Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants: A Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Sources and search strategy
- Study selection and definitions
- Data extraction and assessment of risk of bias
- Bayesian model-averaged meta-analysis
3. Results
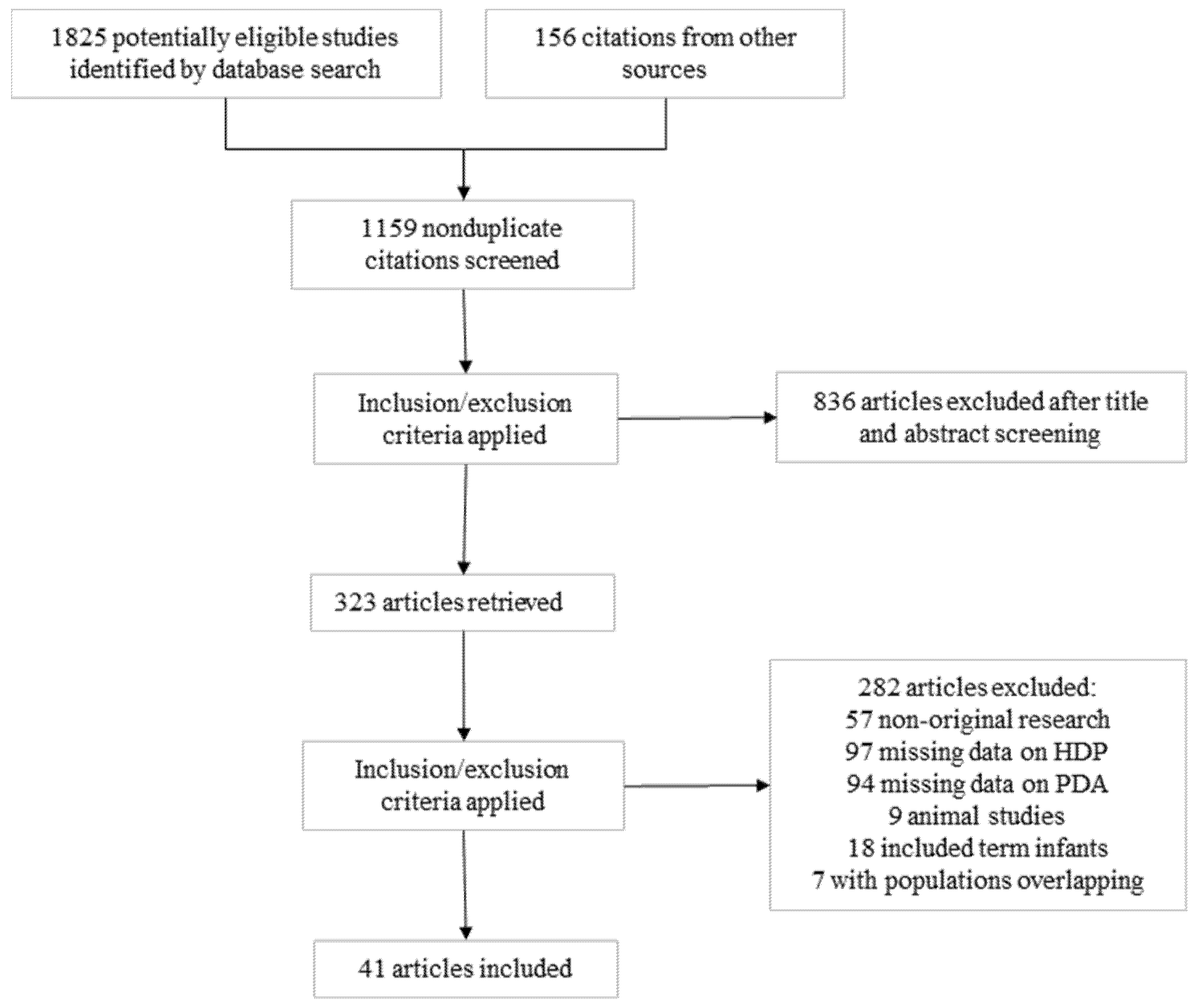
3.1. Description of Studies and Risk of Bias Assessment
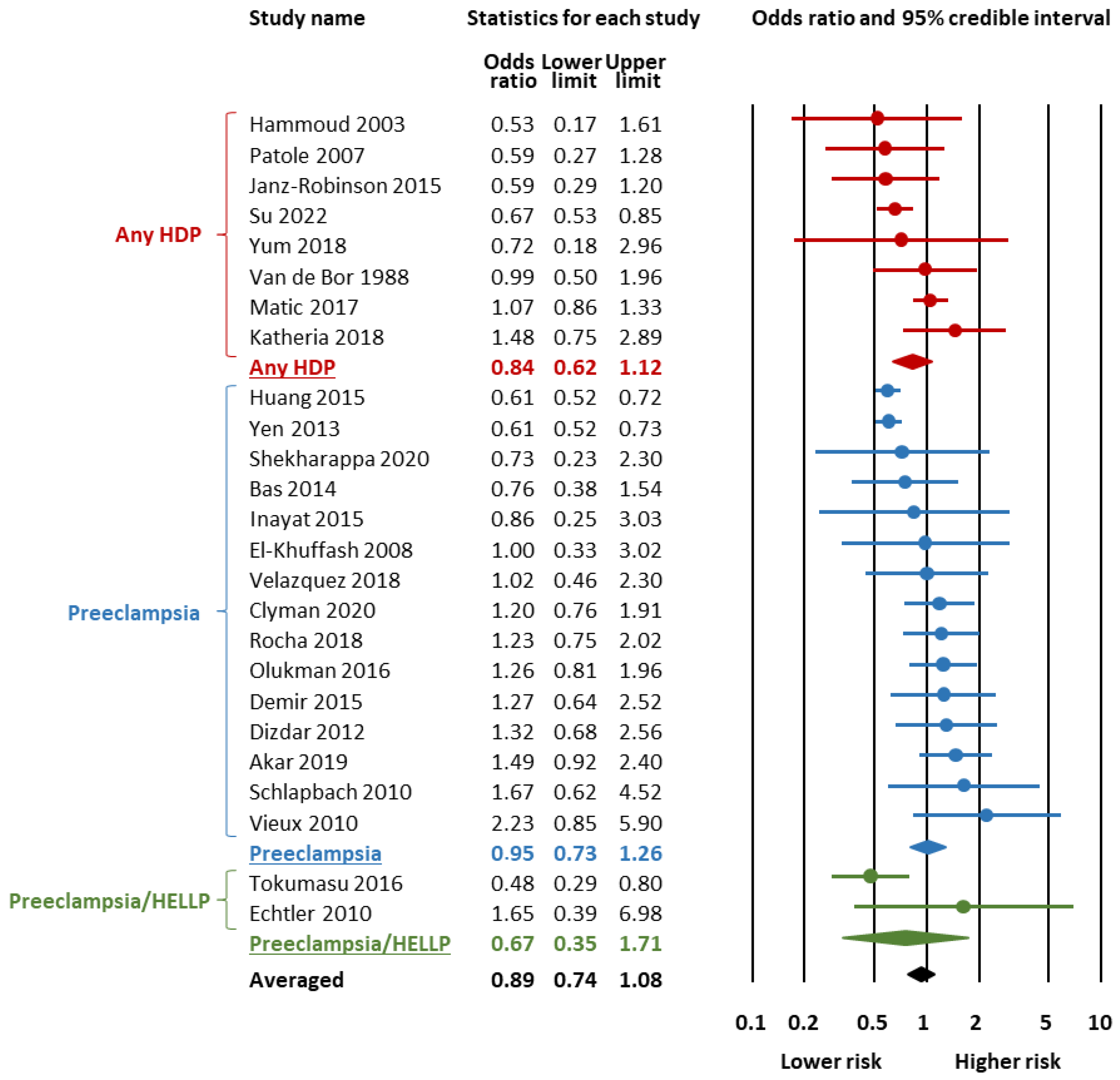
3.2. Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis
3.3. Subgroup Analysis and Meta-Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BF | Bayes factor |
| BMA | Bayesian model-averaged |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CrI | Credible interval |
| DA | Ductus arteriosus |
| GA | Gestational age |
| HDP | Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy |
| H0 | Null hypothesis |
| H1 | Alternative hypothesis |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PDA | Patent ductus arteriosus |
References
- Reese, J.; Laughon, M.M. The patent ductus arteriosus problem: Infants who still need treatment. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillam-Krakauer, M.; Reese, J. Diagnosis and management of patent ductus arteriosus. Neoreviews 2018, 19, e394–e402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, P.; Baczynski, M.; McNamara, P.J.; Jain, A. (Eds.) Patent ductus arteriosus: The physiology of transition. In Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, S.E.; Sallmon, H.; Rose, A.T.; Porras, D.; Shelton, E.L.; Reese, J.; Hansmann, G. Patent ductus arteriosus of the preterm infant. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20201209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agache, I.; Akdis, C.A. Precision medicine and phenotypes, endotypes, genotypes, regiotypes, and theratypes of allergic diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötvall, J.; Akdis, C.A.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bjermer, L.; Casale, T.B.; Custovic, A.; Lemanske, R.F.L., Jr.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Wenzel, S.E.; Greenberger, P.A. Asthma endotypes: A new approach to classification of disease entities within the asthma syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElrath, T.F.; Hecht, J.L.; Dammann, O.; Boggess, K.; Onderdonk, A.; Markenson, G.; Harper, M.; Delpapa, E.; Allred, E.N.; Leviton, A.; et al. Pregnancy disorders that lead to delivery before the 28th week of gestation: An epidemiologic approach to classification. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamor, E.; Borges-Luján, M.; González-Luis, G. (Eds.) Association of patent ductus arteriosus with fetal factors and endotypes of prematurity. In Seminars in Perinatology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Luis, G.E.; Borges-Lujan, M.; Villamor, E. Association between endotypes of prematurity and pharmacological closure of patent ductus arteriosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1078506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbodi, E.; Villamor-Martínez, E.; Degraeuwe, P.L.; Villamor, E. Chorioamnionitis appears not to be a risk factor for patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundscheid, T.M.; Villamor-Martinez, E.; Villamor, E. Association between endotype of prematurity and mortality: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Neonatology 2023, 120, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierro, M.; Villamor-Martinez, E.; van Westering-Kroon, E.; Alvarez-Fuente, M.; Abman, S.H.; Villamor, E. Association of the dysfunctional placentation endotype of prematurity with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Thorax 2022, 77, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamor-Martinez, E.; Kilani, M.A.; Degraeuwe, P.L.; Clyman, R.I.; Villamor, E. Intrauterine growth restriction and patent ductus arteriosus in very and extremely preterm infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, L.A.; Von Dadelszen, P. (Eds.) State-of-the-art diagnosis and treatment of hypertension in pregnancy. