Sleep Disorders in Children with Rett Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Genetics of Rett Syndrome
3. Sleep Disturbances in Rett Syndrome
3.1. Disturbances in Sleep Initiation and Maintenance
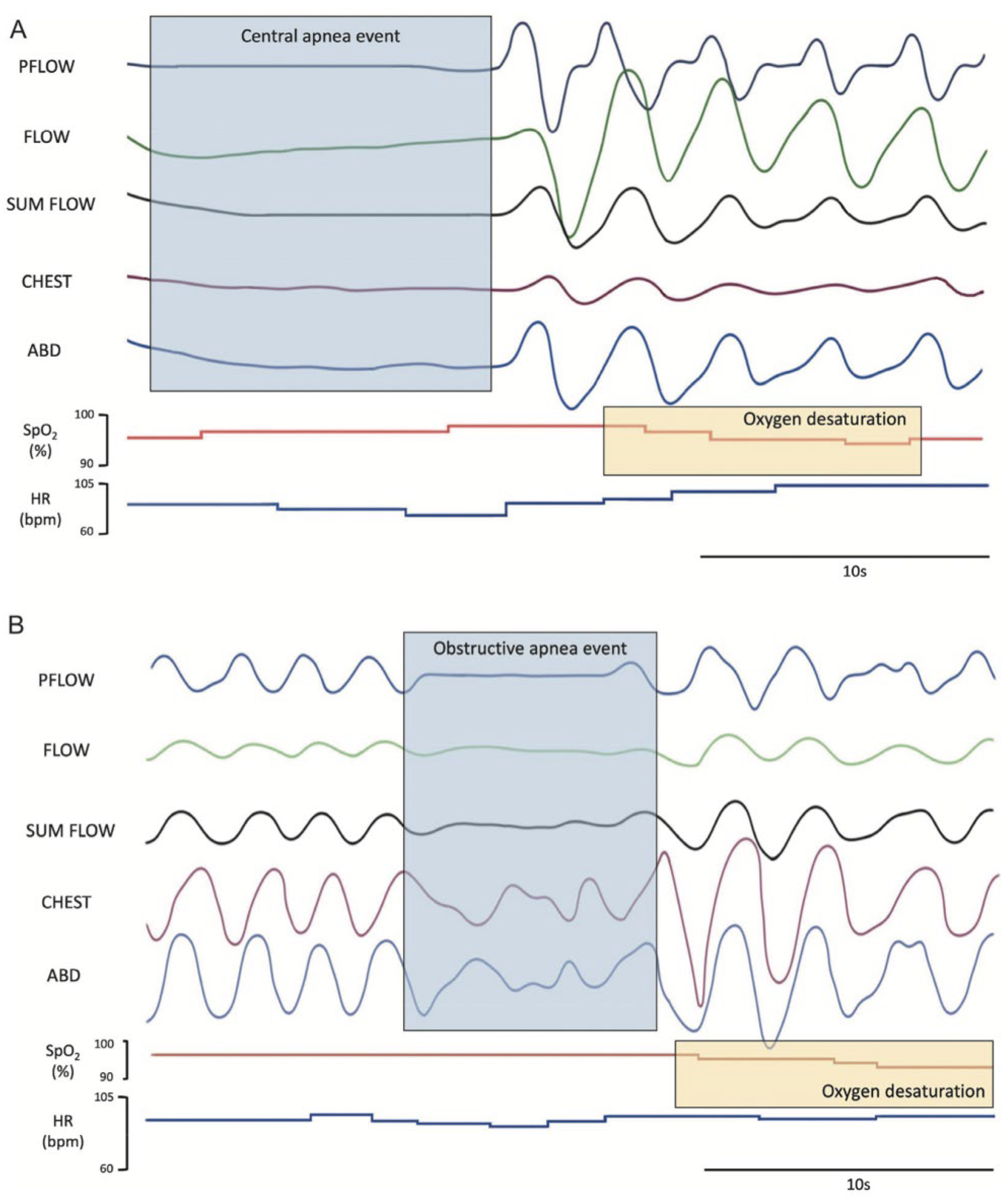
3.2. Abnormal Nocturnal Breathing
3.3. Other Sleep Abnormalities (Vocalizations, Abnormal Movements, Bruxism, and Nocturnal Seizures)
4. Sleep Impacts on Mental and Behavioral Health and Quality of Life
5. Sleep Measurement and Objective Findings in Rett Syndrome
6. Sleep-Directed Therapies
6.1. Disturbances in Sleep Initiation and Maintenance
6.2. Sleep-Related Movement Disorders
6.3. Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders
6.4. Additional Recommendations
| Drug Name | Class or Mechanism | Common Indication | Evidence in RTT Studies | Considerations in RTT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melatonin | Synthetic exogenous hormone; regulates circadian rhythm | Insomnia, delayed sleep phase onset | Most commonly used in RTT based on parent survey [27,28]. One randomized crossover trial showed decreased SE and increased TST [69]. | OTC, variable dosing practices |
| Clonidine | α2-adrenergic agonist | FDA approved for ADHD, >6 years old; off label for insomnia, RLS: indicated for antihypertensive in adults | Often used off-label as sedative in neurodevelopmental disorders [4,28]. | Can lower blood pressure |
| Trazodone | Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor | Antidepressant for adults, off-label for insomnia | Mild sedative effects; discussed in behavioral comorbidity context [28,61]. | QTc prolongation risk; priapism, limited pediatric data [63,68]; no FDA indication for pediatric patients |
| Gabapentin | GABA analog | Anticonvulsant, RLS, neuropathic pain, off -label for insomnia | Occasionally used as sedative for comorbid conditions in RTT with RLS and seizures; few data specific to pediatric RTT [4]. | Sedation and mood effects should be monitored [4] |
| Clonazepam, diazepam, oxazepam | Benzodiazepine; GABA-A receptor agonist | Anticonvulsant, insomnia, anxiety, muscle relaxant | Based on parent survey, for dual use as sedative and for epilepsy management [4,28]. | Dependence risk; respiratory depression in high doses [4] |
| Diphenhydramine | First-generation antihistamine | Allergies, off label OTC sleep aid | Based on parent survey, used as sedating option in refractory insomnia in 1 study [28]. | Can cause paradoxical agitation; not for chronic use [28] |
| Hydroxyzine | First-generation antihistamine | Sedation premedication for procedure, anxiety, pruritus (approved for pediatric use) | Based on parent survey, used for insomnia [28]. | Hypersedation, stupor, nausea, and vomiting |
| Cyproheptadine | Antihistamine | Allergies, appetite stimulant | Based on parent survey, used for insomnia [28]. | Daytime sleepiness, weight gain |
| Escitalopram | SSRI | Antidepressant for >12 years old, general anxiety disorder for adults | One case report shows dramatic sleep and mood improvement in RTT [75]. | Bruxism reported; dosing must be carefully titrated |
| Carnitine | Amino acid and nutritional supplement | Nutritional supplement | Open-label trial with 21 subjects showing improved SE and TST [73]. | Older study and no follow up, 2001 |
| Trofinetide | Synthetic analog of a naturally occurring brain peptide; insulin-like growth factor 1 [63,64] | Indicated for RTT for >2 years old; proposed mechanism of action is to promote synaptic maturation | Improved scores on RSBQ and clinical Global Impression Improvement scale. One case report with sleep improvement [59]. | No direct evidence of improved sleep |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rett, A. On a unusual brain atrophy syndrome in hyperammonemia in childhood. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 1966, 116, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dunn, H.G. Importance of Rett syndrome in child neurology. Brain Dev. 2001, 23, S38–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neul, J.L.