The Frequency and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury in Children with Oncological Diseases: A Single-Center Study in Bulgaria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aim
3. Patients and Methods
- Age between 0 and 18 years;
- The diagnosis of the primary disease—solid tumors or malignant hemopathies;
- Newly diagnosed patients admitted for initial treatment.
- Children with pre-existing kidney diseases;
- Children with CKD;
- Patients who have undergone bone marrow transplantation.
- Age at the diagnosis of the oncological disease;
- The type of disease (solid tumor or malignant hemopathy);
- Renal infiltration at disease onset;
- The presence of other comorbidities (heart failure, neurological impairment, liver dysfunction, respiratory failure, infection—including sepsis);
- Evidence of acute tumor lysis syndrome;
- Laboratory data at admission and during treatment (serum creatinine, urea, electrolytes, blood gas analysis, and urinalysis);
- Chemotherapy with nephrotoxic agents (high-dose Methotrexate, Ifosfamide, Cisplatin, and Carboplatin).
4. AKI Criteria
5. Statistical Methods
6. Results
6.1. The Characteristics of the Patients
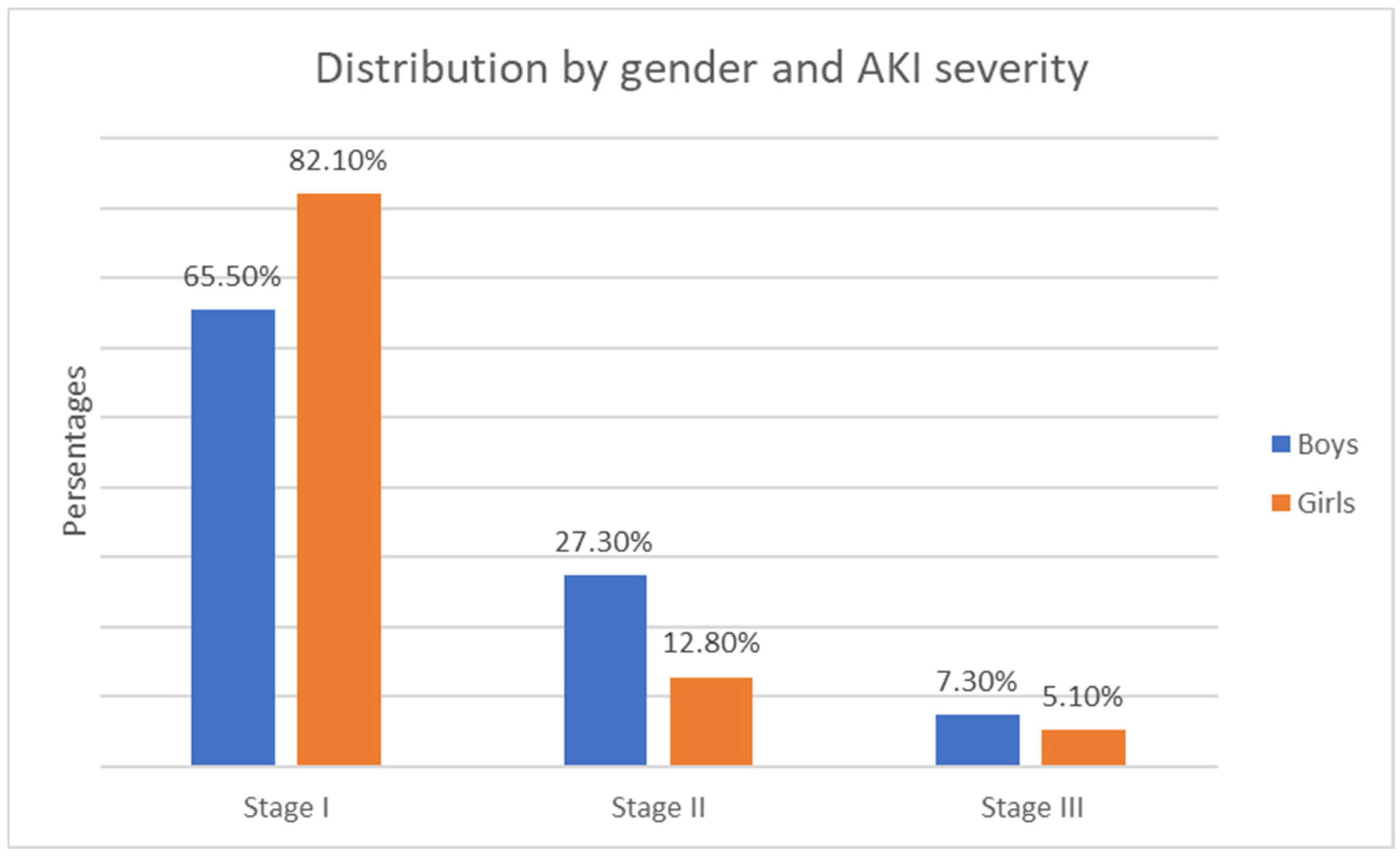
- Gender distribution—122 boys (57.3%) and 91 girls (42.7%). The relative proportion of boys compared to girls is significantly higher in both the solid tumor group and the malignant hematologic disorder group (Figure 1).
