The Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Estimated Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates in Children with Cerebral Palsy Undergoing Single-Event Multi-Level Surgery, a Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Design of This Study
2.4. Perioperative Anesthesia
2.5. Operative Procedure
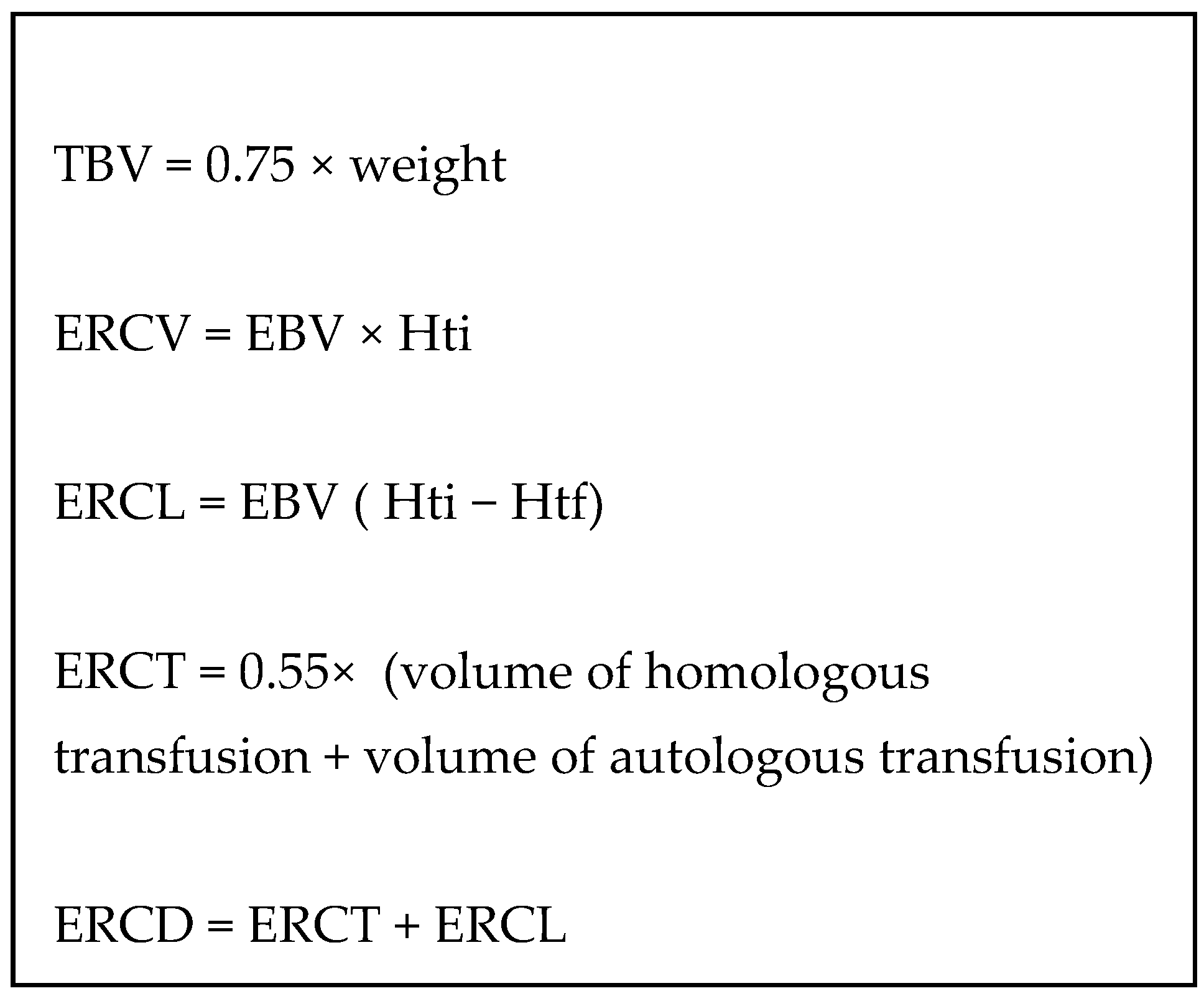
2.6. Data Collection
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Low-Dose TxA Protocol
4.2. Protective and Risk Factors for Blood Transfusion
4.3. Blood Saving Procedures for Early Rehabilitation
4.4. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vitrikas, K.; Dalton, H.; Breish, D. Cerebral Palsy: An Overview. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 101, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Galea, C.; Mcintyre, S.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Reid, S.M.; Gibson, C.; Delacy, M.; Watson, L.; Goldsmith, S.; Badawi, N.; Blair, E.; et al. Cerebral palsy trends in Australia (1995-2009): A population-based observational study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Ma, L.; Luo, K.; Bajaj, M.; Chawla, S.; Natarajan, G.; Hagberg, H.; Tan, S. Chorioamnionitis in the Development of Cerebral Palsy: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20163781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirmudin, N.A.; Lavelle, G.; Theologis, T.; Thompson, N.; Ryan, J.M. Multilevel Surgery for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20183390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Yunus, S.N.; Ng, C.C.; Chan, C.Y.W.; Chiu, C.K.; Kwan, M.K. TRanexamic Acid in Pediatric Scoliosis Surgery (TRIPSS): A Prospective Randomized Trial Comparing High Dose and Low Dose Tranexamic Acid in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS) Undergoing Posterior Spinal Fusion Surgery. Spine 2021, 40, E1170–E1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaifan, T.; Alenazy, A.; Xiang Wang, D.; Fernando, S.M.; Spence, J.; Belley-Cote, E.; Fox-Robichaud, A.; Ainswoth, C.; Karachi, T.; Kyeremanteng, K.; et al. Tranexamic acid in cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis (protocol). BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, I.; Shakur, H.; Coats, T.; Hunt, B.; Balogun, E.; Barnetson, L.; Cook, L.; Kawahara, T.; Perel, P.; Prieto-Merino, D.; et al. The CRASH-2 trial: A randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of the effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events and transfusion requirement in bleeding trauma patients. Health Technol. Assess 2013, 17, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konarski, W.; Poboży, T.; Hordowicz, M. Tranexamic acid in total knee replacement and total hip replacement—A single-center retrospective, observational study. Orthop. Rev. 2022, 14, 33875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentilhes, L.; Winer, N.; Azria, E.; Sénat, M.