Indications, Trends and Outcomes in Pediatric Lung Resections: A 12-Year Study in a Tertiary Referral Center
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
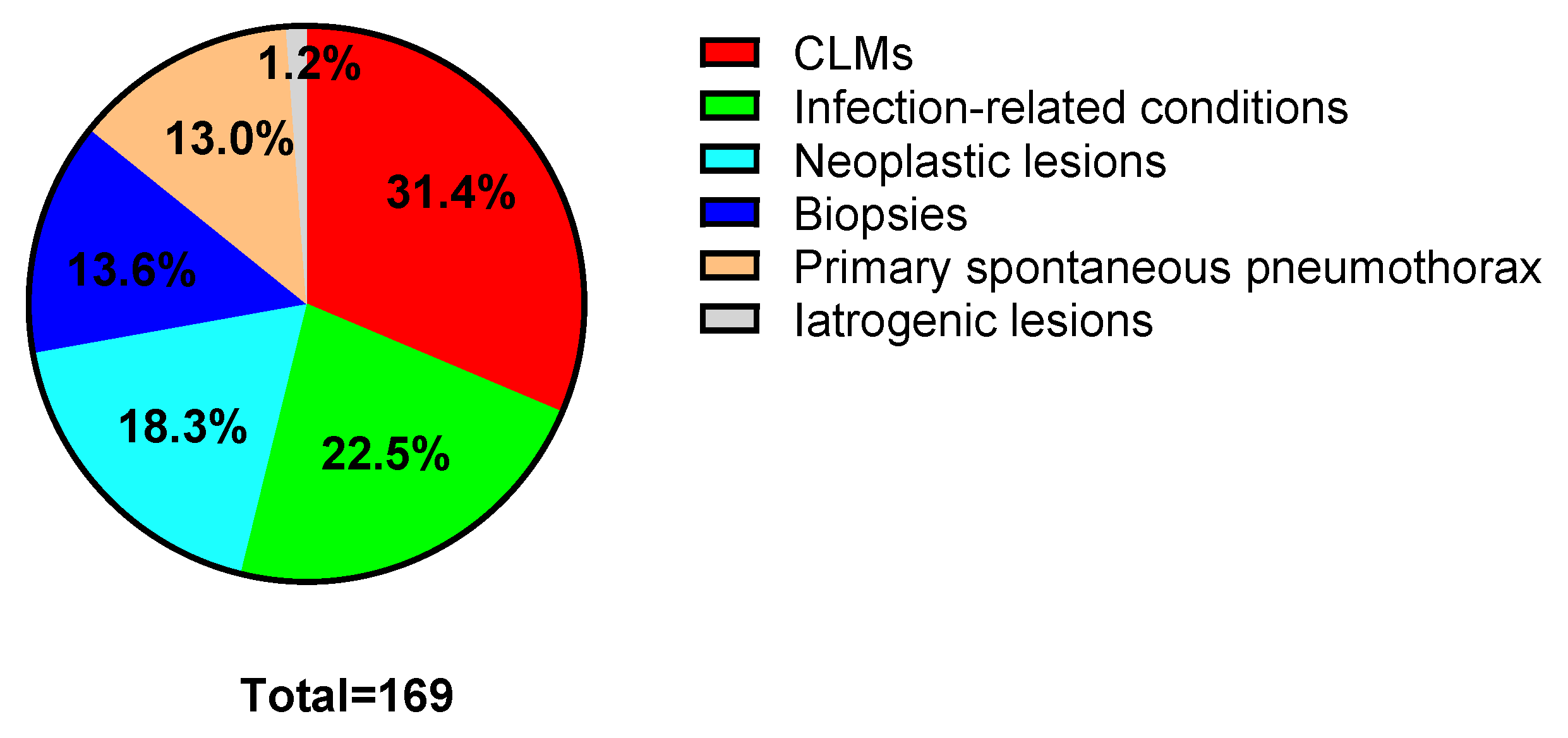
3.1. Population and Procedures
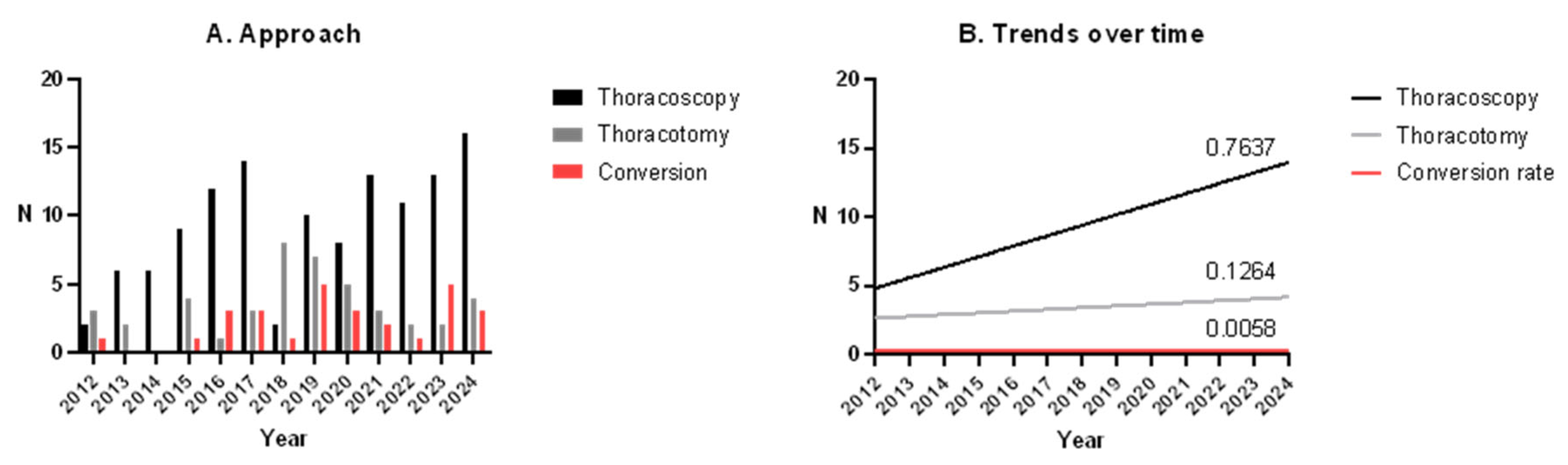
3.2. Thoracoscopy vs. Thoracotomy
3.3. Conversion to Open
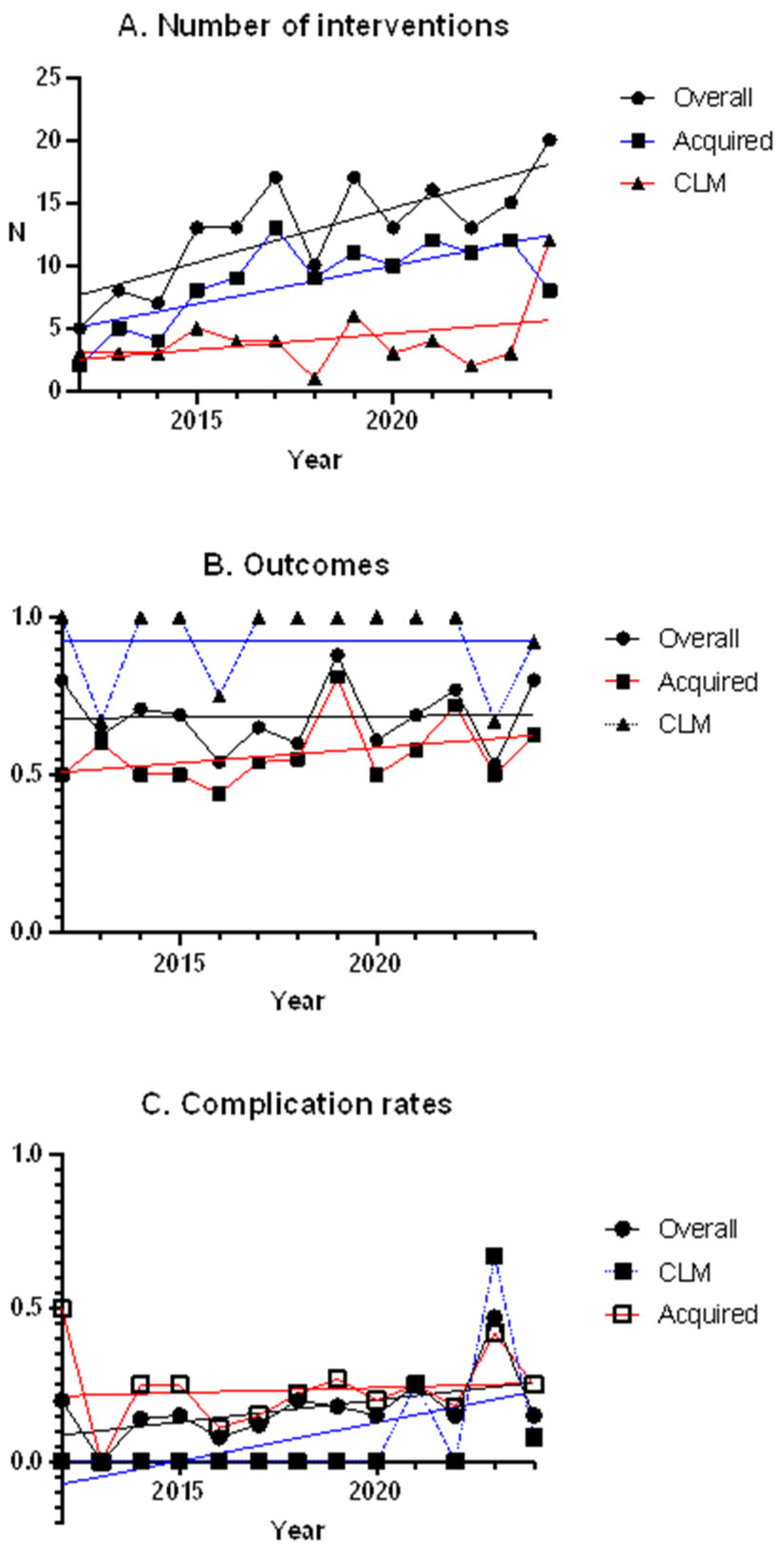
3.4. Congenital Lung Malformations vs. Acquired Lesions
3.5. Trends over the Time
4. Discussion
4.1. Thoracoscopy vs. Thoracotomy
4.2. Congenital Lung Malformations vs. Acquired Lesions
4.3. Trends over Time
4.4. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Böckle, C.E.; Blaser, J.; Schukfeh, N.; Zeidler, J.; Ure, B.M.; Dingemann, J. Analysis of Pulmonary Surgery in Children and Adolescents in Germany: Who Is Doing What? Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2022, 32, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Choudhury, S.; Chadha, R.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, V.; Singh, V.; Dubey, N.K. Lung Resections in Children for Congenital and Acquired Lesions. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2007, 23, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, S.S.; Middlesworth, W.; Kadennhe-Chiweshe, A.; Aspelund, G.; Kuenzler, K.; Cowles, R.; Bodenstein, L.; Kay, S.; Shipman, K.; Rothenberg, C.; et al. Two Decades of Experience with Thoracoscopic Lobectomy in Infants and Children: Standardizing Techniques for Advanced Thoracoscopic Surgery. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2015, 25, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, M.A.; Xu, T.O.; Gander, J.W.; Levin, D.E. Lung Surgery in Children and Their Post-Operative Risk of Respiratory Infection. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2021, 37, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisel, D.; Krupnick, A.S.; Huddleston, C.B. Outcomes and Late Complications after Pulmonary Resections in the Pediatric Population. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 16, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, J.; Urla, C.I.; Baden, W.; Schäfer, J.; Kirschner, H.-J.; Fuchs, J. Experiences and Challenges of Thorcoscopic Lung Surgery in the Pediatric Age Group. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 23, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, C.W.; Ostlie, D.J. Lung Biopsy and Resection. In Fundamentals of Pediatric Surgery; Mattei, P., Nichol, P.F., Rollins, M.D., II, Muratore, C.