Detecting Disordered Eating Behaviors in Greek Youth with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Using the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey—Revised (DEPS-R): Associations with Insulin Restriction, Glycemic Control, and Anthropometric Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
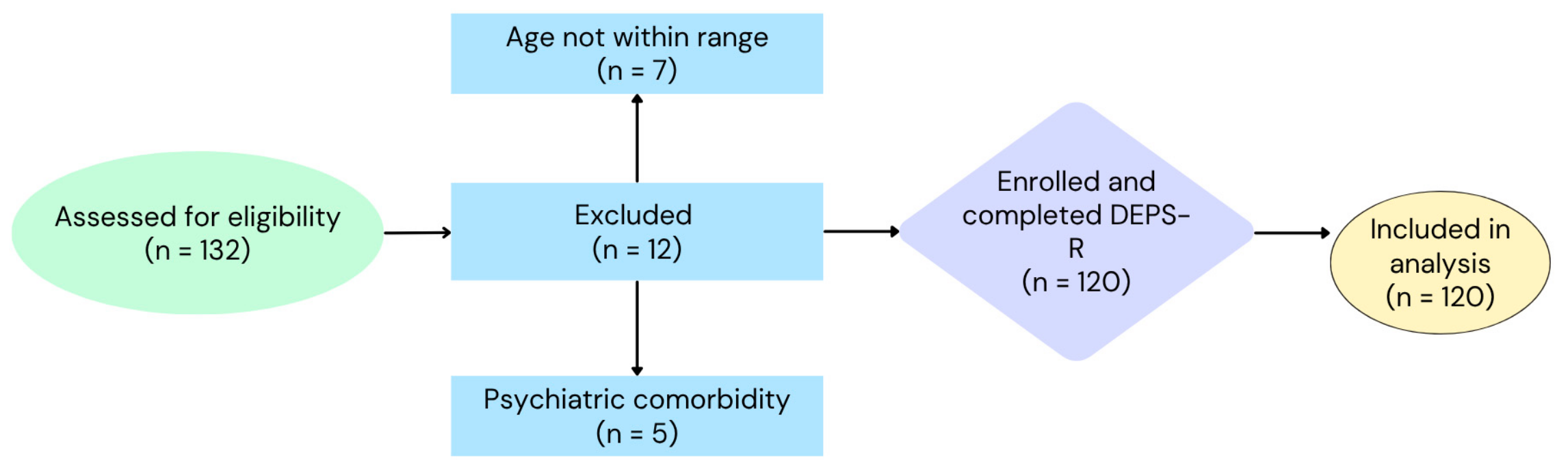
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Tools
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
DEPS-R Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| DEPS-R | Diabetes Eating Problem Survey—Revised |
| DEB | disordered eating behavior |
| ED | eating disorder |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| PCOS | Polycystic Ovary Syndrome |
| T1DM | Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus |
Appendix A
| Boys | Girls | p | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Score | 13.89 ± 8.62 | 20.56 ± 12.34 | 0.003 | 17.17 ± 11.09 |
| Losing weight is an important goal to me | 1.62 ± 1.60 | 2.61 ± 1.66 | <0.001 | 2.11 ± 1.70 |
| I skip main meals and/or snacks | 1.39 ± 1.14 | 1.80 ± 1.44 | 0.161 | 1.59 ± 1.31 |
| Other people have told me that my eating is out of control | 1.03 ± 1.33 | 1.42 ± 1.56 | 0.229 | 1.23 ± 1.45 |
| When I overeat, I don’t take enough insulin | 1.01 ± 1.18 | 1.22 ± 1.20 | 0.260 | 1.12 ± 1.19 |
| I eat more when I am alone than when I am with others | 1.23 ± 1.40 | 1.67 ± 1.46 | 0.071 | 1.45 ± 1.44 |
| I feel that it’s difficult to lose weight and control my diabetes at the same time | 0.72 ± 1.10 | 1.93 ± 1.80 | <0.001 | 1.32 ± 1.60 |
| Ι avoid checking my blood sugar when I feel it is out of range | 1.11 ± 1.34 | 0.98 ± 1.11 | 0.825 | 1.05 ± 1.23 |
| I make myself vomit | 0.07 ± 0.25 | 0.34 ± 0.82 | 0.036 | 0.20 ± 0.62 |
| I try to keep my blood sugar high so that I will lose weight | 0.46 ± 1.29 | 0.68 ± 1.23 | 0.126 | 0.57 ± 1.28 |
| I eat in a way to get ketones | 0.20 ± 0.65 | 0.17 ± 0.50 | 0.604 | 0.18 ± 0.58 |
| I feel fat when I take all of my insulin | 0.18 ± 0.62 | 0.54 ± 1.04 | 0.022 | 0.36 ± 0.87 |
