Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Associated Comorbidities among Preschool-Aged Children with Down Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
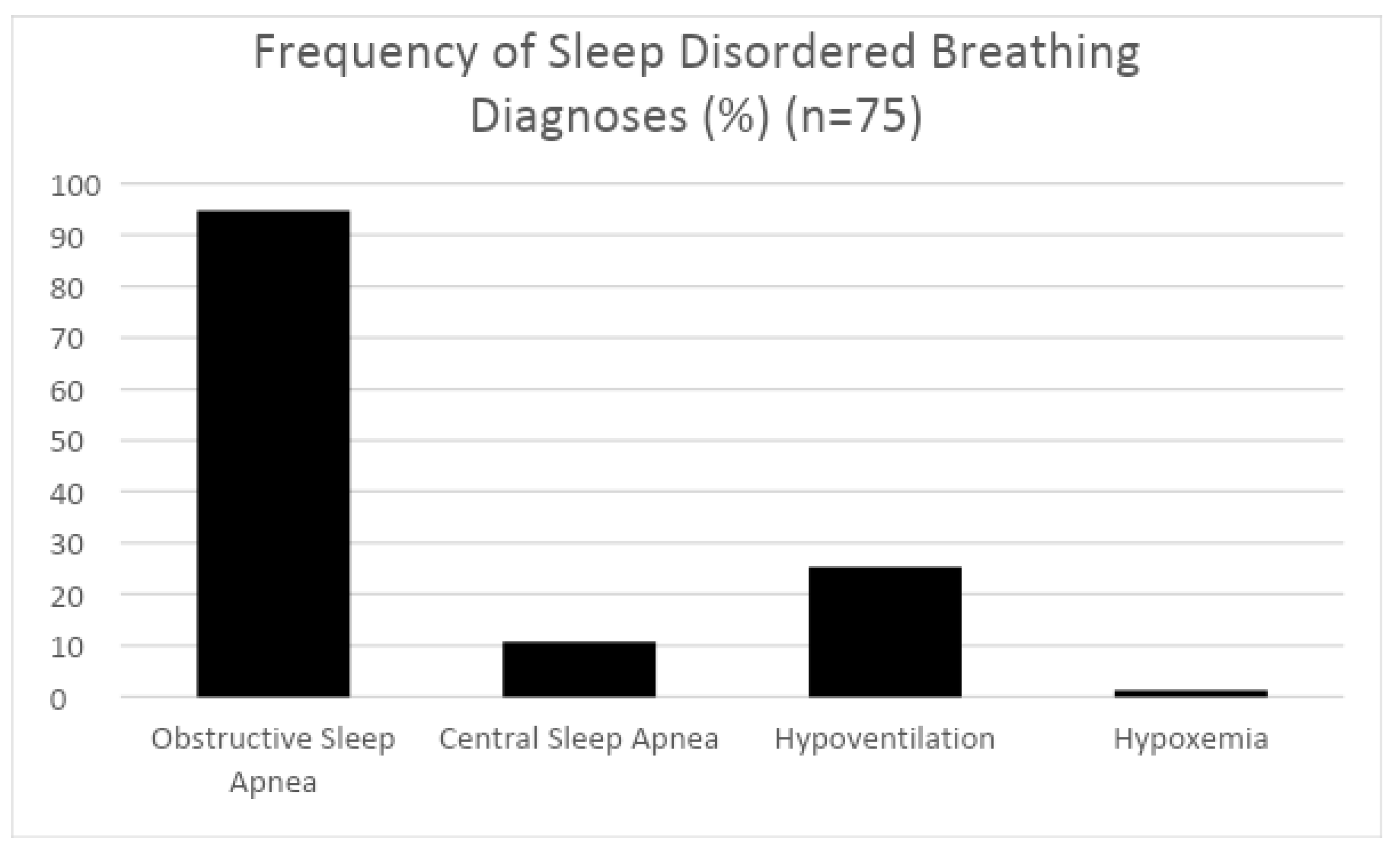
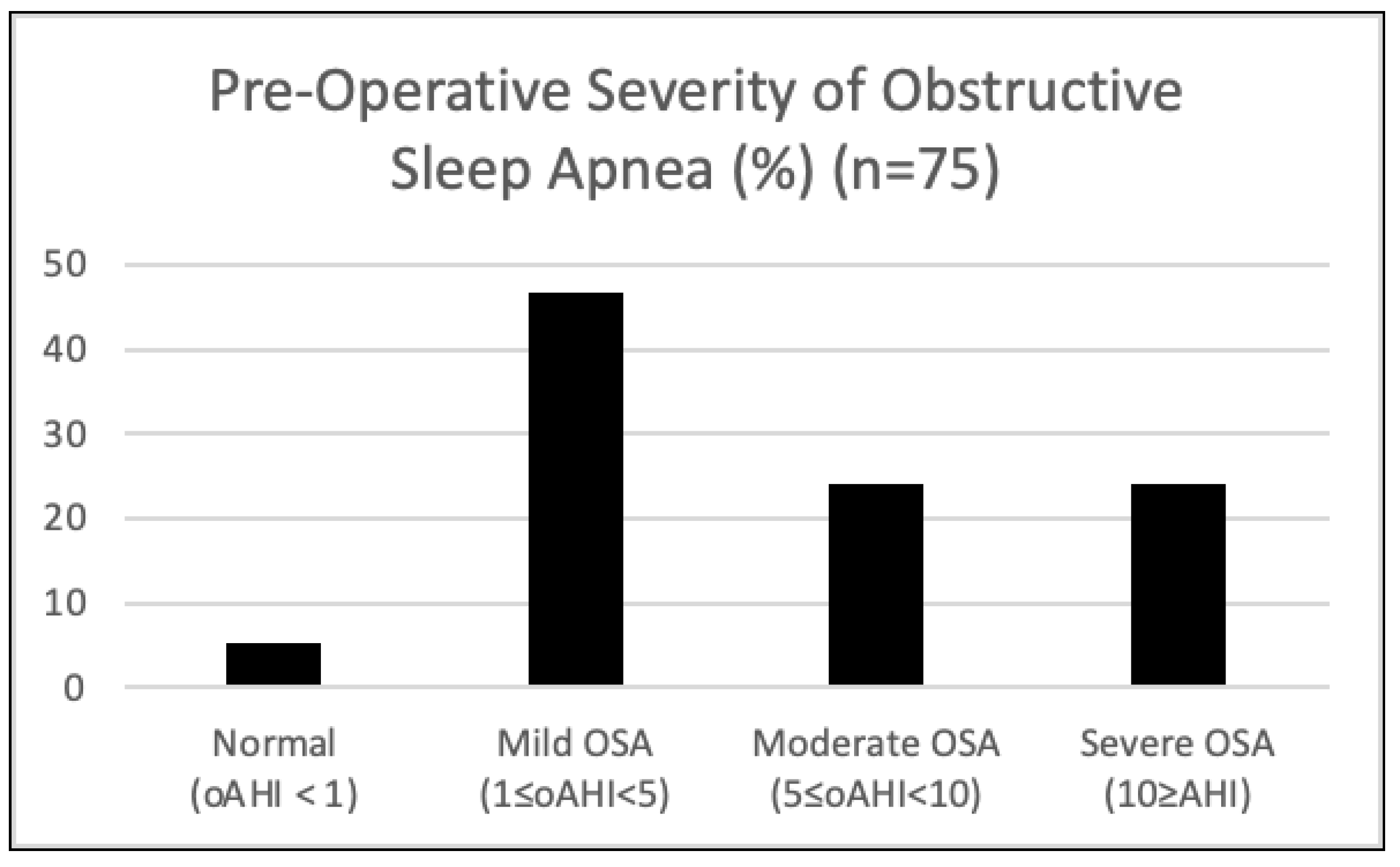
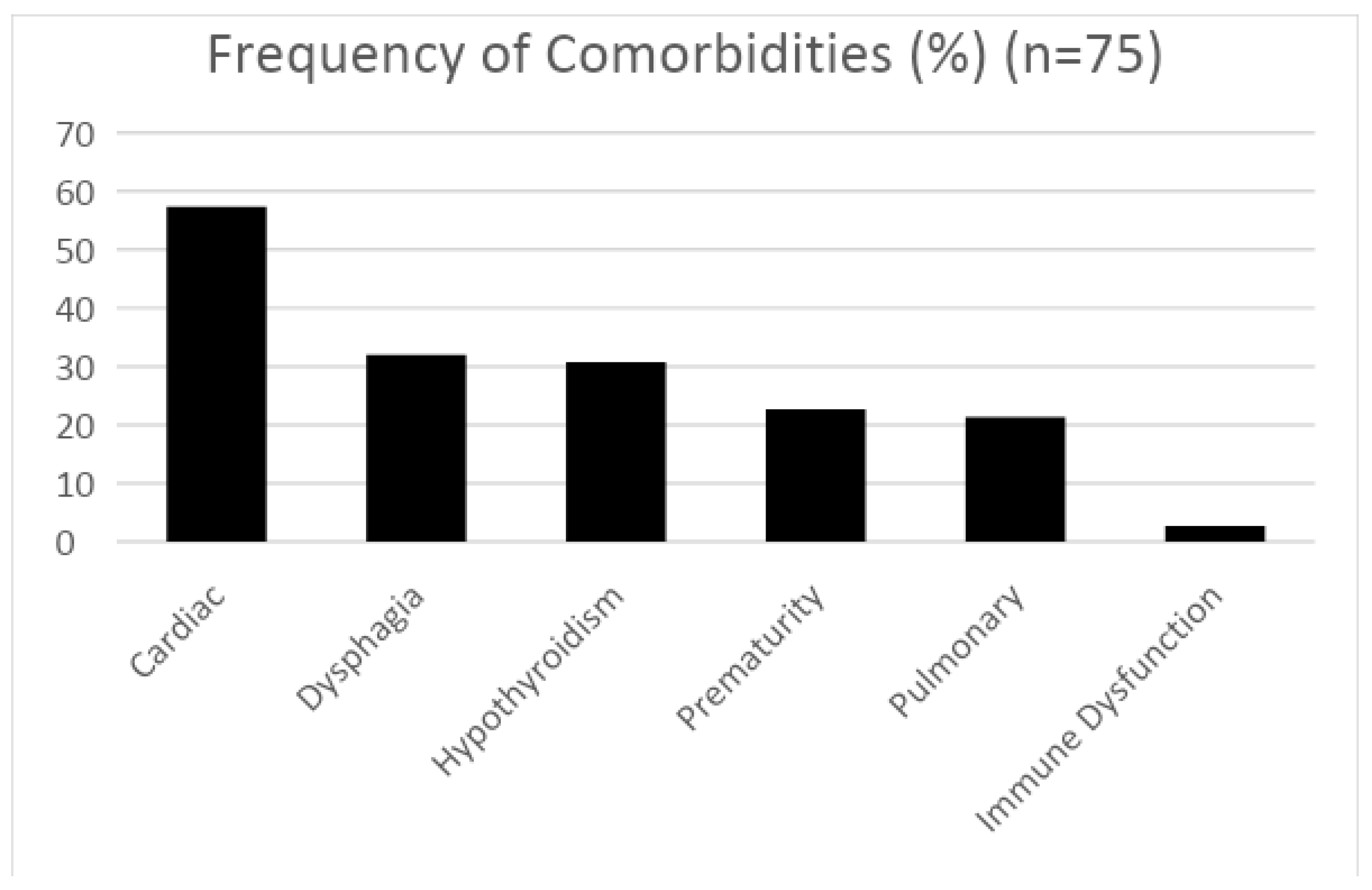
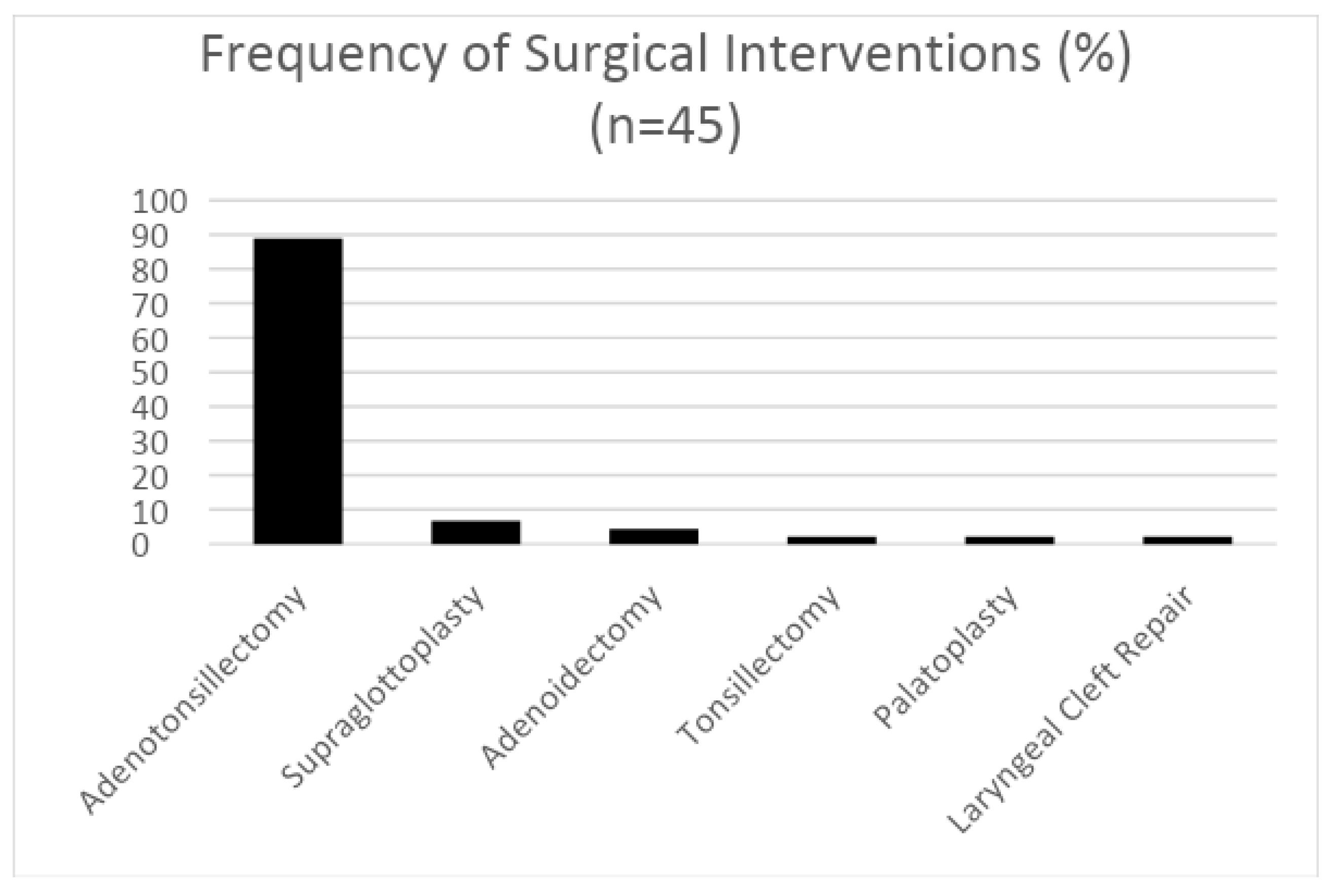
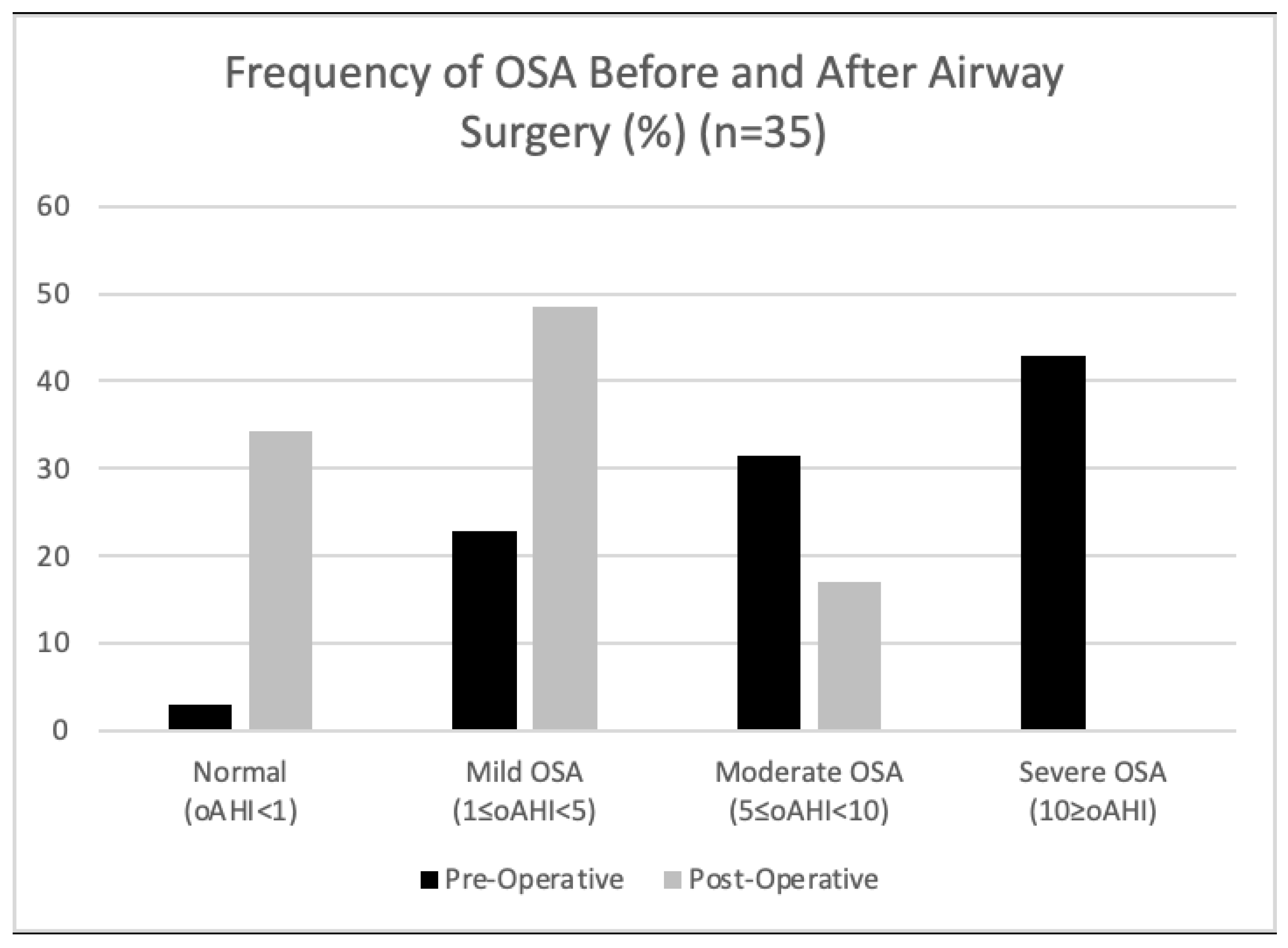
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parker, S.E.; Mai, C.T.; Canfield, M.A.; Rickard, R.; Wang, Y.; Meyer, R.E.; Anderson, P.; Mason, C.A.; Collins, J.S.; Kirby, R.S.; et al. National Birth Defects Prevention Network. Updated National Birth Prevalence estimates for selected birth defects in the United States, 2004–2006. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijerman, M.E.; de Winter, J.P. Clinical practice. The care of children with Down syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastelum, E.; Cummins, M.; Singh, A.; Montoya, A.; Urbano, G.L.; Tablizo, M.A. Treatment Considerations for Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Pediatric Down Syndrome. Children 2021, 8, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-F.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsueh, W.-Y.; Lin, M.-T.; Kang, K.-T. Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Down Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qubty, W.F.; Mrelashvili, A.; Kotagal, S.; Lloyd, R.M. Comorbidities in infants with obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, J.C.; Chervin, R.D. Epidemiology of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, M.; Verhulst, S.; Wojciechowski, M.; Van de Heyning, P.; Boudewyns, A. Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Down Syndrome. Sleep 2016, 39, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, M.J. Health supervision for children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbensen, A.J.; Beebe, D.W.; Byars, K.C.; Hoffman, E.K. Use of sleep evaluations and treatments in children with down syndrome. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2016, 37, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassell, J.L.; Phan, H.; Leu, R.; Kronk, R.; Visootsak, J. Sleep profiles in children with Down syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2015, 167, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, J.; Spanò, G.; Bootzin, R.; Anand, P.; Nadel, L.; Edgin, J. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and cognition in down syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capdevila, O.S.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Dayyat, E.; Gozal, D. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea: Complications, management, and long-term outcomes. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, C.; White, D.R.; Joseph, J.E.; van Bakergem, K.; LaRosa, A. Sleep-disordered breathing in Down syndrome. Chest 2015, 147, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.; Oyekan, A.A.; Ehsan, Z.; Ingram, D.G. Obstructive sleep apnea in patients with Down syndrome: Current perspectives. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2018, 10, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, V.; Shukla, G.; Gupta, N.; Gupta, A.; Sapra, S.; Gulati, S.; Pandey, R.M.; Pandey, S.; Kabra, M. Association of Sleep Apnea with Development and Behavior in Down Syndrome: A Prospective Clinical and Polysomnographic Study. Pediatr. Neurol. 