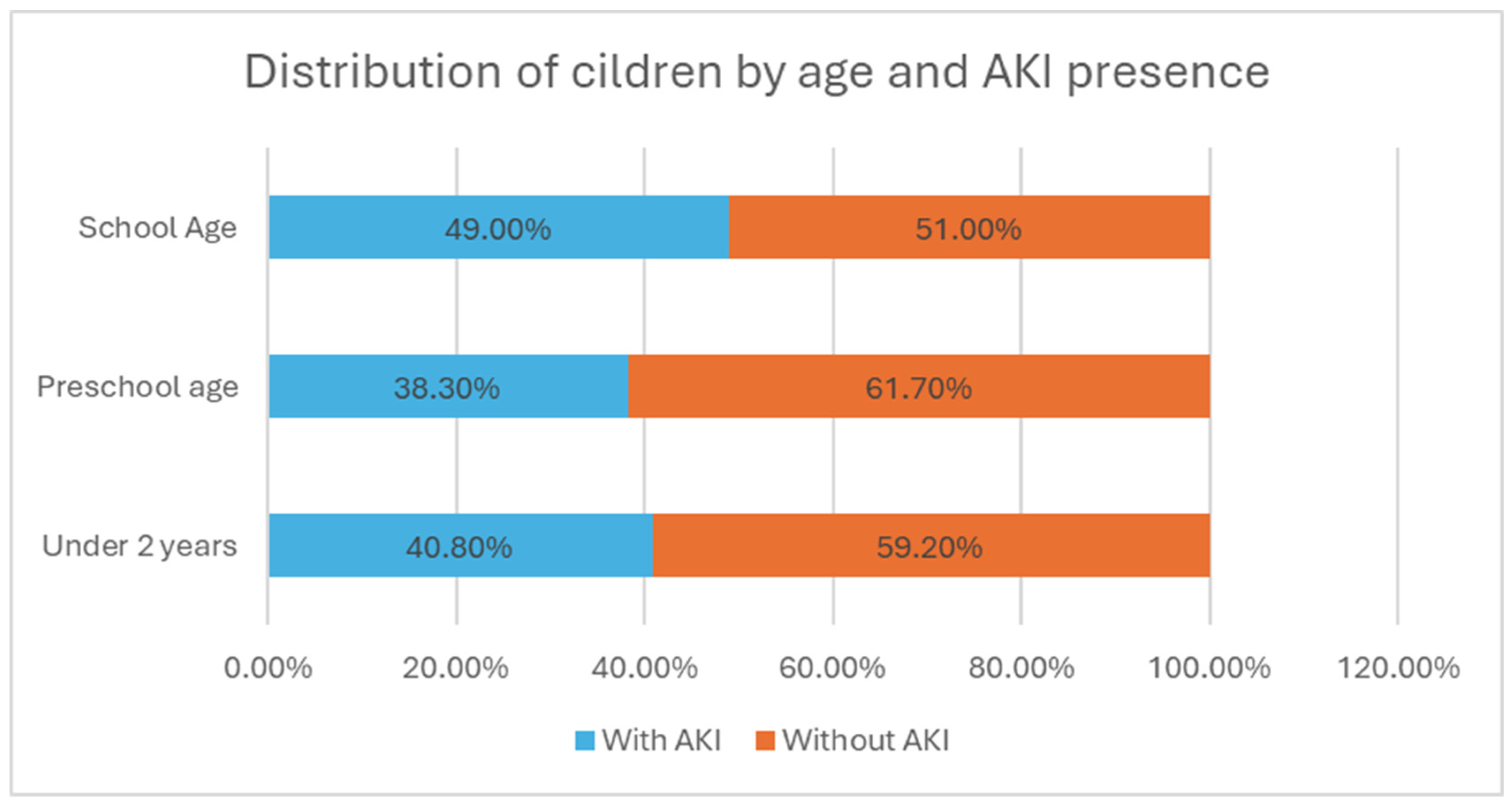
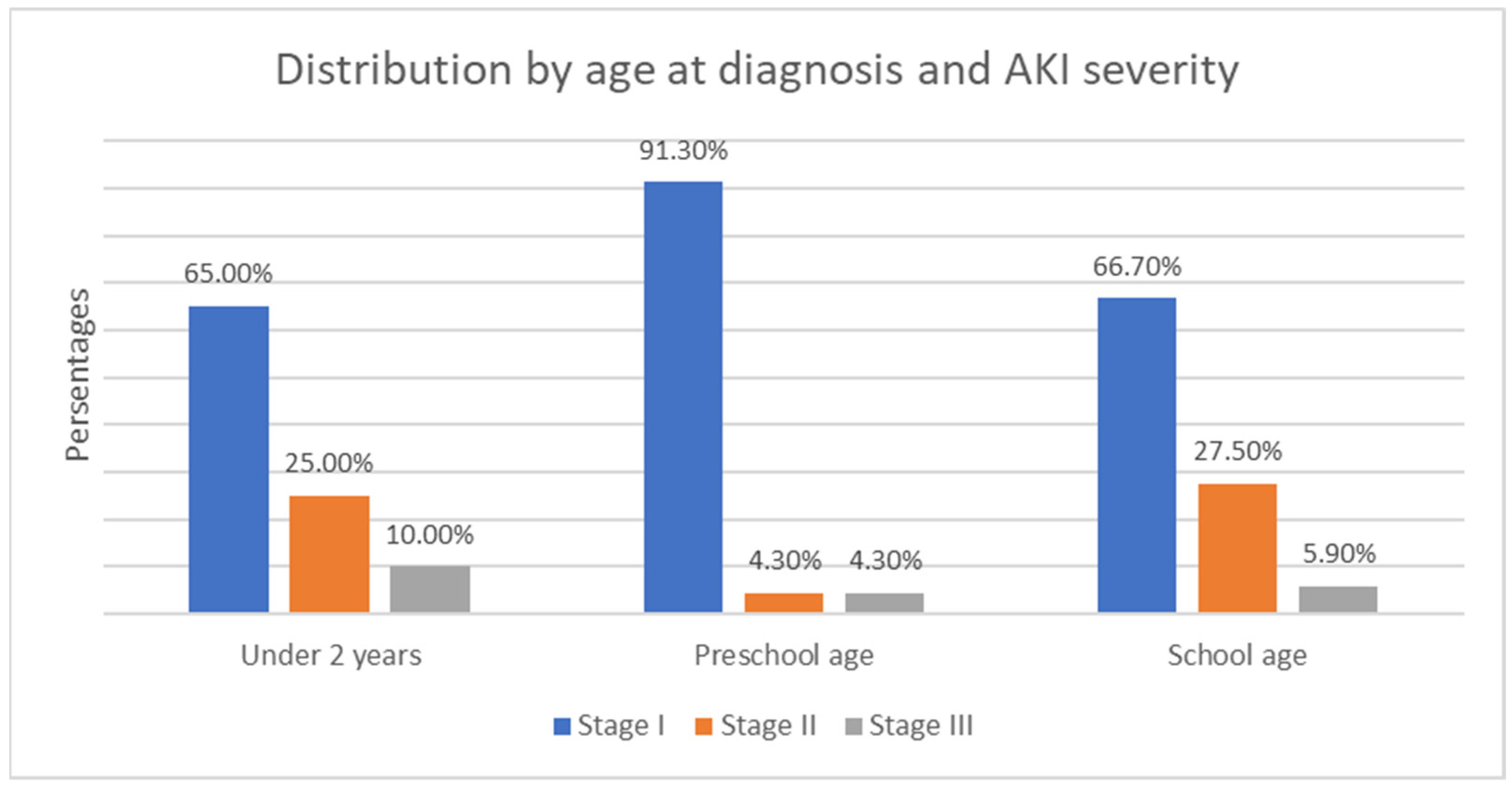
- The age of onset divides the children into three subgroups—under 2 years, preschool age, and school age. In the first group, there were 49 children, (23% of all children); in the second, there were 60 children (28.2%); and in the third, there were 104 children (48.8%) (Figure 2). The