Predictive and Diagnostic Values of Systemic Inflammatory Indices in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Outcome Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Infants with and without BPD
3.2. Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis
3.3. Comparison of the Systemic Inflammatory Indices of the Two Premature Infant Groups
3.4. Value of NLR in BPD
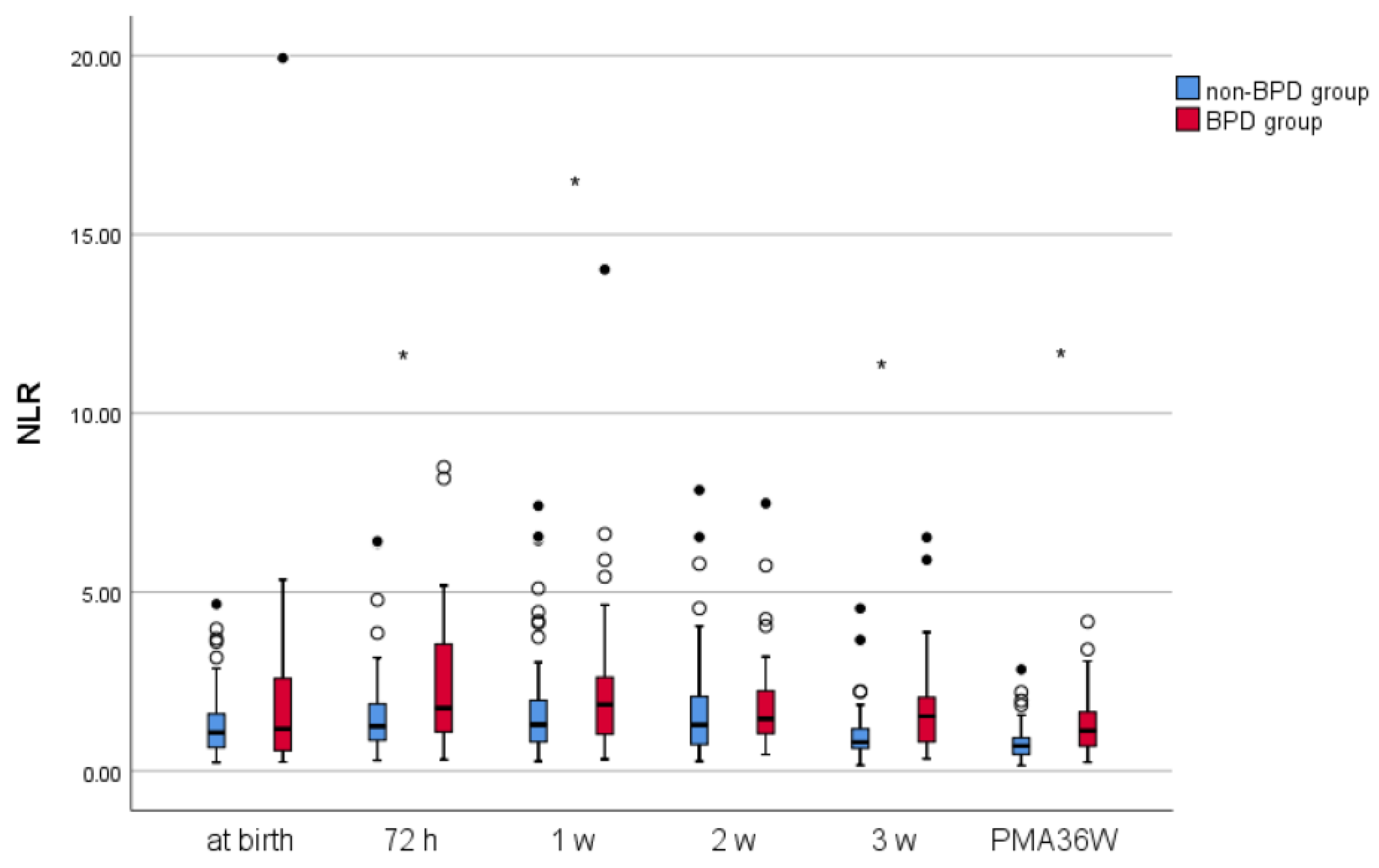
Dynamic Changes in NLR
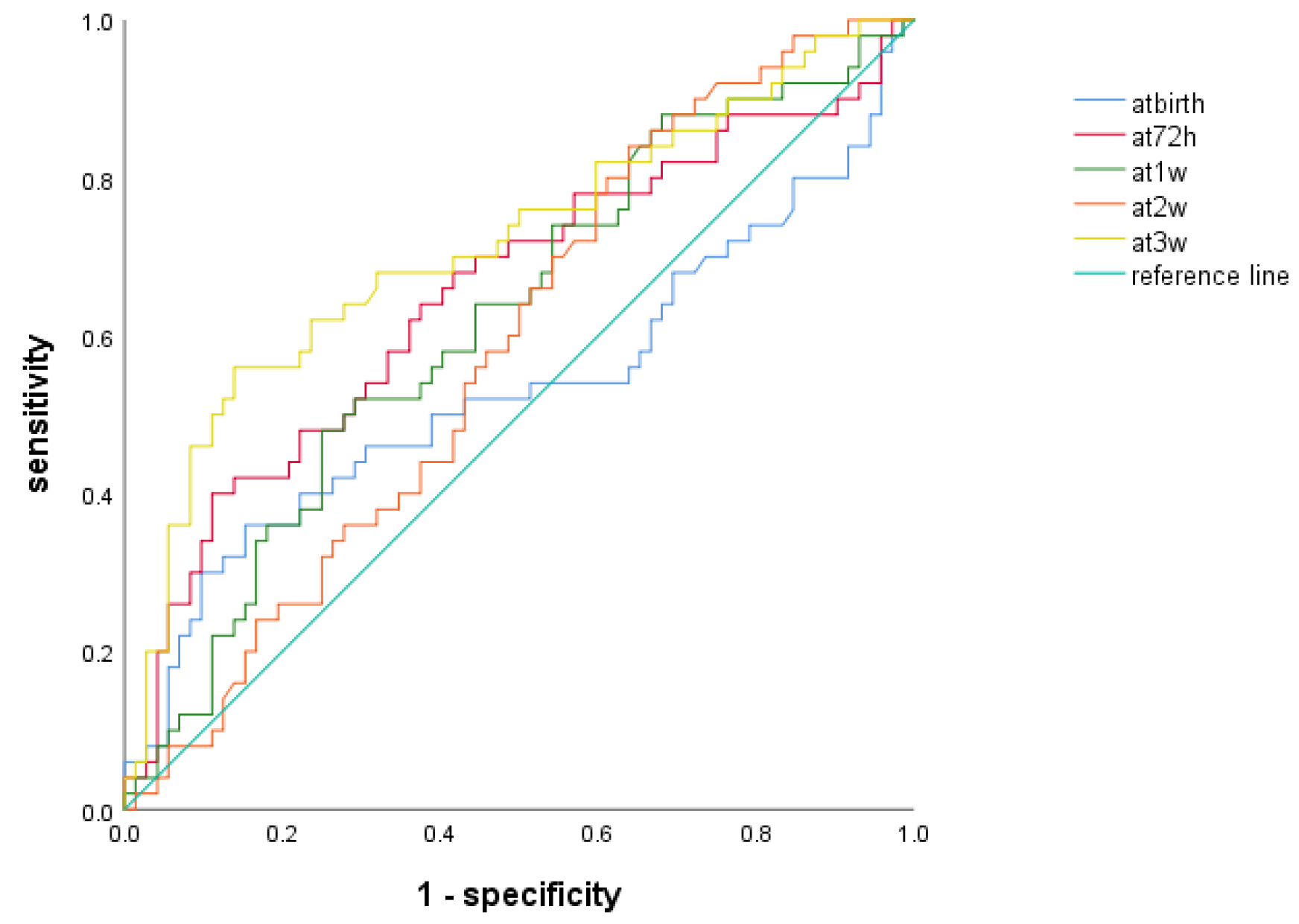
3.5. ROC Analysis of NLR to Predict BPD at Different Time Points
3.6. ROC Analysis of NLR for BPD Diagnosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.I.; Bell, E.F.; Walsh, M.C.; Carlo, W.A.; Shankaran, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Sánchez, P.J.; Van Meurs, K.P.; Wyckoff, M.; et al. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Trends in Care Practices, Morbidity, and Mortality of Extremely Preterm Neonates, 1993–2012. JAMA 2015, 314, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, D. Risk Analys is and Clinical Value of NLR, PLR and SII of BPD for Premature Infants with Gestational Age<32 Weeks. Bachelor Thesis, Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bonadies, L.; Cavicchiolo, M.E.; Priante, E.; Moschino, L.; Baraldi, E. Prematurity and BPD: What general pediatricians should know. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankhara, N.; Holla, I.; Ramarao, S.; Kalikkot Thekkeveedu, R. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, Z.; Spyropoulos, F.; Ghanta, S.; Christou, H. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: An Update of Current Pharmacologic Therapies and New Approaches. Clin. Med. Insights Pediatr. 2018, 12, 1179556518817322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinellu, A.; Zinellu, E.; Mangoni, A.A.; Pau, M.C.; Carru, C.; Pirina, P.; Fois, A.G. Clinical significance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute exacerbations of COPD: Present and future. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyit, M.; Avci, E.; Nar, R.; Senol, H.; Yilmaz, A.; Ozen, M.; Oskay, A.; Aybek, H. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte to monocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio to predict the severity of COVID-19. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 40, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, M.; Yan, X. Prognostic Role of NLR, PLR and MHR in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 882217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Russano, M.; Franchina, T.; Migliorino, M.R.; Aprile, G.; Mansueto, G.; Berruti, A.; Falcone, A.; Aieta, M.; Gelibter, A.