2021, 116, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.C.; Hsu, W.C.; Chang, L.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, P.T.; Chien, C.C.; Chien, Y.H.; Chen, C.L.; Hwu, W.L.; Lee, P.L. REM sleep and sleep apnea are associated with language function in Down syndrome children: An analysis of a community sample. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 119 Pt 3, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, A.; Elphick, H.; Farquhar, M.; Gringras, P.; Evans, H.; Bucks, R.S.; Kreppner, J.; Kingshott, R.; Martin, J.; Reynolds, J.; et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Contributes to Executive Function Impairment in Young Children with Down Syndrome. Behav. Sleep Med. 2020, 18, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhood, Z.; Isley, J.W.; Ong, A.A.; Nguyen, S.A.; Camilon, T.J.; LaRosa, A.C.; White, D.R. Adenotonsillectomy outcomes in patients with Down syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeans, W.D.; Fernando, D.C.; Maw, A.R.; Leighton, B.C. Along itudinal study of the growth of the nasopharynx and its contents in normal children. Br. J. Radiol. 1981, 54, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.A.; Tolisano, A.M.; Cable, B.B.; Camacho, M. Neurocognitive outcomes after pediatric adenotonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 83, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sessa, A.; Messina, G.; Bitetti, I.; Falanga, C.; Farello, G.; Verrotti, A.; Carotenuto, M. Cardiometabolic risk profile in non-obese