Effects of Taekwondo Training on Growth Factors in Normal Korean Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
2.3. Literature Selection and Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
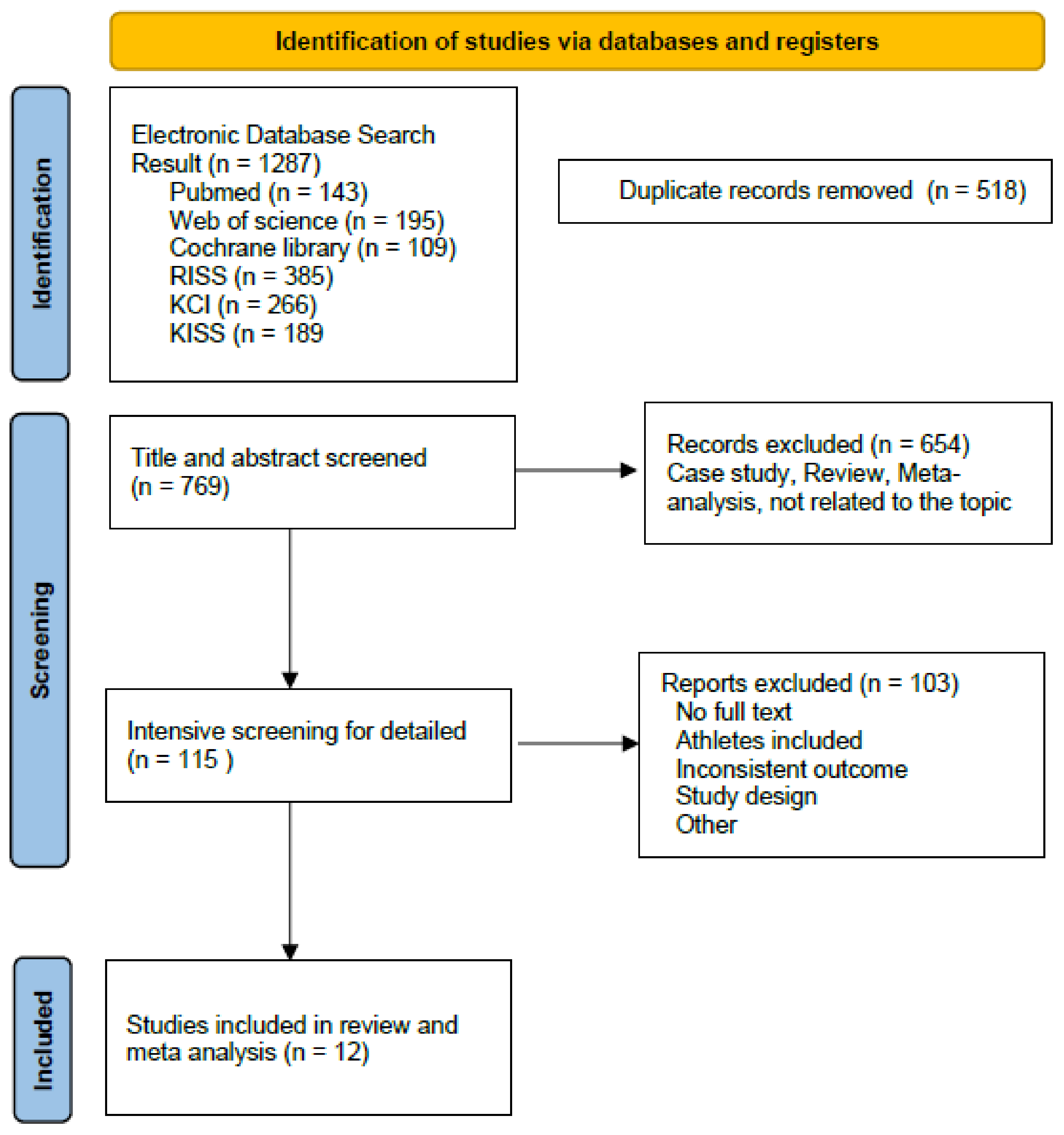
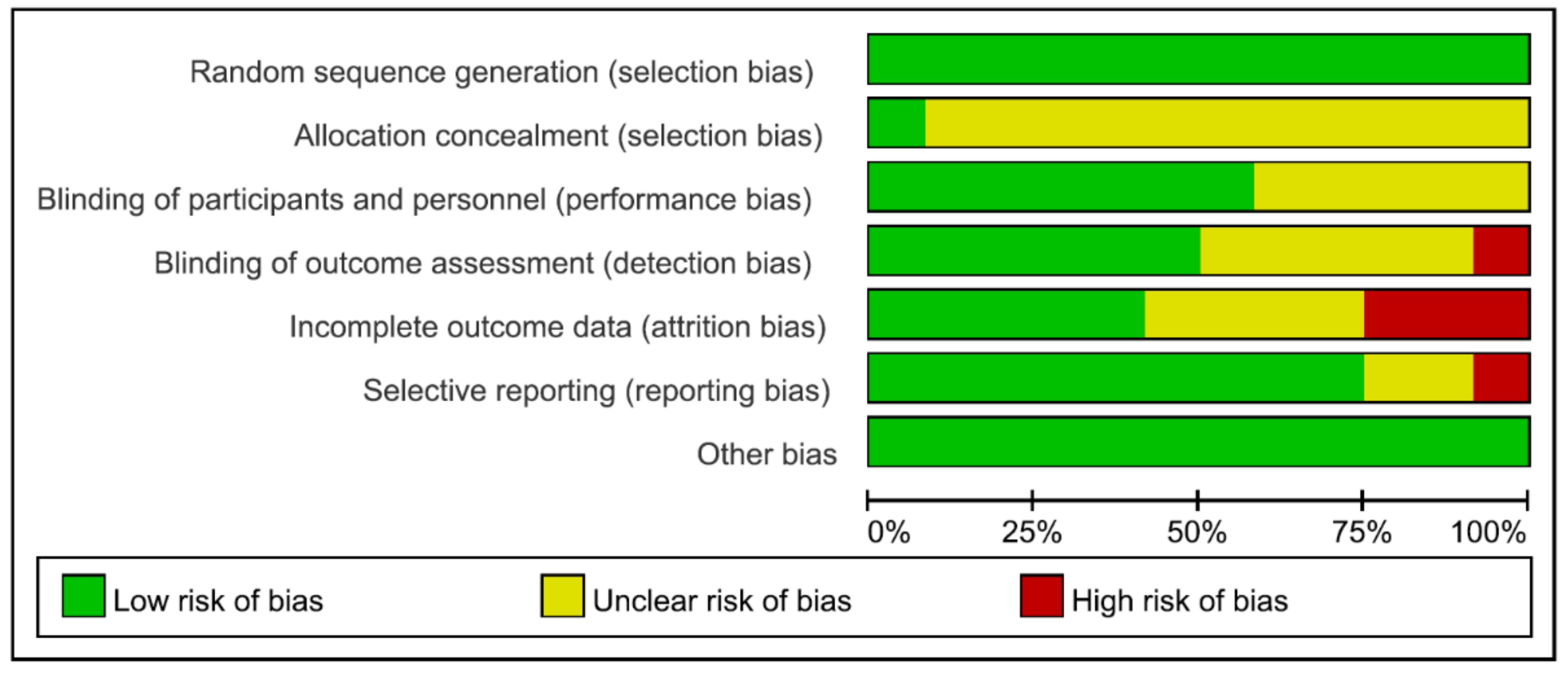
3.1. Study Selection and Quality Assessment
3.2. Characteristics of the Selected Studies and Quality Assessment
4. Effects of Taekwondo on Growth
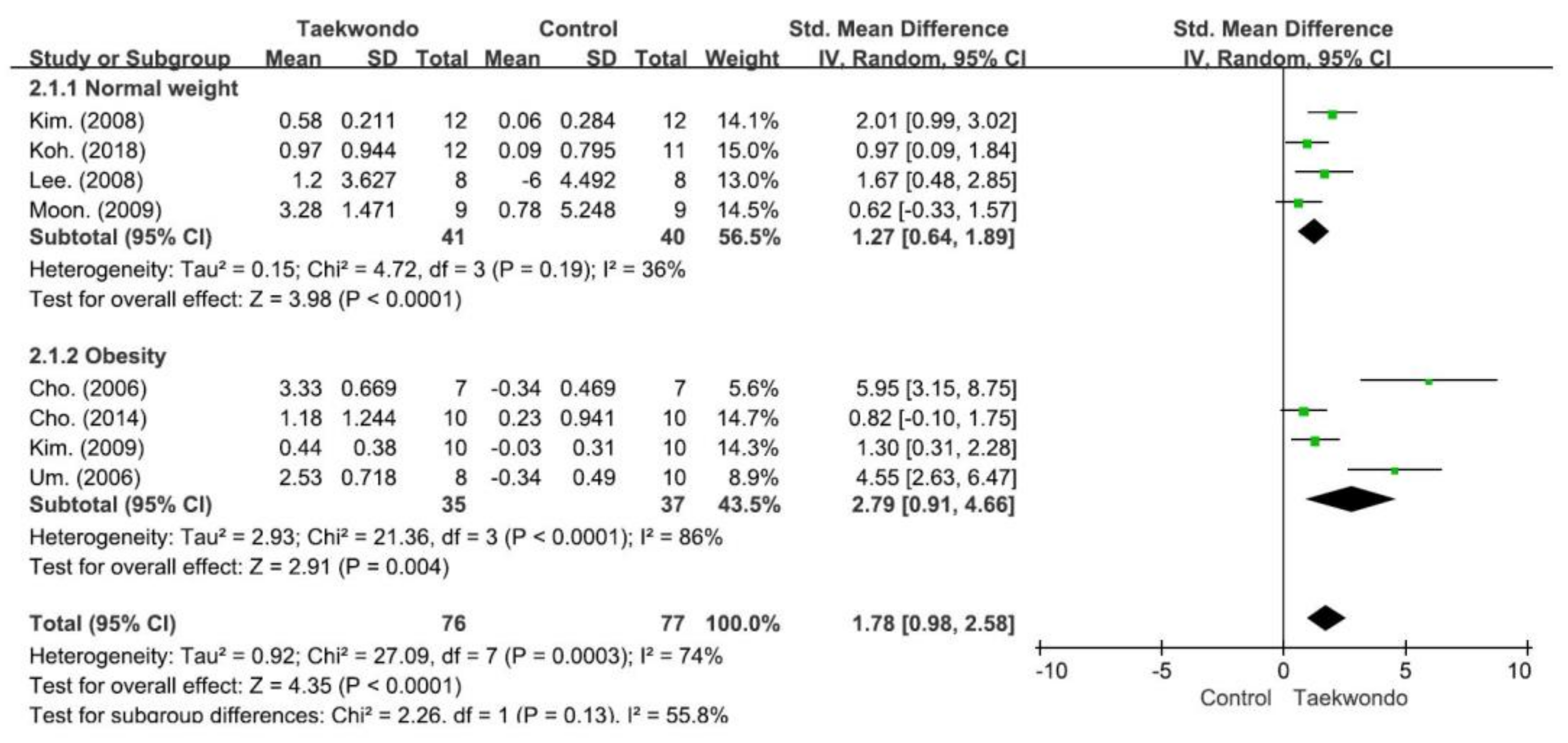
4.1. Effect on GH
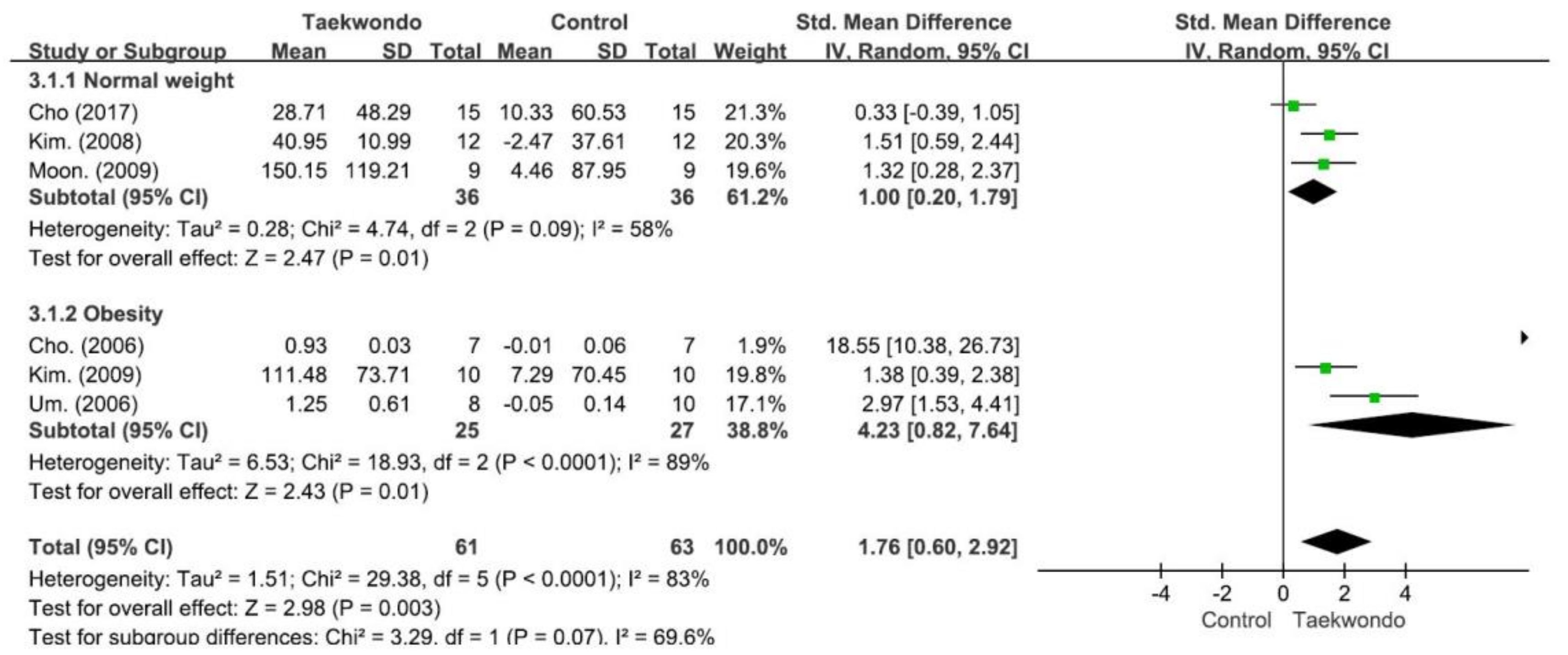
4.2. Effect on the IGF-1
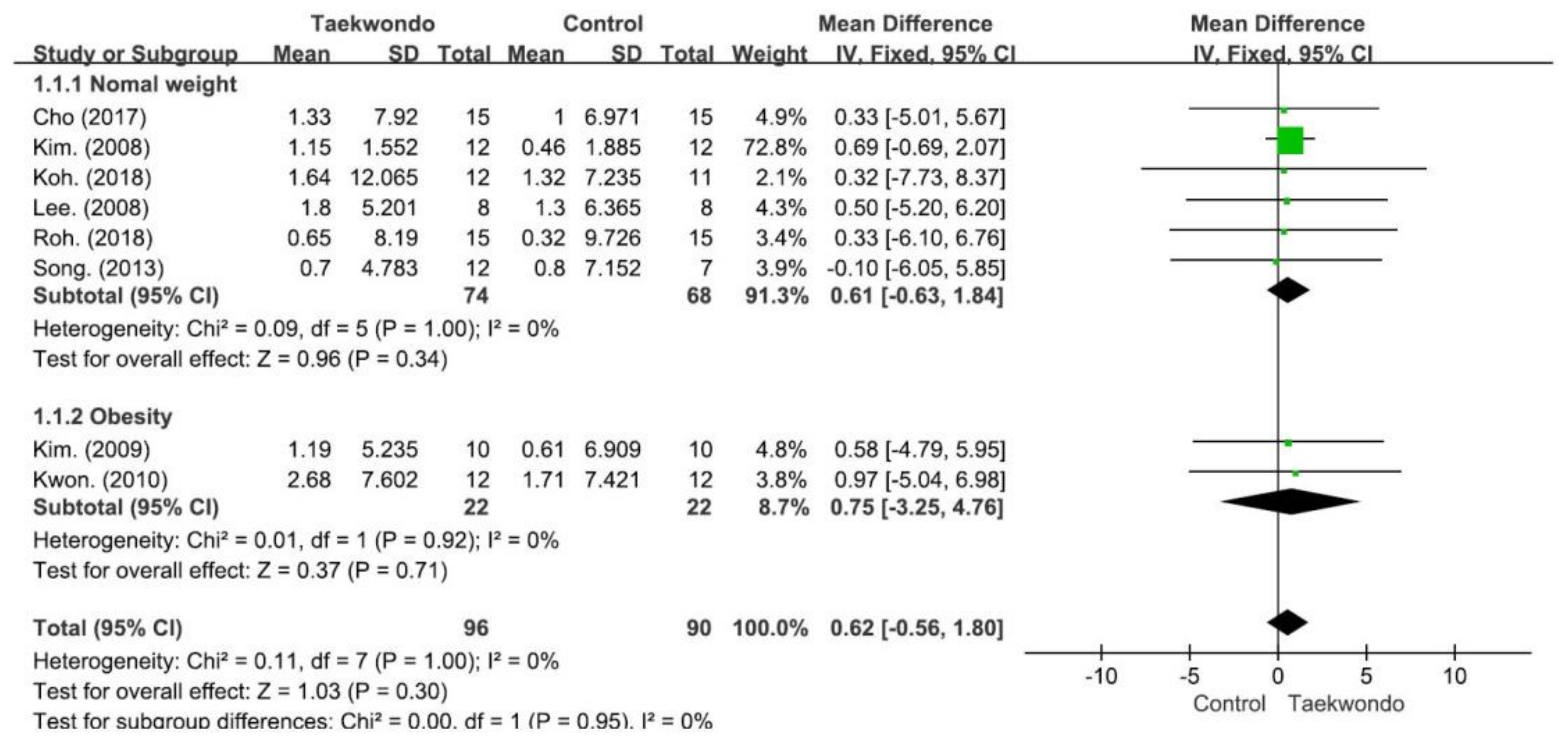
4.3. Effect on Height
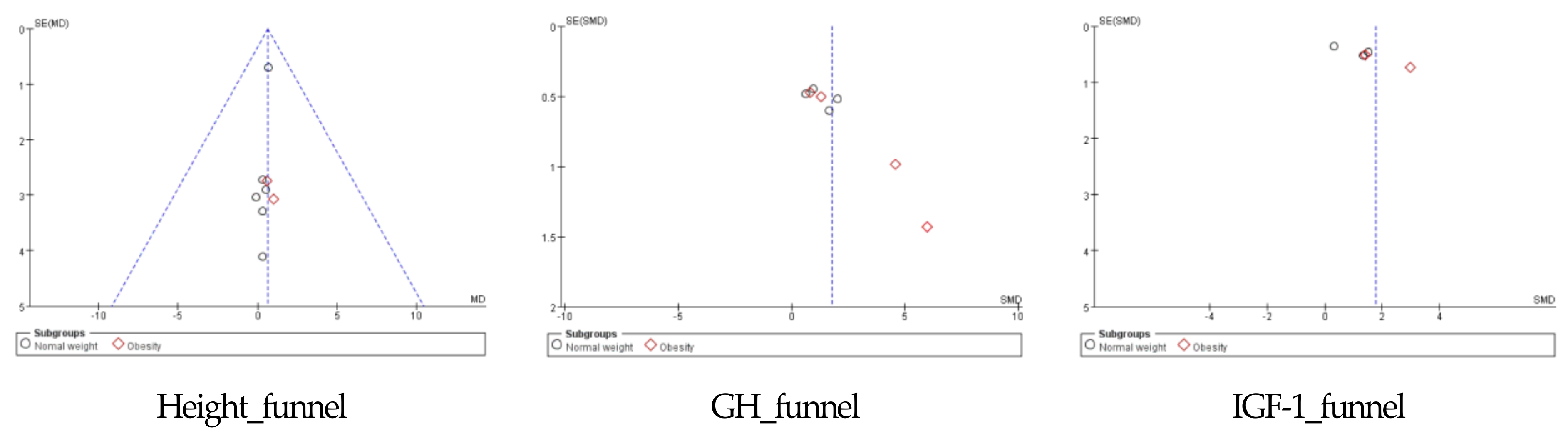
4.4. Publication Bias Assessment
5. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pieter, W.; Fife, G.P.; O’Sullivan, D.M. Competition injuries in taekwondo: A literature review and suggestions for prevention and surveillance. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2012, 46, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, M.; Ingar, A.; Jaffery, A. Injuries in elite Taekwondo Poomsae athletes. J. Can. Chiropr. Assoc. 2016, 60, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Kim, K. Effect of Taekwondo Training on Physical Fitness and Growth Index According to IGF-1 Gene Polymorphism in Children. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Korean Physiol. Soc. Korean Soc. Pharmacol. 2015, 19, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukkiwon. Taekwondo Statistics and Data [Internet] Kukkiwon. 2022. Available online: http://www.kukkiwon.or.kr/front/kor/information/report.action?cmd=View&seq=295&pageNum=1&searchKey=1&searchVal= (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Nam, S.S.; Lim, K. Effects of Taekwondo training on physical fitness factors in Korean elementary students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 23, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beis, K.; Pieter, W.; Abatzides, G. Taekwondo techniques and competition characteristics involved in time-loss injuries. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2007, 6, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, C.A.; Ferreira da Silva Santos, J.; Chaabène, H.; Pieter, W.; Franchini, E. Physical and physiological profiles of taekwondo athletes. Sport. Med. 2014, 44, 713–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Waalen, J.; Morgan, C.; White, A.R. A profile of olympic taekwondo competitors. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2006, 5, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias, N.; Bhatia, S.; Campos, L.F.; Nguyen, D.V.; Chang, E.Y. The relationship between Taekwondo training habits and injury: A survey of a collegiate Taekwondo population. Open Access J. Sport. Med. 2015, 6, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geßlein, M.; Rüther, J.; Bail, H.J.; Schuster, P.; Krutsch, W.; Wolpert, A.K. Injury Incidence Rates and Profiles in Elite Taekwondo during Competition and Training. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 41, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M. Analysis of injuries in taekwondo athletes. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Shearer, H.; Su Choung, Y. Pre-competition habits and injuries in Taekwondo athletes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2005, 26, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.S.; Kim, D.Y. The Effect of Taekwondo on Body Composition, Physical Fitness and Growth Factors in Elderly Women. Korea Sport Res. 2007, 18, 495–506. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter-Jone, A.D.G.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Sherar, L.B. Controlling for Maturation in Pediatric Exercise Science. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2005, 17, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- De Onis, M.; Woynarowska, B. Standardy WHO rozwoju fizycznego dzieci w wieku 0–5 lat i mozliwości ich wykorzystania w Polsce [WHO child growth standards for children 0–5 years and the possibility of their implementation in Poland]. Med. Wieku Rozw. 2010, 14, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.K.; Underwood, L.E.; Clemmons, D.R. Anabolic effects of growth hormone in obese diet-restricted subjects are dose dependent. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaley, J.A.; Dall, R.; Møller, N.; Nielsen, S.C.; Christiansen, J.S.; Jensen, M.D.; Jørgensen, J.O. Acute exposure to GH during exercise stimulates the turnover of free fatty acids in GH-deficient men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, J.; Sanders, W.; Forehand, R. Youth screen time and behavioral health problems: The role of sleep duration and disturbances. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2016, 37, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, F.W.; Roberts, C.K.; Thyfault, J.P.; Ruegsegger, G.N.; Toedebusch, R.G. Role of Inactivity in Chronic Diseases: Evolutionary Insight and Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1351–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44399/9789245599975_chi.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Bartke, A. Pleiotropic effects of growth hormone signaling in aging. Trend Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S.A.; Cohen, P. The somatomedin hypothesis 2007: 50 years later. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakar, S.; Rosen, C.J.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Sun, H.; Mejia, W.; Kawashima, Y.; Wu, Y.; Emerton, K.; Williams, V.; Jepsen, K. Serum complexes of insulin-like growth factor-1. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2009, 23, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scacchi, M.; Pincelli, A.I.; Cavagnini, F. Growth hormone in obesity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 1999, 23, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaley, J.A.; Weatherup-Dentes, M.M.; Jaynes, E.B.; Hartman, M.L. Obesity attenuates the growth hormone response to exercise. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 3156–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisseau, U.; Delamarche, P. Metabolic and hormonal responses to exercise in children and adolescents. Sport. Med. 2000, 30, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirakisoontorn, P.; Nussbaum, E.; Moser, C.; Hill, M.; Cooper, D.M. Fitness, acute exercise, and anabolic and catabolic mediators in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliakim, A.; Brasel, J.A.; Mohan, S.; Wong, W.L.; Cooper, D.M. Increased physical activity and the growth hormone-IGF-I axis in adolescent males. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, R308–R314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Kim, D.J. The effects of taekwondo training program on body composition, bone mineral density and growth factors in the children. J. Life Sci. 2008, 18, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Kwon, Y.C. The effect of taekwondo training on physical fitness and growth hormone, IGF-1 or DHEAs concentration in obesity adolescent. Korean J. Sport. Sci. 2009, 18, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.Y.; Han, S.H.; Yang, C.H.; Jang, H.S.; Jeong, S.H. The effect of taekwondo training on growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in pre-pubertal males. J. Coach. Dev. 2006, 8, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.J.; Yoon, O.N. The Effect of 12 Weeks Taekwondo Training Program on Blood Lipid and Growth Hormone in Obese Children. Korean J. Growth Dev. 2014, 22, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.C.; Park, S.K.; Kim, E.H.; Park, J.K.; Zhang, J.H. Effects of Taekwondo Training on Body Composition, Physical Fitness and Serum Adiponectin in Children Obesity. J. Korean Alliance Martial Arts 2010, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.J.; Jung, W.A.; Lee, M.G. Effects of the 12-weeks Growth and Cognition Focused Taekwondo Program to Fitness, Growth, and Cognitive Function in Elementary Students. Taekwondo J. Kukkiwon 2018, 9, 199–220. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, D.S.; Seo, D.K.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, W.K.; Shin, D.S. The Effect of Taekwondo Training on Physical Fitness, Growth Factors and Women`s Hormones and in Female Students after Menarche. J. Korean Alliance Martial Arts 2009, 11, 247–261. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.K.; Kim, H.B.; Kang, H.J.; Jung, H.C. Effect of 12 weeks Taekwondo Poomsae training on body composition, health-related fitness and dietary intake in male adolescents. Taekwondo J. Kukkiwon 2013, 4, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, H.S.; Jung, K.H.; Jang, K.; Moon, W.J.; Yoo, J.M.; Cho, J.Y.; Yang, D.S.; Yang, C.H. The effect of taekwondo training on growth mediators and inflammatory cytokines in pre-pubertal males. J. Coach. Dev. 2006, 8, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.Y.; So, W.Y.; Roh, H.T. The Effects of Taekwondo Training on Peripheral Neuroplasticity-Related Growth Factors, Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity, and Cognitive Functions in Healthy Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ye, J.B.; Baek, Y.H. Effects of Taekwondo and Calcium Intake on Physique, Growth Hormone and IGF-1 in Elementary School Male Students. J. Life Sci. 2008, 18, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.T.; Cho, S.Y.; So, W.Y. Taekwondo Training Improves Mood and Sociability in Children from Multicultural Families in South Korea: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Nindl, B.C.; Marx, J.O.; Gotshalk, L.A.; Bush, J.A.; Welsch, J.R.; Volek, J.S.; Spiering, B.A.; Maresh, C.M.; Mastro, A.M.; et al. Chronic resistance training in women potentiates growth hormone in vivo bioactivity: Characterization of molecular mass variants. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E1177–E1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Hymer, W.C.; Nindl, B.C.; Fragala, M.S. Growth Hormone(s), Testosterone, Insulin-Like Growth Factors, and Cortisol: Roles and Integration for Cellular Development and Growth with Exercise. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaley, J.A. Growth hormone, arginine and exercise. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdowson, W.M.; Healy, M.L.; Sönksen, P.H.; Gibney, J. The physiology of growth hormone and sport. Growth Horm. IGF Res. Off. J. Growth Horm. Res. Soc. Int. IGF Res. Soc. 2009, 19, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudtzon, J.; Bogsnes, A.; Norman, N. Changes in prolactin and growth hormone levels during hypoxia and exercise. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Und Stoffwechs. Horm. Metab. 1989, 21, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsing, N.E.; Brasel, J.A.; Cooper, D.M. Effect of low and high intensity exercise on circulating growth hormone in men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 75, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Aguilera, B.A.; Terada, M.; Newton, R.U.; Lynch, J.M.; Rosendaal, G.; McBride, J.M.; Gordon, S.E.; Häkkinen, K. Responses of IGF-I to endogenous increases in growth hormone after heavy-resistance exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 79, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, J.; Lazarus, L. Growth hormone in exercise: Comparison of physiological and pharmacological stimuli. J. Appl. Physiol. 