group with the highest relative proportion are the school-age children, both in terms of solid tumors (27.23%) and malignant hematologic disorders (21.60%). However, there is no statistically significant difference in the distribution of age groups between the two types of malignant diseases (χ2 = 4.68, p = 0.096).
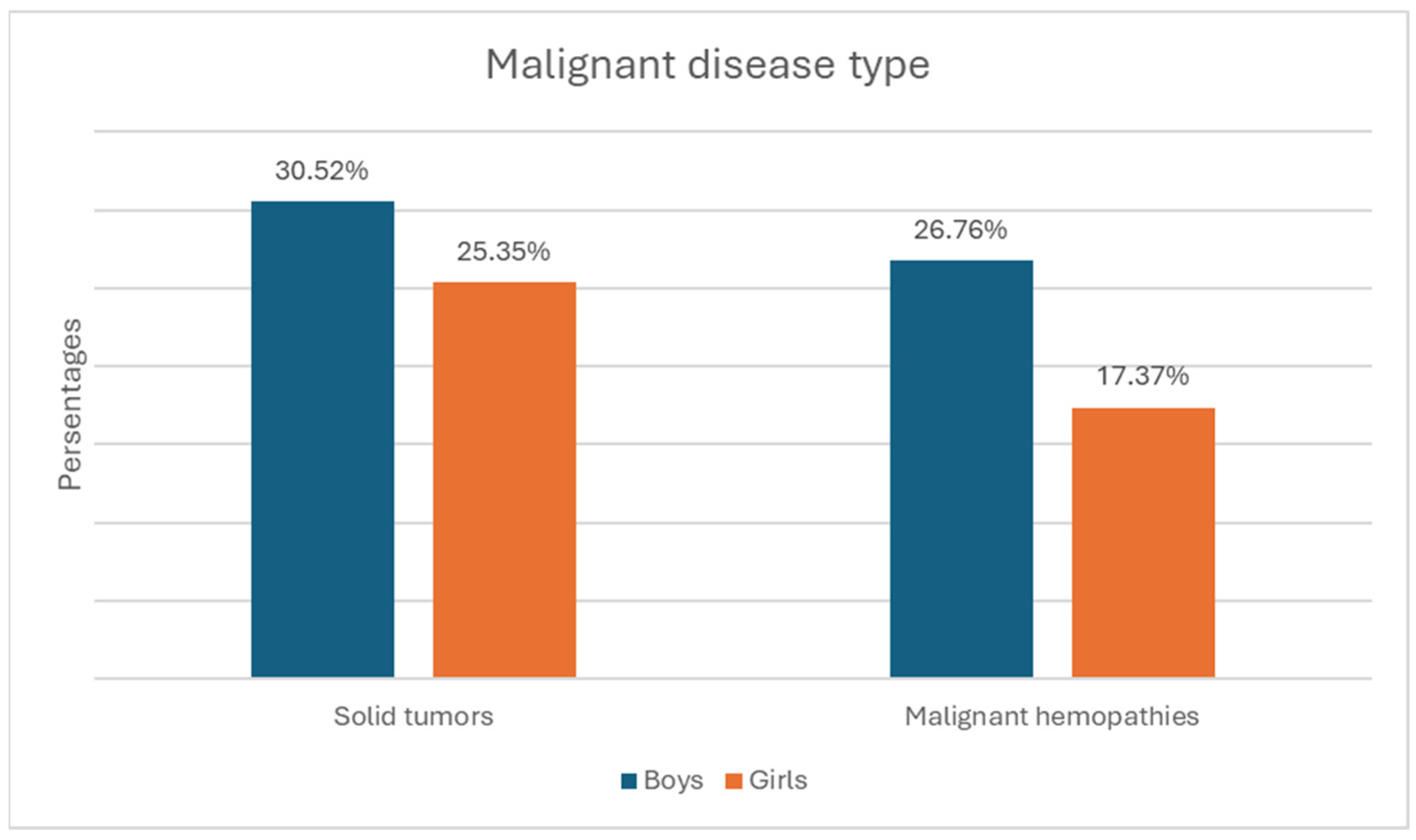