| Other people tell me to take better care of my diabetes | 1.41 ± 1.53 | 1.98 ± 1.61 | 0.041 | 1.69 ± 1.59 |
| After I overeat, I skip my next insulin dose. | 0.61 ± 1.05 | 0.66 ± 0.94 | 0.451 | 0.63 ± 1.00 |
| I feel that my eating is out of control | 1.18 ± 1.19 | 1.61 ± 1.41 | 0.103 | 1.39 ± 1.32 |
| I alternate between eating very little and eating huge amounts | 1.13 ± 1.13 | 1.71 ± 1.53 | 0.060 | 1.42 ± 1.37 |
| I would rather be thin than to have good control of my diabetes | 0.52 ± 1.21 | 1.22 ± 1.78 | 0.042 | 0.87 ± 1.55 |
References
- Marks, B.E.; Wolfsdorf, J.I. Monitoring of pediatric type 1 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harjutsalo, V.; Sjöberg, L.; Tuomilehto, J. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: A cohort study. Lancet 2008, 371, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, A.; Bürger-Büsing, J.; Danne, T.; Dost, A.; Holder, M.; Holl, R.W.; Holterhus, P.M.; Kapellen, T.; Karges, B.; Kordonouri, O.; et al. Diagnosis, therapy and follow-up of diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 39–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, J.J.; Haller, M.J.; Ziegler, A.G.; Knip, M.; Ludvigsson, J.; Craig, M.E. Phases of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 2014, 15, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, I.; Vuorinen, T.; Knip, M.; Veijola, R.; Toppari, J.; Hyöty, H.; Kinnunen, T.; Ilonen, J.; Lempainen, J. Early childhood CMV infection may decelerate the progression to clinical type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2019, 20, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadalla, N.; Hegazy, A.; Abd El-Salam, M.; Elhady, M. Environmental factors associated with type 1 diabetes development: A case control study in Egypt. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.S.; Berg, C.A.; Butner, J.; Butler, J.M.; Wiebe, D.J. Longitudinal trajectories of parental involvement in type 1 diabetes and adolescents’ adherence. Health Psychol. 2014, 33, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, W.S.; Dunbar, S.A.; Boucher, J.L.; Cypress, M.; Evert, A.B.; Franz, M.J.