Comparative Analysis of the GH/IGF-1 Axis during the First Sixth Months in Children with Low Birth Weight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Nutrition Targets 2025: Low Birth Weight Policy Brief; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NMH-NHD-14.5 (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- Rechia, I.C.; Oliveira, L.D.; Crestani, A.H.; Biaggio, E.P.V.; de Souza, A.P.R. Efeitos da prematuridade na aquisição da linguagem e na maturação auditiva: Revisão sistemática. CoDAS 2016, 28, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil, Ministério da Saúde. Caderno de Atenção Básica-Atenção ao Pré-Natal de Baixo Risco [Internet]; Departamento de Atenção Básica, Editora do Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2012; Volume 32. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/cadernos_atencao_basica_32_prenatal.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- World Health Organization. Um em Cada Sete Bebês em Todo o Mundo Nascem Com Baixo Peso. Perspectiva Global Reportagens Humanas. 2019. Available online: https://news.un.org/pt/story/2019/05/1672441 (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- Pessoa, T.A.O.; de Godoy Martins, C.B.; Aguiar Lima, F.C.; Munhoz Gaíva, M.A. O crescimento e desenvolvimento frente à prematuridade e baixo peso ao nascer. Av. Enferm. 2015, 33, 401–411. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn-Santos, R.C.; Suano-Souza, F.I.; Puccini, R.F.; Strufaldi, M.W.L. Fatores associados ao excesso de peso e baixa estatura em escolares nascidos com baixo peso. Cien. Saude Colet. 2019, 24, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescador, M.V.B.; Streher, A.A.F.; da Silva, J.M.F.; Valente, G.C.C.; Nakagiri, M.; Boguszewski, M.C.S. Aspectos Endocrinológicos das Crianças e Adultos Nascidos Pequenos para a Idade Gestacional. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 45, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismarck-Nasr, E.M.; Frutuoso, M.F.P.; Gamabardella, A.M.D. Efeitos tardios do baixo peso ao nascer. Rev. Bras. Desenvolv. Hum. 2008, 1, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lobato, J.C.P.; Costal, A.J.L.; Kele, P.L.; Cavalcanti, M.L.T.; Kuschnir, M.C.C.; Velard, L.G.C.; Nóbrega, A.C.L.d.; Olej, B.; Duarte, L.d.B.; Szklo, M. Programação fetal e alterações metabólicas em escolares: Metodologia de um estudo caso-controle. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2016, 19, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heijmans, B.T.; Tobi, E.W.; Stein, A.D.; Putter, H.; Blauw, G.J.; Susser, E.S.; Lumey, L.H. Persistent epigenetic differences associated with prenatal exposure to famine in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17046–17049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.; Cardenas, A.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Pan, H.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Oken, E.; Hivert, M.-F.; James-Todd, T.; Patti, M.-E.; Isganaitis, E. Association of Periconception Paternal Body Mass Index with Persistent Changes in DNA Methylation of Offspring in Childhood. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1916777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne-Majnik, A.; Fu, Q.; Lane, R.H. Epigenetic mechanisms in fetal origins of health and disease. