A Proposal for Practical Diagnosis of Renal Hypouricemia: Evidenced from Genetic Studies of Nonfunctional Variants of URAT1/SLC22A12 among 30,685 Japanese Individuals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
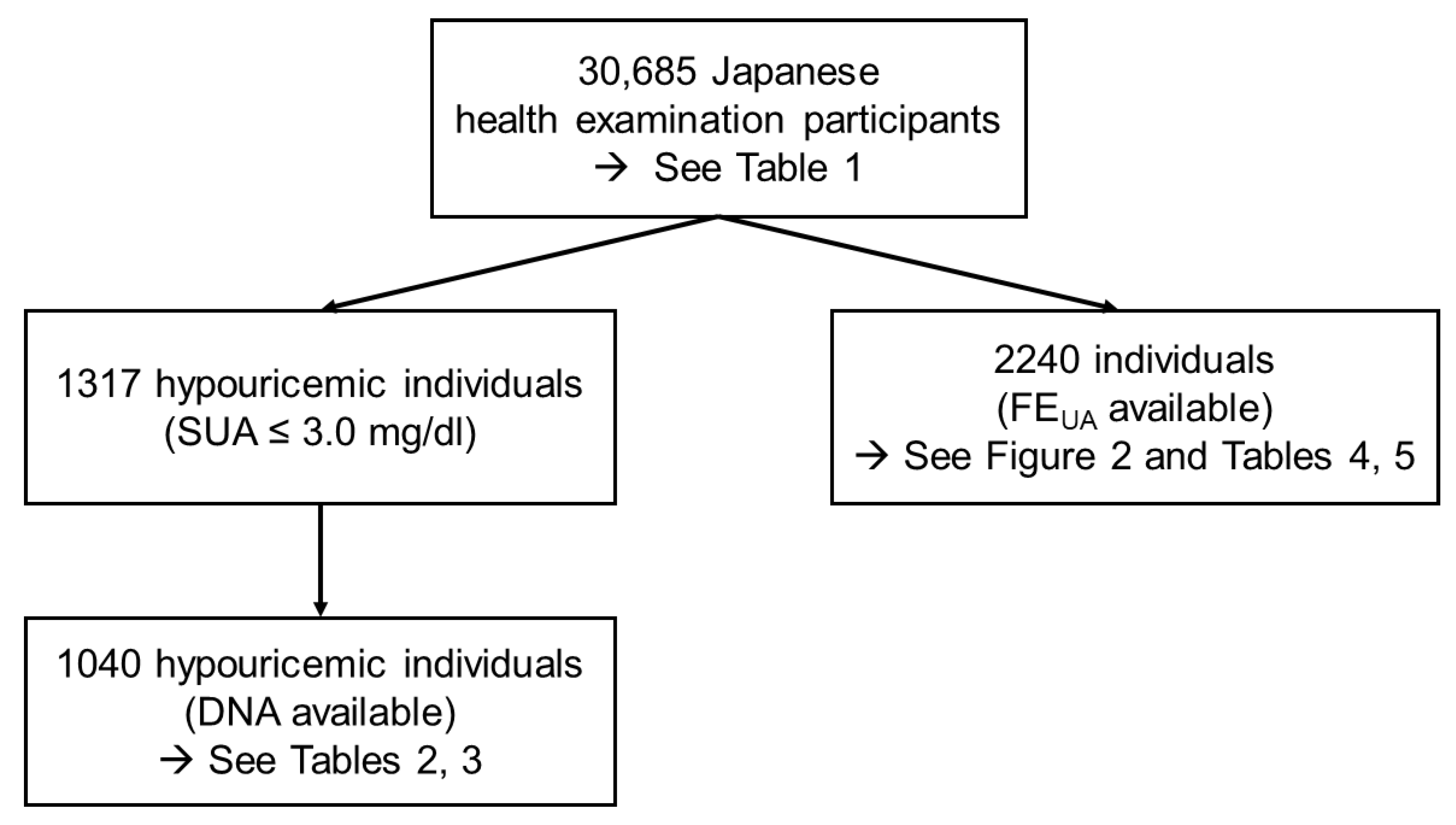
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Genetics Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of SUA Levels in the Japanese Population
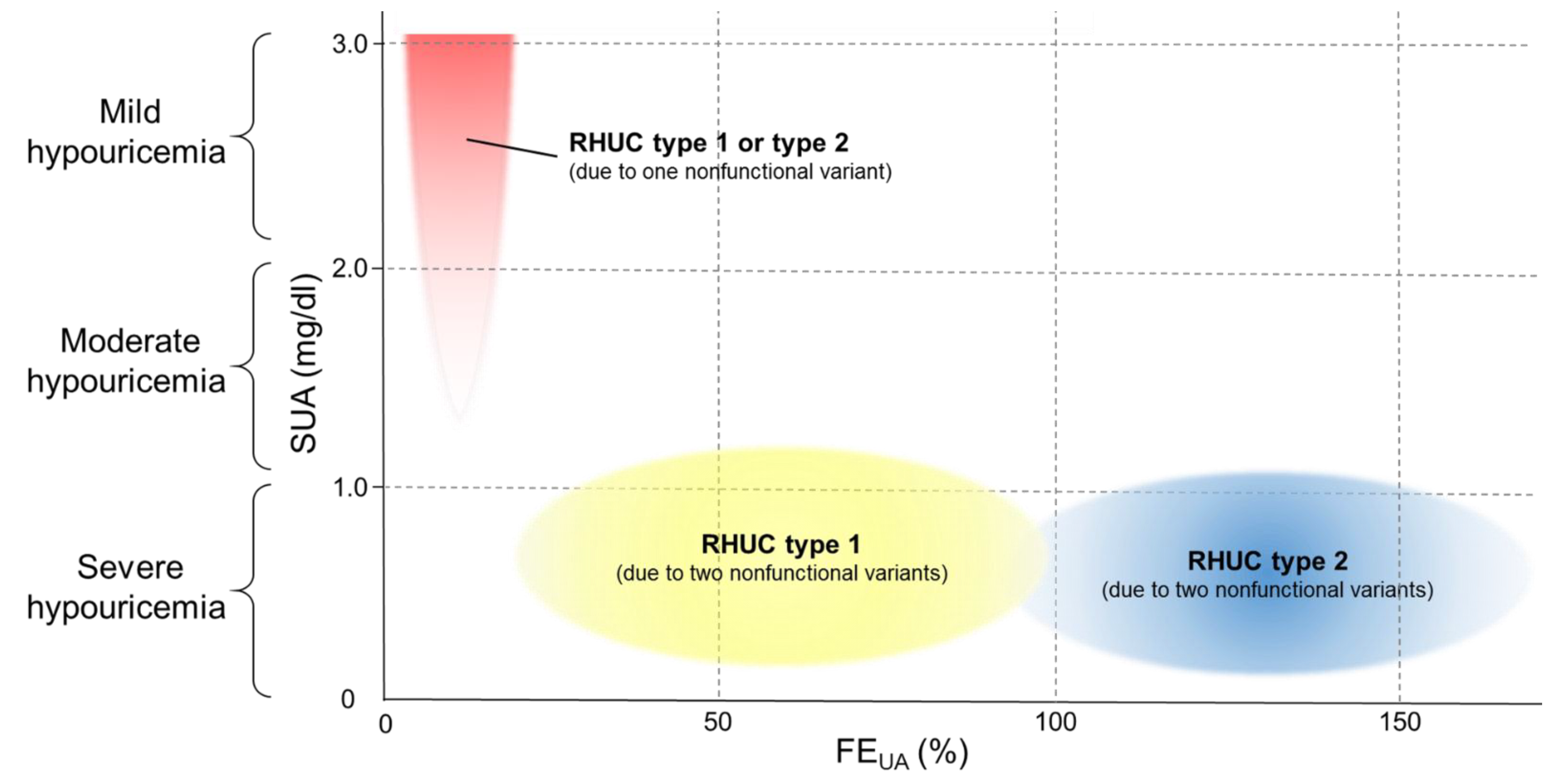
3.2. Frequency of NFV-URAT1 in Hypouricemic Individuals
3.3. Associations between NFV-URAT1 and FEUA or SUA in 2240 Japanese Individuals
3.4. The Effect on FEUA and SUA Levels of the Number of Alleles of NFV-URAT1
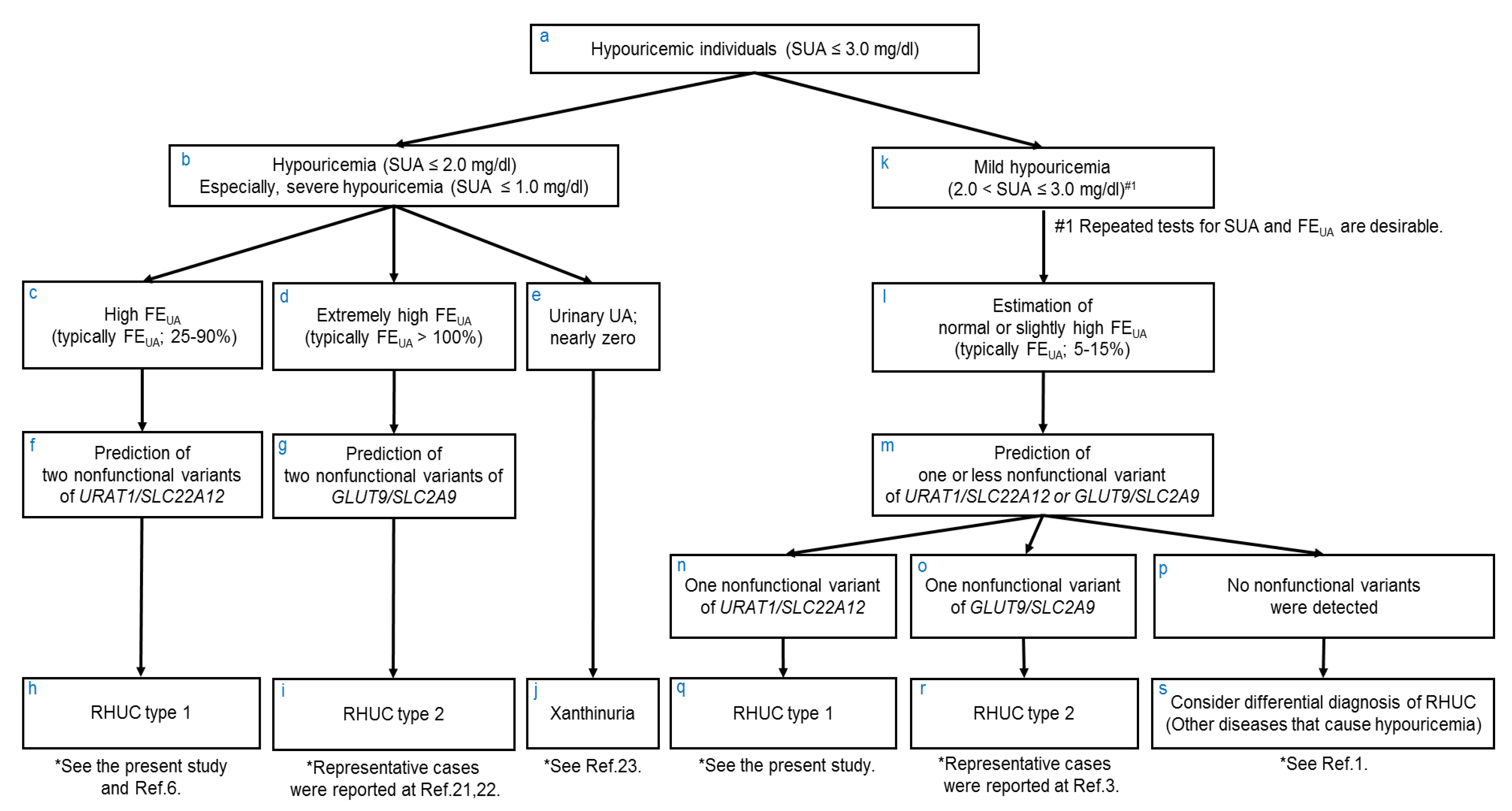
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakayama, A.; Matsuo, H.; Ohtahara, A.; Ogino, K.; Hakoda, M.; Hamada, T.; Hosoyamada, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hisatome, I.; Ichida, K.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for renal hypouricemia (1st edition). Hum. Cell 2019, 32, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, A.; Kimura, H.; Chairoungdua, A.; Shigeta, Y.; Jutabha, P.; Cha, S.H.; Hosoyamada, M.; Takeda, M.; Sekine, T.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Molecular identification of a renal urate anion exchanger that regulates blood urate levels. Nature 2002, 417, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, H.; Chiba, T.; Nagamori, S.; Nakayama, A.; Domoto, H.; Phetdee, K.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oda, T.; Nishiyama, J.; et al. Mutations in glucose transporter 9 gene SLC2A9 cause renal hypouricemia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, I. Acute renal failure with severe loin pain and patchy renal ischemia after anaerobic exercise in patients with or without renal hypouricemia. Nephron 2002, 91, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Koga, H.; Yasutomo, Y.; Kawabata, Y.; Shimizu, E.; Naruse, M.; Kiyama, S.; Nonoguchi, H.; Tomita, K.; Sasatomi, Y.; et al. Patients with renal hypouricemia with exercise-induced acute renal failure and chronic renal dysfunction. Clin. Nephrol. 