Cortical Thinning of Motor and Non-Motor Brain Regions Enables Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Supports Distinction between Upper- and Lower-Motoneuron Phenotypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients and Controls
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subjects
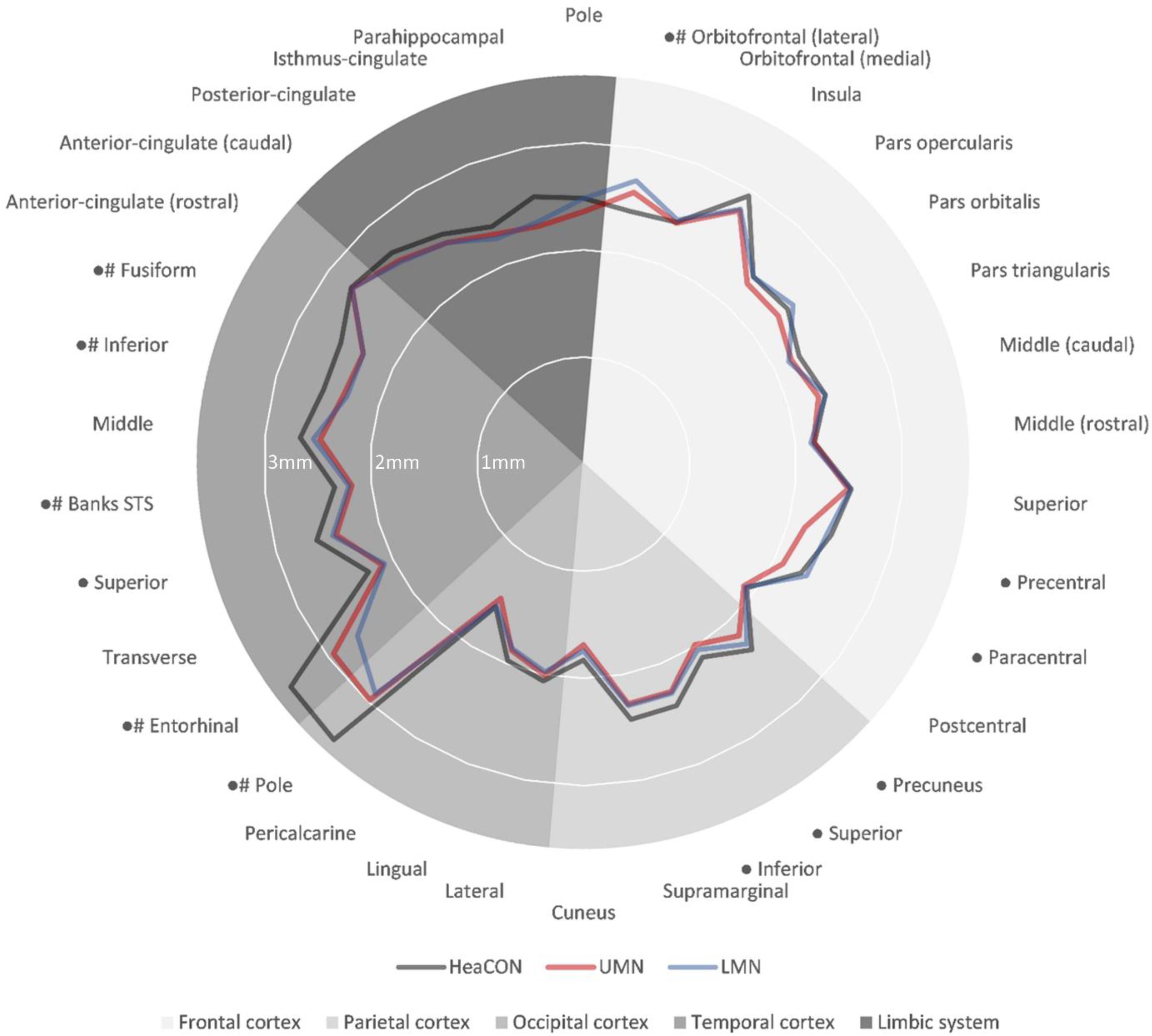
3.2. CT
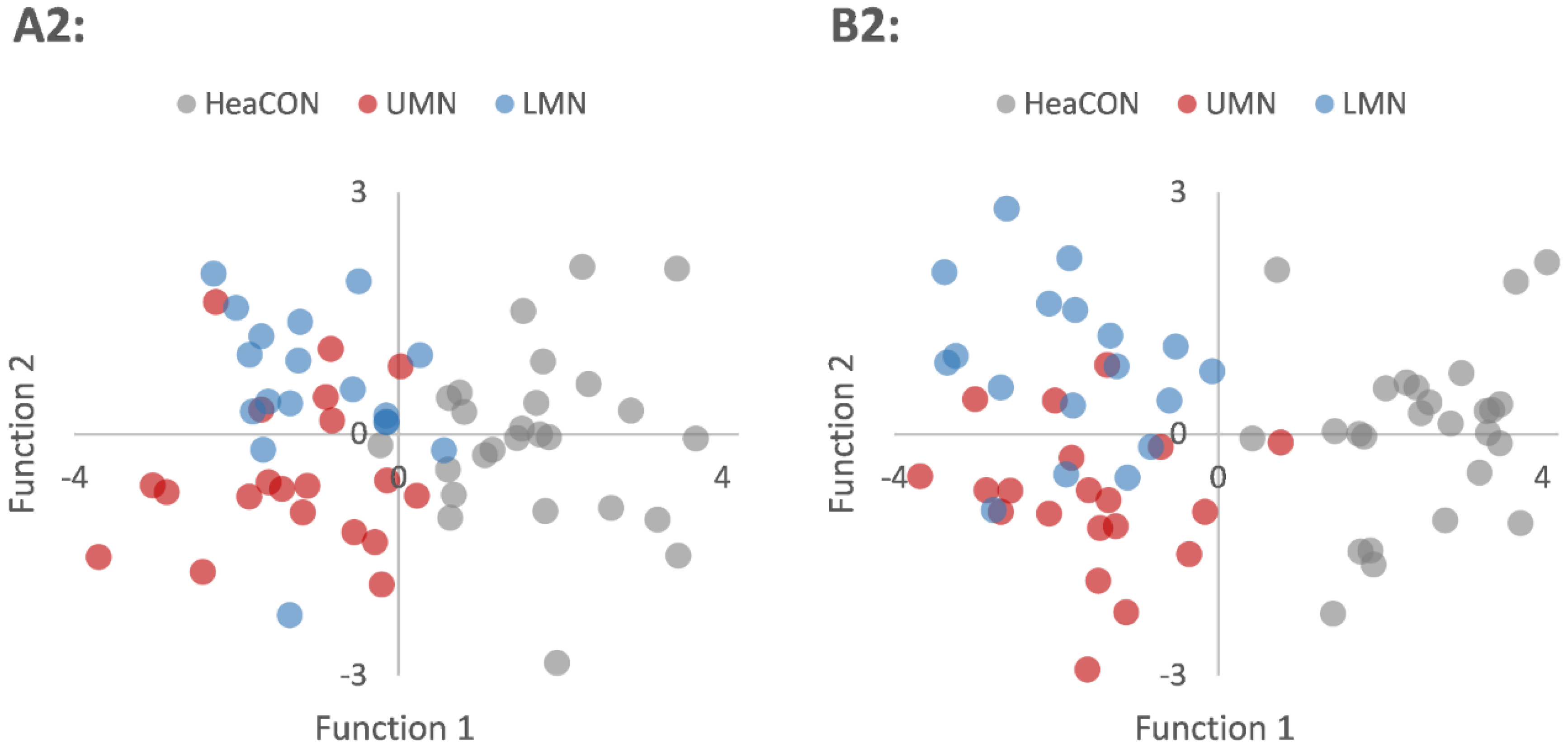
3.3. Classification—Discriminant Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| ALSFRS-R | revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale |
| CT | cortical thickness |
| CT-A | cortical thickness analysis |
| FOV | field of view |
| FTD | frontotemporal dementia |
| HeaCON | healthy controls |
| LE | lower extremity |
| LMN | lower motor neuron |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| PCG | precentral gyrus |
| ROI | region of interest |
| UE | upper extremity |
| UMN | upper motor neuron |
References
- Cetin, H.; Rath, J.; Füzi, J.; Reichardt, B.; Fülöp, G.; Koppi, S.; Erdler, M.; Ransmayr, G.; Weber, J.; Neumann, K.; et al. Epidemiology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Effect of Riluzole on Disease Course. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 44, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grad, L.I.; Rouleau, G.A.; Ravits, J.; Cashman, N.R. Clinical Spectrum of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a024117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzarotti, B.; Palesi, F.; Vitali, P.; Castellazzi, G.; Anzalone, N.; Alvisi, E.; Martinelli, D.; Bernini, S.; Ramusino, M.C.; Ceroni, M.; et al. Frontal and Cerebellar Atrophy Supports FTSD-ALS Clinical Continuum. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 593526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Sato, K.; Takemoto, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Morihara, R.; Nakano, Y.; Tsunoda, K.; Nomura, E.; Hishikawa, N.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Behavioral and affective features of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 381, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libonati, L.; Barone, T.F.; Ceccanti, M.; Cambieri, C.; Tartaglia, G.; Onesti, E.; Petrucci, A.; Frasca, V.; Inghilleri, M. Heteronymous H reflex in temporal muscle as sign of hyperexcitability in ALS patients. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, B.; Robberecht, W. The phenotypic variability of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huynh, W.; Simon, N.G.; Grosskreutz, J.; Turner, M.; Vucic, S.; Kiernan, M.C. Assessment of the upper motor neuron in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2643–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie, Leitlinien der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Neurologie. Available