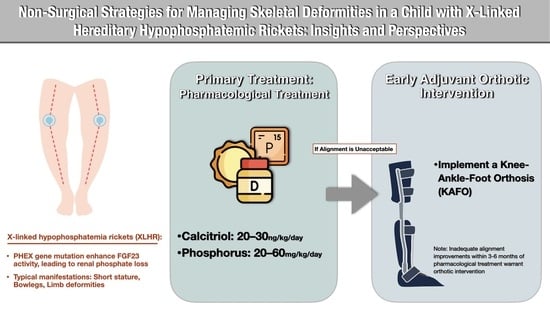
Non-Surgical Strategies for Managing Skeletal Deformities in a Child with X-Linked Hereditary Hypophosphatemic Ricket: Insights and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Description
2.1. Diagnosis
2.2. Treatment Transition
2.3. Skeletal Profile Changes
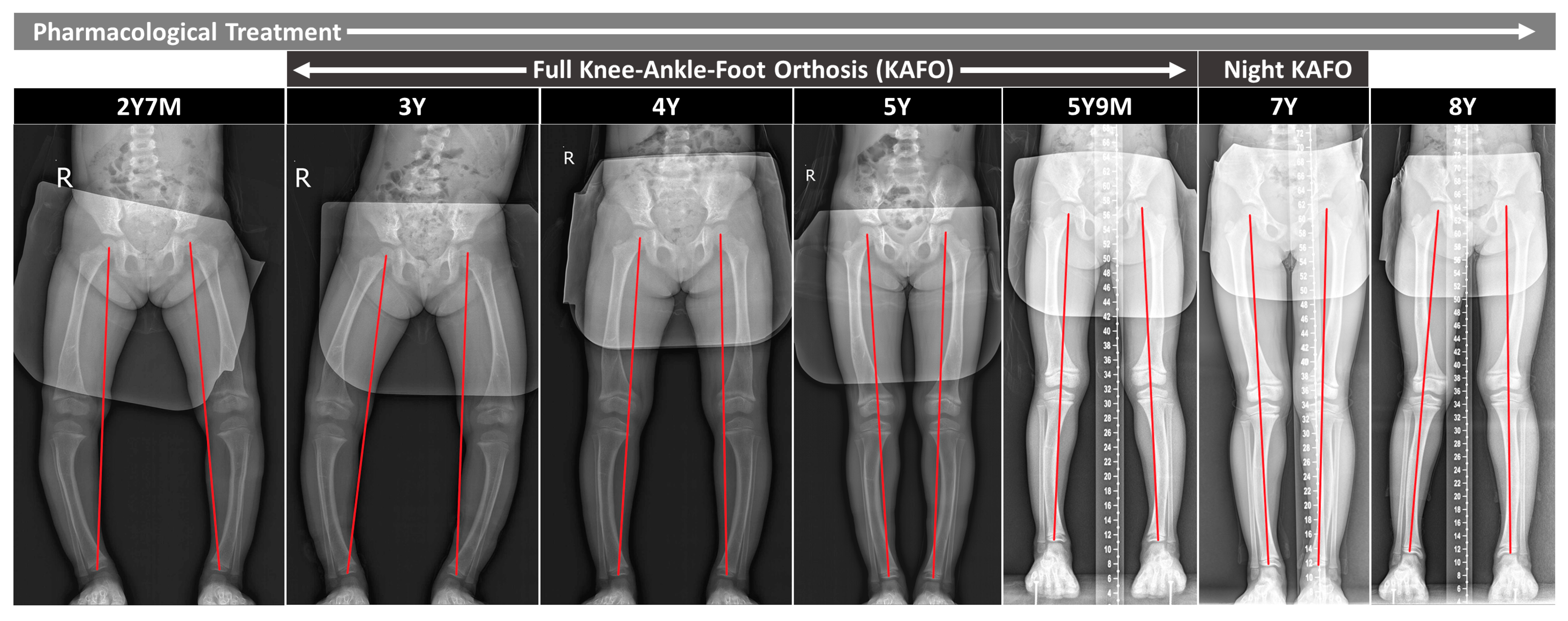
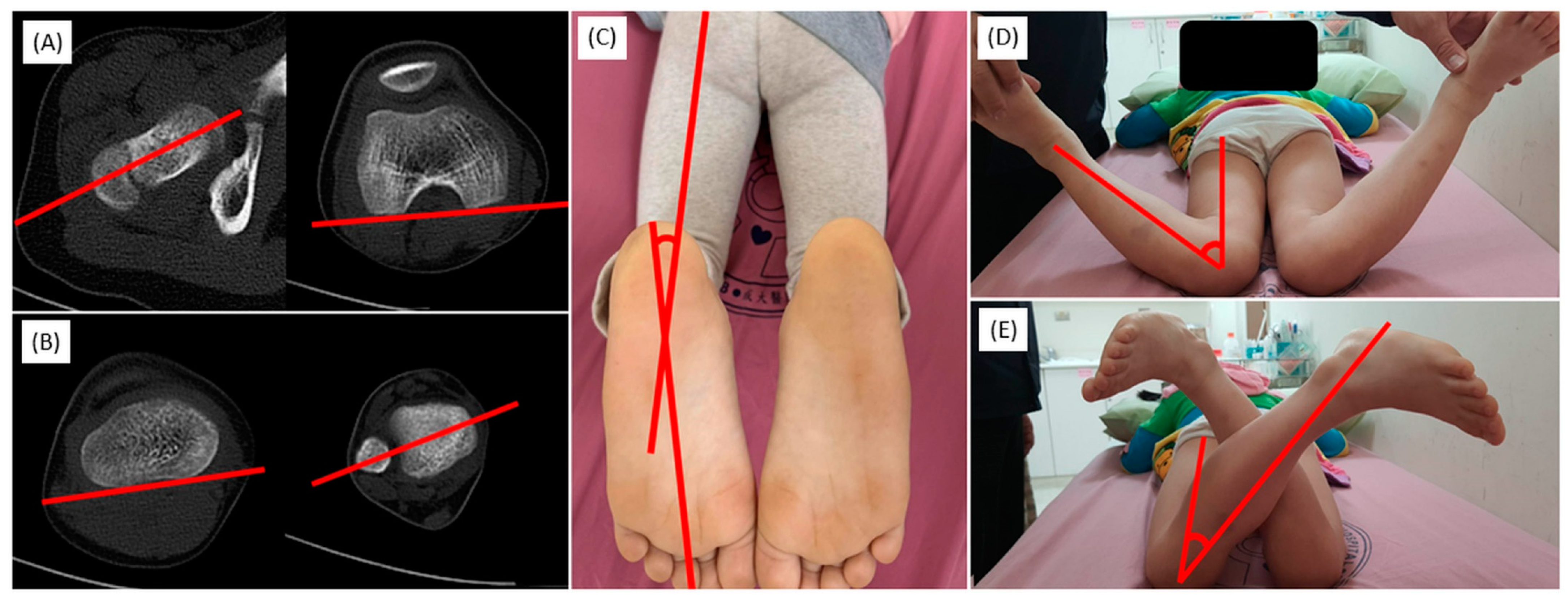
2.3.1. Coronal Alignment
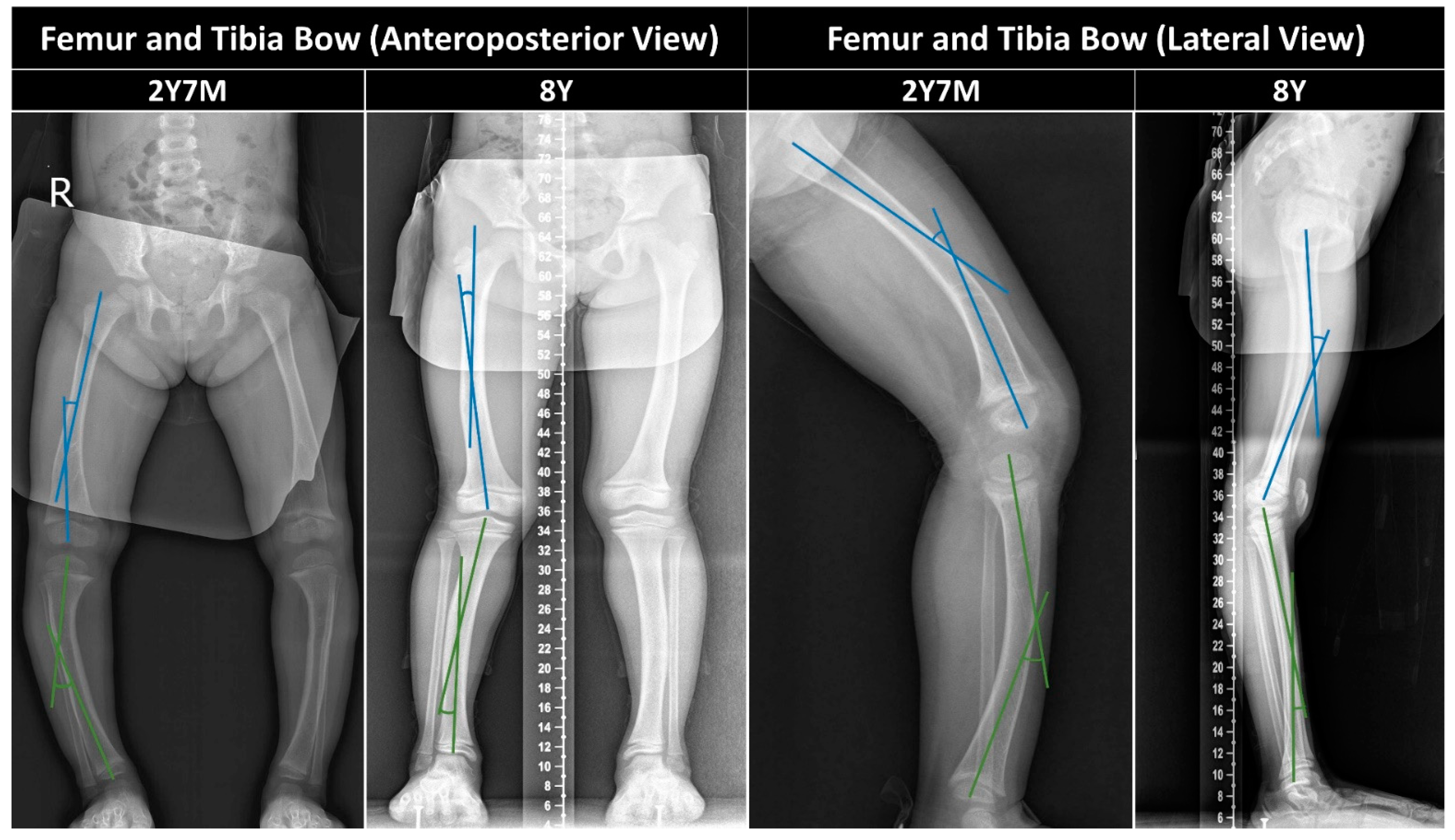
2.3.2. Femur/Tibia Bow and Metaphyseal-Diaphyseal Angle
2.3.3. Axial Alignment
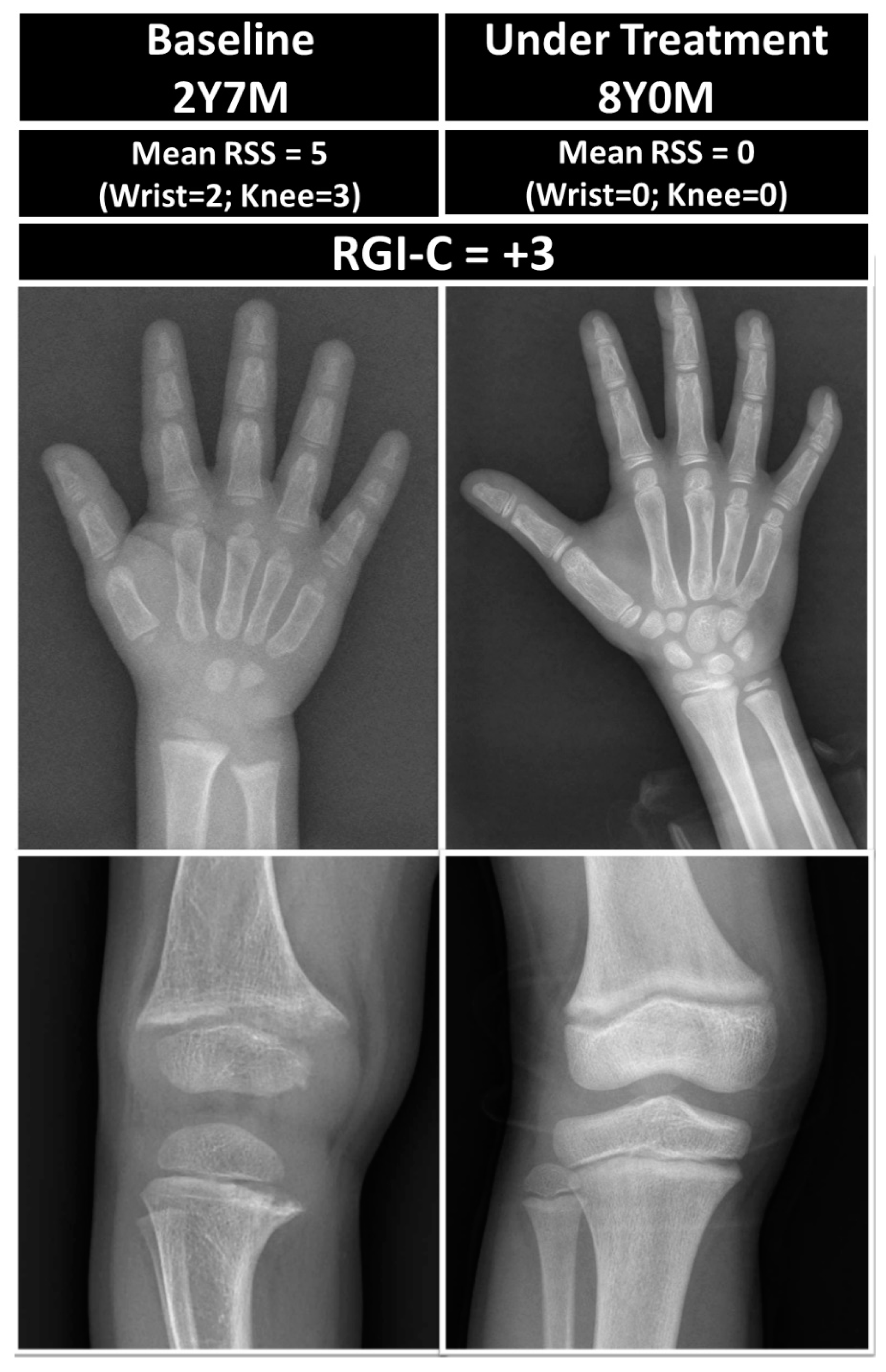
2.3.4. Radiographic Grades and Healing
2.3.5. Growth Chart and Bone Age
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okawa, R.; Hamada, M.; Takagi, M.; Matayoshi, S.; Nakano, K. A Case of X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets with Dentin Dysplasia in Mandibular Third Molars. Children 2022, 9, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, C.F.; Yoo, H.W.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Vasanwala, R.; Chandran, M.; Rhee, Y.; But, W.M.; Kong, A.P.; Su, P.H.; Numbenjapon, N.; et al. Asia-Pacific Consensus Recommendations on X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Diagnosis, Multidisciplinary Management, and Transition From Pediatric to Adult Care. J. Bone Miner. Res. Plus 2023, 7, e10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, D.; Emma, F.; Eastwood, D.M.; Duplan, M.B.; Bacchetta, J.; Schnabel, D.; Wicart, P.; Bockenhauer, D.; Santos, F.; Levtchenko, E.; et al. Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of X-linked hypophosphataemia. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, C. Orthopedic Complications and Management in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Endocrines 2022, 3, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.M.; Glorieux, F.H.; Whyte, M.P.; Munns, C.F.; Portale, A.A.; Högler, W.; Simmons, J.H.; Gottesman, G.S.; Padidela, R.; Namba, N.; et al. Effect of Burosumab Compared With Conventional Therapy on Younger vs. Older Children With X-linked Hypophosphatemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3241–e3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, A.; Wright, J.; Bockenhauer, D.; Van’t Hoff, W.; Eastwood, D.M. The orthopaedic management of lower limb deformity in hypophosphataemic rickets. J. Child. Orthop. 2017, 11, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindler, G.T.; Kranzl, A.; Stauffer, A.; Kocijan, R.; Ganger, R.; Radler, C.; Haeusler, G.; Raimann, A. Lower Limb Deformity and Gait Deviations Among Adolescents and Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 754084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Chawathe, V.; Mhambre, A.; Gaur, A.; Joshi, A. Effect of Lateral Single Bar Knee Orthoses in Correction of Genu Varum in Nutritional Rickets: A Randomized Trial. Indian J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 29, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmazyn, B.; Marine, M.B.; Jones, R.H.; Pfeifer, C.M.; Chapman, T.; Pitt, S.; Shalaby-Rana, E.; Fadell, M.; Forbes-Amrhein, M.; McBee, M.P.; et al. Radiologists’ Diagnostic Performance in Differentiation of Rickets and Classic Metaphyseal Lesions on