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 331–339. ISBN 978-3-319-27441-6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, X. Thoracoscopic versus Thoracotomy Lobectomy in Children with Congenital Lung Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. ANZ J. Surg. 2024, 94, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.-T.; Wong, K.K.Y. Long-Term Pulmonary Function after Lobectomy for Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation: Is Thoracoscopic Approach Really Better than Open? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 2383–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farolfi, A.; Ghezzi, M.; Calcaterra, V.; Riccipetitoni, G.; Pelizzo, G.; Costanzo, S.; Longoni, E.; De Silvestri, A.; Garancini, N.; Zirpoli, S.; et al. Congenital Lung Malformations: Clinical and Functional Respiratory Outcomes after Surgery. Children 2022, 9, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, F.K.F.; Lau, C.-T.; Yu, M.O.; Wong, K.K.Y. Comparison of Thoracoscopy vs. Thoracotomy on Musculoskeletal Outcomes of Children with Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation (CPAM). J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 56, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntean, A.; Marsland, L.; Sikdar, O.; Harris, C.; Ade-Ajayi, N.; Patel, S.B.; Cook, J.; Sellars, M.; Greenough, A.; Nicolaides, K.; et al. Neonatal Surgery for Congenital Lung Malformations: Indications, Outcomes and Association with Malignancy. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2025, 60, 162253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, A.; Bass, J. Thoracoscopic vs Open Resection of Congenital Lung Lesions: A Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2012, 47, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukleska, K.; Teeple, E.A.; Cowan, S.W.; Vinocur, C.D.; Berman, L. Outcomes in Children Undergoing Surgery for Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformations in the First Year of Life. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2018, 226, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polites, S.F.; Habermann, E.B.; Zarroug, A.E.; Thomsen, K.M.; Potter, D.D. Thoracoscopic Vs Open Resection of Congenital Cystic Lung Disease- Utilization and Outcomes in 1120 Children in the United States. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, L.; Gentilino, V.; Macchini, F.; Scarpa, A.A.; Lo Piccolo, R.; Conforti, A.; Ratta, A.; Guanà, R.; Molinaro, F.; Costanzo, S.; et al. Congenital Lung Malformations: A Nationwide Survey on Management Aspects by the Italian Society of Pediatric Surgery. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2024, 40, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemann, C.; Ure, B.; Dingemann, J. Thoracoscopic Procedures in Pediatric Surgery: What Is the Evidence? Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 24, 014–019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Musters, G.; De Beer, S.; Van Schuppen, J.; De Jong, J.; Gorter, R.; Oomen, M. Pediatric Thoracoscopic Lung Resections: A Comprehensive Analysis of Congenital Lesion Cases. Acta Chir. Belg. 2024, 124, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaylat, A.N.; Engbrecht, B.W.; Hollenbeak, C.S.; Safford, S.D.; Cilley, R.E.; Dillon, P.W. Comparing 30-Day Outcomes between Thoracoscopic and Open Approaches for Resection of Pediatric Congenital Lung Malformations: Evidence from NSQIP. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnard, A. Thoracoscopic Lobectomy for Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation: Where Are We in 2019? Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 30, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.-A. Classification of Surgical Complications: A New Proposal with Evaluation in a Cohort of 6336 Patients and Results of a Survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Perez, E.A.; Chung, D.H.; Pandya, S.R. Predictive Factors and Outcomes for Successful Thoracoscopic Lung Resection in Pediatric Patients. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2021, 232, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Lakhoo, K. Comparison between Open and Thoracoscopic Resection of Congenital Lung Lesions. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.T.; Leung, L.; Chan, I.H.Y.; Chung, P.H.Y.; Lan, L.C.L.; Chan, K.L.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Tam, P.K.H. Thoracoscopic Resection of Congenital Cystic Lung Lesions Is Associated with Better Post-Operative Outcomes. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2013, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, I.R.; Herrera, P.; Langer, J.C.; Kim, P.C.W. Thoracoscopic versus Open Resection of Congenital Lung Lesions: A Case-Matched Study. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2007, 42, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederiva, F.; Rothenberg, S.S.; Hall, N.; Ijsselstijn, H.