Sleep Disturbances in Newborns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Development of Sleep
2.1. Sleep States
2.2. Fetal Sleep
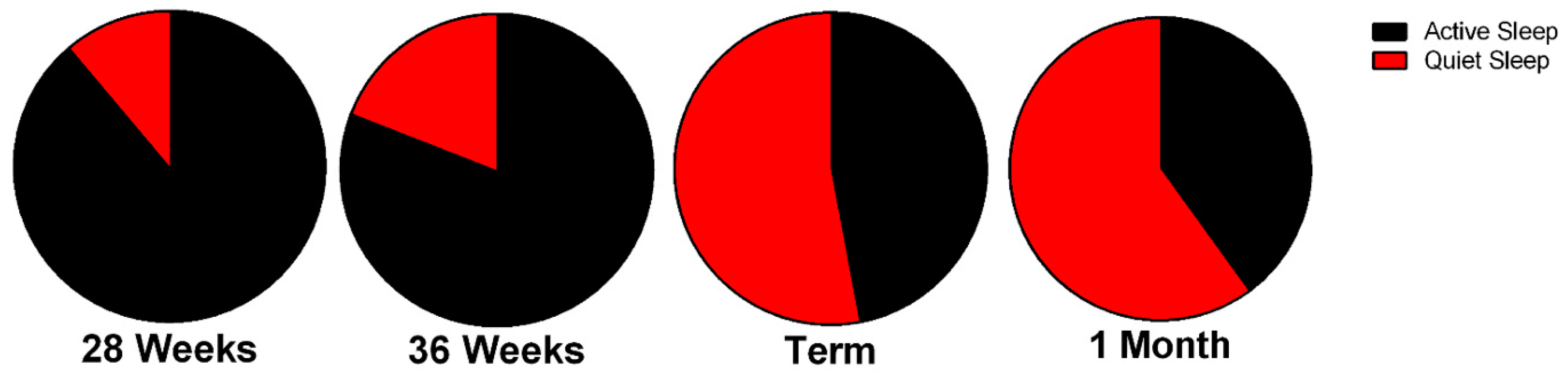
2.3. Sleep in Premature Neonates
2.4. Sleep in Term Neonates
3. Bedside Tools to Monitor Sleep
3.1. Behavioral Classification
3.2. Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
3.3. Polysomnography
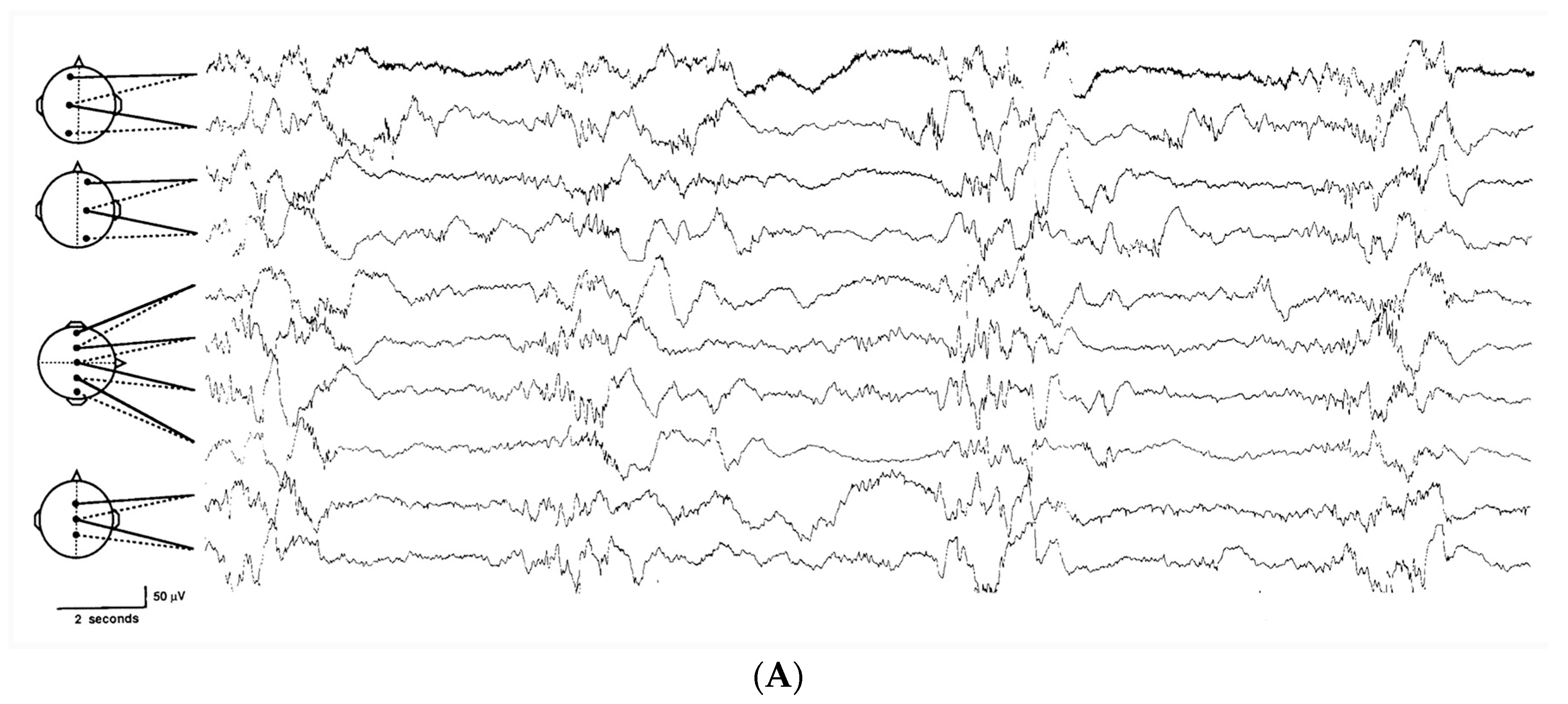
3.4. EEG
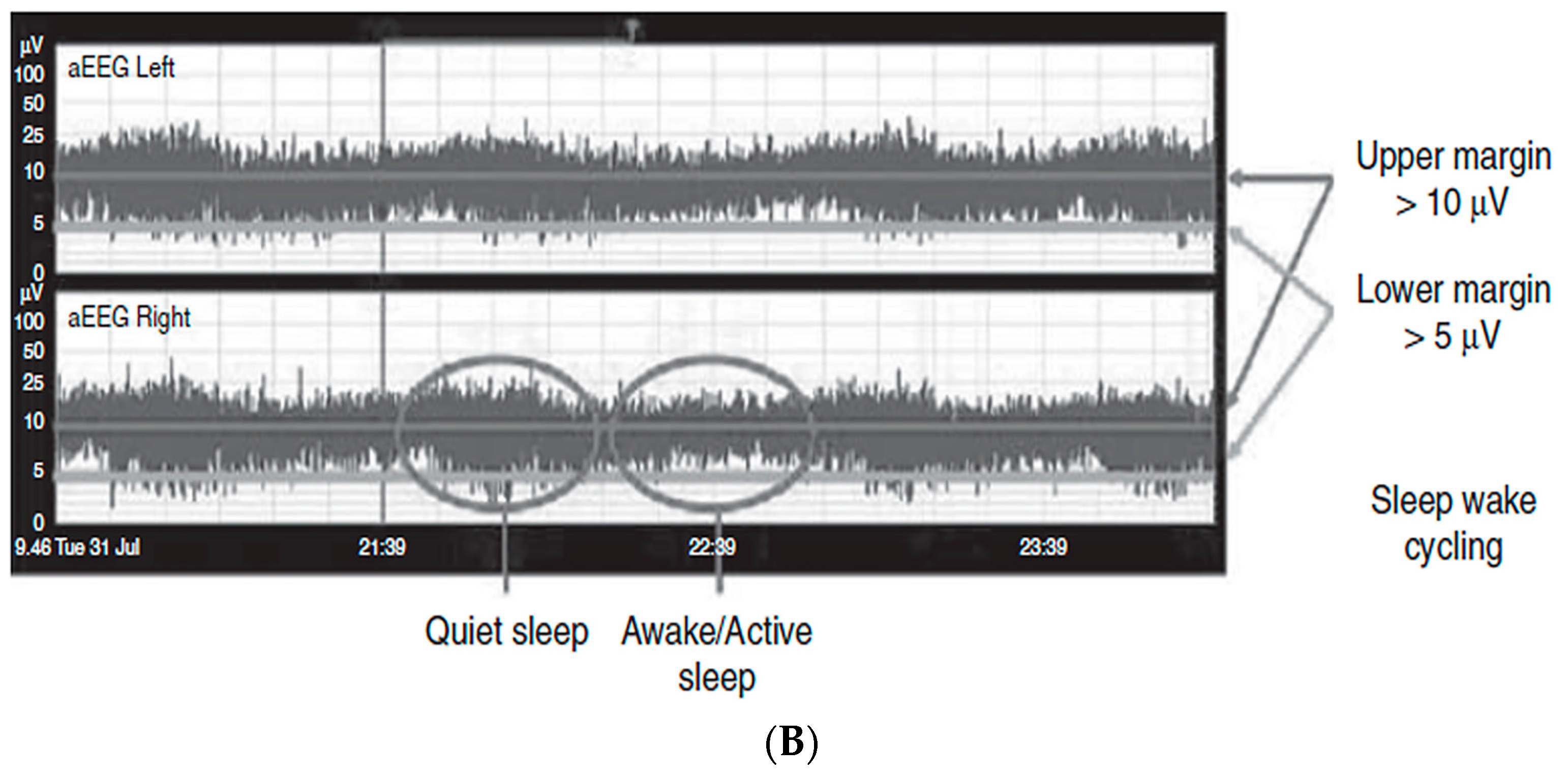
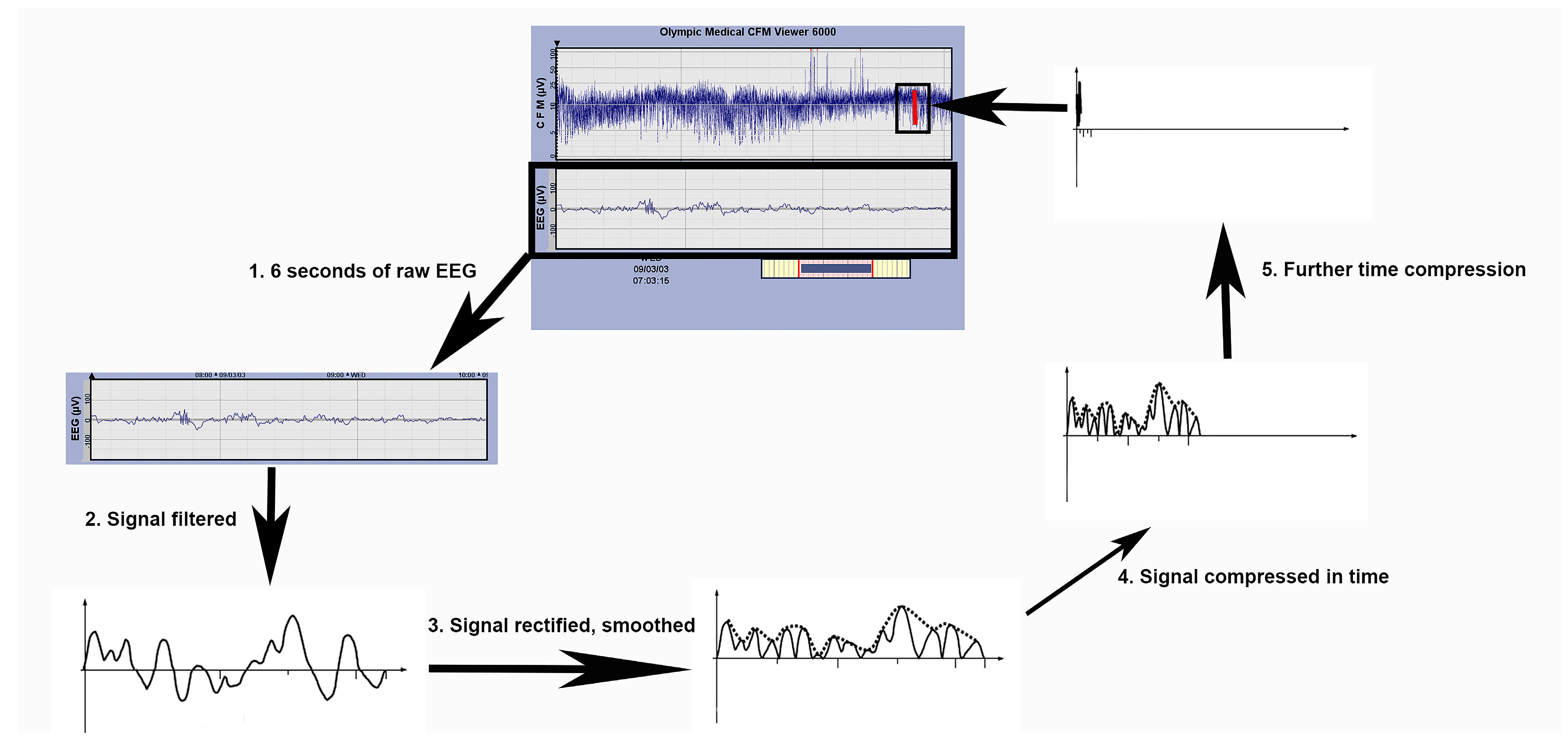
3.5. Amplitude Integrated EEG (aEEG)
4. Alterations of Sleep in the NICU
4.1. Chronic Lung Disease (CLD)
4.2. Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy
4.3. Congenital Heart Disease
4.4. Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)
4.5. Inborn Errors of Metabolism
5. Protecting Infant Sleep
5.1. Kangaroo Care (KC)
5.2. Infant Massage
5.3. Light Modification
5.4. Sound Modification
6. Future Directions for Research
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spielman, R.M.; Dumper, K.; Jenkins, W.; Lacombe, A.; Lovett, M.; Perlmutter, M. States of Consciousness. In Psychology; Openstax: Houston, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 111–148. [Google Scholar]
- Chaput, J.P.; Gray, C.E.; Poitras, V.J.; Carson, V.; Gruber, R.; Olds, T.; Weiss, S.K.; Connor Gorber, S.; Kho, M.E.; Sampson, M.; et al. Systematic review of the relationships between sleep duration and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41 (Suppl. 3), S266–S282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hoogen, A.; Teunis, C.J.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Pillen, S.; Benders, M.; Dudink, J. How to improve sleep in a neonatal intensive care unit: A systematic review. Early Hum. Dev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmiran, M. The importance of fetal/neonatal REM sleep. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1986, 21, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagioli, I.; Salzarulo, P. Temporal organization of sleep cycles in infants over 24-hour periods. Rev. Electroencephalogr. Neurophysiol. Clin. 1982, 12, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirano, P.; Fagioli, I.; Bes, F.; Salzarulo, P. The role of slow-wave sleep on the duration of quiet sleep in infants. J. Sleep Res. 1993, 2, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, T.F.; Keener, M. Developmental course of nighttime sleep-wake patterns in full-term and premature infants during the first year of life. I. Sleep 1985, 8, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficca, G.; Fagioli, I.; Salzarulo, P. Sleep organization in the first year of life: developmental trends in the quiet sleep-paradoxical sleep cycle. J. Sleep Res. 2000, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglowstein, I.; Latal Hajnal, B.; Molinari, L.; Largo, R.H.; Jenni, O.G. Sleep behaviour in preterm children from birth to age 10 years: A longitudinal study. Acta Paediatr. 