online: https://dgn.org/leitlinien/ll-18-ll-amyotrophe-lateralsklerose-motoneuronerkrankungen/ (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Schuster, C.; Kasper, E.; Machts, J.; Bittner, D.; Kaufmann, J.; Benecke, R.; Teipel, S.; Vielhaber, S.; Prudlo, J. Focal thinning of the motor cortex mirrors clinical features of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and their phenotypes: A neuroimaging study. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2856–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contarino, V.E.; Conte, G.; Morelli, C.; Trogu, F.; Scola, E.; Calloni, S.F.; Serpa, L.C.S.; Liu, C.; Silani, V.; Triulzi, F. Toward a marker of upper motor neuron impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A fully automatic investigation of the magnetic susceptibility in the precentral cortex. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 124, 108815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Hu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Qin, X.; Jia, R.; Kang, L.; Dang, Y.; Dang, J. Dominant Heterogeneity of Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Degeneration to Motor Manifestation of Involved Region in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, M.; Esposito, F.; Tedeschi, G.; Caiazzo, G.; Sagnelli, A.; Piccirillo, G.; Conforti, R.; Tortora, F.; Monsurrò, M.R.; Cirillo, S.; et al. Widespread microstructural white matter involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A whole-brain DTI study. ANJN Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douaud, G.F.; Mackay, C.E.; Knight, S.; Talbot, K.; Turner, M.R. Corpus callosum involvement is a consistent feature of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 2010, 75, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Devine, M.S.; Pannek, K.; Coulthard, A.; McCombe, P.A.; Rose, S.E.; Henderson, R.D. Exposing asymmetric gray matter vulnerability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NeuroImage: Clin. 2015, 7, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walhout, R.; Westeneng, H.-J.; Verstraete, E.; Hendrikse, J.; Veldink, J.H.; Heuvel, M.V.D.; Berg, L.H.V.D. Cortical thickness in ALS: Towards a marker for upper motor neuron involvement. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 86, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, S.M.; Menon, P.; Korgaonkar, M.S.; Gomes, L.; Foster, S.; Kiernan, M.C.; Vucic, S. Potential structural and functional biomarkers of upper motor neuron dysfunction in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 17, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Valsasina, P.; Riva, N.; Copetti, M.; Messina, M.J.; Prelle, A.