2000, 53, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ichida, K.; Hosoyamada, M.; Hisatome, I.; Enomoto, A.; Hikita, M.; Endou, H.; Hosoya, T. Clinical and molecular analysis of patients with renal hypouricemia in Japan-influence of URAT1 gene on urinary urate excretion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiyama, M.; Matsuo, H.; Shimizu, S.; Nakashima, H.; Nakamura, T.; Nakayama, A.; Higashino, T.; Naito, M.; Suma, S.; Hishida, A.; et al. The effects of URAT1/SLC22A12 nonfunctional variants, R90H and W258X, on serum uric acid levels and gout/hyperuricemia progression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakasugi, M.; Kazama, J.J.; Narita, I.; Konta, T.; Fujimoto, S.; Iseki, K.; Moriyama, T.; Yamagata, K.; Tsuruya, K.; Asahi, K.; et al. Association between hypouricemia and reduced kidney function: A cross-sectional population-based study in Japan. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, M.; Niwa, K.; Ohtahara, A.; Hamada, T.; Miyazaki, S.; Mizuta, E.; Ogino, K.; Hisatome, I. Prevalence and complications of hypouricemia in a general population: A large-scale cross-sectional study in Japan. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawasoe, S.; Ide, K.; Usui, T.; Kubozono, T.; Yoshifuku, S.; Miyahara, H.; Maenohara, S.; Ohishi, M.; Kawakami, K. Distribution and Characteristics of Hypouricemia within the Japanese General Population: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2019, 55, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asai, Y.; Naito, M.; Suzuki, M.; Tomoda, A.; Kuwabara, M.; Fukada, Y.; Okamoto, A.; Oishi, S.; Ikeda, K.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Baseline data of Shizuoka area in the Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study (J-MICC Study). Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hamajima, N.; Group, J.-M.S. The Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study (J-MICC Study) to detect gene-environment interactions for cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2007, 8, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Ichida, K.; Matsuo, H.; Takada, T.; Nakayama, A.; Murakami, K.; Shimizu, T.; Yamanashi, Y.; Kasuga, H.; Nakashima, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabrikova, D.; Bernasovska, J.; Sokolova, J.; Stiburkova, B. High