Radiographs: A Multicenter Study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.; Shailam, R.; Hulett, R.; Skrinar, A.; Nixon, A.; Williams, A.; Nixon, M.; Thacher, T.D. Validation of the Radiographic Global Impression of Change (RGI-C) score to assess healing of rickets in pediatric X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH). Bone 2021, 148, 115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, M.Z.; Baroncelli, G.I.; de Lucas-Collantes, C.; Linglart, A.; Magnolato, A.; Raimann, A.; Santos, F.; Schnabel, D.; Shaw, N.; Nilsson, O. Burosumab for X-linked hypophosphatemia in children and adolescents: Opinion based on early experience in seven European countries. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1034580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imel, E.A.; Glorieux, F.H.; Whyte, M.P.; Munns, C.F.; Ward, L.M.; Nilsson, O.; Simmons, J.H.; Padidela, R.; Namba, N.; Cheong, H.I.; et al. Burosumab versus conventional therapy in children with X-linked hypophosphataemia: A randomised, active-controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, Y.; Seki, A.; Uchikawa, S.; Tori, A.; Kimura, A.; Takayama, S. Kashisouguryouhou wo okonatta teirinnkesshousei-kurubyo (hypophosphatemic rickets) kannjinokeika. Nippon. Shouniseikeigeka Gakkai Shi 2017, 26, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, N.J.; Dockx, R.B.M.; Witlox, A.M.; Straetemans, S.; Staal, H.M. Windswept Deformity a Disease or a Symptom? A Systematic Review on the Aetiologies and Hypotheses of Simultaneous Genu Valgum and Varum in Children. Children 2022, 9, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Pharmacological Treatment (2 y 7 m–8 y) | Reference Range | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 y 7 m (Diagnosis Age) | 3 y | 4 y | 5 y | 6 y | 7 y | 8 y (Current Age) | ||