children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 08, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, N.; Beydon, N.; Berdah, L.; Corvol, H.; Aubertin, G.; Taytard, J. Nocturnal hypoventilation in Down syndrome children with or without sleep apnea. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trucco, F.; Chatwin, M.; Semple, T.; Rosenthal, M.; Bush, A.; Tan, H.L. Sleep disordered breathing and ventilatory support in children with Down syndrome. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Ahn, M.; Roth, H.L.; Li, L.; Vaughn, B.V. Sleep apnea and hypoventilation in patients with Down syndrome: Analysis of 144 polysomnogram studies. Children 2017, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, S.; Tompson, B.D.; Cornfoot, L. Cranial base, maxillary and mandibular morphology in Down syndrome. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Sakai, N.; Iwasaki, T.; Doyle, T.C.; Mobley, W.C.; Nishino, S. Detailed evaluation of the upper airway in the Dp(16)1Yey mouse model of Down syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lausnay, M.; Verhulst, S.; Van Hoorenbeeck, K.; Boudewyns, A. Obstructive Sleep Disorders in Down Syndrome’s Children with and without Lower Airway Anomalies. Children 2021, 8, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Caples, S.M.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Somers, V.K. Interactions between obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: Implications for treatment. Chest 2010, 137, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gameren-Oosterom, H.B.; van Dommelen, P.; Schönbeck, Y.; Oudesluys-Murphy, A.M.; van