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. The Cortical Signature of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Structural and functional underpinnings of precentral abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, M.; Bella, E.D.; Contarino, V.E.; Bersano, E.; Lauria, G. Cortical thinning trajectories across disease stages and cognitive impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cortex 2020, 131, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consonni, M.; Contarino, V.E.; Catricalà, E.; Bella, E.D.; Pensato, V.; Gellera, C.; Lauria, G.; Cappa, S. Cortical markers of cognitive syndromes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 19, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L.; World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor. Neuron. Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedarbaum, J.M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E.; Fuller, C.; Hilt, D.; Thurmond, B.; Nakanishi, A. The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 169, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casjens, S.; Dydak, U.; Dharmadhikari, S.; Lotz, A.; Lehnert, M.; Quetscher, C.; Stewig, C.; Glaubitz, B.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Edmondson, D.; et al. Association of exposure to manganese and iron with striatal and thalamic GABA and other neurometabolites—Neuroimaging results from the WELDOX II study. NeuroToxicology 2018, 64, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walhout, R.; Schmidt, R.; Westeneng, H.-J.; Verstraete, E.; Seelen, M.; Van Rheenen, W.; De Reus, M.A.; van Es, M.A.; Hendrikse, J.; Veldink, J.H.; et al. Brain morphologic changes in asymptomaticC9orf72repeat expansion carriers. Neurology 2015, 85, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, C.; Kasper, E.; Machts, J.; Bittner, D.; Kaufmann, J.; Benecke, R.; Teipel, S.; Vielhaber, S.; Prudlo, J. Longitudinal course of cortical thickness decline in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiò, A.; Pagani, M.; Agosta, F.; Calvo, A.; Cistaro, A.; Filippi, M. Neuroimaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Insights into structural and functional changes. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojsi, F.; D’Alvano, G.; Bonavita, S.; Tedeschi, G. Genetics and Sex in the Pathogenesis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): Is There a Link? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, J.; Grose, J. The effects of diet and sex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 176, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, P.; Elamin, M.; Byrne, S.; Hardiman, O. Sexual dimorphism in ALS: Exploring gender-specific neuroimaging signatures. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2013, 15, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.; Abrahams, S.; Goldstein, L.; Woolley, S.; Mclaughlin, P.; Snowden, J.; Mioshi, E.; Roberts-South, A.; Benatar, M.; Hortobágyi, T.; et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—Frontotemporal spectrum disorder (ALS-FTSD): Revised diagnostic criteria. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2017, 18, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Localization | Distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex/Areal | HeaCON | UMN | LMN | |
| Frontal | Pole | 0.481 | 0.404 | 0.211 |
| Orbitofrontal-lateral | 0.016 | 0.820 | 0.241 | |
| Orbitofrontal-medial | 0.329 | 0.224 | 0.025 | |
| Insula | 0.991 | 0.291 | 0.683 | |
| Pars opercularis | 0.523 | 0.794 | 0.732 | |
| Pars orbitalis | 0.502 | 0.920 | 0.562 | |
| Pars triangularis | 0.521 | 0.036 | 0.623 | |
| Middle-caudal | 0.955 | 0.902 | 0.979 | |
| Middle-rostral | 0.837 | 0.195 | 0.160 | |
| Superior | 0.730 | 0.246 | 0.261 | |
| Precentral | 0.905 | 0.451 | 0.037 | |
| Paracentral | 0.472 | 0.954 | 0.364 | |
| Parietal | Postcentral | 0.219 | 0.206 | 0.129 |
| Precuneus | 0.413 | 0.029 | 0.431 | |
| Superior | 0.427 | 0.703 | 0.061 | |
| Inferior | 0.452 | 0.971 | 0.222 | |
| Supramarginal | 0.566 | 0.287 | 0.043 | |
| Occipital | Cuneus | 0.464 | 0.705 | 0.293 |
| Lateral | 0.561 | 0.417 | 0.552 | |
| Lingual | 0.261 | 0.786 | 0.897 | |
| Pericalcarine | 0.434 | 0.745 | 0.375 | |
| Temporal | Pole | 0.043 | 0.009 | 0.446 |
| Entorhinal | 0.344 | 0.921 | 0.901 | |
| Transverse | 0.935 | 0.796 | 0.335 | |
| Superior | 0.660 | 0.095 | 0.290 | |
| Banks of superior sulcus | 0.888 | 0.798 | 0.739 | |
| Middle | 0.173 | 0.864 | 0.123 | |
| Inferior | 0.637 | 0.443 | 0.575 | |
| Fusiform | 0.959 | 0.350 | 0.531 | |
| Limbic | Anterior cingulate-rostral | 0.870 | 0.611 | 0.994 |
| Anterior cingulate-caudal | 0.322 | 0.670 | 0.319 | |
| Posterior-cingulate | 0.882 | 0.507 | 0.291 | |
| Isthmus of cingulate | 0.247 | 0.981 | 0.368 | |
| Parahippocampal | 0.041 | 0.173 | 0.760 | |
| HeaCON | UMN | LMN | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | Sum: | 26/0 | 11/9 | 14/4 | 0.139 * |
| Age (years) | Median: | 56.5 | 57.5 | 65.5 | 0.059 |
| IQR: | 14.8 | 18 | 13 | ||
| ALSFRS-R-score | Median: | - | 35 | 39.5 | 0.202 * |
| IQR: | - | 7.5 | 8 |
| Localization | Cortical Thickness (mm) | Statistics | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex/Areal | HeaCON | UMN | LMN | Quade Test | Post-Hoc (p-Value) | ||||||
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Median | IQR | p-value | HeaCON–UMN | HeaCON–LMN | UMN–LMN | ||
| Frontal | Pole | 2.48 | 0.3 | 2.36 | 0.2 | 2.48 | 0.2 | 1 | - | ||
| Orbitofrontal-lateral | 2.40 | 0.5 | 2.58 | 0.4 | 2.69 | 0.3 | 0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.936 | |
