Increased Semantic Memorization in Children with ADHD during a Paradigm of Motor Priming: Exploratory Findings
Abstract
Highlights
- Our paradigm suggested that listening to a story standing up while copying the experimenter’s movements that mimicked the actions told in the story significantly improved the semantic short-term memorization of participants.
- Movement priming may be a useful tool to improve auditory short-term memory in children with ADHD in challenging retention conditions.
- Our results could have repercussions for the management of children with ADHD at school, particularly in terms of the educational framework imposed during school time. More freedom of movement could facilitate learning for children with ADHD in the classroom.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Material
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
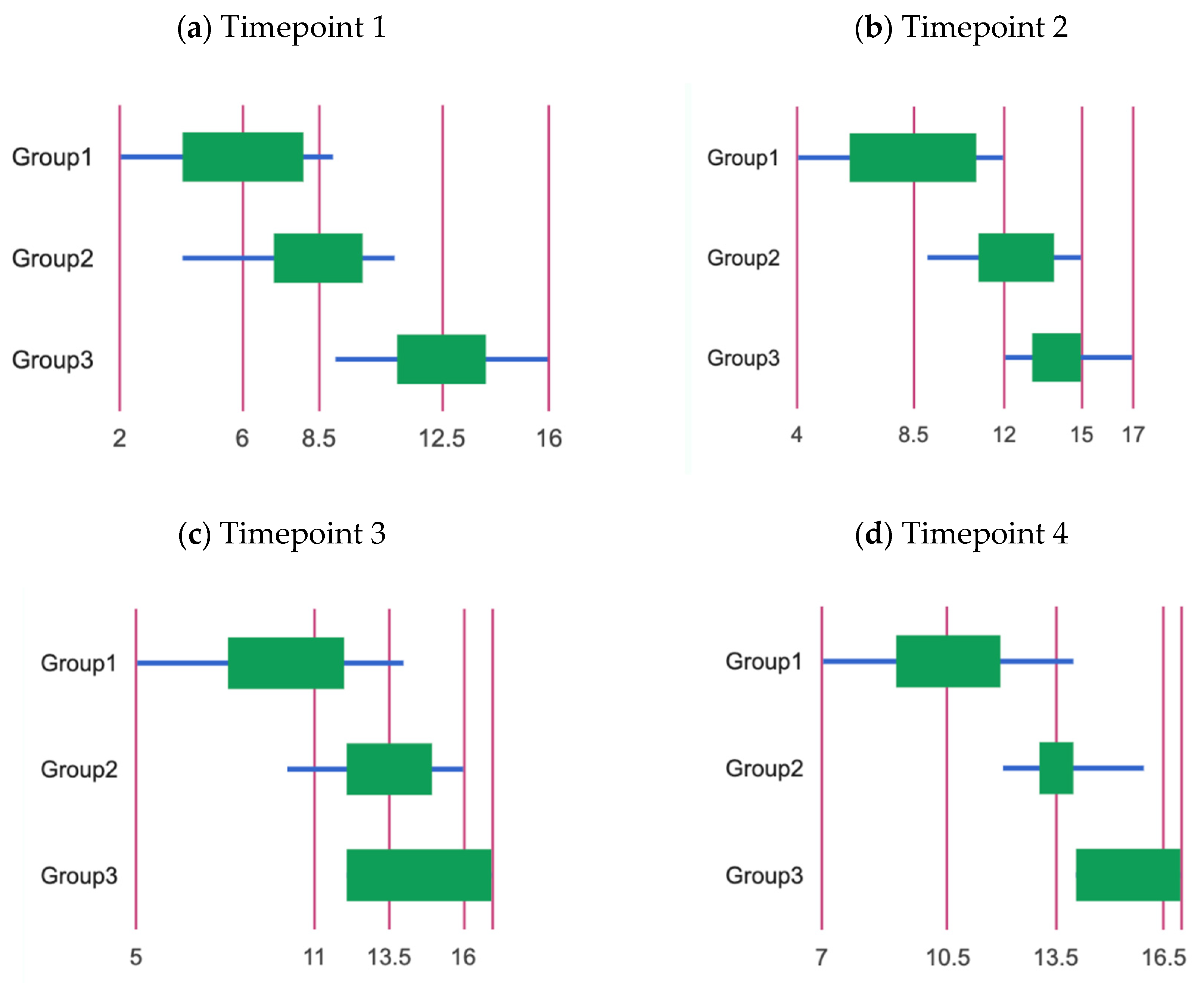
3.1. At Timepoint 1
3.2. At Timepoint 2
3.3. At Timepoint 3
3.4. At Timepoint 4
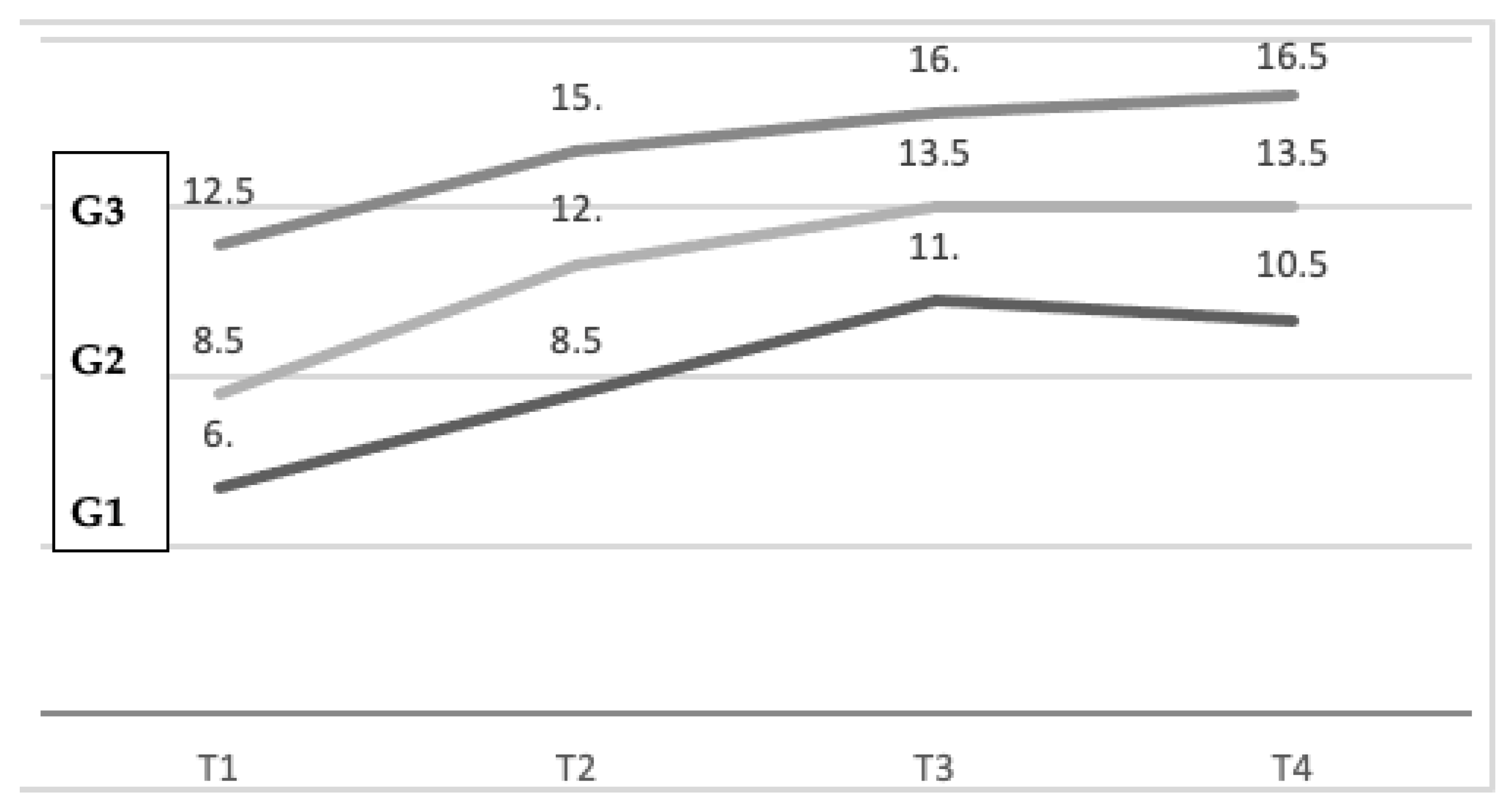
3.5. Learning Curves
3.6. Confounding Factors Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; (DSM-5); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, L.; Beck, M.M.; Bilenberg, N.; Wienecke, J.; Astrup, A.; Lundbye-Jensen, J. Effects of Exercise on Cognitive Performance in Children and Adolescents with ADHD: Potential Mechanisms and Evidence-based Recommendations. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, T.W.; Youngstrom, E.A.; Glutting, J.J.; Watkins, M.W. ADHD and Achievement: Meta-Analysis of the Child, Adolescent, and Adult Literatures and a Concomitant Study with College Students. J. Learn. Disabil. 2007, 40, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, A.L.; Stiles, K.; Lee, S.S. Childhood ADHD with and without Co-occurring Internalizing/Externalizing Problems: Prospective Predictions of Change in Adolescent Academic and Social Functioning. J. Atten. Disord. 