Genetic Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Neonatal Pathologies: A Systematic Search and Narrative Synthesis of the Literature
Abstract
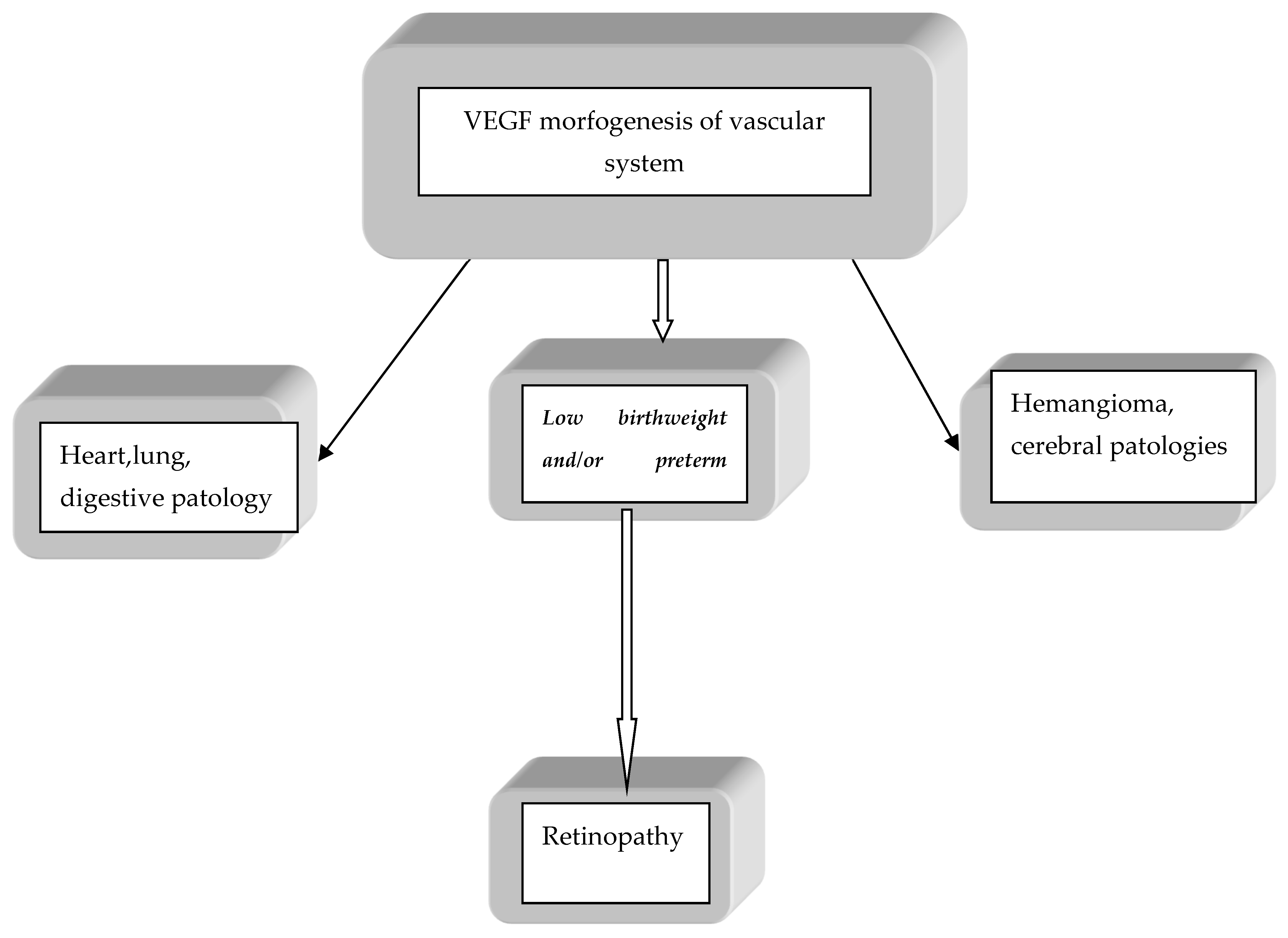
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Pregnancy Induced Hypertension, Pre-Eclampsia, Low-Birth-Weight Infants and Preterm Birth
3.2. Heart Pathologies
3.3. Lung Development and Pathologies
3.4. Eye Conditions
3.5. Hemangioma and Cerebral Pathologies
3.6. Digestive Pathologies
4. Limitations and Further Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welch, S.; Spithoff, K.; Rumble, R.B.; Maroun, J. Bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy for patients with advanced colorectal cancer: A systematic review. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 21, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhpour, E.; Noorbakhsh, P.; Foroughi, E.; Farahnak, S.; Nasiri, R.; Neamatzadeh, H. A Survey on the Role of Interleukin-10 in Breast Cancer: A Narrative. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 7, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ikuhashi, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Kennedy, S.; Zondervan, K.; Takemura, N.; Deguchi, M.; Ohara, N.; Maruo, T. Vascular endothelial growth factor +936 C/T polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of endometriosis in a Japanese population. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2007, 86, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, N.; Zhuang, W.; Wu, X. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese Han population. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 50, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, T.; Shibata, T.; Nakamura, M.; Yamashita, H.; Yoshioka, D.; Hirata, I.; Arisawa, T. Effect of polymorphisms in the 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR) of vascular endothelial growth factor gene on gastric cancer and peptic ulcer diseases in Japan. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Chung, W.C.; Jun, K.-H.; Chin, H.-M. Genetic polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) associated with gastric cancer recurrence after curative resection with adjuvant chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhuang, W.; Liu, G.-J.; Wu, T.-X.; Yao, X.; Du, L.; Wei, M.-L.; Wu, X.-T. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) +936 C/T gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis involving 4138 subjects. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2010, 25, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gao, P.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, H. Positive association of the vascular endothelial growth factor-A +405 GG genotype and poor survival in stage I–II gastric cancer in the Northern Chinese population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 40, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, S.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Z. Interaction between Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Polymorphism and Smoking on Gastric Cancer Risk in Chinese Han Population. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 25, 1610495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; Yu, P. A Meta-Analysis of the Association Between the VEGF +936C>T Gene Polymorphism and Digestive System Cancer Susceptibility. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2020, 24, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Ho, C.-H.; Huang, S.K.-H.; Shen, C.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-H. Association between VEGF gene promoter polymorphisms and bladder cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Cytokine 2020, 131, 155112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Qin, Z.; Shao, C.; Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Shu, Y.; Shen, H. Association between VEGF Gene Polymorphisms and the Susceptibility to Lung Cancer: An Updated Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9271215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhang, L.; Xing, W.; Zhuo, R.; Lin, X.; Hao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, J. The Associations between VEGF Gene Polymorphisms and Diabetic Retinopathy Susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis of 11 Case-Control Studies. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 805801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.-Y.; Sun, Y.-H. Association of VEGF Gene Polymorphisms with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procopciuc, L.M.; Caracostea, G.; Zaharie, G.; Stamatian, F. Maternal/newborn VEGF-C936T interaction and its influence on the risk, severity and prognosis of preeclampsia, as well as on the maternal angiogenic profile. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarzi, F.; Shahrakipoor, M.; Teimoori, B.; Yaghmaei, M.; Narooei-Nejad, M.; Rasooli, A.; Salimi, S. Association of the placental VEGF promoter polymorphisms and VEGF mRNA expression with preeclampsia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 41, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazios, G.; Papazoglou, D.; Tsikouras, P.; Kolios, G. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms and pregnancy. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2009, 22, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atis, A.; Oruc, O.; Aydin, Y.; Cetincelik, U.; Goker, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene +813CC polymorphism of foetus is associated with preterm labour but not with pre-eclampsia in Turkish pregnant women. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2012, 39, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X. Influence of polymorphisms in VEGF, TNF-α, and GSTP1 genes on retinopathy of prematurity risk: A Meta-analysis. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, M.; Bahrami, R.; Dastgheib, S.A.; Lookzadeh, M.H.; Noorishadkam, M.; Mirjalili, S.R.; Zare-Shehneh, M.; Neamatzadeh, H. An Updated and Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Association between VEGA -634G > C, -460T > C, +405G > C and +936C > T Polymorphisms and Retinopathy of Prematurity Risk. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2019, 40, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, D.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Lian, C.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Z. Association of VEGF gene polymorphisms with advanced retinopathy of prematurity: A meta-analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 10731–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokodi, G.; Treszl, A.; Kovács, L.; Tulassay, T.; Vásárhelyi, B. Dysplasia: A review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2007, 42, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fevereiro-Martins, M.; Guimarães, H.; Marques-Neves, C.; Bicho, M. Retinopathy of prematurity: Contribution of inflammatory and genetic factors. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 1739–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csak, K.; Szabo, V.; Szabo, A.; Vannay, A. Pathogenesis and genetic basis for retinopathy of prematurity. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Filippi, L.; Bagnoli, P.; La Marca, G.; Cristofori, G.; Raffaeli, G.; Padrini, L.; Araimo, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Groppo, M.; et al. The pathophysiology of retinopathy of prematurity: An update of previous and recent knowledge. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstrom, G.; van Wijngaarden, P.; Coster, D.J.; Williams, K.A. Genetic susceptibility to retinopathy of prematurity: The evidence from clinical and experimental animal studies. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Ammoscato, C.L.; Scola, L.; Fragapane, T.; Giarratana, R.M.; Lio, D.; Piccione, M. Susceptibility to Heart Defects in Down Syndrome Is Associated with Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in HAS 21 Interferon Receptor Cluster and VEGFA Genes. Genes 2020, 11, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-B.; Zheng, J. Regulation of Placental Angiogenesis. Microcirculation 2013, 21, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, L.; Perez-Garcia, V.; Hemberger, M. Regulation of Placental Development and Its Impact on Fetal Growth—New Insights from Mouse Models. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, S.; Dołęgowska, B.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Rzepka, R.; Torbe, A.; Bednarek-Jędrzejek, M. A Common Profile of Disordered Angiogenic Factor Production and the Exacerbation of Inflammation in Early Preeclampsia, Late Preeclampsia, and Intrauterine Growth Restriction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-N.; Jeng, S.-F.; Su, Y.-N.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chou, H.-C.; Tsao, P.-N.; Hsieh, W.-S. The sFlt-1/PlGF ratio as a predictor for poor pregnancy and neonatal outcomes. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2017, 58, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrar, S.A.; Hong, P.L. Preeclampsia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570611/ (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Yang, Y.; Le Ray, I.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hua, J.; Reilly, M. Preeclampsia Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Pregnancy Outcomes in Sweden and China. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e218401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayrink, J.; Souza, R.T.; Feitosa, F.E.; Filho, E.A.R.; Leite, D.F.; Vettorazzi, J.; Calderon, I.M.; Sousa, M.H.; Costa, M.L.; Baker, P.N.; et al. Incidence and risk factors for Preeclampsia in a cohort of healthy nulliparous pregnant women: A nested case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalos, E.; Cuesta, C.; Grosso, A.L.; Chou, D.; Say, L. Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia: A systematic review. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 170, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khankin, E.V.; Royle, C.; Karumanchi, S.A. Placental Vasculature in Health and Disease. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, L.; Yavarian, M. The association of Q472H variant in the KDR gene with recurrent pregnancy loss in Southern Iran: A case-control study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. (IJRM) 2019, 17, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iciek, R.; Wender-Ozegowska, E.; Mikołajczak, P.; Seremak-Mrozikiewicz, A.; Zawiejska, A.; Mrozikiewicz, P.M.; Drews, K.; Brązert, J. Placental vascular endothelial growth factor expression in pregnancies complicated by type 1 diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2014, 65, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Chedraui, P.; Solis, E.J.; Bocci, G.; Gopal, S.; Russo, E.; Escobar, G.S.; Hidalgo, L.; Pérez-López, F.R.; Genazzani, A.R.; Mannella, P.; et al. Feto-placental nitric oxide, asymmetric dimethylarginine and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels and VEGF gene polymorphisms in severe preeclampsia. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2012, 26, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraweera, P.H.; Dekker, G.A.; Thompson, S.D.; Roberts, C.T. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the KDR Gene in Pregnancies Complicated by Gestational Hypertensive Disorders and Small-for-Gestational-Age Infants. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 19, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmia, I.M.; Apalasamy, Y.D.; Omar, S.Z.; Mohamed, Z. Association of VEGFA gene polymorphisms and VEGFA plasma levels with spontaneous preterm birth. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2015, 25, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, D.; Galazios, G.; Koukourakis, M.I.; Kontomanolis, E.N.; Maltezos, E. Association of −634G/C and 936C/T polymorphisms of the vascular endothelial growth factor with spontaneous preterm delivery. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2004, 83, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, C.; Giusti, B.; Gozzini, E.; Sereni, A.; Romagnuolo, I.; Kura, A.; Pasquini, E.; Abbate, R.; Dani, C. Genetic Contributions to the Development of Complications in Preterm Newborns. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bányász, I.; Bokodi, G.; Vásárhelyi, B.; Treszl, A.; Derzbach, L.; Szabó, A.; Tulassay, T.; Vannay, A. Genetic polymorphisms for vascular endothelial growth factor in perinatal complications. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, J.; Shao, X. Incidence and mortality trend of congenital heart disease at the global, regional, and national level, 1990–2017. Medicine 2020, 99, e20593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouma, B.J.; Mulder, B.J.M. Changing Landscape of Congenital Heart Disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Linde, D.; Konings, E.E.M.; Slager, M.A.; Witsenburg, M.; Helbing, W.A.; Takkenberg, J.J.M.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W. Birth Prevalence of Congenital Heart Disease Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dor, Y.; Camenisch, T.D.; Itin, A.; Fishman, G.I.; McDonald, J.A.; Carmeliet, P.; Keshet, E. Anovel role for VEGF in endocardialcushion formation and itspotential contribution tocongenital heart defects. Development 2001, 128, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hyun, C. Genetic screening of the canine zincfinger protein multitype 2 (cZFPM2) gene in dogs with tetralogyof Fallot (TOF). J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2009, 126, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, M.W.; Willems, P.J. Genetic factors in nonsyndromiccongenital heart malformations. Clin. Genet. 2010, 78, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silversides, C.K.; Lionel, A.C.; Costain, G.; Merico, D.; Migita, O.; Liu, B.; Yuen, T.; Rickaby, J.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; Marshall, C.R.; et al. Rare copy number variations in adults with tetralogy of Fallotimplicate novel risk gene pathways. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Akker, N.M.; Caolo, V.; Wisse, L.J.; Peters, P.P.; Poelmann, R.E.; Carmeliet, P.; Molin, D.G.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C. Developmental coronary maturation is disturbed by aberrant cardiac vascular endothelial growth factor expression and Notch signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 78, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthonisen, I.L.; Salvador, M.L.; Klein, U. Specific sequence elements in the 5′ untranslated regions of rbcL and atpB gene mRNAs stabilize transcripts in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. RNA 2001, 7, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Ge, Q.; Xi, C.