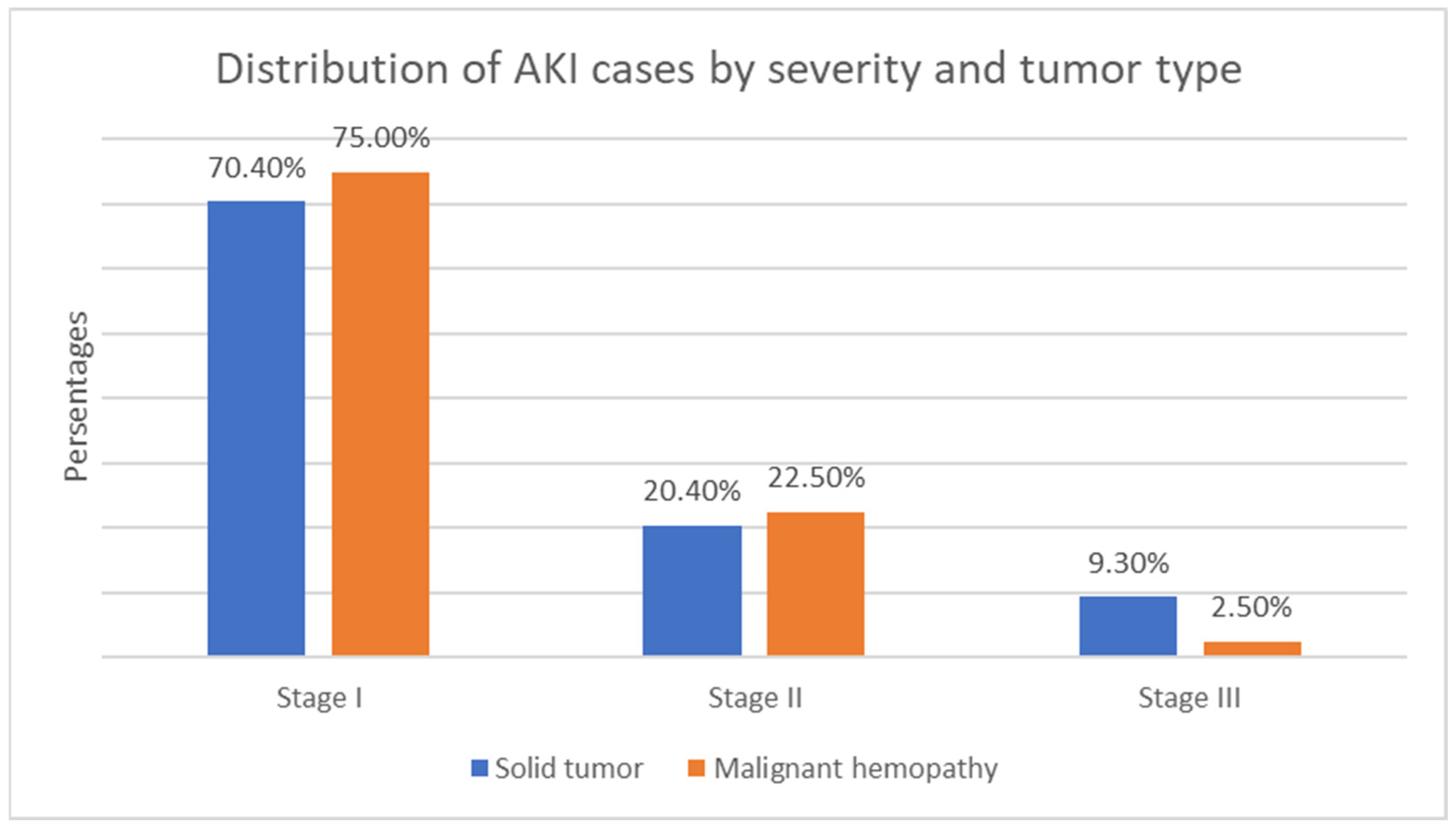
- Malignant disease type—119 children (55.9%) with solid tumors and 94 (44.1%) with malignant hematologic disorders. The relative proportion of boys compared to girls is higher in both the solid tumor group and the malignant hematologic disorder group (Figure 3). However, this difference is not statistically significant (χ2 = 0.55, p = 0.458).
