Abstract
Objective: To test the potential utility of applying machine learning methods to regional cerebral (rcSO2) and peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) signals to detect brain injury in extremely preterm infants. Study design: A subset of infants enrolled in the Management of Hypotension in Preterm infants (HIP) trial were analysed (n = 46). All eligible infants were <28 weeks’ gestational age and had continuous rcSO2 measurements performed over the first 72 h and cranial ultrasounds performed during the first week after birth. SpO2 data were available for 32 infants. The rcSO2 and SpO2 signals were preprocessed, and prolonged relative desaturations (PRDs; data-driven desaturation in the 2-to-15-min range) were extracted. Numerous quantitative features were extracted from the biosignals before and after the exclusion of the PRDs within the signals. PRDs were also evaluated as a stand-alone feature. A machine learning model was used to detect brain injury (intraventricular haemorrhage-IVH grade II–IV) using a leave-one-out cross-validation approach. Results: The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for the PRD rcSO2 was 0.846 (95% CI: 0.720–0.948), outperforming the rcSO2 threshold approach (AUC 0.593 95% CI 0.399–0.775). Neither the clinical model nor any of the SpO2 models were significantly associated with brain injury. Conclusion: There was a significant association between the data-driven definition of PRDs in rcSO2 and brain injury. Automated analysis of PRDs of the cerebral NIRS signal in extremely preterm infants may aid in better prediction of IVH compared with a threshold-based approach. Further investigation of the definition of the extracted PRDs and an understanding of the physiology underlying these events are required.
1. Introduction
Survival in the preterm population is improving, especially for extremely preterm infants. However, long-term adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes remain an ongoing concern, with morbidity increasing with decreasing gestational age [1,2,3]. A recent systematic review suggests that between 5–52% of preterm infants will develop some degree of intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH); the disparity attests to the variability in clinical practice and potential diversity within the patient population [4]. Many studies have associated IVH in extremely preterm infants with poor neurodevelopment in the early years of life [5,6]. A recent study examined children who were born extremely preterm but were assessed during school years (age 8) and reported that all grades of IVH were associated with a higher risk of cerebral palsy and higher grades of IVH were associated with a higher risk of impaired academic scores [7].
The dose and severity of the physiological insults or intrinsic vulnerability corresponding to the different grades of IVH are unknown [8]. Matsushita et al. (2021) performed a retrospective study examining potential similarities using 62 clinical features from 215 individual infants born <1000 g [9]. The cluster analysis revealed six distinct phenotypic clusters, some of which were associated with IVH. The authors’ unsupervised machine learning approach may contribute to a better understanding of the IVH population in the future [9]. Hypoxia is believed to be a contributory factor in the development of IVH. A recent study found that infants with IVH spent a greater percentage of time with a heavier burden of cerebral hypoxia, compared with those who did not have IVH [10]. This is congruent with changes in systematic and cerebral haemodynamics that reveal a pattern consistent with a hypoperfusion–reperfusion cycle [11]. Impaired cerebral autoregulation may result in cerebral blood flow disturbance and potential rupture of the fragile vasculature of the germinal matrix, resulting in IVH [12,13,14].
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a noninvasive optical technology that is used for continuous bedside monitoring of regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rcSO2) and provides information on neonatal cerebral haemodynamics [15]. Regional cerebral oxygenation may be an important tool to guide treatment and prevent cerebral hypoxia [16] in the most immature infants [15]. Cerebral NIRS has become commonplace in clinical practice [17,18]; however, a recent meta-analysis, including data from 2606 infants concluded that there were insufficient data to support or reject the benefit of cerebral NIRS monitoring for improved clinical outcome measures [19]. This is not surprising as there is no general agreement concerning the absolute values of rcSO2 associated with brain damage. These absolute values have ranged from rcSO2 < 50% [20,21] to rcSO2 < 65% [22], and in one recent randomised trial there was no association between rcSO2 < 55% or rcSO2 > 85% and adverse long-term outcomes [17]. The variability in absolute values of rcSO2 between NIRS devices and sensors and between different gestational ages makes it difficult to reach a consensus on normal values of rcSO2 in preterm infants [22,23]. Therefore, alternative methods of describing the continuous signal should be evaluated.
We have previously employed signal processing methods to investigate the association of cerebral oxygenation in preterm infants born less than 32 weeks of GA with IVH and periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). Features of the signal amplitude within certain frequency bands (0.9–3.6 mHz) were useful to detect brain injury [24]. Subsequently, we detected the presence of desaturation waveforms in rcSO2 in extremely preterm NIRS recordings and reported that removing these prolonged relative desaturations (PRDs; data-driven desaturations) increased the predictability of the NIRS signals in detecting brain injury [25]. However, this was based on a relatively small sample size (n = 10). The objective of the current study was to isolate PRDs in rcSO2 and SpO2 signals in preterm infants less than 28 weeks and using machine learning models, explore their putative relationship with brain injury in preterm infants. Furthermore, we sought to examine the potential value of combining clinical features with features from the NIRS signal to detect preterm brain injury.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
The current study analysed data derived from a multicentre clinical trial, the Hypotension in Preterm Infants (HIP, Trial registration number NCT01482559, EudraCT 2010-023988-17) [26]. The infants were recruited between February 2015 and September 2017 at Cork University Maternity Hospital. All infants were extremely preterm, i.e., born less than 28 weeks’ gestation. Data from 46 extremely preterm infants were analysed in this study, including both male (n = 25) and female (n = 21) infants. The mean birth weight of the infants was 767.41 g ± 155.57 g, 20 of whom were diagnosed with hypotension. All infants underwent continuous (>24 h) rcSO2 measurements using NIRS over the first 72 h and cranial ultrasounds performed during the first week of life. A subset of these infants (n = 32) also had continuous SpO2 data available. This study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee, Cork, ECM 5(2) 15 January 2013.