| ALP(U/L) | 635 | 372 | 456 | 416 | 362 | 415 | 388 | 1–10 yrs old: 156–369 |
| Ca(mmol/dL) | 2.31 | 2.25 | 2.37 | 2.27 | 2.27 | 2.34 | 2.29 | 1–5 yrs old: 2.35–2.70 6–12 yrs old: 2.35–2.57 |
| P(mmol/dL) | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 1.59 | 1.10 | 1.17 | 0.97 | 1–5 yrs old: 1.05–1.95 6–12 yrs old: 1.00–1.80 |
| 25(OH)D (ng/mL) | 16.1 | NA | NA | NA | 26.4 | NA | NA | 1–3 yrs old: 45–145 3–19 yrs old: 43–98 |
| Intact PTH (pg/mL) | 60 | 39.5 | 26.2 | 50.8 | 40.9 | 27.1 | 35.7 | 10–65 |
| U-Ca/U-Cre (mg/mg) | 0.06 | NA | NA | NA | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 1–3 yrs old: 0.03–0.56 3–5 yrs old: 0.02–0.41 5–7 yrs old: 0.01–0.30 7–10 yrs old: 0.01–0.25 |
| TmP/GFR mmol/dL) | 0.78 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1–5 yrs old: 1.05–1.78 6–12 yrs old: 0.97–1.64 |
| TRP | 0.84 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.85–0.95 |
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | 111 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 51–218 |
| Phosphorus (mg/kg/day) | 25 | 23 | 55 | 44 | 57 | 49 | 55 | 20–60 mg/kg/day |
| Dihydroxycholecalciferol (mg/kg/day) | 25 | 24 | 29 | 31 | 31 | 27 | 26 | 20–30 ng/kg/day |
| Conventional Therapy (2 y 7 m–8 y) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orthosis Therapy (3 y–7 y) | Mean Correction Rate † | |||||||||
