Lymphopenia as an Independent Marker of Disease Activity in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Sample Size and Statistical Analysis
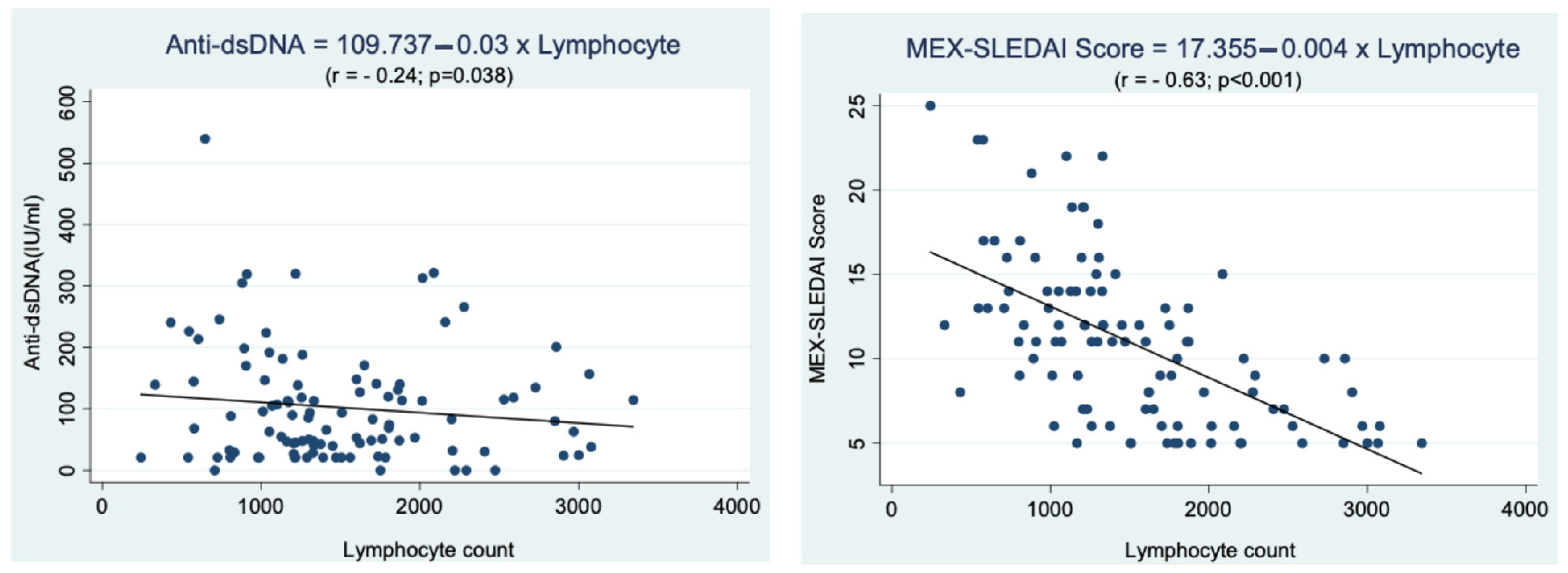
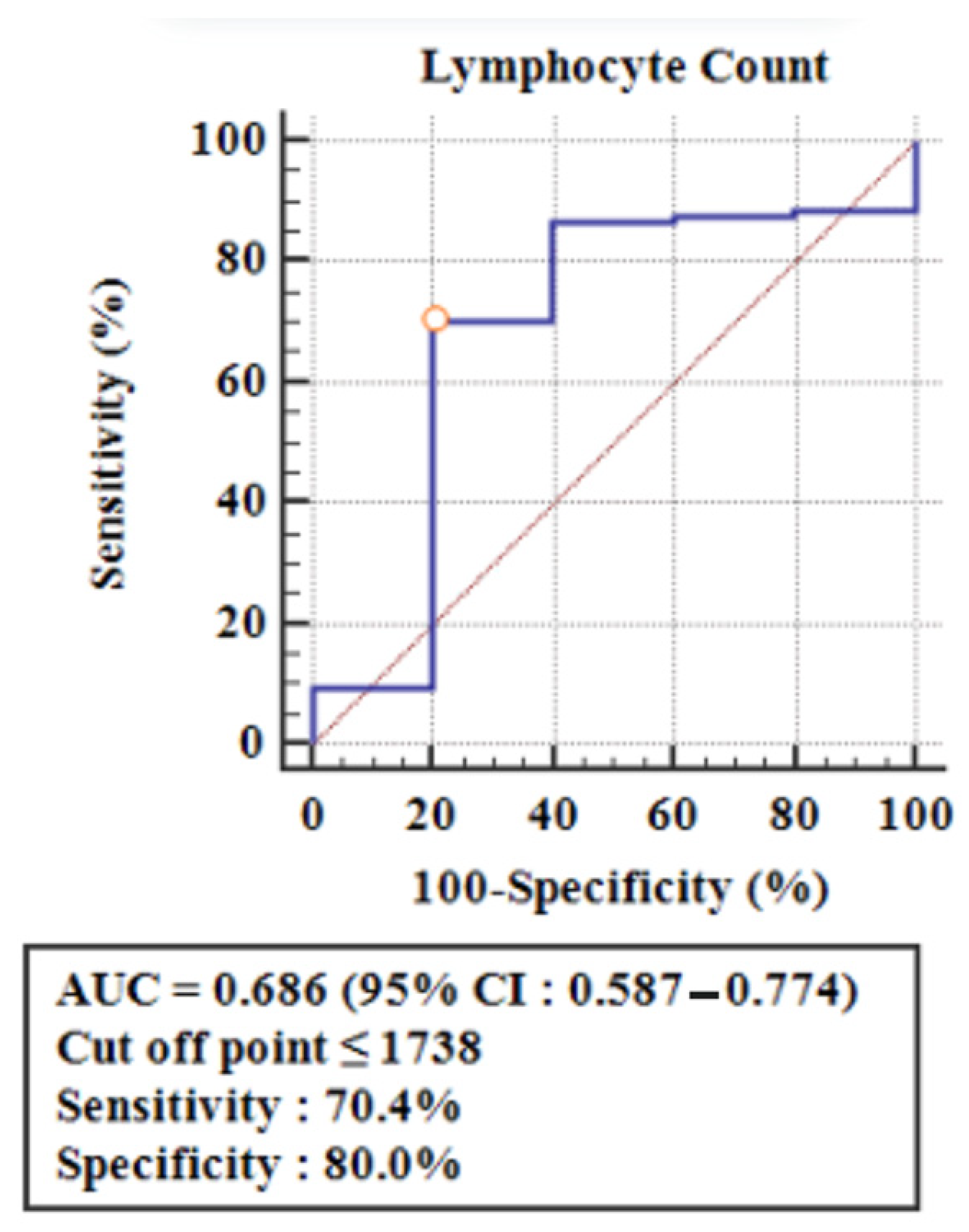
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faddah, S.; Elwakd, M.; Aboelenein, A.; Hussein, M. Lymphopenia and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, a Preliminary Study: Correlation with Clinical Manifestations, Disease Activity and Damage Indices. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2014, 36, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.M.; Kamphuis, S. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 59, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsalou, J.; Levy, D.M.; Silverman, E.D. An Update on Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2013, 25, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.P.; Lim, S.C.; Arkachaisri, T. Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Southeast Asian Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.K.; Satria, C.D.; Arguni, E. Predictors of Infection in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Single Center Study in Indonesia. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2021, 8, 2333794X2110056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, H.I.; Feldman, B.M.; Bombardier, C.; Silverman, E.D. Sensitivity of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index, British Isles Lupus Assessment Group Index, and Systemic Lupus Activity Measure in the Evaluation of Clinical Change in Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, A.G.; Vilá, L.M.; McGwin, G.; Sanchez, M.L.; Reveille, J.D.; Alarcón, G.S. The Systemic Lupus Activity Measure-Revised, the Mexican Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI), and a Modified SLEDAI-2K Are Adequate Instruments to Measure Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Massardo, L.; Metz, C.; Pardo, E.; Mezzano, V.; Babul, M.; Jarpa, E.; Guzmán, A.; André, S.; Kaltner, H.; Gabius, H.; et al. Autoantibodies against Galectin-8: Their Specificity, Association with Lymphopenia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Detection in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Acute Inflammation. Lupus 2009, 18, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merayo-Chalico, J.; Gomez-Martin, D.; Pineirua-Menendez, A.; Santana-De Anda, K.; Alcocer-Varela, J. Lymphopenia as Risk Factor for Development of Severe Infections in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Case-Control Study. QJM Int. J. Med. 2013, 106, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Chu, C.M.; Wu, A.K.L.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Lymphopenia at Presentation Is Associated with Increased Risk of Infections in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. QJM Int. J. Med. 2006, 99, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilá, L.M.; Alarcón, G.S.; McGwin, G.; Bastian, H.M.; Fessler, B.J.; Reveille, J.D. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Multiethnic US Cohort, XXXVII: Association of Lymphopenia with Clinical Manifestations, Serologic Abnormalities, Disease Activity, and Damage Accrual. Arthritis Care Res. 2006, 55, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, S.J.; Díaz-Jouanen, E.; Alarcón-Segovia, D. Lymphopenia In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978, 21, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzayan, M.J. Prognostic Parameters for Flare in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsinger, P.D. Relationship of Lymphocytotoxic Antibodies to Lymphopenia and Parameters of Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 1976, 3, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lenert, P.; Lenert, G.; Senécal, J.-L. CD4-Reactive Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Hum. Immunol. 1996, 49, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, J.; Cardiel, M.H.; Arce-Salinas, A.; Sánchez-Guerrero, J.; Alarcón-Segovia, D. Measurement of Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Prospective Validation of 3 Clinical Indices. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Suszek, D.; Dubaj, M.; Bigosiński, K.; Dembowska, A.; Kaniewski, M.; Sielwanowska, W.; Skierkowski, B.; Dzikowska, I.; Sieczka, J.; Majdan, M. Usefulness in Daily Practice of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 Scale and the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Score Index for Assessing the Activity of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Reumatologia 2024, 62, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.E. Pediatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: More Than a Positive Antinuclear Antibody. Pediatr. Rev. 2012, 33, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, H.I.; Huggins, J.; Klein-Gitelman, M.S. Pediatric SLE—Towards a Comprehensive Management Plan. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrahani, R.; Setiabudiawan, B.; Sapartini, G. Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran. Maj. Kedokt. Bandung 2015, 47, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evalina, R. Gambaran Klinis Dan Kelainan Imunologis Pada Anak Dengan Lupus Eritematosus Sistemik Di Rumah Sakit Umum Pusat Adam Malik Medan. Sari Pediatr. 2016, 13, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, N.; Niazy, M.H.; Kamal, A. Lymphopenia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: Is It More than a Laboratory Finding? Egypt. Rheumatol. 2020, 42, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, K.; Arimura, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Nagasawa, T. Anti-T Cell Antibodies in Primary Glomerulonephritis. Clin. Nephrol. 1985, 23, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuz, S.; Cansu, D.U.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Crisafulli, F.; Antunes, A.M.; Adamichou, C.; Reid, S.; Stagnaro, C.; Andreoli, L.; Tincani, A.; et al. Lymphopenia as a Risk Factor for Neurologic Involvement and Organ Damage Accrual in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Multi-Center Observational Study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-H.; Wang, L.