The Utilization of Acetaminophen for Managing PGE1-Induced Fever in Neonates with Critical Congenital Heart Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistics
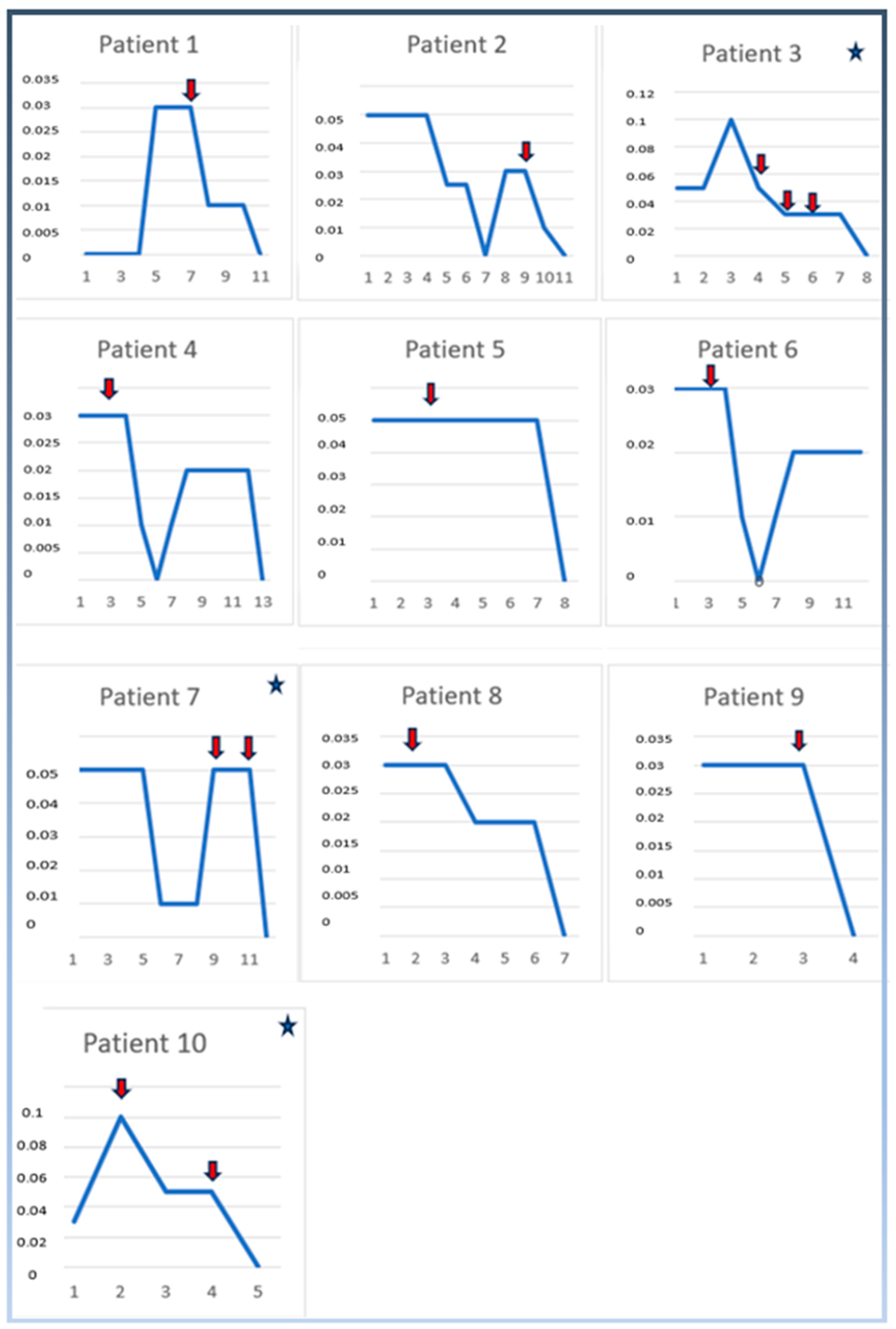
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taksande, A.; Jameel, P.Z. Critical Congenital Heart Disease in Neonates: A Review Article. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2021, 17, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, Y. Evaluation of a child with suspected congenital heart disease. Paediatr. Child. Health 2018, 28, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, M.E.; Kim, C.H.; Kusano, A.S.; Cragan, J.D.; Dressler, P.; Hales, A.R.; Mahle, W.T.; Correa, A. A population-based study of the association of prenatal diagnosis with survival rate for infants with congenital heart defects. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, C.R.; Sen, S.; Levy, P.T. The ductus arteriosus in neonates with critical congenital heart disease. J. Perinatol. 2022, 42, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.; Glickstein, J.S.; Kleinman, C.S.; Levasseur, S.M.; Chen, J.; Gersony, W.M.; Williams, I.A. The impact of prenatal diagnosis of complex congenital heart disease on neonatal outcomes. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2010, 31, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkinapally, S.; Hundalani, S.G.; Kulkarni, M.; Fernandes, C.J.; Cabrera, A.G.; Shivanna, B.; Pammi, M. Prostaglandin E1 for maintaining ductal patency in neonates with ductal-dependent cardiac lesions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 27, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Rabinowitz, E.J.; Epstein, S. Physiologic diagnosis of congenital heart disease in cyanotic neonates. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, E.; Ayatollahi, H.; Abbaszadeh, R.; Fotuhi Siahpirani, A. Adverse Drug Reactions in Children with Congenital Heart Disease: A Scoping Review. Paediatr. Drugs 2024, 26, 519–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Jux, C.; Rueblinger, L.; Behrje, J.; Esmaeili, A.; Schranz, D. Acute therapy of newborns with critical congenital heart disease. Transl. Pediatr. 2019, 8, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, P.; Balaji, S. Cardiac arrhythmias in congenital heart diseases. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2009, 9, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, T.W.; Noori, S. Recognition and management of neonatal hemodynamic compromise. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Vijaykumar, C.; Naik, R.; Moses, P.D.; Antonisamy, B. Comparative effectiveness of tepid sponging and antipyretic drug versus only antipyretic drug in the management of fever among children: A randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatr. 2009, 46, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Florez, I.D.; Tamayo, M.E.; Mbuagbaw, L.; Vanniyasingam, T.; Veroniki, A.A.; Zea, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Sadeghirad, B.; Thabane, L. Association of placebo, indomethacin, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen with closure of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2018, 319, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.M. Pharmacotherapy for patent ductus arteriosus closure. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2019, 14, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasbekar, R.; Naz, A.; Marcos, L.; Liu, Y.; Hendrickson, K.; Gorsich, J.C.; Baun, M. Threshold for defining fever varies with age, especially in children: A multi-site diagnostic accuracy study. Nurs. Open 2021, 8, 2705–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meremikwu, M.; Oyo-Ita, A. Paracetamol for treating fever in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002, 2002, CD003676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haughey, B.S.; Elliott, M.R.; Wiggin, J.Y.; Conaway, M.R.; White, S.C.; Swanson, J.R.; Dean, P.N. Standardizing Prostaglandin Initiation in Prenatally Diagnosed Ductal-Dependent Neonates; A Quality Initiative. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2023, 44, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghanem, F.; Rakestraw, S.L.; Schumacher, K.R.; Owens, G.E. Incidence of Fever and Positive Bacterial Cultures in Neonates Receiving Prostaglandin. