Reference Values for Respiratory Impedance in Bulgarian Children Aged 2–8 Years Using the Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
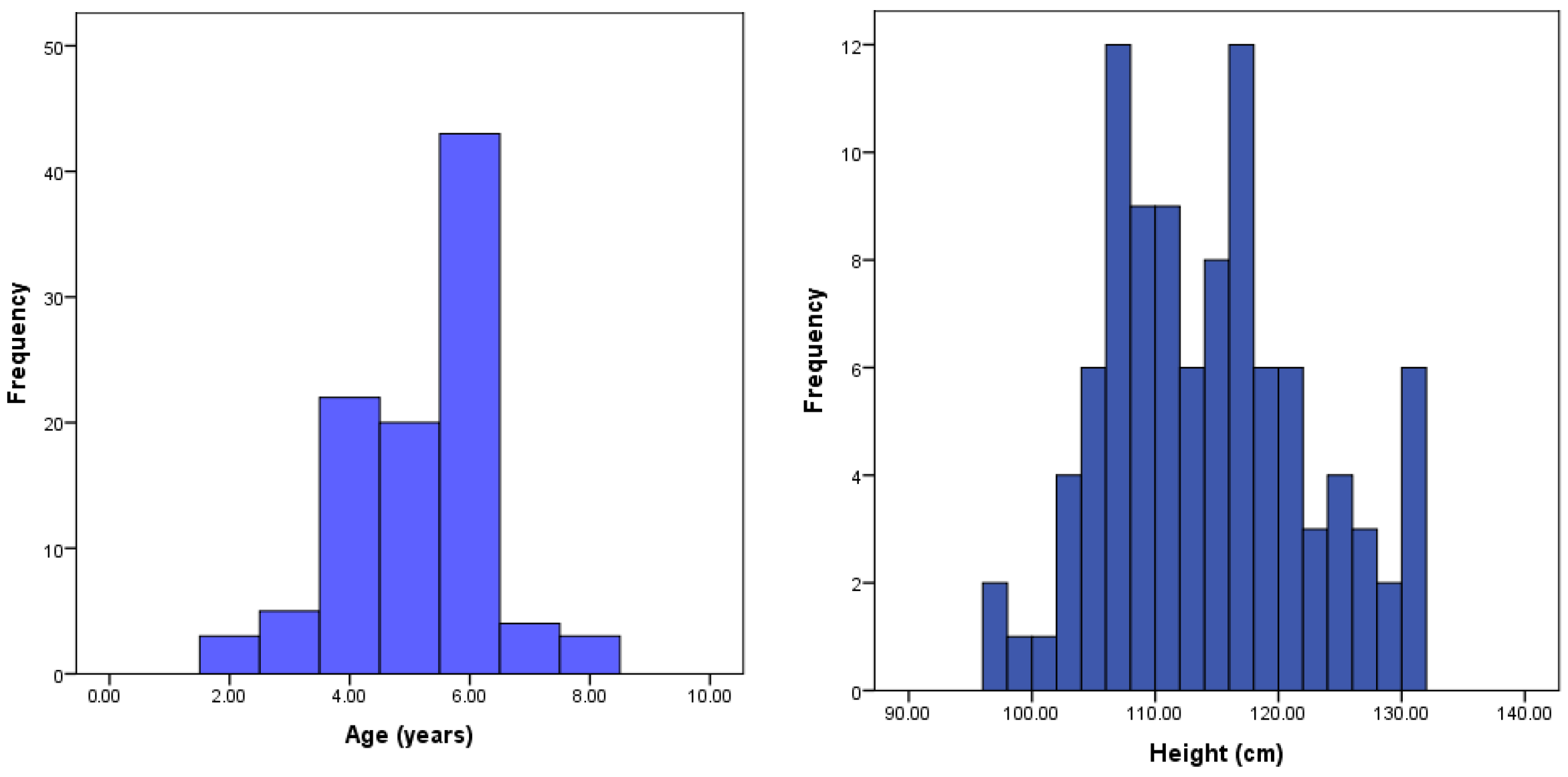
2.1. Participants
2.2. FOT Methodology
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FOT | Forced oscillation technique |
| Rrs | Respiratory resistance |
| Xrs | Respiratory reactance |
| R5–19 | Difference in respiratory resistance between 5 Hz and 19 Hz |
| Rtot 5 | Mean resistance of the whole breath at 5 Hz |
| Xtot 5 | Mean reactance of the whole breath at 5 Hz |
References
- Oostveen, E.; MacLeod, D.; Lorino, H.; Farré, R.; Hantos, Z.; Desager, K.; Marchal, F. The forced oscillation technique in clinical practice: Methodology, recommendations and future developments. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenova, P.; Mandadzhieva, S.; Marinov, B. Clinical applications of forced oscillation technique (FOT) for diagnosis and management of obstructive lung diseases in children. Folia Medica 2024, 66, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockley, J.; Cooper, B.; Stockley, R.; Sapey, E. Small airways disease: Time for a revisit? Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.O.; Faria, A.C.D.; Lopes, A.J.; de Melo, P.L. Forced oscillation technique for early detection of the effects of smoking and COPD: Contribution of fractional-order modeling. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 3281–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, P.; Myers, S.; Chia, C.; Weber, H.C.; Young, S.; Williams, A.D.; Sohal, S.S. Clinical Application of Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT) in Early Detection of Airway Changes in Smokers. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrill, Z.L.; Roy, K.; Vessey, R.S.; Woodcock, A.A.; Singh, D. Non-invasive biomarkers and pulmonary function in smokers. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2008, 3, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schivinski, C.; De Assumpção, M.; De Figueiredo, F.; Wamosy, R.; Ferreira, L.; Ribeiro, J.D. Impulse oscillometry, spirometry, and passive smoking in healthy children and adolescents. Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2017, 23, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashier, B.; Salvi, S. Measuring lung function using sound waves: Role of the forced oscillation technique and impulse oscillometry system. Breathe 2015, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.J.; Eichler, R.; Vogel, J.; Arnold, J. Technische Adaption der Impuls-Oszillometrie an spezielle Untersuchungsbedingungen [Technical adaptation of impulse oscillometry to special research conditions]. Pneumologie 1997, 51 (Suppl. S2), 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, U.; Joshi, J.M. Impulse Oscillometry. Adv. Respir. Med. 2019, 87, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, W.; Du, J.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; et al. Clinical application of oscillometry in respiratory diseases: An impulse oscillometry registry. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00080–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostorz-Nosal, S.; Jastrzębski, D.; Błach, A.; Skoczyński, S. Window of opportunity for respiratory oscillometry: A review of recent research. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2023, 316, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dencker, M.; Malmberg, L.P.; Valind, S.; Thorsson, O.; Karlsson, M.K.; Pelkonen, A.; Pohjanpalo, A.; Haahtela, T.; Turpeinen, M.; Wollmer, P. Reference values for respiratory system impedance by using impulse oscillometry in children aged 2–11 years. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2006, 26, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amra, B.; Soltaninejad, F.; Golshan, M. Respiratory resistance by impulse oscillometry in healthy Iranian children aged 5–19 years. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 7, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frei, J.; Jutla, J.; Kramer, G.; Hatzakis, G.E.; Ducharme, F.M.; Davis, G.M. Impulse oscillometry: Reference values in children 100 to 150 cm in height and 3 to 10 years of age. Chest 2005, 128, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowowiejska, B.; Tomalak, W.; Radlinski, J.; Siergiejko, G.; Latawiec, W.; Kaczmarski, M. Transient reference values for impulse oscillometry for children aged 3–18 years. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2008, 43, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calogero, C.; Simpson, S.J.; Lombardi, E.; Parri, N.; Cuomo, B.; Palumbo, M.; de Martino, M.; Shackleton, C.; Verheggen, M.; Gavidia, T.; et al. Respiratory impedance and bronchodilator responsiveness in healthy children aged 2–13 years. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogero, C.; Parri, N.; Baccini, A.; Cuomo, B.; Palumbo, M.; Novembre, E.; Morello, P.; Azzari, C.; de Martino, M.; Sly, P.; et al. Respiratory impedance and bronchodilator response in healthy Italian preschool