Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 Has a Preventive Effect on the Acceleration of Colonic Permeability and M1 Macrophage Population in Maternally Separated Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Maternal Separation and Experimental Design
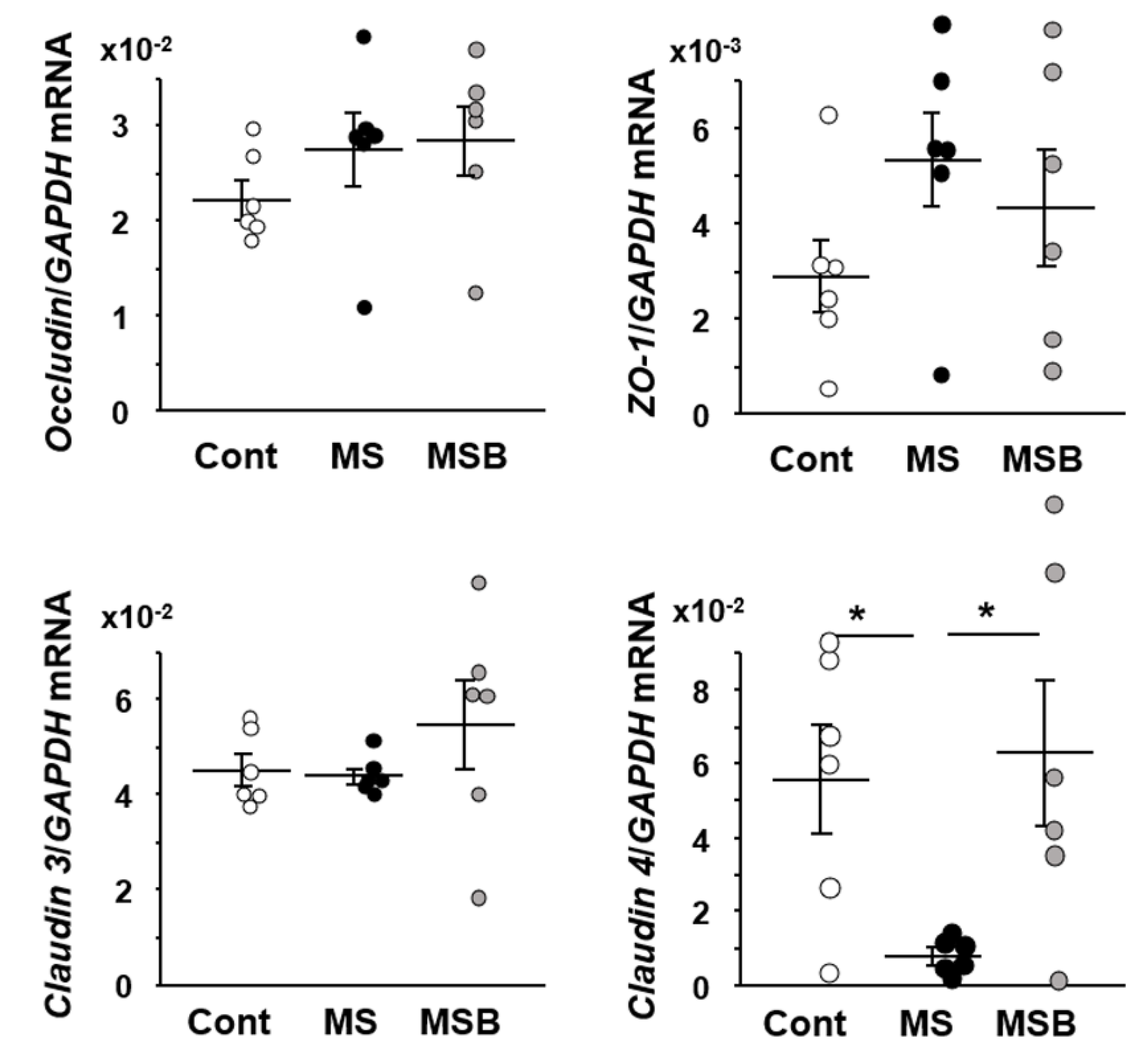
2.2. Real-Time RT-PCR
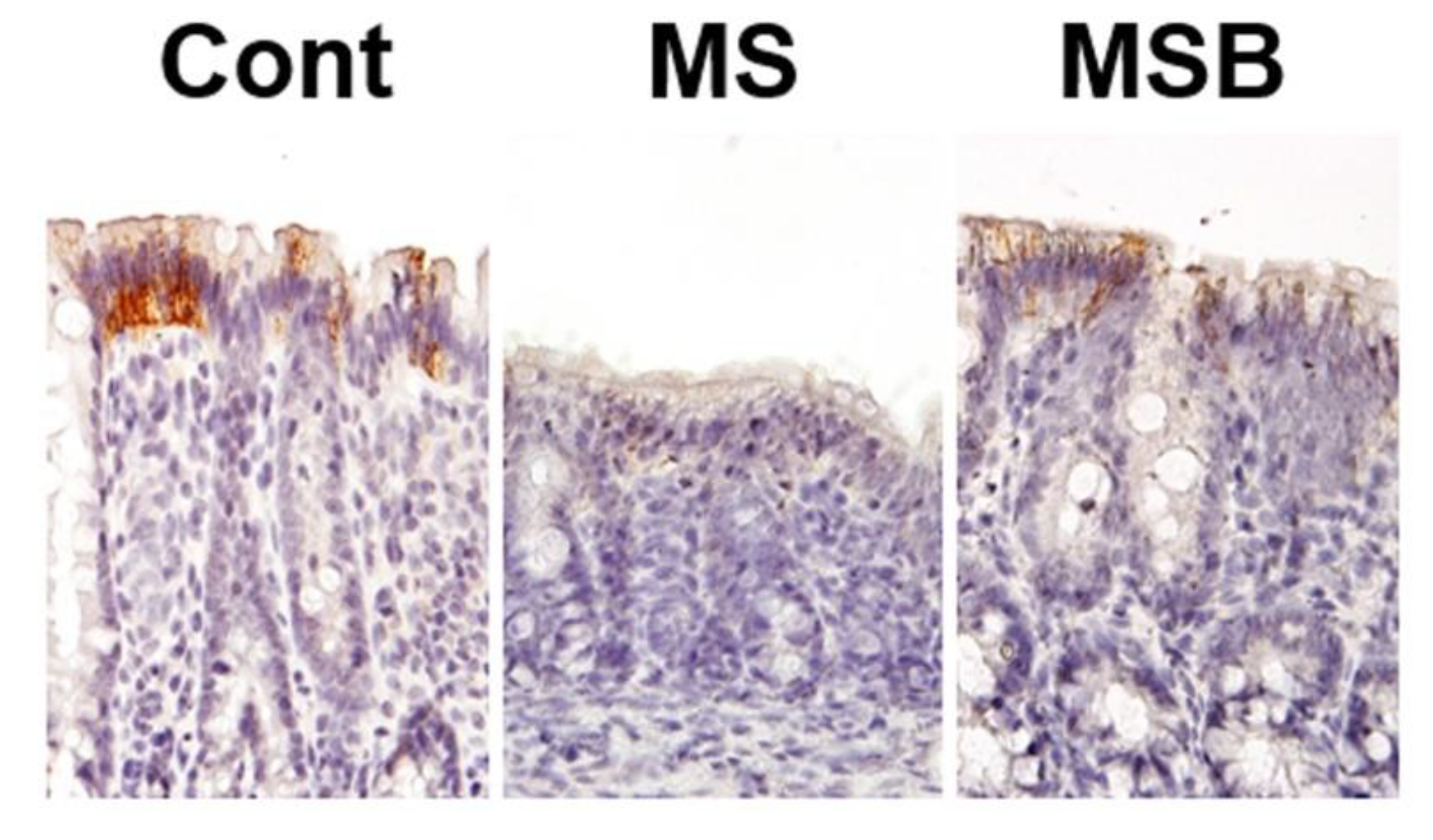
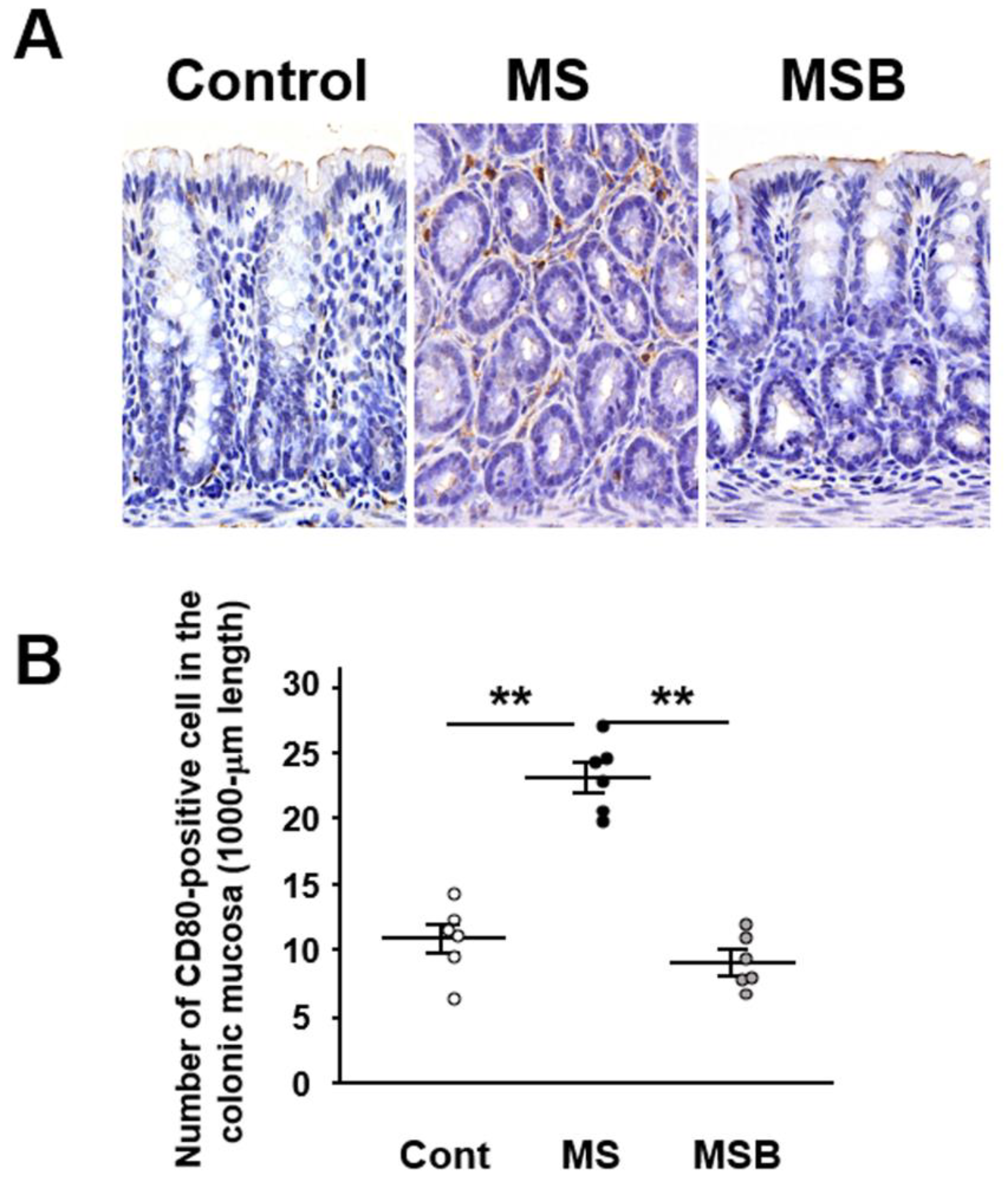
2.3. Tissue Specimen and Immunohistochemistry
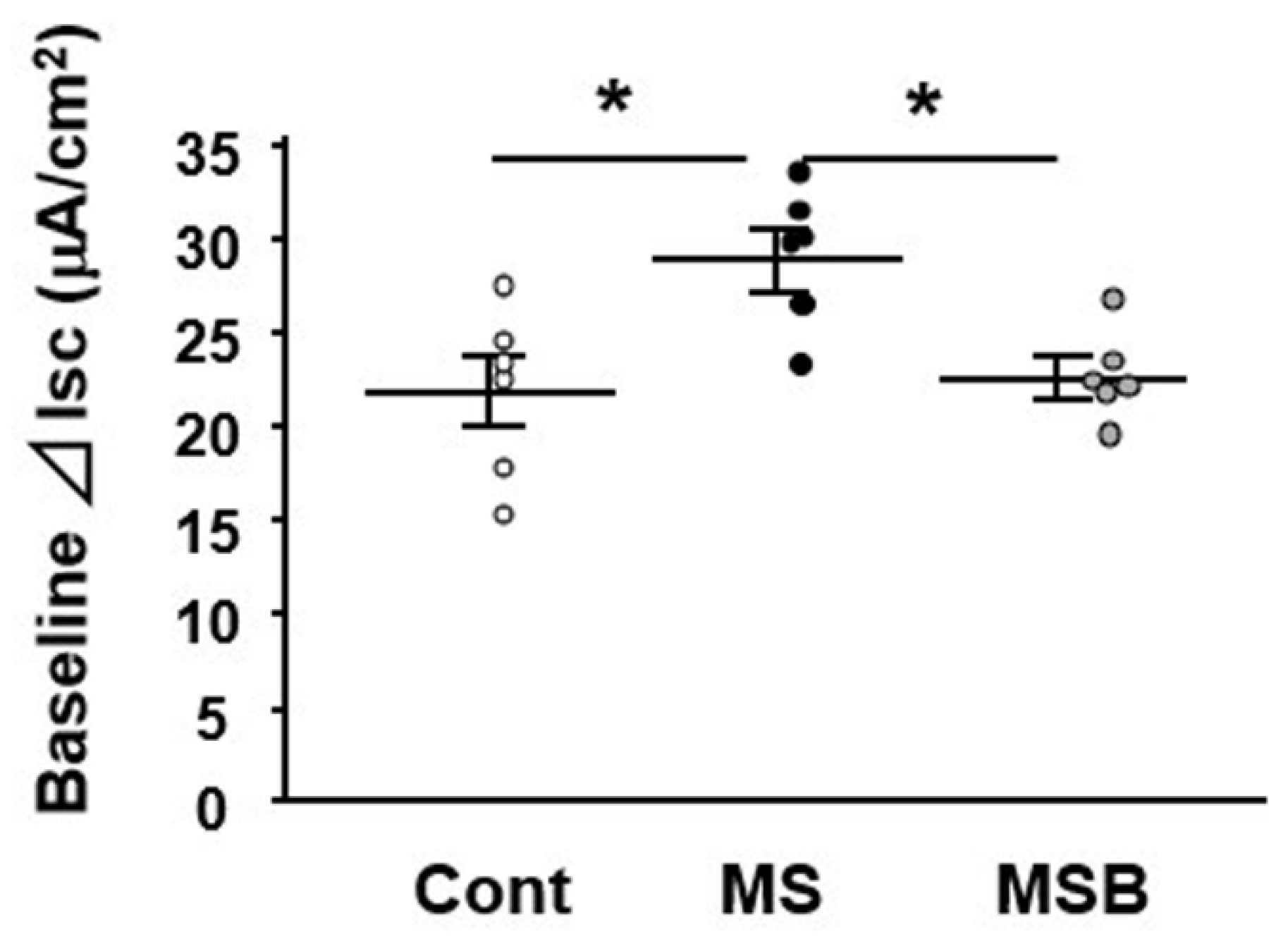
2.4. Ussing Chamber Assay
2.5. Measurement of Transepithelial Electrical Resistance
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of BBG9-1 on Intestinal Permeability in MS Rats
3.2. Effect of BBG9-1 on the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins in the Intestine of MS Rats
3.3. Effect of BBG9-1 on the Population of CD80-Positive Cells in the Intestinal Mucosa of MS Rats
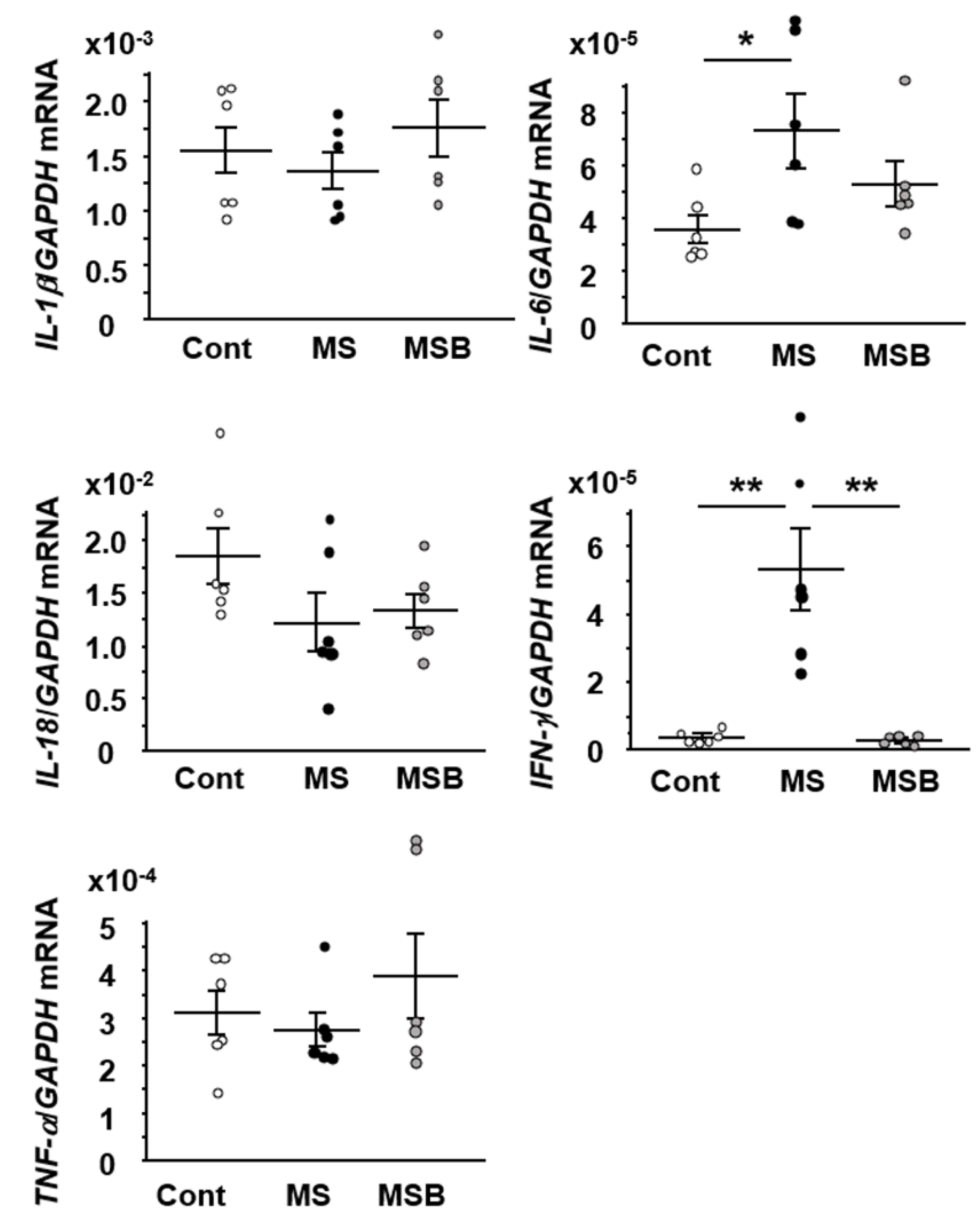
3.4. Effect of BBG9-1 on the Expression of Cytokines in the Intestine of MS Rats
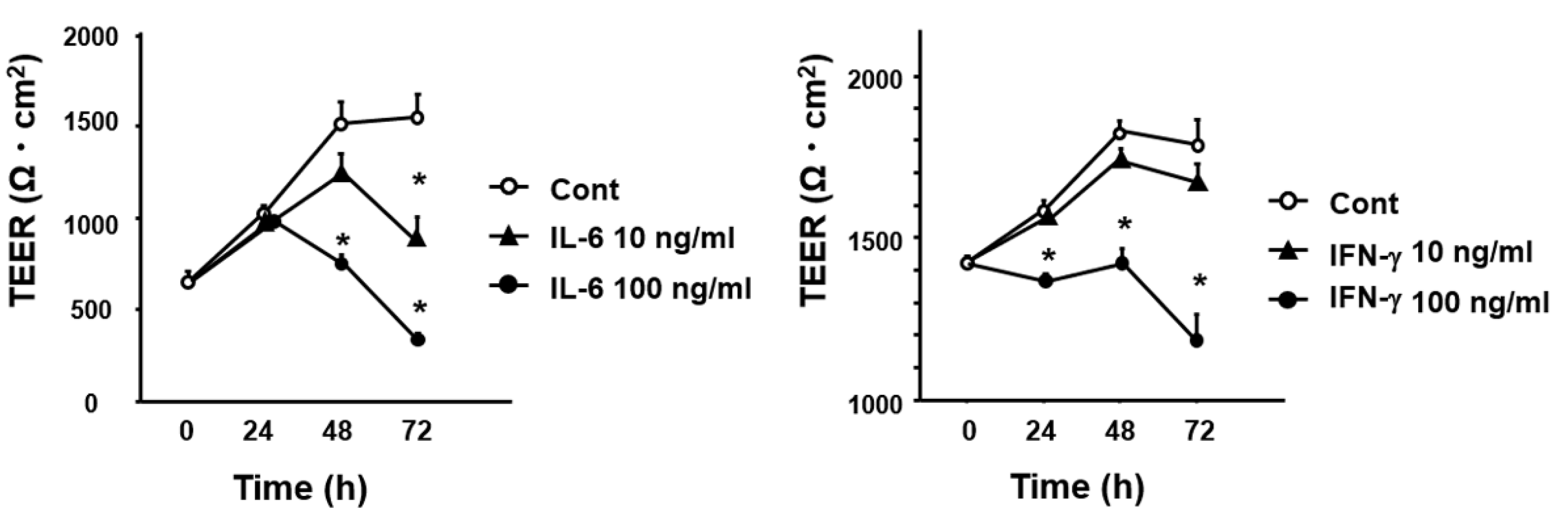
3.5. Effect of Cytokines IL-6 and IFN-γ on Intestinal Permeability In Vitro
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longstreth, G.F.; Thompson, W.G.; Chey, W.D.; Houghton, L.A.; Mearin, F.; Spiller, R.C. Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chey, W.D.; Kurlander, J.; Eswaran, S. Irritable bowel syndrome: A clinical review. JAMA 2015, 313, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, J.; Simren, M. Peripheral factors in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2009, 41, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Scuto, M.; Siracusa, R.; D’amico, R.; Filippo Peritore, A.; Gugliandolo, E.; Fusco, R.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Pozzebon, M.; et al. Effect of N-palmitoylethanolamine-oxazoline on comorbid neuropsychiatric disturbance associated with inflammatory bowel disease. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4085–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, R.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Protective effects of Colomast®, A new formulation of adelmidrol and sodium hyaluronate, in a mouse model of acute restraint stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, K.; Shih, W.; Videlock, E.J.; Presson, A.P.; Naliboff, B.D.; Mayer, E.A.; Chang, L. Association between early adverse life events and irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusijärvi, A.; Bergström, A.; Simrén, M.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Kull, I.; Wickman, M.; Alm, J.; Olén, O. Use of antibiotics in infancy and childhood and risk of recurrent abdominal pain—A Swedish birth cohort study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H.; Oshima, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Makizaki, Y.; Ohno, H.; Tomita, T.; Watari, J.; Miwa, H. Effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 on the relationship between gut microbiota profile and stress sensitivity in maternally separated rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Makizaki, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Maeda, A.; Shimakawa, M.; Komoto, S.; Moriguchi, K.; Ohno, H.; Taniguchi, K. Oral administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 alleviates rotavirus gastroenteritis through regulation of intestinal homeostasis by inducing mucosal protective factors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makizaki, Y.; Maeda, A.; Oikawa, Y.; Tamura, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakajima, S.; Ohno, H.; Yamamura, H. Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 ameliorates phytohemagglutinin-induced diarrhea caused by intestinal dysbiosis. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 63, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, T.; Oikawa, Y.; Kato, T.; Kessoku, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kato, S.; Misawa, N.; Ashikari, K.; Fuyuki, A.; Ohkubo, H.; et al. The protective effect of Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 against mucus degradation by Akkermansia muciniphila following small intestine injury caused by a proton pump inhibitor and aspirin. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1385–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, A.; Favero de Aguiar, C.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Olsen Saraiva Câmara, N. They must hold tight: Junction proteins, microbiota and immunity in intestinal mucosa. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareau, M.G.; Jury, J.; MacQueen, G.; Sherman, P.M.; Perdue, M.H. Probiotic treatment of rat pups normalises corticosterone release and ameliorates colonic dysfunction induced by maternal separation. Gut 2007, 56, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Hara, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Yamasaki, T.; Kondo, T.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; Watari, J.; et al. IL-22 produced by cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes gastric cancer cell invasion via STAT3 and ERK signaling. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, H.; Fukui, H.; Sekikawa, A.; Kono, T.; Fujii, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Tomita, S.; Imura, J.; Hiraishi, H.; Chiba, T.; et al. Expression profile of REG family proteins REG Iα and REG IV in advanced gastric cancer: Comparison with mucin phenotype and prognostic markers. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Fukui, H.; Eda, H.; Xu, X.; Kitayama, Y.; Hara, K.; Kodani, M.