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), and Outcomes with Nivolumab in Pretreated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Large Retrospective Multicenter Study. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, U.; Tayman, C.; Tugcu, A.U.; Yildiz, D. Role of Systemic Inflammatory Indices in the Prediction of Moderate to Severe Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Infants. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 216–222, (In Spanish with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Luo, T.; Li, T. Decreased neutrophil levels in bronchopulmonary dysplasia infants. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2020, 61, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Mereness, J.A.; Baran, A.M.; Misra, R.S.; Peterson, D.R.; Ryan, R.M.; Reynolds, A.M.; Pryhuber, G.S.; Mariani, T.J. Lymphocyte-Specific Biomarkers Associated With Preterm Birth and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 563473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, R.D.; Jobe, A.H.; Koso-Thomas, M.; Bancalari, E.; Viscardi, R.M.; Hartert, T.V.; Ryan, R.M.; Kallapur, S.G.; Steinhorn, R.H.; Konduri, G.G.; et al. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Executive Summary of a Workshop. J. Pediatr. 2018, 197, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Ye, H.; Qiu, X. Practice of Neonatology; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan, M.; Bhandari, A.; Bhandari, V. Diagnosis and management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. BMJ 2021, 375, n1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Weng, X.; Sheng, A.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, X.; Lu, C. High Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Is an Early Predictor of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humberg, A.; Fortmann, I.; Siller, B.; Kopp, M.V.; Herting, E.; Göpel, W.; Härtel, C.; German Neonatal Network, German Center for Lung Research and Priming Immunity at the beginning of life (PRIMAL) Consortium. Preterm birth and sustained inflammation: Consequences for the neonate. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, H.; Ochiai, M.; Inoue, H.; Kusuda, T.; Fujiyoshi, J.; Ichiyama, M.; Wakata, Y.; Takada, H. Inflammation in the neonatal period and intrauterine growth restriction aggravate bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2019, 60, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gazzar, A.G.; Kamel, M.H.; Elbahnasy, O.K.M.; El-Naggar, M.E. Prognostic value of platelet and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in COPD patients. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xiao, H.; Duan, Y.; Li, Q.; Ou, X. Prognostic Value of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio for Predicting 90-Day Poor Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2023, 18, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Tan, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, C.; Jiang, T. Predictive Value of Systemic Immune-Inflammation index and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Severe COVID-19. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 28, 10760296221111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Shobeiri, P.; Kulasinghe, A.; Rezaei, N. Novel Systemic Inflammation Markers to Predict COVID-19 Prognosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 741061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citu, C.; Gorun, F.; Motoc, A.; Sas, I.; Gorun, O.M.; Burlea, B.; Tuta-Sas, I.; Tomescu, L.; Neamtu, R.; Malita, D.; et al. The Predictive Role of NLR, d-NLR, MLR, and SIRI in COVID-19 Mortality. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, A.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Scano, V.; Cau, S.; Babudieri, S.; Perra, R.; Ruzzittu, G.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; et al. The Systemic Inflammation Index on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Molecules 2020, 25, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavò, L.; Perrone, S.; Viola, V.; Marseglia, L.; Di Rosa, G.; Gitto, E. Oxidative Stress and Respiratory Diseases in Preterm Newborns. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Wen, W.X.; Jiang, Z.P.; Du, Z.P.; Ma, Z.H.; Lu, A.L.; Li, H.P.; Yuan, F.; Wu, S.B.; Guo, J.W.; et al. The clinical value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) for predicting the occurrence and severity of pneumonia in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, past, present and future perspectives. Bratisl. Lekárske Listy 2021, 122, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Gharaibeh, F.N.; Kempton, K.M.; Alder, M.N. Olfactomedin-4-Positive Neutrophils in Neonates: Link to Systemic Inflammation and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Neonatology 2023, 120, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Non-BPD (n = 72) | BPD (n = 50) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age (weeks) a | 30.14 (29.43, 31.25) | 30.29 (28.93, 31.18) | 0.739 |
