A Scoring System Based on Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Blood Biochemistry Tests for Diagnosing Biliary Atresia in Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Imaging Data Collection and Postprocessing
2.3. Blood Biochemistry Test
2.4. Histopathological Evaluation
2.5. Development of the Scoring System
2.6. Assessment of the Scoring System
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surgical and Pathological Results
3.2. Comparison of Characteristics Between the BA and Non-BA Groups in the Training and Validation Cohorts
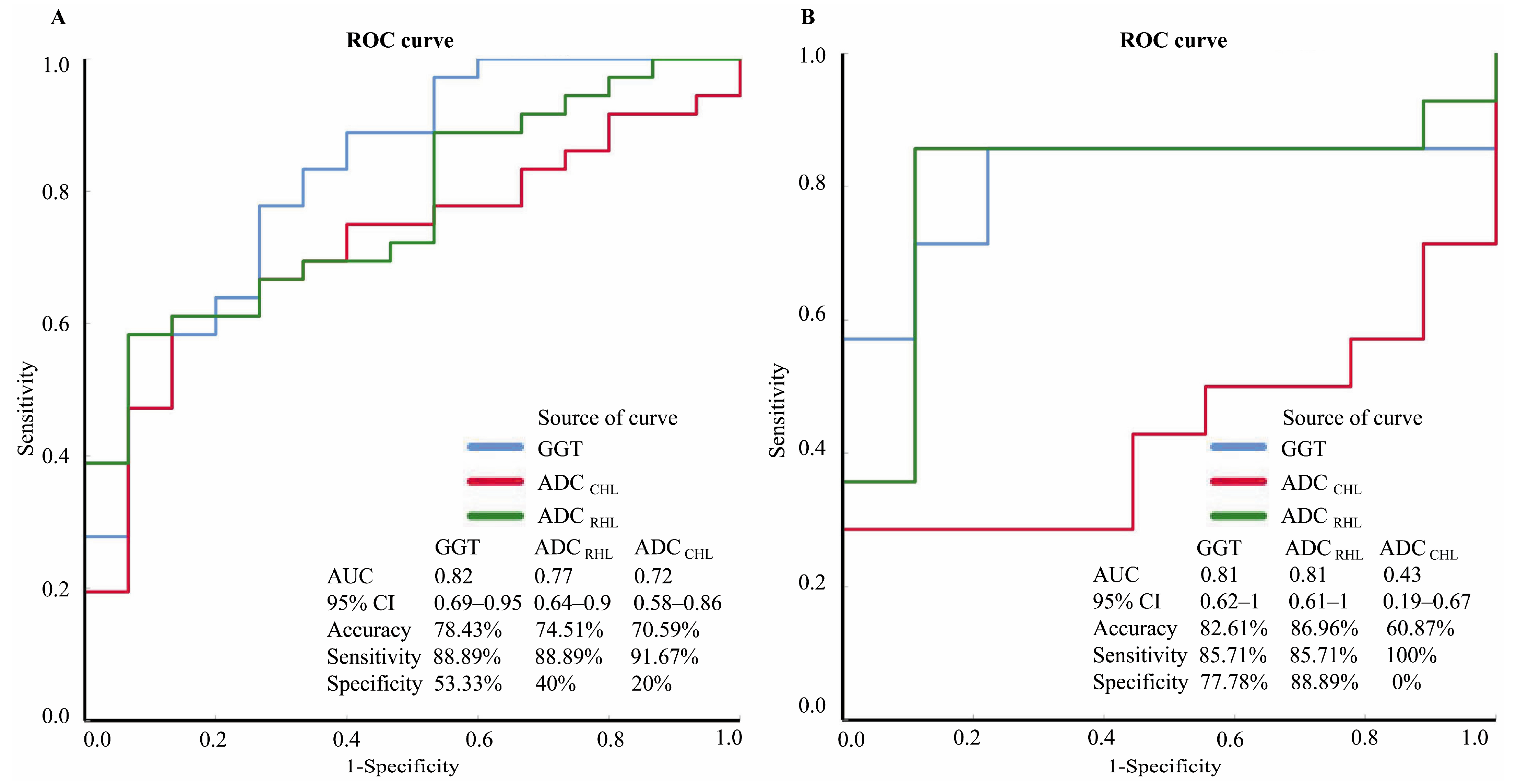
3.3. Diagnostic Performance of Individual Characteristics
3.4. Performance of the Scoring System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BA | Biliary atresia |
| IC | Intraoperative cholangiography |
| LB | Liver biopsy |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| DTI | Diffusion tensor imaging |
| GGT | Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase |
| MMP-7 | Matrix metalloproteinase-7 |
| FA | Fractional anisotropy |
| ADC | Apparent diffusion coefficient |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| RHL | Right hepatic lobe |
| LHL | Left hepatic lobe |
| CHL | Caudate hepatic lobe |
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| TB | Total bilirubin |
| DB | Direct bilirubin |
| IB | Indirect bilirubin |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| M | Male |
| F | Female |
References
- Simmons, C.L.; Harper, L.K.; Patel, M.C.; Katabathina, V.S.; Southard, R.N.; Goncalves, L.; Tran, E.; Biyyam, D.R. Biliary Disorders, Anomalies, and Malignancies in Children. Radiographics 2024, 44, e230109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagi, S.A.M.; Zakaria, H.M.; Elkhadry, S.W.; Hamed, W.E.; Gaballa, N.K.; Elkholy, S.S. APRI and FIB-4 indices as diagnostic noninvasive scores for prediction of severe fibrosis in patients with biliary atresia. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 9, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.H.; Chen, H.L.; Hsu, W.M.; Chang, C.H.; Peng, S.S. A noninvasive index to predict liver cirrhosis in biliary atresia. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021, 51, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, J.L.; Davenport, M.; Kelly, D.A. Biliary atresia. Lancet 2009, 374, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, B.A.; Perera, M.T.; Mirza, D.F. Clinical practice: Management of biliary atresia. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohi, R. Surgery for biliary atresia. Liver 2001, 21, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.H.; Chang, M.H.; Chen, H.L.; Lee, H.C.; Wu, T.C.; Lin, C.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, A.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Lau, B.H.; et al. Universal screening for biliary atresia using an infant stool color card in Taiwan. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, T.H.; Chang, M.H.; Wu, J.F.; Chen, H.L.; Lee, H.C.; Chen, A.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Wu, T.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Lin, C.C.; et al. Effects of the infant stool color card screening program on 5-year outcome of biliary atresia in Taiwan. Hepatology 2011, 53, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Shin, H.J.; Yoon, H.; Han, S.J.; Koh, H.; Roh, Y.H.; Lee, M.J. MRI-based decision tree model for diagnosis of biliary atresia. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, J.M.; Kvist, N.; Johansen, L.S.; Borgwardt, L. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy for early diagnosis of biliary atresia. Dan. Med. J. 2016, 63, A5253. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, T.M.; Stringer, M.D. Biliary atresia: US diagnosis. Radiology 2007, 244, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, M.J.; Yoon, C.S.; Han, S.J.; Oh, J.T.; Park, Y.N. Biliary atresia: Color doppler US findings in neonates and infants. Radiology 2009, 252, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.; Sacks, M.A.; Sapra, A.; Khan, F.A. The Utility of Gallbladder Absence on Ultrasound for Children With Biliary Atresia. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 685268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Cai, J.; Xu, Y.; Peng, X.; Zheng, H.; Huang, K.; Yang, J. Three-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreato graphy for the diagnosis of biliary atresia in infants and neonates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cai, J.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Diffusion Tensor Imaging for Evaluating Biliary Atresia in Infants and Neonates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; Abdalla, A.; Elfar, R.; Ashmalla, G.A.; Ali, K.; Barakat, T. Assessment of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Parameters of Hepatic Parenchyma for Differentiation of Biliary Atresia from Alagille Syndrome. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, M.; Tang, S.T.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D.H.; Xiong, M.; Li, S.; Cao, G.Q.; Wang, Y. Laparoscopic finding of a hepatic subcapsular spider-like telangiectasis sign in biliary atresia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7119–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón-Macías, M.E.; Villasís-Keever, M.A.; Castañeda-Muciño, G.; Sandoval-Mex, A.M. Improvement in accuracy of gamma-glutamyl transferase for differential diagnosis of biliary atresia by correlation with age. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2008, 50, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, P.P.; Mourya, R.; Lei, H.Y.; Cao, G.Q.; Xiong, X.L.; Xu, H.; Duan, X.F.; Wang, N.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 for Biliary Atresia. Hepatology 2018, 68, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Hu, S.Q.; Zhu, J.H.; Cai, X.; Lai, D.M.; Chen, B.H.; Zhu, K.; Tong, Q.; Zhou, X.R.; Deng, J.L.; et al. Accurate prediction of biliary atresia with an integrated model using MMP-7 levels and bile acids. World J. Pediatr. 2024, 20, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangi, S.; Mourya, R.; Nalluri, S.; Fei, L.; Dong, S.; Harpavat, S.; Guthery, S.L.; Molleston, J.P.; Rosenthal, P.; Sokol, R.J.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of serum matrix metalloproteinase-7 as a biomarker of biliary atresia in a large North American cohort. Hepatology 2024, 80, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Guindi, M.A.; Sira, M.M.; Sira, A.M.; Salem, T.A.; El-Abd, O.L.; Konsowa, H.A.; El-Azab, D.S.; Allam, A.A. Design and validation of a diagnostic score for biliary atresia. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, R.; Liu, F.; Dong, Y.; Tang, W. Comparison of Low-Dose Sevoflurane Inhalation with Intranasal Ketamine as Rescue Sedation After Intranasal Dexmedetomidine Failure in Outpatient Children Undergoing MRI: A Randomized Control Trial. J. Perianesth Nurs. 2021, 36, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Shin, H.J.; Yoon, H.; Han, S.J.; Koh, H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, M.J. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Differentiation of Biliary Atresia and Grading of Hepatic Fibrosis in Infants with Cholestasis. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, M.J.; Han, K.; Han, S.J.; Koh, H.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.J. Clinical utility of mono-exponential model diffusion weighted imaging using two b-values compared to the bi- or stretched exponential model for the diagnosis of biliary atresia in infant liver MRI. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Dong, R.; Du, M.; Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.; Yan, W.; Zheng, S. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-7 for discriminating biliary atresia: A diagnostic accuracy and validation study. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.H.; Jaw, F.S.; Ho, M.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Peng, S.S. Hepatic ADC value correlates with cirrhotic severity of patients with biliary atresia. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, e253–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, S.; Onda, M.; Tajiri, T.; Kim, D.Y. Hepatic lobar differences in progression of chronic liver disease: Correlation of asialoglycoprotein scintigraphy and hepatic functional reserve. Hepatology 1997, 25, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Jeng, Y.M.; Hsu, W.M.; Yang, J.C.; Ho, M.C. Hepatic ADC map as an adjunct to conventional abdominal MRI to evaluate hepatic fibrotic and clinical cirrhotic severity in biliary atresia patients. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 2992–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Oei, M.; Babb, J.S.; Niver, B.E.; Taouli, B. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen at 3.0 Tesla: Image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient reproducibility compared with 1.5 Tesla. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, O.F.; Chong, D.; Nanz, D.; Boss, A.; Froehlich, J.M.; Andres, E.; Seifert, B.; Thoeny, H.C. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of upper abdominal organs: Field strength and intervendor variability of apparent diffusion coefficients. Radiology 2014, 270, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takase, K.; Ueno, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Uga, N.; Deguchi, K.; Nomura, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kamiyama, M.; Tazuke, Y.; Kimura, T.; et al. Impact of follow-up liver biopsy on long-term outcomes post-Kasai procedure in patients with biliary atresia. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2025, 41, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.C.; Lo, C.M.; Wong, Y.; Liu, C.L.; Fan, S.T. Long-term biological consequences of donor right hepatectomy including the middle hepatic vein in adult-to-adult live donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2006, 12, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbin, W.P.; Robert, N.J.; Ferrucci, J.T., Jr. Diagnosis of cirrhosis based on regional changes in hepatic morphology: A radiological and pathological analysis. Radiology 1980, 135, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chu, E.