Bromelain Supplementation in the Management of Otitis Media with Effusion in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Tympanometry
2.3. Otoacoustic Emissions
2.4. Audiometry
2.5. Otoscopy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
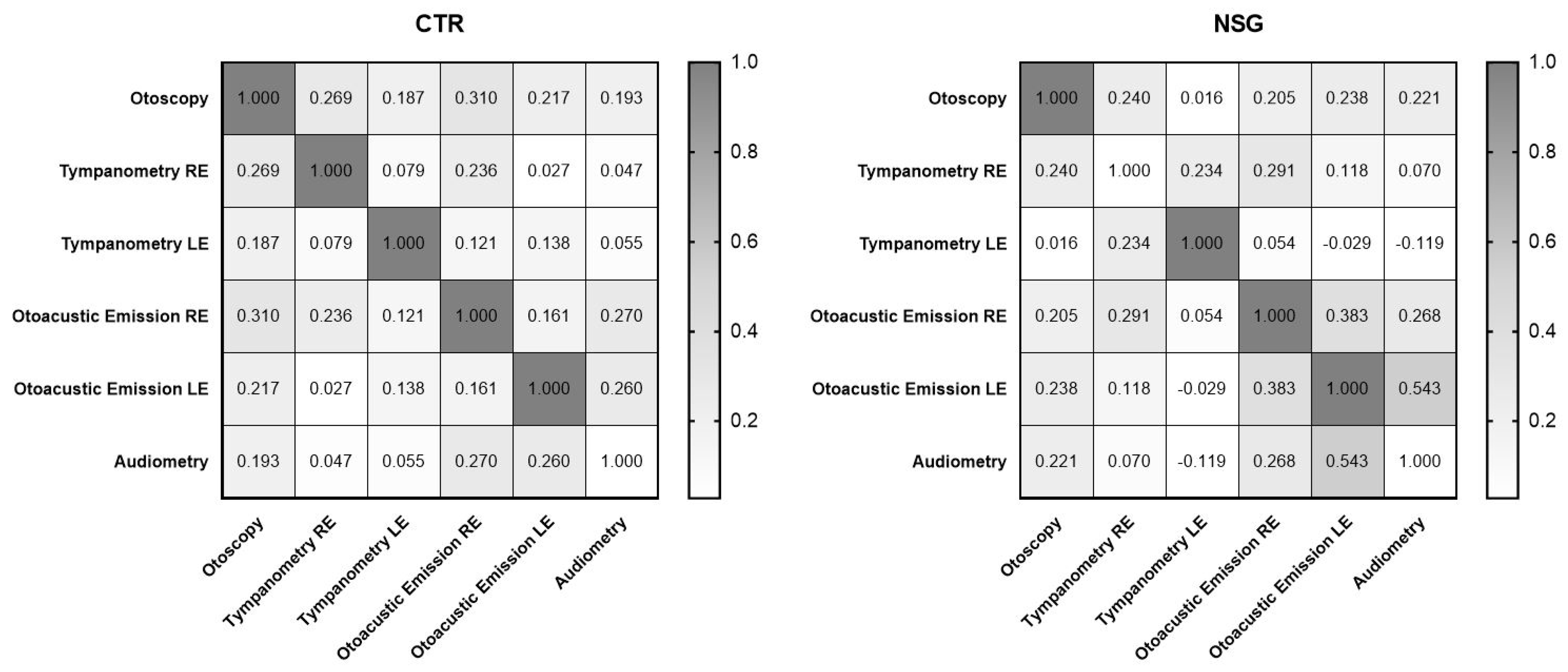
3.1. Correlations
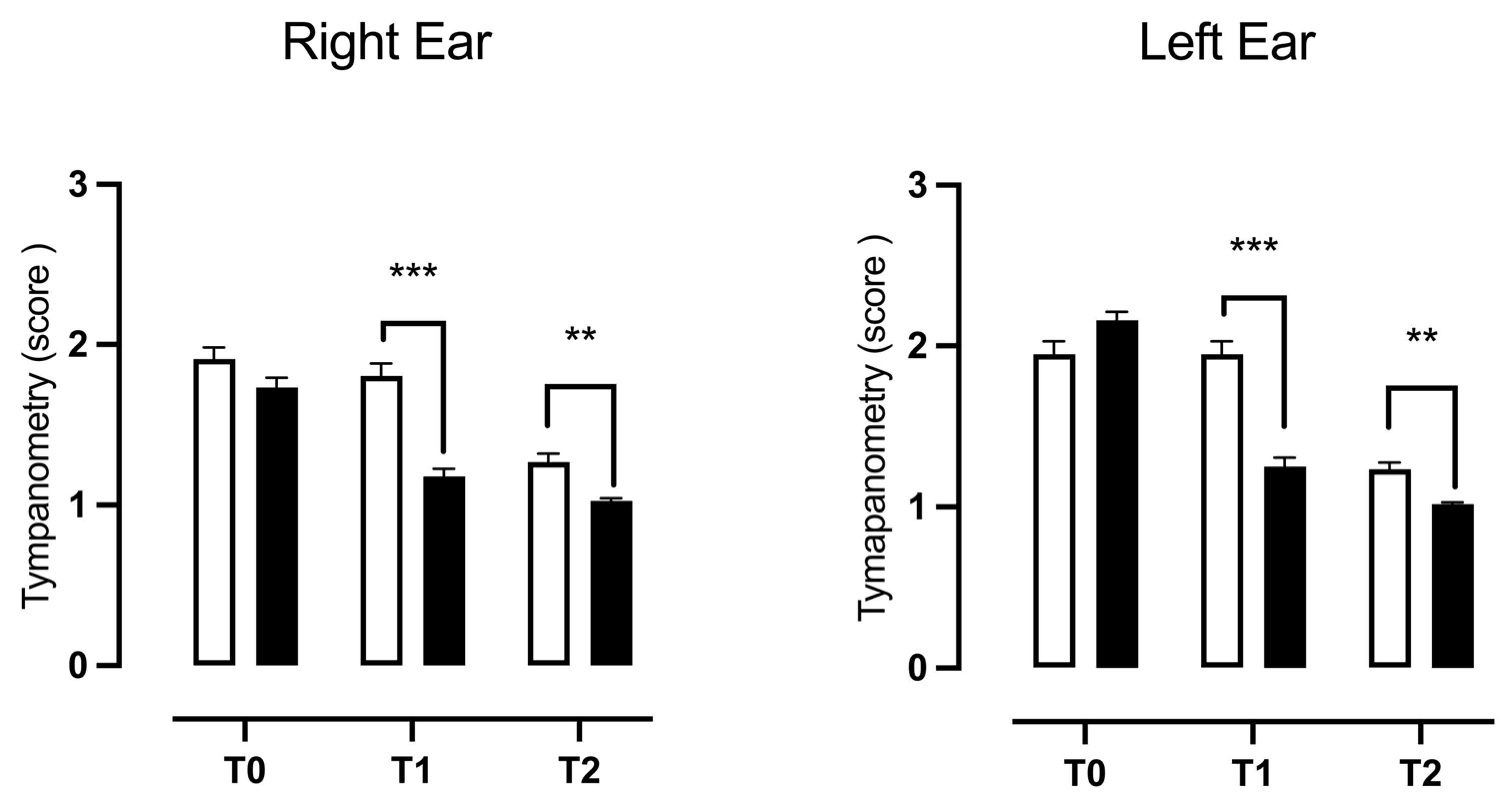
3.2. Tympanometry
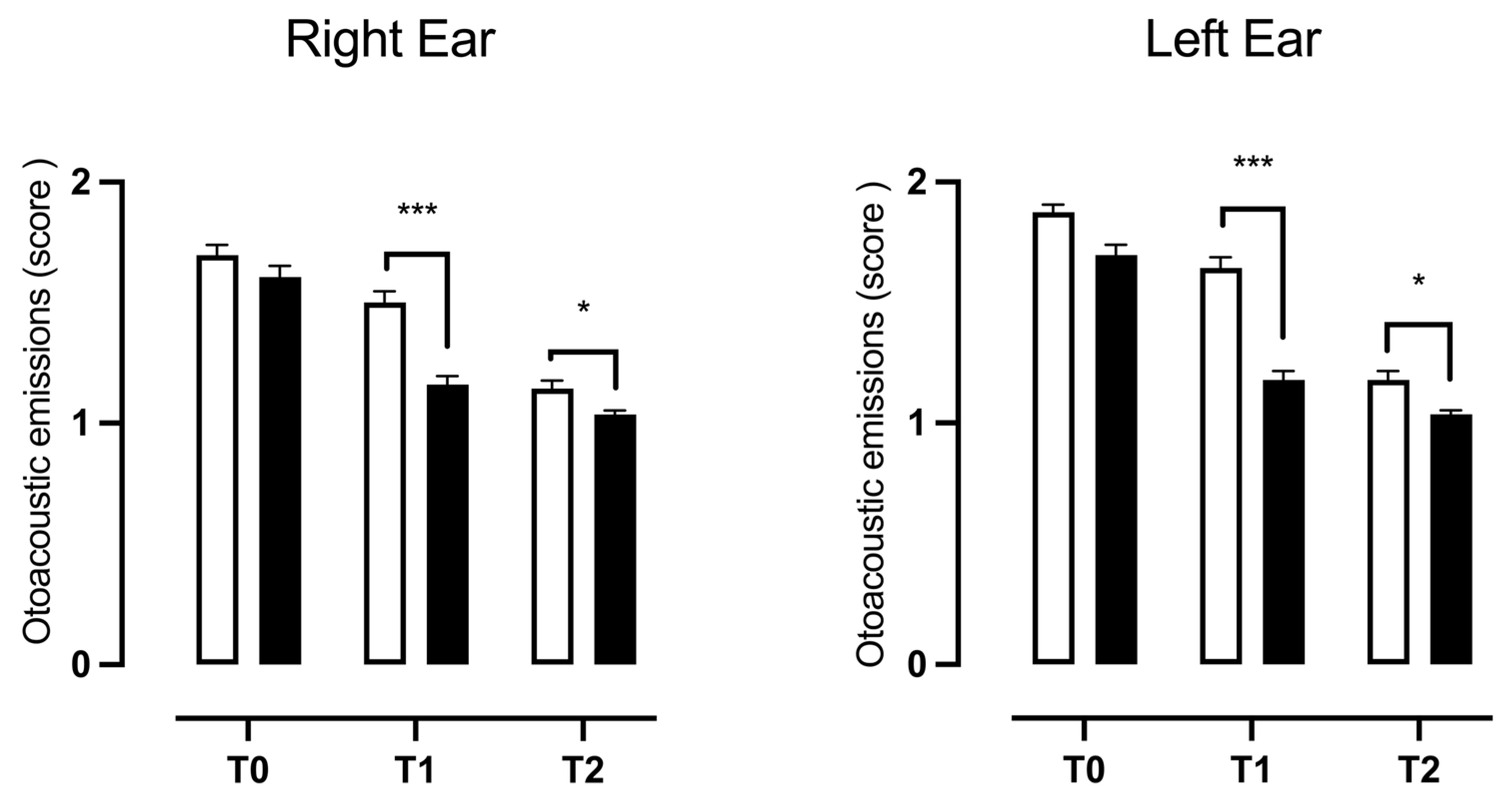
3.3. Otoacoustic Emissions
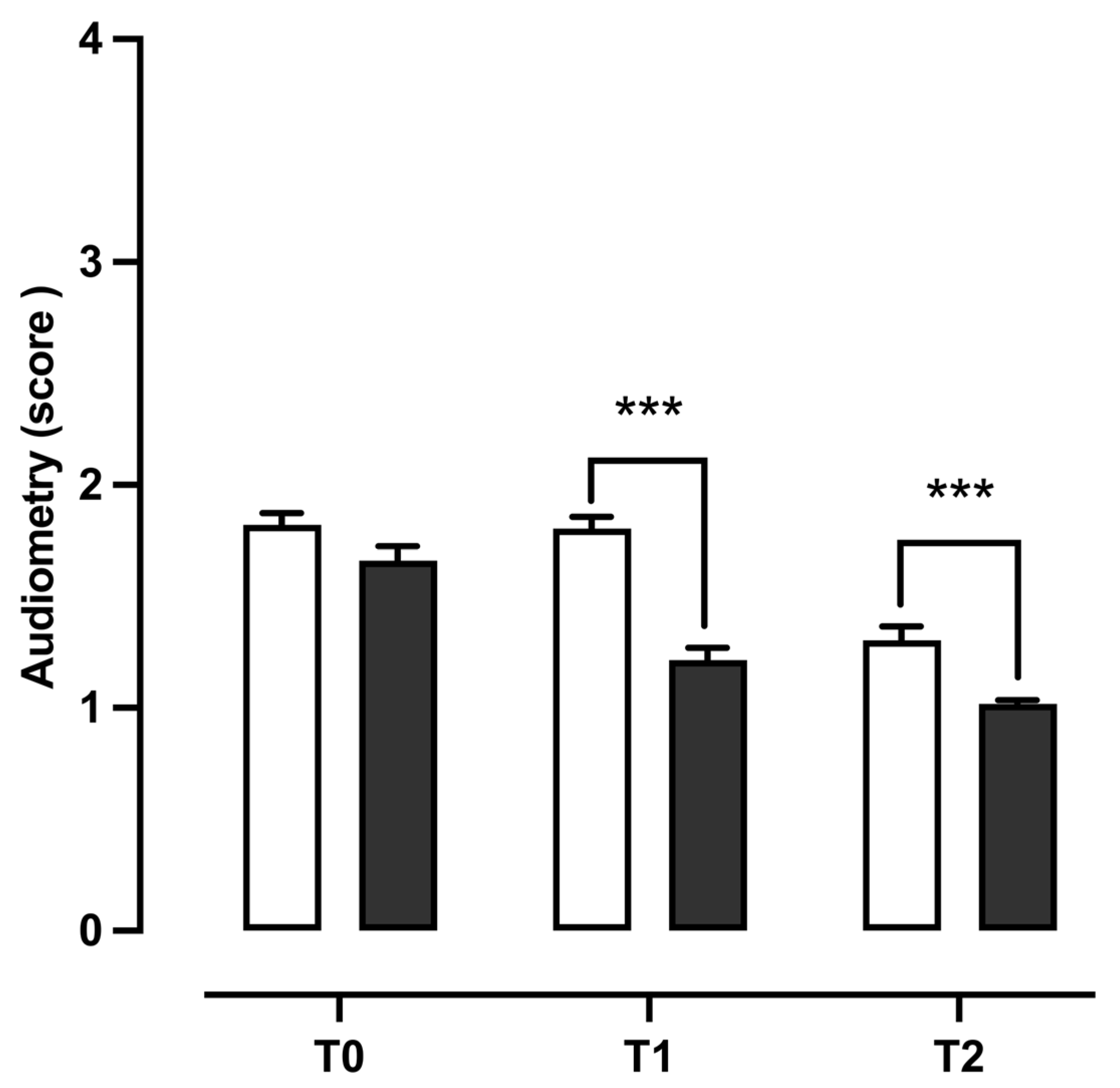
3.4. Audiometry
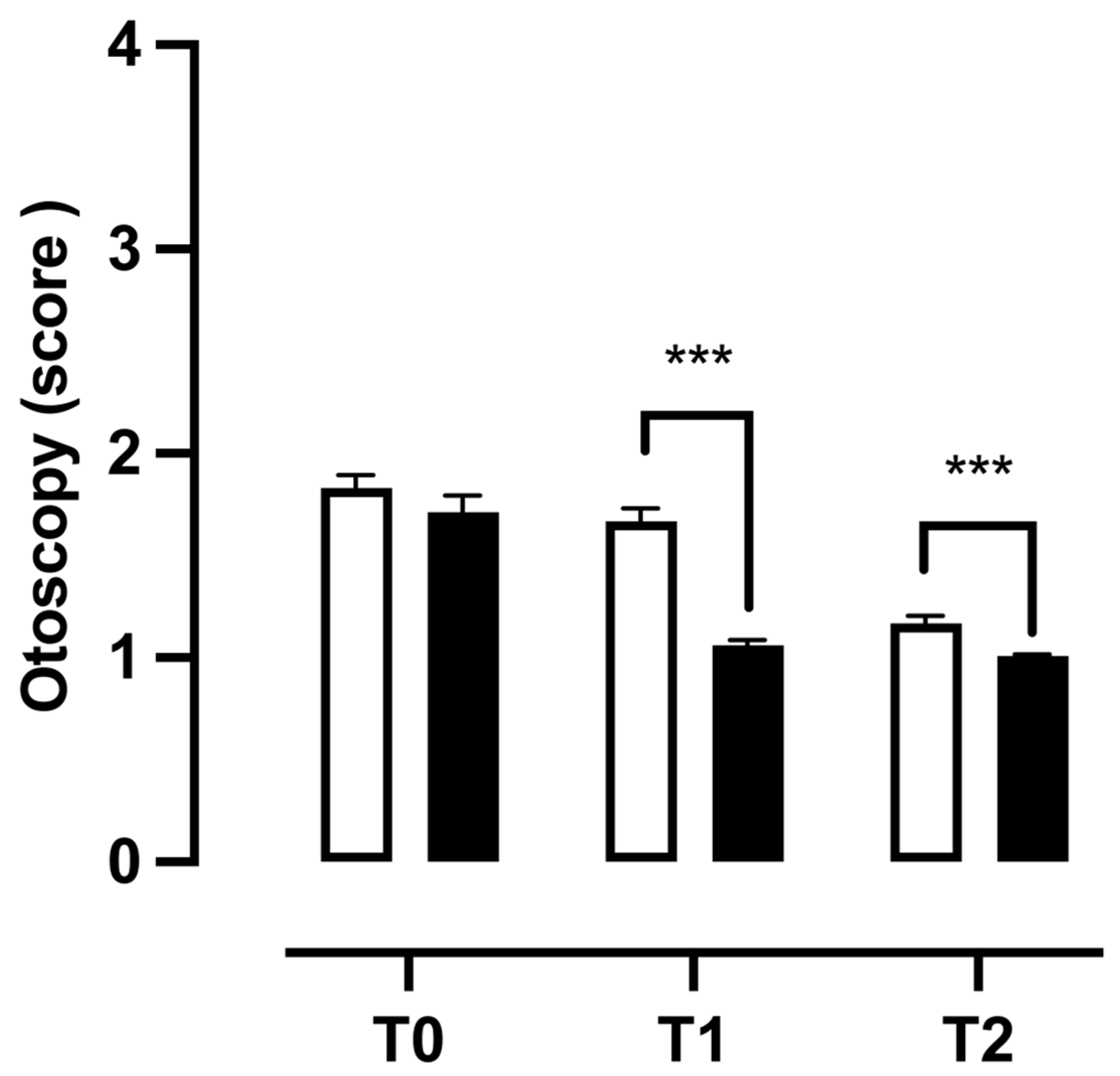
3.5. Clinical Findings Observed During Otoscopy
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ball, M.; Hossain, M.; Padalia, D. Anatomy, Airway. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, M.I.; Cameron, C.G. Infections of the Upper Respiratory Tract. In Pediatric Respiratory Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Lodha, R.; Kabra, S.K. Upper respiratory tract infections. Indian J. Pediatr. 2021, 68, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.; Taylor, J.A. Prevalence of clinical sinusitis in young children followed up by primary care pediatricians. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1998, 152, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martines, F.; Salvago, P.; Ferrara, S.; Messina, G.; Mucia, M.; Plescia, F.; Sireci, F. Factors influencing the development of otitis media among Sicilian children affected by upper respiratory tract infections. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grief, S.N. Upper respiratory infections. Prim. Care 2013, 40, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichichero, M.E.; Chapman, T.J.; Bajorski, P. Pneumonia, Sinusitis, Influenza and Other Respiratory Illnesses in Acute Otitis Media-Prone Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilder, A.G.; Chonmaitree, T.; Cripps, A.W.