Impact of Early Hemoglobin Levels on Neurodevelopment Outcomes of Two-Year-Olds in Very Preterm Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Measurements Collected
Outcomes
2.3. Ethics
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population
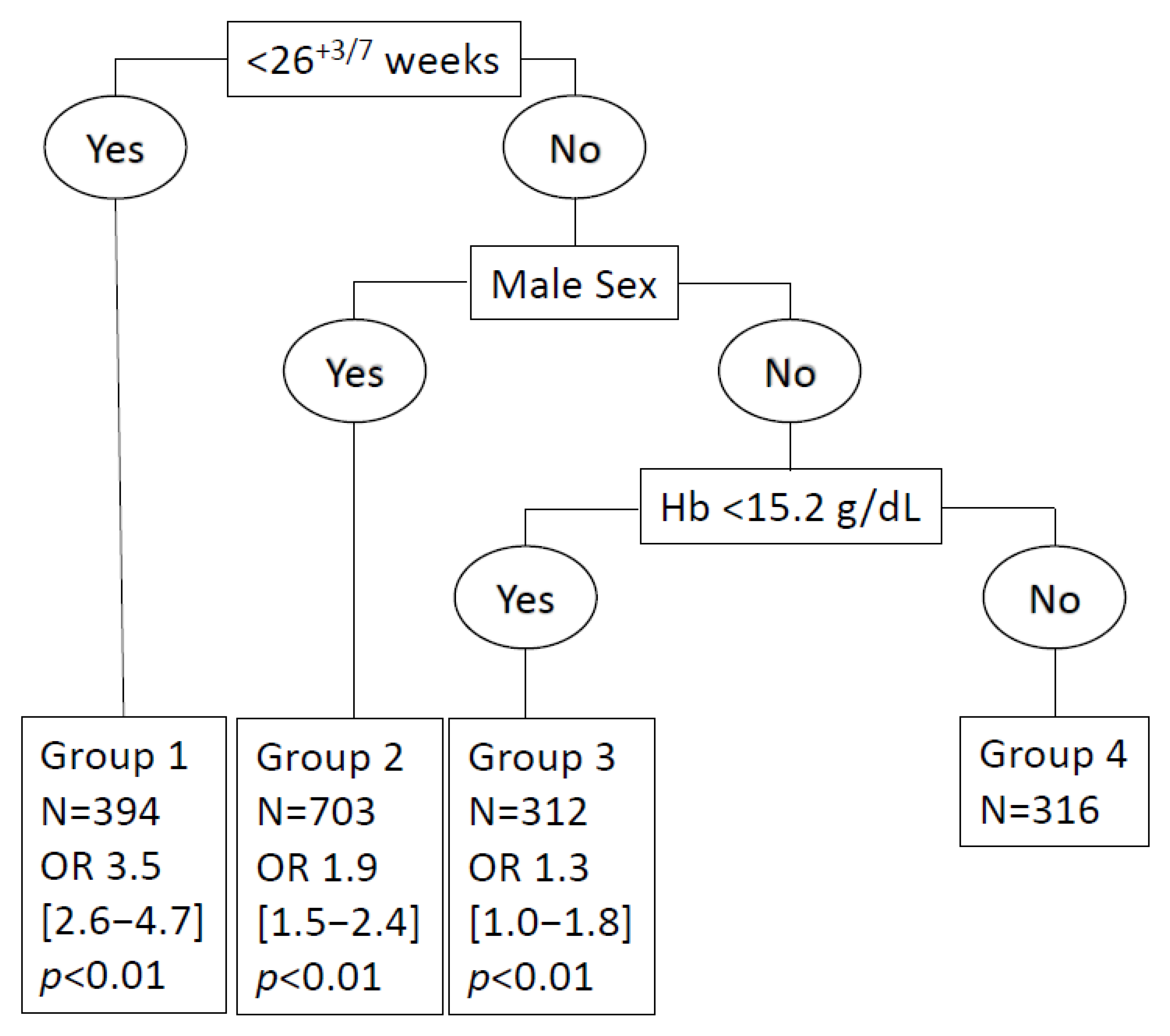
3.2. Values of the Hb Threshold
3.3. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes at 24 Months Corrected Age
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, E.F. Red cell transfusion thresholds for preterm infants: Finally some answers. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022, 107, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aher, S.M.; Ohlsson, A. Early versus late erythropoietin for preventing red blood cell transfusion in preterm and/or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020, 2, CD004865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, R.; Kirpalani, H. Low versus high haemoglobin concentration threshold for blood transfusion for preventing morbidity and mortality in very low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 11, CD000512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergusson, D.A.; Hébert, P.; Hogan, D.L.; Lebel, L.; Rouvinez-Bouali, N.; Smyth, J.A.; Sankaran, K.; Tinmouth, A.; Blajchman, M.A.; Kovacs, L.; et al. Effect of Fresh Red Blood Cell Transfusions on Clinical Outcomes in Premature, Very Low-Birth-Weight Infants: The ARIPI Randomized Trial. JAMA 2012, 308, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Halleux, V.; Truttmann, A.; Gagnon, C.; Bard, H. The effect of blood transfusion on the hemoglobin oxygen dissociation curve of very early preterm infants during the first week of life. Semin. Perinatol. 2002, 26, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Shitara, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Tsuchida, S.; Takahashi, N.; Taga, G. Hemoglobin phase of oxygenation and deoxy-genation in early brain development measured using fNIRS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1737–E1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stutchfield, C.J.; Jain, A.; Odd, D.; Williams, C.; Markham, R. Foetal haemoglobin, blood transfusion, and retinopathy of prematurity in very preterm infants: A pilot prospective cohort study. Eye 2017, 31, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teofili, L.; Papacci, P.; Bartolo, M.; Molisso, A.; Orlando, N.; Pane, L.; Giannantonio, C.; Serrao, F.; Bianchi, M.; Valentini, C.G.; et al. Transfusion-Free Survival Predicts Severe Retinopathy in Preterm Neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 814194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.D.; Carroll, P.D.; Josephson, C.D. Evidence-Based Advances in