Development of the Aquatic Competence Assessment for Children (ACA-C): A Tool for Measuring Personal Aquatic Competence Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
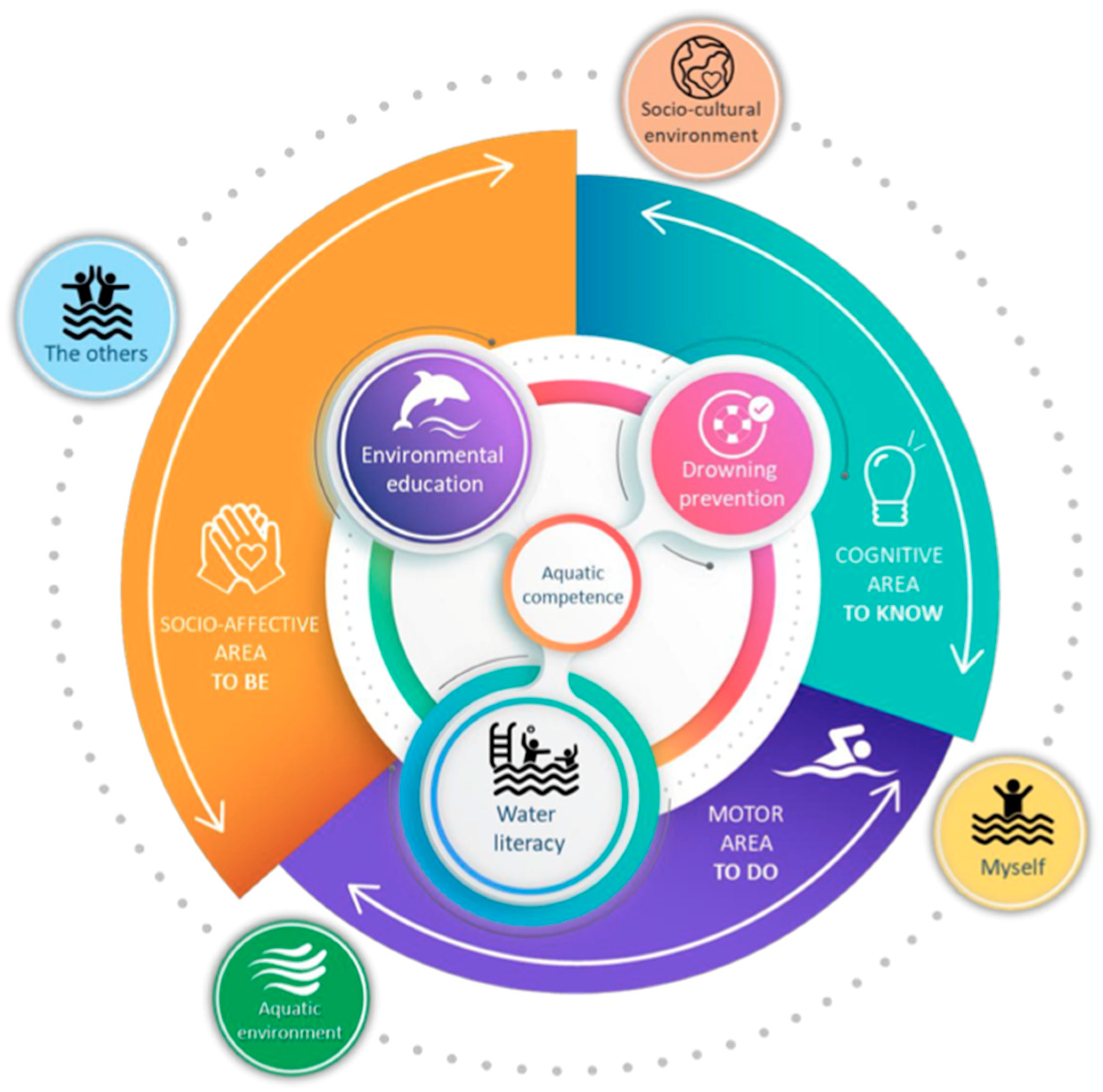
1.1. Concept of Aquatic Competence and Decision Making
1.2. Measuring Instruments for Aquatic Competence
1.3. The Current Study
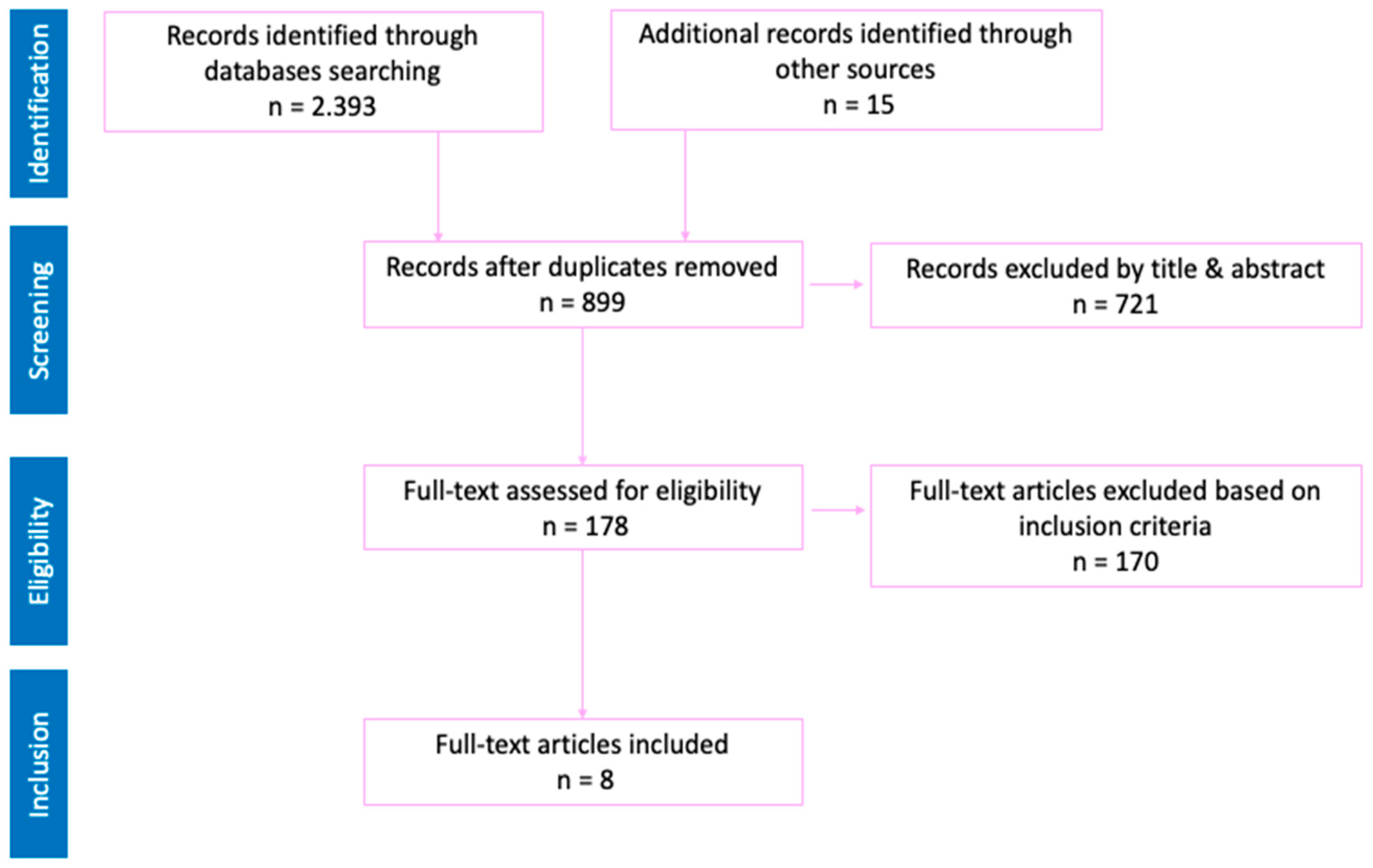
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
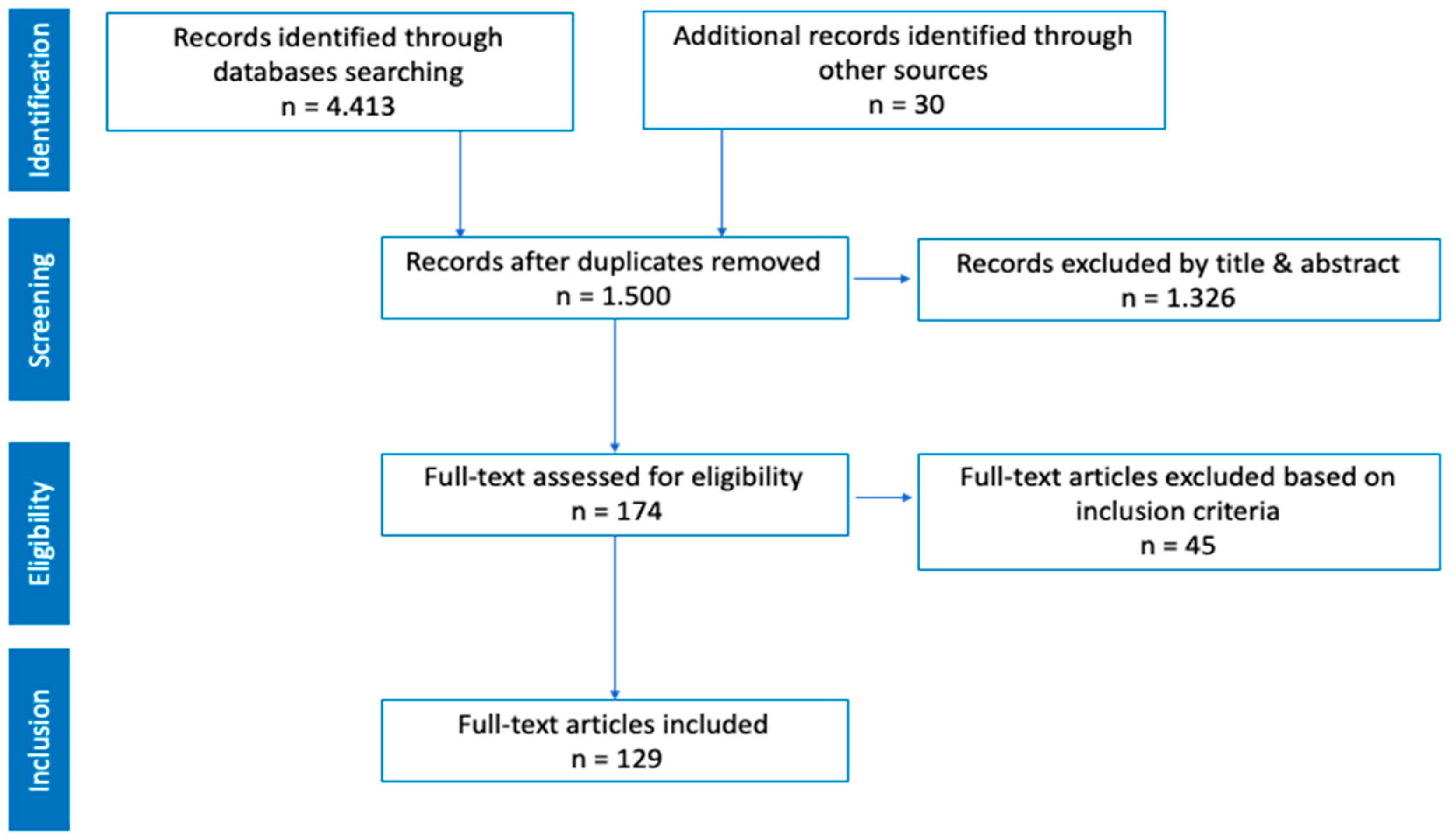
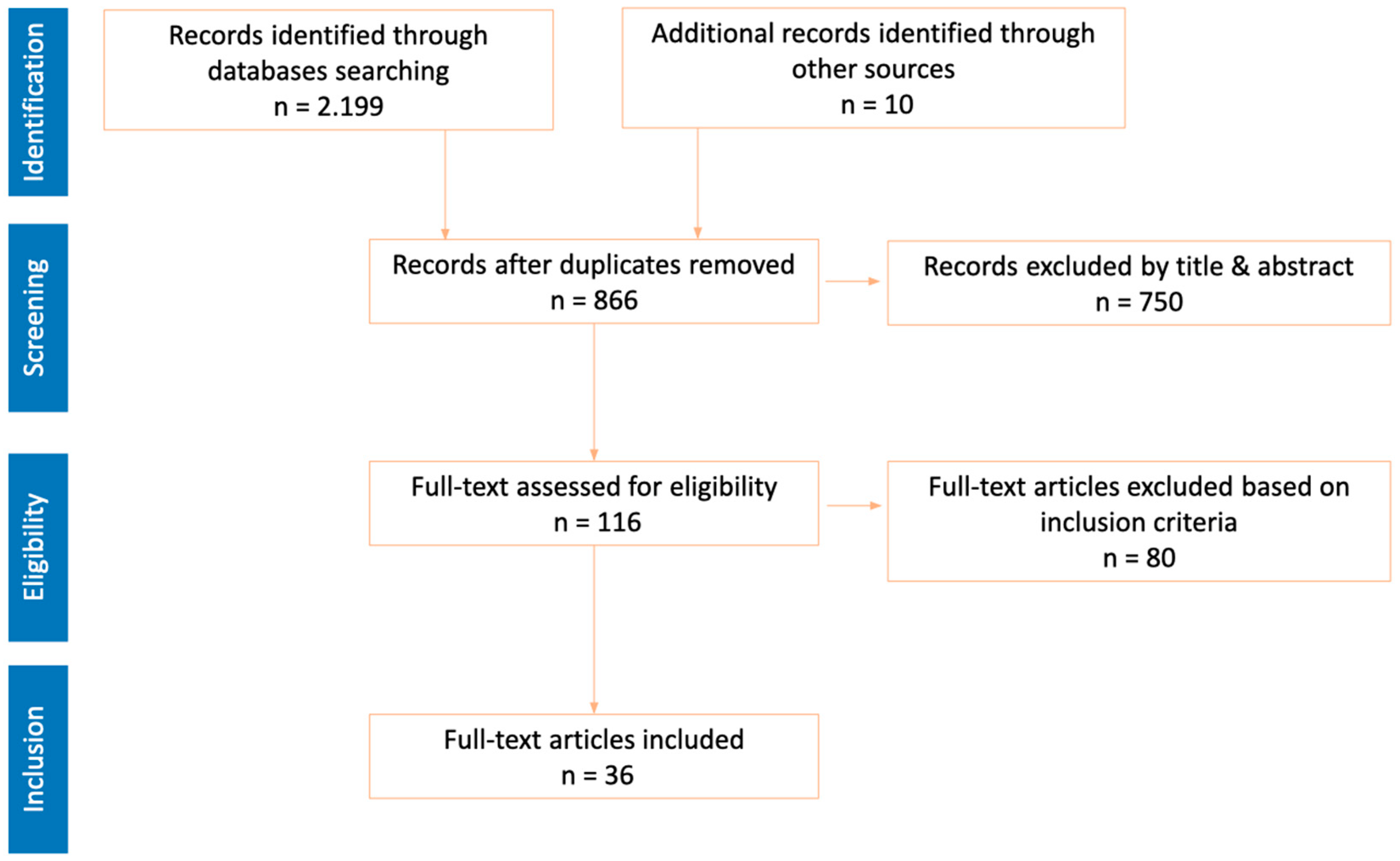
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
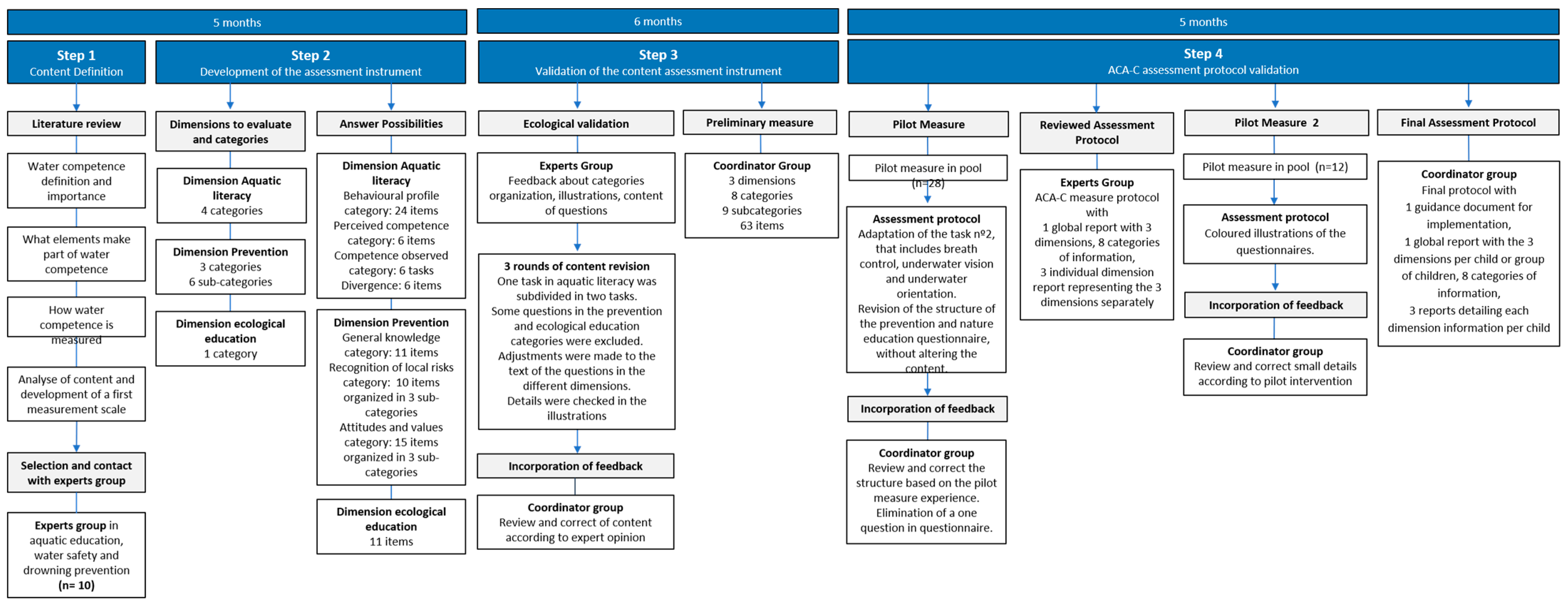
3.1. Step 1: Definition of the Assessment Instrument Construct
3.2. Step 2: Development of the Assessment Instrument
3.3. Step 3: Validation of the Assessment Instrument
3.4. Step 4: Pilot Study
4. Discussion
Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Hondt, D.; Buelens, E.; Barnett, L.; Howells, K.; Sääkslahti, A.; Costa, A.M.; Jidovtseff, B.; Mertens, L.; De Martelaer, K. Differences between young children’s actual, self-perceived and parent-perceived aquatic skills. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2021, 128, 1905–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paula-Borges, L.; Moreno-Murcia, J.A. Efectos del Método Acuático Comprensivo en estudiantes de 6 y 7 años. RIAA. Rev. Investig. Act. Acuát. 2018, 2, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mertens, L.; De Martelaer, K.; Saakslahti, A.; D’Hondt, E. The inter-rater and intrarater reliability of the actual aquatic skills test (AAST) for assessing young children’s motor competence in the water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Murcia, J.A.; Huéscar, E.; De Paula, L.; Gómez, N. Design and Validation of a Scale to Measure Fear of the Aquatic Environment in Children. Motricidade 2020, 16, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varveri, D.; Flouris, A.D.; Smirnios, N.; Pollatou, E.; Karatzaferi, C.; Sakkas, G.K. Developing and testing an instrument to assess aquaticity in humans. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2016, 20, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, T.; Staub, I. Assessment of basic aquatic skills in children: Inter-rater reliability of coaches, teachers, students, and parents. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2020, 20, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbaugh, S.J. Effects of aquatic training on swimming skill development of preschool children. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1986, 62, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Murcia, J.A.; Ruiz Pérez, L.M. Aquatic Perceived Competence Analysis in Children: Development and Preliminary Validation of a Pictorial Scale. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2008, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar-Andreu, C.S.; Moreno-Murcia, J.A.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.M. Validation on the Inventory of Evolutionary Aquatic Development IEAD (IDEA) in 6 To 12 Month Old Babies. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Activ. Fís. Deporte 2018, 18, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendorfer, S.J.; Bruya, L.D. Aquatic Readiness: Developing Water Competence in Young Children; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Guignard, B.; Button, C.; Davids, K.; Seifert, L. Education and transfer of water competencies: An ecological dynamics approach. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2020, 26, 935–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrongiello, B.A.; Matheis, S. Understanding Children’s Injury-Risk Behaviors: The Independent Contributions of Cognitions and Emotions. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2007, 32, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fonseca-Pinto, R.; Moreno-Murcia, J.A. Towards a Globalised Vision of Aquatic Competence. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2023, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa Morgado, L.; De Martelaer, K.; D’Hondt, E.; Barnette, L.; Howells, K.; Sääkslahti, A.; Costa, A.; Jidovtseff, B. Testing manual of the pictorial scale of perceived water competence (PSPWC). In Test Manual, 1st ed.; Early Years SIG AIESEP; 2020; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340793859 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Chan, D.K.; Lee, A.S.Y.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Hagger, M.S.; Hamilton, K. Validation of the swimming competence questionnaire for children. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 38, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.H.; Monroe, M.C. Connection to nature: Children’s affective attitude toward nature. Environ. Behav. 2012, 44, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K.; Blitvich, J.; Petrass, L.; McElroy, K. Getting In: Safe Water Entry Competencies. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2021, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K. Getting Out of the Water: How Hard Can That Be? Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2014, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- World Health Organization [WHO]. Preventing Drowning: An Implementation Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/preventing-drowning-an-implementation-guide (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- Stallman, R.K.; Moran, K.; Quan, L.; Langendorfer, S. From Swimming Skill to Water Competence: Towards a More Inclusive Drowning Prevention Future. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2017, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.M.; Schultz, W.P. Implicit beliefs about self and nature: Evidence from an IAT game. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, P.A. Connection with Nature as an Indicator for the Eco-Schools Programme. Univ. Cph. Found. Environ. Educ. 2021. Available online: https://bvearmb.do/bitstream/handle/123456789/3288/Nature%2bconnection%2bas%2ban%2bindicator%2bfor%2bthe%2bEco-Schools%2bprogramme.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Richardson, M.; Hunt, A.; Hinds, J.; Bragg, R.; Fido, D.; Petronzi, D.; White, M. A measure of nature connectedness for children and adults: Validation, performance, and insights. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkey, N.; Helmer, O. An Experimental Application of the Delphi Method to the Use of Experts. RAND Corp. 1962. AF 49 (638). Available online: http://www.rand.org/content/dam/rand/pubs/research_memoranda/2009/RM727.1.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Pérez, J.; Cuervo-Martínez, A. Validez de contenido y juicio de expertos: Una aproximación a su utilización. Avan. Medición 2008, 6, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.A.; Smith, H.; Heffernan, E.; Fackrell, K.; the Core Outcome Measures in Tinnitus International Delphi (COMiT’ID) Research Steering Group. Recruiting and retaining participants in e-Delphi surveys for core outcome set development: Evaluating the COMiT’ID study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey-Murto, S.; Varpio, L.; Gonsalves, C.; Wood, T.J. Using consensus group methods such as Delphi and Nominal Group in medical education research. Med. Teach. 