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Casselbrant, M.L.; Haggard, M.P.; Venekamp, R.P. Otitis media. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichtle, A.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Wigand, M.C. Otitis media–Definition, Pathogenese, Klinik, Diagnose und Therapie [Otitis media: Definition, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapy]. Laryngo Rhino Otol. 2018, 97, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Wong, A.H.C. Acute Otitis Media in Children. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2017, 11, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, E.; Lavanco, G.; Castelli, V.; Cirrincione, L.; Di Majo, D.; Martines, F.; Argo, A.; Plescia, F. Alcohol and Nicotine Use among Adolescents: An Observational Study in a Sicilian Cohort of High School Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahan, B.; Barstow, C.; Mahowald, M. Respiratory Conditions: Upper Respiratory Tract Infections. FP Essent. 2019, 486, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Murgia, V.; Manti, S.; Licari, A.; De Filippo, M.; Ciprandi, G.; Marseglia, G.L. Upper Respiratory Tract Infection-Associated Acute Cough and the Urge to Cough: New Insights for Clinical Practice. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2020, 33, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romandini, A.; Pani, A.; Schenardi, P.A.; Pattarino, G.A.C.; De Giacomo, C.; Scaglione, F. Antibiotic Resistance in Pediatric Infections: Global Emerging Threats, Predicting the Near Future. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, R.; Jain, S.; Shraddha; Kumar, A. Properties and therapeutic application of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 976203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottega, R.; Persico, I.; De Seta, F.; Romano, F.; Di Lorenzo, G. Anti-inflammatory properties of a proprietary bromelain extract (Bromeyal™) after in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 20587384211034686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insuan, O.; Janchai, P.; Thongchuai, B.; Chaiwongsa, R.; Khamchun, S.; Saoin, S.; Insuan, W.; Pothacharoen, P.; Apiwatanapiwat, W.; Boondaeng, A.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Pineapple Rhizome Bromelain through Downregulation of the NF-κB- and MAPKs-Signaling Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varilla, C.; Marcone, M.; Paiva, L.; Baptista, J. Bromelain, a Group of Pineapple Proteolytic Complex Enzymes (Ananas comosus) and Their Possible Therapeutic and Clinical Effects. A Summary. Foods 2021, 10, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.J.; Mitra, S.; Tallei, T.E.; Tareq, A.M.; Nainu, F.; Cicia, D.; Dhama, K.; Emran, T.B.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Capasso, R. Bromelain a Potential Bioactive Compound: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective. Life 2021, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.F.; Akhtar, S.; Anwar, M. Nutritional value and medicinal benefits of pineapple. Int. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhasz, B.; Thirunavukkarasu, M.; Pant, R.; Zhan, L.; Penumathsa, S.V.; Secor, E.R.; Srivastava, S., Jr.; Raychaudhuri, U.; Menon, V.P.; Otani, H.; et al. Bromelain induces cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury through Akt/FOXO pathway in rat myocardium. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H1365–H1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Corscadden, K.; Lott, C.; Elbatarny, H.S.; Othman, M. Bromelain has paradoxical effects on blood coagulability: A study using thromboelastography. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2016, 27, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, N.C.; Rajesh, A.; Madan, M.; Chaurasia, V.R.; Hiremath, N.V.; Sharma, A.M. In vitro Evaluation of Antibacterial Efficacy of Pineapple Extract (Bromelain) on Periodontal Pathogens. J. Int. Oral Health 2014, 6, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chobotova, K.; Vernallis, A.B.; Majid, F.A. Bromelain’s activity and potential as an anti-cancer agent: Current evidence and perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2010, 290, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargutkar, S.; Brijesh, S. Anti-inflammatory evaluation and characterization of leaf extract of Ananas comosus. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochard, S.; Pontin, J.; Bernay, B.; Boumediene, K.; Conrozier, T.; Baugé, C. The benefit of combining curcumin, bromelain and harpagophytum to reduce inflammation in osteoarthritic synovial cells. BMC Complement Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engwerda, C.R.; Andrew, D.; Murphy, M.; Mynott, T.L. Bromelain activates murine macrophages and natural killer cells in vitro. Cell Immunol. 2001, 210, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Guseo, A.; Klein, R. In vitro study on the immunological effect of bromelain and trypsin on mononuclear cells from humans. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2005, 10, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.L.; Turner, R.B.; Braciale, T.; Heymann, P.W.; Borish, L. Pathogenesis of rhinovirus infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.H.; Cardani, A.; Braciale, T.J. The host immune response in respiratory virus infection: Balancing virus clearance and immunopathology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Bomar, P.A. Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.A. Directing transition from innate to acquired immunity: Defining a role for IL-6. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3463–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijaro, J.R. The role of cytokine responses during influenza virus pathogenesis and potential therapeutic options. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 386, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, J.V.; Dickey, B.F. Airway mucus function and dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, A.; Bath, J.; Jaramillo, A.M.; Ridley, C.; Walsh, A.A.; Evans, C.M.; Thornton, D.J.; Ribbeck, K. Mucus. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R938–R945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, H.M.; Lim, D.J.; Kurono, Y.; Cripps, A.W. Middle Ear and Eustachian Tube Mucosal Immunology. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 2, 1923–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruohola, A.; Meurman, O.; Nikkari, S.; Skottman, T.; Salmi, A.; Waris, M.; Osterback, R.; Eerola, E.; Allander, T.; Niesters, H.; et al. Microbiology of acute otitis media in children with tympanostomy tubes: Prevalences of bacteria and viruses. Clin. Infec. Dis. 2006, 43, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. Fluticasone propionate: Safety profile. Cutis 1996, 57 (Suppl. 