A Systematic Review on Ketamine and Esketamine for Treatment-Resistant Depression and Suicidality in Adolescents: A New Hope?
Abstract
1. Introduction
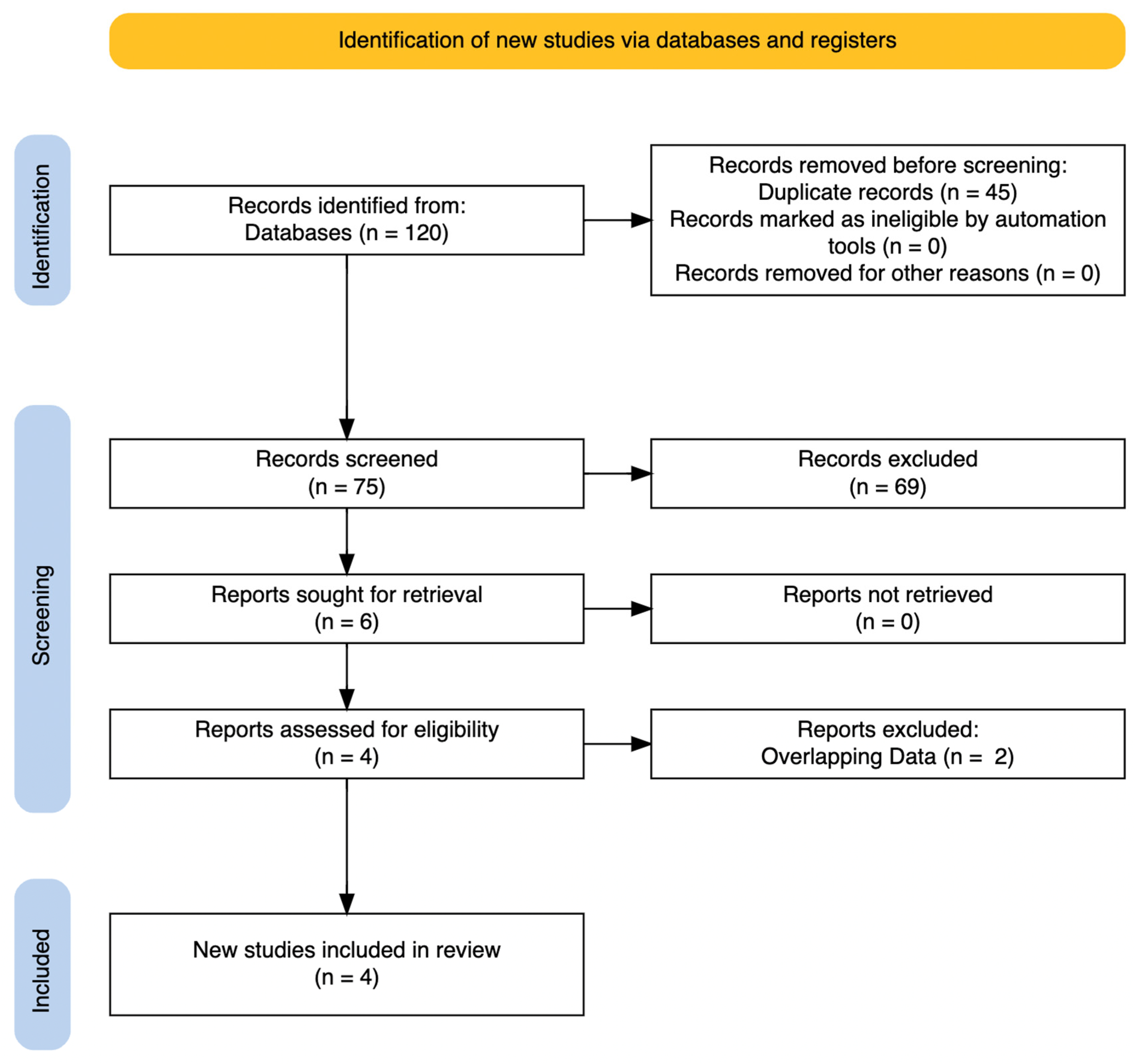
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pine, D.S.; Cohen, E.L.; Cohen, P.; Brook, J.S. Adolescent Depressive Symptoms as Predictors of Adult Depression: Moodiness or Mood Disorder? Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorey, S.; Ng, E.D.; Wong, C. Global Prevalence of Depression and Elevated Depressive Symptoms Among Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2021, 61, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Lee, S.-J.; Hwang, S.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Reliability and Validity of the Beck Depression Inventory-Ii Among Korean Adolescents. Psychiatry Investig. 2017, 14, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.F.; Miller, M.T.; Khan, N. Screening and Managing Depression in Adolescents. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2010, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gu, J. Physical Activity and Depression in Adolescents: Evidence From China Family Panel Studies. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaif, E.R.; Sussman, S.; Newcomb, M.D.; Locke, T.F. Suicidality, Depression, and Alcohol Use among Adolescents: A Review of Empirical Findings. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2007, 19, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalsma, M.; Keys, J.; Ferrin, S.; Shan, M.; Garbuz, T.; Scott, T.; Adams, Z.; Hulvershorn, L.; Downs, S. Adolescent Suicide Assessment and Management in Primary Care. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, S.J.; Bridge, J.A. Epidemiology of Youth Suicide and Suicidal Behavior. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2009, 21, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, B.