2023, 27, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Soto, E.F.; Irwin, L.N.; Chan, E.S.M.; Spiegel, J.A.; Kofler, M.J. Executive functions and writing skills in children with and without ADHD. Neuropsychology 2021, 35, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldani, S.; Acquaviva, E.; Moscoso, A.; Peyre, H.; Delorme, R.; Bucci, M.P. Reading performance in children with ADHD: An eye-tracking study. Ann. Dyslexia 2022, 72, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapport, M.D.; Bolden, J.; Kofler, M.J.; Sarver, D.E.; Raiker, J.S.; Alderson, R.M. Hyperactivity in boys with ADHD: A ubiquitous core symptom or manifestation of working memory deficits? J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2009, 37, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickstein, S.G.; Bannon, K.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. The neural correlates of ADHD: An ALE meta-analysis. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2006, 47, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, D.E.; Rapport, M.D.; Kofler, M.J.; Raiker, J.S.; Friedman, L.M. Hyperactivity in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Impairing Deficit or Compensatory Behavior? J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 2015, 43, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartanto, T.A.; Krafft, C.E.; Iosif, A.M.; Schweitzer, J.B. A trial-by-trial analysis reveals more intense physical activity is associated with better cognitive control performance in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child. Neuropsychol. 2016, 22, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, K.J.; Reeves, L.; Howlett, N.; Fletcher, B.C. Giving cognition a helping hand: The effect of congruent gestures on object name retrieval. Br. J. Psychol. 2013, 104, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin-Meadow, S.; Wagner, S.M. How our hands help us learn. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine, K.J.; Knott, T.; Fletcher, B.C. Quand faire des gestes permet de mieux apprendre. Enfance 2010, 3, 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Neudecker, C.; Mewes, N.; Reimers, A.K.; Woll, A. ‘Exercise Interventions in Children and Adolescents with ADHD: A Systematic Review’. J. Atten. Disord. 2019, 23, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, H.; Hirsch, O.; Albrecht, B.; Chavanon, M.L. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Emotion Regulation Over the Life Span. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPaul, G.J.; Power, T.J.; Anastopoulos, A.D.; Reid, R. ADHD Rating Scale-IV: Checklists, Norms, and Clinical Interpretation; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Retrieved 9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Feuillerat, B.; Dhellemmes, J. Normative data for two tracking tests of visual and verbal memory. Evol. Psychomot. 2003, 62, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, N. What are the differences between long-term, short-term, and working memory? Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 169, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W. A SAS macro for testing differences among three or more independent groups using Kruskal-Wallis and Nemenyi tests. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2012, 32, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldin-Meadow, S.; Nusbaum, H.; Kelly, S.D.; Wagner, S. Explaining math: Gesturing lightens the load. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 12, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Stigchel, S.; Meeter, M.; Theeuwes, J. Eye movement trajectories and what they tell us. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, V. L’approche Kinesthésique dans L’apprentissage de la Grammaire Anglaise; Editions Universitaires Euroepeénnes: 2016. Available online: https://dumas.ccsd.cnrs.fr/dumas-01221442/document (accessed on 28 October 2015).