2.2. Data Collection
The INVOS 5100 device, (Covidien Mansfield, MI, USA) was used with the neonatal transducer, INVOS OxyAlert NIRSensor (Covidien, Mansfield, MI, USA) to make continuous measurements of rcSO2. The cerebral sensor was placed on the right frontotemporal area of the forehead, measuring the ratio of oxygenated haemoglobin to the total haemoglobin in the tissue beneath. When available, the Moberg CNS device (Moberg, PA, USA) was used to time-synchronise and store the rcSO2 and peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) data.
SpO2 was recorded using a pulse oximeter (IntelliVue, MP70, Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands, or equivalent). SpO2 data were only available for the infants whose rcSO2 data was stored using a connected device (Moberg Neuroscan, Ambler, PA, USA) (32/46). SpO2 data were collected with two sampling frequencies of 1 and 0.5 Hz and stored for later analysis, and all patient information was replaced by individual research codes.
Clinical ultrasound recordings were performed using a Philips HD-11XE ultrasound system and probe C8-5. Ultrasounds were reviewed and graded by experienced paediatric radiologists, who were blinded to the patients’ clinical characteristics and haemodynamic findings. Volpe’s criteria [27] were used to classify IVH, and the highest grade of IVH identified by ultrasound in the first week of life was used in a dichotomous outcome label. For the purpose of our machine learning model, brain injury was defined as IVH grade II-IV in the first week of life, and IVH grade I or no IVH was classified as non/mild brain injury for this study [28]. It is important to note that infants that were labelled as IVH grade I in our study did not progress to IVH II, and their haemorrhage often improved within the first week.
A combination of clinical data, used by clinicians for the early identification of infants at risk of IVH, were analysed in this study. These clinical attributes included the following binary variables: sex, hypotension, receiving any inotrope, and the presence of chorioamnionitis in utero. Other continuous variables included birth weight (g) and head circumference (cm), and discrete variables included Apgar score in the first 5 min of life and gestational age (GA, days).
2.3. Signal Processing
The INVOS device records using a nonuniform sampling frequency, typically between 1/5 and 1/6 Hz. At this sampling frequency, these devices need external memory to store the data. When this device was not available, the INVOS device stored the data in internal memory with a nonuniform sampling frequency typically between 1/34 and 1/35 Hz. To generate a uniform sampling rate, cubic spline interpolation was used to fill in the missing data [29]. Then, the rcSO2 signal was up-sampled to a sampling frequency of 10 Hz, and a low-pass filter (a zero-phase finite impulse response filter, FIR) was used to prevent aliasing before down-sampling to 1/6 Hz. Missing data that were filled in using cubic spline interpolation were removed.
In some cases, the NIRS probe became loose or detached or was temporarily removed during recordings over 72 h. In these cases, rcSO2 was not recorded or saturated at the minimum value of 15% [30]. Thus, in data points equivalent to 15%, a collar of 30 s was applied, and those data points were removed.
To preprocess the SpO2 signals, first values of less than 20% or sudden changes (more than 4% in one second) with a collar of 30 s were removed [31]. Missing data were interpolated using cubic spline interpolation [29], and the signal was down-sampled, after applying an appropriate anti-aliasing low-pass filter, to 1/6 Hz for agreement with the rcSO2 signal. Missing data prior to down-sampling was then removed.
2.4. Extracting Prolonged Relative Desaturations
A decomposition method, designed specifically to extract PRDs from rcSO2 signals in preterm infants [32], was used to extract PRDs from both the rcSO2 and SpO2 signals. The method applies a discrete cosine transform to the signals before using singular spectrum analysis to extract the transient-like components [24]. This PRD decomposition method is a data-driven operation that we have shown to be effective in isolating the PRDs from synthesised NIRS-like signals [32]. The duration of these PRDs typically lies in the 2-to-15-min range, and these desaturations have been defined and excluded using data-driven methods rather than using an absolute value as a threshold.
Three different modalities of the rcSO2 were analysed: the rcSO2 unprocessed, the rcSO2 signal without the PRD component, and the rcSO2 PRD component alone. For the first two modalities (i.e., rcSO2 and rcSO2 without the PRDs), the following methods were employed. First, the signals were filtered using a filter bank according to a dyadic frequency response. Five zero-phase finite-impulse response filters—with a frequency bandwidth of a/(2b), where a = fs /2 and b = 0,1,2,3,4—were used for band-pass filtering. Next, quantitative features were extracted for each filtered signal over a 4 h epoch with a 50% overlap. The number of epochs varied between 14 and 37, depending on the duration of recorded NIRS.