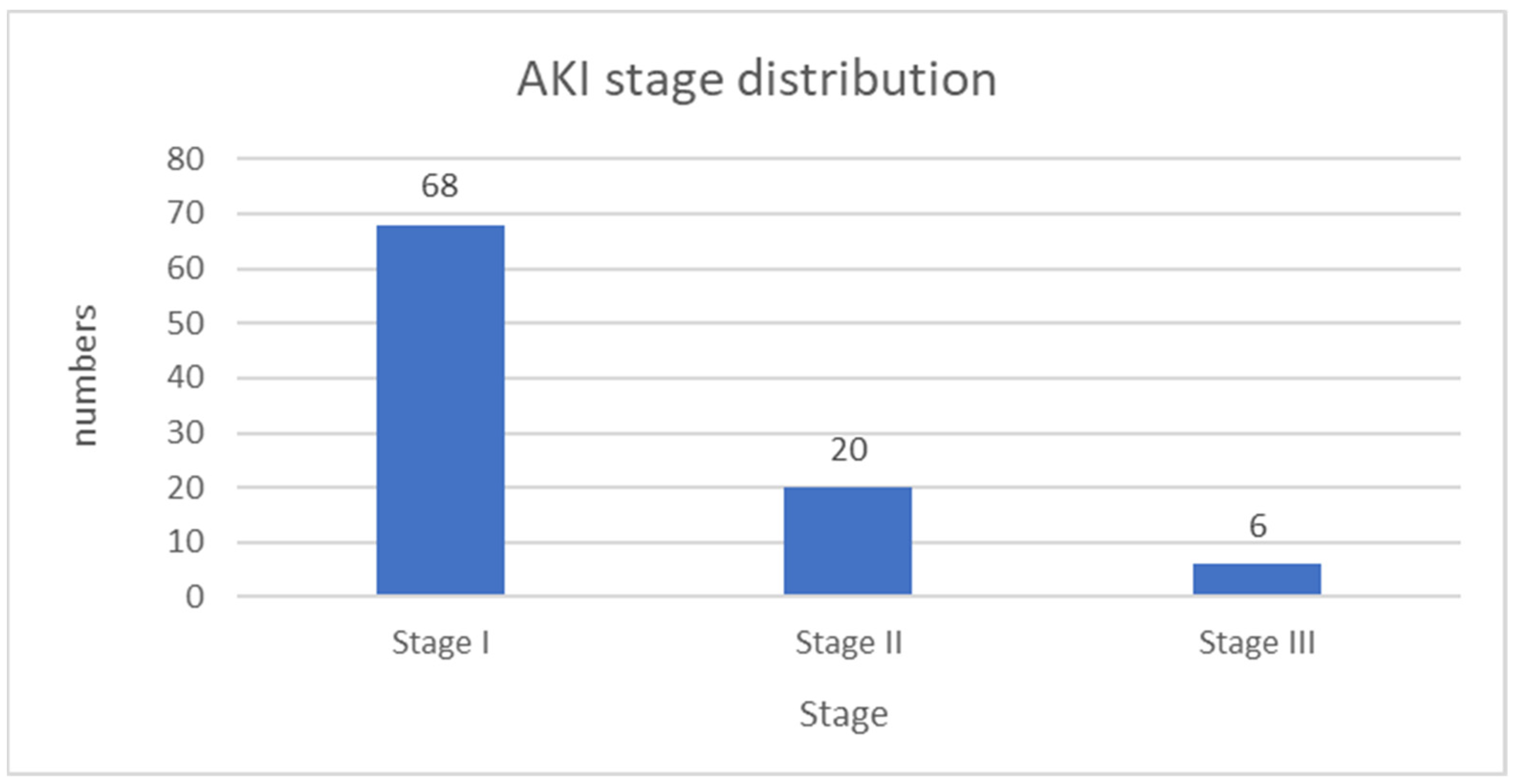
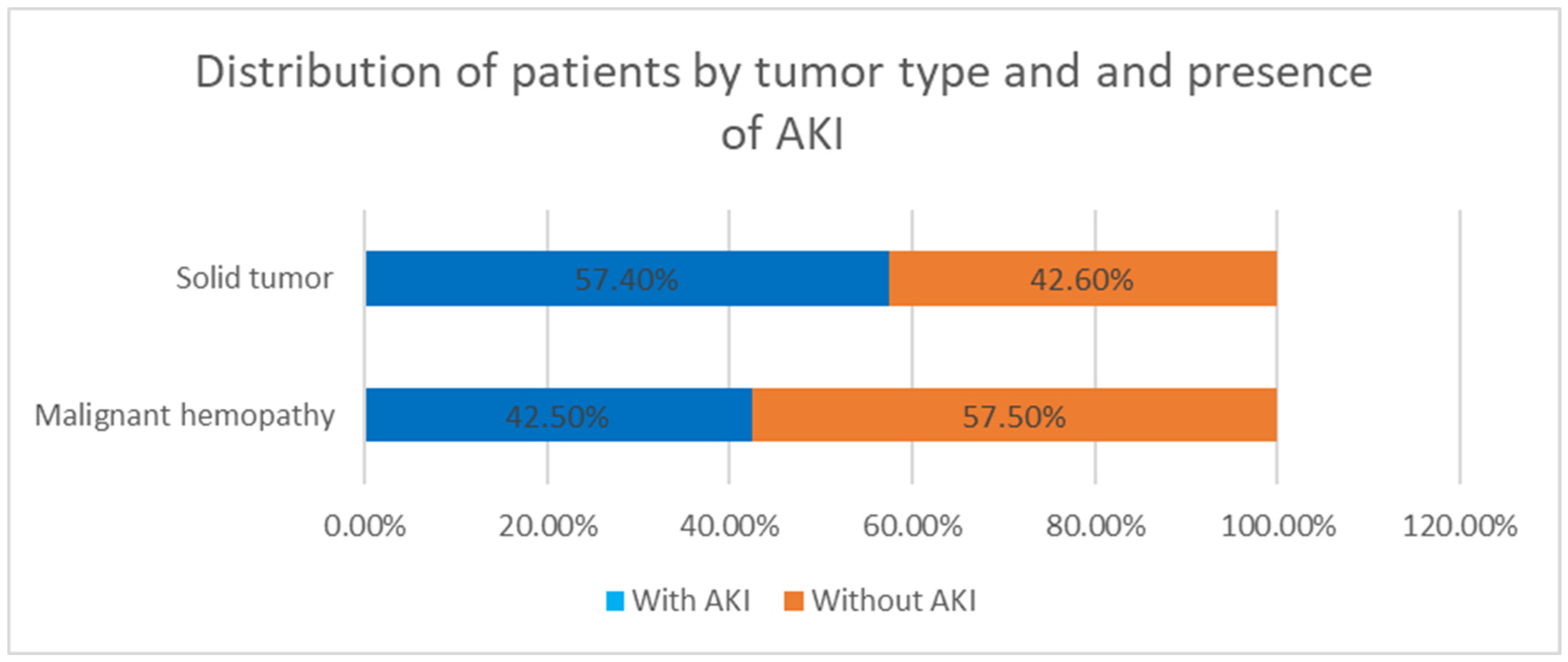
6.2. Acute Kidney Injury
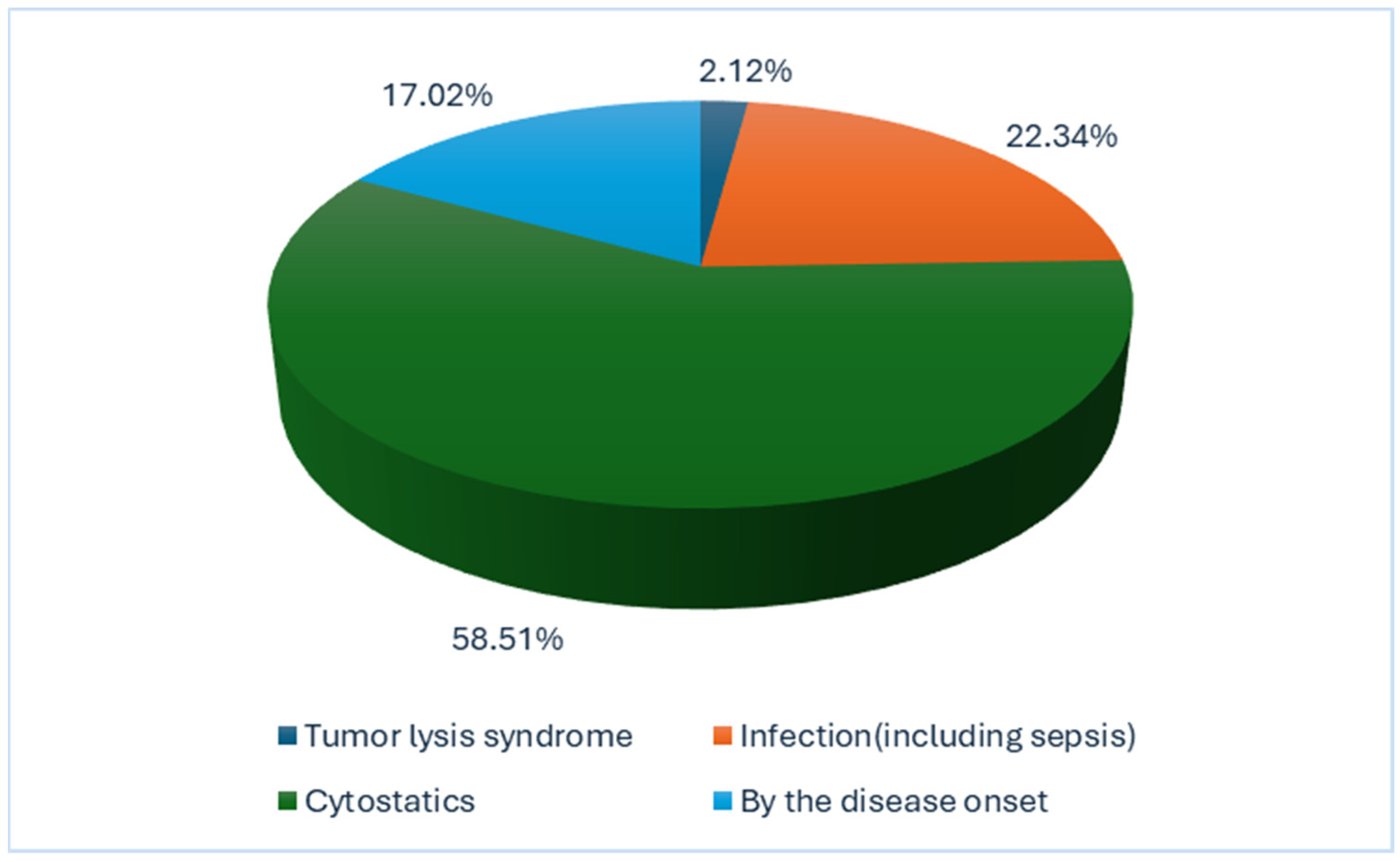
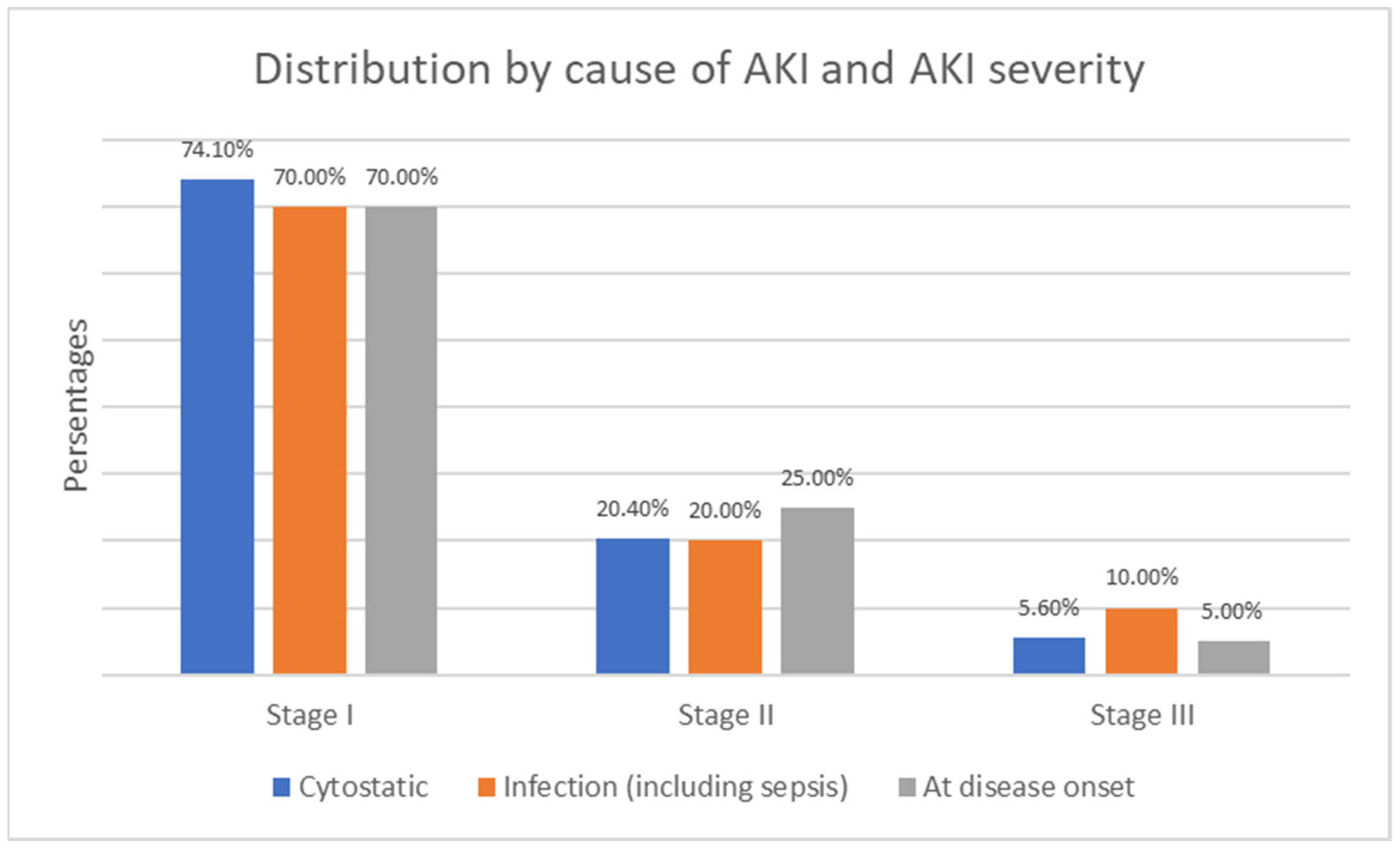
6.3. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Risk Factors
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, M.; Wang, L.; Su, L.; Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Nie, S.; Hou, F.F. Acute kidney injury among hospitallised children with cancer. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.P.; Luiz, G.C.F.; De-Oliveira, S.T.; De-Santa, L.N.; Borsato, G.S.; João, P.R.D. Acute kidney injury in children with cancer admitted in an intensive care unit. Braz. J. Oncol. 2022, 18, e-20220291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabbagh, E.M.; Hashmat, S. Acute kidney injury in childhood cancer: An insight from Kids’ Inpatient Database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e18379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.G.; Hong, C.R.; Kang, E.; Park, M.; Lee, H.; Kang, H.J.; Shin, H.Y.; Ha, I.-S.; Cheong, H.I.; Yoon, H.J.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Cancer Patients. J. Pediatr. 2019, 208, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, B.T.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Leckerman, K.H.; Localio, R.; Aplenc, R. Risk Factors for Renal Failure in Pediatric Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kist-van Holthe, J.E.; Goedvolk, C.A.; Brand, R.; van Weel, M.H.; Bredius, R.G.; van Oostayen, J.A.; Vossen, J.M.; van der Heijden, B.J. Prospective study of renal insufficiency after bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2002, 17, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.L.; Hingorani, S. Outcomes of kidney injury including dialysis and kidney transplantation in pediatric oncology and hematopoietic cell transplant patients. J. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didsbury, M.S.; Mackie, F.E.; Kennedy, S.E. A systematic review of acute kidney injury in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell recipients. Pediatr. Transplant. 2015, 19, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habas, E.; Akbar, R.M.; Farfar, K.M.; Arrayes, N.M.; Habas, A.M.; Rayani, A.M.; Alfitori, G.M.; Habas, E.M.; Magassabi, Y.S.; Ghazouani, H.M.; et al. Malignancy diseases and kidneys: A nephrologist prospect and updated review. Medicine 2023, 102, e33505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, R.L.; Brewster, U.C. Kidney Involvement in Leukemia and Lymphoma. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014, 21, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-N.; Diao, Z.-L.; Guan, Y.-M.; Liu, W.-H. Acute Kidney Injury in Oncology Patients. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meraz-Munoz, A.; Langote, A.; Jhaveri, K.D.; Izzedine, H.; Gudsoorkar, P. Acute Kidney Injury in the Patient with Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.Y.; Chan, E.Y.-H.; Cheng, F.W.T.; Ma, A.L.T.; Ha, S.Y. Acute kidney injury in children with haematological malignancy: A territory-wide study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 3823–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.K.; Norbert, L.; Peter, A.; Rashad, S.B.; Emmanuel, A.B.; Stuart, L.G.; Charles, A.H.; Michael, J.; Andreas, K.; Andrew, S.L. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, M.; Johnson, R.J.; May, W.S.; Lingegowda, V.; Sood, P.; Nakagawa, T.; Van, Q.C.; Dass, B.; Ejaz, A.A. A novel role for uric acid in acute kidney injury associated with tumour lysis syndrome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2960–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, M.S.; Bishop, M. Tumour lysis syndrome: New therapeutic strategies and classification. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 127, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.L.; Hon, K.L.; Fung, C.M.; Leung, A.K. Tumor lysis syndrome in childhood malignancies. Drugs Context 2020, 9, 2019-8-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Altman, A.; Pui, C.