frequency of SLC22A12 variants causing renal hypouricemia 1 in the Czech and Slovak Roma population; simple and rapid detection method by allele-specific polymerase chain reaction. Urolithiasis 2015, 43, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiburkova, B.; Gabrikova, D.; Cepek, P.; Simek, P.; Kristian, P.; Cordoba-Lanus, E.; Claverie-Martin, F. Prevalence of URAT1 allelic variants in the Roma population. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2016, 35, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, A.; Matsuo, H.; Abhishek, A.; Ichida, K.; Shinomiya, N. Guideline Development Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline for Renal Hypouricemia., First clinical practice guideline for renal hypouricemia: A rare disorder that aided the development of urate-lowering drugs for gout. Rheumatology 2021, keab322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichida, K.; Hosoyamada, M.; Kamatani, N.; Kamitsuji, S.; Hisatome, I.; Shibasaki, T.; Hosoya, T. Age and origin of the G774A mutation in SLC22A12 causing renal hypouricemia in Japanese. Clin. Genet. 2008, 74, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakida, N.; Tuyen, D.G.; Adachi, M.; Miyoshi, T.; Nonoguchi, H.; Oka, T.; Ueda, O.; Tazawa, M.; Kurihara, S.; Yoneta, Y.; et al. Mutations in human urate transporter 1 gene in presecretory reabsorption defect type of familial renal hypouricemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2169–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toyoda, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Nakayama, A.; Nakaoka, H.; Higashino, T.; Shimizu, S.; Ooyama, H.; Morimoto, K.; Uchida, N.; Shigesawa, R.; et al. Substantial anti-gout effect conferred by common and rare dysfunctional variants of URAT1/SLC22A12. Rheumatology 2021, keab327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Toyoda, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Hisatomi, R.; Higashino, T.; Nakayama, A.; Shimizu, S.; Yanagi, M.; Kamimaki, I.; Fujimaru, R.; et al. Identification of a dysfunctional splicing mutation in the SLC22A12/URAT1 gene causing renal hypouricaemia type 1: A report on two families. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3988–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinour, D.; Gray, N.K.; Campbell, S.; Shu, X.; Sawyer, L.; Richardson, W.; Rechavi, G.; Amariglio, N.; Ganon, L.; Sela, B.A.; et al. Homozygous SLC2A9 mutations cause severe renal hypouricemia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinour, D.; Gray, N.K.; Ganon, L.; Knox, A.J.; Shalev, H.; Sela, B.A.; Campbell, S.; Sawyer, L.; Shu, X.; Valsamidou, E.; et al. Two novel homozygous SLC2A9 mutations cause renal hypouricemia type 2. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichida, K.; Amaya, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Nishino, T. Mutations associated with functional disorder of xanthine oxidoreductase and hereditary xanthinuria in humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15475–15495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higashino, T.; Morimoto, K.; Nakaoka, H.; Toyoda, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Nakamura, T.; Hosomichi, K.; Nakayama, A.; Ooyama, K.; et al. Dysfunctional missense variant of OAT10/SLC22A13 decreases gout risk and serum uric acid levels. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| SUA (mg/dL) | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Frequency (%) | Number | Frequency (%) | |
| 0.0–1.0 | 20 | 0.15 | 23 | 0.13 |
| 1.1–2.0 | 4 | 0.03 | 70 | 0.41 |
| 2.1–3.0 | 107 | 0.79 | 1093 | 6.40 |
| 3.1–7.0 | 10,716 | 78.75 | 15,703 | 91.95 |
| 7.1–8.0 | 1956 | 14.37 | 149 | 0.87 |
| 8.1–9.0 | 625 | 4.59 | 32 | 0.19 |
| 9.1– | 179 | 1.32 | 8 | 0.05 |
| Total | 13,607 | 100 | 17,078 | 100 |
| Male | Female | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Age (year) | BMI (kg/m2) | Number | Age (year) | BMI (kg/m2) | |
| Severe hypouricemia (0.0–1.0 mg/dL) | 17 | 56.4 ± 8.1 | 24.2 ± 2.6 | 19 | 55.7 ± 8.1 | 22.1 ± 2.9 |
| Moderate hypouricemia (1.1–2.0 mg/dL) | 4 | 53.5 ± 8.3 | 24.1 ± 2.1 | 57 | 50.2 ± 8.4 | 21.3 ± 3.1 |
| Mild hypouricemia (2.1–3.0 mg/dL) | 87 | 56.0 ± 8.9 | 22.6 ± 2.9 | 856 | 51.8 ± 9.2 | 21.1 ± 2.9 |
| Hypouricemia (≤2.0 mg/dL) | 21 | 55.8 ± 8.2 | 24.2 ± 2.5 | 76 | 51.6 ± 8.7 | 21.5 ± 3.1 |
