Clinical Application of Custom Neck Collar with Negative Sensory Feedback in Children with Intractable Torticollis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
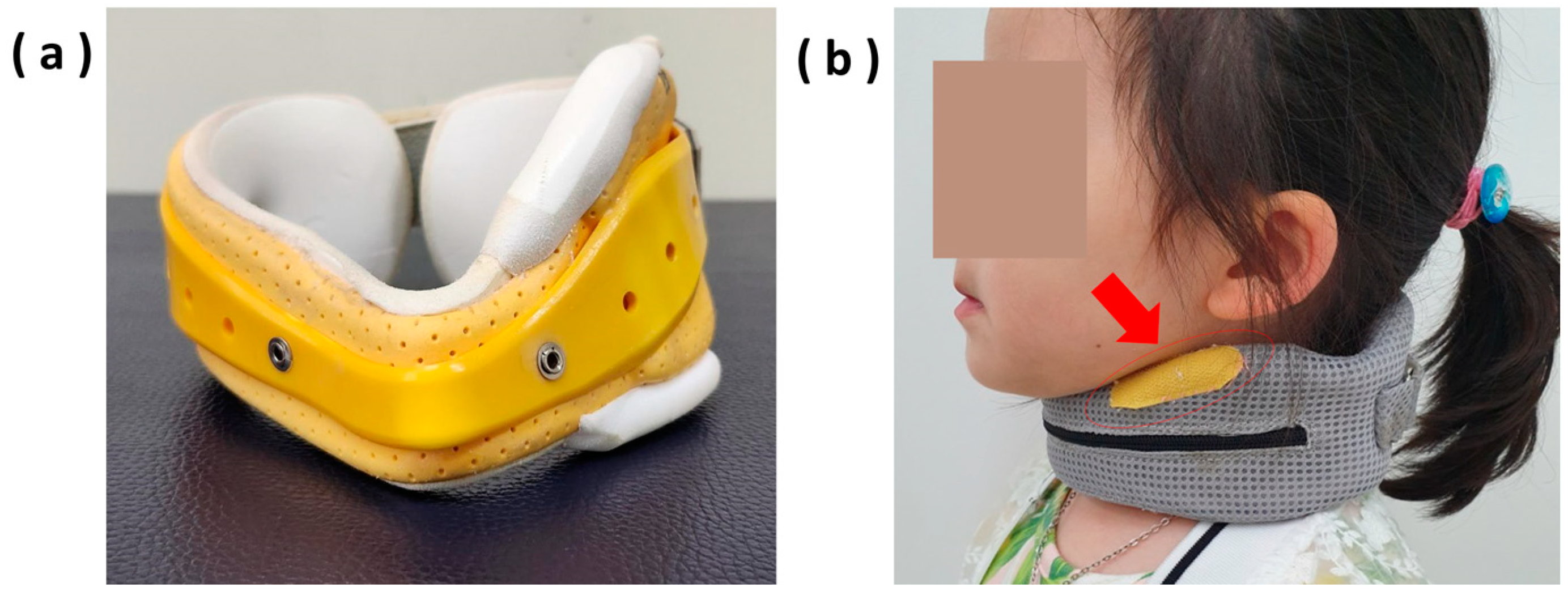
2.2. Design of Neck Collar
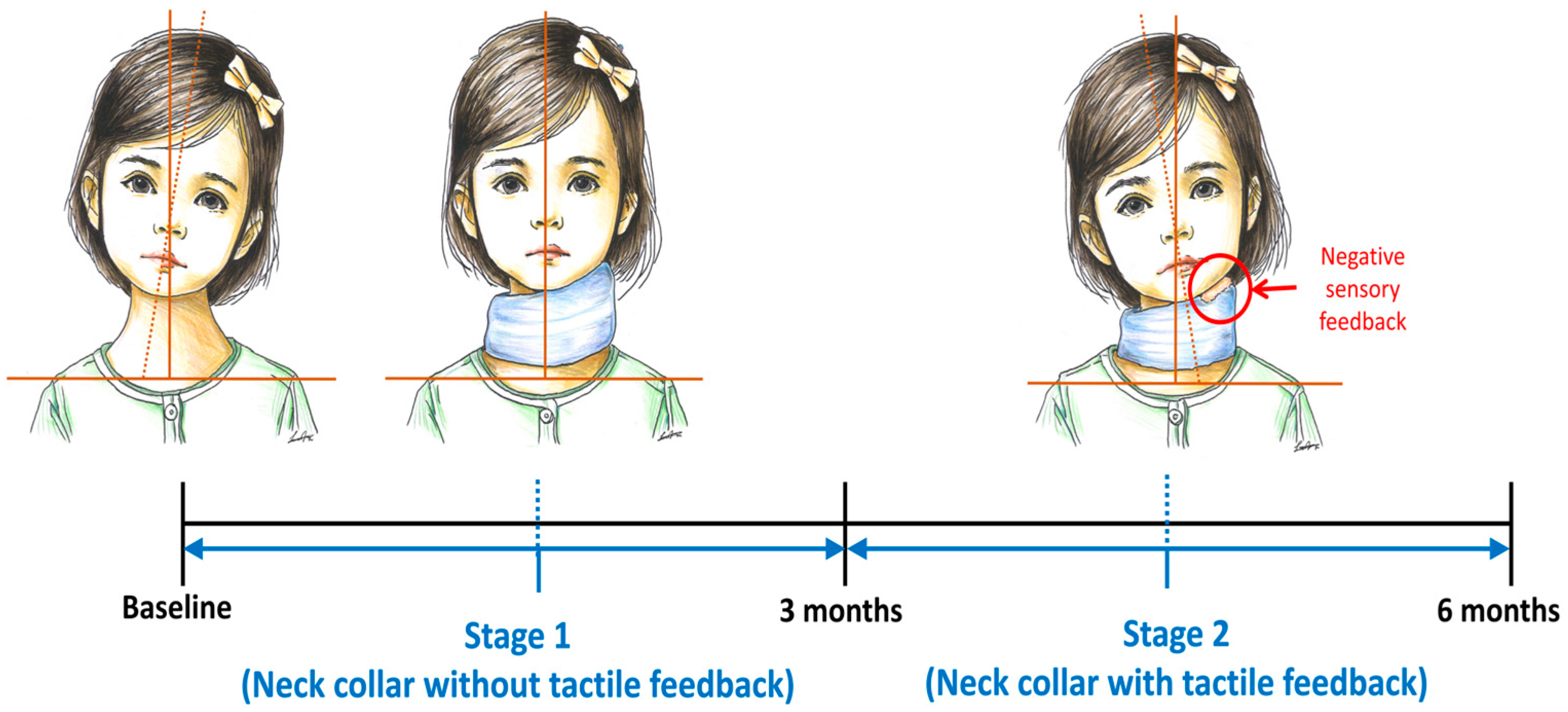
2.3. Study Protocol
2.4. Outcome Measurement
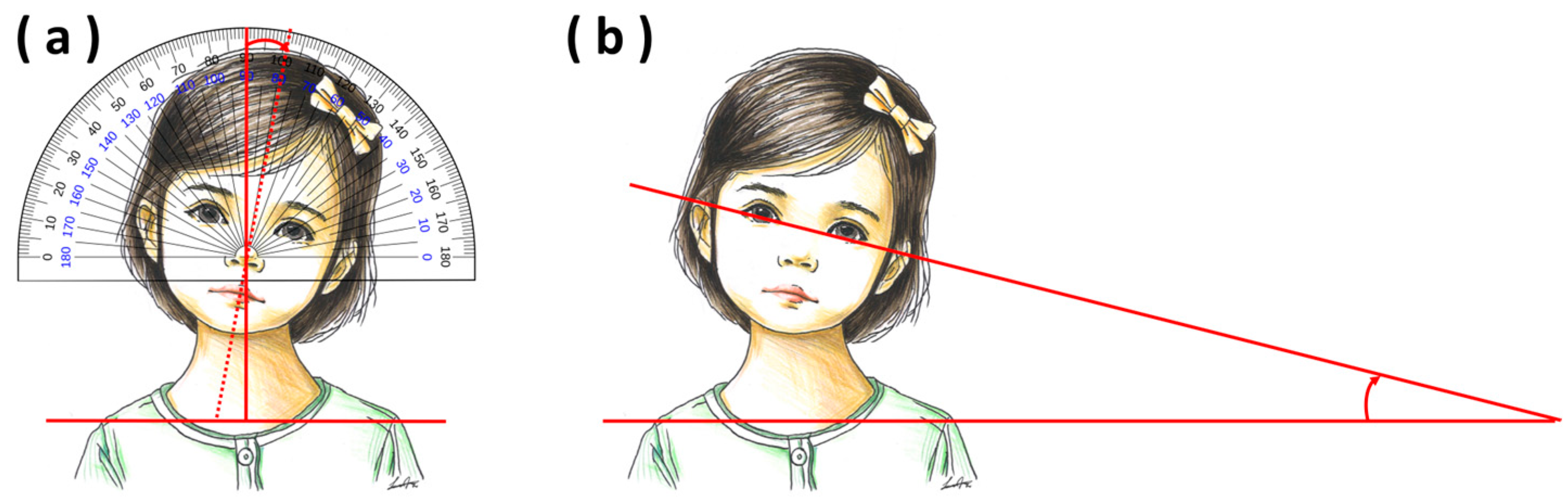
2.4.1. Inclination of the Head (Torticollis Angle)
2.4.2. Brace Tolerance Assessment
2.4.3. Safety Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Subjects
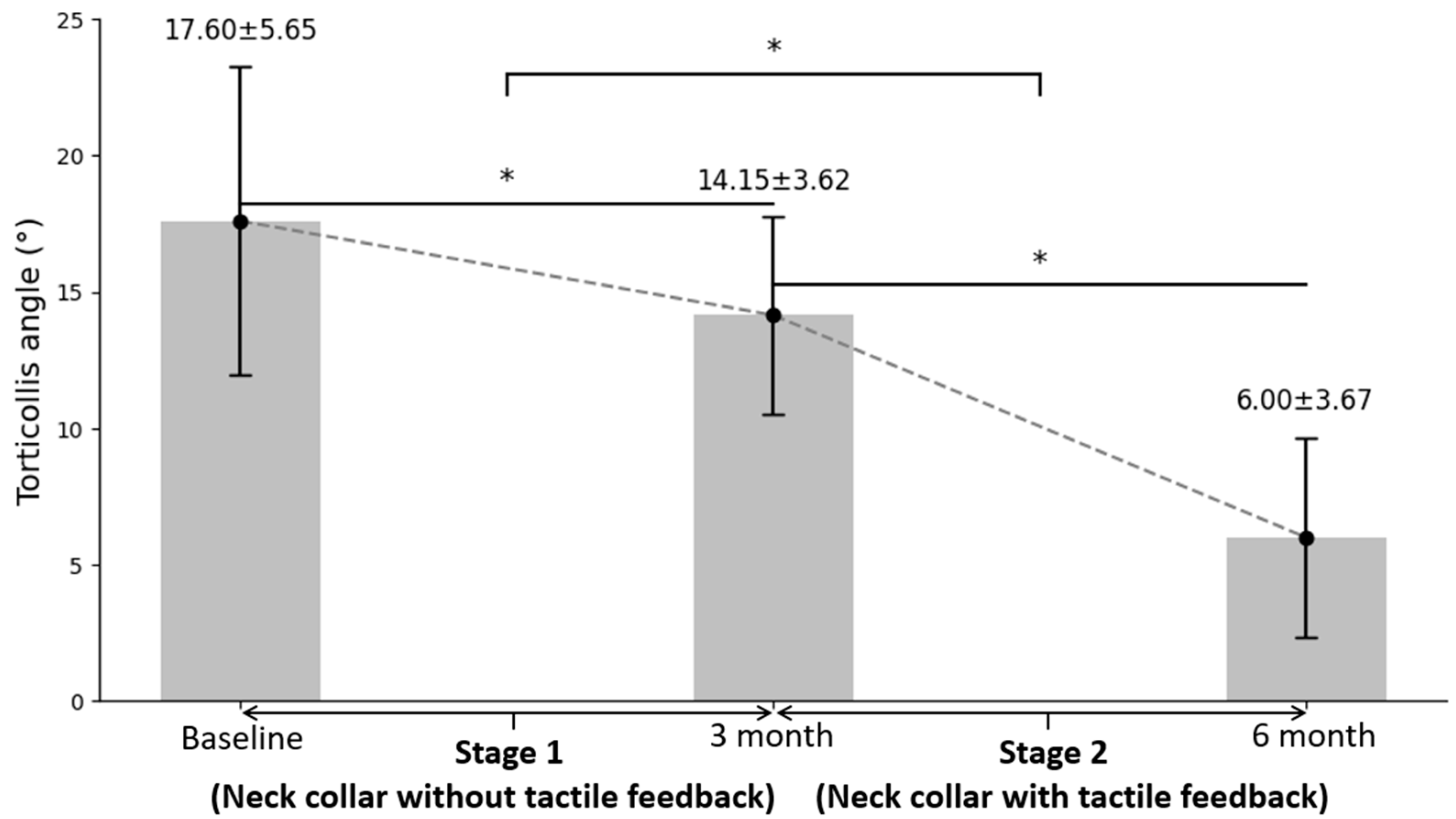
3.2. Therapeutic Effect of Custom Neck Collar without and with Negative Sensory Feedback on Torticollis Angle
3.3. Impact of Characteristics on Treatment Effect
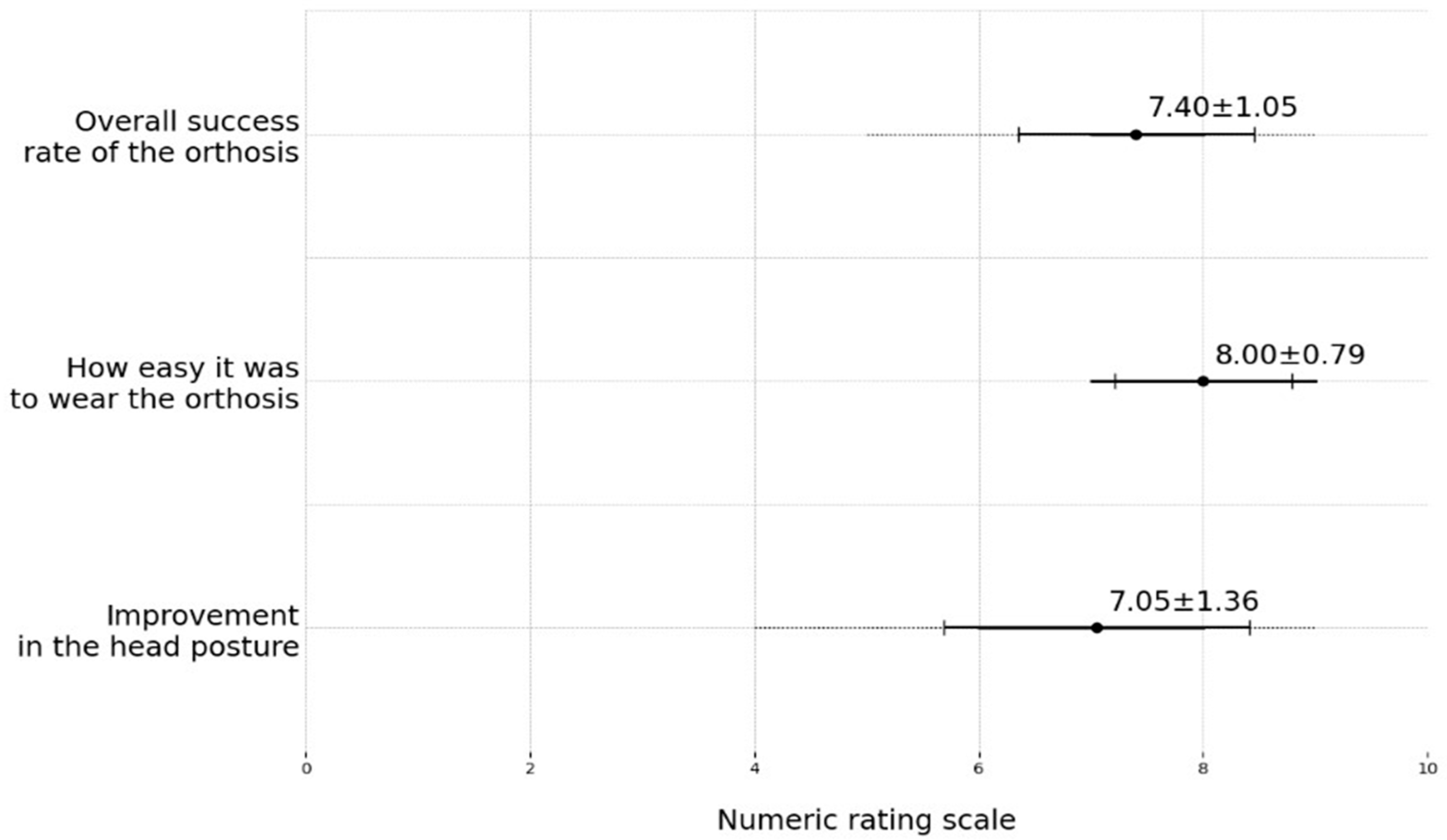
3.4. Treatment Satisfaction
3.5. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomczak, K.K.; Rosman, N.P. Torticollis. J. Child Neurol. 2013, 28, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilesh, K.; Mukherji, S. Congenital muscular torticollis. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 3, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, A.A.; Tritasavit, S.; Graham, J.M., Jr. Congenital muscular torticollis and positional plagiocephaly. Pediatr. Rev. 2014, 35, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubby, A. A Clinical Lecture On Torticollis, Or Wry-Neck. Br. Med. J. 1906, 1, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Per, H.; Canpolat, M.; Tümtürk, A.; Gumuş, H.; Gokoglu, A.; Yikilmaz, A.; Özmen, S.; Kaçar Bayram, A.; Poyrazoğlu, H.G.; Kumandas, S. Different etiologies of acquired torticollis in childhood. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2014, 30, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballock, R.T.; Song, K.M. The prevalence of nonmuscular causes of torticollis in children. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1996, 16, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapetropoulos, S.; Baez, S.; Zitser, J.; Sengun, C.; Singer, C. Retrocollis: Classification, clinical phenotype, treatment outcomes and risk factors. Eur. Neurol. 2007, 59, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D. Sternomastoid tumour and muscular torticollis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1969, 51, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaplan, S.L.; Coulter, C.; Sargent, B. Physical therapy management of congenital muscular torticollis: A 2018 evidence-based clinical practice guideline from the APTA Academy of Pediatric Physical Therapy. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 30, 240–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, T.; Tang, S.; Shum, S.; Wong, M.; Metreweli, C. Snapping during manual stretching in congenital muscular torticollis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 384, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wong, M.; Tang, S.; Chen, T.; Shum, S.; Wong, E. Clinical determinants of the outcome of manual stretching in the treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants: A prospective study of eight hundred and twenty-one cases. JBJS 2001, 83, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Tang, S.; Chen, T.; Wong, M.; Wong, E. The clinical presentation and outcome of treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants—A study of 1,086 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2000, 35, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollier, L.; Kim, J.; Grayson, B.H.; McCarthy, J.G. Congenital muscular torticollis and the associated craniofacial changes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepetsos, P.; Anastasopoulos, P.P.; Leonidou, A.; Kenanidis, E.; Flieger, I.; Tsiridis, E.; Macheras, G.A.; Leonidou, O. Surgical management of congenital torticollis in children older than 7 years with an average 10-year follow-up. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2017, 26, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamitani, K.; Inoue, A.; Okuno, T. Results of surgical treatment of muscular torticollis for patients > 6 years of age. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1990, 10, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.S.; Shim, J.S.; Lee, Y.S. Is sternocleidomastoid muscle release effective in adults with neglected congenital muscular torticollis? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boricean, I.-D.; Bărar, A. Understanding ocular torticollis in children. Oftalmologia 2011, 55, 10–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nucci, P.; Curiel, B. Abnormal head posture due to ocular problems: A review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2009, 5, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, E.; Johnson, R.; Sargent, B. Informing the update to the physical therapy management of congenital muscular torticollis evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 30, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.F.; Oh, A.K.; Mulliken, J.B. The role of congenital muscular torticollis in the development of deformational plagiocephaly. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 123, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.F.; Pollard, Z.F. Ocular plagiocephaly: Ocular torticollis with skull and facial asymmetry. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, H.; Eng, G.; Gaiser, J.; Koch, B. Congenital muscular torticollis: Results of conservative management with long-term follow-up in 85 cases. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1987, 68, 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-I.; Kee, J.-H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yang, S.-S. Is Longstanding Congenital Muscular Torticollis Provoking Pelvic Malalignment Syndrome? Children 2021, 8, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, C. The determinants of treatment duration for congenital muscular torticollis. Phys. Ther. 1994, 74, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Ahn, H.S.; Yim, S.-Y. Effectiveness of surgical treatment for neglected congenital muscular torticollis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 67e–77e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillinghast, A.B.; Greve, K.R.; Le Cras, S.P. TOT Collar Use in Complex Case of Congenital Muscular Torticollis with Persistent Head Tilt. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2024, 36, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sönmez, K.; Türkyilmaz, Z.; Demiroğulları, B.; Özen, I.O.; Karabulut, R.; Bağbancı, B.; Başaklar, A.C.; Kale, N. Congenital muscular torticollis in children. ORL 2005, 67, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemiya, M.; Kikkawa, I.; Watanabe, H.; Hoshino, Y. Outcome of treatment for congenital muscular torticollis: A study on ages for treatment, treatment methods, and postoperative therapy. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2009, 19, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, E.; Funayama, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kamio, K.; Sakurai, M. Tenotomy and postoperative brace treatment for muscular torticollis. Contemp. Orthop. 1990, 20, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Koh, S.-E.; Lee, I.-S.; Jung, H.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.-I.; Bang, H. The cervical range of motion as a factor affecting outcome in patients with congenital muscular torticollis. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 37, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langensiepen, S.; Stark, C.; Sobottke, R.; Semler, O.; Franklin, J.; Schraeder, M.; Siewe, J.; Eysel, P.; Schoenau, E. Home-based vibration assisted exercise as a new treatment option for scoliosis-a randomised controlled trial. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2017, 17, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, F.-C.; Hong, C.-Z.; Lai, C.-L.; Tan, S.-H. Postural control strategies related to anticipatory perturbation and quick perturbation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2011, 36, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, R.; Jung, H.; Cui, X.; Huh, S.; Lee, W.; You, H.; Kim, S. Quantitative Analysis of the Head Tilt Using Three-Dimensional Temporal Scan in Children with Torticollis. Children 2023, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.-K.; Kim, J.-R.; Park, R.-J.; Cho, M.-S. Effect of Myofascial Release Therapy on Newborns and Infants with Congenital Torticollis. J. Korean Phys. Ther. 2006, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kekunnaya, R.; Isenberg, S.J. Effect of strabismus surgery on torticollis caused by congenital superior oblique palsy in young children. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahlin, M.; Sarmiento, B. Reliability of still photography measuring habitual head deviation from midline in infants with congenital muscular torticollis. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2010, 22, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.I.; Shin, H.-I. Application of Fabric-Type Spinal Orthosis for Flexible Neuromuscular Scoliosis: A Preliminary Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 99, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, N.; Uesugi, M.; Inaba, Y.; Machida, J.; Okuzumi, S.; Saito, T. Use of dynamic spinal brace in the management of neuromuscular scoliosis: A preliminary report. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2014, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelzalts, S.; Ballardini, G.; Avraham, C.; Pagano, M.; Casadio, M.; Nisky, I. Integrating tactile feedback technologies into home-based telerehabilitation: Opportunities and challenges in light of COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Neurorobot. 2021, 15, 617636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, C.; Karmel-Ross, K. The use of splinting in conservative and post-operative treatment of congenital muscular torticollis. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 1997, 17, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (months) | 63.95 ± 13.44 | |
| Baseline torticollis angle | 17.6 ± 5.65 | |
| N (%) | ||
| Gender | Male | 11 (55.0) |
| Female | 9 (45.0) | |
| Side of lesion | Right | 12 (60.0) |
| Left | 8 (40.0) | |
| Diagnosis | Postural torticollis | 11 (55.0) |
| Postoperative state of ocular torticollis | 5 (25.0) | |
| Postoperative state of congenital muscular torticollis | 4 (20.0) | |
| Diagnosis | Baseline Angle (Mean ± SD) | Angle at End of Stage 1 (Mean ± SD) | Angle at End of Stage 2 (Mean ± SD) | SS | df | MS | Χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSCMT | 18.75 ± 4.79 | 14.75 ± 3.77 | 6.75 ± 5.38 | 27 | 2 | 13.5 | 8.000 | 0.018 * |
| PSOT | 15.60 ± 5.18 | 12.80 ± 2.77 | 6.40 ± 3.51 | 75 | 2 | 37.5 | 7.600 | 0.022 * |
| PT | 18.09 ± 6.35 | 14.55 ± 4.03 | 5.55 ± 3.39 | 1056 | 2 | 528 | 21.140 | 0.000 * |