-C.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chiang, B.-L. Lymphopenia Is Associated with Neuropsychiatric Manifestations and Disease Activity in Paediatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1492–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mu, R.; Lu, X.; He, J.; Jia, R.; Li, Z. Antilymphocyte Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association with Disease Activity and Lymphopenia. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 672126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Igoe, A.; Kurien, B.T.; Danda, D.; James, J.A.; Stafford, H.A.; Scofield, R.H. Haematological Manifestations of Lupus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2015, 2, e000078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguia-Realpozo, P.; Mendoza-Pinto, C.; Sierra Benito, C.; Escarcega, R.O.; Garcia-Carrasco, M.; Mendez Martinez, S.; Etchegaray Morales, I.; Galvez Romero, J.L.; Ruiz-Arguelles, A.; Cervera, R. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Hypertension. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Ueno, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Watanabe, T.; Kuroda, T.; Ito, S.; Arakawa, M. Renal Haemodynamic Characteristics in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.; Garcia, A.B.; Donadi, E.A. Increased Lymphocyte Death by Neglect-Apoptosis Is Associated with Lymphopenia and Autoantibodies in Lupus Patients Presenting with Neuropsychiatric Manifestations. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandane-Rathnayake, R.; Louthrenoo, W.; Golder, V.; Luo, S.-F.; Wu, Y.-J.J.; Lateef, A.; Cho, J.; Li, Z.; An, Y.; Hamijoyo, L.; et al. Independent Associations of Lymphopenia and Neutropenia in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Longitudinal, Multinational Study. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 5185–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.K.; Wysham, K.D.; Cain, K.C.; Tyden, H.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Lood, C. Neutrophil and Lymphocyte Counts Are Associated with Different Immunopathological Mechanisms in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2020, 7, e000382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Lymphopenia (n = 58) | Non-Lymphopenia (n = 45) | Total (n = 103) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 12.67 ± 2.76 | 11.3 ± 3.17 | |
| 2–6 years | 0 (0%) | 2 (100%) | 2 (100%) |
| 6–12 years | 23 (47.9%) | 25 (52.1%) | 48 (100%) |
| 12–18 years | 35 (66%) | 18 (34%) | 53 (100%) |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 4 (66.7%) | 2 (33.3%) | 6 (100%) |
| Female | 54 (55.7%) | 43 (44.3%) | 97 (100%) |
| Clinical Manifestation | Lymphopenia (n = 58) | Non lymphopenia (n = 45) | p-Value | Prevalence Ratio (CI 95%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constitutional | ||||
| Fever | 21 (36.2%) | 11 (24.4%) | 0.201 | 1.48 (0.80–2.74) |
| Fatigue | 19 (32.8%) | 19 (42.2%) | 0.323 | 0.70 (0.47–1.28) |
