Clinical Effectiveness of Biological Immunomodulators in SARS-CoV-2-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
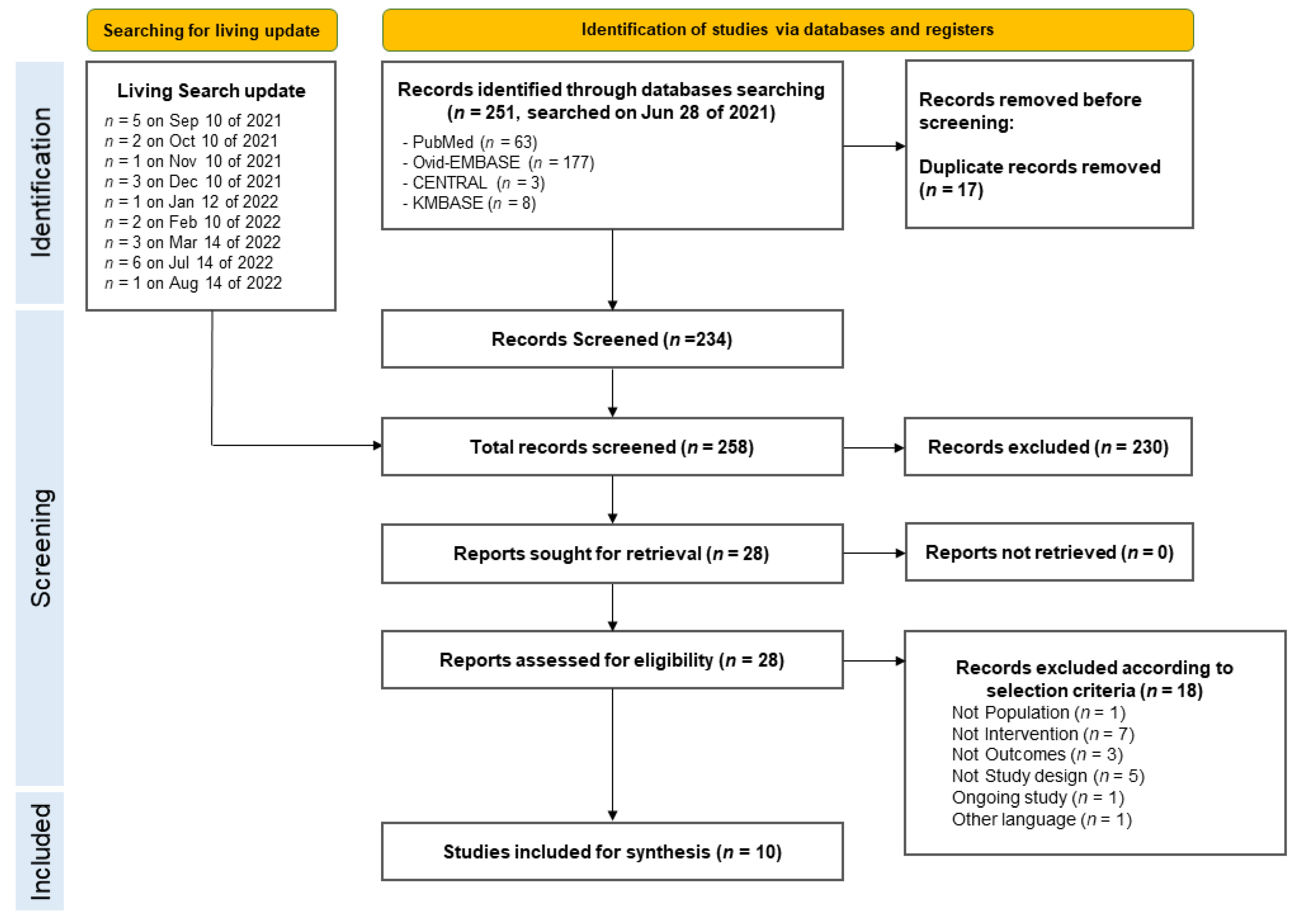
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria and Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Methodological Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
2.5. Rating Certainty of Evidence
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications
4.2. Comparison to Pre-Existing Evidence and Guidelines
4.3. Considerations Regarding Choice of Biologic Agents
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riphagen, S.; Gomez, X.; Gonzalez-Martinez, C.; Wilkinson, N.; Theocharis, P. Hyperinflammatory shock in children during COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1607–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.N.; Patel, R.S.; Trachtman, R.; Lepow, L.; Amanat, F.; Krammer, F.; Wilson, K.M.; Onel, K.; Geanon, D.; Tuballes, K.; et al. Mapping systemic inflammation and antibody responses in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Cell 2020, 183, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouldali, N.; Toubiana, J.; Antona, D.; Javouhey, E.; Madhi, F.; Lorrot, M.; Léger, P.L.; Galeotti, C.; Claude, C.; Widemann, A.; et al. Association of Intravenous Immunoglobulins Plus Methylprednisolone vs Immunoglobulins Alone with Course of Fever in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. JAMA 2021, 325, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.A.; Canna, S.W.; Friedman, K.G.; Gorelik, M.; Lapidus, S.K.; Bassiri, H.; Behrens, E.M.; Kernan, K.F.; Schulert, G.S.; Seo, P.; et al. American College of Rheumatology Clinical Guidance for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with SARS-CoV-2 and Hyperinflammation in Pediatric COVID-19: Version 3. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, e1–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Interim Guidance Updated 8 Feb 2023. Available online: https://www.aap.org/en/pages/2019-novel-coronavirus-covid-19-infections/clinical-guidance/multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-mis-c-interim-guidance/ (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Government of Western Australia Child and Adolescent Health Service. Paediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome (PIMS-TS) Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Diagnosis and Management. Available online: https://pch.health.wa.gov.au/For-health-professionals/Clinical-Practice-Guidelines/Paediatric-Inflammatory-Multisystem-Syndrome (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Boretti, A.; Banik, B. Modulation of COVID-19 cytokine storm by tocilizumab. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celikel, E.; Tekin, Z.E.; Aydin, F.; Emeksiz, S.; Uyar, E.; Ozcan, S.; Perk, O.; Sezer, M.; Tekgoz, N.; Coskun, S.; et al. Role of Biological Agents in the Treatment of SARS-CoV-2-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 28, e381–e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, L.D.; Osborne, C.M.; Silveira, L.J.; Rao, S.; Lockwood, J.M.; Kunkel, M.J.; MacBrayne, C.E.; Heizer, H.R.; Anderson, M.S.; Jone, P.N.; et al. IVIG Compared with IVIG Plus Infliximab in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021052702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, C.; Al Obaidi, M.; Moraitis, E.; Compeyrot-Lacassagne, S.; Eleftheriou, D.; Brogan, P. Management of severe hyperinflammation in the COVID-19 era: The role of the rheumatologist. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Haq, N.; Asmar, B.I.; Deza Leon, M.P.; McGrath, E.J.; Arora, H.S.; Cashen, K.; Tilford, B.; Charaf Eddine, A.; Sethuraman, U.; Ang, J.Y. SARS-CoV-2-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: Clinical manifestations and the role of infliximab treatment. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.Y.; Day-Lewis, M.; Henderson, L.A.; Friedman, K.G.; Lo, J.; Roberts, J.E.; Lo, M.S.; Platt, C.D.; Chou, J.; Hoyt, K.J.; et al. Distinct clinical and immunological features of SARS-CoV-2-induced multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5942–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanello, C.; Mercuri, C.; Derchi, M.; Trocchio, C.; Consolaro, A.; Caorsi, R.; Ravelli, A.; Rimini, A.; Marasini, M.; Gattorno, M. Cardiovascular Manifestations in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with COVID-19 According to Age. Children 2022, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisca, G.; Consolaro, A.; Caorsi, R.; Pirlo, D.; Tuo, G.; Campanello, C.; Castagnola, E.; Moscatelli, A.; Gattorno, M.; Ravelli, A. Timely Recognition and Early Multi-Step Antinflammatory Therapy May Prevent ICU Admission of Patients with MIS-C: Proposal for a Severity Score. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 783745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozeri, B.; Caglayan, S.; Atasayan, V.; Ulu, K.; Coskuner, T.; Pelin Akbay, O.; Hasbal Akkuş, C.; Atay, G.; Sali, E.; Karacan, M. The clinical course and short-term health outcomes of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in the single pediatric rheumatology center. Postgrad. Med. 2021, 133, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savas Sen, Z.; Tanir, G.; Gumuser Cinni, R.; Uysal Yazici, M.; Yoldas, T.; Ozturk, Z.; Han Kizilkaya, M.; Ozdem, S.; Yalcinkaya, R.; Ozturk, C.; et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 pandemic in Turkey: A single-centre experience. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2022, 58, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Anakinra Condition: Systemic Onset Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis with Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/essential-medicines/2021-eml-expert-committee/applications-for-addition-of-new-medicines/a.2_anakinra.pdf?sfvrsn=1de47f03_4 (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Ahn, J.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Yun, K.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, M. The clinical efficacy of biological immunomodulators in SARS-CoV-2-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: A systematic review. Authorea 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Design | Study Period | Cases Using Biologics/Total MIS-C Cases (%) | Median Age of Patients Treated with Biologics (Range) /No. of Cases < 10 Years Old (%) | Biologics Used | ICU Admission Cases (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celikel et al. [8], 2021 | Case-control | 2020.9–2020.10 | 23/33 (70) | 12.0 (3–17)/ 17 (52) | Anakinra | 33 (100) |
| Cole et al. [9], 2021 | Retrospective observational | 2020.4–2021.2 | 52/72 (72) | 9.0 (6–12)/ N/A | Infliximab | 42 (58) |
| Gruber et al. [2], 2020 | Case series | 2020.4–2020.6 | 7/9 (78) | 12.0 b/c | Tocilizumab | N/A |
| Papadopoulou et al. [10], 2021 | Case series | 2020.4–2020.5 | 5/19 (26) | 13.9 (7.1–14.4)/ 10 (53) | Anakinra (4), Infliximab (1) | 17 (90) |
| Abdel-Haq et al. [11], 2021 | Case series | 2020.4–2020.6 | 12/33 (36) | 8.0 (IQR 7–14)/ 28 (85) | Infliximab | 22 (67) |
| Lee et al. [12], 2020 | Case series | 2020.3–2020.6 | 5/28 (18) | 9.0 (0.1–17)/ d | Anakinra | 17 (61) |
| Campanello et al. [13], 2022 | Retrospective observational | 2020.3–2021.9 | 8/25 (32) | 5.0 (IQR 3–12) a/e | Anakinra | N/A |