children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, G.L.; Sly, P.D.; Fukushima, T.; Kusel, M.M.; Franklin, P.J.; Horak, F., Jr.; Patterson, H.; Gangell, C.; Stick, S.M. Respiratory function in healthy young children using forced oscillations. Thorax 2007, 62, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducharme, F.M.; Smyrnova, A.; Lawson, C.C.; Miles, L.M. Reference values for respiratory sinusoidal oscillometry in children aged 3 to 17 years. Pediatr. Pulmonol 2022, 57, 2092–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.G.; Bates, J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; De Melo, P.L.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farre, R.; Hall, G.; Ioan, I.; Irvin, C.G.; et al. Technical standards for respiratory oscillometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, D.A.; Irvin, C.G.; Lundblad, L.; Moriya, H.T.; Lang, S.; Allen, J.; Viola, T.; Lynn, M.; Bates, J.H.T. Oscillation mechanics of the human lung periphery in asthma. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, S.; Popler, J.; Lesnick, B.; Eid, N. Impulse oscillometry: Interpretation and practical applications. Chest 2014, 146, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmberg, L.P.; Pelkonen, A.; Poussa, T.; Pohianpalo, A.; Haahtela, T.; Turpeinen, M. Determinants of respiratory system input impedance and bronchodilator response in healthy Finnish preschool children. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2002, 22, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Shin, Y.H.; Jee, H.M.; Wee, Y.S.; Chang, S.J.; Sim, J.H.; Yum, H.Y.; Han, M.Y. Reference values for respiratory system impedance using impulse oscillometry in healthy preschool children. Korean J. Pediatr. 