Transfusion Practice in Neonatal Intensive Care Units. Neonatology 2014, 106, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonim, A.D.; Joseph, J.G.; Turenne, W.M.; Sharangpani, A.; Luban, N.L.C. Blood transfusions in children: A multi-institutional analysis of practices and complications. Transfusion 2007, 48, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, Ú.; Cummings, J.J.; Bell, E.F.; Hosono, S.; Frantz, A.R.; Maier, R.F.; Kirpalani, H. International survey of transfusion practices for ex-tremely premature infants. Semin. Perinatol. 2012, 36, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidler, A.L.; Gyte, G.M.; Rabe, H.; Díaz-Rossello, J.L.; Duley, L.; Aziz, K.; Costa-Nobre, D.T.; Davis, P.G.; Schmölzer, G.M.; Ovelman, C.; et al. Umbilical Cord Management for Newborns <34 Weeks’ Gestation: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e20200576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendolia, B.; Kilic, N.; Afridi, F.; Qari, O.; Bhat, V.; Nakhla, D.; Sadre, S.; Eckardt, R.; Nakhla, T.; Bhandari, V.; et al. Delayed Cord Clamping for 45 Seconds in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: Impact on Hemoglobin at Birth and Close to Discharge. Am. J. Perinatol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.; Asamoah, F.K.; Singhvi, D.; Kwan, A.W.G.; Morris, J.K.; Aladangady, N. Haemoglobin level at birth is associated with short term outcomes and mortality in preterm infants. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ancel, P.-Y.; Goffinet, F.; EPIPAGE 2 Writing Group. EPIPAGE 2: A preterm birth cohort in France in 2011. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ancel, P.Y.; Goffinet, F.; Kuhn, P.; Langer, B.; Matis, J.; Hernandorena, X.; Chabanier, P.; Joly-Pedespan, L.; Lecomte, B.; Vendittelli, F.; et al. Survival and morbidity of preterm children born at 22 through 34 weeks’ gestation in France in 2011: Results of the EPIPAGE-2 cohort study. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierrat, V.; Marchand-Martin, L.; Arnaud, C.; Kaminski, M.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Lebeaux, C.; Bodeau-Livinec, F.; Morgan, A.S.; Goffinet, F.; Marret, S.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years for preterm children born at 22 to 34 weeks’ gestation in France in 2011: EPIPAGE-2 cohort study. BMJ 2017, 358, j3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EUROPE, Socpi. A collaboration of cerebral palsy surveys and registers. Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe (SCPE). Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2000, 42, 816–824. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, A.R.; Engel, C.; Bassler, D.; Rüdiger, M.; Thome, U.H.; Maier, R.F.; Krageloh-Mann, I.; Kron, M.; Essers, J.; Buhrer, C.; et al. Effects of Liberal vs Restrictive Transfusion Thresholds on Survival and Neurocognitive Outcomes in Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants: The ETTNO Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpalani, H.; Bell, E.F.; Hintz, S.R.; Tan, S.; Schmidt, B.; Chaudhary, A.S.; Das, A. Higher or Lower Hemoglobin Transfusion Thresholds for Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2639–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Khan, R.; Curley, A.; New, H.; Stanworth, S. How we decide when a neonate needs a transfusion. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, R.K.; Kirpalani, H.; Asztalos, E.V.; Andersen, C.; Blajchman, M.; Heddle, N.; LaCorte, M.; Robertson, C.M.T.; Clarke, M.C.; Vincer, M.J.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Outcome of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants Randomly Assigned to Restrictive or Liberal Hemoglobin Thresholds for Blood Transfusion. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul, S.E.; Comstock, B.A.; Wadhawan, R.; Mayock, D.E.; Courtney, S.E.; Robinson, T.; Ahmad, K.A.; Bendel-Stenzel, E.; Baserga, M.; LaGamma, E.F.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Erythropoietin for Neuroprotection in Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roudil, P.; Vasselon, C.; Trombert-Paviot, B.; Berger, C.; Patural, H. Blood parameters of preterm neonates: Postnatal evolution according to gestational age. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 39, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.D.; Henry, E.; Jopling, J.; Wiedmeier, S.E. The CBC: Reference Ranges for Neonates. Semin. Perinatol. 2009, 33, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Sex and age discrepancy of HbA1c and fetal hemoglobin determined by HPLC in a large Chinese Han pop-ulation. J. Diabetes 2018, 10, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavides, A.; Bell, E.F.; Conrad, A.L.; Feldman, H.A.; Georgieff, M.K.; Josephson, C.D.; Koscik, T.R.; Stowell, S.R.; Sola-Visner, M.; Nopoulos, P. Sex Differences in the Association of Pretransfusion Hemoglobin Levels with Brain Structure and Function in the Preterm Infant. J. Pediatr. 2022, 243, 78–84.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, H.; Diaz-Rossello, J.L.; Duley, L.; Dowswell, T. Effect of timing of umbilical cord clamping and other strategies to influence placental transfusion at preterm birth on maternal and infant outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012, 9, CD003248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, H.; Reynolds, G.; Diaz-Rossello, J. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Brief Delay in Clamping the Umbilical Cord of Preterm Infants. Neonatology 2008, 93, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wassia, H.; Shah, P.S. Efficacy and safety of umbilical cord milking at birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosono, S.; Mugishima, H.; Kitamura, T.; Inami, I.; Fujita, H.; Hosono, A.; Minato, M.; Okada, T.; Takahashi, S.; Harada, K. Effect of hemoglobin on transfusion and neonatal adaptation in extremely low-birthweight infants. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2008, 50, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellström, W.; Martinsson, T.; Morsing, E.; Gränse, L.; Ley, D.; Hellström, A. Low fraction of fetal haemoglobin is associated with retinopathy of prematurity in the very preterm infant. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 106, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.M.; Knezevic, A.; Shenvi, N.; Hinkes, M.; Keene, S.; Roback, J.D.; Easley, K.; Josephson, C.D. Association of Red Blood Cell Transfusion, Anemia, and Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Very Low-Birth-Weight Infants. JAMA 2016, 315, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colombatti, R.; Sainati, L.; Trevisanuto, D. Anemia and transfusion in the neonate. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 21, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slidsborg, C.; Jensen, A.; Forman, J.L.; Rasmussen, S.; Bangsgaard, R.; Fledelius, H.C.; Greisen, G.; la Cour, M. Neonatal Risk Factors for Treat-ment-Demanding Retinopathy of Prematurity: A Danish National Study. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Henry, E.; D’Amato, G.; Cannuscio, A.; Corriero, L.; Motta, M.; Christensen, R.D. Instituting a program to reduce the erythrocyte transfusion rate was accompanied by reductions in the incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, retinopathy of prematurity and necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Matern-Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2013, 2, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkaluk, M.-L.; Rousseau, J.; Benhammou, V.; Datin-Dorrière, V.; Flamant, C.; Gire, C.; Kern, S.; Pierrat, V.; Kaminski, M.; Marret, S. Association of Language Skills with Other Developmental Domains in Extremely, Very, and Moderately Preterm Children: EPIPAGE 2 Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2019, 208, 114–120.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritišanac, E.; Urlesberger, B.; Schwaberger, B.; Pichler, G. Fetal Hemoglobin and Tissue Oxygenation Measured With Near-Infrared Spectroscopy—A Systematic Qualitative Review. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 710465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, A.; Bell, E.F.; Georgieff, M.K.; Josephson, C.D.; Stowell, S.R.; Feldman, H.A.; Nalbant, D.; Tereshchenko, A.; Sola-Visner, M.; Nopoulos, P. Sex-specific cytokine responses and neurocognitive outcome after blood transfusions in preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 91, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Population, n = 2158 | Missing Data | |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal Characteristics | ||
| Age at childbirth in years (mean ± SD) | 29.4 (±6.0) | 1 (0.05) |
| Parity (mean ± SD) | 1.58 (±1.87) | 3 (0.1) |
| Multiparity | 1389 (64.3) | |
| Socio-economic status | 126 (5.8) | |
| Higher and intermediate professions | 1329 (61.9) | |
| Other | 611 (28.1) | |
| No occupation | 92 (4.2) | |
| Tobacco use during pregnancy | 525 (24.4) | 80 (3.7) |
| Antidiabetic treatment | 78 (3.7) | 71 (3.3) |
| Cause of prematurity | ||
| Idiopathic premature labor | 826 (37.3) | 74 (3.5) |
| Premature rupture of membranes | 496 (22.7) | 74 (3.5) |
| Vascular placenta pathology | 585 (27.9) | 74 (3.5) |
| Without IUGR | 285 (13.6) | |
| With IUGR | 300 (14.3) | |
| Isolated IUGR | 113 (5.5) | |
| Isolated retro-placental hematoma | 64 (3.1) | |
| Metrorrhagia | 97 (4.5) | 11 (0.5) |
| Maternal infections | 494 (22.2) | 395 (18.2) |
| Other causes of premature birth * | 138 (6.5) | 11 (0.5) |
| Delivery | ||
| Gestational age (GA) (mean ± SD) | 28.7 (±1.997) | 0 |
| ≤27 Weeks GA | 678 (27.4) | |
| (28–32) Weeks GA | 1480 (72.6) | |
| Cesarean | 355 (63.9) | 25 (1.2) |
| Antenatal corticosteroid therapy | 1713 (79.6) | 45 (2.1) |
| Antenatal magnesium sulfate | 195 (9.2) | 36 (1.6) |
| Delayed cord clamping | 87 (4.1) | 96 (4.4) |
| Newborn | ||
| Birth weight, g (mean ± SD) | 1201(±361) | 0 |
| ≤ 1000 g | 785 (33) | |
| >1000 g | 1373 (67) | |
| Male sex | 1129 (52.3) | 370 (16.7) |
| Apgar at 10 min (mean ± SD) | 9.1 (±1.5) | |
| Apgar <7 at 10 min | 106 (4.7) | 370 (16.7) |
| Tracheal intubation | 1266 (56.7) | 51 (2.4) |
| Oxygen therapy | 1552 (71.4) | 94 (4.3) |
| Chest compressions | 116 (5.2) | 86 (3.9) |
| Hb, transfusion, Erythropoietin | ||
| Hb at birth, g/dL (mean ± SD) | 15.4 (±2.4) | 0 |
| Centiles 25 Centile 50 Centiles 75 | 13,8462 15,4000 16,8000 | |
| Hb at birth GA | ||
| 22–25+6, (n = 216) | 13,8 (±2.14) | |
| 26–27+6, (n = 536) | 14,6 (±2.24) | |
| 28–31+6, (n = 1992) | 15,7 (±2.32) | |
| Lowest Hb level during hospitalization, g/dL (mean ± SD) | 10.3 (±3.4) | 107 (5) |
| Hb at discharge, g/L (mean ± SD) | 11 (±1.97) | 500 (22.6) |
| Transfusion | 956 (42) | 27 (1.3) |
| Number of RBC transfusions (mean ± SD) | 2.1 (±1.65) | 12 (1.2) |
| Without erythropoietin | 1101 (51.6) | 21 (0.9) |