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Glaze, D.G.; Christodoulou, J.; Clarke, A.J.; Bahi-Buisson, N.; Leonard, H.; Bailey, M.E.S.; Schanen, N.C.; Zappella, M.; et al. Rett syndrome: Revised diagnostic criteria and nomenclature. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, A.M.; Ricciardello, A.; Cucinotta, F. The psychopharmacology of autism spectrum disorder and Rett syndrome. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 165, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurvick, C.L.; de Klerk, N.; Bower, C.; Christodoulou, J.; Ravine, D.; Ellaway, C.; Williamson, S.; Leonard, H. Rett syndrome in Australia: A review of the epidemiology. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.D. Review of Rett syndrome. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Nagarajan, L.; de Klerk, N.; Jacoby, P.; Ellaway, C.; Leonard, H. Sleep problems in Rett syndrome. Brain Dev. 2007, 29, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchón, S.; Carrillo-López, I.; Cauli, O. Quality of life related to clinical features in patients with Rett syndrome and their parents: A systematic review. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, R.E.; Van den Veyver, I.B.; Wan, M.; Tran, C.Q.; Francke, U.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townend, G.S.; Ehrhart, F.; van Kranen, H.J.; Wilkinson, M.; Jacobsen, A.; Roos, M.; Willighagen, E.L.; van Enckevort, D.; Evelo, C.T.; Curfs, L.M.G. MECP2 variation in Rett syndrome-An overview of current coverage of genetic and phenotype data within existing databases. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Smits, M.; Curfs, L.; Spruyt, K. Sleep Respiratory Disturbances in Girls with Rett Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2022, 19, 13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, L.M.; Baker, S.A.; Zoghbi, H.Y. MECP2 disorders: From the clinic to mice and back. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrou, A.; Papaevripidou, I.; Alexandrou, I.M.; Theodosiou, A.; Evangelidou, P.; Kousoulidou, L.; Tanteles, G.; Christophidou-Anastasiadou, V.; Sismani, C. De novo mosaic MECP2 mutation in a female with Rett syndrome. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Lee, S.S.J.; Zhang, X.; Houwink-Manville, I.; Song, H.-R.; Amir, R.E.; Budden, S.; Naidu, S.; Pereira, J.L.P.; Lo, I.F.; et al. Rett Syndrome and beyond: Recurrent spontaneous and familial MECP2 mutations at CpG hotspots. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 65, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, W.A.; Krishnarajy, R.; Ellaway, C.; Christodoulou, J. Rett Syndrome: A Genetic Update and Clinical Review Focusing on Comorbidities. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.; Pozzer, D.; Landsberger, N. Advanced genetic therapies for the treatment of Rett syndrome: State of the art and future perspectives. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1172805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, J.; Wong, K.; Leonard, H. Associations between genotype, phenotype and behaviours measured by the Rett syndrome behaviour questionnaire in Rett syndrome. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2024, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, C.; Leonard, H.; Smith, J.; Wong, K.; Downs, J. Genotype and sleep independently predict mental health in Rett syndrome: An observational study. J. Med. Genet. 2023, 60, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boban, S.; Wong, K.; Epstein, A.; Anderson, B.; Murphy, N.; Downs, J.; Leonard, H. Determinants of sleep disturbances in Rett syndrome: Novel findings in relation to genotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2016, 170, 2292–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, A.; Lee, J.T. Variable expression of MECP2, CDKL5, and FMR1 in the human brain: Implications for gene restorative therapies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2312757121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, B. Clinical manifestations and stages of rett syndrome. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2002, 8, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, S.; Murphy, M.; Moser, H.W.; Rett, A.; Opitz, J.M.; Reynolds, J.F. Rett syndrome—natural history in 70 cases. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1986, 25, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Leonard, H.; Piek, J.; Downs, J. Early development and regression in Rett syndrome. Clin. Genet. 2013, 84, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.; Leonard, H.; Jacoby, P.; Ellaway, C.; Downs, J. The trajectories of sleep disturbances in Rett syndrome. J. Sleep Res. 2015, 24, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, N.; Smeets, E.; Steinbusch, C.; Maaskant, M.; van Waardenburg, D.; Curfs, L. Aging in Rett syndrome: A longitudinal study. Clin. Genet. 2013, 84, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tascini, G.; Dell’ISola, G.B.; Mencaroni, E.; Di Cara, G.; Striano, P.; Verrotti, A. Sleep Disorders in Rett Syndrome and Rett-Related Disorders: A Narrative Review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 817195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leven, Y.; Wiegand, F.; Wilken, B. Sleep Quality in Children and Adults with Rett Syndrome. Neuropediatrics 2020, 51, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boban, S.; Leonard, H.; Wong, K.; Wilson, A.; Downs, J. Sleep disturbances in Rett syndrome: Impact and management including use of sleep hygiene practices. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2018, 176, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Smits, M.; Curfs, L.; Spruyt, K. Sleep and the Social Profiles of Individuals With Rett Syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2024, 152, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Wong, L.-C.; Chu, Y.-J.; Hsu, C.-J.; Wang, H.-P.; Tsai, W.-C.; Lee, W.-T. The sleep problems in individuals with Rett syndrome and their caregivers. Autism 2024, 28, 3118–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, W.A.; Percy, A.K.; Neul, J.L.; Cobb, S.R.; Pozzo-Miller, L.; Issar, J.K.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Vignoli, A.; Kaufmann, W.E. Rett syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2024, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, C.C.; Fisher, W.; Moser, H. Behavioral treatment of sleep dysfunction in patients with the rett syndrome. Brain Dev. 1991, 13, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragich, J.M.; Kim, Y.; Arnold, A.P.; Schanen, N.C. Differential distribution of the MeCP2 splice variants in the postnatal mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 501, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Hong, E.J.; Cohen, S.; Zhao, W.-N.; Ho, H.-Y.H.; Schmidt, L.; Chen, W.G.; Lin, Y.; Savner, E.; Griffith, E.C.; et al. Brain-Specific Phosphorylation of MeCP2 Regulates Activity-Dependent Bdnf Transcription, Dendritic Growth, and Spine Maturation. Neuron 2006, 52, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.-M.; Karlen-Amarante, M.; Wang, J.-D.J.; Huff, A.; Burgraff, N. Breathing disturbances in Rett syndrome. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 189, pp. 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugaresi, E.; Cirignotta, F.; Montagna, P. Abnormal breathing in the Rett syndrome. Brain Dev. 1985, 7, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese-Mayer, D.E.; Lieske, S.P.; Boothby, C.M.; Kenny, A.S.; Bennett, H.L.; Ramirez, J. Autonomic dysregulation in young girls with Rett Syndrome during nighttime in-home recordings. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2008, 43, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaddeo, A.; De Sanctis, L.; Arroyo, J.O.; Khirani, S.; Bahi-Buisson, N.; Fauroux, B. Polysomnographic findings in Rett syndrome. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2019, 23, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, E.; Heinle, R.; Johnston, D. Sleep Apnea in Patients With Rett Syndrome: Roles for Polysomnography and Adenotonsillectomy. J. Child. Neurol. 