2011, 54, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapletal, A.; Paul, T.; Samanek, M. Lung function in children and adolescents: Methods and reference values. Prog. Respir. Res. 1976, 9, 1–210. [Google Scholar]
- Eigen, H.; Bieler, H.; Grant, D.; Christoph, K.; Terrill, D.; Heilman, D.K. Spirometric pulmonary function in healthy preschool children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydon, N.; Davis, S.D.; Lombardi, E.; Allen, J.L.; Arets, H.G.M.; Aurora, P.; Bisgaard, H.; Davis, G.M.; Ducharme, F.M.; Eigen, H.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Pulmonary function testing in preschool children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 1304–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, G.L.; Reinero, C.R.; Bates, J.H.T.; King, G.G. Oscillometry: An alternative and complementary respiratory function test to spirometry. Thorax 2021, 76, 738–744. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.-L.; Gao, Y.; Guan, W.-J.; Du, J.; Chen, L.; Han, W.; Liu, J.-M.; Lu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, B.-R.; et al. Reference values of respiratory impedance with impulse oscillometry in healthy Chinese adults. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 3680–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Han, A.; Fang, J. Determination of respiratory impedance of healthy adults by pulsating pulmonary function. Chin. J. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2002, 25, 636. [Google Scholar]
- Oostveen, E.; Boda, K.; van der Grinten, C.P.; James, A.L.; Young, S.; Nieland, H.; Hantos, Z. Respiratory impedance in healthy subjects: Baseline values and bronchodilator response. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y. Investigations of impulse oscillation technique and predictive equations in Macao healthy adults. Chin. J. Pract. Intern. Med. 2015, 35, 431–435. [Google Scholar]
- Kalchiem-Dekel, O.; Hines, S.E. Forty years of reference values for respiratory system impedance in adults: 1977-2017. Respir. Med. 2018, 136, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, X.; Wan, Y. Analysis of the normal Values of pulmonary function by impulse oscillometry in healthy adults in Lanzhou. Prog. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 40, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hellinckx, J.; De Boeck, K.; Bande-Knops, J.; van der Poel, M.; Demedts, M. Bronchodilator response in 3–6.5 years old healthy and stable asthmatic children. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, B.; Bisgaard, H. Specific airway resistance, interrupter resistance, and respiratory impedance in healthy children aged 2–7 years. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1998, 25, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Assumpção, M.S.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Martins, R.; Bobbio, T.G.; Schivinski, C.I. Reference Equations for Impulse Oscillometry System Parameters in Healthy Brazilian Children and Adolescents. Respir. Care. 2016, 61, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Banerjee, N.; Tiwari, R.R. Regression Equations of Respiratory Impedance Measured by Forced Oscillation Technique for Indian Children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
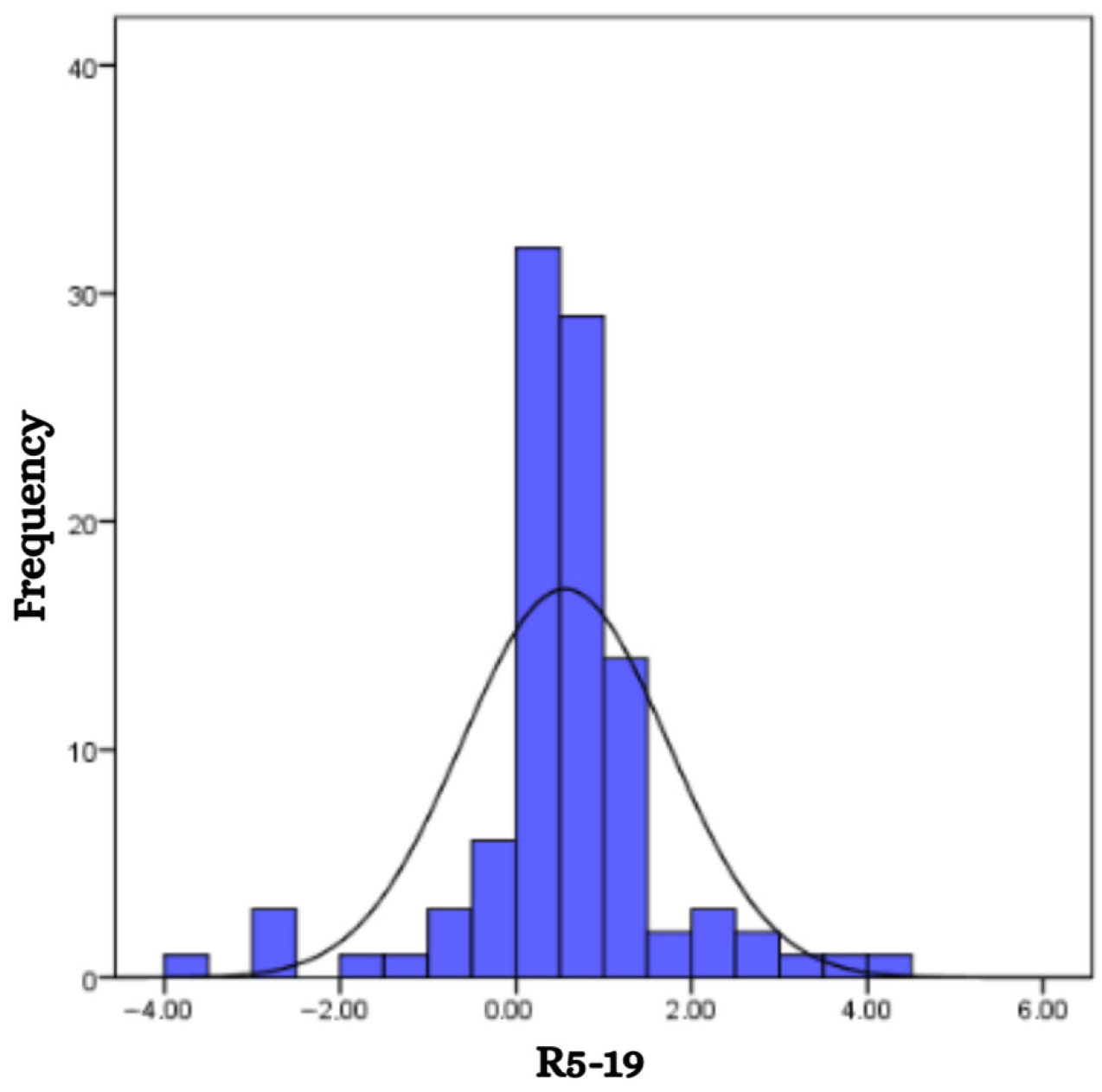
