Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: How to Stay out of Trouble?
Abstract
1. Introduction
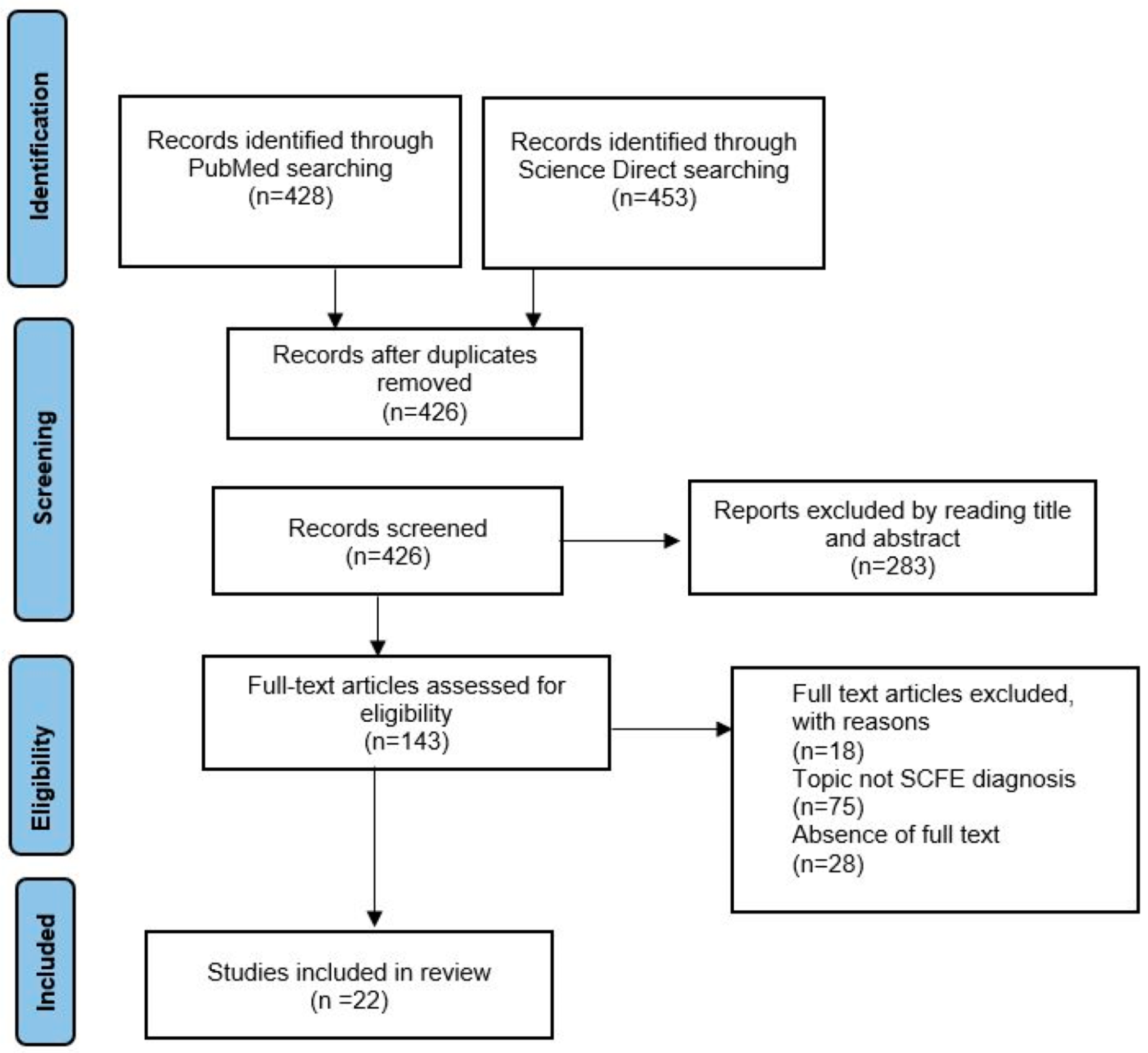
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection Criteria
2.2. Literature Search Strategy and Data Extraction
2.3. Assessment of Bias Risk
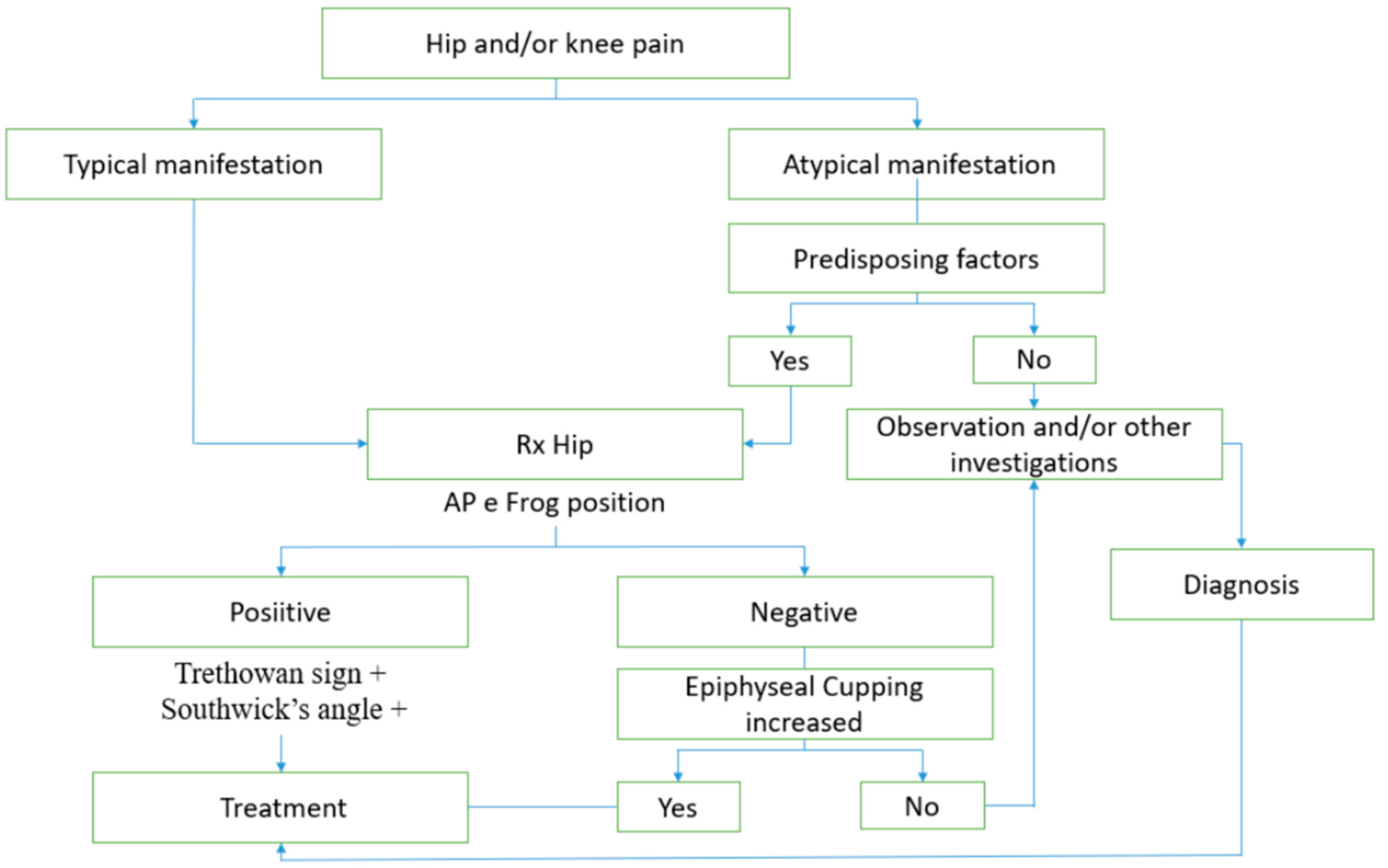
3. Results
3.1. Anatomical Factors
3.2. Body Weight
3.3. Metabolic Disorders
3.4. Bone Dysmetabolism
3.5. Hormonal Disorders
3.6. Socio-Economic Deprivation
3.7. Late Diagnosis
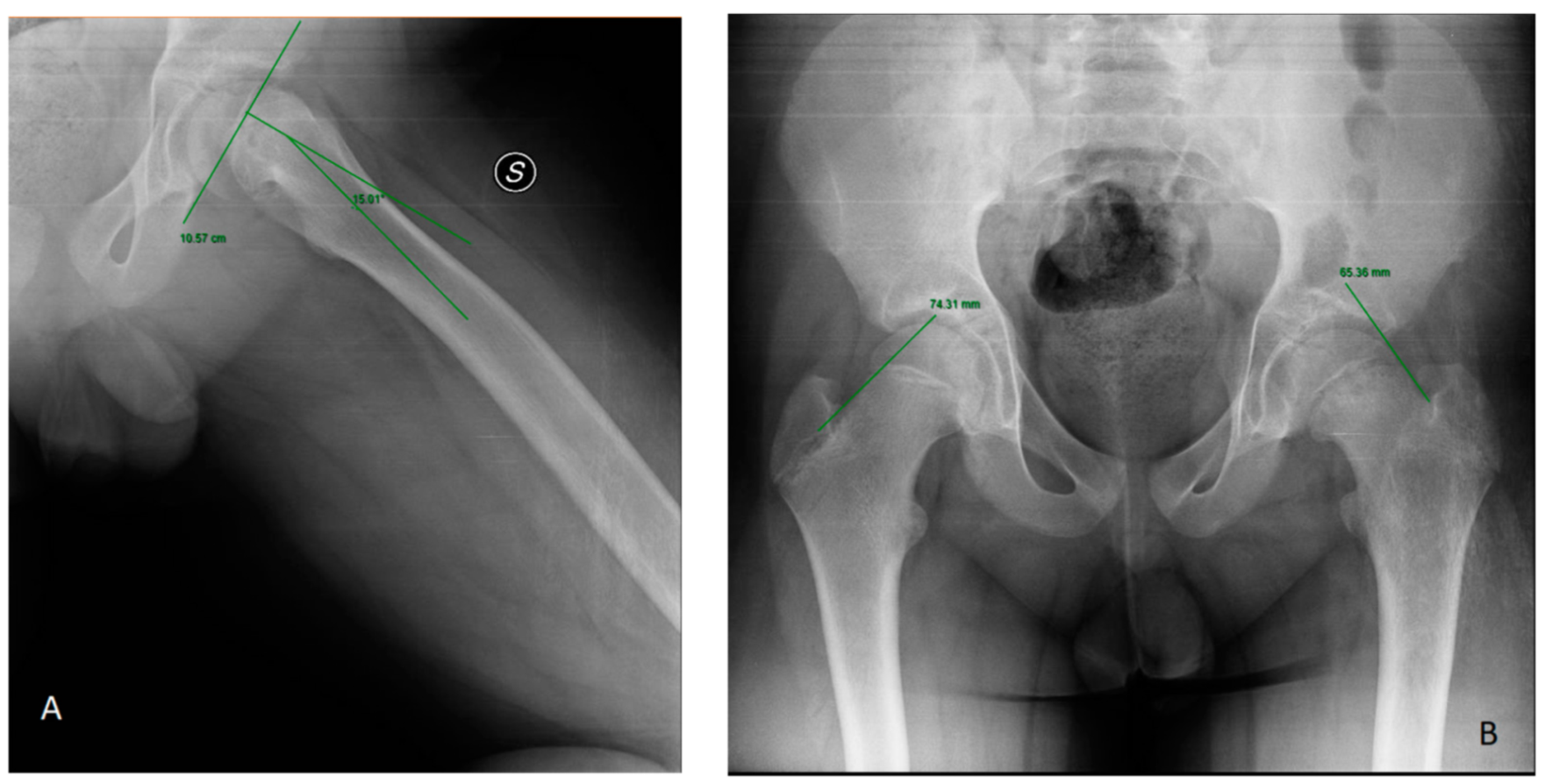
3.7.1. Radiological Assessment
3.7.2. Misleading Symptoms
3.7.3. Patient Presentation Delay
3.7.4. First Contact
3.7.5. Demographic Information
3.7.6. Types of SCFE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathew, S.E.; Larson, A.N. Natural History of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39 (Suppl. S1), S23–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, C.L.; Arons, R.R.; Loder, R.T.; Vitale, M.G. The Epidemiology of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: An Update. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2006, 26, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Örtegren, J. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. In Growth, Remodeling and Cartilage Quality after Unthreaded Fixation; Lund University: Lund, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Millis, M.B.; Novais, E.N. In Situ Fixation for Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Perspectives in 2011. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2011, 93 (Suppl. S2), 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.N.; McIntosh, A.L.; Trousdale, R.T.; Lewallen, D.G. Avascular Necrosis Most Common Indication for Hip Arthroplasty in Patients With Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2010, 30, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Growth of Bone. Available online: https://bio.libretexts.org/@go/page/13997 (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Sarraf, K.M.; Popat, R.; Kneale, K.L.; Bhattacharya, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Achan, P.; Hanna, S.A. Functional Outcomes, Complications and Revision Rate of Hip Arthroplasty in Patients with Sequelae of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: A Systematic Review. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thillemann, T.M.; Pedersen, A.B.; Johnsen, S.P.; Søballe, K. Implant Survival after Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Due to Childhood Hip Disorders Results from the Danish Hip Arthroplasty Registry. Acta Orthop. 