| Hypouricemia + mild hypouricemia (≤3.0 mg/dL) | 108 | 56.0 ± 8.7 | 22.9 ± 2.9 | 932 | 51.8 ± 9.1 | 21.2 ± 2.9 |
| Hypouricemic Population (SUA) | Male | Female | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allele Number of NFV-URAT1 | Total | Allele Number of NFV-URAT1 | Total | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |||
| Severe hypouricemia (0.0–1.0 mg/dL) | 2 (11.8%) | 4 (23.5%) | 11 (64.7%) | 17 (100%) | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (31.6%) | 13 (68.4%) | 19 (100%) |
| Moderate hypouricemia (1.1–2.0 mg/dL) | 1 (25.0%) | 3 (75.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (100%) | 20 (35.1%) | 37 (64.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 57 (100%) |
| Mild hypouricemia (2.1–3.0 mg/dL) | 29 (33.3%) | 58 (66.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 87 (100%) | 570 (66.6%) | 286 (33.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 856 (100%) |
| Hypouricemia (≤2.0 mg/dL) | 3 (14.3%) | 7 (33.3%) | 11 (52.4%) | 21 (100%) | 20 (26.3%) | 43 (56.6%) | 13(17.1%) | 76 (100%) |
| Hypouricemia + mild hypouricemia (≤3.0 mg/dL) | 32 (29.6%) | 65 (60.2%) | 11 (10.2%) | 108 (100%) | 590 (63.3%) | 329 (35.3%) | 13 (1.4%) | 932 (100%) |
| Case No. | Sex | Age | NFV-URAT1 | FEUA (%) | SUA (mg/dL) | SCr (mg/dL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Alleles | Amino Acid Substitution | ||||||
| 1 | Female | 69 | 2 | W258X/W258X | 51.32 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| 2 | Male | 63 | 2 | W258X/W258X | 60.71 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| 3 | Female | 68 | 2 | W258X/W258X | 40.55 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| 4 | Male | 57 | 2 | W258X/W258X | 24.52 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| 5 | Female | 45 | 1 | W258X/ | 12.08 | 2.3 | 0.6 |
| 6 | Female | 56 | 1 | W258X/ | 5.67 | 2.4 | 0.8 |
| 7 | Male | 69 | 1 | W258X/ | 7.80 | 2.4 | 0.7 |
| 8 | Female | 61 | 1 | W258X/ | 6.04 | 2.5 | 0.5 |
| 9 | Female | 51 | 1 | W258X/ | 6.40 | 2.6 | 0.6 |
| 10 | Female | 70 | 1 | W258X/ | 6.97 | 2.6 | 0.6 |
| 11 | Female | 68 | 1 | W258X/ | 2.17 | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| 12 | Female | 55 | 1 | W258X/ | 10.41 | 2.9 | 0.7 |
| 13 | Female | 41 | 1 | W258X/ | 11.12 | 2.9 | 0.4 |