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 56, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Yu, X.; Callaway, C.W.; Lane, R.H.; McKnight, R.A. Epigenetics: Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) modifies the histone code along the rat hepatic IGF–1 gene. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2438–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Lima, M.C.; de Lira, P.I.C.; da Silva, G.A.P. Baixo peso ao nascer e obesidade: Associação causal ou casual? Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2015, 33, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, A. On the importance—And the unimportance—Of birthweight. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 30, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pico, C.; Palou, A. Perinatal programming of obesity: An introduction to the topic. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, P.F.; Hansen, M.; Frystyk, J.; Espelund, U.; Christiansen, J.S.; Jorgensen, J.O.L.; Fisker, S. Serum levels of bioactive IGF1 and physiological markers of ageing in healthy adults. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 170, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupu, F.; Terwilliger, J.D.; Lee, K.; Segre, G.V.; Efstratiadis, A. Roles of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in mouse postnatal growth. Dev. Biol. 2001, 229, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.J.; Waters, M.J. The growth hormone receptor: Mechanism of activation and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, N.; Barkan, A. Factors regulating growth hormone secretion in humans. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, P.E. Genetics of growth hormone deficiency. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde (BR), Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde. Atenção à Saúde do Recém-Nascido: Guia para os Profissionais de Saúde. Brasília (DF). 2014. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/atencao_saude_recem_nascido_v1.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- Fávero, L.P. Métodos Quantitativos com Stata Ebook; Grupo GEN: Barueri, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- de Barros, M.V.G.; Hallal, P.C.; Florindo, A.A.; de Farias Júnior, J.D. Análise de Dados em Saúde, 1st ed.; Midiograf: Londrina, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, S. Introdução à Bioestatística, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aline, B.V.C.; Andréa, R. Prematuridade e Baixo Peso ao Nascimento e Sua Associação com Fatores de Risco Cardiovascular em Adolescentes. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Regional do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016. Available online: http://www.ppgn.ufrj.br/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/TESE-Aline-Bull-Ferreira-Campos.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- Remmers, F.; Delemarre-van de Wall, H.A. Developmental programming of energy balance and its hypothalamic regulation. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 272–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Low Birthweight. 2023. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/nutrition/low-birthweight (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- Reynolds, R.M.; Phillips, D.I.W. Long-term consequences of intrauterine growth retardation. Horm. Res. 1998, 49 (Suppl. S2), 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfon, N.; Larson, K.; Lu, M.; Tullis, E.; Russ, S. Lifecourse health development: Past, present and future. Matern. Child Health J. 2014, 18, 344–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco-Solís, R.; Matos, R.J.B.; Guzmán-Quevedo, O.; de Souza, S.L.; Bihouée, A.; Houlgatte, R.; de Castro, R.M.; Bolaños-Jiménez, F. Nutritional Programming in the Rat Is Linked to Long-Lasting Changes in Nutrient Sensing and Energy Homeostasis in the Hypothalamus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley-Evans, S.C. Developmental programming of health and disease. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2006, 65, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labayen, I.; Ruiz, J.R.; Huybrechts, I.; Ortega, F.B.; Rodríguez, G.; DeHenauw, S.; Breidenassel, C.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Vyncke, K.E.; Censi, L.; et al. Sexual Dimorphism in the Early Life Programming of Serum Leptin Levels in European Adolescents: The HELENA Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1330–E1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouret, S.G.; Simerly, R.B. Developmental programming of hypothalamic feeding circuits. Clin. Genet. 2006, 70, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newnham, J.P.; Pennell, C.E.; Lye, S.J.; Rampono, J.; Challis, J.R.G. Early life origins of obesity. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 36, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthaya, S.; Thomas ELHamilton, G.; Doré, C.J.; Bell, J.; Modi, N. Altered adiposity after extremely preterm birth. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmrayed, S.; Ye, X.Y.; Zhu, J.; Hanley, J.A. Are small-for-gestational-age preterm infants at increased risk of overweight? Statistical pitfalls in overadjustment for body size. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, P.L.; Regan, F.; Jackson, W.E.; Jefferies, C.; Knight, D.B.; Robinson, E.M. Premature birth and later insulin resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2179–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteels, K.; Ong, K.; Phillips, D.; Bendall, H.; Pembrey, M. Mitochondrial 16189 variant, thinness at birth, and type-2 diabetes. ALSPAC study team. Avon Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood. Lancet 1999, 353, 1499–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, C.R.P.; Salvatori, R.; Meneguz-Moreno, R.A.; Aguiar-Oliveira, M.H.; Pereira, R.M.C.; Valença, E.H.A.; Araujo, V.P.; Farias, N.T.; Silveira, D.C.R.; Vieira, J.G.H.; et al. Adipokine profile and urinary albumin excretion in isolated growth hormone deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, N.; Gjedsted, J.; Gormsen, L.; Fuglsang, J.; Djurhuus, C. Effects of growth hormone on lipid metabolism in humans. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2003, 13 (Suppl. A), S18–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakharova, A.A.; Horowitz, J.F.; Surya, S.; Goldenberg, N.; Harber, M.P.; Symons, K.; Barkan, A. Role of growth hormone in regulating lipolysis, proteolysis, and hepatic glucose production during fasting. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2755–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silveira, V.M.F.; Horta, B.L. Peso ao nascer e síndrome metabólica em adultos: Meta-análise. Rev. Saude Publica 2008, 42, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Soto, I.N.M.; Mericq, G.V. Restricción del crecimiento fetal e insulinorresistencia: Nuevos hallazgos y revisión de la literatura. Rev. Med. Chile 2005, 133, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hypponen, E.; Power, C.; Smith, G.D. Prenatal growth, BMI, and risk of type 2 diabetes by early midlife. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2512–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, C.N.; Barker, D.J.; Clark, P.M.; Cox, L.J.; Fall, C.; Osmond, C.; Winter, P.D. Fetal and infant growth and impaired glucose tolerance at age 64. BMJ 1991, 303, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Bull, A.R.; Osmond, C.; Simmonds, S.J. Fetal and placental size and risk of hypertension in adult life. BMJ 1990, 301, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A.; Spencer, H.G.; Bateson, P. Environmental influences during development and their later consequences for health and disease: Implications for the interpretation of empirical studies. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.K.; Loos, R.J.F. Rapid infancy weight gain and subsequent obesity: Systematic reviews and hopeful suggestions. Acta Pediatr. 2006, 95, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlee, S.D.; MacDougald, O.A. Maternal nutrition and risk of obesity in offspring: The Trojan horse of developmental plasticity. Biochim. Bophysica Acta 2014, 1842, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Ross, M.G. Fetal programming of adipose tissue: Effects of intrauterine growth restriction and maternal obesity/high-fat diet. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2011, 29, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All Newborns | Newborns with Normal Birth Weight | Newborns with Low Birth Weight | p Value | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | n | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | n | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | ||
| Approximate gestational age | 30 | 37 | 3 | 27 | 41 | 15 | 39 | 1 | 37 | 41 | 15 | 35 | 3 | 27 | 36 | 0.000 * |
| Birth weight | 30 | 2616 | 830 | 965 | 3985 | 15 | 3324 | 466 | 2520 | 3985 | 15 | 1908 | 368 | 965 | 2465 | 0.000 ** |
| Weight at 3 months | 25 | 6744 | 757 | 5400 | 8000 | 12 | 6704 | 805 | 5700 | 8000 | 13 | 6780 | 740 | 5400 | 7900 | 0.808 ** |
| Weight at 6 months | 25 | 9298 | 1420 | 7100 | 13,000 | 12 | 9038 | 1447 | 7495 | 13,000 | 13 | 9538 | 1407 | 7100 | 11,300 | 0.390 ** |
| Weight gain at 3 months | 25 | 4116 | 1080 | 2370 | 5915 | 12 | 3374 | 880 | 2370 | 5290 | 13 | 4800 | 752 | 3615 | 5915 | 0.000 ** |
| Weight gain from the third to the sixth month | 25 | 2555 | 1252 | 120 | 6100 | 12 | 2334 | 1562 | 120 | 6100 | 13 | 2758 | 898 | 1400 | 4200 | 0.408 ** |
| Total weight gain (from birth to the sixth month) | 25 | 6670 | 1627 | 4370 | 9315 | 12 | 5708 | 1250 | 4370 | 9015 | 13 | 7559 | 1443 | 5315 | 9315 | 0.004 * |