-V.; Le Ray, C.; Vardon, D.; Perrotin, F.; Desbrière, R.; Fuchs, F.; Kayem, G.; et al. Tranexamic Acid for the Prevention of Blood Loss after Vaginal Delivery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnik, N.M.; Pflibsen, L.R.; Do, A.; Bristol, R.; Singh, D.J. Craniosynostosis Surgery and the Impact of Tranexamic Acid Dosing. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, J.M.; Huynh, H.H.; Drone, H.M.; Jantzer, J.L.; Tsai, A.K.; Jancik, J.T. Experience in an Urban Level 1 Trauma Center with Tranexamic Acid in Pediatric Trauma: A Retrospective Chart Review. J. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 36, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongun, E.A.; Dursun, O.; Kazan, M.S. Tranexamic Acid Utilization in Craniosynostosis Surgery. Turk. Neurosurg. 2020, 30, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masrouha, K.Z.; Shabin, Z.M.; Bhutada, K.; Sala, D.A.; Godfried, D.H.; Karamitopoulos, M.S. Impact of tranexamic acid on blood loss and transfusion rate in children with cerebral palsy undergoing hip reconstruction with two or more osteotomies. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2021, 32, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzatzairis, T.; McMahon, S.; Shilpa, J.; Maizen, C. Safety and efficacy of tranexamic acid in children with cerebral palsy undergoing femoral varus derotational osteotomy: A double cohort study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2020, 30, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, M.A.; Segar, W.E. The maintenance need for water in parenteral fluid therapy. Pediatrics 1957, 19, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelet, D.; Julien-Marsollier, F.; Hilly, J.; Diallo, T.; Vidal, C.; Dahmani, S. Predictive factors of intraoperative cell salvage during pediatric scoliosis surgery. Cell saver during scoliosis surgery in children. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2018, 37, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goobie, S.M.; Staffa, S.J.; Meara, J.G.; Proctor, M.R.; Tumolo, M.; Cangemi, G.; Disma, N. High-dose versus low-dose tranexamic acid for paediatric craniosynostosis surgery: A double-blind randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazareth, A.; Shymon, S.J.; Andras, L.; Goldstein, R.Y.; Kay, R.M. Impact of tranexamic acid use on blood loss and transfusion rates following femoral varus derotational osteotomy in children with cerebral palsy. J. Child Orthop. 2019, 13, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosencher, N.; Bellamy, L.; Chabbouh, T.; Arnaout, L.; Ozier, Y. Blood conservation approaches in orthopedic surgery. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2008, 15, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhevskaia, A.A.; Prusakova, Z.B. Epidural analgesia in surgical treatment of scoliosis. Anesteziol. Reanimatol. 2012, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.J.; Johnson, C.C.; Goobie, S.M.; Nami, N.; Wetzler, J.A.; Sponseller, P.D.; Frank, S.M. High-dose Versus Low-dose Tranexamic Acid to Reduce Transfusion Requirements in Pediatric Scoliosis Surgery. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2017, 37, e552–e557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goobie, S.M.; Faraoni, D. Tranexamic acid and perioperative bleeding in children: What do we still need to know? Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 32, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.Z.H.; Reid, S.M.; Lundine, K.; Crighton, G. Blood transfusion following major orthopaedic surgery in cerebral palsy: A retrospective analysis. ANZ J. Surg. 2021, 91, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, A.; Kim, A.; Casale, P.; Cucchiaro, G. Low-dose intrathecal morphine for postoperative analgesia in children. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 104, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.G.; McNaull, P.P.; Jooste, E.; Tuchman, J.B. Perioperative crystalloid and colloid fluid management in children: Where are we and how did we get here? Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien-Marsollier, F.; Michelet, D.; Assaker, R.; Doval, A.; Louisy, S.; Madre, C.; Simon, A.-L.; Ilharreborde, B.; Brasher, C.; Dahmani, S. Enhanced recovery after surgery: Many ways for the same destination. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2021, 31, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien-Marsollier, F.; Michelet, D.; Assaker, R.; Doval, A.; Louisy, S.; Madre, C.; Simon, A.-L.; Ilharreborde, B.; Brasher, C.; Dahmani, S. Enhanced recovery after surgical correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2020, 30, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control Group N = 50 | TxA Group N = 51 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 10.75 [4.2–17.8] | 9.2 [1.8–14.6] | 0.114 |
| Weight (Kg) | 27 [13.5–52] | 24 [9–50] | 0.131 |
| ASA | |||
| 1 | 1 (3.3) | 2 (6.7) | |
| 2 | 22 (73.3) | 21 (70) | |
| 3 | 7 (23.3) | 7 (23.3) | |
| Hemoglobin day before surgery | 13.1 [11.2–15.1] | 13.2 [9.1–15.1] | 0.636 |
| Duration of anesthesia (h) | 4.5 [3–7.5] | 4.6 [2.5–5] | 0.192 |
| Duration of surgery (h) | 3 [2–6.5] | 3 [1.5–4] | 0.280 |
| Perioperative epidural analgesia | 43 (83.3) | 46 (90.1) | 0.373 |
| Proximal Femoral osteotomie | 32 (64) | 34 (66) | 0.232 |
| Distal femoral osteotomie | 22 (44) | 24 (47) | 0.187 |
| Tibial osteotomie | 22 (44) | 24 (47) | 0.187 |
| Pelvic osteotomie | 18 (60) | 19 (37) | 0.254 |
| Control Group N = 50 | TxA Group N = 51 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemogobin at postoperative day 1 (g/dL) | 9.2 [6.4–13.1] | 9.5 [7–13.1] | 0.129 |
| Hemoglobin at postoperative day 3 (g/dL) | 8.9 [5.6–14.2] | 10.6 [8.2–13.3] | 0.011 |
| Intraoperatrive Transfusion | 3 (10) | 0 (0) | 0.001 |
| Postoperative Transfusion | 13 (43.3) | 1 (3.3) | <0.001 |
| Fluid intake (L·Kg−1) | 1.5 [0.5–4] | 1 [0.4–3.5] | 0.015 |
| Hospital length (day) | 7 [6,7,8] | 6 [6–7] | 0.001 |
| ERCV lost (mL·kg−1) at day 3 | 33.78 [27.37–40.2] | 22.33 [17.33–27.34] | 0.005 |
| Control Group | TxA Group | p Value | |