2), 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, L.A.; DeClue, A.E.; Reinero, C.R. Endocrine and immunologic effects of inhaled fluticasone propionate in healthy dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008, 22, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bosscher, K.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Haegeman, G. Cross-talk between nuclear receptors and nuclear factor kappaB. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6868–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, R.C.-W.; Chen, Y.S.; Huang, J.R.; Jeng, K.C. Cross-linked bromelain inhibits lipopolysaccharideinduced cytokine production involving cellular signaling suppression in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2193–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, L.P.; Greer, P.K.; Trinh, C.T.; Gottfried, M.R. Treatment with oral bromelain decreases colonic inflammation in the IL-10-deficient murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.S.; Li, S.; Chai, C.Y.; Lo, C.Y.; Ho, C.T.; Wang, Y.J.; Pan, M.H. Inhibitory effect of citrus 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced skin inflammation and tumor promotion in mice. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhui, K.; Prasad, S.; George, J.; Shukla, Y. Bromelain inhibits COX-2 expression by blocking the activation of MAPK regulated NF-kappa B against skin tumor-initiation triggering mitochondrial death pathway. Cancer Lett. 2009, 282, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M.; Gunupuru, R. Targeting cyclooxygenase enzyme for the adjuvant COVID-19 therapy. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fitzhugh, D.J.; Shan, S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Hale, L.P. Bromelain treatment decreases neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 128, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Z.A.; Ahmad, T. Therapeutic uses of pineapple-extracted bromelain in surgical care-A review. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2017, 67, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Büttner, L.; Achilles, N.; Böhm, M.; Shah-Hosseini, K.; Mösges, R. Efficacy and tolerability of bromelain in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis—A pilot study. B-ENT 2013, 9, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho Dos Reis, J.G.A.; Ferreira, G.M.; Lourenço, A.A.; Ribeiro, Á.L.; da Mata, C.P.D.S.M.; de Melo Oliveira, P.; Marques, D.P.A.; Ferreira, L.L.; Clarindo, F.A.; da Silva, M.F.; et al. Ex-vivo mucolytic and anti-inflammatory activity of BromAc in tracheal aspirates from COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CTR | NSG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson r | p Values | CI (95%) | Pearson r | p Values | CI (95%) | |
| Otoscopy | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000–1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000–1.000 |
| Tympanometry RE | 0.269 | 0.004 ** | 0.08761–0.4328 | 0.240 | 0.011 * | 0.05662–0.4071 |
| Tympanometry LE | 0.187 | 0.048 * | 0.001412–0.3600 | 0.016 | 0.867 | 0.1701–0.2010 |
| Otoacoustic Emissions RE | 0.310 | 0.01 ** | 0.1322–0.4687 | 0.205 | 0.030 * | 0.02066–0.3766 |
| Otoacoustic Emissions LE | 0.217 | 0.022 * | 0.03279–0.3870 | 0.238 | 0.011 * | 0.05490–0.4057 |
| Audiometry | 0.193 | 0.042 * | 0.007578–0.3653 | 0.221 | 0.019 * | 0.03731–0.3908 |
| Tympanometry | T1 vs. T0 | T2 vs. T1 |
|---|---|---|
| Type B | ||
| RE | χ2 = 12.10, z = 3.478, p = 0.0005 *** | χ2 = 2.526, z = 1.589, p = 0.1120 |
| LE | χ2 = 29.86, z = 5.465, p < 0.0001 *** | χ2 = 0.1623, z = 0.4029, p = 0.6870 |