1976, 41, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.J. Growth hormone and exercise. Clin. Endocrinol. 1999, 50, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindl, B.C.; Pierce, J.R.; Rarick, K.R.; Tuckow, A.P.; Alemany, J.A.; Sharp, M.A.; Kellogg, M.D.; Patton, J.F. Twenty-hour growth hormone secretory profiles after aerobic and resistance exercise. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2014, 46, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, E.; Rogol, A.D. Treatment of growth hormone deficiency in children, adolescents and at the transitional age. Best practice & research. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 30, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranke, M.B. Short and Long-Term Effects of Growth Hormone in Children and Adolescents with GH Deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 720419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, J.S.; Thomas, M.J. Human growth hormone. Pharmacol. Rev. 1994, 46, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Benyi, E.; Sävendahl, L. The Physiology of Childhood Growth: Hormonal Regulation. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 88, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fideleff, H.L.; Boquete, H.R.; Suárez, M.G.; Azaretzky, M. Burden of Growth Hormone Deficiency and Excess in Children. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016, 138, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, A.R.; Holt, R.I. Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1. Front. Horm. Res. 2016, 47, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfäffle, R.; Kiess, W. GH and IGF-1 Replacement in Children. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 261, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimberg, A.; Allen, D.B. Growth hormone treatment for growth hormone deficiency and idiopathic short stature: New guidelines shaped by the presence and absence of evidence. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2017, 29, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäntyselkä, A.; Haapala, E.A.; Lindi, V.; Häkkinen, M.R.; Auriola, S.; Jääskeläinen, J.; Lakka, T.A. Associations of IGF-1 and Adrenal Androgens with Cognition in Childhood. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 91, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sävendahl, L.; Battelino, T.; Højby Rasmussen, M.; Brod, M.; Saenger, P.; Horikawa, R. Effective GH Replacement with Once-weekly Somapacitan vs Daily GH in Children with GHD: 3-year Results from REAL 3. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laron, Z. IGF-1 and insulin as growth hormones. Novartis Found. Symp. 2004, 262, 56–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kriström, B.; Lundberg, E.; Jonsson, B.; Albertsson-Wikland, K.; study group. IGF-1 and growth response to adult height in a randomized GH treatment trial in short non-GH-deficient children. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saracoglu, K.T.; Simsek, T.; Kahraman, S.; Bombaci, E.; Sezen, Ö.; Saracoglu, A.; Demirhan, R. The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 Disease is more Severe on Intensive Care Unit Healthcare Providers: A Cross-sectional Study. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. Off. Sci. J. Korean Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 18, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliakim, A.; Nemet, D.; Zaldivar, F.; McMurray, R.G.; Culler, F.L.; Galassetti, P.; Cooper, D.M. Reduced exercise-associated response of the GH-IGF-I axis and catecholamines in obese children and adolescents. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, S.R.; Rosa, J.S.; Minh, T.D.; Pontello, A.M.; Flores, R.L. Barnett, M. Galassetti, P.R. Dose-dependent relationship between severity of pediatric obesity and blunting of the growth hormone response to exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemet, D.; Cooper, D.M. Exercise, diet, and childhood obesity: The GH-IGF-I connection. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 15 (Suppl. S2), 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.A.; Kraemer, W.J.; Comstock, B.A.; Dunn-Lewis, C.; Maresh, C.M.; Volek, J.S. Obesity, growth hormone and exercise. Sport. Med. 2013, 43, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Delafontaine, P. Mechanisms of IGF-1-Mediated Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy and Atrophy. Cells 2020, 9, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frystyk, J. Exercise and the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2010, 42, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, R.; Lange, K.H.; Kjaer, M.; Jørgensen, J.O.; Christiansen, J.S.; Orskov, H.; Flyvbjerg, A. No evidence of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 proteolysis during a maximal exercise test in elite athletes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendal, L.; Langberg, H.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Frystyk, J.; Ørskov, H.; Kjaer, M. Physical capacity influences the response of insulin-like growth factor and its binding proteins to training. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poehlman, E.T.; Copeland, K.C. Influence of physical activity on insulin-like growth factor-I in healthy younger and older men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 71, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.D.; Cuneo, R.C.; Baxter, R.; Orskov, H.; Keay, N.; Pentecost, C.; Dall, R.; Rosén, T.; Jørgensen, J.O.; Cittadini, A.; et al. Responses of the growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor axis to exercise, GH administration, and GH withdrawal in trained adult males: A potential test for GH abuse in sport. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.M.; Bouchard, C.; Bar-Or, O. (Eds.) Growth, Maturation and Physical Activity; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 623–641. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, J.M.; Healy, M.; Goldstein, H.; Cameron, N. Assessment of Skeletal Maturity and Prediction of Adult Height (TW3 Method), 3rd ed.; WB Saunders: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chulani, V.L.; Gordon, L.P. Adolescent growth and development. Prim. Care 2014, 41, 465–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinyerd, B.; Zipf, W.B. Puberty-timing is everything! J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2005, 20, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.; Baker, D.; Pacey, V.; Wollin, M.; Drew, M.K. What is the most accurate and reliable methodological approach for predicting peak height velocity in adolescents? A systematic review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Mendes, H.; Freitas, D.; Prista, A.; Tani, G.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.G.; Valdivia, A.B.; Maia, J. Development of Physical Performance Tasks during Rapid Growth in Brazilian Children: The Cariri Healthy Growth Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author (Year) | Location (Language) | Participants | Study Design | Duration (Weeks) | Experimental Group (n) (Mean Age ± SD) Frequency/Week, Min/Session | Control Group (n) (Mean Age ± SD) | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [29] Kim. (2008) | Korea (Korean) | 12–13-year-old boys | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 12) (12.35 ± 0.48 years) 5 days/w, 70 min/session | Control (n = 12) (12.42 ± 0.50 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH; IGF-1; and height |
| [30] Kim. (2009) | Korea (Korean) | 13–16-year-old obese boys | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 10) (14.70 ± 1.25 years) 5 days/w, 50 min/session | Control (n = 10) (15.10 ± 0.88 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH; IGF-1; and height |
| [31] Cho. (2006) | Korea (Korean) | 9–12-year-old obese boys | RCT | 8 | Taekwondo (n = 7) (11.75 ± 0.62 years) 5 days/w, 90 min/session | Control (n = 7) (11.75 ± 0.62 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH and IGF-1 |
| [32] Cho. (2014) | Korea (Korean) | 11–13-year-old obese boys | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 10) (11.77 ± 1.25 years) 3 days/w, 60 min/session | Control (n = 10) (11.1 ± 0.3 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH |
| [33] Kwon. (2010) | Korea (Korean) | 8–12-year-old obese girls and boys | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 12) (11.92 ± 0.90 years) 3 days/w, 60 min/session | Control (n = 12) (12.50 ± 0.80 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | Height |