2016, 31, 1633–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.A.; Glaze, D.G. Sleep and sleep disorders in Rett syndrome. In Neurological Modulation of Sleep; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, J.; Downs, J.; Wong, K.; Heyworth, J.; Epstein, A.; Leonard, H. Autonomic breathing abnormalities in Rett syndrome: Caregiver perspectives in an international database study. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2017, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, D.G.; Percy, A.K.; Skinner, S.; Motil, K.J.; Neul, J.L.; Barrish, J.O.; Lane, J.B.; Geerts, S.P.; Annese, F.; Graham, J.; et al. Epilepsy and the natural history of Rett syndrome. Neurology 2010, 74, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolce, A.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Naidu, S.; Kossoff, E.H. Rett syndrome and epilepsy: An update for child neurologists. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 48, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricker, K.; Vaughn, B.V. Rett syndrome: A review of clinical manifestations and therapeutic approaches. Front. Sleep 2024, 3, 1373489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissenkorn, A.; Gak, E.; Vecsler, M.; Reznik, H.; Menascu, S.; Ben Zeev, B. Epilepsy in Rett syndrome—The experience of a National Rett Center. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.; Downs, J.; Wong, K.; Leonard, H. Determinants of quality of life in Rett syndrome: New findings on associations with genotype. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 58, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, W.E.; Percy, A.K.; Neul, J.L.; Downs, J.; Leonard, H.; Nues, P.; Sharma, G.D.; Bartolotta, T.E.; Townend, G.S.; Curfs, L.M.G.; et al. Burden of illness in Rett syndrome: Initial evaluation of a disorder-specific caregiver survey. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2024, 19, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merbler, A.M.; Byiers, B.J.; Garcia, J.J.; Feyma, T.J.; Symons, F.J. The feasibility of using actigraphy to characterize sleep in Rett syndrome. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2018, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byiers, B.J.; Merbler, A.M.; Burkitt, C.C.; Symons, F.J. Challenges in Using Parent-Reported Bed and Wake Times for Actigraphy Scoring in Rett-Related Syndromes. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2025, 130, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarber, K.M.; Howard, J.J.M.; Dye, T.J.; Pascoe, J.E.; Simakajornboon, N. Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Pediatric Patients With Rett Syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Spruyt, K. Literature Cases Summarized Based on Their Polysomnographic Findings in Rett Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, M.; Esposito, M.; D’aNiello, A.; Rippa, C.D.; Precenzano, F.; Pascotto, A.; Bravaccio, C.; Elia, M. Polysomnographic findings in Rett syndrome: A case–control study. Sleep Breath. 2013, 17, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammanuel, S.; Chan, W.C.; Adler, D.A.; Lakshamanan, B.M.; Gupta, S.S.; Ewen, J.B.; Johnston, M.V.; Marcus, C.L.; Naidu, S.; Kadam, S.D.; et al. Heightened Delta Power during Slow-Wave-Sleep in Patients with Rett Syndrome Associated with Poor Sleep Efficiency. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.; Takach, K.; Maski, K.; Levin, A. A circuit-level biomarker of Rett syndrome based on ectopic phase-amplitude coupling during slow-wave-sleep. Cereb. Cortex 2022, 33, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, G.D.; Cordani, R.; Veneruso, M.; Chiarella, L.; Prato, G.; Ferri, R.; Carandina, A.; Tobaldini, E.; Nobili, L.; Montano, N. Predominant cardiac sympathetic modulation during wake and sleep in patients with Rett syndrome. Sleep Med. 2024, 119, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furqan, M. Trofinetide—A new chapter in rett syndrome’s treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1284035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.G.; Loganathan, S.K.; Caliaperumal, J. Rett Syndrome and the Role of MECP2: Signaling to Clinical Trials. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, A.K.; Ananth, A.; Neul, J.L. Rett Syndrome: The Emerging Landscape of Treatment Strategies. CNS Drugs 2024, 38, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camillo, L.; Pozzi, M.; Bernardo, P.; Pisano, S.; Nobile, M. Profile of Trofinetide in the Treatment of Rett Syndrome: Design, Development and Potential Place in Therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 5023–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, K.; Vaughn, B.V. Review of Sleep Disorders and Therapeutic Approaches in Patients With Autism Spectrum Disorder and Rett Syndrome. Sleep Med. Res. 2024, 15, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Armstrong, D.; Marsh, E.; Lieberman, D.; Motil, K.; Witt, R.; Standridge, S.; Nues, P.; Lane, J.; Dinkel, T.; et al. Consensus guidelines on managing Rett syndrome across the lifespan. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2020, 4, e000717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Rett Syndrome Foundation. Rett Syndrome: Comprehensive Care Guidelines. 2024. Available online: https://www.rettsyndrome.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Comprehensive-Care-Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Blackmer, A.B.; Feinstein, J.A. Management of Sleep Disorders in Children With Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Review. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2016, 36, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.W.; Hirtz, D.; Oskoui, M.; Armstrong, M.J.; Batra, A.; Bridgemohan, C.; Coury, D.; Dawson, G.; Donley, D.; Findling, R.L.; et al. Practice guideline: Treatment for insomnia and disrupted sleep behavior in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2020, 94, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg-Damberger, M.; Ralls, F. Treatment strategies for complex behavioral insomnia in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2013, 19, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, J.E.; Owens, J.A.; Weiss, M.D.; Johnson, K.P.; Wasdell, M.B.; Freeman, R.D.; Ipsiroglu, O.S. Sleep hygiene for children with neurodevelopmental disabilities. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, A.; Leonard, H.; Davis, E.; Williams, K.; Reddihough, D.; Murphy, N.; Whitehouse, A.; Downs, J. Conceptualizing a quality of life framework for girls with Rett syndrome using qualitative methods. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2016, 170, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, E.C.; France, K.G.; Blampied, N.M.; Hanning, U.; Swan, C.E.; McLay, L.K. Behavioral Sleep Interventions for Children with Rare Genetic Neurodevelopmental Conditions: A Retrospective Analysis of Overall Outcomes for 26 Cases. Adv. Neurodev. Disord. 2024, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, A.J.; Budden, S.S. Sleep dysfunction in Rett syndrome: A trial of exogenous melatonin treatment. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1998, 40, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.A.; Avula, B.; Wang, Y.-H.; Katragunta, K.; Khan, I. Quantity of Melatonin and CBD in Melatonin Gummies Sold in the US. JAMA 2023, 329, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.A.; Rosen, C.L.; Mindell, J.A.; Kirchner, H.L. Use of pharmacotherapy for insomnia in child psychiatry practice: A national survey. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, O.; Angriman, M.; Calisti, F.; Comandini, A.; Esposito, G.; Cortese, S.; Ferri, R. Practitioner Review: Treatment of chronic insomnia in children and adolescents with neurodevelopmental disabilities. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2018, 59, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellaway, C.J.; Peat, J.; Williams, K.; Leonard, H.; Christodoulou, J. Medium-term open label trial of L-carnitine in Rett syndrome. Brain Dev. 2001, 23, S85–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motil, K.J.; Caeg, E.; Barrish, J.O.; Geerts, S.; Lane, J.B.; Percy, A.K.; Annese, F.; McNair, L.; Skinner, S.A.; Lee, H.; et al. Gastrointestinal and nutritional problems occur frequently throughout life in girls and women with rett syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, E.; Usman, M. SSRIs in Rett syndrome. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2015, 49, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchietti, D.L.; Bruni, O.; de Weerd, A.; Durmer, J.S.; Kotagal, S.; Owens, J.A.; Simakajornboon, N. Pediatric restless legs syndrome diagnostic criteria: An update by the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, W.; Riederer, P.; Linkesch, W. Serum iron status in Rett syndrome. Brain Dev. 1987, 9, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, J.W.; Berkowski, J.A.; DelRosso, L.M.; Koo, B.B.; Scharf, M.T.; Sharon, D.; Zak, R.S.; Kazmi, U.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Shelgikar, A.V.; et al. Treatment of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2025, 21, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherchi, C.; Chiappini, E.; Amaddeo, A.; Testa, M.B.C.; Banfi, P.; Veneselli, E.; Cutrera, R. Management of respiratory issues in patients with Rett syndrome: Italian experts’ consensus using a Delphi approach. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toward, M.A.; Abdala, A.P.; Knopp, S.J.; Paton, J.F.R.; Bissonnette, J.M. Increasing brain serotonin corrects CO2 chemosensitivity in methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (Mecp2)-deficient mice. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökben, S.; Ardıç, Ü.A.; Serdaroğlu, G. Use of Buspirone and Fluoxetine for Breathing Problems in Rett Syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 46, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Saito, Y.; Ueda, R.; Togawa, M.; Ohmae, T.; Matsuda, E.; Fujiyama, M.; Maegaki, Y. Effect of Serotonin 1A Agonists and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors on Behavioral and Nighttime Respiratory Symptoms in Rett Syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 60, 54–59.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdala, A.P.L.; Dutschmann, M.; Bissonnette, J.M.; Paton, J.F.R. Correction of respiratory disorders in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18208–18213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarquinio, D.C.; Hou, W.; Neul, J.L.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Glaze, D.G.; Motil, K.J.; Skinner, S.A.; Lee, H.-S.; Percy, A.K. The Changing Face of Survival in Rett Syndrome and MECP2-Related Disorders. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 53, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruyt, K.; Curfs, L.M.G. Non-pharmacological management of problematic sleeping in children with developmental disabilities. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2014, 57, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, P.L.; Wu, K.L.H.; Chen, C.J.; Siu, K.K.; Hsin, Y.J.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, F.S. Music-Based Intervention Ameliorates Mecp2-Loss-Mediated Sociability Repression in Mice through the Prefrontal Cortex FNDC5/BDNF Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harner, C.; Gaffey, T.A.; Sullivan, S.S.; Witmans, M.; DelRosso, L.M.; Tablizo, M.A. Sleep Disorders in Children with Rett Syndrome. Children 2025, 12, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070869
Harner C, Gaffey TA, Sullivan SS, Witmans M, DelRosso LM, Tablizo MA. Sleep Disorders in Children with Rett Syndrome. Children. 2025; 12(7):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070869
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarner, Christopher, Thomas A. Gaffey, Shannon S. Sullivan, Manisha Witmans, Lourdes M. DelRosso, and Mary Anne Tablizo. 2025. "Sleep Disorders in Children with Rett Syndrome" Children 12, no. 7: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070869
APA StyleHarner, C., Gaffey, T. A., Sullivan, S. S., Witmans, M., DelRosso, L. M., & Tablizo, M. A. (2025). Sleep Disorders in Children with Rett Syndrome. Children, 12(7), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070869