| Orbitofrontal-medial | 2.42 | 0.2 | 2.42 | 0.2 | 2.44 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Insula | 2.95 | 0.2 | 2.78 | 0.2 | 2.80 | 0.2 | 0.934 | - | |||
| Pars opercularis | 2.37 | 0.5 | 2.28 | 0.4 | 2.37 | 0.7 | 0.73 | - | |||
| Pars orbitalis | 2.40 | 0.2 | 2.29 | 0.2 | 2.47 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Pars triangularis | 2.26 | 0.2 | 2.18 | 0.2 | 2.15 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Middle-caudal | 2.36 | 0.2 | 2.29 | 0.2 | 2.36 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Middle-rostral | 2.18 | 0.3 | 2.17 | 0.3 | 2.14 | 0.3 | 1 | - | |||
| Superior | 2.53 | 0.2 | 2.50 | 0.2 | 2.52 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Precentral | 2.42 | 0.2 | 2.16 | 0.3 | 2.38 | 0.3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.866 | <0.001 | |
| Paracentral | 2.29 | 0.2 | 2.09 | 0.1 | 2.34 | 0.2 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Parietal | Postcentral | 1.92 | 0.1 | 1.89 | 0.2 | 1.90 | 0.1 | 1 | - | ||
| Precuneus | 2.35 | 0.2 | 2.17 | 0.2 | 2.28 | 0.1 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.793 | 0.007 | |
| Superior | 2.12 | 0.3 | 2.00 | 0.5 | 2.04 | 0.4 | 0.01 | <0.001 | 0.538 | 0.032 | |
| Inferior | 2.42 | 0.2 | 2.28 | 0.2 | 2.29 | 0.2 | 0.01 | <0.001 | 0.334 | 0.057 | |
| Supramarginal | 2.42 | 0.2 | 2.28 | 0.2 | 2.29 | 0.1 | 0.052 | - | |||
| Occipital | Cuneus | 1.83 | 0.3 | 1.69 | 0.3 | 1.75 | 0.3 | 0.183 | - | ||
| Lateral | 2.06 | 0.2 | 2.00 | 0.2 | 1.97 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Lingual | 1.97 | 0.2 | 1.87 | 0.2 | 1.85 | 0.2 | 0.167 | - | |||
| Pericalcarine | 1.57 | 0.2 | 1.48 | 0.1 | 1.55 | 0.1 | 1 | - | |||
| Temporal | Pole | 3.48 | 0.2 | 3.00 | 0.2 | 2.90 | 0.1 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1 |
| Entorhinal | 3.45 | 0.2 | 2.94 | 0.2 | 2.66 | 0.1 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.92 | |
| Transverse | 2.26 | 0.2 | 2.11 | 0.2 | 2.10 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Superior | 2.61 | 0.3 | 2.42 | 0.4 | 2.45 | 0.2 | 0.012 | <0.001 | 0.107 | 0.207 | |
| Banks of superior sulcus | 2.35 | 0.1 | 2.18 | 0.2 | 2.21 | 0.2 | 0.023 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 1 | |
| Middle | 2.67 | 0.2 | 2.48 | 0.2 | 2.55 | 0.2 | 0.059 | - | |||
| Inferior | 2.54 | 0.2 | 2.34 | 0.2 | 2.31 | 0.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1 | |
| Fusiform | 2.54 | 0.3 | 2.31 | 0.2 | 2.31 | 0.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.765 | |
| Limbic | Anterior-cingulate-rostral | 2.73 | 0.2 | 2.73 | 0.3 | 2.73 | 0.2 | 1 | - | ||
| Anterior-cingulate-caudal | 2.67 | 0.3 | 2.57 | 0.4 | 2.55 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Posterior-cingulate | 2.52 | 0.6 | 2.43 | 0.3 | 2.43 | 0.4 | 1 | - | |||
| Isthmus of cingulate | 2.38 | 0.4 | 2.30 | 0.3 | 2.29 | 0.3 | 1 | - | |||