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; Watari, J.; et al. Involvement of gut microbiota in association between GLP-1/GLP-1 receptor expression and gastrointestinal motility. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G367–G373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Fukui, H.; Xu, X.; Ran, Y.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; Watari, J.; Miwa, H. Colonic M1 macrophage is associated with the prolongation of gastrointestinal motility and obesity in mice treated with vancomycin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosztoczy, A.; Fioramonti, J.; Jármay, K.; Barreau, F.; Wittmann, T.; Buéno, L. Influence of sex and experimental protocol on the effect of maternal deprivation on rectal sensitivity to distension in the adult rat. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2003, 15, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, Y.; Fukui, H.; Hara, K.; Eda, H.; Kodani, M.; Yang, M.; Sun, C.; Yamagishi, H.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; et al. Role of regenerating gene I in claudin expression and barrier function in the small intestine. Transl. Res. 2016, 173, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, Y.; Fukui, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Ebisutani, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Maeda, A.; Makizaki, Y.; Ohno, H.; Kondo, T.; et al. Alteration of colonic mucosal permeability during antibiotic-induced dysbiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Park, J.M.; Lim, C.H.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, M.G.; Chung, I.S.; Chung, Y.K. Anxiety, depression and quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Liver 2011, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, S.W.; Auyeung, K.K.; Bian, Z.X.; Ko, J.K. Pathogenesis, experimental models and contemporary pharmacotherapy of irritable bowel syndrome: Story about the brain-gut axis. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Q.X.; Soh, A.Y.S.; Loke, W.; Lim, D.Y.; Yeo, W.S. The role of inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piche, T. Tight junctions and IBS—The link between epithelial permeability, low-grade inflammation, and symptom generation? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H.; Nishida, A.; Matsuda, S.; Kira, F.; Watanabe, S.; Kuriyama, M.; Kawakami, K.; Aikawa, Y.; Oda, N.; Arai, K.; et al. Usefulness of machine learning-based gut microbiome analysis for identifying patients with irritable bowels syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, S.V.; Plotsky, P.M.; Sablad, M.; Miller, J.C.; Zhou, H.; Bayati, A.I.; McRoberts, J.A.; Mayer, E.A. Neonatal maternal separation alters stress-induced responses to viscerosomatic nociceptive stimuli in rat. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G307–G316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreau, F.; Ferrier, L.; Fioramonti, J.; Bueno, L. New insights in the etiology and pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome: Contribution of neonatal stress models. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 62, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Feldon, J. Long-term biobehavioral effects of maternal separation in the rat: Consistent or confusing? Rev. Neurosci. 2000, 11, 383–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palma, G.; Blennerhassett, P.; Lu, J.; Deng, Y.; Park, A.J.; Green, W.; Denou, E.; Silva, M.A.; Santacruz, A.; Sanz, Y.; et al. Microbiota and host determinants of behavioural phenotype in maternally separated mice. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, C.T.; Powell, D.N.; Kalman, D. Layered defense: How mucus and tight junctions seal the intestinal barrier. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodiño-Janeiro, B.K.; Alonso-Cotoner, C.; Pigrau, M.; Lobo, B.; Vicario, M.; Santos, J. Role of corticotropin-releasing factor in gastrointestinal permeability. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 21, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichlowski, M.; Hale, L.P. Bacterial-mucosal interactions in inflammatory bowel disease: An alliance gone bad. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G1139–G1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Linglong, P.; Weixia, D.; Hong, W. Protective effects of Bifidobacterium on intestinal barrier function in LPS-induced enterocyte barrier injury of Caco-2 monolayers and in a rat NEC model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khailova, L.; Mount Patrick, S.K.; Arganbright, K.M.; Halpern, M.D.; Kinouchi, T.; Dvorak, B. Bifidobacterium bifidum reduces apoptosis in the intestinal epithelium in necrotizing enterocolitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G1118–G1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Birchenough, G.M.H.; Ståhlman, M.; Arike, L.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C.; Bäckhed, F. Bifidobacteria or fiber protects against diet-induced microbiota-mediated colonic mucus deterioration. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Wasan, A.; Sharma, R.K. Recent developments in probiotics: An emphasis on Bifidobacterium. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. The role of mucin and oligosaccharides via cross-feeding activities by Bifidobacterium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jeong, Y.; Kang, S.; You, H.J.; Ji, G.E. Co-culture with Bifidobacterium catenulatum improves the growth, gut colonization, and butyrate production of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii: In vitro and in vivo studies. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Ran, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; He, D.; Huang, B.; Fu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, W. Sodium butyrate inhibits inflammation and maintains epithelium barrier integrity in a TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease mice model. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Gurav, A.; Sivaprakasam, S.; Brady, E.; Padia, R.; Shi, H.; Thangaraju, M.; Prasad, P.D.; Manicassamy, S.; Munn, D.H.; et al. Activation of Gpr109a, receptor for niacin and the commensal metabolite butyrate, suppresses colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis. Immunity 2014, 40, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, N.; Bai, C.; Song, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z. Bifidobacterium plays a protective role in TNF-α-induced inflammatory response in Caco-2 cell through NF-κB and p38MAPK pathways. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020, 464, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Direction | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | Forward Reverse | 5′-AATGCCTCGTGCTGTCTGACC-3′ 5′-GGGTGGGTGTGCCGTCTTTC-3′ |
| IL-6 | Forward Reverse | 5′-TCCTACCCCAACTTCCAATGCTC-3′ 5′-TTGGATGGTCTTGGTCCTTAGCC-3′ |
| IL-18 | Forward Reverse | 5′-AAACCCGCCTGTGTTCGA-3′ 5′-TCAGTCTGGTCTGGGATTCGT-3′ |
| IFN-γ | Forward Reverse | 5′-AGGTGAACAACCCACAGAT-3′ 5′-CTTCTTATTGGCACACTCTCTAC-3′ |
| TNF-α | Forward Reverse | 5′-TGGCGTGTTCATCCGTTCTCTACC-3′ 5′-CCCGCAATCCAGGCCACTACTT-3′ |
| ZO-1 | Forward Reverse | 5′-GGAAACCCGAAACTGATGCTATGG-3′ 5′-AACTGGCTGGCTGTACTGTGAG-3′ |
| occludin | Forward Reverse | 5′-AGCAACGATAACCTAGAGACA-3′ 5′-TGTCTCTGTTGATCTGAAGTG-3′ |
| claudin 3 | Forward Reverse | 5′-GGGTTGTACGTGGGCTGGGC-3′ 5′-GTGGATCGCGGCGCGGAATA-3′ |