Wouwe, J.P.; Buitendijk, S.E. Prevalence of overweight in Dutch children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1520–e1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Sarber, K.M.; Howard, J.J.M.; Huang, G.; Hossain, M.M.; Heubi, C.H.; Lu, X.; Simakajornboon, N. Children with Down syndrome and mild OSA: Treatment with medication versus observation. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Kwon, Y.; DelRosso, L.; Sobremonte-King, M. Dysphagia severity is associated with worse sleep-disordered breathing in infants with Down Syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2023, 19, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, H.V.; Tomaselli, L.T.; McKenna, B.M.K. Adenotonsillectomy for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: How to Predict Those at Risk for Postoperative Complications. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayasam, S.; Johnson, R.; Lenahan, D.; Abijay, C.; Mitchell, R.B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children Under 3 Years of Age. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E2603–E2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, M.; Verhulst, S.; Wojciechowski, M.; Van de Heyning, P.; Boudewyns, A. Outcome of adenotonsillectomy in children with Down syndrome and obstructive sleep apnoea. Arch. Dis. Child. 2017, 102, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerfeldt, P.; Sundelin, A. Obstructive sleep apnea in children with Down Syndrome—Prevalence and evaluation of surgical treatment. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 133, 109968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, D.G.; Amanda, G.; Ruiz, D.G.; Norman, R.F. Success of Tonsillectomy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Down Syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarsan, S.S.; Vijaya, K.P.; Senthil, V.A.; Sathiya, M.; Mohan, K. Comparison of Treatment Modalities in Syndromic Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea—A Randomized Cohort Study. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shete, M.M.; Stocks, R.M.S.; Sebelik, M.E.; Schoumacher, R.A. Effects of Adeno-Tonsillectomy on Polysomnography Patterns in Down Syndrome Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Comparative Study with Children without Down Syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Race | % |
| American Indian | 0.0 |
| Asian | 13.3 |
| Black or African American | 1.3 |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 1.3 |
| White | 54.7 |
| Other or multiple races | 24.0 |
| Declined to answer | 5.3 |
| Ethnicity | % |
| Hispanic | 20.0 |
| Non-Hispanic | 74.7 |
| Declined to answer | 5.3 |
| Mean (SD) | n | |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep efficiency (%) | 85.2% (8.68) | 75 |
| Total sleep time (min) | 481.2 (79.92) | 75 |
| Stage N1 % of sleep time | 8.4% (6.74) | 75 |
| Stage N2 % of sleep time | 42.5% (8.1) | 74 |
| Stage N3 % of sleep time | 29.9% (7.22) | 75 |
| Stage REM % of sleep time | 21.5% (14.93) | 75 |
| Total arousal index | 13.1 (4.74) | 75 |
| Respiratory Parameters | Mean (SD) | n |
|---|---|---|
| Total AHI | 10.30 (10.20) | 75 |
| OAHI | 7.9 (9.40) | 75 |
| CAI | 2.40 (2.40) | 75 |
| REM AHI | 19.8 (20.36) | 74 |
| NREM AHI | 8.6 (9.56) | 73 |
| Mean O2 saturation during sleep | 96.9% (1.92) | 75 |