| Weight loss | 12 (20.7%) | 12 (26.7%) | 0.477 | 0.70 (0.39–1.56) |
| Mucocutaneous | ||||
| Malar rash | 35 (60.3%) | 26 (57.8%) | 0.631 | 1.04 (0.75–1.45) |
| Discoid rash | 15 (25.9%) | 15 (33.3%) | 0.408 | 0.78 (0.43–1.41) |
| Photosensitivity | 17 (29.3%) | 13 (28.9%) | 0.963 | 1.01 (0.55–1.86) |
| Oral ulcer | 23 (39.7%) | 16 (35.6%) | 0.671 | 1.12 (0.67–1.85) |
| Alopecia | 25 (43.1%) | 26 (57.8%) | 0.140 | 0.75 (0.51–1.10) |
| Joints | ||||
| Arthralgia | 22 (37.9%) | 18 (40%) | 0.831 | 0.95 (0.50–1.54) |
| Arthritis | 17 (29.3%) | 16 (35.6%) | 0.500 | 0.82 (0.47–1.44) |
| Cardiopulmonary | ||||
| Pleural effusion | 13 (22.4%) | 5 (11.1%) | 0.134 | 2.02 (0.78–5.24) |
| Pericardial effusion | 12 (20.7%) | 13 (28.9%) | 0.336 | 0.72 (0.36–1.42) |
| Valve anomaly | 3 (5.2%) | 2 (4.4%) | 1.000 * | 1.16 (0.20–6.67) |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 3 (5.2%) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.410 * | 2.33 (0.25–21.63) |
| Dilated cardiomyopathy | 4 (6.9%) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.303 * | 3.10 (0.36–26.82) |
| Vascular | ||||
| Raynaud’s phenomenon | 1 (1.7%) | 1 (2.2%) | 1.000 * | 0.70 (0.05–12.07) |
| Gangrene | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Kidney | ||||
| Nephritis | 42 (72.4%) | 6 (13.3%) | <0.001 # | 10.86 (3.60–32.79) |
| Hypertension | 14 (24.1%) | 3 (6.7%) | 0.018 # | 3.62 (1.11–11.84) |
| Neuropsychiatry | ||||
| Psychosis and seizure | 16 (27.6%) | 0 | <0.001 # | - |
| Hematology | ||||
| Hemolytic anemia | 41 (70.7%) | 33 (73.3%) | 0.767 | 0.96 (0.76–1.23) |
| Leukopenia | 21 (36.2%) | 3 (6.7%) | <0.001 # | 5.43 (1.73–17.07) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 6 (10.3%) | 3 (6.7%) | 0.728 * | 1.55 (0.41–5.87) |
| Anti-dsDNA Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Reactive n (%) | Non-Reactive (%) | Total n (%) |
| Lymphocyte ≤ 1738 | 69 (70.4%) | 1 (20%) | 70 (68%) |
| Lymphocyte > 1738 | 29 (29.6%) | 4 (80%) | 33 (32%) |
| Total | 98 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 103 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sapartini, G.; Ghrahani, R.; Setiabudiawan, B. Lymphopenia as an Independent Marker of Disease Activity in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Children 2025, 12, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040486
Sapartini G, Ghrahani R, Setiabudiawan B. Lymphopenia as an Independent Marker of Disease Activity in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Children. 2025; 12(4):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040486
Chicago/Turabian StyleSapartini, Gartika, Reni Ghrahani, and Budi Setiabudiawan. 2025. "Lymphopenia as an Independent Marker of Disease Activity in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Children 12, no. 4: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040486
APA StyleSapartini, G., Ghrahani, R., & Setiabudiawan, B. (2025). Lymphopenia as an Independent Marker of Disease Activity in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Children, 12(4), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040486