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Neumiller, J.J.; Urbanski, P.; Verdi, C.L.; et al. Response to comments on Evert et al. Nutrition therapy recommendations for the management of adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, C.; Aslander-van Vliet, E.; Waldron, S. Nutritional management in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2009, 10, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, F.J.; Garvey, K.; Hood, K.K.; Acerini, C.L.; Codner, E. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Diabetes in adolescence. Pediatr. Diabetes 2018, 19, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, R.; Lösch-Binder, M.; Hayn, C.; Friz, S.; Uber, J.; Ziegler, J.; Liebrich, F.; Neu, A. Transition from childhood to adult care in patients with type 1 diabetes: 20 years of experience from the Tübinger Transition Study. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2023, 131, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecilia-Costa, R.; Volkening, L.K.; Laffel, L.M. Factors associated with disordered eating behaviours in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarifsaniey, N.; Shirazi, M.O.; Mehrabi, M.; Bagheri, Z. Promoting self-management behaviors in adolescents with type 1 diabetes, using digital storytelling: A pilot randomized controlled trial. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, M.A.; Foster, N.C.; Maahs, D.M.; Schatz, D.A.; Olson, B.A.; Tsalikian, E.; Lee, J.M.; Burtsolorzano, C.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Chen, V.; et al. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) changes over time among adolescent and young adult participants in the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry. Pediatr. Diabetes 2016, 17, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, M.M.; Zeitler, P.S. Insulin Resistance of Puberty. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2016, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich-Reiterer, E.E.; Rosenbauer, J.; Bechtold-Dalla Pozza, S.; Hofer, S.E.; Schober, E.; Holl, R.W. Predictors of increasing BMI during the course of diabetes in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Data from the German/Austrian DPV multicentre survey. Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.; Berardelli, R.; Gazzaruso, C.; Mazziotti, G. Insulin and GH–IGF-I axis: Endocrine pacer or endocrine disruptor? Acta Diabetol. 2015, 52, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolosowicz, M.; Lukaszuk, B.; Chabowski, A. The causes of insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes mellitus: Is there a place for quaternary prevention? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, V.; Eiser, C.; Johnson, B.; Brierley, S.; Epton, T.; Elliott, J.; Heller, S. Eating problems in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, E.; Rotella, F.; Ricca, V.; Moretti, S.; Placidi, G.F.; Rotella, C.M. Eating disorders in patients with type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2005, 28, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, P.A.; Olmsted, M.P.; Daneman, D.; Farquhar, J.C.; Wong, H.; Muskat, S.; Rodin, G.M. Eating disorders in girls and women with type 1 diabetes: A longitudinal study of prevalence, onset, remission, and recurrence. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadley, M.M.; Zaremba, N.; Andrew, B.; Ismail, K.; Treasure, J.; White, M.J.; Stadler, M. 25 years of psychological research investigating disordered eating in people with diabetes: What have we learnt? Diabet. Med. 2020, 37, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, A.P. Eating disorders and diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2020, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmsted, M.P.; Colton, P.A.; Daneman, D.; Rydall, A.C.; Rodin, G.M. Prediction of the onset of disturbed eating behavior in adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1978–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, G.; Berioli, M.; Cerquiglini, L.; Ceccarini, G.; Grohmann, U.; Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Eating disorders and disordered eating