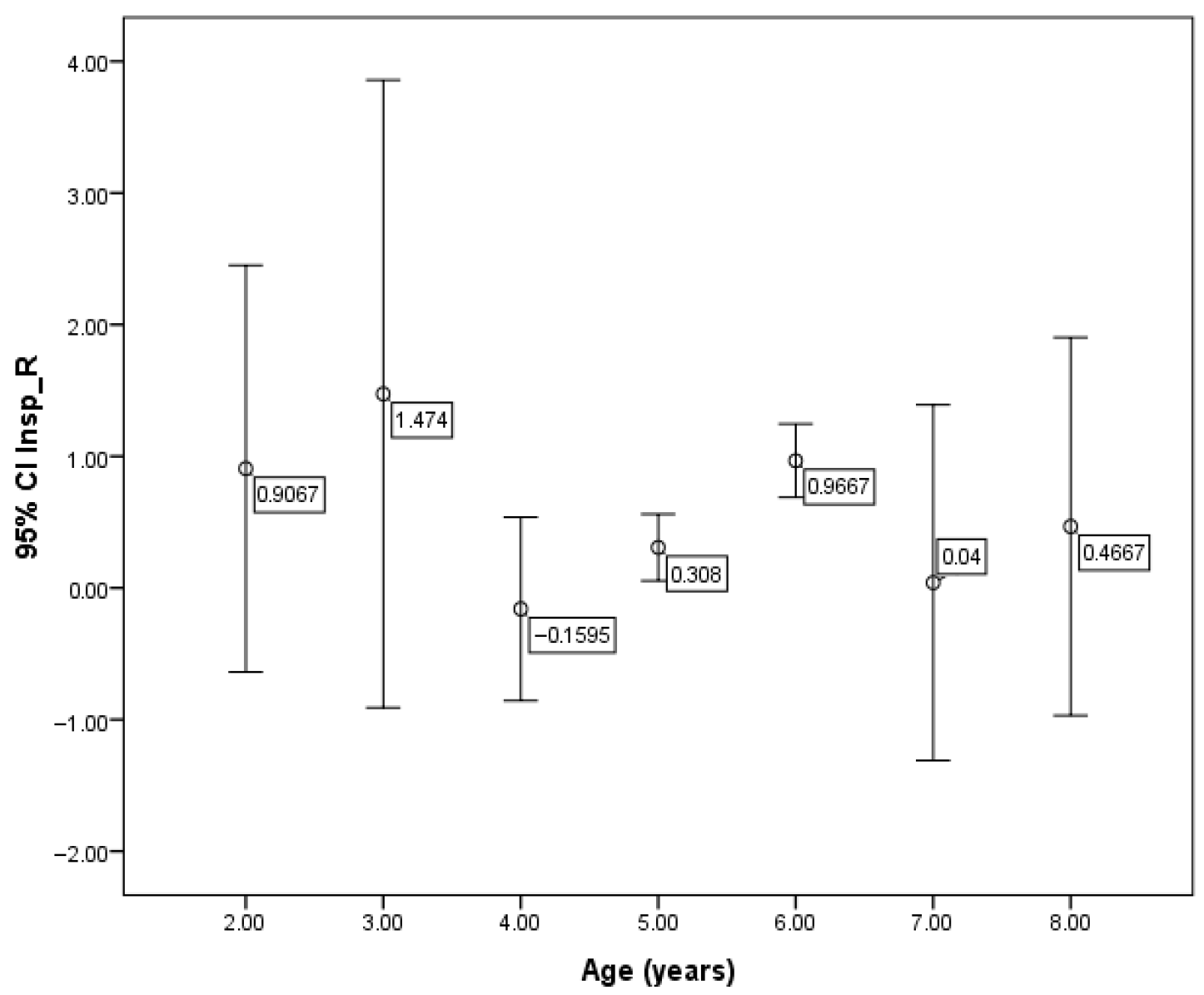
| Variable | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Boys | 56 (56.0%) |
| Girls | 44 (44.0%) | |
| Weight (kg) | Mean ± SD (range) | 20.4 ± 4.6 (12–37) |
| Height (cm) | Mean ± SD (range) | 113.89 ± 8.46 (91–136) |
| BMI | Mean ± SD (range) | 15.55 ± 2.11 (11.60–28.20) |
| Boys | Girls | Combined (Boys and Girls) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Height | Weight | Age | Height | Weight | Age | Height | Weight | |
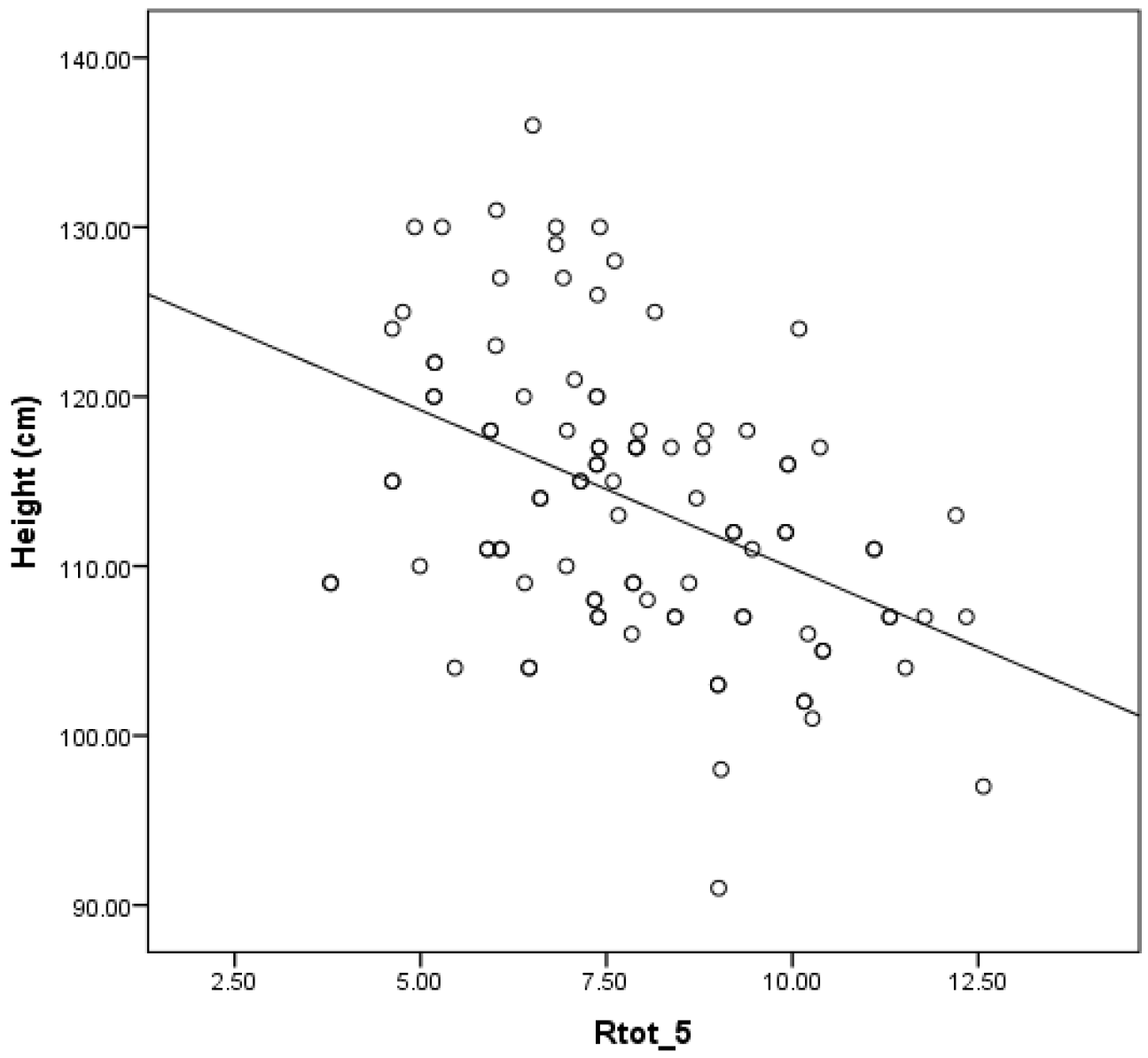
| R5 Hz | −0.227 p = 0.092 | −0.448 p = 0.001 | −0.121 p = 0.373 | −0.423 p = 0.004 | −0.452 p = 0.002 | −0.358 p = 0.017 | −0.308 p = 0.002 | −0.446 p < 0.001 | −0.221 p = 0.027 |
| R11 Hz | −0.205 p = 0.129 | −0.451 p < 0.001 | −0.217 p = 0.108 | −0.466 p = 0.001 | −0.442 p = 0.003 | −0.304 p = 0.045 | −0.318 p = 0.001 | −0.452 p < 0.001 | −0.251 p = 0.012 |
| R19 Hz | −0.203 p = 0.134 | −0.427 p = 0.001 | −0.272 p = 0.042 | −0.476 p = 0.001 | −0.459 p = 0.002 | −0.281 p = 0.065 | −0.318 p = 0.001 | −0.443 p < 0.001 | −0.270 p = 0.007 |
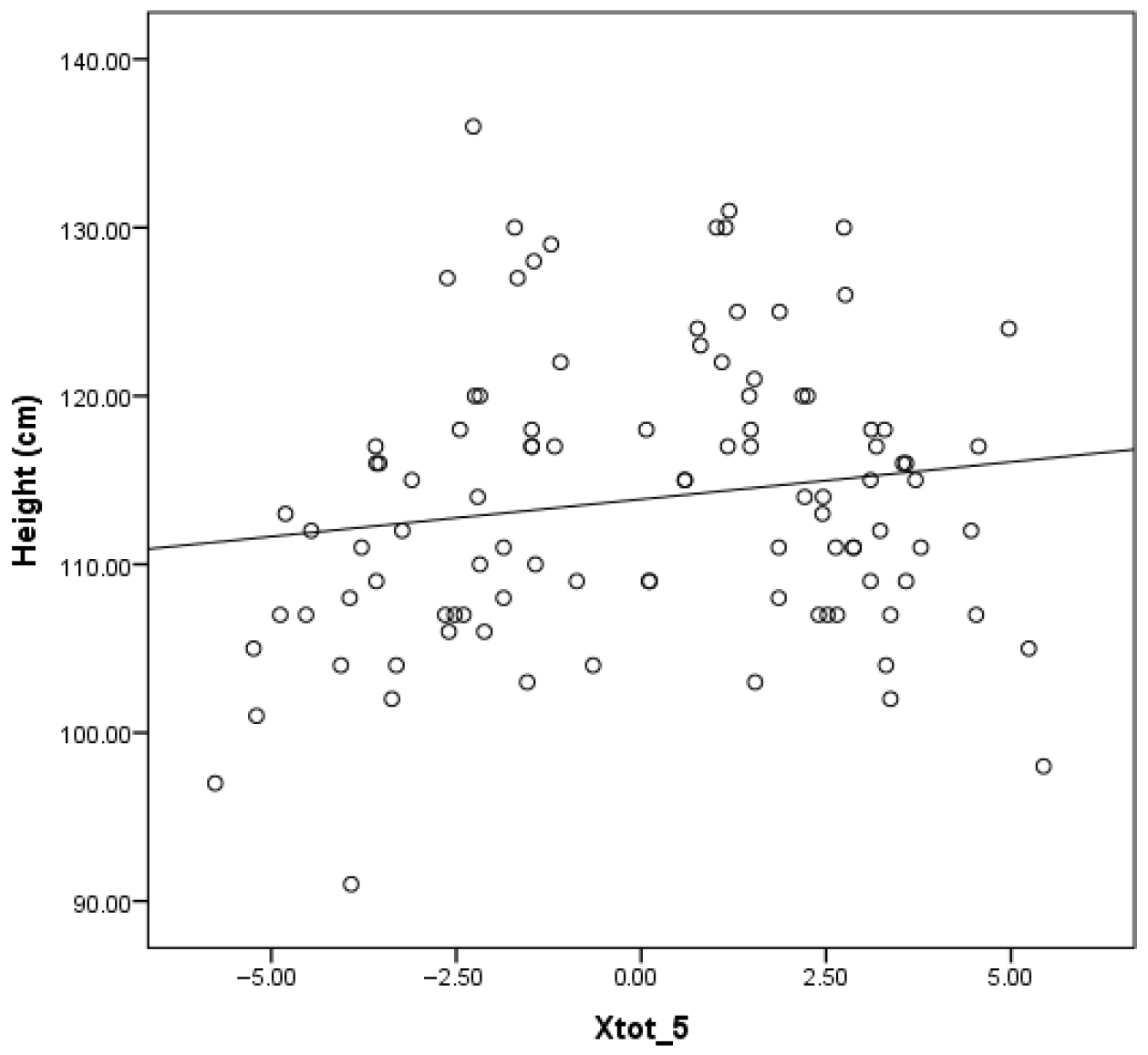
| Х5 Hz | 0.591 p < 0.001 | 0.117 p = 0.392 | 0.056 p = 0.683 | 0.473 p < 0.001 | 0.180 p = 0.242 | 0.111 p = 0.471 | 0.555 p < 0.001 | 0.153 p = 0.128 | 0.084 p = 0.405 |
| Х11 Hz | 0.634 p < 0.001 | 0.093 p = 0.497 | −0.025 p = 0.856 | 0.430 p = 0.002 | 0.207 p = 0.178 | 0.147 p = 0.340 | 0.557 p < 0.001 | 0.142 p = 0.160 | 0.053 p = 0.602 |
| Х19 Hz | 0.580 p < 0.001 | 0.223 p = 0.099 | 0.139 p = 0.307 | 0.523 p < 0.001 | 0.364 p = 0.015 | 0.290 p = 0.057 | 0.555 p < 0.001 | 0.269 p = 0.007 | 0.195 p = 0.052 |
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | T | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | Beta | ||||