- Bonini, L.; Rotunno, C.; Arcuri, E.; Gallese, V. Mirror neurons 30 years later: Implications and applications. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2022, 26, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, L.J.; Alderson, R.M.; Hudec, K.L. Moderators of working memory deficits in children with ADHD: A meta-analytic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2012, 32, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofler, M.J.; Spiegel, J.A.; Austin, K.; Irwin, L.N.; Soto, E.F.; Sarver, D.E. Are Episodic Buffer Processes Intact in ADHD? Experimental Evidence and Linkage with Hyperactive Behavior. J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 2018, 46, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderson, R.M.; Kasper, L.J.; Patros, C.H.G.; Hudec, K.L.; Tarle, S.J.; Lea, S.E. Working memory deficits in boys with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): An examination of orthographic coding and episodic buffer processes. Child Neuropsychol. 2015, 21, 509–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ‘Yesterday the child went to the park, and he did…. Cycling, he climbed on a tree, jumped on the sandbox, lay down in the grass, then fell asleep looking at the clouds. He woke up to go slide down the yellow slide and back home running to get his snack’. |
| G1 Freeze | G2 Minimal | G3 Prescribed Movement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 10) | (n = 10) | (n = 10) | |
| Age at inclusion (years) (SD) | 8.1 ± 0.4 | 8.5 ± 0.4 | 8.2 ± 0.6 |
| ADHD-Rating scale mean (SD) | |||
| Total score | 34.1 ± 2.5 | 35.2 ± 2.5 | 33.0 ± 2.0 |
| Inattention sub-score | 16.9 ± 1.6 | 18.5 ± 1.1 | 16.7 ± 1.2 |
| Hyperactivity/impulsivity sub-score | 19.4 ± 1.8 | 20.1 ± 2.3 | 17.1 ± 1.9 |
| Wechsler scale | |||
| Mean Total IQ (SD) | 103.6 ± 8.5 | 100 ± 15.5 | 105.7 ± 13.8 |
| Median Total IQ | 101.5 | 100 | 108 |
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verbal subscale | Spearman’s rho | −0.072 | −0.115 | −0.027 | −0.128 |
| p-value | 0.709 | 0.554 | 0.891 | 0.508 | |
| Visuo-spatial subscale | Spearman’s rho | 0.117 | 0.079 | 0.145 | 0.063 |
| p-value | 0.545 | 0.682 | 0.454 | 0.745 | |
| Perceptual reasoning subscale | Spearman’s rho | 0.279 | 0.114 | 0.107 | 0.114 |
| p-value | 0.143 | 0.554 | 0.579 | 0.555 | |
| Working memory subscale | Spearman’s rho | 0.424 | 0.424 | 0.335 | 0.353 |
| p-value | 0.022 * | 0.022 * | 0.076 | 0.060 | |
| Processing speed subscale | Spearman’s rho | 0.304 | 0.348 | 0.251 | 0.339 |
| p-value | 0.109 | 0.065 | 0.190 | 0.072 | |
| Total IQ | Spearman’s rho | 0.217 | 0.156 | 0.126 | 0.123 |
| p-value | 0.258 | 0.420 | 0.513 | 0.526 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moscoso, A.; Louisin, C.; Caldani, S.; Worms Ehrminger, M.; Fefeu, M.; Acquaviva, E.; Delorme, R.; Bucci, M.P. Increased Semantic Memorization in Children with ADHD during a Paradigm of Motor Priming: Exploratory Findings. Children 2024, 11, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070787
Moscoso A, Louisin C, Caldani S, Worms Ehrminger M, Fefeu M, Acquaviva E, Delorme R, Bucci MP. Increased Semantic Memorization in Children with ADHD during a Paradigm of Motor Priming: Exploratory Findings. Children. 2024; 11(7):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070787
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoscoso, Ana, Clarisse Louisin, Simona Caldani, Mickael Worms Ehrminger, Mylene Fefeu, Eric Acquaviva, Richard Delorme, and Maria Pia Bucci. 2024. "Increased Semantic Memorization in Children with ADHD during a Paradigm of Motor Priming: Exploratory Findings" Children 11, no. 7: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070787
APA StyleMoscoso, A., Louisin, C., Caldani, S., Worms Ehrminger, M., Fefeu, M., Acquaviva, E., Delorme, R., & Bucci, M. P. (2024). Increased Semantic Memorization in Children with ADHD during a Paradigm of Motor Priming: Exploratory Findings. Children, 11(7), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070787