symptoms in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Nutrients 2017, 9, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevelke, L.K.; Albrecht, C.; Busse-Widmann, P.; Kranz, J.; Lange, K.; Markowitz, J.T.; Marshall, L.F.; Meurs, S.; de Soye, I.H.; Saßmann, H. Prävalenz gestörten Essverhaltens bei Typ 1 Diabetes im Kindes- und Jugendalter: Erfassungsmöglichkeiten und Vergleich mit gesunden Gleichaltrigen—Ergebnisse einer multizentrischen Fragebogenstudie. Psychother. Psychosom. Med. Psychol. 2016, 66, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peveler, R.C.; Bryden, K.S.; Neil, H.A.W.; Fairburn, C.G.; Mayou, R.A.; Dunger, D.B.; Turner, H.M. The relationship of disordered eating habits and attitudes to clinical outcomes in young adult females with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, D.; Kulzer, B.; Roos, T.; Haak, T.; Al-Khatib, M.; Hermanns, N. Risk factors and prevention strategies for diabetic ketoacidosis in people with established type 1 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, J.T.; Butler, D.A.; Volkening, L.K.; Antisdel, J.E.; Anderson, B.J.; Laffel, L.M.B. Brief screening tool for disordered eating in diabetes: Internal consistency and external validity in a contemporary sample of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergi, K.; Romanidou, M.; Abdelkhalek, H.; Tripsianis, G.; Gonidakis, F. Reliability and validity of the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey in Greek adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Psychiatriki 2020, 31, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karastogiannidou, C.; Giannoulaki, P.; Samaras, I.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Didangelos, T.; Bocsan, I.C.; Vassilopoulou, E. The Diabetes Eating Problem Survey-Revised (DEPS-R) in a Greek adult population with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Model comparison supporting a single factor structure. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altınok, Y.A.; Özgür, S.; Meseri, R.; Özen, S.; Darcan, Ş.; Gökşen, D. Reliability and validity of the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey in Turkish children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saßmann, H.; Albrecht, C.; Busse-Widmann, P.; Hevelke, L.K.; Kranz, J.; Markowitz, J.T.; Marshall, L.F.; Meurs, S.; de Soye, I.H.; Lange, K. Psychometric properties of the German version of the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey-Revised: Additional benefit of disease-specific screening in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2015, 32, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummadi, A.; Yafei, S.; Badedi, M.; Abutaleb, R.; Darraj, H.; Alhagawy, A.J.; Khawaji, A.; Solan, Y.; Alzughbi, T.; Hakami, M.; et al. Validation of the Arabic version of Diabetes Eating Problem Survey–Revised (DEPS-R) among adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, C.L.; Kuczmarski, R.J.; Flegal, K.M.; Mei, Z.; Guo, S.; Wei, R.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Curtin, L.R.; Roche, A.F.; Johnson, C.L. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2000 growth charts for the United States: Improvements to the 1977 National Center for Health Statistics version. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Molina, Y.G.; Herrera-Ávila, J.; Espinosa-Juárez, J.V.; Esquinca-Avilés, H.A.; Tejas-Juárez, J.G.; Flores-Guillén, E.; Morales-Martínez, L.A.; Briones-Aranda, A.; Jiménez-Ceballos, B.; Sierra-Ramírez, J.A.; et al. Association of Overweight and Obesity with Impaired Executive Functioning in Mexican Adolescents: The Importance of Inhibitory Control. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Boys | CI 95% | Std Error | Girls | CI 95% | Std Error | p | Total | CI 95% | Std Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 13.77 ± 2.45 | 13.14–14.40 | 0.31 | 13.60 ± 2.54 | 12.93–14.26 | 0.33 | 0.704 | 13.69 ± 2.50 | 13.24–14.14 | 0.23 |
| Disease duration (years) | 5.00 ± 3.24 | 4.16–5.82 | 0.42 | 5.89 ± 3.77 | 4.91–6.88 | 0.49 | 0.277 | 5.43 ± 3.53 | 4.80–6.07 | 0.32 |
| Weight (kg) | 58.04 ± 18.13 | 53.40–62.69 | 2.32 | 56.72 ± 17.92 | 52.05–61.39 | 2.33 | 0.689 | 57.39 ± 17.96 | 54.15–60.64 | 1.64 |