| Neonatal morbidity | ||
| Neonatal morbidity ** | 397 (17.2) | 157 (7) |
| Severe BPD | 131 (5.6) | 314 (13.3) |
| Stage 2–3 NEC | 80 (3.6) | 42 (1.8) |
| ROP stage 3–4 | 17 (0.6) | 1348 (63) |
| Severe brain abnormalities | 209 (9) | 38 (1.7) |
| Death (before discharge) | 222 (9.2) | 0 |
| Hb > 15.2 g/dL n (%) | Hb <= 15.2 g/dL n (%) | p-Value | aOR after Multivariate Analysis (CI95%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Death | 89/1181 (6.9) | 133/977 (12.1) | <10–3 | 1.009 (0.703–1.448) | 0.96 |
| Neonatal morbidity * | 184/1104 (15.8) | 213/897 (21.9) | <10–3 | 1.322 (1.003–1.743) | 0.04 |
| Patients N/Total (%) | aOR after Multivariate Analysis | p-Value | aOR after Multivariate Analysis and Imputation | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (IC95%) | (IC95%) | ||||
| 2-year Prognosis | |||||
| Cerebral palsy | 80/1588 (5) | 1.121 (0.646–1.944) | 0.685 | 1.129 (0.639–1.996) | 0.675 |
| High risk of developmental delay * | 835/1512 (55.2) | 0.974 (0.781–1.214) | 0.812 | 0.949 (0.760–1.186) | 0.646 |
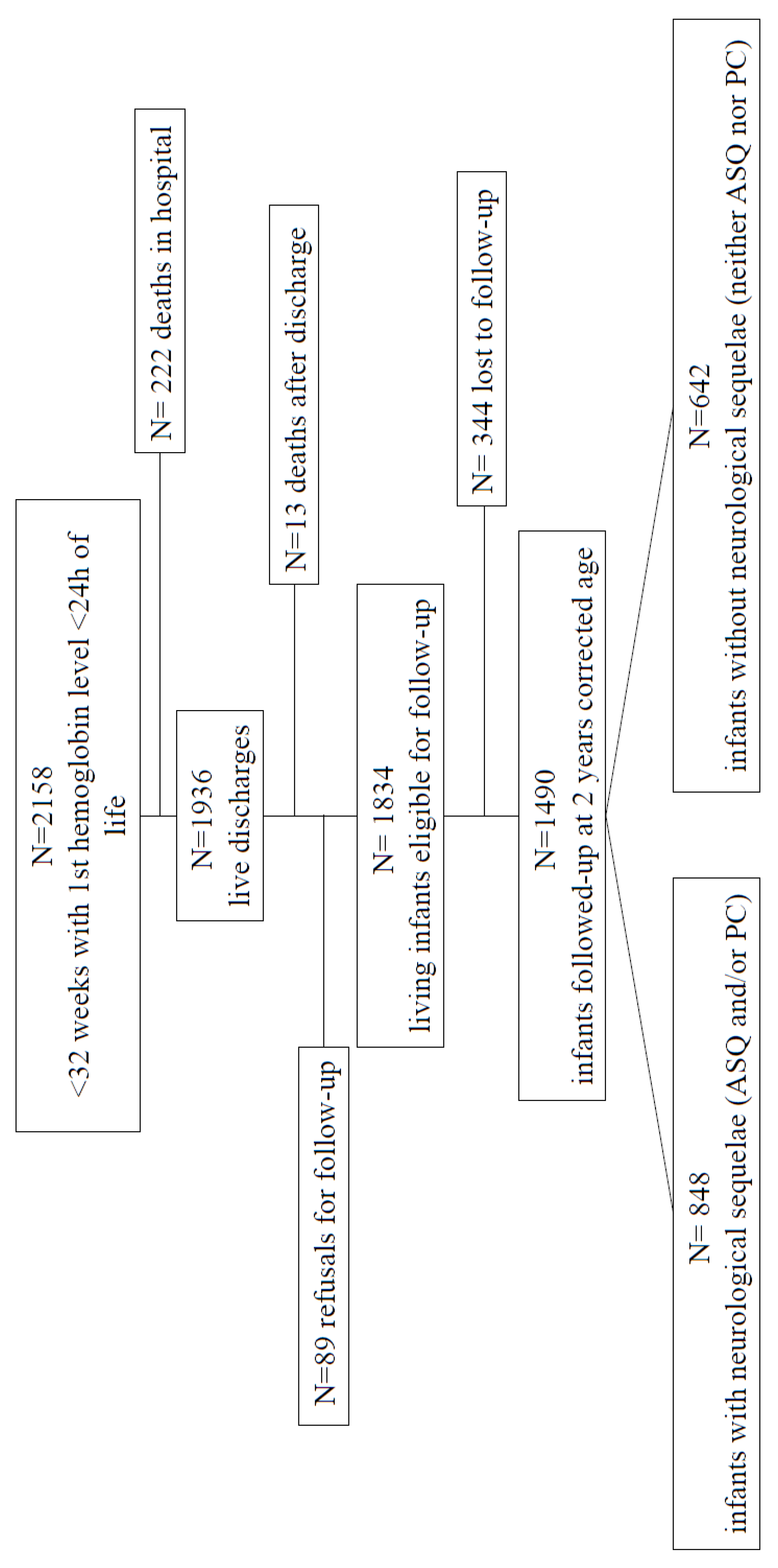
| High risk of developmental delay and/or PC | 848/1490 (57) | 0.961 (0.768–1.203) | 0.731 | 0.960 (0.769–1.200) | 0.723 |
| Alive without sequelae ** | 642/1725 (38.1) | 1.039 (0.833–1.295) | 0.737 | 0.966 (0.775–1.204) | 0.758 |
| Death or disability *** | 1083/1725 (61.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gire, C.; Fournier, N.; Pirrello, J.; Marret, S.; Patural, H.; Flamant, C.; Pierrat, V.; Kaminski, M.; Ancel, P.-Y.; Tosello, B.; et al. Impact of Early Hemoglobin Levels on Neurodevelopment Outcomes of Two-Year-Olds in Very Preterm Children. Children 2023, 10, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020209
Gire C, Fournier N, Pirrello J, Marret S, Patural H, Flamant C, Pierrat V, Kaminski M, Ancel P-Y, Tosello B, et al. Impact of Early Hemoglobin Levels on Neurodevelopment Outcomes of Two-Year-Olds in Very Preterm Children. Children. 2023; 10(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleGire, Catherine, Ninon Fournier, Johanna Pirrello, Stéphane Marret, Hugues Patural, Cyril Flamant, Véronique Pierrat, Monique Kaminski, Pierre-Yves Ancel, Barthélémy Tosello, and et al. 2023. "Impact of Early Hemoglobin Levels on Neurodevelopment Outcomes of Two-Year-Olds in Very Preterm Children" Children 10, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020209
APA StyleGire, C., Fournier, N., Pirrello, J., Marret, S., Patural, H., Flamant, C., Pierrat, V., Kaminski, M., Ancel, P.-Y., Tosello, B., & Berbis, J. (2023). Impact of Early Hemoglobin Levels on Neurodevelopment Outcomes of Two-Year-Olds in Very Preterm Children. Children, 10(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020209