| R5 Hz | Height | −0.173 | 0.034 | −0.722 | −5.021 | 0.000 |
| Weight | 0.154 | 0.064 | 0.349 | 2.427 | 0.017 | |
| R11 Hz | Height | −0.107 | 0.021 | −0.452 | −5.010 | 0.000 |
| R19 Hz | Height | −0.084 | 0.017 | −0.443 | −4.894 | 0.000 |
| Х5 Hz | Height | −0.087 | 0.036 | −0.252 | −2.441 | 0.016 |
| Х11 Hz | Height | −0.054 | 0.020 | −0.273 | −2.675 | 0.009 |
| Х19 Hz | Height | 0.441 | 0.069 | 0.543 | 6.394 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoimenova, P.; Mandadzhieva, S.; Marinov, B. Reference Values for Respiratory Impedance in Bulgarian Children Aged 2–8 Years Using the Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT). Children 2025, 12, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070957
Stoimenova P, Mandadzhieva S, Marinov B. Reference Values for Respiratory Impedance in Bulgarian Children Aged 2–8 Years Using the Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT). Children. 2025; 12(7):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070957
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoimenova, Plamena, Stoilka Mandadzhieva, and Blagoi Marinov. 2025. "Reference Values for Respiratory Impedance in Bulgarian Children Aged 2–8 Years Using the Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT)" Children 12, no. 7: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070957
APA StyleStoimenova, P., Mandadzhieva, S., & Marinov, B. (2025). Reference Values for Respiratory Impedance in Bulgarian Children Aged 2–8 Years Using the Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT). Children, 12(7), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070957







