Current Uses of Bromelain in Children: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Effects of Bromelain
4. Pharmacological Profile
4.1. Toxicity and Side Effects
4.2. Methods of Extraction, Purification, and Stabilizing
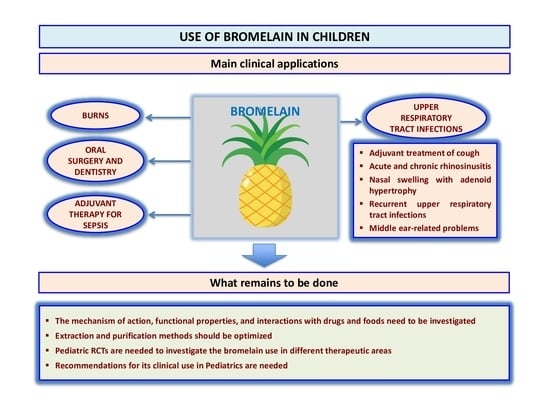
5. Use of Bromelain in Children and Adolescents
5.1. Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
5.2. Systemic Infections (Sepsis)
5.3. Dental Disorders
5.4. Burns and Associated Complications
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamdy, S. Bromelain. Monograph. Altern. Med. Rev. 2010, 15, 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Ramli, A.N.; Aznan, T.N.; Illias, R.M. Bromelain: From production to commercialisation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, Z.I.M.; Amid, A.; Yusof, F.; Jaswir, I.; Ahmad, K.; Loke, S.P. Bromelain: An overview of industrial application and purification strategies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7283–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikisz, P.; Bernasinska-Slomczewska, J. Beneficial Properties of Bromelain. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, H.R. Bromelain: Biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colletti, A.; Li, S.; Marengo, M.; Adinolfi, S.; Cravotto, G. Recent Advances and Insights into Bromelain Processing, Pharmacokinetics and Therapeutic Uses. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministero della Salute. Decreto 9 luglio 2012. Disciplina Dell’impiego negli Integratori Alimentari di Sostanze e Preparati Vegetali (G.U. 21-7-2012 Serie Generale n. 169) Linee Guida Ministeriali di Riferimento per gli Effetti Fisiologici. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_3668_listaFile_itemName_0_file.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Mameli, A.; Natoli, V.; Casu, C. Bromelain: An Overview of Applications in Medicine and Dentistry. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 11, 8165–8170. [Google Scholar]
- de A C Almeida, R.; de Sousa Lima, F.C.M.; do E Vasconcelos, B.C. Is bromelain an effective drug for the control of pain and inflammation associated with impacted third molar surgery? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.L.T.; do Nascimento-Júnior, E.M.; Reinheimer, D.M.; Martins-Filho, P.R.S. Efficacy of proteolytic enzyme bromelain on health outcomes after third molar surgery. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal. 2019, 24, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ma, C. Oral Bromelain for the Control of Facial Swelling, Trismus, and Pain After Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, G.M.; Fernandes, I.A.; Dos Santos, C.R.R.; Falci, S.G.M. Is bromelain effective in controlling the inflammatory parameters of pain, edema, and trismus after lower third molar surgery? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Jagdeo, J.; Waldorf, H.A. Is There a Role for Arnica and Bromelain in Prevention of Post-Procedure Ecchymosis or Edema? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Dermatol. Surg. 2016, 42, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangesi, L.; Zakarija-Grkovic, I. Treatments for breast engorgement during lactation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD006946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, C.M.; Tsiami, A.; Ni, Q.; Robinson, N. A review of the use of bromelain in cardiovascular diseases. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2011, 9, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzhugh, D.J.; Shan, S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Hale, L.P. Bromelain treatment decreases neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 128, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secor, E.R.; Carson, W.F.; Singh, A.; Pensa, M.; Guernsey, L.A.; Schramm, C.M.; Thrall, R.S. Oral Bromelain Attenuates Inflammation in an Ovalbumin-Induced Murine Model of Asthma. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 5, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onken, J.E.; Greer, P.K.; Calingaert, B.; Hale, L.P. Bromelain treatment decreases secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by colon biopsies in vitro. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, L.P.; Greer, P.K.; Trinh, C.T.; Gottfried, M.R. Treatment with oral bromelain decreases colonic inflammation in the IL-10-deficient murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; März, R.; Schmolz, M.; Drewelow, B.; Eschmann, K.; Meiser, P. Placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial on the immunomodulating activities of low- and high- dose bromelain after oral administration—New evidence on the antiinflammatory mode of action of bromelain. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnavelu, V.; Alitheen, N.B.; Sohila, S.; Kanagesan, S.; Ramesh, R. Potential role of bromelain in clinical and therapeutic applications (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taussig, S.J.; Batkin, S. Bromelain, the enzyme complex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1988, 22, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusini, F.; Bisicchia, S.; Bottegoni, C.; Gigante, A.; Zanchini, F.; Busilacchi, A. Nutraceutical supplement in the management of tendinopathies: A systematic review. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2016, 6, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, V.; Hareendran, A.; Nair, C.S. Double-blind cross-over trial of an enzyme preparation in pancreatic steatorrhoea. J. Assoc. Physicians India 1981, 29, 207–209. [Google Scholar]