| [34] Koh. (2018) | Korea (Korean) | 8–11 years girls and boys | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 12) 5 days/w, 50 min/session | Control (n = 11) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH and height |
| [35] Moon. (2009) | Korea (Korean) | 11–13-year-old girls | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 9) (12.18 ± 2.12 years) 5 days/w, 60 min/session | Control (n = 9) (12.73 ± 1.82 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH; IGF-1 and height |
| [36] Song. (2013) | Korea (Korean) | 13–14-year-old boys | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 12) (14.0 ± 0.64 years) 3 days/w, 50 min/session | Control (n = 10) (13.9 ± 0.46 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | Height |
| [37] Um. (2006) | Korea (Korean) | 9–12-year-old obese boys | RCT | 8 | Taekwondo (n = 8) (11.82 ± 0.65 years) 5 days/w, 100 min/session | Control (n = 11) (11.68 ± 0.59 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH and IGF-1 |
| [38] Cho. (2017) | Korea (English) | 11–13-year-old girls and boys | RCT | 16 | Taekwondo (n = 15) (11.20 ± 0.77 years) 5 days/w, 60 min/session | Control (n = 15) (11.33 ± 0.72 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | IGF-1 and height |
| [39] Lee. (2008) | Korea (Korean) | 11-year-old boys | RCT | 12 | Taekwondo (n = 8) (11.1 ± 0.4 years) 5 days/w, 50 min/session | Control (n = 8) (11.1 ± 0.3 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | GH and IGF-1 |
| [40] Roh. (2018) | Korea (English) | 11–13-year old girls and boys from multicultural families | RCT | 16 | Taekwondo (n = 15) (11.53 ± 0.64 years) 1 days/w, 60 min/session | Control (n = 15) (11.40 ± 0.63 years) No regular exercise Usual daily living | Height |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, G.; Jung, H.; So, W.-Y.; Chun, B. Effects of Taekwondo Training on Growth Factors in Normal Korean Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Children 2023, 10, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020326
Jeong G, Jung H, So W-Y, Chun B. Effects of Taekwondo Training on Growth Factors in Normal Korean Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Children. 2023; 10(2):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020326
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Guyeol, Hongyong Jung, Wi-Young So, and Buongo Chun. 2023. "Effects of Taekwondo Training on Growth Factors in Normal Korean Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Children 10, no. 2: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020326
APA StyleJeong, G., Jung, H., So, W.-Y., & Chun, B. (2023). Effects of Taekwondo Training on Growth Factors in Normal Korean Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Children, 10(2), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020326