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Von Der Thüsen, J.; Ciet, P.; Achiron, R.; Pio d’Adamo, A.; Schnater, J.M. Congenital Lung Malformations. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2023, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, A.K.; Al-Rowayeh, A. Lung Resection in Children for Infectious Pulmonary Diseases. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2005, 21, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.-C.; Liang, S.; Lu, H.-W.; Fei, K.; Xu, J.-F. Efficiency and Safety of Surgical Intervention to Patients with Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sırmalı, M.; Karasu, S.; Türüt, H.; Gezer, S.; Kaya, S.; Taştepe, İ.; Karaoğlanoğlu, N. Surgical Management of Bronchiectasis in Childhood. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2007, 31, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kapralik, J.; Wayne, C.; Chan, E.; Nasr, A. Surgical versus Conservative Management of Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolini, S.; Tofani, L.; Zolpi, E.; Montalva, L.; Lotti, C.; Morabito, A.; Chiarenza, F.; Bonnard, A. Morbidity Related to Major Lung Thoracoscopic Resections in Children. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 2024, 46, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 82 (51.2%) |
| Female | 78 (48.8%) | |
| Age | Mean | 7.8 years |
| Standard deviation | 6.3 years | |
| Range | 3 days–24.4 years | |
| Clinical presentation | Symptomatic cases | 121 (71.6%) |
| Respiratory infections | 60 (35.5%) | |
| Pneumothorax | 22 (13.0%) | |
| Respiratory distress/dyspnea | 13 (7.7%) | |
| Thoracic pain | 7 (4.1%) | |
| Cough | 6 (3.5%) | |
| Systemic symptoms | 6 (3.5%) | |
| Others (Pleural effusion, hemoptysis, hemothorax) | 7 (4.1%) | |
| Asymptomatic | 48 (28.4%) |
| n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Intraoperative | Major intra-thoracic injuries | 4 (2.3%) |
| Bleeding | 2 (1.2%) | |
| Short-term postoperative | Pneumothorax | 10 (5.9%) |
| Atelectasis | 8 (4.8%) | |
| Wound infections | 4 (2.4%) | |
| Hematoma/bleeding | 2 (1.2%) | |
| Subglottic stenosis | 2 (1.2%) | |
| Nerve lesions | 2 (1.2%) | |
| Others (pneumonia, pleural effusion, thoracic drain dislocation) | 3 (1.8%) | |
| Long-term postoperative | Bronchial obstruction | 1 (0.6%) |
| Broncho-pleural fistula | 1 (0.6%) | |
| Pneumothorax | 1 (0.6%) |
| Thoracoscopy | Thoracotomy | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 95 | 74 | |
| Age, month (mean ± st.dev.) | 107.2 ± 81.2 | 75.3 ± 63.9 | 0.005 * |