2008, 79, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, W.Z.; Liu, R.W.; Marshall, D.C.; Maranho, D.A.; Novais, E.N. Capital Femoral Epiphyseal Cupping and Extension May Be Protective in Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: A Dual-Center Matching Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2020, 40, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoff, E.M.; Banffy, M.B.; Winell, J.J. Relationship Between Body Mass Index and Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2005, 25, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-S.; Oh, C.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, S.-D. Epidemiology and Demographics of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Korea: A Multicenter Study by the Korean Pediatric Orthopedic Society. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2009, 29, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhuri, V.; Arora, S.K.; Dutt, V. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis Associated with Vitamin D Deficiency: A Series of 15 Cases. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.C.; Metcalfe, D.; Costa, M.L.; Van Staa, T. A Nationwide Cohort Study of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. Arch. Dis. Child 2017, 102, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obana, K.K.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Broom, A.M.; Barrett, K.; Andras, L.M.; Millis, M.B.; Goldstein, R.Y. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Children without Obesity. J. Pediatr. 2020, 218, 192–197.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, S.J.; Warhoover, T.; Mencio, G.A.; Lovejoy, S.A.; Martus, J.E.; Schoenecker, J.G. Leptin Elevation as a Risk Factor for Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis Independent of Obesity Status. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2017, 99, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montañez-Alvarez, M.; Flores-Navarro, H.H.; Cuevas-De Alba, C.; Arana-Hernández, E.I.; Ramírez-Ruiz, M. The Role of Hyperinsulinemia in Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2020, 40, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taussig, M.D.; Powell, K.P.; Cole, H.A.; Nwosu, S.K.; Hunley, T.; Romine, S.E.; Iwinski, H.; Talwalkar, V.; Warhoover, T.; Lovejoy, S.A.; et al. Prevalence of Hypertension in Pediatric Tibia Vara and Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2016, 36, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavasiliou, K.A.; Kapetanos, G.A.; Kirkos, J.M.; Beslikas, T.A.; Dimitriadou, A.S.; Papavasiliou, V.A. The Pathogenetic Influence of I-Parathyroid Hormone on Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. Towards a New Etiologic Approach? J. Musculoskelet. NeuronalInteract. 