| 14 | Male | 69 | 1 | W258X/ | 12.51 | 3.0 | 0.9 |
| 15 | Male | 55 | 1 | W258X/ | 8.19 | 3.0 | 0.9 |
| 16 | Female | 46 | 1 | R90H/ | 6.55 | 3.0 | 0.5 |
| 17 | Female | 65 | 0 | 12.45 | 2.0 | 0.5 | |
| 18 | Male | 54 | 0 | 4.07 | 2.3 | 0.6 | |
| 19 | Female | 61 | 0 | 14.75 | 2.3 | 0.5 | |
| 20 | Female | 62 | 0 | 3.40 | 2.5 | 0.5 | |
| 21 | Female | 45 | 0 | 3.10 | 2.6 | 0.6 | |
| 22 | Female | 71 | 0 | 12.32 | 2.6 | 0.6 | |
| 23 | Male | 52 | 0 | 4.91 | 2.6 | 0.7 | |
| 24 | Female | 50 | 0 | 2.94 | 2.7 | 0.6 | |
| 25 | Female | 54 | 0 | 6.16 | 2.7 | 0.6 | |
| 26 | Female | 52 | 0 | 2.05 | 2.7 | 0.6 | |
| 27 | Female | 62 | 0 | 9.51 | 2.8 | 0.5 | |
| 28 | Female | 41 | 0 | 7.86 | 2.8 | 0.6 | |
| 29 | Female | 62 | 0 | 11.76 | 2.8 | 0.5 | |
| 30 | Female | 58 | 0 | 12.11 | 2.8 | 0.6 | |
| 31 | Female | 47 | 0 | 6.77 | 2.8 | 0.7 | |
| 32 | Female | 43 | 0 | 8.11 | 2.8 | 0.5 | |
| 33 | Female | 41 | 0 | 8.17 | 2.8 | 0.6 | |
| 34 | Female | 60 | 0 | 5.88 | 2.8 | 0.7 | |
| 35 | Male | 59 | 0 | 16.86 | 2.8 | 0.8 | |
| 36 | Female | 51 | 0 | 5.27 | 2.8 | 0.7 | |
| 37 | Female | 58 | 0 | 12.61 | 2.9 | 0.5 | |
| 38 | Female | 43 | 0 | 6.64 | 2.9 | 0.7 | |
| 39 | Female | 47 | 0 | 7.90 | 2.9 | 0.6 | |
| 40 | Female | 68 | 0 | 8.14 | 2.9 | 0.7 | |
| 41 | Female | 72 | 0 | 14.10 | 2.9 | 0.4 | |
| 42 | Female | 52 | 0 | 5.91 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| 43 | Female | 63 | 0 | 6.07 | 3.0 | 0.5 | |
| 44 | Female | 51 | 0 | 8.29 | 3.0 | 0.5 | |
| 45 | Female | 69 | 0 | 8.17 | 3.0 | 0.5 | |
| 46 | Female | 47 | 0 | 8.15 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| 47 | Female | 74 | 0 | 3.34 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| 48 | Female | 59 | 0 | 10.43 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| 49 | Female | 50 | 0 | 8.68 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| 50 | Female | 60 | 0 | 9.96 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| 51 | Female | 56 | 0 | 7.68 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| 52 | Female | 64 | 0 | 4.17 | 3.0 | 0.6 | |
| Male | Female | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partial Regression Coefficient | p Value | Partial Regression Coefficient | p Value | ||