2.5. Feature Extraction
Amplitude-modulation features included the mean, standard deviation (SD), the 5th and 95th percentiles of the envelope, skewness, and kurtosis of the signal. Instantaneous frequency (IF) was estimated using a central-finite difference of the phase of the signal; mean, SD, skewness, kurtosis, and the 5th and 95th percentiles of the IF were again used as features. Fractal dimension (FD) was estimated using the Higuchi method. The postnatal age of the infants in each epoch was added to the feature set, resulting in a total feature set of 66 features.
A distinct set of features were measured directly from the extracted PRDs: frequency of the PRDs per hour, total power, envelope summarised in mean and SD, Hjorth parameters (activity, mobility, and complexity), interspike interval summarised in mean and standard deviation, time spent below 63% rcSO2 (85% for SpO2 transients), the average of the nadir amplitude of PRDs, the average of the downward slope (the slope of the line between the PRD’s baseline and nadir), the average of the upward slope (the slope of the line between the PRD’s nadir and baseline), and averaged duration of the PRDs. The total feature set for PRDs contained 14 features.
The entire process, from signal decomposition to feature extraction, was also applied to the SpO2 signal.
2.6. Machine Learning Models
A predictive model of brain injury was developed using a sequential ensemble of decision trees, known as an extreme gradient boosting machine (XGBoost). To reduce variance in the model, a common problem with small noisy data sets, regularisation was increased from default values by setting the maximum tree depth to 3. The total number of trees was 50, and the learning rate was 0.1. The feature set of 66 features per each 4 h epoch was used to train and test the model, using a leave-one-baby-out cross-validation procedure. In this method, the features derived from one infant were left out, and the remaining data were used to make the model, and then the model was tested on the excluded infant. This process was repeated for all the infants in the study, a total of 46 times, to overcome overfitting.
This approach was used to develop separate models for the rcSO2 and SpO2 signals, and then again for extracted PRD components. Feature importance was estimated for significant models, to examine how each feature contributed to the model’s prediction.
Due to its superior performance on nosier data sets, a bagging ensemble known as a random forest was used to develop a predictive model using the clinical attributes. The random forest combines multiple decision trees developed independently on different subsets of the data. The default parameters of the random forest were used with 500 trees. Similarly, a leave-one-baby-out cross-validation procedure was used to train and test the model.
2.7. Combining Models
To test if clinical information could enhance the predictability of detecting brain injury, the rcSO2 model and clinical model were combined using a late-stage fusion approach. Specifically, the probabilities generated from the rcSO2 model were combined with the probability of the clinical-feature model using the geometric mean. The same approach was applied to combining the SpO2 and clinical models. All the steps taken to process the signal, extract the PRDs and features, and utilise the machine learning model are presented in Figure 1.
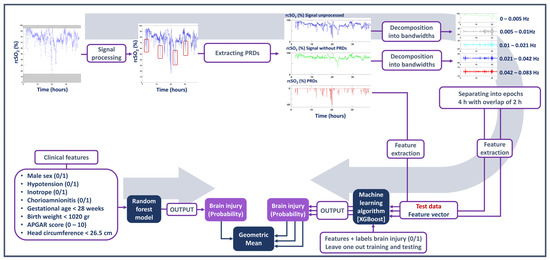
Figure 1.
Summary of the steps taken to process the signal, extract the prolonged relative desaturations (PRDs) and features, and utilise the machine learning model.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Fisher’s exact test was used to compare the proportion of infants with brain injury between the two rcSO2 sampling frequencies (~1/6 and ~1/35 Hz). To evaluate the ability of each model to detect brain injury, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) were analysed. AUC was considered significant if the value of AUC and the lower CI were greater than 0.5. An AUC value of 0.5 indicates that the model performs no better than a chance in distinguishing between true and false positives, so any value greater than 0.5 is an improvement over random guessing [33]. CIs were calculated using a bootstrapping procedure with resampling (with replacement) on a per-infant basis. In SpO2 XGBoost models, a hyperparameter, scale_pos_weight, was added and set to the ratio of the number of negative to positive samples to account for class imbalance in the dataset. The threshold used on the model probability for calculating sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy was 0.4; thus, any predicted probability scores greater than or equal to 0.4 were considered positive predictions. Matthew’s correlation coefficient (MCC) was also used as a performance metric of the classification models. Additional analysis was performed to calculate the AUC of the separate variables of PRDs, to test how each variable performs in distinguishing between outcome labels. Furthermore, the use of time spent below threshold values (<63% rcSO2, <85% SpO2) in the predictability of brain injury was examined. This analysis was conducted to compare the efficacy of our machine learning models, which utilises numerous quantitative features, with that of current threshold-based methodologies. The grand average of all extracted PRDs from IVH and non/mild IVH groups was calculated and reported in Figure 2 to illustrate the conformation of the PRDs in each group.