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2018, 39, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vari, D.; Xiao, W.; Behere, S.; Spurrier, E.; Tsuda, T.; Baffa, J.M. Low-dose prostaglandin E1 is safe and effective for critical congenital heart disease: Is it time to revisit the dosing guidelines? Cardiol. Young 2021, 31, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.J.; van Lingen, R.A.; Hansen, T.G.; Lin, Y.-C.; Holford, N.H.G. Acetaminophen developmental pharmacokinetics in premature neonates and infants: A pooled population analysis. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.J.; Pons, G.; Autret-Leca, E.; Allegaert, K.; Boccard, E. Pediatric intravenous paracetamol (propacetamol) pharmacokinetics: A population analysis. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2005, 15, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, A.; Corey, R.; Leonard, M.; Eghtesad, B. Acetaminophen: Old drug, new warnings. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2010, 77, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, A.; Saunders, L.; Dunlop, A.; Abbas, A. Neurodevelopmental outcomes following paracetamol use for treatment of patent ductus arteriosus: A review. Acta Paediatr. 2024, 113, 2378–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srajer, A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Tang, S.; Hasan, S.U.; Momin, S.; Hendson, L.; Alshaikh, B.; Yusuf, K. Postnatal acetaminophen exposure and neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18-21 months corrected gestational age in preterm infants <29 weeks gestation: A retrospective cohort study. Pediatr Res. 2024, 96, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, R.H. Acute liver failure in children. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008, 28, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; McKiernan, P.; Kelly, D.A. Etiology, Outcome and Prognostic Indicators of Childhood Fulminant Hepatic Failure in the United Kingdom. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 40, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, R.H.; Shneider, B.L.; Bucuvalas, J.; Alonso, E.; Sokol, R.J.; Narkewicz, M.R.; Dhawan, A.; Rosenthal, P.; Rodriguez-Baez, N.; Murray, K.F.; et al. Acute liver failure in children: The first 348 patients in the pediatric acute liver failure study group. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 652–658.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasani, B.; Mitra, S.; Shah, P.S. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) for patent ductus arteriosus in preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 2022, CD010061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.J. Acetaminophen and the Developing Lung: Could There Be Lifelong Consequences? J. Pediatr. 2021, 235, 264–276.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulley, D.J.; Jensen, E.A.; Sucre, J.M.S.; McKenna, S.; Sherlock, L.G.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Wright, C.J. Racing against time: Leveraging preclinical models to understand pulmonary susceptibility to perinatal acetaminophen exposures. Am. J. Physiol-Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2022, 323, L1–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, G.M.; Allegaert, K. Clinical Pharmacology of Paracetamol in Neonates: A Review. Curr. Ther. Res. 2015, 77, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H. Metabolism and Disposition of Acetaminophen: Recent Advances in Relation to Hepatotoxicity and Diagnosis. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2174–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Acetaminophen Toxicity: Novel Insights Into Mechanisms and Future Perspectives. Gene Expr. 2018, 18, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.; Babar, A.; Choudhary, M.; Kutner, M.; Pyrsopoulos, N. Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Comprehensive Update. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.F.; Hamilton, E.G.; Lam, J.; Chen, H.; Woodruff, T.J. Differences in cytochrome p450 enzyme expression and activity in fetal and adult tissues. Placenta 2020, 100, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, N.C.; Nandhikonda, P.; Webb-Robertson, B.