| Weight Z-score | 0.62 ± 1.06 | 0.35–0.90 | 0.14 | 0.76 ± 0.97 | 0.51–1.01 | 0.13 | 0.469 | 0.69 ± 1.02 | 0.51–0.87 | 0.09 |
| Height (cm) | 164.00 ± 15.17 | 160.00–167.77 | 1.94 | 157.86 ± 11.43 | 154.88–160.84 | 1.49 | 0.016 | 160.92 ± 13.74 | 158.44–163.40 | 1.26 |
| Height Z-score | 0.59 ± 1.14 | 0.30–0.88 | 0.15 | 0.49 ± 1.13 | 0.20–0.79 | 0.15 | 0.642 | 0.54 ± 1.13 | 0.34–0.75 | 0.10 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.12 ± 3.67 | 20.17–22.06 | 0.47 | 22.28 ± 4.95 | 21.00–23.57 | 0.64 | 0.144 | 21.69 ± 4.37 | 20.90–22.48 | 0.40 |
| BMI Z-score | 0.47 ± 0.89 | 0.24–0.70 | 0.11 | 0.68 ± 0.92 | 0.44–0.92 | 0.12 | 0.181 | 0.57 ± 0.91 | 0.41–0.74 | 0.08 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.21 ± 1.19 | 6.91–7.52 | 0.15 | 7.41 ± 1.13 | 7.11–7.70 | 0.15 | 0.226 | 7.31 ± 1.16 | 7.10–7.52 | 0.11 |
| WHtI (cm) | 0.47 ± 0.06 | 0.45–0.48 | 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.46–0.49 | 0.01 | 0.600 | 0.47 ± 0.06 | 0.46–0.48 | 0.01 |
| Sex | DEPS-R < 20 n (%) | DEPS-R ≥ 20 n (%) | Total n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | 49 (80.3%) | 12 (19.7%) | 61 (50.8%) | <0.001 |
| Females | 29 (49.2%) | 30 (50.8%) | 59 (49.2%) | |
| Total | 78 (65.0%) | 42 (35.0%) | 120 (100.0%) |
| Parameter | Correlation with Total Questionnaire Score |
|---|---|
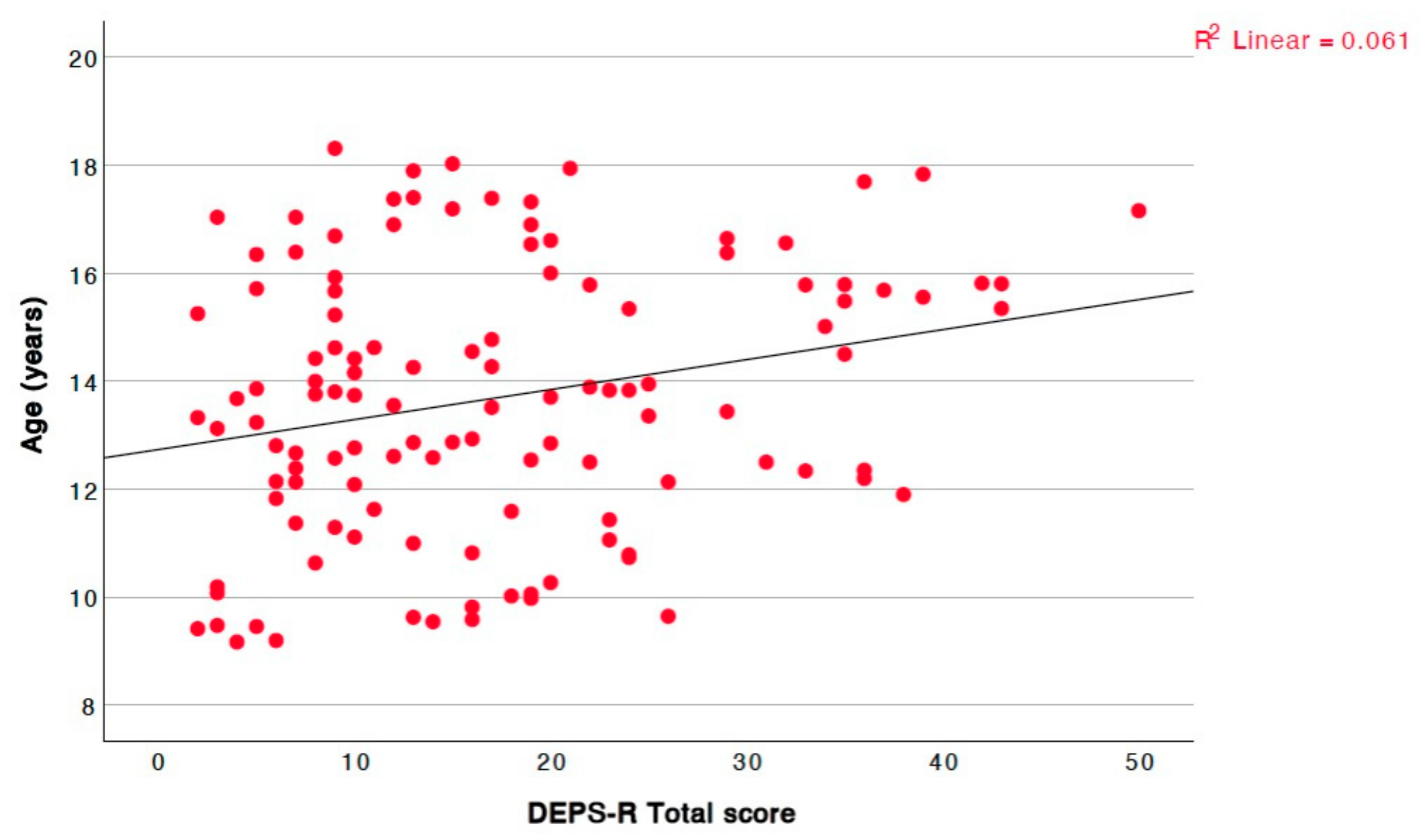
| Age | r = 0.212, p = 0.020, 95% CI = [0.03, 0.38] |
| Disease duration | r = 0.058, p = 0.531 |
| Weight | r = 0.319, p = <0.001, 95% CI = [0.15, 0.47] |
| Weight Z-score | r = 0.329, p = <0.001, 95% CI = [0.16, 0.48] |
| Height | r = 0.104, p = 0.260 |
| Height Z-score | r = −0.002, p = 0.979 |
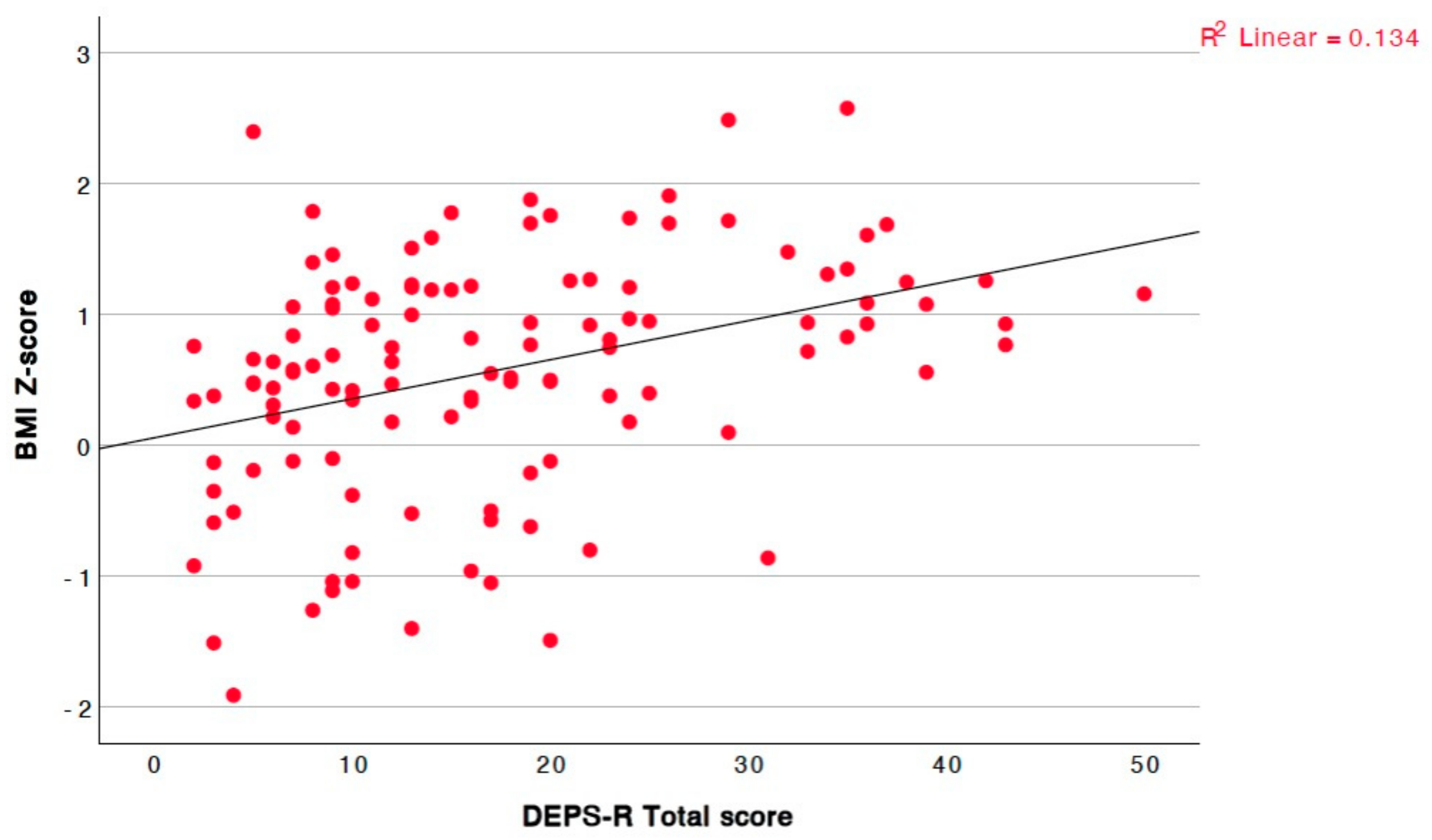
| BMI | r = 0.419, p = <0.001, 95% CI = [0.26, 0.56] |
| BMI Z-score | r = 0.394, p = <0.001, 95% CI = [0.23, 0.54] |
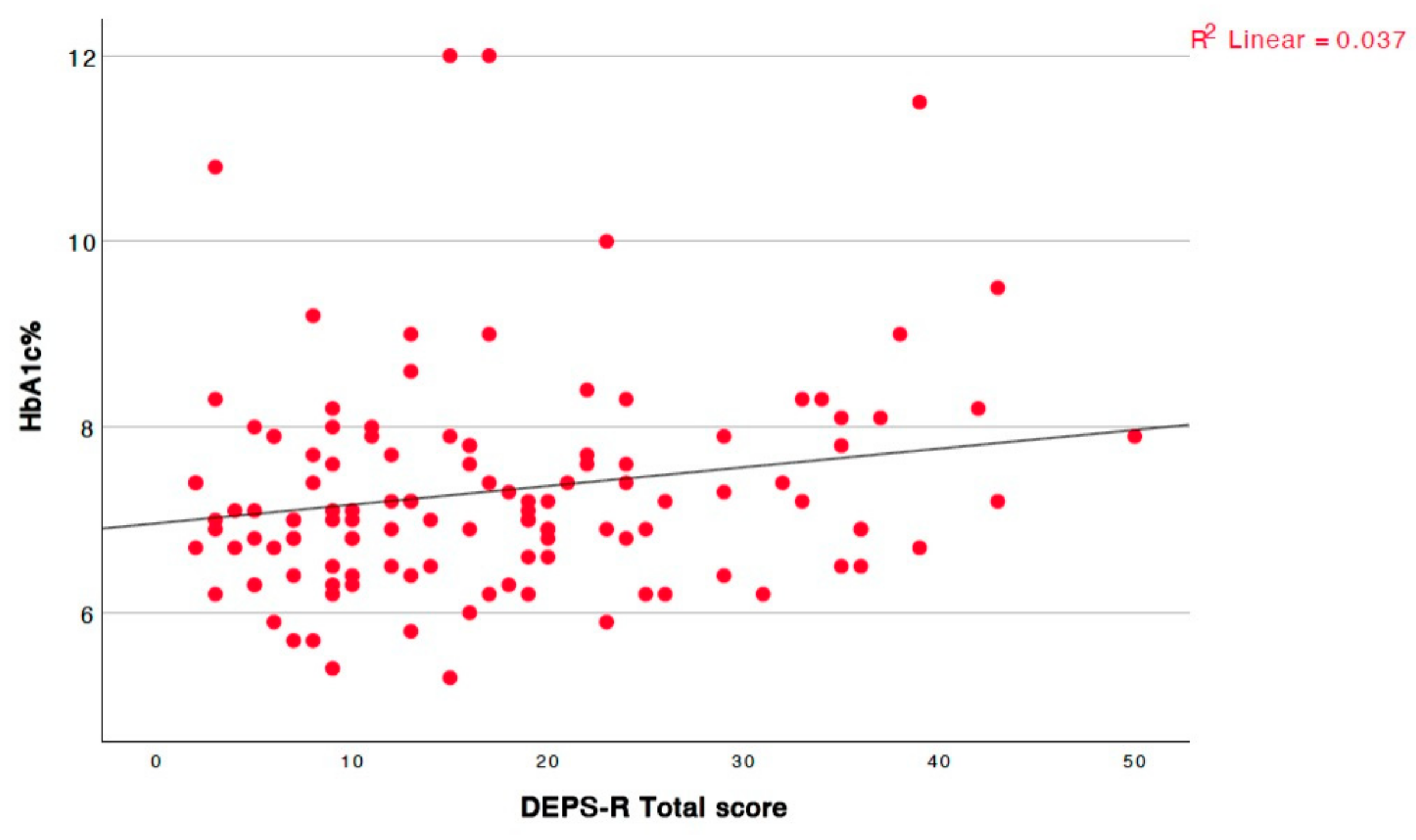