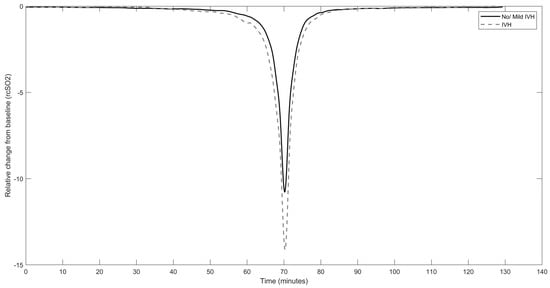
Figure 2.
Averaged curve of all rcSO2 PRDs in the intraventricular haemorrhage group (dashed line) vs. no/mild intraventricular haemorrhage group (solid line); X-axis indicates the time in minutes when the grand average of rcSO2 PRDs starts to deviate from baseline, reaches the nadir, and increases to baseline again.
3. Results
There were 46 infants born less than 28 weeks of GA with rcSO2 recorded for >24 h. The clinical characteristics of infants included in this study are detailed in Table 1. There was no significant association between sampling frequency and outcome indicating that sampling frequency was not a confounding factor (p = 0.505, Fisher’s exact test). The average duration of the rcSO2 recordings and deleted data due to artefact removal were 60.98 h and 0.004 h, respectively. Averaged duration of recorded SpO2 and deleted data due to artefact removal were 63.79 h and 1.49 h, respectively.

Table 1.
Clinical data of the subset of infants from the HIP trial included in the current study.
Neither a single clinical attribute nor the combination of all attributes in our model was predictive of the short-term clinical outcome: the random forest model had a median (95% CI) testing AUC of 0.57 (0.39–0.76) (Table 2). Thus, we did not find evidence that clinical data, individually or combined, can detect IVH in the first week after birth.

Table 2.
Area under the curve (AUC) values for the signals used to predict brain injury in the first week of life.
The rcSO2 models before and after PRD removal were not significantly associated with IVH injury (AUC 0.53, CI = 0.31–0.74 and AUC = 0.54, CI = 0.33–0.74, respectively). Combining these rcSO2 models with the clinical model did not improve the performance of the models (Table 2). However, the model using the isolated rcSO2 PRDs was significantly associated with brain injury, with an AUC of 0.85 (0.72–0.95). The sensitivity and specificity of this model were 0.85 and 0.58, respectively. Matthew’s correlation coefficient (MCC) was 0.57. Adding the clinical model to the rcSO2 PRD model showed no practical improvement in performance (AUC = 0.86 (0.74–0.96), sensitivity = 0.94, specificity = 0.25, MCC = 0.61) (Table 2). For comparison with the current literature, we also tested if the threshold value of 63%, i.e., the time rcSO2 spent below 63%, was a useful predictor, but this marker was not predictive of brain injury in our cohort (AUC 0.59, CI = 0.40–0.78) (Table 2).
Estimating feature importance in the rcSO2 PRD model showed that a range of features contributed to the XGBoost model, with the top three features being the mean amplitude and negative and positive slope of the PRDs (Figure 3).
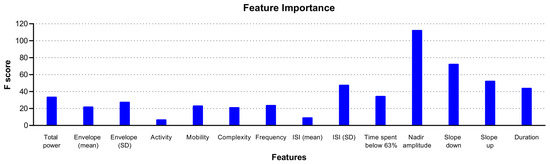
Figure 3.
Illustration of feature importance of the XGBoost model using rcSO2 prolonged relative desaturations (PRDs) in predicting intraventricular haemorrhage.
Following analysis of the individual features extracted from rcSO2 PRDs, we report that only mean amplitude was significantly associated with IVH with an AUC of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.53–0.92) (Table 3), which was less robust than the XGBoost rcSO2 PRDs model. The grand average of the extracted PRDs among all infants in the IVH group vs. non/mild IVH group is presented in Figure 2. A higher amplitude of deflection from the baseline in the IVH group compared with the non/mild IVH group is evident. SpO2 was recorded for 32 infants. None of the three SpO2 models were significantly associated with brain injury (Table 2). Combination with the clinical model did not improve the detection of brain injury. For comparison with the current literature, we also tested if the threshold value of 85%, i.e., the time SpO2 spent below 85%, was a useful predictor, but this marker was not predictive of brain injury in our cohort (AUC 0.52, CI = 0.28–0.76) (Table 2).

Table 3.
Area under the curve (AUC) values for the individual features of rcSO2 PRDs used to predict brain injury in the first week of life.
4. Discussion
This study set out to examine the potential utility of machine learning models of rcSO2 signals recorded in the first 72 h after birth in extremely preterm infants and their usefulness in detecting IVH in the first week after birth. The results of this study demonstrate that a data-driven combination of extracted features from isolated PRDs of rcSO2 signal was associated with IVH in this cohort of extremely preterm infants.