2016, 39, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.C. Managing Delphi surveys using nonparametric statistical techniques. Decis. Sci. 1997, 28, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, C.; Button, A.J.; Jackson, A.M.; Cotter, J.D.; Maraj, B. Teaching foundational aquatic skills to children in open water environments. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, C.; McGuire, T.; Cotter, J.; Jackson, A.M. Assessing the Water Survival Skills Competency of Children; Research Report Prepared for Water Safety New Zealand; University of Otago: Dunebin, New Zealand, 2017; Available online: https://cdn-flightdec.userfirst.co.nz/uploads/sites/watersafety/files/PDFs/Resources_Section/WSNZ_Assessing_Child_Water_Survival_Skills_Competency_ResearchReport_July2017.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Drowning Prevention Auckland. WAI Survival. An Aquatic Education Resource for Secondary Schools. Available online: www.dpanz.org.nz (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Karatrantou, K.; Stavrou, V.; Hasioti, P.; Varveri, D.; Krommidas, C.; Gerodimos, V. An enjoyable school-based swimming training programme improves students’ aquaticity. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 109, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Murcia, J.A.; Ruiz, L.M. Cómo Lograr la Competencia Acuática [How to Achieve Aquatic Competence]; SB Editorial: Madrid, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, A.; Fonseca-Pinto, R.; Albarracín, A.; Moreno-Murcia, J.A. Educación acuática para la prevención [Aquatic education for prevention]. RIAA Rev. Investig. Activ. Acuáticas 2021, 5, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Scarr, J. Measuring Australian Children’s Water Safety Knowledge: The National Water Safety Quiz. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2017, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox-Pidgeon, S.M.; Peden, A.E.; Scarr, J. Exploring children’s participation in commercial swimming lessons through the social determinants of health. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2020, 32, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarracín, A.; Moreno-Murcia, J.A. Natación a la escuela. Hacia una alfabetización acuática. RIAA. Rev. Investig. Act. Acuát. 2018, 2, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, D.A. Physical Literacy in Aquatic Environments—A Discussion Paper. Sport Life 2019. Available online: http://sportforlife.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/physical_literacy_aquatic_environments_Jan2020_Web.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2022).
- International Physical Literacy Association. Canada’s Physical Literacy Consensus Statement Definition. Retrieved 27 November 2019. Available online: http://physicalliteracy.ca/physical-literacy/consensus-statement/ (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Álvarez, P.; Veja, P. Actitudes Ambientales y Conductas Sostenibles. Implicaciones para la Educación. Rev. Psicolidact. 2009, 14, 245–260. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/175/17512724006.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Maas, J.; van Dillen, S.; Verheij, R.; Groenewegen, P. Social contacts as a possible mechanism behind the relation between green space and health. Health Place 2009, 15, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.J.; Boddy, K.; Stein, K.; Whear, R.; Barton, J.; Depledge, M. Does Participating in Physical Activity in Outdoor Natural Environments Have a Greater Effect on Physical