- Brakebusch, M.; Wintergerst, U.; Petropoulou, T.; Notheis, G.; Husfeld, L.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Adam, D. Bromelain is an accelerator of phagocytosis, respiratory burst and Killing of Candida albicans by human granulocytes and monocytes. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2001, 6, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Stepek, G.; Lowe, A.E.; Buttle, D.J.; Duce, I.R.; Behnke, J.M. In vitro and in vivo anthelmintic efficacy of plant cysteine proteinases against the rodent gastrointestinal nematode, Trichuris muris. Parasitology 2006, 132, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepek, G.; Buttle, D.J.; Duce, I.R.; Lowe, A.; Behnke, J.M. Assessment of the anthelmintic effect of natural plant cysteine proteinases against the gastrointestinal nematode, Heligmosomoides polygyrus, in vitro. Parasitology 2005, 130, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynott, T.L.; Guandalini, S.; Raimondi, F.; Fasano, A. Bromelain prevents secretion caused by Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins in rabbit ileum in vitro. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D.S.; Mynott, T.L. Bromelain protects piglets from diarrhoea caused by oral challenge with K88 positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Gut 1998, 43, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mynott, T.L.; Luke, R.K.; Chandler, D.S. Oral administration of protease inhibits enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli receptor activity in piglet small intestine. Gut 1996, 38, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, M.; Britti, M.S.; Le Huërou-Luron, I.; Marfaing, H.; Zhu, W.Y.; Mengheri, E. Effect of different plant extracts and natural substances (PENS) against membrane damage induced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 in pig intestinal cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2007, 21, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinozzi, S.; Venegoni, A. Effect of bromelain on serum and tissue levels of amoxicillin. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1978, 4, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Luerti, M.; Vignali, M.L. Influence of bromelain on penetration of antibiotics in uterus, salpinx and ovary. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1978, 4, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.K.; Turakhia, N.H.; Kundra, M.; Shanbag, P.; Daftary, G.V.; Schiess, W. Efficacy and safety of phlogenzym—A protease formulation, in sepsis in children. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2002, 50, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer, R.A. A plant protease for potentiation of and possible replacement of antibiotics. Exp. Med. Surg. 1961, 19, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.E. A double-blind clinical evaluation of bromelains in the treatment of acute sinusitis. Headache 1967, 7, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Ojima, Y.; Hirose, T.; Sasaki, T.; Hashimoto, Y. The clinical effect of proteolytic enzyme containing bromelain and trypsin on urinary tract infection evaluated by double blind method. Acta Obstet. Gynaecol. Jpn. 1972, 19, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.H.; Momeni, M.; Vahdani, M.; Moradi, M. Clinical Value of Debriding Enzymes as an Adjunct to Standard Early Surgical Excision in Human Burns: A Systematic Review. J. Burn. Care Res. 2020, 41, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Evolutionary families of peptidases. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, A.D.; Buttle, D.J.; Barrett, A.J. The cysteine proteinases of the pineapple plant. Biochem. J. 1990, 266, 869–875. [Google Scholar]
- Varilla, C.; Marcone, M.; Paiva, L.; Baptista, J. Bromelain, a Group of Pineapple Proteolytic Complex Enzymes (Ananas comosus) and Their Possible Therapeutic and Clinical Effects. A Summary. Foods 2021, 10, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrach, T.; Eckert, K.; Schulze-Forster, K.; Nuck, R.; Grunow, D.; Maurer, H.R. Isolation and partial characterization of basic proteinases from stem bromelain. J. Protein Chem. 1995, 14, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopes, R.K. Separation by Precipitation. In Protein Purification: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; Scopes, R.K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 41–65. [Google Scholar]