Previous studies have employed different methods in interpreting NIRS data as an early predictor of IVH. The absolute value of the NIRS signal is used as a criterion for intervention in some NICUs; however, the NIRS values are variable with gestational age and are dependent upon different algorithms incorporated into the devices [21]. The absolute value of NIRS, predictive of adverse outcome, ranged from <50% [20,21] to <65% [22] with varying sensors. SafeBoosC-III phase 3 of the randomised clinical trial used cerebral oximetry during the first 72 h after birth to guide intervention in extremely preterm infants. The authors report that the use of cerebral oximetry did not alter the incidence of death or severe brain injury at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age after birth compared with infants assigned to receive usual care [34]. In this trial, if infants randomised to the NIRS group had cerebral oxygenation below the threshold for hypoxia, treatment was considered [35]. Of note, the time rcSO2 spent below 63% was not predictive of brain injury in the current preterm cohort (AUC 0.593 CI 0.399–0.775). The potential uncertainty relating to absolute NIRS values necessitates the development of alternative methods, including the use of other features of the signal for their potential to predict outcomes.
The results of the current study indicate that features we extracted from the rcSO2 signal, before and after excluding PRDs, were not predictive of IVH. These findings are in contrast with previous signal processing methods that proposed an improvement in performance when the PRDs were removed [24]. However, this study covered a wider GA (<32 weeks), used shorter epochs (2 h), had a different sampling frequency (1/35 Hz) compared with what we used (1/6 Hz), and was limited by a small sample size (n = 10). Interestingly, however, in this current study, features arising from the rcSO2 PRDs were associated with IVH. If validated, AI recognition of this novel feature of NIRS signal during bedside monitoring could facilitate the timely implementation of neuroprotective strategies for the infant.
The PRDs were extracted from the NIRS signal using a previously described method; this procedure is a data-driven tool that identifies transient-like waveforms of the order of one to tens of minutes within a signal. Therefore, the PRDs are not predefined events determined by absolute amplitude, duration, or frequency. Post-extraction analysis of the PRDs, as illustrated in Figure 2, indicates that they are events lasting minutes with a relative change in signal of approximately 11–14%. Features of these estimated PRDs are then combined using a machine learning model, a process that can detect variances not discernible visually and also a process that due to its complexity can be difficult to relate back to signal characteristics.
This study contributes to the recent debate about the role of rcSO2 in predicting early outcomes. We must strive to overcome current limitations in the interpretation of NIRS with the use of innovative analysis. The quantification of rcSO2 is considered to arise from venous/arterial blood (70%/30%) and is influenced by many potential variables, including perfusion, cerebral autoregulation, cerebral activity, and oxygen extraction, which makes it more challenging to interpret [36]. Previous studies have reported a strong correlation between cerebral oxygen desaturation and low cardiac output in preterm infants [37,38]. The continuous and simultaneous measurement of mean arterial blood pressure, cardiac output, and EEG brain activity could provide additional insight if incorporated into the analysis of rcSO2.
SpO2 has been used to guide respiratory care. In 2007, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommended a range of 85–95% in preterm infants, and in 2010 the recommended target range was set to 85–93% by the European Association of Perinatal Medicine [39,40]. More recently, large clinical studies, such as NeOProM (Neonatal Oxygenation Prospective Meta-analysis) have narrowed the range of SpO2 [41]. Pooled data from that clinical trial reported that extremely preterm infants with SpO2 values of 85–89% were at higher risk of mortality and necrotizing enterocolitis compared with ones with SpO2 values of 91–95%. However, the risk of retinopathy of prematurity was higher in preterm infants with higher levels of SpO2 [41]. Sullivan et al. [42] suggested that the combined features of SpO2 (mean, SD, kurtosis, and skewness) with clinical data in the first 12 h and the first 7 days of life were associated with severe IVH (grade III and IV) and NEC. In terms of absolute values, Vesoulis et al. [43] studied 645 infants born <32 weeks of GA and proposed that the time spent with SpO2 ≤ 70% was associated with severe grade III and IV IVH. Moreover, a lower level of SpO2 was associated with IVH grades III and IV in very low birth weight infants [44]. However, in the current study, we did not find an association between features extracted from the SpO2 signal, including and excluding PRDs or with time spent below SpO2 ≤ 85%, with IVH outcome. If the isolated PRDs in the rcSO2 were caused by systemic hypoxemia, we reasoned that PRDs isolated from the SpO2 signal would also be predictive of IVH outcome. This would be significantly advantageous as the use of pulse oximetry is more widespread than cerebral oxygen monitoring. However, we did not find features of isolated PRDs from the SpO2 signal that were associated with IVH injury.
SpO2 is dependent on detecting a variance in transmitted light. Thus, when perfusion decreases, pulse amplitude gets smaller and pulse oximetry readings are adversely affected. As a result, hypotension and hypothermia that cause poor peripheral perfusion can render pulse oximetry prone to error [45]. Furthermore, pulse oximetry is influenced by the presence of foetal haemoglobin (FHb) [46]. FHb is the main oxygen carrier during pregnancy and starts to be replaced by adult haemoglobin from the 20th week of gestation [47]. FHb has a higher affinity for oxygen compared with adult haemoglobin and does not provide enough oxygen diffusion and delivery in neonates. Thus, the probability of higher concentration of FHb and increased affinity for oxygen and the fact that 20 out of 46 infants were hypotensive might contribute to the poor association between SpO2 and IVH outcome in our cohort.