| Type C | ||
| RE | χ2 = 2.233, z = 1.494, p = 0.1351 | χ2 = 0.3958, z = 0.6292, p = 0.5292 |
| LE | χ2 = 5.734, z = 2.395, p = 0.0166 * | χ2 = 0.5492, z = 0.7411, p = 0.4586 |
| TEOAEs | T1 vs. T0 | T2 vs. T1 |
|---|---|---|
| Refer | ||
| RE | χ2 = 17.78, z = 4.217, p < 0.0001 *** | χ2 = 0.1642, z = 0.4053, p = 0.6853 |
| LE | χ2 = 7.238, z = 2.690, p = 0.0071 ** | χ2 = 0.3368, z = 0.5804, p = 0.5617 |
| Pass | ||
| RE | χ2 = 9.061, z = 3.010, p = 0.0026 ** | χ2 = 3.337, z = 1.827, p = 0.0677 |
| LE | χ2 = 0.02165, z = 0.1471, p = 0.8830 | χ2 = 8.180, z = 2.860, p = 0.0042 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martines, F.; Malta, G.; Cannizzaro, E.; Kelly, T.; Salvago, P.; Plescia, F. Bromelain Supplementation in the Management of Otitis Media with Effusion in Children. Children 2024, 11, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121440
Martines F, Malta G, Cannizzaro E, Kelly T, Salvago P, Plescia F. Bromelain Supplementation in the Management of Otitis Media with Effusion in Children. Children. 2024; 11(12):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121440
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartines, Francesco, Ginevra Malta, Emanuele Cannizzaro, Theodoridou Kelly, Pietro Salvago, and Fulvio Plescia. 2024. "Bromelain Supplementation in the Management of Otitis Media with Effusion in Children" Children 11, no. 12: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121440
APA StyleMartines, F., Malta, G., Cannizzaro, E., Kelly, T., Salvago, P., & Plescia, F. (2024). Bromelain Supplementation in the Management of Otitis Media with Effusion in Children. Children, 11(12), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11121440