-J.; Ansong, C.; Anderson, L.N.; Smith, J.N.; Corley, R.A.; Wright, A.T. Hepatic Cytochrome P450 Activity, Abundance, and Expression Throughout Human Development. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, R.N. The ontogeny of drug metabolism enzymes and implications for adverse drug events. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 118, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, S.N.; Cui, Y.; Klaassen, C.D.; Zhong, X. Three Patterns of Cytochrome P450 Gene Expression during Liver Maturation in Mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-F.; Hu, A.-L.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.-J.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J. Age-associated changes of cytochrome P450 and related phase-2 gene/proteins in livers of rats. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.D.; Shires, T.K.; Fischer, L.J. Hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen in neonatal and young rats: I. Age-related changes in susceptibility. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1984, 74, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.G.; Timbrell, J.A. The effect of age on paracetamol hepatotoxicity in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1979, 28, 3015–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, J.M.; Bae, E. Increasing Alprostadil Requirements in a Neonate With Cardiac Anomalies and Co-administration of Rectal and Oral Acetaminophen. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 27, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Maternal age (yrs), mean ± SD | 31.6 ± 6.71 |
| Gestational age (weeks), mean ± SD | 37.44 ± 1.79 |
| Birth weight (grams), mean ± SD | 3187 ± 615.5 |
| Mode of delivery | |
| Cesarean section, (%) | 6 (60) |
| Gender | |
| Female, (%) | 8 (80) |
| Prenatal diagnosis of CHD, (%) | 2 (20) |
| Consanguinity, (%) | 6 (60) |
| Referred from outer centers, (%) | 8 (80) |
| Echocardiographic Evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|
| CCHD Types | PDA Diameter Before Acetaminophen Treatment | PDA Diameter After Acetaminophen Treatment |
| 1. Fallot Tetralogy | large PDA (5 mm) | large PDA (5 mm) |
| 2. HLHS | large PDA (5 mm) | large PDA (4.7 mm) |
| 3. Pulmonary atresia (*) | large PDA (4.2 mm) | large PDA (4 mm; 4.2 mm; 4.1 mm) |
| 4. Pulmonary atresia (*) | large PDA (4.5 mm) | large PDA (4.4 mm) |
| 5. DORV | large PDA (4.8 mm) | large PDA (4.6 mm) |
| 6. TGA | large PDA (6 mm) | large PDA (4.8 mm; 4.9 mm) |
| 7. Tricuspid atresia type 1 (*) | tortuous PDA (4.1 mm) | tortuous PDA (4.1 mm; 4.2 mm) |
| 8. Ebstein anomaly | large PDA (4.8 mm) | large PDA (4.5 mm) |
| 9. Pulmonary atresia | tortuous large PDA (5.5 mm) | tortuous vertical PDA (5.6 mm) |
| 10. Pulmonary atresia, DORV | tortuous vertical PDA (5.2 mm) | vertical PDA (5.3 mm; 5.0 mm) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaya, B.; Akduman, H.; Dilli, D.; Kaya, Ö.; Çitli, R.; Zenciroğlu, A. The Utilization of Acetaminophen for Managing PGE1-Induced Fever in Neonates with Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Children 2024, 11, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121547
Kaya B, Akduman H, Dilli D, Kaya Ö, Çitli R, Zenciroğlu A. The Utilization of Acetaminophen for Managing PGE1-Induced Fever in Neonates with Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Children. 2024; 11(12):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121547
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaya, Başak, Hasan Akduman, Dilek Dilli, Özkan Kaya, Rumeysa Çitli, and Ayşegül Zenciroğlu. 2024. "The Utilization of Acetaminophen for Managing PGE1-Induced Fever in Neonates with Critical Congenital Heart Disease" Children 11, no. 12: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121547
APA StyleKaya, B., Akduman, H., Dilli, D., Kaya, Ö., Çitli, R., & Zenciroğlu, A. (2024). The Utilization of Acetaminophen for Managing PGE1-Induced Fever in Neonates with Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Children, 11(12), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121547