| Nadir O2 saturation during sleep | 87.6% (5.48) | 75 |
| % Total sleep time O2 < 88% | 0.8% (6.16) | 75 |
| Oxygen desaturation index | 7.03 (7.65) | 75 |
| % Total sleep time ETCO2 > 50 mmHg | 7.9% (18.2) | 48 |
| % Total sleep time TcCO2 > 50 mmHg | 17.9% (24.46) | 45 |
| Respiratory Parameters | Pre-Surgery Mean (SD) | Post-Surgery Mean (SD) | * p Value (95% CI) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total AHI | 14.9 (12.63) | 7.4 (5.42) | 0.0014 (−11.98, −3.143) | 35 |
| OAHI | 12.1 (11.99) | 4.8 (3.72) | 0.001 (−11.52, −3.18) | 35 |
| CAI | 2.8 (2.69) | 2.6 (2.49) | 0.63 (−1.07, 0.66) | 35 |
| REM AHI | 28.8 (26) | 12.2 (8.57) | 0.0007 (−25.64, −7.58) | 34 |
| NREM AHI | 12.0 (11.63) | 6.5 (5.15) | 0.013 (−9.70, −1.24) | 34 |
| Mean O2 saturation | 96.2% (2.43) | 96.9% (1.37) | 0.15 (−0.23, 0.9) | 35 |
| O2 saturation nadir | 85.4% (5.91) | 88.4% (3.97) | 0.009 (0.78, 5.14) | 35 |
| % Sleep time O2 < 88% | 1.6% (9.01) | 0.02% (0.05) | 0.3 (−4.68, 1.5) | 35 |
| ODI | 10.4 (9.59) | 5.3 (4.84) | 0.006 (−8.68, −1.6) | 35 |
| % Sleep time ETCO2 > 50 mmHg | 12.9% (27.33) | 7.2% (17.41) | 0.34 (−18.38, 6.88) | 14 |
| % Sleep time TcCO2 > 50 mmHg | 16.7% (22.4) | 12.2% (23.97) | 0.58 (−21.36, 12.27) | 19 |
| Sleep Parameters | Pre-Surgery Mean (SD) | Post Surgery Mean (SD) | * p Value (95% CI) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sleep efficiency (%) | 86.1% (6.69) | 85.5% (8.31) | 0.013 (−3.49, 2.24) | 35 |
| Total sleep rime (min) | 469.5 (89.36) | 515.03 (54.59) | 0.013 (10.39, 80.6) | 35 |
| Stage N1 % of sleep time | 9.8% (7.19) | 7.7% (6.02) | 0.17 (−5.1, 0.96) | 35 |