- Arnon, R.; Shapira, E. Antibodies to papain. A selective fractionation according to inhibitory capacity. Biochemistry 1967, 6, 3942–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, J.V.; Friedrich, G.; Kuhn, C.S.; Poppe, G.E. Intestinal absorption of undegraded proteins in men: Presence of bromelain in plasma after oral intake. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1997, 273, G139–G146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, A.D.; Buttle, D.J. Pineapple cysteine endopeptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 244, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orsini, R.A. Plastic surgery educational foundation technology assessment committee. Bromelain. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.R.; Crawley, F.E.; Vellini, M.; Rovati, L.A. Bioavailability of 125I bromelain after oral administration to rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1988, 9, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, R.; Jain, S.; Shraddha; Kumar, A. Properties and therapeutic application of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 976203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataide, J.A.; de Carvalho, N.M.; Rebelo, M.d.A.; Chaud, M.V.; Grotto, D.; Gerenutti, M.; Rai, M.; Mazzola, P.G.; Jozala, A.F. Bacterial Nanocellulose Loaded with Bromelain: Assessment of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Physical-Chemical Properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.J.; Mitra, S.; Tallei, T.E.; Tareq, A.M.; Nainu, F.; Cicia, D.; Dhama, K.; Emran, T.B.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Capasso, R. Bromelain a Potential Bioactive Compound: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective. Life 2021, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errasti, M.E.; Prospitti, A.; Viana, C.A.; Gonzalez, M.M.; Ramos, M.V.; Rotelli, A.E.; Caffini, N.O. Effects on fibrinogen, fibrin, and blood coagulation of proteolytic extracts from fruits of Pseudananas macrodontes, Bromelia balansae, and B. hieronymi (Bromeliaceae) in comparison with bromelain. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2016, 27, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devakate, R.; Patil, V.; Waje, S.; Thorat, B. Purification and drying of bromelain. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 64, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lencastre Novaes, L.C.; Jozala, A.F.; Lopes, A.M.; de Carvalho Santos-Ebinuma, V.; Mazzola, P.G.; Pessoa Junior, A. Stability, purification, and applications of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernela, M.; Ahuja, M.; Thakur, R. Enhancement of anti-inflammatory activity of bromelain by its encapsulation in katira gum nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 143, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwagu, T.N.; Ugwuodo, C.J. Stabilization of bromelain for therapeutic applications by adsorption immobilization on probiotic Bacillus spores. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, D.M.; Rizzo, J.A.; Schor, D.; Silva, A.R.; Oliveira, D.C.; Solé, D.; Sarinho, E. Use of honey associated with Ananas comosus (Bromelin) in the treatment of acute irritative cough. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2016, 34, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.M.; Schneider, B.; Beuth, H.J. Therapeutic use, efficiency and safety of the proteolytic pineapple enzyme Bromelain-POS in children with acute sinusitis in Germany. In Vivo 2005, 19, 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, A.S.; Cabot, P.; Wallwork, B.; Panizza, B. Alternative therapies for chronic rhinosinusitis: A review. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018, 97, E25–E33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Canter, P.H.; Ernst, E. Herbal medicines for the treatment of rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2006, 135, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.W.; Gettelfinger, J.D.; Ting, J.Y.; Mort, C.; Higgins, T.S. Alternative therapies for sinusitis and rhinitis: A systematic review utilizing a modified Delphi method. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkos, P.D.; Leong, S.C.; Arya, A.K.; Papouliakos, S.M.; Apostolidou, M.T.; Issing, W.J. “Complementary ENT”: A systematic review of commonly used supplements. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 121, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, P.; D’Ascanio, L.; Cingolani, C.; Latini, G.; Grigaliute, E.; Di Mauro, P.; Ralli, M.; La Mantia, I.; Di Stadio, A. A Supplement with Ribes Nigrum, Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain and Vitamin D to Stop Local Inflammation in Chronic Sinusitis: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervo, M.M.; Llido, L.O.; Barrios, E.B.; Panlasigui, L.N. Effects of canned pineapple consumption on nutritional status, immunomodulation, and physical health of selected school children. J. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 2014, 861659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Volpe, A.; De Luca, P.; De Lucia, A.; Martines, F.; Piroli, P.; D’Ascanio, L.; Camaioni, A.; La Mantia, I.; Di Stadio, A. Single-Center-Single-Blinded Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy of a Nutraceutical Containing Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain, Zinc, Magnesium, Honey, Tyndallized Lactobacillus Acidophilus and Casei to Fight Upper Respiratory Tract Infection and Otitis Media. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, V.K.; Nagar, P.; Reddy, S.; Ragulakollu, R.; Tirupathi, S.P.; Ravi, R.; Purumadla, U. Bromelain vs Papain Gel for Caries Removal in Primary Teeth. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2019, 20, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, F.; Tatullo, M.; Marrelli, M.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Picciariello, V.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Dipalma, G.; Vermesan, D.; Cagiano, R. Clinical trial with bromelain in third molar exodontia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 14, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Majid, O.W.; Al-Mashhadani, B.A. Perioperative bromelain reduces pain and swelling and improves quality of life measures after mandibular third molar surgery: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormann, K.H.; Weber, K.; Kloppenburg, H.; Staude, P.; Koch, A.; Meiser, P.; Gellrich, N.C. Perioperative Bromelain Therapy after Wisdom Teeth Extraction—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded, Three-Armed, Cross-Over Dose-Finding Study. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 2012–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wala, L.J.; Choudhary, A.; Reddy, B.C. Clinical Evaluation of Anti- Inflammatory Properties of Combination of Bromelain, Trypsin and Rutoside with Combination of Ibuprofen, Trypsin and Chymotrypsin following third Molar Extraction– A Comparative Study. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res. 2020, 8, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeniowski, T.; Strużyna, J.; Torres, K. Evaluation of Bromelain-Based Enzymatic Debridement Combined with Laser Doppler Imaging and Healing of Burn Wounds. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e936713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, K.E.Y.; Amar, S.; Hoeksema, H.; Kornhaber, R.; de Jong, A.; Monstrey, S.; Haik, J.; Biros, E.; Harats, M. Pain management during a bromelain-based selective enzymatic debridement in paediatric and adult burn patients. Burns 2022, 48, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoham, Y.; Gasteratos, K.; Singer, A.J.; Krieger, Y.; Silberstein, E.; Goverman, J. Bromelain-based enzymatic burn debridement: A systematic review of clinical studies on patient safety, efficacy and long-term outcomes. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 4364–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, A.P. Adjunctive use of bromelains in sinusitis: A controlled study. Eye Ear Nose Throat Mon. 1967, 46, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Taub, S.J. The use of bromelains in sinusitis: A double-blind clinical evaluation. Eye Ear Nose Throat Mon. 1967, 46, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi, R.; Ginesu, F.; Giura, R. The use of bromelain in pneumological therapy. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1978, 4, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ako, H.; Cheung, A.H.; Matsuura, P.K. Isolation of a fibrinolysis enzyme activator from commercial bromelain. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1981, 254, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Buttner, L.; Achilles, N.; Bohm, M.; Shah-Hosseini, K.; Mosges, R. Efficacy and tolerability of bromelain in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis–A pilot study. B-ENT 2013, 9, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Passali, D.; Passali, G.C.; Bellussi, L.M.; Sarafoleanu, C.; Loglisci, M.; Manea, C.; Iosif, C.; Passali, F.M. Bromelain’s penetration into the blood and sinonasal mucosa in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, J.; Quéromès, G.; Pillai, K.; Kepenekian, V.; Badar, S.; Mekkawy, A.H.; Frobert, E.; Valle, S.J.; Morris, D.L. The Combination of Bromelain and Acetylcysteine (BromAc) Synergistically Inactivates SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2021, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho Dos Reis, J.G.A.; Ferreira, G.M.; Lourenço, A.A.; Ribeiro, Á.L.; da Mata, C.P.D.S.M.; de Melo Oliveira, P.; Marques, D.P.A.; Ferreira, L.L.; Clarindo, F.A.; da Silva, M.F.; et al. Ex-vivo mucolytic and anti-inflammatory activity of BromAc in tracheal aspirates from COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.R.; Wu, C.C.; Hou, R.C.; Jeng, K.C. Bromelain inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production in human THP-1 monocytes via the removal of CD14. Immunol. Investig. 