| Birth weight (g) b | 1389.44 ± 220.56 | 1251 ± 294.16 | 0.006 * |
| Multiple pregnancies, n (%) | 13 (18.1) | 17 (34) | 0.044 * |
| Cesarean delivery, n (%) | 28 (38.9) | 28 (56) | 0.062 |
| Apgar score at 1 min < 7, n (%) | 10 (13.9) | 8 (16) | 0.746 |
| Apgar score at 5 min < 7, n (%) | 3 (4.2) | 6 (12) | 0.202 |
| Male, n (%) | 27 (37.5) | 24 (48) | 0.248 |
| SGA, n (%) | 5 (6.9) | 15 (30) | 0.001 * |
| Postnatal dexamethasone treatment, n (%) | 21 (29.2) | 38 (76) | 0.000 * |
| Surfactant administration, n (%) | 50 (69.4) | 43 (86) | 0.035 * |
| Duration of hospitalization (days) a | 48.5 (41.25, 56) | 65.5 (53.75, 77.5) | 0.000 * |
| Days of O2 therapy (days) a | 22.88 (13.00, 32.05) | 49.66 (37.38, 59.62) | 0.000 * |
| O2 inhalation in the box (5 L/min)(days) a | 3.01 (1.94, 7.09) | 7.26 (4.52, 11.11) | 0.001 * |
| Hood O2 (5 or 7 L/min)(days) a | 2.04 (0, 4.99) | 1.98 (0.42, 9.50) | 0.242 |
| Days of CPAP therapy (days) a | 7.34 (4.39, 16.63) | 14.10 (6.97, 26.47) | 0.001 * |
| Mechanical ventilation time (days) a | 0 (0,6.76) | 7.72 (0, 29.28) | 0.000 * |
| PROM, n (%) | 33 (45.8) | 18 (36) | 0.279 |
| NRDS, n (%) | 63 (87.5) | 48 (96) | 0.197 |
| EOS, n (%) | 2 (2.8) | 13 (26) | 0.000 * |
| Congenital pneumonia, n (%) | 5 (6.9) | 6 (12) | 0.524 |
| PDA, n (%) | 24 (33.3) | 19 (38) | 0.596 |
| PH, n (%) | 18 (25) | 12 (24) | 0.900 |
| ROP, n (%) | 22 (30.6) | 17 (34) | 0.688 |
| Neonatal intracranial hemorrhage, n (%) | 57 (79.2) | 42 (84) | 0.502 |
| NEC, n (%) | 4 (5.6) | 4 (8) | 0.869 |
| Maternal age (year) b | 28.76 ± 4.52 | 30.38 ± 5.19 | 0.070 |
| Gestational hypertension, n (%) | 17 (23.6) | 19 (38) | 0.087 |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 17 (23.6) | 5 (10) | 0.054 |
| Influencing Factors | B | SE | Wald X2 | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth weight | 0.004 | 0.002 | 5.029 | 1.004 | 1.000–1.008 | 0.025 * |
| SGA | −3.878 | 1.403 | 7.644 | 0.021 | 0.001–0.323 | 0.021 * |
| Days of O2 therapy | 0.173 | 0.086 | 4.042 | 1.189 | 1.004–1.407 | 0.044 * |
| 3 Weeks | Non-BPD (n = 72) | BPD (n = 50) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 4.44 (3.27, 6.12) | 5.97 (4.16, 9.72) | 0.001 * |