| Males, n (%) | 53 (55.8%) | 34 (45.9%) | 0.218 |
| Operative time, min (mean +/− st.dev.) | |||
| Overall | 93.2 ± 54.0 | 175.2 ± 85.9 | <0.001 * |
| Lobectomies | 132.7 ± 66.9 | 200.6 ± 93.2 | 0.002 * |
| Segmentectomies | 105.8 ± 77.9 | 145.0 ± 49.5 | 0.542 |
| Atypical resections | 79.1 ± 37.5 | 146.3 ± 67.5 | <0.001 * |
| Operative time ITT, min (mean ± st.dev.) | |||
| Overall | 120.2 ± 78.2 | 154.1 ± 84.7 | 0.022 * |
| Lobectomies | 175.8 ± 93.0 | 178.2 ± 91.6 | 0.919 |
| Segmentectomies | 115.7 ± 82.1 | 135.0 ± 65.6 | 0.710 |
| Atypical resections | 95.7 ± 55.6 | 121.9 ± 67.4 | 0.149 |
| Length of stay, days (mean ± st.dev.) | |||
| Overall | 9.6 ± 13.8 | 17.9 ± 19.8 | 0.001 * |
| Lobectomies | 8.5 ± 11.1 | 20.6 ± 23.5 | 0.010 * |
| Segmentectomies | 4.5 ± 2.1 | 8.5 ± 5.0 | 0.262 |
| Atypical resections | 10.3 ± 15.0 | 15.7 ± 14.4 | 0.104 |
| Complications, n (%) | |||
| Overall | 17 (17.9%) | 16 (21.6%) | 0.681 |
| Lobectomies | 6 (28.6%) | 10 (25%) | 0.763 |
| Segmentectomies | 1 (16.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0.389 |
| Atypical resections | 10 (14.7%) | 6 (20%) | 0.513 |
| Favorable outcome, n (%) | |||
| Overall | 69 (72.6%) | 49 (66.2%) | 0.464 |
| Lobectomies | 16 (76.2%) | 27 (67.5%) | 0.479 |
| Segmentectomies | 4 (66.7%) | 2 (50.0%) | 0.598 |
| Atypical resections | 53 (77.9%) | 20 (66.7%) | 0.239 |
| Pathological Subgroup | Variable | Thoracoscopy | Thoracotomy | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLMs | 33 (62.2%) | 20 (37.7%) | ||
| Age, months | 27.6 ± 31.9 | 29.3 ± 49.3 | 0.890 | |
| Males | 19 (57.6%) | 6 (30%) | 0.088 | |
| Operative time, min | 113.1 ± 62.6 | 172.2 ± 90.1 | 0.010 * | |
| Operative time ITT, min | 141.8 ± 83.0 | 108.0 ± 52.2 | 0.119 | |
| LOS, days | 6.4 ± 9,4 | 11.1 ± 10.0 | 0.105 | |
| Complications | 3 (9.1%) | 2 (11.1%) | 0.902 | |
| Favorable outcome | 31 (93.9%) | 19 (95.0%) | 0.819 | |
| Infection-related conditions | 13 (34.2%) | 25 (65.8%) | ||
| Age, months | 111.5 ± 45.3 | 100.8 ± 58.8 | 0.542 | |
| Males | 7 (53.8%) | 12 (48.0%) | 1 | |
| Operative time, min | 113.2 ± 60.3 | 188.9 ± 81.7 | 0.003 * | |
| Operative time ITT, min | 141.8 ± 79.7 | 189.3 ± 80.8 | 0.078 | |
| LOS, days | 10.6 ± 16.6 | 26.3 ± 19.6 | 0.015 * | |
| Complications | 8 (61.5%) | 5 (20.0%) | 0.028 * | |
| Favorable outcome | 11 (84.6%) | 7 (28.0%) | 0.002 * | |
| Neoplastic lesions | 9 (29.0%) | 22 (71.0%) | ||
| Age, months | 155.1 ± 79.2 | 91.0 ± 51.7 | 0.047 * | |
| Males | 2 (22.2%) | 12 (54.5%) | 0.132 | |