| Length of hospital stay, days | 30 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 22 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 5 | 9 | 0 | 22 | 0.622 * |
| All Newborns | Newborns with Normal Birth Weight | Newborns with Low Birth Weight | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Gestational age classification | |||||||
| Preterm (<37 weeks) | 16 | 53.3 | 1 | 6.7 | 15 | 100.0 | 0.000 * |
| Term (37 to 41 weeks) | 14 | 46.7 | 14 | 93.3 | - | ||
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 15 | 50.0 | 7 | 46.7 | 8 | 53.3 | 0.715 * |
| Female | 15 | 50.0 | 8 | 53.3 | 7 | 46.7 | |
| Classification of weight at 3 months | |||||||
| Normal weight | 18 | 75.0 | 8 | 72.7 | 10 | 76.9 | 1.000 ** |
| Overweight | 6 | 25.0 | 3 | 27.3 | 3 | 23.1 | |
| Classification of weight at 6 months | |||||||
| Normal weight | 14 | 56.0 | 8 | 66.7 | 6 | 46.2 | 0.233 ** |
| Overweight | 5 | 20.0 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 15.4 | |
| Obesity | 6 | 24.0 | 1 | 8.3 | 5 | 38.5 | |
| Classification of birth weight | |||||||
| Normal weight | 15 | 50.0 | 15 | 100.0 | - | 0.000 * | |
| Low weight | 15 | 50.0 | - | 15 | 100.0 | ||
| Type of delivery | |||||||
| Vaginal | 24 | 80.0 | 15 | 100.0 | 9 | 60.0 | 0.017 ** |
| Cesarean | 6 | 20.0 | - | 6 | 40.0 | ||
| Complications during delivery | |||||||
| No | 23 | 76.7 | 15 | 100.0 | 8 | 53.3 | 0.006 ** |
| Yes | 7 | 23.3 | - | 7 | 46.7 | ||
| GH/IGF-1 curve, at birth | |||||||
| Normal | 7 | 28.0 | 7 | 58.3 | - | 0.002 ** | |
| Altered | 18 | 72.0 | 5 | 41.7 | 13 | 100.0 | |
| GH/IGF-1 curve, at 3 months | |||||||
| Normal | 13 | 52.0 | 9 | 75.0 | 4 | 30.8 | 0.027 * |
| Altered | 12 | 48.0 | 3 | 25.0 | 9 | 69.2 | |
| GH/IGF-1 curve, at 6 months | |||||||
| Normal | 20 | 76.9 | 12 | 100.0 | 8 | 57.1 | 0.017 ** |
| Altered | 6 | 23.1 | - | 6 | 42.9 | ||
| Postpartum referral | |||||||
| Rooming-in | 20 | 66.7 | 15 | 100.0 | 5 | 33.3 | 0.000 ** |
| Internal nursery | 8 | 26.7 | 8 | 53.3 | |||
| Intensive care unit | 2 | 6.7 | 2 | 13.3 | |||
| Breastfed within the first hour of life | |||||||
| No | 17 | 56.7 | 3 | 20.0 | 14 | 93.3 | 0.000 * |
| Yes | 13 | 43.3 | 12 | 80.0 | 1 | 6.7 | |
| Reason for not breastfeeding with the first hour | |||||||
| Mother not producing milk | 1 | 5.9 | 1 | 33.3 | 0.010 ** | ||
| Respiratory distress | 10 | 58.8 | 10 | 71.4 | |||
| Mother referred to the intensive care unit and respiratory distress | 2 | 11.8 | 2 | 14.3 | |||
| Newborn dyspnea | 1 | 5.9 | 1 | 7.1 | |||
| Lethargic newborn | 2 | 11.8 | 2 | 66.7 | |||
| Ventilatory support | 1 | 5.9 | 1 | 7.1 | |||
| All Newborns | Normal Weight | Low Weight | p Value | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | SD | Min | Max | n | Mean | SD | Min | Max | n | Mean | SD | Min | Max | ||
| GH & result, at birth | 30 | 15.6 | 9.4 | 1.4 | 37.8 | 15 | 11.9 | 9.4 | 1.4 | 37.8 | 15 | 19.4 | 7.9 | 6.6 | 34.8 | 0.011 * |
| IGF-1 & result, at birth | 30 | 43.0 | 19.0 | 14.0 | 78.0 | 15 | 44.9 | 20.8 | 18.0 | 78.0 | 15 | 41.1 | 17.6 | 14.0 | 76.0 | 0.593 ** |
| GH & result, third month | 25 | 5.5 | 3.5 | 0.6 | 12.0 | 12 | 4.3 | 3.8 | 0.6 | 12.0 | 13 | 6.7 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 11.5 | 0.083 ** |
| IGF-1 & result, third month | 25 | 50.9 | 19.8 | 20.0 | 91.0 | 12 | 45.9 | 18.9 | 20.0 | 71.0 | 13 | 55.5 | 20.2 | 28.0 | 91.0 | 0.236 ** |
