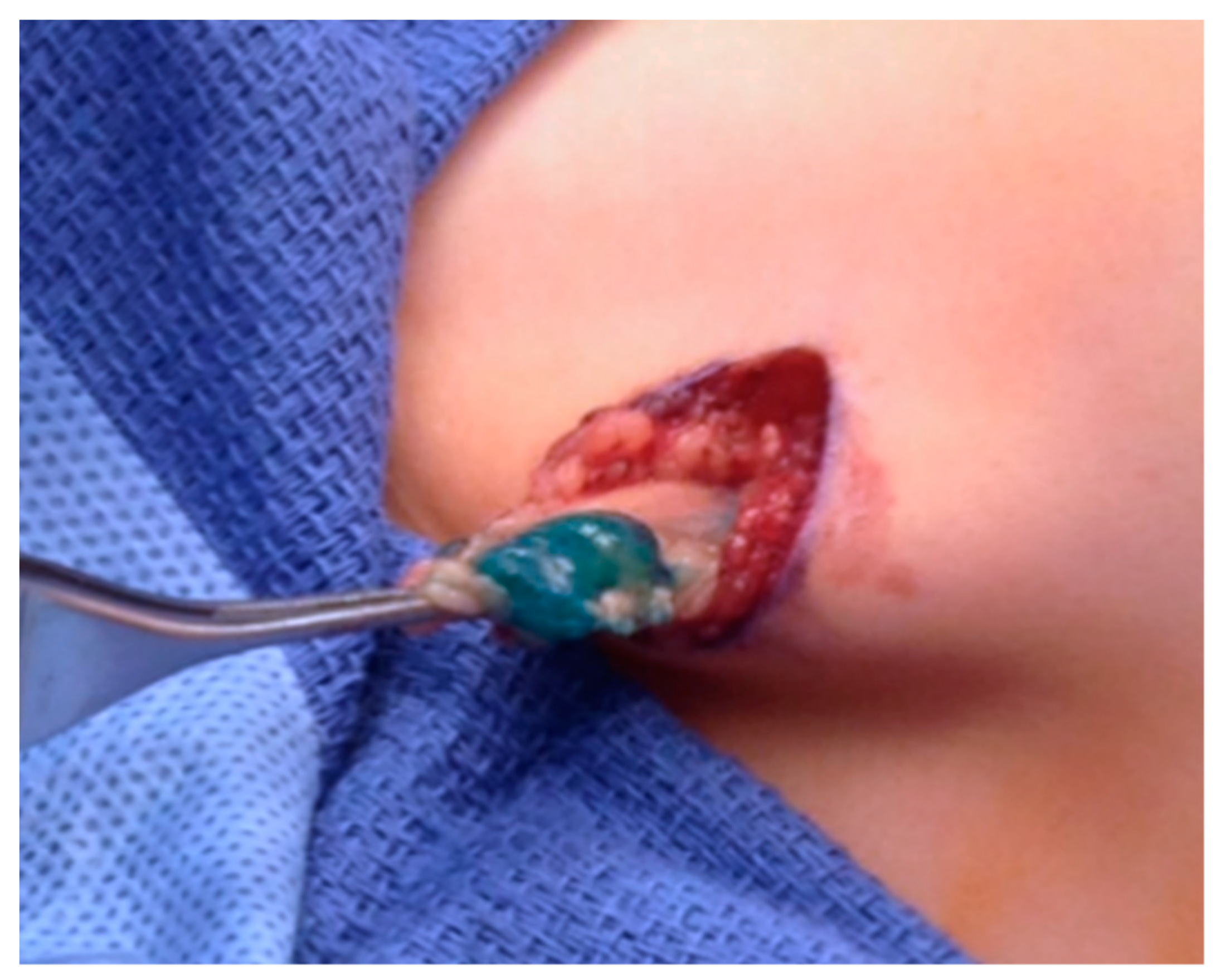
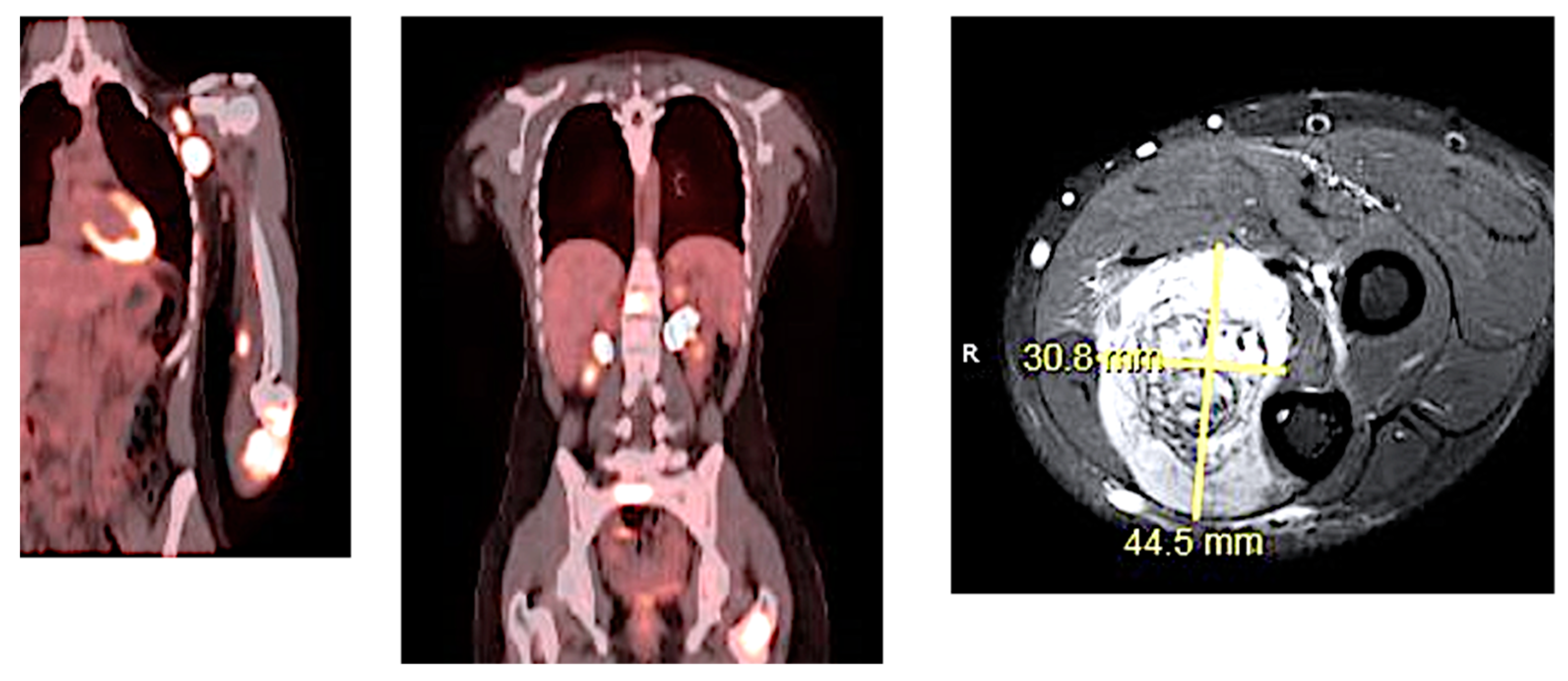
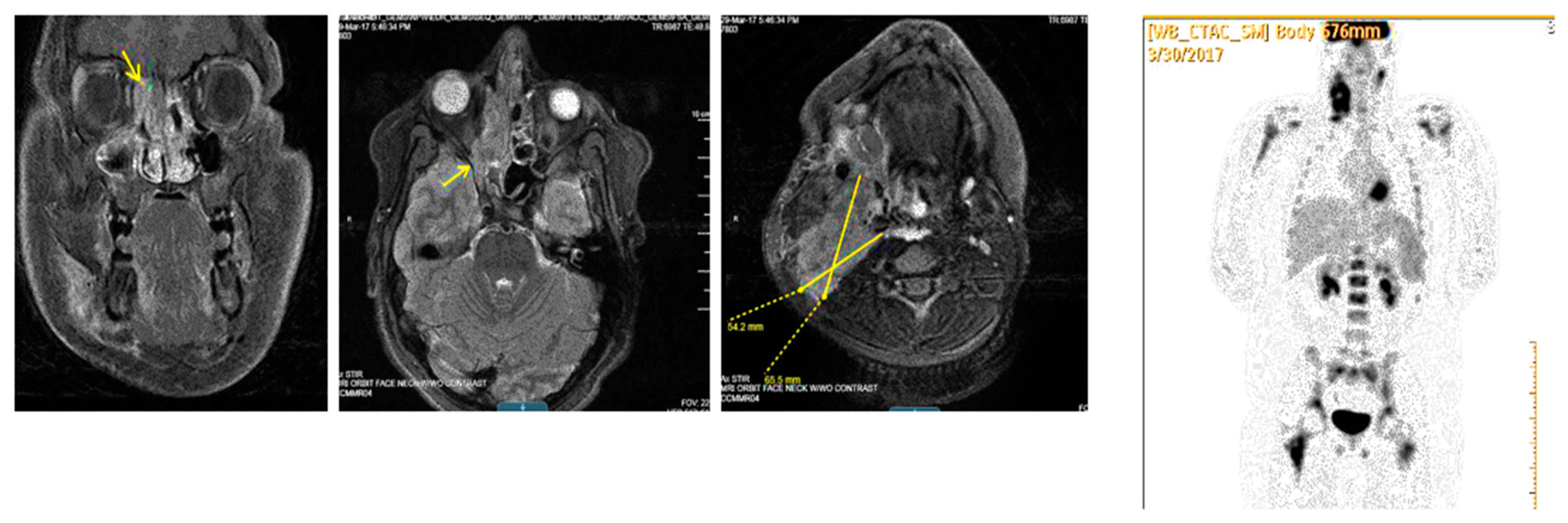
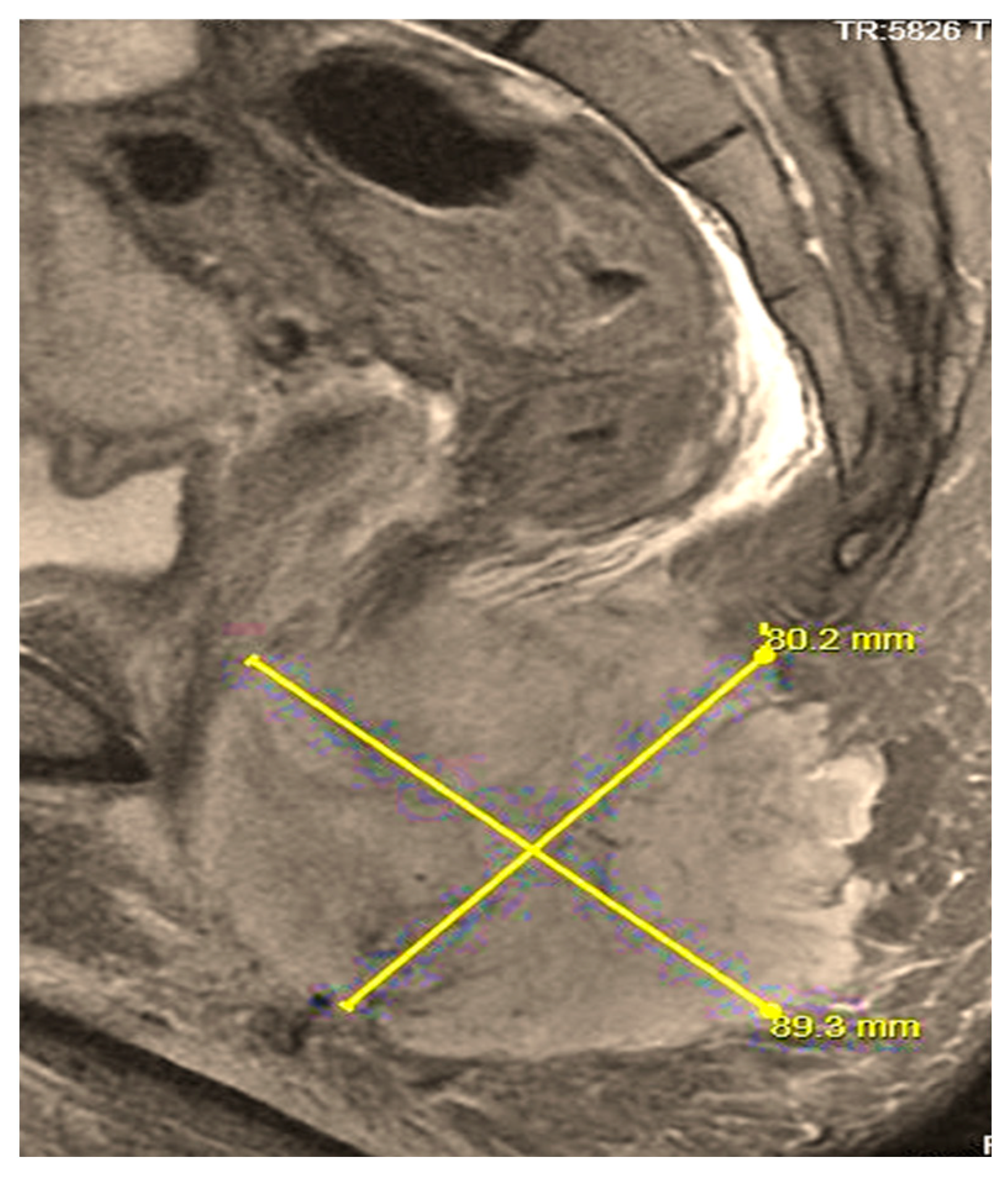
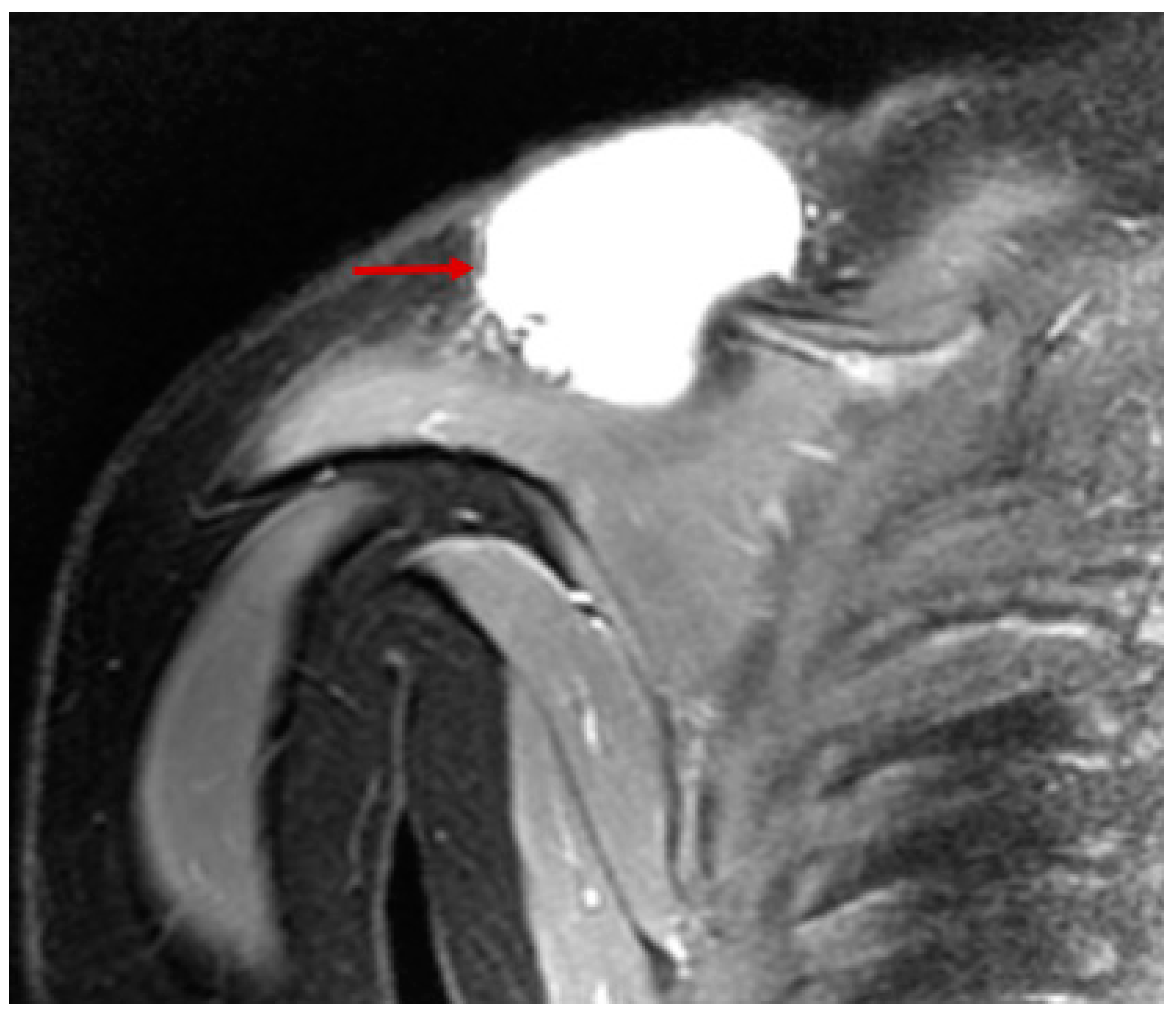
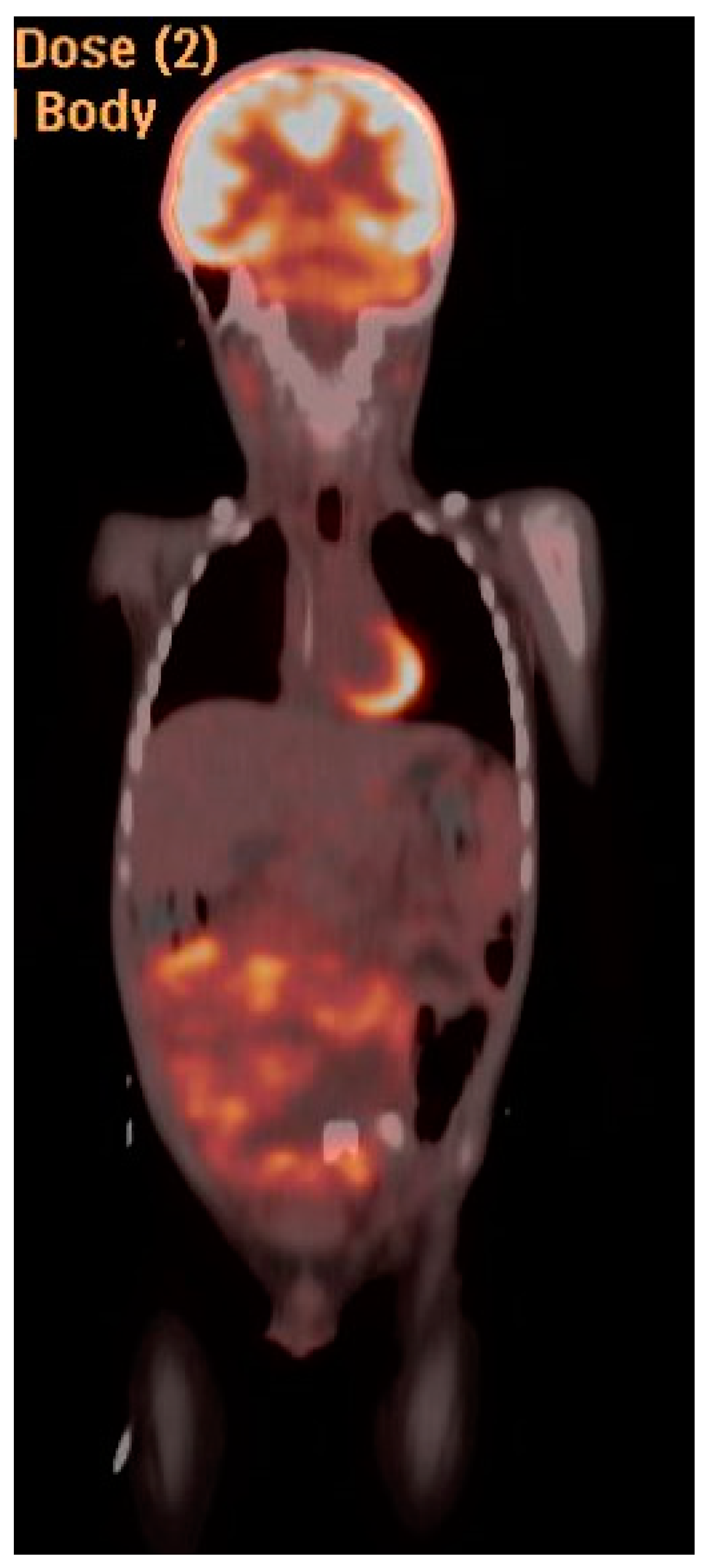
| Stage | Sites | T | Size | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Orbit, head and neck a, genitourinary e, Biliary tract | T1 or T2 | A or B | N0 or N1 or Nx | M0 |