and Mental Wellbeing than Physical Activity Indoors? A Systematic Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordovil, R.; Araújo, D.; Pepping, G.J.; Barreiros, J. An ecological stance on risk and safe behaviors in children: The role of affordances and emergent behaviors. New Ideas Psychol. 2015, 36, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrongiello, B.A.; Cusimano, M.; Barton, B.; Orr, E.; Chipman, M.; Tyberg, J.; Kulkarini, A.; Khanlou, N.; Mais, R.; Bekele, T. Development of the BACKIE questionnaire: A measure of children’s behaviors, attitudes, cognitions, knowledge, and injury experiences. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2010, 42, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonseca-Pinto, R.; Moreno Murcia, J.A. Development of the Aquatic Competence Assessment for Children (ACA-C): A Tool for Measuring Personal Aquatic Competence Index. Children 2025, 12, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040484
Fonseca-Pinto R, Moreno Murcia JA. Development of the Aquatic Competence Assessment for Children (ACA-C): A Tool for Measuring Personal Aquatic Competence Index. Children. 2025; 12(4):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040484
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonseca-Pinto, Rita, and Juan Antonio Moreno Murcia. 2025. "Development of the Aquatic Competence Assessment for Children (ACA-C): A Tool for Measuring Personal Aquatic Competence Index" Children 12, no. 4: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040484
APA StyleFonseca-Pinto, R., & Moreno Murcia, J. A. (2025). Development of the Aquatic Competence Assessment for Children (ACA-C): A Tool for Measuring Personal Aquatic Competence Index. Children, 12(4), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040484