| GH & result, sixth month | 25 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 18.0 | 12 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 4.0 | 13 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 0.3 | 18.0 | 0.008 * |
| IGF-1 & result, sixth month | 25 | 44.0 | 28.9 | 15.0 | 126.0 | 12 | 44.8 | 28.6 | 20.0 | 126.0 | 13 | 43.2 | 30.3 | 15.0 | 97.0 | 0.479 * |
| GH & at Birth | IGF-1 & at Birth | GH & at 3 Months | IGF-1 & at 3 Months | GH & at 6 Months | IGF-1 & at 6 Months | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | p Value | Coef. | p Value | Coef. | p Value | Coef. | p Value | Coef. | p Value | Coef. | p Value | |
| All newborns | ||||||||||||
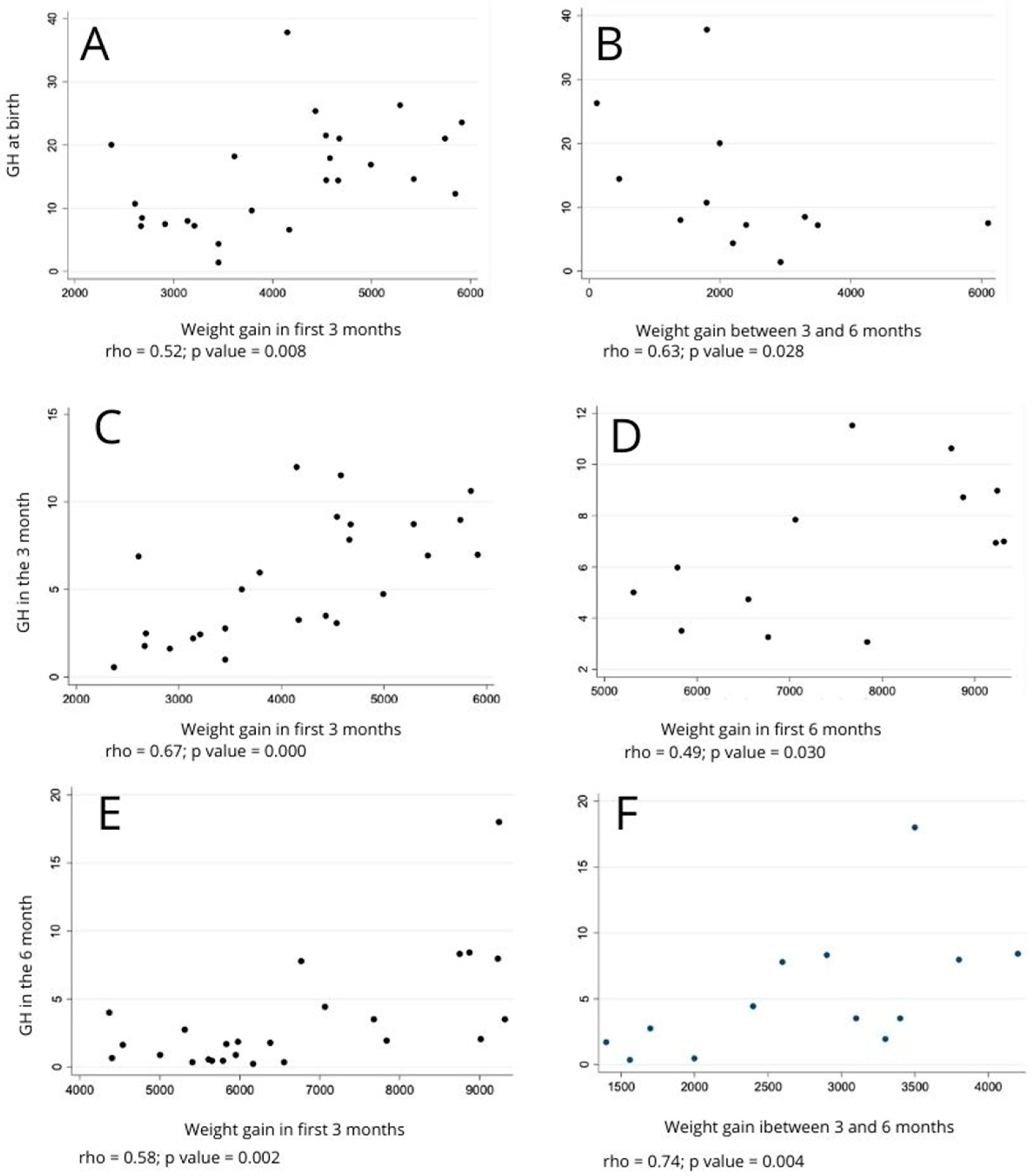
| Weight gain during the first 3 months | 0.52 | 0.008 ** | −0.21 | 0.323 * | 0.67 | 0.000 * | 0.09 | 0.686 * | ||||
| Weight gain between the third and sixth month | −0.16 | 0.431 ** | 0.10 | 0.627 * | −0.15 | 0.472 * | 0.47 | 0.018 * | 0.53 | 0.007 ** | −0.02 | 0.913 ** |
| Weight gain during the first 6 months | 0.14 | 0.514 ** | −0.06 | 0.782 * | 0.29 | 0.154 ** | 0.39 | 0.054 ** | 0.58 | 0.002 ** | −0.07 | 0.732 ** |
| Newborns with low birth weight | ||||||||||||
| Weight gain during the first 3 months | 0.16 | 0.591 ** | −0.01 | 0.972 * | 0.48 | 0.099 * | 0.40 | 0.171 * | ||||
| Weight gain between the third and sixth month | 0.17 | 0.578 ** | −0.02 | 0.946 * | 0.48 | 0.093 * | 0.34 | 0.253 * | 0.74 | 0.004 ** | 0.09 | 0.760 ** |
| Weight gain during the first 6 months | 0.27 | 0.364 ** | −0.02 | 0.952 * | 0.49 | 0.030 ** | 0.39 | 0.187 ** | 0.69 | 0.009 ** | 0.10 | 0.753 ** |
| Newborns with normal birth weight | ||||||||||||
| Weight gain during the first 3 months | 0.15 | 0.640 ** | −0.45 | 0.144 * | 0.72 | 0.009 * | −0.63 | 0.029 * | ||||
| Weight gain between the third and sixth month | −0.63 | 0.028 ** | 0.18 | 0.586 * | −0.56 | 0.060 * | 0.55 | 0.061 * | 0.22 | 0.485 ** | −0.27 | 0.397 ** |
| Weight gain during the first 6 months | −0.52 | 0.085 ** | −0.10 | 0.766 * | −0.04 | 0.897 * | 0.17 | 0.587 ** | 0.01 | 0.983 ** | −0.31 | 0.330 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diniz, L.P.M.; Cavalcante, T.C.F.; da Silva, A.A.M. Comparative Analysis of the GH/IGF-1 Axis during the First Sixth Months in Children with Low Birth Weight. Children 2023, 10, 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121842
Diniz LPM, Cavalcante TCF, da Silva AAM. Comparative Analysis of the GH/IGF-1 Axis during the First Sixth Months in Children with Low Birth Weight. Children. 2023; 10(12):1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121842
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiniz, Luciana Pessoa Maciel, Taisy Cinthia Ferro Cavalcante, and Amanda Alves Marcelino da Silva. 2023. "Comparative Analysis of the GH/IGF-1 Axis during the First Sixth Months in Children with Low Birth Weight" Children 10, no. 12: 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121842
APA StyleDiniz, L. P. M., Cavalcante, T. C. F., & da Silva, A. A. M. (2023). Comparative Analysis of the GH/IGF-1 Axis during the First Sixth Months in Children with Low Birth Weight. Children, 10(12), 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121842