2006, 95, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiselt, M.; Curzi-Dascalova, L.; Clairambault, J.; Kauffmann, F.; Médigue, C.; Peirano, P. Heart-rate variability in low-risk prematurely born infants reaching normal term: A comparison with full-term newborns. Early Hum. Dev. 1993, 32, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.L.; Barfield, C.; Davis, P.G.; Horne, R.S. Randomized controlled trial to compare sleep and wake in preterm infants less than 32 weeks of gestation receiving two different modes of non-invasive respiratory support. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werth, J.; Atallah, L.; Andriessen, P.; Long, X.; Zwartkruis-Pelgrim, E.; Aarts, R.M. Unobtrusive sleep state measurements in preterm infants—A review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 32, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rurak, D. Fetal Sleep and Spontaneous Behavior In Utero: Animal. In Prenatal and Postnatal Determinants of Development; Humana Press: Melbourne, Australia, 2016; pp. 89–146. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, J.I.; Visser, G.H.; Prechtl, H.F. Fetal behaviour in early pregnancy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1986, 21, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhuis, J.G.; Prechtl, H.F.; Martin, C.B., Jr.; Bots, R.S. Are there behavioural states in the human fetus? Early Hum. Dev. 1982, 6, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, T.F.; Keener, M.A.; Kraemer, H. Sleep-wake state organization, neonatal assessment and development in premature infants during the first year of life. II. Sleep 1985, 8, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardura, J.; Andrés, J.; Aldana, J.; Revilla, M.A. Development of sleep-wakefulness rhythm in premature babies. Acta Paediatr. 1995, 84, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmiran, M.; Maas, Y.G.; Ariagno, R.L. Development of fetal and neonatal sleep and circadian rhythms. Sleep Med. Rev. 2003, 7, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curzi-Dascalova, L. Development of the sleep and autonomic nervous system control in premature and full-term newborn infants. Arch. Pediatr. 1995, 2, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holditch-Davis, D.; Scher, M.; Schwartz, T.; Hudson-Barr, D. Sleeping and waking state development in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2004, 80, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafna, E.; Halevi, M.; Ben Or, D.; Tarasiuk, A.; Zigel, Y. Estimation of Macro Sleep Stages from whole Night Audio Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 38th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arditi-Babchuk, H.; Feldman, R.; Eidelman, A.I. Rapid eye movement (REM) in premature neonates and developmental outcome at 6 months. Infant Behav. Dev. 2009, 32, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.; Hassan, F.; Plegue, M.A.; Sokoloff, M.D.; Kushwaha, J.S.; Chervin, R.D.; Barks, J.D.; Shellhaas, R.A. Impact of hands-on care on infant sleep in the neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyer, C.; Huber, R.; Fontijn, J.; Bucher, H.U.; Nicolai, H.; Werner, H.; Molinari, L.; Latal, B.; Jenni, O.G. Very preterm infants show earlier emergence of 24-hour sleep-wake rhythms compared to term infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Paiva, T.; Hsu, J.-F.; Kuo, M.