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.; Shi, Y. Related factors of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 605879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeysundera, D.N.; Austin, P.C.; Hux, J.E.; Beattie, W.S.; Laupacis, A. Bayesian statistical inference enhances the interpretation of contemporary randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 13–21.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoš, F.; Gronau, Q.F.; Timmers, B.; Otte, W.M.; Ly, A.; Wagenmakers, E.J. Bayesian model-averaged meta-analysis in medicine. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 6743–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronau, Q.F.; Heck, D.W.; Berkhout, S.W.; Haaf, J.M.; Wagenmakers, E.-J. A primer on Bayesian model-averaged meta-analysis. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 2021, 4, 25152459211031256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, J.; van den Bergh, D.; Böhm, U.; Dablander, F.; Derks, K.; Draws, T.; Etz, A.; Evans, N.J.; Gronau, Q.F.; Haaf, J.M.; et al. The JASP guidelines for conducting and reporting a Bayesian analysis. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2021, 28, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Wagenmakers, E.-J. Bayesian Data Analysis for Cognitive Science: A Practical Course; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoš, F.; Maier, M.; Wagenmakers, E.J.; Doucouliagos, H.; Stanley, T. Robust Bayesian meta-analysis: Model-averaging across complementary publication bias adjustment methods. Res. Synth. Methods 2023, 14, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoš, F.; Maier, M.; Stanley, T.; Wagenmakers, E.-J. Robust Bayesian Meta-Regression—Model-Averaged Moderation Analysis in the Presence of Publication Bias. Psychol. Methods, 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.G.; Samra, N.M.; Amin, S.A.; Borayek, H.A.; Abdelrazek, G. Platelets and platelet derived growth factor and ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates. Prog. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2020, 57, 101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, S.; Topcuoglu, S.; Tuten, A.; Ozalkaya, E.; Karatepe, H.O.; Gokmen, T.; Ovali, F.; Karatekin, G. Is the First Postnatal Platelet Mass as an Indicator of Patent Ductus Arteriosus? Arch. Iran. Med. 2019, 22, 687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bas-Suárez, M.P.; González-Luis, G.E.; Saavedra, P.; Villamor, E. Platelet counts in the first seven days of life and patent ductus arteriosus in preterm very low-birth-weight infants. Neonatology 2014, 106, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossung, V.; Fortmann, M.I.; Fusch, C.; Rausch, T.; Herting, E.; Swoboda, I.; Rody, A.; Härtel, C.; Göpel, W.; Humberg, A. Neonatal outcome after preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome: A population-based cohort study in Germany. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 579293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, B.; Hoeck, M.; Schermer, E.; Streif, W.