PRDs were evident in all infants and were extracted from both rcSO2 and SpO2. Further investigation in a subset of infants revealed that there were both asynchronous and synchronous PRDs in both signals. These events in SpO2 may represent systemic hypoxemia brought about by poor gas exchange or decreased perfusion. Independent decreases in rcSO2 may reflect selective overt impairment of regional cerebral perfusion or instances of increased oxygen utilisation in the face of enhanced functional demand with inadequate neurovascular coupling.
A limitation of this study is that the outcome was defined based on the highest grade of IVH diagnosed using ultrasound in the first week of life, and the exact time of the IVH occurrence was unknown. Furthermore, SpO2 was recorded for only 32 out of 46 infants, and SpO2 and rcSO2 were time-synchronised for only 26 infants. Moreover, the signal decomposition method used to extract the PRDs performed well in isolating the desaturations that were long (average of 8 min), but many shorter (approximately <1 min) desaturation events were not captured using this method. Algorithms could be developed to isolate these short transients and test their predictability of IVH in future studies.
This study proposes that the features extracted from the rcSO2 signal contain information that may be useful in the early detection of brain injury, which may not be the case for the SpO2 signal. Decreases in cerebral oxygen saturation may reflect hypoxia, vasoconstriction, low blood flow, and/or impaired autoregulation. It is not possible to determine the individual or combined elements of each of these possibilities. However, what is clear is that a combination of quantitative features of these relative cerebral desaturations (PRDs) are associated with brain injury in extremely preterm infants. The incorporation of machine learning methods needs to be validated in future large cohorts of extremely preterm infants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.O., K.D.O., E.M.D. and F.B.M.; Methodology, M.A., J.M.O., K.D.O., G.N., L.T., J.M., P.-Y.C., A.E.-K., D.V.L., Z.S., E.M.D. and F.B.M.; Software, M.A. and J.M.O.; Validation, M.A. and J.M.O.; Formal analysis, M.A., J.M.O. and E.M.D.; Investigation, M.A., E.M.D. and F.B.M.; Resources, K.D.O. and F.B.M.; Writing—original draft, M.A.; Writing—review & editing, J.M.O., G.N., L.T., J.M., P.-Y.C., A.E.-K., D.V.L., Z.S., E.M.D. and F.B.M.; visualization, M.A. and F.B.M.; Supervision, J.M.O., K.D.O., E.M.D. and F.B.M.; Project administration, E.M.D. and F.B.M.; Funding acquisition, J.M.O., K.D.O., E.M.D. and F.B.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Science Foundation Ireland (SFI 18/SIRG/5483 [to F.B.M]), EU FP7/2007-2013 under grant agreement number 260777 (the HIP Trial), Science Foundation Ireland Research Centre Award (12/RC/2272 and SFI 15/SIRG/3580 [to JOT]), and Department of Physiology, UCC [to M.A.].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee, Cork, ECM 5(2) 15 January 2013 for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained for all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data used and analyzed during the current study involve sensitive patient information.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all the families for participating and to the staff of Cork University Maternity Hospital, CUMH, for collecting the data. The authors would also like to acknowledge the assistance of CRN Ita Herily, INFANT Research Centre, in data collation for this study. Graphical abstract includes an image by Macrovector on Freepik.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| rcSO2 | Regional cerebral oxygen saturation |
| SpO2 | Peripheral oxygen saturation |
| NIRS | Near-infrared spectroscopy |
| IVH | Intraventricular haemorrhage |
| PRD | Prolonged relative desaturation |
| US | Ultrasound |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
References
- Cheong, J.L.; Doyle, L.W.; Burnett, A.C.; Lee, K.J.; Walsh, J.M.; Potter, C.R.; Treyvaud, K.; Thompson, D.K.; Olsen, J.E.; Anderson, P.J.; et al. Association between Moderate and Late Preterm Birth and Neurodevelopment and Social-Emotional Development at Age 2 Years. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, e164805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulbul, L.; Elitok, G.K.; Ayyıldız, E.; Kabakcı, D.; Uslu, S.; Köse, G.; Tiryaki Demir, S.; Bulbul, A. Neuromotor Development Evaluation of Preterm Babies Less than 34 Weeks of Gestation with Bayley III at 18–24 Months. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5480450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul, S.E.; Wood, T.R.; Comstock, B.A.; Perez, K.; Gogcu, S.; Puia-Dumitrescu, M.; Berkelhamer, S.; Heagerty, P.J. Deaths in a Modern Cohort of Extremely Preterm Infants from the Preterm Erythropoietin Neuroprotection Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2146404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffel, C.; Kistler, K.D.; Sarda, S.P. Global incidence of intraventricular hemorrhage among extremely preterm infants: A systematic literature review. J. Perinat. Med. 2021, 49, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, W.C.; Vohr, B.; Makuch, R.W.; Katz, K.H.; Ment, L.R. Antecedents of Cerebral Palsy in a Multicenter Trial of Indomethacin for Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1997, 151, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams-Chapman, I.; Hansen, N.I.; Stoll, B.J.; Higgins, R. Neurodevelopmental outcome of extremely low birth weight infants with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus requiring shunt insertion. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e1167–e1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollebrandse, N.L.; Spittle, A.J.; Burnett, A.C.; Anderson, P.J.; Roberts, G.; Doyle, L.W.; Cheong, J.L.Y. School-age outcomes following intraventricular haemorrhage in infants born extremely preterm. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2021, 106, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Plessis, A.J.; Volpe, J.J. Perinatal brain injury in the preterm and term newborn. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2002, 15, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, F.A.-O.; Krebs, V.L.J.; de Carvalho, W.B. Identifying clinical phenotypes in extremely low birth weight infants-an unsupervised machine learning approach. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, I.A.-O.; da Costa, C.S.; Zeiler, F.A.; Wong, F.Y.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M.; Austin, T. Burden of hypoxia and intraventricular haemorrhage in extremely preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020, 105, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, S.; McCoy, M.; Anderson, M.P.; Ramji, F.; Seri, I. Changes in cardiac function and cerebral blood flow in relation to peri/intraventricular hemorrhage in extremely preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, e261–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, H.; Gregas, M.C.; Limperopoulos, C.; Zaretskaya, I.; Bassan, H.; Soul, J.S.; Di Salvo, D.N.; du Plessis, A.J. Elevated cerebral pressure passivity is associated with prematurity-related intracranial hemorrhage. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderliesten, T.; Lemmers, P.M.; Smarius, J.J.; van de Vosse, R.E.; Baerts, W.; van Bel, F. Cerebral oxygenation, extraction, and autoregulation in very preterm infants who develop peri-intraventricular hemorrhage. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 698–704.e692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, S.; Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; Iommi, M.; Galletti, S.; Vitali, F.; Paoletti, V.; Camela, F.; Austin, T.; Corvaglia, L. Clinical determinants of cerebrovascular reactivity in very preterm infants during the transitional period. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlek, L.R.; Mueller, C.; Jebbia, M.R.; Kielt, M.J.; Fathi, O. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Extremely Preterm Infants. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 624113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalteren, W.S.; Verhagen, E.A.; Mintzer, J.P.; Bos, A.F.; Kooi, E.M.W. Anemia and Red Blood Cell Transfusions, Cerebral Oxygenation, Brain Injury and Development, and Neurodevelopmental Outcome in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 644462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomgaard, A.M.; Alderliesten, T.; van Bel, F.; Benders, M.; Claris, O.; Cordeiro, M.; Dempsey, E.; Fumagalli, M.; Gluud, C.; Hyttel-Sorensen, S.; et al. No neurodevelopmental benefit of cerebral oximetry in the first randomised trial (SafeBoosC II) in preterm infants during the first days of life. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bel, F.; Lemmers, P.; Naulaers, G. Monitoring neonatal regional cerebral oxygen saturation in clinical practice: Value and pitfalls. Neonatology 2008, 94, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.L.; Hyttel-Sørensen, S.; Jakobsen, J.C.; Gluud, C.; Kooi, E.M.W.; Mintzer, J.; de Boode, W.P.; Fumagalli, M.; Alarcon, A.; Alderliesten, T.; et al. Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring (NIRS) in children and adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Pediatr. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderliesten, T.; Lemmers, P.M.; van Haastert, I.C.; de Vries, L.S.; Bonestroo, H.J.; Baerts, W.; van Bel, F. Hypotension in preterm neonates: Low blood pressure alone does not affect neurodevelopmental outcome. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, E.A.; Van Braeckel, K.N.; van der Veere, C.N.; Groen, H.; Dijk, P.H.; Hulzebos, C.V.; Bos, A.F. Cerebral oxygenation is associated with neurodevelopmental outcome of preterm children at age 2 to 3 years. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2015, 57, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderliesten, T.; Dix, L.; Baerts, W.; Caicedo, A.; van Huffel, S.; Naulaers, G.; Groenendaal, F.; van Bel, F.; Lemmers, P. Reference values of regional cerebral oxygen saturation during the first 3 days of life in preterm neonates. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, L.M.; van Bel, F.; Baerts, W.; Lemmers, P.M. Comparing near-infrared spectroscopy devices and their sensors for monitoring regional cerebral oxygen saturation in the neonate. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, J.M.; Kenosi, M.; Finn, D.; Boylan, G.B.; Dempsey, E.M. Features of cerebral oxygenation detects brain injury in premature infants. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 3614–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, J.M.; Dempsey, E.M.; Boylan, G.B. Extracting transients from cerebral oxygenation signals of preterm infants: A new singular-spectrum analysis method. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 5882–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, E.M.; Barrington, K.J.; Marlow, N.; O’Donnell, C.P.F.; Miletin, J.; Naulaers, G.; Cheung, P.Y.; Corcoran, J.D.; El-Khuffash, A.F.; Boylan, G.B.; et al. Hypotension in Preterm Infants (HIP) randomised trial. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2021, 106, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.J. Neurology of the Newborn, 5th ed.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, A.H.; Hintz, S.R.; Hibbs, A.M.; Walsh, M.C.; Vohr, B.R.; Bann, C.M.; Wilson-Costello, D.E. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of extremely low-gestational-age neonates with low-grade periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, E.; Usuniwa, H.; Nemoto, K.; Inagaki, T. Simultaneous measurement under resting-state of autonomic nervous activity and brain activity by near-infrared spectroscopy alone. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 122, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, T.W.; Hyttel-Sorensen, S.; Greisen, G. Cerebral oxygenation after birth—A comparison of INVOS(®) and FORE-SIGHT™ near-infrared spectroscopy oximeters. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buekers, J.; Theunis, J.; De Boever, P.; Vaes, A.W.; Koopman, M.; Janssen, E.V.; Wouters, E.F.; Spruit, M.A.; Aerts, J.M. Wearable Finger Pulse Oximetry for Continuous Oxygen Saturation Measurements during Daily Home Routines of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) over One Week: Observational Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019, 7, e12866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashoori, M.; Dempsey, E.M.; McDonald, F.B.; O’Toole, J.M. Sparse-Denoising Methods for Extracting Desaturation Transients in Cerebral Oxygenation Signals of Preterm Infants. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Upadhye, S.; Worster, A. Understanding receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Cjem 2006, 8, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.L.; Pellicer, A.; Hyttel-Sørensen, S.; Ergenekon, E.; Szczapa, T.; Hagmann, C.; Naulaers, G.; Mintzer, J.; Fumagalli, M.; Dimitriou, G.; et al. Cerebral Oximetry Monitoring in Extremely Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.L.; Pellicer, A.; Gluud, C.; Dempsey, E.; Mintzer, J.; Hyttel-Sørensen, S.; Heuchan, A.M.; Hagmann, C.; Ergenekon, E.; Dimitriou, G.; et al. Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring versus treatment as usual for extremely preterm infants: A protocol for the SafeBoosC randomised clinical phase III trial. Trials 2019, 20, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppan, E.; Pichler, G.; Binder-Heschl, C.; Schwaberger, B.; Urlesberger, B. Three Physiological Components That Influence Regional Cerebral Tissue Oxygen Saturation. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 913223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresesti, I.; Avian, A.; Bruckner, M.; Binder-Heschl, C.; Schwaberger, B.; Baik-Schneditz, N.; Schmölzer, G.; Pichler, G.; Urlesberger, B. Impact of bradycardia and hypoxemia on oxygenation in preterm infants requiring respiratory support at birth. Resuscitation 2021, 164, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janaillac, M.; Beausoleil, T.P.; Barrington, K.J.; Raboisson, M.J.; Karam, O.; Dehaes, M.; Lapointe, A. Correlations between near-infrared spectroscopy, perfusion index, and cardiac outputs in extremely preterm infants in the first 72 h of life. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, D.; Bevilacqua, G.; Carnielli, V.; Greisen, G.; Plavka, R.; Didrik, S.O.; Simeoni, U.; Speer, C.P.; Soler, A.; Valls, I.; et al. European consensus guidelines on the management of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2008, 46, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Guidelines for Perinatal Care; American Academy of Pediatrics: Elk Grove Village, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Askie, L.M.; Darlow, B.A.; Finer, N.; Schmidt, B.; Stenson, B.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.; Davis, P.G.; Carlo, W.A.; Brocklehurst, P.; Davies, L.C.; et al. Association between Oxygen Saturation Targeting and Death or Disability in Extremely Preterm Infants in the Neonatal Oxygenation Prospective Meta-analysis Collaboration. JAMA 2018, 319, 2190–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, B.A.; Wallman-Stokes, A.; Isler, J.; Sahni, R.; Moorman, J.R.; Fairchild, K.D.; Lake, D.E. Early Pulse Oximetry Data Improves Prediction of Death and Adverse Outcomes in a Two-Center Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesoulis, Z.A.; Bank, R.L.; Lake, D.; Wallman-Stokes, A.; Sahni, R.; Moorman, J.R.; Isler, J.R.; Fairchild, K.D.; Mathur, A.M. Early hypoxemia burden is strongly associated with severe intracranial hemorrhage in preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 2019, 39, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, S.A.-O.; Abubakar, M.; Andris, R.; Patwardhan, K.; Fairchild, K.D.; Vesoulis, Z.A. Early Vital Sign Differences in Very Low Birth Weight Infants with Severe Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Am. J. Perinatol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMeulenaere, S. Pulse Oximetry: Uses and Limitations. J. Nurse Pract. 2007, 3, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritišanac, E.; Urlesberger, B.; Schwaberger, B.; Pichler, G. Accuracy of Pulse Oximetry in the Presence of Fetal Hemoglobin-A Systematic Review. Children 2021, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaran, V.G.; Orkin, S.H. The switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a011643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).