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y. Genetic Variations of VEGF Gene Were Associated with Tetralogy of Fallot Risk in a Chinese Han Population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2015, 19, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.J.; Webb, N.J.; Bottomley, M.J.; Brenchley, P. Identification of polymorphisms within the vascular endothelial growth FACTOR (vegf) gene: Correlation with variation in vegf protein production. Cytokine 2000, 12, 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedts, H.P.M.; Isaacs, A.; de Costa, D.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; van Duijn, C.M.; Groot, A.C.G.-D.; Helbing, W.A.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. VEGF Polymorphisms Are Associated with Endocardial Cushion Defects: A Family-Based Case-Control Study. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, E.J.; Bischoff, J. Heart valve development: Endothelial cell signalling and differentiation. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roybal, C.N.; Yang, S.; Sun, C.-W.; Hurtado, D.; Jagt, D.L.V.; Townes, T.M.; Abcouwer, S.F. Homocysteine Increases the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by a Mechanism Involving Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Transcription Factor ATF4. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14844–14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S.; Ehsan, F.; Shabana; Tahir, A.; Jamil, M.; Shahid, S.U.; Khan, A.; Hasnain, S. First report of polymorphisms in MTRR, GATA4, VEGF, and ISL1 genes in Pakistani children with isolated ventricular septal defects (VSD). Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S.; Shabana; Tahir, A.; Liaqat, Z.; Naseer, S.; Seme, R.S.; Mehmood, S.; Shahid, S.U.; Hasnain, S. Study of variants associated with ventricular septal defects (VSDs) highlights the unique genetic structure of the Pakistani population. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Gu, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Qiu, W. Polymorphisms of VEGF and congenital heart disease in a Chinese population. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 7281–7288. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; Burt, A.A.; Crosslin, D.R.; Burnham, N.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Zackai, E.H.; Nicolson, S.C.; Spray, T.L.; Stanaway, I.B.; et al. Patient Genotypes Impact Survival after Surgery for Isolated Congenital Heart Disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 98, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroudis, C.D.; Kim, D.S.; Burnham, N.; Morss, A.H.; Kim, J.H.; Burt, A.A.; Crosslin, D.R.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Zackai, E.H.; Cohen, M.S.; et al. A vascular endothelial growth factor A genetic variant is associated with improved ventricular function and transplant-free survival after surgery for non-syndromic CHD. Cardiol. Young 2017, 28, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatana, V.; Gillis, J.; Webster, B.H. Ades LC.Deletion 22q11.2 syndrome-implications for theintensive care physician. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 8, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón, J.F.; Puga, A.R.; Guzmán, M.L.; Astete, C.P.; Arriaza, M.; Aracena, M.; Aravena, T.; Sanz, P.; Repetto, G.M. VEGFA polymorphisms and cardiovascular anomalies in 22q11 microdeletion syndrome: A case-control and family-based study. Biol. Res. 2009, 42, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalmans, I.; Lambrechts, D.; De Smet, F.; Jansen, S.; Wang, J.; Maity, S.; Kneer, P.; Von Der Ohe, M.; Swillen, A.; Maes, C.; et al. VEGF: A modifier of the del22q11 (DiGeorge) syndrome? Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.C.; Rheinlaender, C.; Sarioglu, N.; Peiser, C.; Rüdiger, M.; Obladen, M.; Koehne, P.S. The Expression of VEGF and its Receptors in the Human Ductus Arteriosus. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyman, R.I.; Seidner, S.R.; Kajino, H.; Roman, C.; Koch, C.J.; Ferrara, N.; Waleh, N.; Mauray, F.; Chen, Y.Q.; Perkett, E.A.; et al. VEGF regulates remodeling duringpermanent anatomic closure of the ductus arteriosus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 282, R199–R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waleh, N.; Seidner, S.; McCurnin, D.; Giavedoni, L.; Hodara, V.; Goelz, S.; Liu, B.M.; Roman, C.; Clyman, R.I. Anatomic Closure of the Premature Patent Ductus Arteriosus: The Role of CD14+/CD163+ Mononuclear Cells and VEGF in Neointimal Mound Formation. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallmon, H.; Aydin, T.; Hort, S.; Kubinski, A.; Bode, C.; Klippstein, T.; Endesfelder, S.; Bührer, C.; Koehne, P. Vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphism rs2010963 status does not affect patent ductus arteriosus incidence or cyclooxygenase inhibitor treatment success in preterm infants. Cardiol. Young 2019, 29, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, H.H.; Risau, W. Systemic hypoxia changes the organ-specific distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15809–15814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelkel, N.F.; Vandivier, R.W.; Tuder, R.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor in the lung. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L209–L221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor: Basic Science and Clinical Progress. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Endo, M.; Moriya, T.; Chida, M.; Kondo, T.; Sasano, H. Analysis of Intrapulmonary Vessels and Epithelial-Endothelial Interactions in the Human Developing Lung. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailaparambil, B.; Krueger, M.; Heizmann, U.; Schlegel, K.; Heinze, J.; Heinzmann, A. Genetic and epidemiological risk factors in the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Dis. Markers 2010, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, E.G.; Knupp, A.M.; Welty, E.S.; Susey, K.; Gardner, W.; Gest, A.L. An interdisciplinary bronchopulmonary dysplasia program is associated with improved neurodevelopmental outcomes and fewer rehospitalizations. J. Perinatol. 2011, 32, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-H.; Tsao, P.-N. Phenotypes of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, S.; Manti, S.; Buttarelli, L.; Petrolini, C.; Boscarino, G.; Filonzi, L.; Gitto, E.; Esposito, S.M.R.; Marzano, F.N. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor as Molecular Target for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Prevention in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, M.; Bhandari, A.; Bhandari, V. Diagnosis and management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. BMJ 2021, 375, n1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlman, M.; Huusko, J.M.; Karjalainen, M.K.; Kaukola, T.; Marttila, R.; Ojaniemi, M.; Haataja, R.; Lavoie, P.M.; Rämet, M.; Hallman, M.; et al. Genes Encoding Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGF-A) and VEGF Receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) and Risk for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Neonatology 2015, 108, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-H.; Li, J.; Snyder, M.; Shaw, G.M.; O’brodovich, H.M. The genetic predisposition to bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.; Soden, J.; Brenchley, P.E.; Ralph, S.; Ray, D.W. Haplotype Analysis of the Polymorphic Human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Promoter. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Association of VEGF Gene Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Diabetic Retinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, P.; Furriol, J.; Tormo, E.; Ballester, S.; Lluch, A.; Eroles, P. The single-nucleotide polymorphisms +936 C/T VEGF and −710 C/T VEGFR1 are associated with breast cancer protection in a Spanish population. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwinta, P.; Bik-Multanowski, M.; Mitkowska, Z.; Tomasik, T.; Legutko, M.; Pietrzyk, J.J. Genetic Risk Factors of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filonzi, L.; Perrone, S.; Tataranno, M.L.; Magnani, C.; Dadomo, H.; Bottoni, A.; Vaghi, M.; Marzano, F.N. Molecular Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 2793846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, K.; Shibata, A.; Yokota, T.; Koda, T.; Nagasaka, M.; Yagi, M.; Takeshima, Y.; Yamada, H.; Iijima, K.; Morioka, I. Association of a vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphism with the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in Japanese premature newborns. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Ierardi, V.; Daleno, C.; Scala, A.; Terranova, L.; Tagliabue, C.; Rios, W.P.; Pelucchi, C.; Principi, N. Genetic polymorphisms and risk of recurrent wheezing in pediatric age. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiner-Møller, E.; Chawes, B.L.K.; Vissing, N.H.; Koppelman, G.H.; Postma, D.S.; Madsen, J.S.; Olsen, D.A.; Baty, F.; Vonk, J.M.; Kerkhof, M.; et al. VEGFA variants are associated with pre-school lung function, but not neonatal lung function. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, A.; Sukgen, E.A.; Wu, W.-C.; Lepore, D.; Nakanishi, H.; Mazela, J.; Moshfeghi, D.M.; Vitti, R.; Athanikar, A.; Chu, K.; et al. Effect of Intravitreal Aflibercept vs Laser Photocoagulation on Treatment Success of Retinopathy of Prematurity: The FIREFLEYE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 328, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; McLeod, D.S.; Prow, T.; Merges, C.; Grebe, R.; Lutty, G.A. Vascular Precursors in Developing Human Retina. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2178–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmeh, Z.A.; Azarpira, N.; Mosallaei, M.; Hosseini, H.; Malekpour, Z. Genetic polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor and risk for retinopathy of prematurity in South of Iran. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 4613–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, R.W.I.; Drury, J.A.; Mountford, R.; Clark, D. Genetic polymorphisms and retinopathy of prematurity. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 1712–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunai, G.; Vásárhelyi, B.; Szabó, M.; Hajdú, J.; Mészáros, G.; Tulassay, T.; Treszl, A. Published Genetic Variants in Retinopathy of Prematurity: Random Forest Analysis Suggests a Negligible Contribution to Risk and Severity. Curr. Eye Res. 2008, 33, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartnett, M.E.; Penn, J.S. Mechanisms and Management of Retinopathy of Prematurity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.A.; Hussien, N.F.; Samy, R.M.; Al Husseiny, K. Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Retinopathy of Prematurity. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2015, 52, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Çokakli, M.; Berk, A.T.; Yaman, A.; Yesilirmak, D.; Kumral, A.; Atabey, N. Associations of VEGF/VEGF-Receptor and HGF/c-Met Promoter Polymorphisms with Progression/Regression of Retinopathy of Prematurity. Curr. Eye Res. 2012, 38, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, B.S.; Qu, X. Lack of association of the VEGF gene promoter (−634 G→C and −460 C→T) polymorphism and the risk of advanced retinopathy of prematurity. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2006, 245, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannay, A.; Dunai, G.; Bányász, I.; Szabó, M.; Vámos, R.; Treszl, A.; Hajdú, J.; Tulassay, T.; Vásárhelyi, B. Association of Genetic Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Risk for Proliferative Retinopathy of Prematurity. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bányász, I.; Bokodi, G.; Vannay, A.; Szebeni, B.; Treszl, A.; Vásárhelyi, B.; Tulassay, T.; Szabó, A. Genetic Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiopoietin 2 in Retinopathy of Prematurity. Curr. Eye Res. 2006, 31, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movsas, T.Z.; Muthusamy, A. Associations between VEGF isoforms and impending retinopathy of prematurity. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2020, 80, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwinta, P.; Bik-Multanowski, M.; Mitkowska, Z.; Tomasik, T.; Pietrzyk, J.J. The clinical role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) system in the pathogenesis of retinopathy of prematurity. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuda, T.; Hikino, S.; Ohga, S.; Kinjo, T.; Ochiai, M.; Takahata, Y.; Tokunaga, S.; Ihara, K.; Hata, Y.; Hara, T. Genetic variation of vascular endothelial growth factor pathway does not correlate with the severity of retinopathy of prematurity. J. Perinatol. 2010, 31, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, K.; Morioka, I.; Honda, S.; Tsukahara, Y.; Miwa, A.; Shibata, A.; Tanimura, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Yamada, H.; Iijima, K. Severe retinopathy of prematurity with retinal detachment in monozygotic twins. Pediatr. Int. 2013, 55, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, K.; Drury, J.A.; Clark, D.I. An unusual case of retinopathy of prematurity. J. Perinatol. 2007, 27, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhuang, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Feng, Z. Relationship between the 5′UTR of vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphism and retinopathy of prematurity in Chinese premature newborns. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 11695–11702. [Google Scholar]
- Ilguy, S.; Cilingir, O.; Bilgec, M.D.; Ozalp, O.; Gokalp, E.E.; Arslan, S.; Tekin, N.; Aydemir, O.; Erol, N.; Colak, E.; et al. The relationship of retinopathy of prematurity with brain-derivated neurotrophic factor, vascular endotelial growth factor-A, endothelial PAD domain protein 1 and nitric oxide synthase 3 gene polymorphisms. Ophthalmic Genet. 2021, 42, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, M.J.; Sankar, J.; Bhat, V.; Srinivasan, R. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) drugs for treatment of retinopathy of prematurity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2, CD009734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Anti-VEGF therapy in the management of retinopathy of prematurity: What we learn from representative animal models of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Eye Brain 2016, 8, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oszajca, K.; Szemraj, J.; Wyrzykowski, D.; Chrzanowska, B.; Salamon, A.; Przewratil, P. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of VEGF-A and VEGFR-2 genes and risk of infantile hemangioma. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, H. Management of infantile hemangiomas: Recent advances. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1064048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vugt, L.J.; van der Vleuten, C.J.; Flucke, U.; Blokx, W.A. The utility of GLUT1 as a diagnostic marker in cutaneous vascular anomalies: A review of literature and recommendations for daily practice. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandera, A.I.R.; Sebaratnam, D.F.; Wargon, O.; Wong, L.-C.F. Infantile hemangioma. Part 1: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, S.; Itinteang, T.; Withers, A.H.J.; Davis, P.F.; Tan, S.T. Does hypoxia play a role in infantile hemangioma? Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2016, 308, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harter, N.; Mancini, A.J. Diagnosis and Management of Infantile Hemangiomas in the Neonate. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 66, 437–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.F.; Friedlander, S.F.; Guma, M.; Kavanaugh, A.; Chambers, C.D. Infantile Hemangiomas: An Updated Review on Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabh, P. Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Premature Infants: Mechanism of Disease. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.-P.; Qiao, N.-D.; Gu, Y.-X.; Song, J.-P.; Li, P.-L.; Qiu, H.-J.; Fan, W.-W.; Mao, Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y. Polymorphisms of VEGFA gene and susceptibility to hemorrhage risk of brain arteriovenous malformations in a Chinese population. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasun, P.; Madan, R.; Puthuraya, S.; Subramanian, D.; Datta, I.; Kalra, V.; Thomas, R.; Stockton, D.W.; Sundaram, S.; Callaghan, J.; et al. Can Functional Polymorphisms in VEGF and MMP Predict Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Extremely Preterm Newborns? Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 40, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shimi, M.S.; Hassanein, S.M.A.; Mohamed, M.H.; Abdou, R.M.; Roshdy, A.; Atef, S.H.; Aly, H. Predictive value of vascular endothelial growth factor in preterm neonates with intraventricular haemorrhage. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Baumann, J.M.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Tang, M.; Dunn, R.S.; Akeson, A.L.; Kernie, S.G.; Kallapur, S.; Lindquist, D.M.; Huang, E.J.; et al. Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in the Germinal Matrix Induces Neurovascular Proteases and Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 193ra90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, R.M.; Yan, X.; De Plaen, I.G. Intestinal microcirculation and necrotizing enterocolitis: The vascular endothelial growth factor system. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Managlia, E.; Liu, S.X.; Tan, X.-D.; Wang, X.; Marek, C.; De Plaen, I.G. Lack of VEGFR2 signaling causes maldevelopment of the intestinal microvasculature and facilitates necrotizing enterocolitis in neonatal mice. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G716–G725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonen, R.M.; Huizing, M.J.; González-Luis, G.E.; Cavallaro, G.; Mosca, F.; Villamor, E. Risk of Necrotizing Enterocolitis Associated with the Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms VEGF C-2578A, IL-18 C-607A, and IL-4 Receptor α-Chain A-1902G: A Validation Study in a Prospective Multicenter Cohort. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H.; Feng, Z. Association of polymorphism in the VEGFA gene 3′-UTR +936T/C with susceptibility to biliary atresia in a Southern Chinese Han population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 32, e22342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Chang, T.-Y.; Yeung, C.-Y.; Chan, W.-T.; Jiang, C.-B.; Chen, W.-F.; Chan, H.-W.; Liu, H.-F.; Lin, M.; Lee, Y.-J. Genetic Variation in the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene is Associated with Biliary Atresia. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Country Origin of the Studied Population | Type of Study | Inclusion Number | Type of Polymorphism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pregnancy | ||||
| Australia | Cohort | 1169 | VEGF 634CC | Andraweera PH et al. (2012) [40] |
| Romania | Case-control | 164 | VEGF-CT936 | Procopciuc LM et al. (2014) [15] |
| Ecuador | Case-control | 31 | VEGF: -2578A/C, -1498C/T, -1154A/G, -634C/G and +936C/T. | Chedraui P et al. (2013) [39] |
| Poland | Cohort | 67 | VEGF SNP | Iciek R et al. (2014) [38] |
| Greece | Case-control | 133 | VEGF 936C/T | Galazios G et al. (2009) [17] |