-N.; Bae, J.-H.; Shin, M.-S.; Yoo, H.-J.; Cho, S.-C. Clinical Characteristics and Precipitating Factors of Adolescent Suicide Attempters Admitted for Psychiatric Inpatient Care in South Korea. Psychiatry Investig. 2015, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hua, L.L.; Lee, J.; Rahmandar, M.H.; Sigel, E.J.; Committee on Adolescence; Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Suicide and Suicide Risk in Adolescents. Pediatrics 2024, 153, e2023064800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, M.; Anastasia, A.; Valchera, A.; Carano, A.; Orsolini, L.; Vellante, F.; Rapini, G.; Olivieri, L.; Di Natale, S.; Perna, G.; et al. The FDA “Black Box” Warning on Antidepressant Suicide Risk in Young Adults: More Harm Than Benefits? Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill-Skoch, S.; Hicks, P.B.; Prieto-Hicks, X. The Use of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in the Treatment of Resistant Depression in Adolescents. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2012, 3, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration Prozac (Fluoxetine) Label 2017. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018936s108lbl.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration Lexapro (Escitalopram) Label 2017. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/021365s038,021323s053lbl.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- European Medicines Agency. Summary Information for Referral Opinion following Arbitration Pursuant to Article 30 of Council Directive 2001/83/EC for Prozac and Associated Names (Fluoxetine); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006.
- European Medicines Agency. Questions and Answers on Generic Escitalopram-Containing Medicines (Tablets Containing Escitalopram Oxalate, 5, 10, 15 and 20 Mg); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010.