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U. Patent ductus arteriosus, low platelets, cyclooxygenase inhibitors, and intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyman, R.I.; Hills, N.K. The effect of prolonged tracheal intubation on the association between patent ductus arteriosus and bronchopulmonary dysplasia (grades 2 and 3). J. Perinatol. 2020, 40, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Rugolo, L.M.S.; de Sá, M.P.A.; Kurokawa, C.S.; Madoglio, R.J.; Bentlin, M.R.; Rugolo, A., Jr.; Corrente, J.E. There is no difference in nitric oxide metabolites and neonatal outcome between premature infants born to pre-eclamptic and those born to normotensive women. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2015, 35, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, N.; Peker, E.; Ece, İ.; Ağengin, K.; Bulan, K.A.; Tuncer, O. Is platelet mass a more significant indicator than platelet count of closure of patent ductus arteriosus? J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdar, A.E.; Ozdemir, R.; Nur Sari, F.; Yurttutan, S.; Gokmen, T.; Erdeve, O.; Canpolat, F.E.; Uras, N.; Oguz, S.S.; Dilmen, U. Low platelet count is associated with ductus arteriosus patency in preterm newborns. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echtler, K.; Stark, K.; Lorenz, M.; Kerstan, S.; Walch, A.; Jennen, L.; Rudelius, M.; Seidl, S.; Kremmer, E.; Emambokus, N.R.; et al. Platelets contribute to postnatal occlusion of the ductus arteriosus. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khuffash, A.F.; Molloy, E.J. Influence of a patent ductus arteriosus on cardiac troponin T levels in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.H.; Hurley, T.M.; Rogers, Y.M.; O’Callaghan, M.J.; Tudehope, D.I.; Burns, Y.R.; Phty, M.; Mohay, H.A. Survival and neonatal and neurodevelopmental outcome of 24–29 week gestation infants according to primary cause of preterm delivery. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1997, 37, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, M.S.; Elsori, H.A.; Hanafi, E.A.; Shalabi, A.A.; Fouda, I.A.; Devarajan, L.V. Incidence and risk factors associated with the patency of ductus arteriosus in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome in Kuwait. Saudi Med. J. 2003, 24, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hentges, C.R.; Silveira, R.C.; Procianoy, R.S. Angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors in preterm neonates born to mothers with and without preeclampsia. Am. J. Perinatol. 2015, 32, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Yang, H.-I.; Chou, H.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Tsou, K.-I.; Tsao, P.-N.; Taiwan Premature Infant Developmental Collaborative Study Group. Preeclampsia and retinopathy of prematurity in very-low-birth-weight infants: A population-based study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, M.; Bany-Mohammed, F.; Valencia, A.; Tay, C.; Jacinto, J.; Aranda, J.V.; Beharry, K.D. Antioxidants and biomarkers of oxidative stress in preterm infants with symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus. Am. J. Perinatol. 2015, 32, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz-Robinson, E.M.; Badawi, N.; Walker, K.; Bajuk, B.; Abdel-Latif, M.E.; Bowen, J.; Sedgley, S.; Carlisle, H.; Smith, J.; Craven, P.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of premature infants treated for patent ductus arteriosus: A population-based cohort study. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 1025–1032.