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Man, K.; Go, M.Y.; Huang, X.R.; Lan, H.Y.; Sung, J.J.; Yu, J. microRNA-29b prevents liver fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7325–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, P.; Wu, P.; Kong, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; et al. BCL6B expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and its efficacy in the inhibition of liver damage and fibrogenesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20252–20265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, Z.; Ren, J.; Qiu, Y. Oleoylethanolamide, an endogenous PPAR-α ligand, attenuates liver fibrosis targeting hepatic stellate cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42530–42540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, M.; Inan, N.; Sarisoy, H.T.; Akansel, G.; Gumustas, S.; Gürbüz, Y.; Demirci, A. Diagnostic performance of conventional diffusion weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging for the liver fibrosis and inflammation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haafiz, A.B. Liver fibrosis in biliary atresia. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 4, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.T.; Chen, H.L.; Ho, M.C.; Shinn-Forng Peng, S. Computed tomography indices and criteria for the prediction of esophageal variceal bleeding in survivors of biliary atresia awaiting liver transplantation. Asian J. Surg. 2011, 34, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Training Cohort (n = 51) | Validation Cohort (n = 23) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | BA Group (n = 36) | Non-BA Group (n = 15) | p Value | BA Group (n = 14) | Non-BA Group (n = 9) | p Value |
| TB (μmol/L) | 181.6 (147.08–211.9) ● | 173.2 (154.6–221) ● | 0.85 ★ | 150 (127.53–184.45) ● | 161.8 (74.45–195.05) ● | 0.56 ★ |
| DB (μmol/L) | 118.43 ± 39.98 | 110.6 ± 38.19 | 0.52 ▲ | 111.62 ± 36.77 | 97.28 ± 56.13 | 0.47 ▲ |
| IB (μmol/L) | 69.15 (51.33–83.05) ● | 58.5 (42–90.8) ● | 0.61 ★ | 50.6 (31.4–72.78) ● | 45.4 (23–54.5) ● | 0.37 ★ |
| AST (IU/L) | 209.2 (166.75–316.6) ● | 232.4 (169.8–321.8) ● | 0.9 ★ | 271.2 (198.85–287.33) ● | 168.4 (124.85–244.95) ● | 0.06 ★ |
| ALT (IU/L) | 155.35 (87.43–225.33) ● | 135.2 (76.7–209) ● | 0.43 ★ | 151.05 (116.08–233.48) ● | 124.7 (63.95–218.8) ● | 0.28 ★ |
| GGT (IU/L) | 511.55 (274.83–973.78) ● | 170.8 (77.4–339.6) ● | <0.001 ★ | 570.4 (351.5–1039.73) ● | 157.2 (126.65–329.55) ● | 0.01 ★ |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 403.58 ± 140.77 | 412.13 ± 192.95 | 0.86 ▲ | 470.07 ± 196.89 | 382.67 ± 133.7 | 0.26 ▲ |
| FA LHL | 0.4 (0.33–0.47) ● | 0.4 (0.38–0.43) ● | 0.76 ★ | 0.54 (0.44–0.61) ● | 0.43 (0.42–0.49) ● | 0.05 ★ |
| FA CHL | 0.41 ± 0.12 | 0.4 ± 0.12 | 0.74 ▲ | 0.47 ± 0.1 | 0.43 ± 0.08 | 0.38 ▲ |
| FA RHL | 0.4 ± 0.07 | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.58 ▲ | 0.62 ± 0.11 | 0.63 ± 0.11 | 0.73 ▲ |
| ADC LHL (×10−3 mm2/s) | 1.22 (1.12–1.51) ● | 1.41 (1.22–1.44) ● | 0.34 ★ | 1.3 (1.13–1.54) ● | 1.29 (1.16–1.33) ● | 0.83 ★ |
| ADC CHL (×10−3 mm2/s) | 1.23 ± 0.22 | 1.38 ± 0.17 | 0.02 ▲ | 1.18 (0.95–1.48) ● | 1.22 (1.13–1.28) ● | 0.6 ★ |
| ADC RHL (×10−3 mm2/s) | 1.22 ± 0.13 | 1.37 ± 0.13 | 0.001 ▲ | 0.64 (0.57–0.96) ● | 1.11 (1.03–1.17) ● | 0.01 ★ |
| Age (days) | 66.5 (54–107.8) ● | 67 (49–82) ● | 0.61 ★ | 82 (45–101.5) ● | 74 (57.5–145) ● | 0.83 ★ |
| Sex | M/F (17/19) | M/F (9/6) | 0.89 ❆ | M/F (7/7) | M/F (6/3) | 0.53 ❆ |
| Characteristics | AUC | p Value | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training cohort (n = 51) | |||||||