| Stage N2 % of sleep time | 42.0% (9.3) | 43.3% (8.59) | 0.49 (−2.49, 5.11) | 34 |
| Stage N3 % of sleep time | 30.5% (8.74) | 29.1% (9.99) | 0.53 (−5.48, 2.85) | 35 |
| Stage REM % of sleep time | 20.5% (14.35) | 19.4% (6.48) | 0.005 (−6.65, 4.40) | 35 |
| Total arousal index | 14.7 (4.84) | 12.5 (4.80) | 0.014 (−3.94, −0.47) | 35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolstad, T.K.; DelRosso, L.M.; Tablizo, M.A.; Witmans, M.; Cho, Y.; Sobremonte-King, M. Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Associated Comorbidities among Preschool-Aged Children with Down Syndrome. Children 2024, 11, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060651
Kolstad TK, DelRosso LM, Tablizo MA, Witmans M, Cho Y, Sobremonte-King M. Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Associated Comorbidities among Preschool-Aged Children with Down Syndrome. Children. 2024; 11(6):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060651
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolstad, Tessa K., Lourdes M. DelRosso, Mary Anne Tablizo, Manisha Witmans, Yeilim Cho, and Michelle Sobremonte-King. 2024. "Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Associated Comorbidities among Preschool-Aged Children with Down Syndrome" Children 11, no. 6: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060651
APA StyleKolstad, T. K., DelRosso, L. M., Tablizo, M. A., Witmans, M., Cho, Y., & Sobremonte-King, M. (2024). Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Associated Comorbidities among Preschool-Aged Children with Down Syndrome. Children, 11(6), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060651