| 2 y 7 m | 3 y | 4 y | 5 y | 5 y 9 m | 7 y | 8 y | Before Orthosis (2 y 7 m–3 y) | During Orthosis (3 y–7 y) | ||
| Mechanical axis (°) * | R | 24 | 26 | 10 | 3 | 0 | −2 | −3 | +4°/year | −7°/year |
| L | 20 | 27 | 11 | 3 | 0 | −1 | −2 | |||
| Mechanical axis deviation (mm) * | R | 35 | 40 | 17 | 4 | 0 | −4 | −0.5 | +15 mm/year | −10.5 mm/year |
| L | 28 | 38 | 16 | 5 | 0 | −2 | −0.6 | |||
| mLPFA (°) | R | 74 | 73 | 69 | 73 | 69 | 81 | 83 | −8.0°/year | +2.6°/year |
| L | 72 | 65 | 65 | 68 | 68 | 78 | 82 | |||
| mLDFA (°) | R | 96 | 97 | 94 | 91 | 89 | 89 | 88 | +1.0°/year | −1.9°/year |
| L | 96 | 96 | 97 | 93 | 90 | 89 | 87 | |||
| mMPTA (°) | R | 70 | 73 | 80 | 87 | 90 | 90 | 91 | +5.0°/year | +3.8°/year |
| L | 75 | 77 | 81 | 87 | 90 | 90 | 90 | |||
| mLDTA (°) | R | 94 | 93 | 92 | 86 | 88 | 90 | 90 | +1.0°/year | −1.0°/year |
| L | 93 | 95 | 90 | 86 | 88 | 90 | 90 | |||
| Metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle (°) | R | 19 | 13 | 7 | 2 | 1 | −2 | −1 | −9°/year | −3.5°/year |
| L | 14 | 11 | 7 | 2 | 1 | −2 | −1 | |||
| Coronal femoral diaphyseal bow (°) | R | 16 | 20 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 7 | +10°/year | −2.3°/year |
| L | 14 | 20 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 8 | 8 | |||
| Coronal tibia diaphyseal bow (°) | R | 28 | 23 | 23 | 19 | 17 | 10 | 8 | −5.0°/year | −4.0°/year |
| L | 29 | 29 | 26 | 21 | 14 | 10 | 8 | |||
| Sagittal femoral diaphyseal bow (°) | R | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 18 | 6 | −3.5°/year ‡ | |
| L | 31 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 20 | 18 | |||