| Turkey | Case-control | 123 | VEGF +813 | Atis A et al. (2012) [18] |
| Italia | Cohort | 342 | VEGFA rs1547651, rs833058, s833061, rs3025039 | Poggi C et al. (2015) [43] |
| Heart pathologies | ||||
| USA | Cohort | 422 | VEGFA rs833069 minor allele | Mavroudis CD et al. (2018) [63] |
| Italia | Case-control | 198 | VEGFA rs3025039 SNPs | Balistreri CR et al. (2020) [27] |
| Chile | Case-control | 122 | VEGFA c.-2578C>A (rs699947), c.-1154G>A (rs1570360), c.-634C>G (rs2010963) | Calderón JF et al. (2009) [65] |
| USA | Cohort | 550 | VEGFA rs833069 | Kim DS et al. (2014) [62] |
| Pakistan | Case-control | 242 | VEGF rs699947 (c.-2578C > A) | Sarwar S et al. (2021) [59] |
| Pakistan | Case-control | 350 | VEGF, rs36208048 (NG_008732.1:g.3877C > A | Sarwar S et al. (2022) [60] |
| Lung diseases | ||||
| Finland, Canada | Case-control | 160 | six tagging single nucleotide polymorphism (tSNPs) | Mahlman M et al. (2015) [80] |
| Japan | Case-control | 97 | VEGF -1498T>C, -1154G>A, -634C>G, -7C>T, 936C>T, and 1612G>A | Fujioka K et al. (2014) [87] |
| Germany | Case-control | 155 | VEGF rs699947, rs2010963, rs3025039 | Mailaparambil B et al. (2010) [75] |
| Italy | Case-control | 82 | VEGF+936 C/T | Filonzi L et al. (2022) [86] |
| Poland | Case-control | 181 | VEGF -460T>C and 405G>C | Kwinta P et al. (2008) [85] |
| Italy | Case-control | 238 | VEGFA-rs833058CT, VEGFA-rs2146323AA | Esposito S et al. (2014) [88] |
| Denmark | Cohort | 411 | 13 SNPs. | Kreiner-Møller E et al. (2013) [89] |
| Eye conditions | ||||
| Japan | Case-control | 204 | VEGF(g.-634G>C, +13553C>T) | Kusuda T et al. (2011) [103] |
| United Kingdom | Case-control | 188 | VEGF -634 G>C, VEGF 936C>T | Cooke RW et al. (2004) [93] |
| United Kingdom | Study case | 1 | Chromosomal VEGF analysis | Mandal K et al. (2007) [105] |
| Turkey | Case-control | 148 | VEGFA rs2010963 and rs3025039 | Ilguy S et al. (2021) [107] |
| Hungary, | Case-control | 200 | VEGF(-2578) A and G”allele polymorphisms | Bányász I et al. (2006) [100] |
| USA | Case-control | 122 | VEGF promoter region (containing -634 G>C and -460C>T polymorphism) | Shastry BS et al. (2007) [98] |
| China | Case-control | 174 | VEGF -165C/T, -141A/C, T-165C-141 and C-165A-141 haplotypes | Zang S et al. (2017) [106] |
| Egypt | Case-control | 102 | VEGF 634 C/G and 936 C/T polymorphisms | Ali AA et al. (2015) [96] |
| Turkey | Case-control | 123 | VEGF (-634) C and (-460) C polymorphisms | Kaya M et al. (2013) [97] |
| Iran | Case-control | 111 | VEGF +405 (rs2010963) and VEGF +936 (rs3025039) | Kalmeh ZA et al. (2013) [92] |
| Hungary and Poland | Case-control | 181, 211 | VEGF 405G>C and -460T>C | Vannay A et al. (2005) [99] and Kwinta P et al. (2008) [102] |
| Japan | Case report | 2 | VEGF 936C>T polymorphism | Fujioka K et al. (2013) [104] |
| Hungary | Case-control | 237 | VEGF T(-460)C, G(+405)C, and C(-2578)A | Dunai G et al. (2008) [94] |
| Hemangioma and cerebral pathologies | ||||
| USA | Case-control | 382 | VEGF (RS699947, RS2010963, RS3025039, and RS1570360) | Prasun P et al. (2018) [119] |
| Poland | Case-control | 99 | VEGF-A (+405G/C, rs2010963; +936 C/T, rs3025039 | Oszajca K et al. (2018) [110] |
| Digestive pathologies | ||||
| Netherlands, Spain, Italy | Case-control | 358 | VEGF C-2578A (rs699947) | Moonen RM et al. (2020) [124] |
| Hungary | Case-control | 328 | VEGF T-460C, C-2578A, G+405C | Bányász I et al. (2006) [44] |
| China, Han population | Case-control | 1979 | VEGFA rs3025039 | Liu F et al. (2018) [125] |
| Taiwan | Case-control | 205 | VEGF (-2578 A/C, -634 G/C, and +936 C/T) | Lee HC et al. (2010) [126] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hăşmăşanu, M.G.; Procopciuc, L.M.; Matyas, M.; Zonda, G.I.; Zaharie, G.C. Genetic Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Neonatal Pathologies: A Systematic Search and Narrative Synthesis of the Literature. Children 2023, 10, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040744
Hăşmăşanu MG, Procopciuc LM, Matyas M, Zonda GI, Zaharie GC. Genetic Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Neonatal Pathologies: A Systematic Search and Narrative Synthesis of the Literature. Children. 2023; 10(4):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040744
Chicago/Turabian StyleHăşmăşanu, Monica G., Lucia M. Procopciuc, Melinda Matyas, Gabriela I. Zonda, and Gabriela C. Zaharie. 2023. "Genetic Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Neonatal Pathologies: A Systematic Search and Narrative Synthesis of the Literature" Children 10, no. 4: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040744
APA StyleHăşmăşanu, M. G., Procopciuc, L. M., Matyas, M., Zonda, G. I., & Zaharie, G. C. (2023). Genetic Polymorphisms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Neonatal Pathologies: A Systematic Search and Narrative Synthesis of the Literature. Children, 10(4), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040744