| Operative time, min | 92.5 ± 45.4 | 170.1 ± 96.5 | 0.007 * | |
| Operative time ITT, min | 139.1 ± 88.2 | 157.7 ± 97.0 | 0.594 | |
| LOS, days | 13.0 ± 23.0 | 11.9 ± 8.3 | 0.892 | |
| Complications | 4 (44.4%) | 2 (9.1%) | 0.043 * | |
| Favorable outcome | 5 (55.5%) | 15 (68.2%) | 0.683 | |
| Biopsies | 20 (86.9%) | 3 (13.1%) | ||
| Age, month | 133.8 ± 76.2 | 83.3 ± 82.7 | 0.404 | |
| Males | 9 (45.0%) | 2 (66.7%) | 0.590 | |
| Operative time, min | 58.1 ± 32.7 | 183.3 ± 62.9 | 0.069 | |
| Operative time ITT, min | 74.4 ± 56.1 | None | ||
| LOS, days | 13.3 ± 16.8 | 5.0 ± 1.0 | 0.041 * | |
| Complications | 2 (10.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 | |
| Favorable outcome | 12 (60.0%) | 2 (66.7%) | 0.759 | |
| PSP | 20 (90.9%) | 2 (9.1%) | ||
| Age, month | 187.5 ± 38.7 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | <0.001 * | |
| Males | 16 (80.0%) | 1 (50%) | 0.411 | |
| Operative time, min | 81.1 ± 33.1 | 92.5 ± 3.5 | 0.179 | |
| Operative time ITT, min | Unchanged | Unchanged | ||
| LOS, days | 8.7 ± 9.3 | 14.5 ± 3.5 | 0.179 | |
| Complications | 5 (25.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 | |
| Favorable outcome | 14 (70.0%) | 2 (100%) | 0.190 |
| Associated Factors | Variable | Attempted Thoracoscopy | Converted to Open | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathological subgroup | Total | 122 | 27 (22.1%) | 0.013 * |
| CLMs | 43 | 10 (23.3%) | 0.823 | |
| Infection-related conditions | 21 | 8 (38.1%) | 0.080 | |
| Neoplastic lesions | 15 | 6 (40.0%) | 0.097 | |
| Biopsies | 23 | 3 (13.0%) | 0.402 | |
| PSP | 20 | 0 (0.0%) | 0.006 * | |
| Age < 1 year | Total | 27 | 6 (22.2%) | 1 |
| CLMs | 25 | 5 (25.0%) | 0.717 | |
| Infection-related conditions | 1 | 1 (100%) | 0.381 | |
| Neoplastic lesions | 0 | N/A | ||
| Biopsies | 1 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 | |
| PSP | 0 | N/A | ||
| Age < 8 years | Total | 65 | 20 (30.8%) | 0.017 * |
| CLMs | 40 | 9 (22.5%) | 0.558 | |
| Infection-related conditions | 10 | 5 (50%) | 0.387 | |
| Neoplastic lesions | 6 | 4 (66.7%) | 0.136 | |
| Biopsies | 8 | 2 (25.0%) | 0.269 | |
| PSP | 0 | N/A | ||
| Previous respiratory infections | Total | 27 | 4 (14.8%) | 0.774 |
| CLMs | 15 | 1 (6.7%) | 0.127 | |
| Neoplastic lesions | 4 | 3 (75.0%) | 0.235 | |
| Biopsies | 6 | 0 (0.0%) | 0.539 | |
| PSP | 2 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 | |
| Comorbidities | Total | 58 | 13 (22.4%) | 0.942 |
| CLMs | 4 | 1 (25.0%) | 1 | |