-C.; Guilleminault, C. Sleep and breathing in premature infants at 6 months post-natal age. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dib, M.; Massaro, A.N.; Glass, P.; Aly, H. Sleep wake cycling and neurodevelopmental outcome in very low birth weight infants. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geva, R.; Yaron, H.; Kuint, J. Neonatal sleep predicts attention orienting and distractibility. J. Atten. Disord. 2016, 20, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanski, M.; Schulze, K.; Bateman, D.; Kairam, R.; Pedley, T.A.; Masterson, J.; James, L.S. A scoring system for states of sleep and wakefulness in term and preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 1984, 18, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tracey, K.J. Reflex control of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, K.; Müller-Putz, G.R.; Urlesberger, B.; Müller, W.; Pfurtscheller, G. Relationship between slow-wave EEG bursts and heart rate changes in preterm infants. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 385, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werth, J.; Long, X.; Zwartkruis-Pelgrim, E.; Niemarkt, H.; Chen, W.; Aarts, R.M.; Andriessen, P. Unobtrusive assessment of neonatal sleep state based on heart rate variability retrieved from electrocardiography used for regular patient monitoring. Early Hum. Dev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, K.; De Goederen, R.; Pijpers, A.; Allegaert, K. Sleep related breathing disorders and indications for polysomnography in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butkov, N.; Keenan, S.A. An Overview of Polysomnographic Technique. In Sleep Disorders Medicine: Basic Science, Technical Considerations and Clinical Aspects; Chokroverty, S., Ed.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Dereymaeker, A.; Pillay, K.; Vervisch, J.; De Vos, M.; Van Huffel, S.; Jansen, K.; Naulaers, G. Review of sleep-EEG in preterm and term neonates. Early Hum. Dev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weerd, A.W.; Van den Bossche, R.A. The development of sleep during the first months of life. Sleep Med. Rev. 2003, 7, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, M.S.; Johnson, M.W.; Holditch-Davis, D. Cyclicity of neonatal sleep behaviors at 25 to 30 weeks’ postconceptional age. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Globus, G.G. Quantification of the REM sleep cycle as a rhythm. Psychophysiology 1970, 7, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellstrom-Westas, L.; Rosén, I.; De Vries, L.S.; Greisen, G. Amplitude-integrated EEG Classification and Intepretation in Preterm and Term Infants. Neoreviews 2006, 7, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerre, I.; Hellström-Westas, L.; Rosén, I.; Svenningsen, N. Monitoring of cerebral function after severe asphyxia in infancy. Arch. Dis. Child. 1983, 58, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viniker, D.A.; Maynard, D.E.; Scott, D.F. Cerebral function monitor studies in neonates. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 1984, 15, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, J.W.; Frey, L.C.; Hopp, J.L.; Korb, P.; Koubeissi, M.Z.; Lievens, W.; Pestana-Knight, E.M.; St. Louis, E.K. Electroencephalography (EEG): An Introductory Text and Atlas of Normal and Abnormal Findings in Adults, Children, and Infants; American Epilepsy Society: Chicago, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.D.; Mathur, A.M. Using amplitude-integrated EEG in neonatal intensive care. J. Perinatol. 2010, 30 (Suppl. 1), S73–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornberg, E.; Thiringer, K. Normal pattern of the cerebral function monitor trace in term and preterm neonates. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1990, 79, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugelman, A.; Reichman, B.; Chistyakov, I.; Boyko, V.; Levitski, O.; Lerner-Geva, L.; Riskin, A.; Bader, D.; Israel Neonatal Network. Postdischarge infant mortality among very low birth weight infants: A population-based study. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e788–e794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piecuch, R.E.; Leonard, C.H.; Clyman, R.I.; Cooper, B.A. Risk factors associated with infant death among very low birth weight infants after discharge from an intensive care nursery. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 1998, 19, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer-Mileur, L.J.; Nielson, D.W.; Pfeffer, K.D.; Witte, M.K.; Chapman, D.L. Eliminating sleep-associated hypoxemia improves growth in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 1996, 98, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McGrath-Morrow, S.A.; Ryan, T.; McGinley, B.M.; Okelo, S.O.; Sterni, L.M.; Collaco, J.M. Polysomnography in preterm infants and children with chronic lung disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2012, 47, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, J.M.; Fontana, N.; Pugh, J.E.; Mcgregor, C.; Yielder, P.; James, A.G.; Keyzers, M.; Hahn, C.; McNamara, P. Automated Sleep-Wake Detection in Neonates from Cerebral Function Monitor Signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE 27th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, New York, NY, USA, 27–29 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Scher, M.S.; Steppe, D.A.; Beggarly, M.E.; Salerno, D.G.; Banks, D.L. Neonatal EEG-sleep disruption mimicking hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy after intrapartum asphyxia. Sleep Med. 2002, 3, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoresen, M.; Hellström-Westas, L.; Liu, X.; De Vries, L.S. Effect of hypothermia on amplitude-integrated electroencephalogram in infants with asphyxia. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e131–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Horst, H.J.; Mud, M.; Roofthooft, M.T.; Bos, A.F. Amplitude integrated electroencephalographic activity in infants with congenital heart disease before surgery. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulkey, S.B.; Yap, V.L.; Bai, S.; Ramakrishnaiah, R.H.; Glasier, C.M.; Bornemeier, R.A.; Schmitz, M.L.; Bhutta, A.T. Amplitude-integrated EEG in newborns with critical congenital heart disease predicts preoperative brain magnetic resonance imaging findings. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 52, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.; Torrioli, M.G.; Casella, G.; Tempesta, E.; Fundarò, C. Sleep in babies born to chronically heroin addicted mothers. A follow up study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1988, 21, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.M.; Jeffery, H.E. Sleep deprivation, disorganization and fragmentation during opiate withdrawal in newborns. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2002, 38, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinges, D.F.; Davis, M.M.; Glass, P. Fetal exposure to narcotics: Neonatal sleep as a measure of nervous system disturbance. Science 1980, 209, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olischar, M.; Shany, E.; Aygün, C.; Azzopardi, D.; Hunt, R.W.; Toet, M.C.; Hamosh, A.; De Vries, L.S.; Hellström-Westas, L.; Theda, C. Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography in newborns with inborn errors of metabolism. Neonatology 2012, 102, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, R.; Weller, A.; Sirota, L.; Eidelman, A.I. Skin-to-Skin contact (Kangaroo care) promotes self-regulation in premature infants: Sleep-wake cyclicity, arousal modulation, and sustained exploration. Dev. Psychol. 2002, 38, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baley, J. Skin-to-skin care for term and preterm infants in the neonatal ICU. Pediatrics 2015, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juneau, A.L.; Aita, M.; Heon, M. Review and critical analysis of massage studies for term and preterm infants. Neonatal Netw. 2015, 34, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standley, J. Music therapy research in the NICU: An updated meta-analysis. Neonatal Netw. 2012, 31, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heijden, M.J.; Araghi, S.O.; Jeekel, J.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Hunink, M.G.M.; Van Dijk, M. Do hospitalized premature infants benefit from music interventions? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurinczuk, J.J.; White-Koning, M.; Badawi, N. Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucci, R.C. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Am. J. Perinatol. 2000, 17, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzopardi, D.V.; Strohm, B.; Edwards, A.D.; Dyet, L.; Halliday, H.L.; Juszczak, E.; Kapellou, O.; Levene, M.; Marlow, N.; Porter, E.; et al. Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Wyatt, J.S.; Azzopardi, D.; Ballard, R.; Edwards, A.D.; Ferriero, D.M.; Polin, R.A.; Robertson, C.M.; Thoresen, M.; Whitelaw, A.; et al. Selective head cooling with mild systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy: Multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 2005, 365, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankaran, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Tyson, J.E.; McDonald, S.A.; Donovan, E.F.