| 2 | Bladder/prostate, extremity, cranial, parameningeal, other o, non-Biliary tract | T1 or T2 | A | N0 or Nx | M0 |
| 3 | Bladder/prostate, extremity, cranial, parameningeal, other o, non-Biliary tract | T1 or T2 | A B | N1 N0 or N1 or Nx | M0 M0 |
| 4 | Any | T1 or T2 | A or B | N0 or N1 | M1 |
| Group | Definition |
|---|---|
| Group I | Complete resection of localized disease |
| Group II | Regional resection |
| IIA | Regional resection Inadequate microscopic margins |
| IIB | Regional resection Lymph node disease Adequate microscopic margins |
| IIC | Regional resection Lymph node disease Inadequate microscopic margins |
| Group III | Incomplete resection Biopsy only |
| Group IV | Distant metastatic disease |
| Risk | Stage | Group | Histology | Overall Survival |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low, Subset 1 | 1 or 2 1 | I or II III or bit | ERMS ERMS | 90% |
| Low, Subset 2 | 1 3 | III non-orbit I or II | ERMS ERMS | |
| Intermediate | 2 or 3 1, 2, or 3 | II or III I, II or III | ERMS ARMS | 60–80% |
| High | 4 | IV | ERMS or ARMS | 20–40% |
| Metastasis | N-Status | Pathology | IRS-Group | Localization | Size/Age | Subgroup | Risk Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | N0 | ERMS | I | Any | ≤5 cm and <10 years | A | Low |
| >5 cm or ≥10 years | B | Standard | |||||
| II, III | ORB, UG-non BP, HN-non PM | Any | C | ||||
| EXT, UG-BP, HN-PM, others | ≤5 cm and <10 years | D | |||||
| >5 cm or ≥10 years | E | High | |||||
| N1 | ERMS | II, III | Any | F | |||
| N0 | ARMS | Any | G | ||||
| N1 | ARMS | Any | H | Very High | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gurria, J.P.; Dasgupta, R. Rhabdomyosarcoma and Extraosseous Ewing Sarcoma. Children 2018, 5, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5120165
Gurria JP, Dasgupta R. Rhabdomyosarcoma and Extraosseous Ewing Sarcoma. Children. 2018; 5(12):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5120165
Chicago/Turabian StyleGurria, Juan P., and Roshni Dasgupta. 2018. "Rhabdomyosarcoma and Extraosseous Ewing Sarcoma" Children 5, no. 12: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5120165
APA StyleGurria, J. P., & Dasgupta, R. (2018). Rhabdomyosarcoma and Extraosseous Ewing Sarcoma. Children, 5(12), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5120165