| NLRa | 0.80 (0.62, 1.81) | 1.53 (0.79, 2.06) | 0.000 * |
| PLRa | 55.06 (41.02, 72.99) | 48.45 (31.60, 71.21) | 0.200 |
| MLRa | 0.27 (0.22, 0.37) | 0.35 (0.25, 0.53) | 0.026 * |
| SIIa | 256.84 (141.69, 394.04) | 344.77 (199.98, 595.75) | 0.035 * |
| SIRIa | 1.28 (0.70, 1.89) | 2.29 (1.12, 4.05) | 0.001 * |
| PIVa | 355.99 (180.40, 664.01) | 686.03 (190.20, 1315.89) | 0.033 * |
| PMA 36 Weeks | Non-BPD (n = 72) | BPD (n = 50) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 3.50 (2.63, 5.05) | 5.09 (3.05, 8.54) | 0.003 * |
| NLRa | 0.70 (0.46, 0.92) | 1.12 (0.68, 1.65) | 0.000 * |
| PLRa | 64.43 (52.40, 88.02) | 62.81 (38.54, 77.33) | 0.138 |
| MLRa | 0.25 (0.18, 0.33) | 0.30 (0.23, 0.45) | 0.022 * |
| SIIa | 253.78 (160.09, 348.50) | 276.60 (140.87, 609.69) | 0.338 |
| SIRIa | 0.90 (0.55, 1.46) | 1.62 (0.89, 3.82) | 0.002 * |
| PIVa | 332.14 (196.83, 529.39) | 412.80 (197.86, 1311.62) | 0.252 |
| AUC | 95%CI | Cutoff Level | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden Index | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At birth | 0.534 | 0.422–0.645 | 1.914 | 36 | 84.7 | 0.207 | 0.525 |
| At 72 h | 0.653 | 0.551–0.755 | 2.429 | 40 | 88.9 | 0.289 | 0.004 * |
| At 1 w | 0.620 | 0.519–0.721 | 1.911 | 48 | 75 | 0.23 | 0.025 * |
| At 2 w | 0.584 | 0.484–0.685 | 0.8735 | 84 | 36.1 | 0.201 | 0.114 |
| At 3 w | 0.717 | 0.621–0.813 | 1.416 | 56 | 86.1 | 0.421 | 0.000 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, T.; Cheng, H.; Tian, Z. Predictive and Diagnostic Values of Systemic Inflammatory Indices in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Children 2024, 11, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010024
Cao L, Liu X, Sun T, Zhang Y, Bao T, Cheng H, Tian Z. Predictive and Diagnostic Values of Systemic Inflammatory Indices in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Children. 2024; 11(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Linxia, Xiangye Liu, Tingting Sun, Yuan Zhang, Tianping Bao, Huaiping Cheng, and Zhaofang Tian. 2024. "Predictive and Diagnostic Values of Systemic Inflammatory Indices in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia" Children 11, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010024
APA StyleCao, L., Liu, X., Sun, T., Zhang, Y., Bao, T., Cheng, H., & Tian, Z. (2024). Predictive and Diagnostic Values of Systemic Inflammatory Indices in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Children, 11(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010024