| claudin 4 | Forward Reverse | 5′-GCCAGCAACTATGTGTAAG-3′ 5′-GCCGTTATGAGTTCAATCC-3′ |
| GAPDH | Forward Reverse | 5′-CTTGGGCTACACTGAGGACC-3′ 5′-CTGTTGCTGTAGCCGTATTC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Fukui, H.; Ran, Y.; Xu, X.; Ebisutani, N.; Nakanishi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Maeda, A.; Makizaki, Y.; Tomita, T.; et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 Has a Preventive Effect on the Acceleration of Colonic Permeability and M1 Macrophage Population in Maternally Separated Rats. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060641
Wang X, Fukui H, Ran Y, Xu X, Ebisutani N, Nakanishi T, Tanaka Y, Maeda A, Makizaki Y, Tomita T, et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 Has a Preventive Effect on the Acceleration of Colonic Permeability and M1 Macrophage Population in Maternally Separated Rats. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(6):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060641
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuan, Hirokazu Fukui, Ying Ran, Xin Xu, Nobuhiko Ebisutani, Takashi Nakanishi, Yoshiki Tanaka, Ayako Maeda, Yutaka Makizaki, Toshihiko Tomita, and et al. 2021. "Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 Has a Preventive Effect on the Acceleration of Colonic Permeability and M1 Macrophage Population in Maternally Separated Rats" Biomedicines 9, no. 6: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060641
APA StyleWang, X., Fukui, H., Ran, Y., Xu, X., Ebisutani, N., Nakanishi, T., Tanaka, Y., Maeda, A., Makizaki, Y., Tomita, T., Oshima, T., & Miwa, H. (2021). Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 Has a Preventive Effect on the Acceleration of Colonic Permeability and M1 Macrophage Population in Maternally Separated Rats. Biomedicines, 9(6), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9060641