- Emslie, G.J.; Mayes, T.L.; Porta, G.; Vitiello, B.; Clarke, G.; Wagner, K.D.; Asarnow, J.R.; Spirito, A.; Birmaher, B.; Ryan, N.D.; et al. Treatment of Resistant Depression in Adolescents (TORDIA): Week 24 Outcomes. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, J.B.; Stringaris, A.; Brent, D.A.; Bloch, M.H. Annual Research Review: Defining and Treating Pediatric Treatment-resistant Depression. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2020, 61, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Michael, K.D.; Liu, Y.; Giovane, C.D.; Qin, B.; Cohen, D.; Gentile, S.; Xie, P. Systematic Review of Management for Treatment-Resistant Depression in Adolescents. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynes, B.N.; Lux, L.; Gartlehner, G.; Asher, G.; Forman-Hoffman, V.; Green, J.; Boland, E.; Weber, R.P.; Randolph, C.; Bann, C.; et al. Defining Treatment-Resistant Depression. Depress. Anxiety 2020, 37, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmaher, B.; Ryan, N.D.; Williamson, D.E.; Brent, D.A.; Kaufman, J.; Dahl, R.E.; Perel, J.; Nelson, B. Childhood and Adolescent Depression: A Review of the Past 10 Years. Part I. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1996, 35, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwuere, P.C.; Sehularo, L.A.; Manyedi, E. Experiences of Adolescents and Parents on the Mental Health Management of Depression in Adolescents, North West Province, South Africa. Curationis 2022, 45, a2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, F.T.; Mia Atwi, B.A.; Brent, D.A. Treatment-Resistant Depression in Adolescents: Review and Updates on Clinical Management. Depress. Anxiety 2011, 28, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, T.H.; Croarkin, P.E.; Strawn, J.R.; McClintock, S.M. Comorbid Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms in Children and Adolescents. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2016, 22, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, D.; Emslie, G.; Clarke, G.; Wagner, K.D.; Asarnow, J.R.; Keller, M.; Vitiello, B.; Ritz, L.; Iyengar, S.; Abebe, K.; et al. Switching to Another SSRI or to Venlafaxine With or Without Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Adolescents With SSRI-Resistant Depression: The TORDIA Randomized Con-trolled Trial. JAMA 2008, 299, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobon, A.L.; Stevens, H.E. Adolescents with SSRI-Resistant Depression; Bhalla, I.P., Tampi, R.R., Srihari, V.H., Hochman, M.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Croarkin, P.E.; Elmaadawi, A.Z.; Aaronson, S.T.; Schrodt, G.R.; Holbert, R.C.; Verdoliva, S.; Heart, K.L.; Demitrack, M.A.; Strawn, J.R. Left Prefrontal Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression in Adolescents: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.N.; VandenBerg, A. Retracing Our Steps to Understand Ketamine in Depression: A Focused Review of Hypothesized Mechanisms of Action. Ment. Health Clin. 2021, 11, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yao, X.; Li, B.; Cui, R.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W. Uncovering the Underlying Mechanisms of Ketamine as a Novel Antidepressant. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 740996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanos, P.; Gould, T.D. Mechanisms of Ketamine Action as an Antidepressant. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-Regulated Signalling Pathways. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lee, B.; Liu, R.-J.; Banasr, M.; Dwyer, J.M.; Iwata, M.; Li, X.-Y.; Aghajanian, G.; Duman, R.S. mTOR-Dependent Synapse Formation Underlies the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of NMDA Antagonists. Science 2010, 329, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Sang, K.; Dong, Y.; Ni, Z.; Ma, S.; Hu, H. Ketamine Blocks Bursting in the Lateral Habenula to Rapidly Relieve Depression. Nature 2018, 554, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, O.H.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.-C.; Hargroder, E.A.; Zhang, Y.; Delpire, E.; Hall, B.J. GluN2B-Containing NMDA Receptors Regulate Depression-like Behavior and Are Critical for the Rapid Antidepressant Actions of Ketamine. eLife 2014, 3, e03581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.; Bu, W.; Lin, W.-Z.; Zoubak, L.; Yeliseev, A.; Liu, R.; Eckenhoff, R.G.; Brannigan, G. Keta-mine Metabolite (2R,6R)-Hydroxynorketamine Interacts with Μ and Κ Opioid Recep-tors. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ago, Y.; Yokoyama, R.; Asano, S.; Hashimoto, H. Roles of the Monoaminergic System in the Anti-depressant Effects of Ketamine and Its Metabolites. Neuropharmacology 2023, 223, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.-H.; Diao, Y.-G.; Ren, Z.-Y.; Zang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, G.-F.; Wang, X.-M.; Duan, G.-F.; Shen, J.-C.; Hashimoto, K.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; et al. A Role of GABAA Receptor A1 Subunit in the Hippocampus for Rapid-Acting Antidepressant-like Effects of Ketamine. Neuropharmacology 2023, 225, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.V.; Thai, M.; Klimes-Dougan, B.; Westlund Schreiner, M.; Mueller, B.A.; Albott, C.S.; Lim, K.O.; Fiecas, M.; Tye, S.J.; Cullen, K.R. Brain Entropy and Neurotrophic Molecular Markers Accompanying Clinical Improvement after Ketamine: Preliminary Evidence in Adolescents with Treatment-Resistant Depression. J. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 35, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, M.; Başgöze, Z.; Klimes-Dougan, B.; Mueller, B.A.; Fiecas, M.; Lim, K.O.; Albott, C.S.; Cullen, K.R. Neural and Behavioral Correlates of Clinical Improvement to Ketamine in Adolescents With Treatment Resistant Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canuso, C.M.; Singh, J.B.; Fedgchin, M.; Alphs, L.; Lane, R.; Lim, P.; Pinter, C.; Hough, D.; Sanacora, G.; Manji, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Intranasal Esketamine for the Rapid Reduction of Symptoms of Depression and Suicidality in Patients at Imminent Risk for Suicide: Results of a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. AJP 2018, 175, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedgchin, M.; Trivedi, M.H.; Daly, E.; Melkote, R.; Lane, R.; Lim, P.; Vitagliano, D.; Blier, P.; Fava, M.; Liebowitz, M.R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Fixed-Dose Esketamine Nasal Spray Combined With a New Oral Antidepressant in Treatment-Resistant Depression: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled Study (TRANSFORM-1). Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, E.; Singh, J.; Fedgchin, M.; Cooper, K.; Lim, P.; Shelton, R.C.; Thase, M.E.; Winokur, A.; Nueten, L.V.; Manji, H.K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Intranasal Esketamine Adjunctive to Oral Antidepressant Therapy in Treatment-Resistant Depression. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.P. Efficacy and Safety of Esketamine Nasal Spray in Addition to Standard of Care in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Who Have Active Suicidal Ideation with Intent: A Subgroup Analysis of the Asian Cohort of ASPIRE I (A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study). Asia-Pac. Psychiatry 2023, 15, e12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kim, N.-Y.; Na, H.-R.; Lim, H.K.; Woo, Y.S.; Pae, C.; Bahk, W. Rapid Onset of Intranasal Esketamine in Patients with Treatment Resistant Depression and Major Depression With Suicide Ideation: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2021, 19, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.-J.; Ionescu, D.F.; Li, X.; Lane, R.; Lim, P.; Sanacora, G.; Hough, D.; Manji, H.K.; Drevets, W.C.; Canuso, C.M. Esketamine Nasal Spray for Rapid Reduction of Major Depressive Disorder Symptoms in Patients Who Have Active Suicidal Ideation With Intent. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2020, 81, 6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.; Hosanagar, A. Ketamine Use in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry: Emerging Data in Treatment-Resistant Depression, Insights from Adults, and Future Directions. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2023, 25, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkat, S.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Ho, R.C.; Rhee, T.G.; Cao, B.; Ceban, F.; Danayan, K.; Chisamore, N.; Vincenzo, J.D.D.; McIntyre, R.S. Ketamine Use in Pediatric Depression: A Systematic Review. Psychiatry Res. 2022, 317, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruton, A.M.; Wesemann, D.G.; Machingo, T.A.; Majak, G.; Johnstone, J.M.; Marshall, R.D. Ketamine for Mood Disorders, Anxiety, and Suicidality in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry, 2024; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (Robvis): An R Package and Shiny Web App for Visualizing Risk-of-bias Assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.E.