| HbA1c | r = 0.182, p = 0.047, 95% CI = [0.0, 0.35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oikonomou, A.; Christoforidis, A.; Kotanidou, E.P.; Giannopoulou, I.; Paschalidou, E.; Tsinopoulou, V.R.; Sotiriou, G.; Tsiroukidou, K.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A. Detecting Disordered Eating Behaviors in Greek Youth with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Using the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey—Revised (DEPS-R): Associations with Insulin Restriction, Glycemic Control, and Anthropometric Parameters. Children 2025, 12, 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060795
Oikonomou A, Christoforidis A, Kotanidou EP, Giannopoulou I, Paschalidou E, Tsinopoulou VR, Sotiriou G, Tsiroukidou K, Galli-Tsinopoulou A. Detecting Disordered Eating Behaviors in Greek Youth with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Using the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey—Revised (DEPS-R): Associations with Insulin Restriction, Glycemic Control, and Anthropometric Parameters. Children. 2025; 12(6):795. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060795
Chicago/Turabian StyleOikonomou, Anastasia, Athanasios Christoforidis, Eleni P. Kotanidou, Ioanna Giannopoulou, Eleni Paschalidou, Vasiliki Rengina Tsinopoulou, Georgia Sotiriou, Kyriaki Tsiroukidou, and Assimina Galli-Tsinopoulou. 2025. "Detecting Disordered Eating Behaviors in Greek Youth with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Using the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey—Revised (DEPS-R): Associations with Insulin Restriction, Glycemic Control, and Anthropometric Parameters" Children 12, no. 6: 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060795
APA StyleOikonomou, A., Christoforidis, A., Kotanidou, E. P., Giannopoulou, I., Paschalidou, E., Tsinopoulou, V. R., Sotiriou, G., Tsiroukidou, K., & Galli-Tsinopoulou, A. (2025). Detecting Disordered Eating Behaviors in Greek Youth with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Using the Diabetes Eating Problem Survey—Revised (DEPS-R): Associations with Insulin Restriction, Glycemic Control, and Anthropometric Parameters. Children, 12(6), 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060795