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheria, V.; Poeltler, D.; Brown, M.; Hassen, K.; Patel, D.; Rich, W.; Finer, N.; Katheria, A. Early prediction of a significant patent ductus arteriosus in infants < 32 weeks gestational age. J. Neonatal Perinat. Med. 2018, 11, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, E.-K.; Kim, H.-S. Association of increased cord blood soluble endoglin with the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants with maternal preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018, 13, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Sohn, J.A.; Oh, S.; Choi, B.M. Perinatal risk factors of symptomatic preterm patent ductus arteriosus and secondary ligation. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2020, 61, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matić, M.; Inati, V.; Abdel-Latif, M.E.; Kent, A.L.; Network, N.A.N. Maternal hypertensive disorders are associated with increased use of respiratory support but not chronic lung disease or poorer neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm neonates at <29 weeks of gestation. J. Paediatr. Child. Health. 2017, 53, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Soares, P.; Flor-de-Lima, F.; Neves, A.L.; Guimarães, H. PDA management in VLBW infants: Experience of a level III NICU. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2016, 5, e050227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olukman, O.; Ozdemir, R.; Karadeniz, C.; Calkavur, S.; Mese, T.; Vergin, C. Is there a relationship between platelet parameters and patency of ductus arteriosus in preterm infants? Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2017, 28, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patole, S.K.; Kumaran, V.; Travadi, J.N.; Brooks, J.M.; Doherty, D.A. Does patent ductus arteriosus affect feed tolerance in preterm neonates? Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007, 92, F53–F55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.; de Lima, F.F.; Machado, A.P.; Guimaraes, H. Preeclampsia predicts higher incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, V.; Pedini, A.; Santoni, M.; Scutti, G.; Colaneri, M.; Pozzi, M.; Cogo, P.E.; Carnielli, V.P. Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants born before 30 weeks’ gestation: High rate of spontaneous closure after hospital discharge. Cardiol. Young 2018, 28, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlapbach, L.J.; Ersch, J.; Adams, M.; Bernet, V.; Bucher, H.U.; Latal, B. Impact of chorioamnionitis and preeclampsia on neurodevelopmental outcome in preterm infants below 32 weeks gestational age. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellmer, A.; Bjerre, J.V.; Schmidt, M.R.; McNamara, P.J.; Hjortdal, V.E.; Høst, B.; Bech, B.H.; Henriksen, T.B. Morbidity and mortality in preterm neonates with patent ductus arteriosus on day 3. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013, 98, F505–F510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.A.; Hills, N.K.; Waleh, N.; McCurnin, D.; Seidner, S.; Chemtob, S.; Clyman, R. Relationship between circulating platelet counts and ductus arteriosus patency after indomethacin treatment. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 919–923.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekharappa, C.B.; Elizabeth, E.A.B.; Balachander, B. Association of patent ductus arteriosus size with clinical features and short-term outcomes in preterm infants less than 34 weeks. Indian J. Child Health. 2020, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.; Chaput, K.; Alshaikh, B.; Yusuf, K. Preeclampsia and the risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants less than 32 weeks’ gestation. Am. J. Perinatol. 