| Sagittal tibia diaphyseal bow (°) | R | 25 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 8 | 2 | −4.1°/year ‡ | |
| L | 28 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6 | 6 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tie, T.-H.; Lin, W.-H.; Huang, M.-T.; Wu, P.-T.; Tsai, M.-C.; Chou, Y.-Y.; Hong, C.-K.; Lin, C.-J.; Shih, C.-A. Non-Surgical Strategies for Managing Skeletal Deformities in a Child with X-Linked Hereditary Hypophosphatemic Ricket: Insights and Perspectives. Children 2024, 11, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11040487
Tie T-H, Lin W-H, Huang M-T, Wu P-T, Tsai M-C, Chou Y-Y, Hong C-K, Lin C-J, Shih C-A. Non-Surgical Strategies for Managing Skeletal Deformities in a Child with X-Linked Hereditary Hypophosphatemic Ricket: Insights and Perspectives. Children. 2024; 11(4):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11040487
Chicago/Turabian StyleTie, Tung-Hee, Wei-Han Lin, Ming-Tung Huang, Po-Ting Wu, Meng-Che Tsai, Yen-Yin Chou, Chih-Kai Hong, Chii-Jeng Lin, and Chien-An Shih. 2024. "Non-Surgical Strategies for Managing Skeletal Deformities in a Child with X-Linked Hereditary Hypophosphatemic Ricket: Insights and Perspectives" Children 11, no. 4: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11040487
APA StyleTie, T.-H., Lin, W.-H., Huang, M.-T., Wu, P.-T., Tsai, M.-C., Chou, Y.-Y., Hong, C.-K., Lin, C.-J., & Shih, C.-A. (2024). Non-Surgical Strategies for Managing Skeletal Deformities in a Child with X-Linked Hereditary Hypophosphatemic Ricket: Insights and Perspectives. Children, 11(4), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11040487