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Poole, W.K.; Wright, L.L.; Higgins, R.D.; et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osredkar, D.; Toet, M.C.; Van Rooij, L.G.; Van Huffelen, A.C.; Groenendaal, F.; De Vries, L.S. Sleep-wake cycling on amplitude-integrated electroencephalography in term newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschuren, O.; Gorter, J.W.; Pritchard-Wiart, L. Sleep: An underemphasized aspect of health and development in neurorehabilitation. Early Hum. Dev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotchikova, I.; Connolly, S.; Ryan, C.A.; Murray, D.M.; Temko, A.; Greene, B.R.; Boylan, G.B. EEG in the healthy term newborn within 12 hours of birth. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotchikova, I.; Stevenson, N.J.; Livingstone, V.; Ryan, C.A.; Boylan, G.B. Sleep-wake cycle of the healthy term newborn infant in the immediate postnatal period. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocherlakota, P. Neonatal abstinence syndrome. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e547–e561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeskind, P.S.; Stephens, L.E. Maternal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use during pregnancy and newborn neurobehavior. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, S.W.; Schumacher, R.E.; Benneyworth, B.D.; Krans, E.E.; McAllister, J.M.; Davis, M.M. Neonatal abstinence syndrome and associated health care expenditures: United States, 2000–2009. JAMA 2012, 307, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Theophilopoulos, D.; Seng, S.K.; Calhoun, D.A. Pharmacologic management of neonatal abstinence syndrome in a community hospital. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 56, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommers, D.R.; Joshi, R.; Van Pul, C.; Atallah, L.; Feijs, L.; Oei, G.; Bambang Oetomo, S.; Andriessen, P. Features of heart rate variability capture regulatory changes during kangaroo care in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2017, 182, 92–98.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, R.; Eidelman, A.I. Skin-to-skin contact (Kangaroo Care) accelerates autonomic and neurobehavioural maturation in preterm infants. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2003, 45, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, T.; Diego, M.; Hernandez-Reif, M. Preterm infant massage therapy research: A review. Infant Behav. Dev. 2010, 33, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, A.; Ohlsson, A.; Lacy, J.B.; Horsley, A. Massage for promoting growth and development of preterm and/or low birth-weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morag, I.; Ohlsson, A. Cycled light in the intensive care unit for preterm and low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, P.; Zores, C.; Langlet, C.; Escande, B.; Astruc, D.; Dufour, A. Moderate acoustic changes can disrupt the sleep of very preterm infants in their incubators. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G. NICU noise and the preterm infant. Neonatal Netw. 2009, 28, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curzi-Dascalova, L.; Figueroa, J.M.; Eiselt, M.; Christova, E.; Virassamy, A.; D’Allest, A.M.; Guimarâes, H.; Gaultier, C.; Dehan, M. Sleep state organization in premature infants of less than 35 weeks’ gestational age. Pediatr. Res. 1993, 34, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetters, L.; Huang, H.H. Motor development and sleep, play, and feeding positions in very-low-birthweight infants with and without white matter disease. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudink, J.; Van den Hoogen, A. Assessing, improving and utilizing sleep in high risk neonates. Early Hum. Dev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.L.; Haley, S.; Slater, H.; Moyer-Mileur, L.J. Heart rate variability during caregiving and sleep after massage therapy in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2013, 89, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Eyes | Body Movements | Facial Movements | Respirations | EEG Findings | aEEG Findings a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quiet Sleep | Closed | Relatively no body movement | Few rhythmic mouth movements | Regular | Trace alternant (medium to high voltage) 30–200 µV | Wide bandwidth |
| No eye movements | Relaxed Sighs | Slow | ||||
| Active Sleep (AS) | Closed | Slow, small twitches | Frowns and smiles | Irregular | Continuous (low voltage) 30–70 µV | Narrow bandwidth |
| Rapid eye movements | Low tone between startles | Burst of sucking Some vocalizations | ||||
| Transitional Sleep | Periods of opening and closing | Slow startles | Grimace, intermittent sucking | Regular | Continuous (high voltage) 100–200 µV | Variable |
| Slow eye movements | Increase in vocalizations | |||||
| Awake | Open | Rapid startles | Frowns, smiles, grimace, sucks, crying | Irregular | Continuous (medium voltage) 70–100 µV | Narrow bandwidth |
| Rapid or slow eye movements | Gross motor movements | Vocalization |
| Alteration/Protective | Overview | How Sleep Is Affected | Comments | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy | Alteration | Brief disruption of blood flow to the infant brain can have a profound effect on neurodevelopment. | Delayed SWC-progressive with worse injury | Infants undergoing cooling who developed SWC by 36 h of age had better outcomes | [48,49,50] |
| Decreased AS | |||||
| Congenital Heart Disease | Alteration | Many anatomic cardiac defects produce hypoxemia | Delayed SWC for age | May be accompanied by HIE, prolonged hospitalization and surgery, which also complicate sleep | [51,52] |
| Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS) | Alteration | Prenatal illicit or prescription drug exposure is becoming an increasing concern | SSRI: More AS and increased motor activity during AS | [53,54,55] | |
| Opiate: more AS, low threshold for arousal, fragmented sleep | |||||
| Inborn Errors of Metabolism | Alteration | A family of disorders caused by enzyme deficiencies in the metabolic pathways | Spectrum of pathology from no cycling to normal cycling depending on enzyme deficiency | Encephalopathy itself alters the aEEG | [56] |
| Chronic Lung Disease | Alteration | Babies with prolonged oxygen needs | Lower saturations while asleep | Infants on oxygen should be evaluated while asleep before discontinuation | [32,46,47] |
| Increased respiratory events and arousals during sleep | |||||
| Kangaroo Care | Protective | Placing an infant skin to skin with a parent provides warmth and familiar stimulation | More mature SWC | [57,58] | |