2017, 34, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Huang, W.; Meng, Q.; Jia, C.; Shi, B.; Fan, X.; Cui, Q.; Chen, J.; Wu, F. Mothers with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy increased risk of periventricular leukomalacia in extremely preterm or extremely low birth weight infants: A propensity score analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 978373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumasu, H.; Tokumasu, S.; Kawakami, K. Impact of pre-eclampsia in extremely premature infants: Population-based study. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turunen, R.; Andersson, S.; Laivuori, H.; Kajantie, E.; Siitonen, S.; Repo, H.; Nupponen, I. Increased postnatal inflammation in mechanically ventilated preterm infants born to mothers with early-onset preeclampsia. Neonatology 2011, 100, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Bor, M.; Verloove-Vanhorick, S.P.; Brand, R.; Ruys, J.H. Patent ductus arteriosus in a cohort of 1338 preterm infants: A collaborative study. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 1988, 2, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, D.M.; Reidy, K.J.; Sharma, M.; Kim, M.; Vega, M.; Havranek, T. The effect of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus on acute kidney injury and systemic hypertension in extremely low gestational age newborns. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 32, 3209–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieux, R.; Desandes, R.; Boubred, F.; Semama, D.; Guillemin, F.; Buchweiller, M.-C.; Fresson, J.; Hascoet, J.-M. Ibuprofen in very preterm infants impairs renal function for the first month of life. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withagen, M.I.; Visser, W.; Wallenburg, H.C. Neonatal outcome of temporizing treatment in early-onset preeclampsia. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001, 94, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, T.-A.; Yang, H.-I.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Chou, H.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Tsou, K.-I.; Tsao, P.-N.; for the Taiwan Premature Infant Developmental Collaborative Study Group. Preeclampsia and the risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in VLBW infants: A population-based study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, Y.; Kutman, H.G.K.; Ulu, H.Ö.; Canpolat, F.E.; Uraş, N.; Oğuz, S.S.; Dilmen, U. Preeclampsia is an independent risk factor for spontaneous intestinal perforation in very preterm infants. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, S.K.; Moon, C.-J.; Youn, Y.-A.; Lee, J.Y.; Sung, I.K. Echocardiographic assessment of patent ductus arteriosus in very low birthweight infants over time: Prospective observational study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, N.; Fraser, W.D.; Healy-Profitós, J.; Arbour, L. Association between preeclampsia and congenital heart defects. JAMA 2015, 314, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, H.A.; Basit, S.; Behrens, I.; Leirgul, E.; Bundgaard, H.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Melbye, M.; Øyen, N. Association between fetal congenital heart defects and maternal risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in the same pregnancy and across pregnancies. Circulation 2017, 136, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwa, K.; Mebazaa, A. Possible joint pathways of early pre-eclampsia and congenital heart defects via angiogenic imbalance and potential evidence for cardio-placental syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llurba, E.; Sanchez, O.; Ferrer, Q.; Nicolaides, K.H.; Ruíz, A.; Domínguez, C.; Sánchez-De-Toledo, J.; García-García, B.; Soro, G.; Arévalo, S.; et al. Maternal and foetal angiogenic imbalance in congenital heart defects. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, H.; Dagle, J.M. Genetics of patent ductus arteriosus susceptibility and treatment. Semin. Perinatol. 2012, 36, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.J. The patent ductus arteriosus in term infants, children, and adults. Semin. Perinatol. 2012, 36, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterbrook, P.J.; Gopalan, R.; Berlin, J.; Matthews, D.R. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 1991, 337, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwan, K.; Altman, D.G.; Arnaiz, J.A.; Bloom, J.; Chan, A.-W.; Cronin, E.; Decullier, E.; Easterbrook, P.J.; Von Elm, E.; Gamble, C. Systematic review of the empirical evidence of study publication bias and outcome reporting bias. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Syngelaki, A.; Nicolaides, K.H.; von Dadelszen, P.; Magee, L.A. Impact of new definitions of preeclampsia at term on identification of adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 224, 518.e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Outcome | Subgroup | K | OR | 95% Credible Interval | BF10 | Evidence for | p-Value a | BFrf | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | H1 | H0 | |||||||
| Any PDA | All | 17 | 1.06 | 0.78 | 1.42 | 0.20 | Mod. | 0.514 | >107 | |
| Any HDP | 5 | 1.20 | 0.70 | 2.01 | 0.44 | Weak | 0.524 | 60.89 | ||
| Preeclampsia | 7 | 0.84 | 0.51 | 1.37 | 0.30 | Mod. | 0.605 | 21.94 | ||
| Preeclampsia/HELLP | 5 | 1.19 | 0.70 | 2.03 | 0.39 | Weak | 0.543 | >103 | ||
| Hemodynamically significant PDA | All | 25 | 0.89 | 0.74 | 1.08 | 0.27 | Mod. | 0.348 | >106 | |
| Any HDP | 8 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 1.12 | 0.45 | Weak | 0.316 | 4.56 | ||
| Preeclampsia | 15 | 0.95 | 0.73 | 1.26 | 0.17 | Mod. | 0.401 | >105 | ||
| Preeclampsia/HELLP | 2 | 0.67 | 0.35 | 1.71 | 1.20 | Weak | 0.603 | 2.15 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borges-Luján, M.; Galán-Henríquez, G.; Rodríguez-Viera, R.I.; Bartoš, F.; González-Luis, G.E.; Villamor, E. Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants: A Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis. Children 2025, 12, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060762
Borges-Luján M, Galán-Henríquez G, Rodríguez-Viera RI, Bartoš F, González-Luis GE, Villamor E. Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants: A Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis. Children. 2025; 12(6):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060762
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorges-Luján, Moreyba, Gloria Galán-Henríquez, Rosa I. Rodríguez-Viera, František Bartoš, Gema E. González-Luis, and Eduardo Villamor. 2025. "Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants: A Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis" Children 12, no. 6: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060762
APA StyleBorges-Luján, M., Galán-Henríquez, G., Rodríguez-Viera, R. I., Bartoš, F., González-Luis, G. E., & Villamor, E. (2025). Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants: A Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis. Children, 12(6), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060762