| Variables | Improvement in Neck Angle | |
|---|---|---|
| r-Value | p-Value | |
| Age when starting treatment (months) | 0.026 | 0.915 |
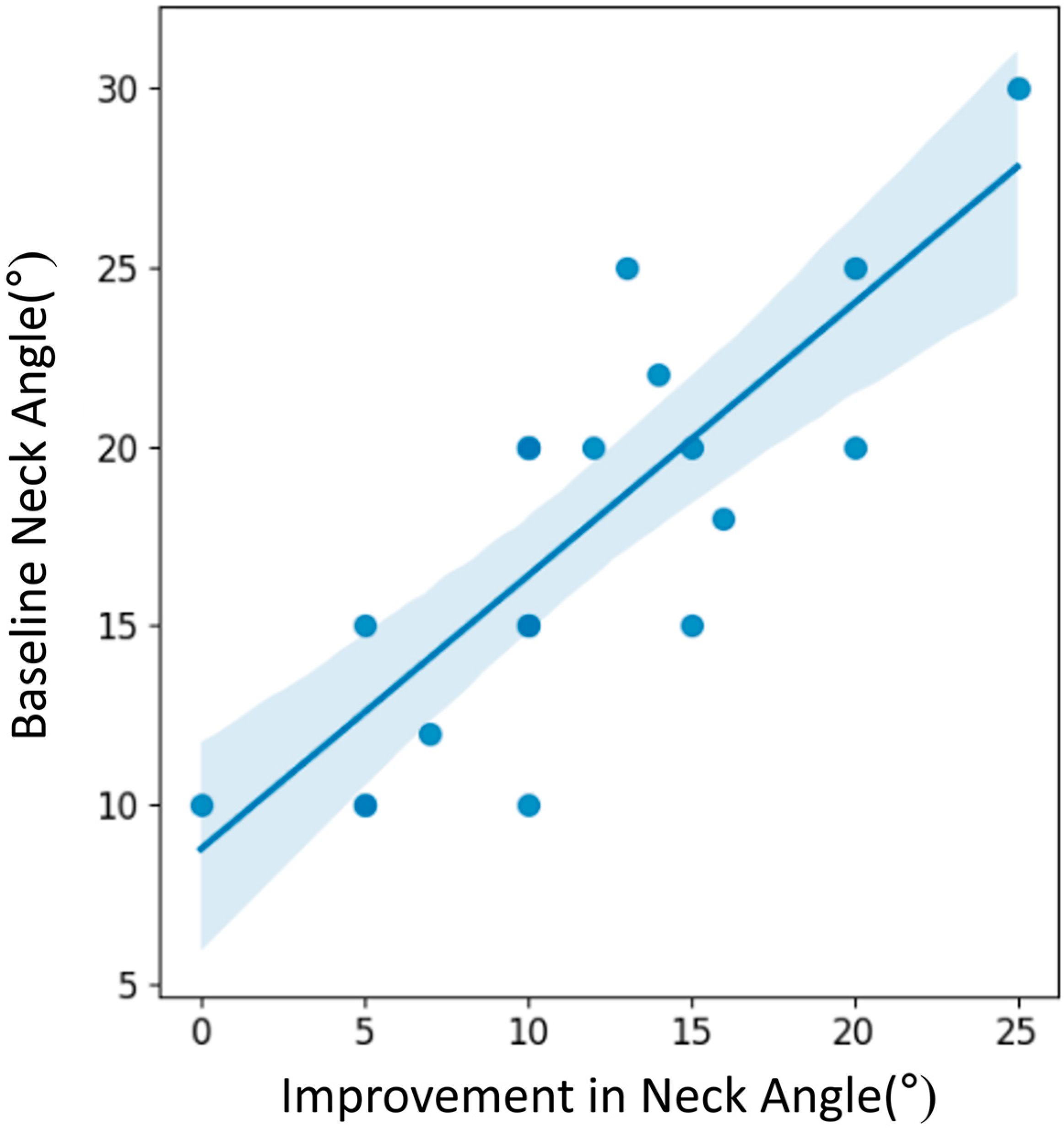
| Baseline neck angle (°) | 0.751 | 0.000 * |
| Gender | 0.292 | 0.211 |
| Side of tilt | 2.216 | 0.361 |
| Diagnosis | −0.081 | 0.736 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, J.; Yun, R.; Huh, S.; Baik, J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.-Y. Clinical Application of Custom Neck Collar with Negative Sensory Feedback in Children with Intractable Torticollis. Children 2024, 11, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11081001
Yoon J, Yun R, Huh S, Baik J, Lee JM, Kim S-Y. Clinical Application of Custom Neck Collar with Negative Sensory Feedback in Children with Intractable Torticollis. Children. 2024; 11(8):1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11081001
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Jeewon, Rayu Yun, Sungchul Huh, Jisoo Baik, Jae Meen Lee, and Soo-Yeon Kim. 2024. "Clinical Application of Custom Neck Collar with Negative Sensory Feedback in Children with Intractable Torticollis" Children 11, no. 8: 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11081001
APA StyleYoon, J., Yun, R., Huh, S., Baik, J., Lee, J. M., & Kim, S.-Y. (2024). Clinical Application of Custom Neck Collar with Negative Sensory Feedback in Children with Intractable Torticollis. Children, 11(8), 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11081001