| Brisca et al. [14], 2021 | Retrospective observational | 2020.4–2021.6 | 6/23 (26) | 5.8 (4–12) a/N/A | Anakinra | 0 (0) |
| Sozeri et al. [15], 2021 | Prospective observational | 2020.4–2021.4 | 18/67 (27) | 11.2 b/N/A | Anakinra (17), Tocilizumab (1) | 21 (31) |
| Savas Sen et al. [16], 2020 | Case series | 2020.8–2021.3 | 9/45 (20) | 14.0 (IQR 12–14)/ f | Anakinra (9) | 11 (24) |
| Outcomes a | Summary | No. of Participants (Studies) | Certainty of the Evidence (GRADE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | Not reported | ||
| Mechanical ventilation | Not reported | ||
| Hemodynamic support | Not reported | ||
| Coronary aneurysm at discharge | Not reported | ||
| Cardiac dysfunction | 1. Celikel et al.: Decreased cardiac function in biological immunomodulator group vs. control group (p = 0.08) [8]. 2. Cole et al.: Worsened left ventricular systolic function in 4/52 cases with IVIg + infliximab compared to 5/20 cases with IVIg alone [9]. | 102 (2 observational studies) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low b,c (important) |
| Fever | 1. Cole et al.: Time to defervescence was 3 days (IQR 2–4) for IVIg alone vs. 2 days (IQR 1–3) for IVIg + infliximab [9]. | 72 (1 observational study) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low c (important) |
| Outcomes | Summary | No of Participants (Studies) | Certainty of the Evidence (GRADE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | 100 (2 observational study) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low a (Critical) | |
| Mechanical ventilation |
| 92 (5 observational studies) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low a (Critical) |
| Hemodynamic support |
| 92 (4 observational studies) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low a (Critical) |
| Coronary aneurysm at discharge |
| 164 (6 observational studies) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low a (important) |
| Cardiac dysfunction |
| 84 (4 observational studies) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low a (important) |
| Clinical improvement |
| 9 (1 observational study) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low a (important) |
| Fever | 47 (2 observational studies) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low a (important) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, D.H.; Yun, K.W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Cao, G.P.H.; Choi, M.; Ahn, J.G. Clinical Effectiveness of Biological Immunomodulators in SARS-CoV-2-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review. Children 2024, 11, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101180
Lee JY, Kim J, Choi S-H, Kim DH, Yun KW, Kim Y-J, Cao GPH, Choi M, Ahn JG. Clinical Effectiveness of Biological Immunomodulators in SARS-CoV-2-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review. Children. 2024; 11(10):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Young, Jimin Kim, Soo-Han Choi, Dong Hyun Kim, Ki Wook Yun, Yae-Jean Kim, Giang Pham Ha Cao, Miyoung Choi, and Jong Gyun Ahn. 2024. "Clinical Effectiveness of Biological Immunomodulators in SARS-CoV-2-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review" Children 11, no. 10: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101180
APA StyleLee, J. Y., Kim, J., Choi, S.-H., Kim, D. H., Yun, K. W., Kim, Y.-J., Cao, G. P. H., Choi, M., & Ahn, J. G. (2024). Clinical Effectiveness of Biological Immunomodulators in SARS-CoV-2-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review. Children, 11(10), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101180