| FEUA | β0 | 3.94 | 0 | 5.40 | 1.61 × 10−249 |
| β1 | 2.63 | 4.04 × 10−20 | ― | ― | |
| β2 | 38.68 | 1.35 × 10−108 | 40.54 | 2.15 × 10−79 | |
| SUA | β0 | 6.10 | 0 | 4.56 | 0 |
| β1 | –1.93 | 6.56 × 10−45 | −1.25 | 1.53 × 10−7 | |
| β2 | –5.35 | 2.39 × 10−12 | −3.91 | 2.97 × 10−8 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawamura, Y.; Nakayama, A.; Shimizu, S.; Toyoda, Y.; Nishida, Y.; Hishida, A.; Katsuura-Kamano, S.; Shibuya, K.; Tamura, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; et al. A Proposal for Practical Diagnosis of Renal Hypouricemia: Evidenced from Genetic Studies of Nonfunctional Variants of URAT1/SLC22A12 among 30,685 Japanese Individuals. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9081012
Kawamura Y, Nakayama A, Shimizu S, Toyoda Y, Nishida Y, Hishida A, Katsuura-Kamano S, Shibuya K, Tamura T, Kawaguchi M, et al. A Proposal for Practical Diagnosis of Renal Hypouricemia: Evidenced from Genetic Studies of Nonfunctional Variants of URAT1/SLC22A12 among 30,685 Japanese Individuals. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(8):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9081012
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawamura, Yusuke, Akiyoshi Nakayama, Seiko Shimizu, Yu Toyoda, Yuichiro Nishida, Asahi Hishida, Sakurako Katsuura-Kamano, Kenichi Shibuya, Takashi Tamura, Makoto Kawaguchi, and et al. 2021. "A Proposal for Practical Diagnosis of Renal Hypouricemia: Evidenced from Genetic Studies of Nonfunctional Variants of URAT1/SLC22A12 among 30,685 Japanese Individuals" Biomedicines 9, no. 8: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9081012
APA StyleKawamura, Y., Nakayama, A., Shimizu, S., Toyoda, Y., Nishida, Y., Hishida, A., Katsuura-Kamano, S., Shibuya, K., Tamura, T., Kawaguchi, M., Suzuki, S., Iwasawa, S., Nakashima, H., Ibusuki, R., Uemura, H., Hara, M., Takeuchi, K., Takada, T., Tsunoda, M., ... Matsuo, H. (2021). A Proposal for Practical Diagnosis of Renal Hypouricemia: Evidenced from Genetic Studies of Nonfunctional Variants of URAT1/SLC22A12 among 30,685 Japanese Individuals. Biomedicines, 9(8), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9081012