| GGT | 0.82 | <0.001 | 78.43% | 88.89% (0.78–1) ■ | 53.33% (0.25–0.82) ■ | 82.05% (0.69–0.95) ■ | 66.67% (0.35–0.98) ■ |
| ADC CHL | 0.72 | 0.02 | 70.59% | 91.67% (0.82–1.01) ■ | 20% (−0.03–0.43) ■ | 73.33% (0.6–0.87) ■ | 50% (−0.08–1.08) ■ |
| ADC RHL | 0.77 | 0.002 | 74.51% | 88.89% (0.78–1) ■ | 40% (0.12–0.68) ■ | 78.05% (0.65–0.91) ■ | 60% (0.23–0.97) ■ |
| Validation cohort (n = 23) | |||||||
| GGT | 0.81 | 0.01 | 82.61% | 85.71% (0.65–1.07) ■ | 77.78% (0.44–1.12) ■ | 85.71% (0.65–1.07) ■ | 77.78% (0.44–1.12) ■ |
| ADC CHL | 0.43 | 0.57 | 60.87% | 100% (1–1) ■ | 0% (0–0)■ | 60.87% (0.39–0.82) ■ | N/A |
| ADC RHL | 0.81 | 0.01 | 86.96% | 85.71% (0.65–1.07) ■ | 88.89% (0.63–1.15)■ | 92.31% (0.75–1.09) ■ | 80% (0.5–1.1) ■ |
| Gold Standard | Training Cohort (n = 51) | Validation Cohort (n = 23) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA | Non-BA | BA | Non-BA | |
| BA | 33 | 3 | 14 | 0 |
| Non-BA | 6 | 9 | 1 | 8 |
| Accuracy | 82.35% (42/51) | 95.65% (22/23) | ||
| Sensitivity | 91.67% (0.82–1.01) ■ (33/36) | 100% (1–1) ■ (14/14) | ||
| Specificity | 60% (0.32–0.88) ■ (9/15) | 88.89% (0.63–1.15) ■ (8/9) | ||
| PPV | 84.62% (0.73–0.97) ■ (33/39) | 93.33% (0.79–1.08) ■ (14/15) | ||
| NPV | 75% (0.46–1.04) ■ (9/12) | 100% (1–1 )■ (8/8) | ||
| AUC | 0.87 (p < 0.001) | 0.94 (p = 0.001) | ||
| Patient Number | Diagnostic Score | Diagnosis by the Scoring System | Confirmed Diagnosis | Patient Number | Diagnostic Score | Diagnosis by the Scoring System | Confirmed Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.41 | BA | Correct | 13 | 0.97 | Non-BA | Correct |
| 2 | 0.4 | BA | Correct | 14 | 0.09 | BA | Correct |
| 3 | 0.12 | BA | Correct | 15 | 0.91 | Non-BA | Correct |
| 4 | <0.001 | BA | Correct | 16 | 0.01 | BA | Correct |
| 5 | <0.001 | BA | Correct | 17 | 0.08 | BA | Correct |
| 6 | 0.68 | Non-BA | Correct | 18 | <0.001 | BA | Correct |
| 7 | 0.78 | Non-BA | Correct | 19 | 0.96 | Non-BA | Correct |
| 8 | 0.03 | BA | Correct | 20 | 0.07 | BA | Correct |
| 9 | 0.92 | Non-BA | Correct | 21 | 0.48 | BA | Correct |
| 10 | 0.03 | BA | Incorrect | 22 | 0.01 | BA | Correct |
| 11 | 0.23 | BA | Correct | 23 | 0.94 | Non-BA | Correct |
| 12 | 0.88 | Non-BA | Correct |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Ni, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, S.; Zheng, H.; Liu, D.; Xu, H.; Cai, J. A Scoring System Based on Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Blood Biochemistry Tests for Diagnosing Biliary Atresia in Infants. Children 2025, 12, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070877
Liu B, Ni X, Zhu J, Ding S, Zheng H, Liu D, Xu H, Cai J. A Scoring System Based on Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Blood Biochemistry Tests for Diagnosing Biliary Atresia in Infants. Children. 2025; 12(7):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bo, Xiaoying Ni, Jin Zhu, Shuang Ding, Helin Zheng, Daisong Liu, Hongrong Xu, and Jinhua Cai. 2025. "A Scoring System Based on Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Blood Biochemistry Tests for Diagnosing Biliary Atresia in Infants" Children 12, no. 7: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070877
APA StyleLiu, B., Ni, X., Zhu, J., Ding, S., Zheng, H., Liu, D., Xu, H., & Cai, J. (2025). A Scoring System Based on Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Blood Biochemistry Tests for Diagnosing Biliary Atresia in Infants. Children, 12(7), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070877