| More time asleep Fewer arousals | |||||
| Infant Massage | Protective | Various techniques: firm pressure, gentle stroking, containment | Increased sleep state and decreased awake state | [3,59] | |
| Light Modification | Protective | Intensive care unit is inherently bright | Cycled light long term associated with differences in day night activity | [3,24] | |
| Options are to provide day/light patterns for light or to reduce light | Longer night time sleeping | ||||
| Sound Modification | Protective | Intensive care unit is inherently noisy | Episodes of noise can cause arousals | Live music, either mother singing or instruments in the unit, associated with best outcomes | [60,61] |
| Can decrease noxious noise or increase pleasant noise | music improved infant sleep |
| Age | Questions Answered | Questions Remaining |
|---|---|---|
| Fetus | Fetuses do appear to have cyclical behavioral patterns [13,14,15,16] | Does maternal activity significantly impact fetal sleep wake behaviors? Do maternal and fetal conditions/pathology affect fetal sleep wake behaviors? Do fetal patterns by gestational age match their premature counterparts? |
| Preterm Infant | Preterm infants do have predictable sleep development [7,17,20,24,26,36,82] REM sleep is particularly important in development [4,22] Routine care impacts sleep in the NICU [11,23,25,83] EEG and HRV can be used to follow infant sleep progression and estimate infant sleep stage [12,30,34,42,75] Disease of premature infants do impact sleep [32,46,47] Interventions in the NICU can help improve infant sleep [3,75,84,85] | Do preterm infants with poor sleep have worse outcomes than preterm infants with better sleep? What effect do interventions in the NICU have on long term development? Can monitoring of preterm sleep performed in a manner that is noninvasive and unobtrusive over time? Can monitoring of preterm sleep direct goals of care? Do diseases of prematurity that dysregulate sleep impact long-term outcomes? |
| Term Infant | Full term infants have predictable sleep development [7,16,18] REM sleep is particularly important in development [4,6] Sleep dysregulation can impact school aged outcomes [2] | Do sleep interventions in the home affect long-term outcomes? Do different methods of infant “sleep training” effect infant sleep and long term outcomes? What are the long-term effects of sleep dysregulation in infants with HIE and NAS? |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbeau, D.Y.; Weiss, M.D. Sleep Disturbances in Newborns. Children 2017, 4, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/children4100090
Barbeau DY, Weiss MD. Sleep Disturbances in Newborns. Children. 2017; 4(10):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/children4100090
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbeau, Daphna Yasova, and Michael D. Weiss. 2017. "Sleep Disturbances in Newborns" Children 4, no. 10: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/children4100090
APA StyleBarbeau, D. Y., & Weiss, M. D. (2017). Sleep Disturbances in Newborns. Children, 4(10), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/children4100090