2003, 3, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Papavasiliou, K.A.; Kirkos, J.M.; Kapetanos, G.A.; Pournaras, J. Potential Influence of Hormones in the Development of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: A Preliminary Study. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2007, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, A.C.; Longui, C.A.; Damasceno FL, V.; Santili, C. Southwick’s Angle Determination during Growth Hormone Treatment and Its Usefulness to Evaluate Risk of Epiphysiolysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2009, 18, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebich, E.J.; Lee, S.S.; Schlechter, J.A. The S Sign: A New Radiographic Tool to Aid in the Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 54, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samelis, P.V.; Loukas, C.; Kantanoleon, S.; Lalos, H.; Anoua, N.; Kolovos, P.; Georgiou, F.; Konstantinou, A.-L. Causes of Delayed Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: The Importance of the Frog Lateral Pelvis Projection. Cureus 2020, 12, e7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvodich, M.; Schwend, R.; Stevanovic, O.; Wurster, W.; Leamon, J.; Hermanson, A. Patterns of Pain in Adolescents with Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. 2019, 206, 184–189.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, M.S.; Bishop, J.A.; Weed, B.; Hresko, M.T.; Millis, M.B.; Kim, Y.J.; Kasser, J.R. Delay in Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. Pediatrics 2004, 113, e322–e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schur, M.D.; Andras, L.M.; Broom, A.M.; Barrett, K.K.; Bowman, C.A.; Luther, H.; Goldstein, R.Y.; Fletcher, N.D.; Millis, M.B.; Runner, R. Continuing Delay in the Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. 2016, 177, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, P.; Iwinski, H.J.; Salava, J.; Oeffinger, D. Delay in the Diagnosis of Stable Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2017, 37, e19–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örtegren, J.; Österman, J.; Tiderius, C.J. Patients’ Delay Is the Major Cause for Late Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2021, 30, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahme, D.; Comley, A.; Foster, B.; Cundy, P. Consequences of Diagnostic Delays in Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2006, 15, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billing, L.; Bogren, H.; Wallin, J. Reliable X-Ray Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis by Combining the Conventional and a New Simplified Geometrical Method. Ped. Radiol. 2002, 32, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkowsky, G.J.; Hennrikus, W.L. Klein Line on the Anteroposterior Radiograph Is Not a Sensitive Diagnostic Radiologic Test for Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihl, M.; Sonne-Holm, S.; Christoffersen, J.K.; Wong, C. Doctor’s Delay in Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. Dan. Med. J. 2014, 61, A4905. [Google Scholar]
- Herring, J.A.; Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children. Tachdjian’s Pediatric Orthopaedics: From the Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children; Elsevier Health Sciences: Maryland Heights, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Litchman, H.M.; Duffy, J. Slipped Capital Femoral Epipysis: Factors affecting shear forces on the epiphyseal plate. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 1984, 4, 745–748. [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith, R.T.; Gelberman, R.H.; Hajek, P.C.; Baker, L.A.; Sartoris, D.J.; Rab, G.T.; Cohen, M.S.; Griffin, P.P. Obesity and Decreased Femoral Anteversion in Adolescence. J. Orthop. Res. 1987, 5, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witbreuk, M.; van Kemenade, F.J.; van der Sluijs, J.A.; Jansma, E.P.; Rotteveel, J.; van Royen, B.J. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis and Its Association with Endocrine, Metabolic and Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ref. | Subjects | Association |
|---|---|---|
| Morris et al. [10] (2020) | 279 SCFE radiographs 279 Control radiographs | Anatomical factors |
| Manoff et al. [11] (2005) | 106 patients with SCFE; 46 Controls | BMI, Gender |
| Song et al. [12] (2009) | 231 patients with SCFE | BMI |
| Madhuri et al. [13] (2013) | 15 patients with SCFE; 15 Controls | Vitamin D, BMI |
| Perry et al. [14] (2017) | 596 patients with SCFE | BMI, Socio-economic deprivation |
| Obana et al. [15] (2020) | Normal weight (34 pz) Overweight (48 pz) Obese (193 pz) | BMI |
| Halverson et al. [16] (2017) | SCFE 40; Controls 30 | Leptin |