-H.; Younes, A.; Cairo, M.S. Guidelines for the Management of Pediatric and Adult Tumor Lysis Syndrome: An Evidence-Based Review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2767–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105 (Suppl. S4), S117–S314. [Google Scholar]
- Du Plessis, L.; Rassekh, S.R.; Mammen, C. High incidence of acute kidney injury during chemotherapy for childhood acute myeloid leukemia. J. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, R.; Haq, A.U.; Ahmed, A.R.; Saeed, A.; Khan, M.R. Prevalence, risk factors and outcomes of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with hematological malignancies. Int. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2024, 11, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoti, A.; Chen, S. Acute kidney injury—Incidence, pathogenesis, outcomes. In Onco-Nephrology; Finkel, K., Perazella, M., Cohen, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 270–274. [Google Scholar]
- Stotter, B.R.; Chan, C.; Chanchlani, R. Late Kidney Effects of Childhood Cancer and Cancer Therapies. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2021, 28, 490–501.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.A.S.; Elsalam, H.B.A.; El-Deeb, S.M.; Zanaty, F.M.; Aboelghar, H.M.; Elharoun, M.S. Evaluation of kidney dysfunction in childhood cancer survivors. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Category | Average Number of Episodes | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKI severity | Stage I | 1.15 | 0.3964 | 1 | 3 |
| Stage II | 1.4 | 0.5982 | 1 | 3 | |
| Stage III | 1.33 | 0.5164 | 1 | 2 | |
| AKI cause | Drug cytostatic | 1.22 | 0.4196 | 1 | 2 |
| Infection; sepsis | 1.3 | 0.6569 | 1 | 3 | |
| Renal infiltration at disease onset | 1.13 | 0.3416 | 1 | 2 | |
| Tumor type | Solid tumor | 1.24 | 0.4733 | 1 | 3 |