| Infection-related conditions | 18 | 7 (38.9%) | 1 | |
| Neoplastic lesions | 10 | 2 (20%) | 0.089 | |
| Biopsies | 17 | 3 (17.6%) | 0.539 | |
| PSP | 9 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 | |
| Adhesions | Total | 14 | 8 (57.1%) | 0.003 * |
| CLMs | 3 | 2 (66.7%) | 0.130 | |
| Infection-related conditions | 2 | 2 (100%) | 0.133 | |
| Neoplastic lesions | 3 | 3 (100%) | 0.044 * | |
| Biopsies | 4 | 1 (25.0%) | 0.453 | |
| PSP | 2 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 |
| CLMs | Acquired Lesions | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 52 | 108 | |
| Symptomatic patients, n (%) | 23 (44.2%) | 99 (91.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Operative time, min (mean ± st.dev.) | 135.4 ± 78.1 | 126.2 ± 81.9 | 0.486 |
| Length of stay, days (mean ± st.dev.) | 8.2 ± 9.8 | 15.5 ± 19.3 | 0.001 * |
| Type of interventions, n (%) | |||
| Successful thoracoscopies | 32 (61.5%) | 60 (55.6%) | 0.473 |
| Converted thoracoscopies | 10 (23.8%) | 17 (21.1%) | 0.478 |
| Thoracotomies | 10 (19.2%) | 32 (42.1%) | 0.161 |
| Lobectomies | 25 (48.1%) | 35 (32.4%) | 0.081 |
| Segmentectomies | 4 (7.7%) | 6 (5.6%) | 0.861 |
| Atypical resections | 23 (44.2%) | 75 (69.4%) | 0.004 * |
| Complications, n (%) | 4 (7.7%) | 24 (22.2%) | 0.041 * |
| Favorable Outcome, n (%) | 49 (94.2%) | 66 (61.1%) | <0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandrile, G.; Barone, G.; Guerriero, V.; Mattioli, G.; Torre, M. Indications, Trends and Outcomes in Pediatric Lung Resections: A 12-Year Study in a Tertiary Referral Center. Children 2025, 12, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111438
Mandrile G, Barone G, Guerriero V, Mattioli G, Torre M. Indications, Trends and Outcomes in Pediatric Lung Resections: A 12-Year Study in a Tertiary Referral Center. Children. 2025; 12(11):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111438
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandrile, Gloria, Giulia Barone, Vittorio Guerriero, Girolamo Mattioli, and Michele Torre. 2025. "Indications, Trends and Outcomes in Pediatric Lung Resections: A 12-Year Study in a Tertiary Referral Center" Children 12, no. 11: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111438
APA StyleMandrile, G., Barone, G., Guerriero, V., Mattioli, G., & Torre, M. (2025). Indications, Trends and Outcomes in Pediatric Lung Resections: A 12-Year Study in a Tertiary Referral Center. Children, 12(11), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111438