2008, 37, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasemsuk, T.; Vivithanaporn, P.; Unchern, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of bromelain in Lps-induced human U937 macrophages. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2018, 45, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, J.S.; de Oliveira da Rosa, W.L.; da Silva, A.F.; Piva, E.; Lund, R.G. Efficacy of natural, peroxide-free tooth-bleaching agents: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and technological prospecting. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MediWound Announces FDA Approval of NexoBrid® for the Treatment of Severe Thermal Burns in Adults—Press Release 29.12.2022. Available online: https://ir.mediwound.com/news-releases/news-release-details/mediwound-announces-fda-approval-nexobridr-treatment-severe (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Secor, E.R.; Szczepanek, S.M.; Castater, C.A.; Adami, A.J.; Matson, A.P.; Rafti, E.T.; Guernsey, L.; Natarajan, P.; McNamara, J.T.; Schramm, C.M.; et al. Bromelain Inhibits Allergic Sensitization and Murine Asthma via Modulation of Dendritic Cells. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 702196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Feng, P.; Yin, L.; Wang, C.; Zhi, S.; Dong, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. Inhibition of Epithelial TNF-α Receptors by Purified Fruit Bromelain Ameliorates Intestinal Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction in Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Indication |
|---|
Upper Respiratory Tract infections
|
Oral surgery and dentistry
|
| Burns |
| Author, Year [ref.] | Study Design | Study Population | Type of Disease Treated | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peixoto et al., 2016 [57] | pragmatic, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group study | 60 children aged 2–15 years | irritative cough (for at least 24 h) | The rate of cough improvement was similar in patients treated with pineapple comosus extract + honey (Bromelin®) compared to those receiving honey alone (placebo). |
| Braun et al., 2005 [58] | multicentric, epidemiological cohort study | 116 children aged < 11 years | acute sinusitis | The monotherapy group (verum) had a shorter mean symptom duration (6.66 days) and significantly faster symptom resolution (p = 0.005) than the other groups. |
| Buttner et al., 2013 [78] | prospective, open-label observational pilot study | 12 patients aged > 25 years | CRS (with or without nasal polyps) previously treated with sinus surgery | Adjunctive treatment with bromelain had positive effects on symptom reduction and quality of life. |
| De Luca et al., 2023 [63] | prospective case-control study | 60 patients (children > 12 years adolescents and adults) | chronic sinusitis without nasal polyps (according to clinical EPOS classification) | Bromelain, Ribes nigrum, Boswellia serrata (Casperome®), and vitamin D added to standard topical treatment of chronic sinusitis may reduce mucosal inflammation and improve symptoms. |
| Cervo et al., 2014 [64] | randomized controlled trial | 98 schoolchildren | Evaluation of effects of canned pineapple on the physical health, immune modulation, and nutritional status | In both groups that consumed pineapple, the incidence of infection was reduced, with increased granulocyte production. |
| Della Volpe et al., 2022 [65] | prospective case-control study | 120 children aged > 12 months | OME and conductive hearing loss | Auditory, otoscopic, and fibroscopic findings improved in the group treated for 30 days compared to the control group, with a positive impact on patient well-being. |
| Coelho Dos Reis et al., 2022 [81] | blinded crossover study | 20 COVID-19 patients aged ≥ 18 years | Critical COVID-19 (requiring mechanical ventilation) | Strong mucolytic effect of bromelain on COVID-19 sputum and anti-inflammatory activity. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Locci, C.; Chicconi, E.; Antonucci, R. Current Uses of Bromelain in Children: A Narrative Review. Children 2024, 11, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030377
Locci C, Chicconi E, Antonucci R. Current Uses of Bromelain in Children: A Narrative Review. Children. 2024; 11(3):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030377
Chicago/Turabian StyleLocci, Cristian, Elena Chicconi, and Roberto Antonucci. 2024. "Current Uses of Bromelain in Children: A Narrative Review" Children 11, no. 3: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030377
APA StyleLocci, C., Chicconi, E., & Antonucci, R. (2024). Current Uses of Bromelain in Children: A Narrative Review. Children, 11(3), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030377