| Malignant hemopathy | 1.18 | 0.4465 | 1 | 3 | |
| Neprotoxic Drug | Number of Children Who Developed AKI |
|---|---|
| Methotrexate | 20 |
| Ifosfamide | 9 |
| Cisplatin | 2 |
| Carboplatin | 3 |
| Year | Number of Patients | Disease Type | AKI Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Park at all [4] 2004–2013 | 1868 | Malignant hemopathies and solid tumors | 52.6% |
| Xiong M. at all [1] 2013–2015 | 9829 | Malignant hemopathies and solid tumors | 16.9% |
| Plessis L. at all [20] 2018 | 53 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 64% |
| Tariq R. at all [21] 2017–2019 | 399 | Malignant hemopathies and solid tumors | 21.33% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markova, P.; Yaneva, A.; Markov, S.; Spasova, M.; Spasov, N. The Frequency and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury in Children with Oncological Diseases: A Single-Center Study in Bulgaria. Children 2025, 12, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050540
Markova P, Yaneva A, Markov S, Spasova M, Spasov N. The Frequency and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury in Children with Oncological Diseases: A Single-Center Study in Bulgaria. Children. 2025; 12(5):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050540
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkova, Petya, Antoniya Yaneva, Stoyan Markov, Mariya Spasova, and Neofit Spasov. 2025. "The Frequency and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury in Children with Oncological Diseases: A Single-Center Study in Bulgaria" Children 12, no. 5: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050540
APA StyleMarkova, P., Yaneva, A., Markov, S., Spasova, M., & Spasov, N. (2025). The Frequency and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury in Children with Oncological Diseases: A Single-Center Study in Bulgaria. Children, 12(5), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050540