| Montañez-Alvarez et al. [17] (2020) | SCFE 14 (3 overweight; 11 obese) Controls 23 (23 obese) | Hyperinsulinemia, HOMA, Triglycerides (VLDL, LDL, HDL) Total cholesterol Glycemia, Neutrophils, HbA1c |
| Taussig et al. [18] (2016) | 127 patients with SCFE (obese 72%; overweight 14%) 127 Controls (obese 97%; overweight 3%) | Hypertension |
| Papavasiliou et al. [19] (2007) | A: 14 patients with SCFE B: 5 patients treated for SCFE | Parathormone, Calcium and Phosphorus |
| Papavasiliou et al. [20] (2007) | 16 hips | Hormones |
| De Andrade et al. [21] (2009) | 44 GHD patients | Southwick angle |
| Ref. | Subjects | Association |
|---|---|---|
| Rebich et al. [22] (2018) | 35 patients with SCFE | Radiological evaluation |
| Samelis et al. [23] (2020) | 36 stable slips | Radiological evaluation |
| Uvodich et al. [24] (2019) | 107 patients with SCFE | Misleading symptoms, first contact |
| Kocher et al. [25] (2004) | 196 patients with SCFE | Demographics characteristics Misleading symptoms |
| Schur et al. [26] (2016) | 481 patients with SCFE | Misleading symptoms Demographic information First contact |
| Hosseinzadeh et al. [27] (2015) | 149 patients with SCFE | Demographic characteristics, misleading symptoms, Type of medical provider, patient’s delay |
| Ortegren et al. [28] (2021) | 54 patients with stable SCFE | Demographic information, misleading symptoms, first contact, patient’s delay |
| Rahme et al. [29] (2006) | 102 patients with SCFE | First contact |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavone, V.; Testa, G.; Torrisi, P.; McCracken, K.L.; Caldaci, A.; Vescio, A.; Sapienza, M. Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: How to Stay out of Trouble? Children 2023, 10, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050778
Pavone V, Testa G, Torrisi P, McCracken KL, Caldaci A, Vescio A, Sapienza M. Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: How to Stay out of Trouble? Children. 2023; 10(5):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050778
Chicago/Turabian StylePavone, Vito, Gianluca Testa, Paola Torrisi, Kathryn Louise McCracken, Alessia Caldaci, Andrea Vescio, and Marco Sapienza. 2023. "Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: How to Stay out of Trouble?" Children 10, no. 5: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050778
APA StylePavone, V., Testa, G., Torrisi, P., McCracken, K. L., Caldaci, A., Vescio, A., & Sapienza, M. (2023). Diagnosis of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: How to Stay out of Trouble? Children, 10(5), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10050778