| Proximal Femoral osteotomie | N = 32 | N = 34 | |
| Hemogobin at postoperative day 1 (g/dL) | 8.6 [6.9–12.1] | 9.5 [7–12.9] | 0.03 |
| Hemoglobin at postoperative day 3 (g/dL) | 8.2 [6.6–14.2] | 9.6 [8.6–13.2] | 0.02 |
| Intraoperative Transfusion | 1 | 0 | 0.04 |
| Postoperative Transfusion | 6 | 0 | <0.001 |
| Distal femoral osteotomie | N = 22 | N = 24 | |
| Hemogobin at postoperative day 1 (g/dL) | 9.0 [6.4–13.0] | 9.5 [7–13.1] | 0.19 |
| Hemoglobin at postoperative day 3 (g/dL) | 8.6 [5.6–14.2] | 9.2 [8.2–12.9] | 0.01 |
| Intraoperative Transfusion | 0 | 0 | 0.001 |
| Postoperative Transfusion | 0 | 0 | <0.02 |
| Pelvic osteotomie | N = 18 | N = 19 | |
| Hemogobin at postoperative day 1 (g/dL) | 8.4 [6.4–11.8] | 9.1 [7–12.9] | 0.001 |
| Hemoglobin at postoperative day 3 (g/dL) | 8.0 [5.6–11.2] | 10.4 [8.1–13.0] | 0.04 |
| Intraoperative Transfusion | 2 | 0 | <0.02 |
| Postoperative Transfusion | 7 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Univariate | Multivariable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Transfusion (N, %) | Transfusion (N, %) | p Value | OR | 95% Confidence Interval of OR | |
| TxA | 35 (47.9) | 1 (1.4) | <0.001 | 0.028 | [0.002–0.38] |
| Epidural analgesia | 50 (68.5) | 11 (83.6) | 0.07 | 0.082 | [0.01–0.681] |
| Length of surgery (h) | 3 [1.5–4] | 3.25 [2–6.5] | 0.15 | 3.1 | [1.2–7.6] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Julien-Marsollier, F.; Simon, A.-L.; Pardessus, P.; Presedo, A.; Ilharreborde, B.; Dahmani, S. The Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Estimated Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates in Children with Cerebral Palsy Undergoing Single-Event Multi-Level Surgery, a Retrospective Study. Children 2025, 12, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030267
Julien-Marsollier F, Simon A-L, Pardessus P, Presedo A, Ilharreborde B, Dahmani S. The Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Estimated Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates in Children with Cerebral Palsy Undergoing Single-Event Multi-Level Surgery, a Retrospective Study. Children. 2025; 12(3):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030267
Chicago/Turabian StyleJulien-Marsollier, Florence, Anne-Laure Simon, Pierre Pardessus, Ana Presedo, Brice Ilharreborde, and Souhayl Dahmani. 2025. "The Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Estimated Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates in Children with Cerebral Palsy Undergoing Single-Event Multi-Level Surgery, a Retrospective Study" Children 12, no. 3: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030267
APA StyleJulien-Marsollier, F., Simon, A.-L., Pardessus, P., Presedo, A., Ilharreborde, B., & Dahmani, S. (2025). The Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Estimated Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates in Children with Cerebral Palsy Undergoing Single-Event Multi-Level Surgery, a Retrospective Study. Children, 12(3), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030267