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Schünemann, H.J. What Is “Quality of Evidence” and Why Is It Important to Clinicians? BMJ 2008, 336, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Schünemann, H.J.; Tugwell, P.; Knottnerus, A. GRADE Guidelines: A New Series of Articles in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Fu, L.; Li, W.; Ye, Y.; Hu, Z.; Mai, S.; Ning, Y.; et al. Efficacy of Repeated Intravenous Esketamine in Adolescents with Anxious Versus Non-Anxious Depression. Gen. Psychiatry 2023, 36, e101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Ye, Y.; Hu, Z.; Mai, S.; Ning, Y.; Zhou, Y. Short-Term Cognitive Effects of Repeated-Dose Esketamine in Adolescents with Major Depressive Disorder and Suicidal Ideation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Heal. 2023, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lan, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Fu, L.; Li, W.; Ye, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chao, Z.; et al. Effect of Repeated Intravenous Esketamine on Adolescents with Major Depressive Disorder and Suicidal Ideation: A Randomized Active-Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2024, 63, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.B.; Landeros-Weisenberger, A.; Johnson, J.A.; Londono Tobon, A.; Flores, J.M.; Nasir, M.; Couloures, K.; Sanacora, G.; Bloch, M.H. Efficacy of Intravenous Ketamine in Adolescent Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Randomized Midazolam-Controlled Trial. FOC 2022, 20, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, K.R.; Amatya, P.; Roback, M.G.; Albott, C.S.; Westlund Schreiner, M.; Ren, Y.; Eberly, L.E.; Carstedt, P.; Samikoglu, A.; Gunlicks-Stoessel, M.; et al. Intravenous Ketamine for Adolescents with Treatment-Resistant Depression: An Open-Label Study. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 28, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT03185819 Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of 3 Fixed Doses of Intranasal Esketamine in Addition to Comprehensive Standard of Care for the Rapid Reduction of the Symptoms of Major Depressive Disorder, Including Suicidal Ideation, in Pediatric Participants Assessed to Be at Imminent Risk for Suicide (NCT03185819). 2017. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03185819 (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- Shain, B.; Committee on Adolescence; Braverman, P.K.; Adelman, W.P.; Alderman, E.M.; Breuner, C.C.; Levine, D.A.; Marcell, A.V.; O’Brien, R.F. Suicide and Suicide Attempts in Adolescents. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Abraham, C.; Bruzzese, J.-M.; Smaldone, A. Longitudinal Relationships Between Depression and Chronic Illness in Adolescents: An Integrative Review. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2020, 34, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertha, E.A.; Balázs, J. Subthreshold Depression in Adolescence: A Systematic Review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2013, 22, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGorry, P.D.; Mei, C. Early Intervention in Youth Mental Health: Progress and Future Directions. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2018, 21, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, S.N.; Hetrick, S.E.; Cox, G.R.; Brudevold-Iversen, T.; Bir, J.J.; McDowell, H. Psychological and Educational Interventions for Preventing Depression in Children and Adolescents. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; The Cochrane Collaboration, Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011; p. CD003380.pub3. [Google Scholar]
- DelBello, M.P.; Kosik-Gonzalez, C.; Fu, D.-J.; Chen, L.; Lane, R.; Drevets, W.C.; Moreno, C.; Canuso, C.M. Efficacy and Safety of Intranasal Esketamine for the Rapid Reduction of Depressive Symptoms in Adolescents With MDD at Imminent Risk for Suicide: Results of a Double-Blind, Ran-domized, Psychoactive-Controlled Study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 62, S319–S320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineham, A.; Avila-Quintero, V.J.; Bloch, M.H.; Dwyer, J. Exploring Predictors of Ketamine Response in Adolescent Treatment-Resistant Depression. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 34, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, C.A.; Stoep, A.V.; McCauley, E. Cognitive Features Associated With Depressive Symptoms in Adolescence: Directionality and Specificity. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2007, 36, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, B.A.; Nguyen, T.N.B.; Tobe, R.H.; Walker, A.M.; Gabbay, V. Multimodal Investigations of Reward Circuitry and Anhedonia in Adolescent Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 678709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinnegar, P.; Kothari, J.; Cheng, K. Successful Use of Ketamine for the Treatment of Psychotic Depression in a Teenager. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 472–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterly, C.W.; Taylor, R. Ketamine Augmentation of Electroconvulsive Therapy in an Adolescent Patient with Suicidal Ideation, Disordered Eating, and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report. J. ECT 2023, 39, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerath, A.U.; Oldak, S.E.; Parrish, M.S.; Zaydlin, M.; Martin, S.; Brown, K.; Cara, V.; Coffey, B.J. Ketamine and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in an Adolescent with Treatment-Resistant Depression. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2023, 33, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, P.E.; Andries, J.; Ahlers, D.; Whippo, M. Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy in Adolescents with Multiple Psychiatric Diagnoses. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1141988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, J.D.; Siegel, A.; Lipsitz, O.; Ho, R.; Teopiz, K.M.; Ng, J.; Lui, L.M.W.; Lin, K.; Cao, B.; Rodrigues, N.B.; et al. The Effectiveness, Safety and Tolerability of Ketamine for Depression in Adolescents and Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 137, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Country | Study Design | Drug | Populations | Interventions | Outcome | Results Concerning Depressive Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou, 2024 [57] | China | RCT | Esketamine (intravenous) | 54 participants (ages 13–18) with MDD and suicidal ideation: 27 in the ketamine group, and 27 in the midazolam group | Three infusions (day 1, day 3, and day 5) of Esketamine 0.25 mg/kg (vs. three infusions of midazolam 0.02 mg/kg | MADRS C-SSRS | Both groups had significant MADRS and C-SSRS reduction at day 6; the esketamine group had significantly lower MADRS and C-SSRS score compared with the midazolam group at day 6 |
| NCT03185819, 2018 [60] | USA | RCT | Esketamine (intranasal) | 147 participants (ages 12–18) with MDD and suicidal ideation: 84 in the esketamine group, and 63 in the midalozapm group | Esketamine (28.56 or 84 mg) or oral midalozam (0.125 mg/kg) twice a week for 4 weeks | CDRS-R | Esketamine was more effective than midazolam in reducing CDRS-R scores 24 h after the initial dose, although the differences were not statistically significant |
| Dwyer, 2021 [58] | USA | RCT (crossover) | Ketamine (intravenous) | 17 participants (ages 13–17) with TRD | A single intravenous infusion of either ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) or midazolam (0.045 mg/kg) and the alternate compound 2 weeks later | MADRS CDRS-R | Ketamine significantly reduced MADRS scores compared to midazolam over a 14-day period, with notable differences on days 1, 5, 6, 10, and 14. Both treatments significantly improved CDRS-R scores immediately after infusion, but there were no significant differences in symptom change rates over the subsequent 14 days |
| Cullen, 2018 [59] | USA | Open-label study | Ketamine (intravenous) | 13 participants (ages 13–18) with TRD | Six ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) infusions over the course of 2 weeks | MADRS CDRS-R BDI-II SHAPS TEPS | Significant improvements were observed in CDRS-R, MADRS, BDI-II, and CGI scores, while changes in SHAPS and TEPS were not significant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pardossi, S.; Fagiolini, A.; Scheggi, S.; Cuomo, A. A Systematic Review on Ketamine and Esketamine for Treatment-Resistant Depression and Suicidality in Adolescents: A New Hope? Children 2024, 11, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070801
Pardossi S, Fagiolini A, Scheggi S, Cuomo A. A Systematic Review on Ketamine and Esketamine for Treatment-Resistant Depression and Suicidality in Adolescents: A New Hope? Children. 2024; 11(7):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070801
Chicago/Turabian StylePardossi, Simone, Andrea Fagiolini, Simona Scheggi, and Alessandro Cuomo. 2024. "A Systematic Review on Ketamine and Esketamine for Treatment-Resistant Depression and Suicidality in Adolescents: A New Hope?" Children 11, no. 7: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070801
APA StylePardossi, S., Fagiolini, A., Scheggi, S., & Cuomo, A. (2024). A Systematic Review on Ketamine and Esketamine for Treatment-Resistant Depression and Suicidality in Adolescents: A New Hope? Children, 11(7), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070801