| Parahippocampal | 2.54 | 0.2 | 2.26 | 0.3 | 2.30 | 0.2 | 1 | - | |||
| Group | Prediction | Validation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeaCON | UMN | LMN | Leave-One-Out | ||
| A1 | HeaCON | 96.2% | 3.8% | 95.3% | |
| ALS | 2.6% | 97.4% | |||
| A2 | HeaCON | 96.2% | 0% | 3.8% | 81.2% |
| UMN | 0% | 70% | 30% | ||
| LMN | 5.6% | 11.1% | 83.3% | ||
| B1 | HeaCON | 100% | 0% | 100% | |
| ALS | 0% | 100% | |||
| B2 | HeaCON | 100% | 0% | 0% | 82.8% |
| UMN | 5% | 80% | 15% | ||
| LMN | 0% | 22.2% | 77.8% | ||
| Localization | Discriminant Analyses | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex/Areal | A1 | A2 | B1 | B2 | |||||
| r | r1 | r2 | n-Step | r | n-Step | r1 | r2 | ||
| Frontal | Pole | - | - | 6 | 0.439 | - | |||
| Orbitofrontal-lateral | - | - | 2 | −1.15 | 2 | −0.988 | −0.036 | ||
| Precentral | 0.114 | 0.167 | 1.03 | - | 4 | 0.153 | 1.12 | ||
| Parietal | Postcentral | - | - | 10 | −0.525 | - | |||
| Inferior | - | - | 9 | 0.728 | - | ||||
| Occipital | Lingual | - | - | 3 | 0.831 | 3 | 0.682 | −0.452 | |
| Temporal | Pole | 0.811 | 0.801 | −0.239 | 1 | 0.863 | 1 | 0.818 | 0.182 |
| Entorhinal | - | - | 4 | 0.411 | 5 | 0.342 | −0.684 | ||
| Transverse | - | - | 8 | −0.374 | - | ||||
| Inferior | 0.553 | 0.535 | −0.357 | 7 | 0.449 | - | |||
| Limbic | Anterior-cingulate-rostral | - | - | 5 | −0.572 | - | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrea, S.; Junker, F.; Korth, M.; Gruhn, K.; Grehl, T.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T. Cortical Thinning of Motor and Non-Motor Brain Regions Enables Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Supports Distinction between Upper- and Lower-Motoneuron Phenotypes. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091195
Ferrea S, Junker F, Korth M, Gruhn K, Grehl T, Schmidt-Wilcke T. Cortical Thinning of Motor and Non-Motor Brain Regions Enables Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Supports Distinction between Upper- and Lower-Motoneuron Phenotypes. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091195
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrea, Stefano, Frederick Junker, Mira Korth, Kai Gruhn, Torsten Grehl, and Tobias Schmidt-Wilcke. 2021. "Cortical Thinning of Motor and Non-Motor Brain Regions Enables Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Supports Distinction between Upper- and Lower-Motoneuron Phenotypes" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091195
APA StyleFerrea, S., Junker, F., Korth, M., Gruhn, K., Grehl, T., & Schmidt-Wilcke, T. (2021). Cortical Thinning of Motor and Non-Motor Brain Regions Enables Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Supports Distinction between Upper- and Lower-Motoneuron Phenotypes. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091195






