FAK Regulates VEGFR2 Expression and Promotes Angiogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Short Interfering RNA and Plasmid of FAK Transfections
2.5. FAK shRNA Clone Transfection
2.6. RNA Extraction, Genome-Wide Transcriptome Characterization, and Expression Profiling by RNA Sequencing
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.8. Preparation of Conditioned Medium and Matrigel Tube Formation Experiment
2.9. Human Specimens
2.10. Ethics Statement
2.11. Animal Grouping
2.12. Zebrafish Assay
2.13. Immunohistochemical Staining and Scoring
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
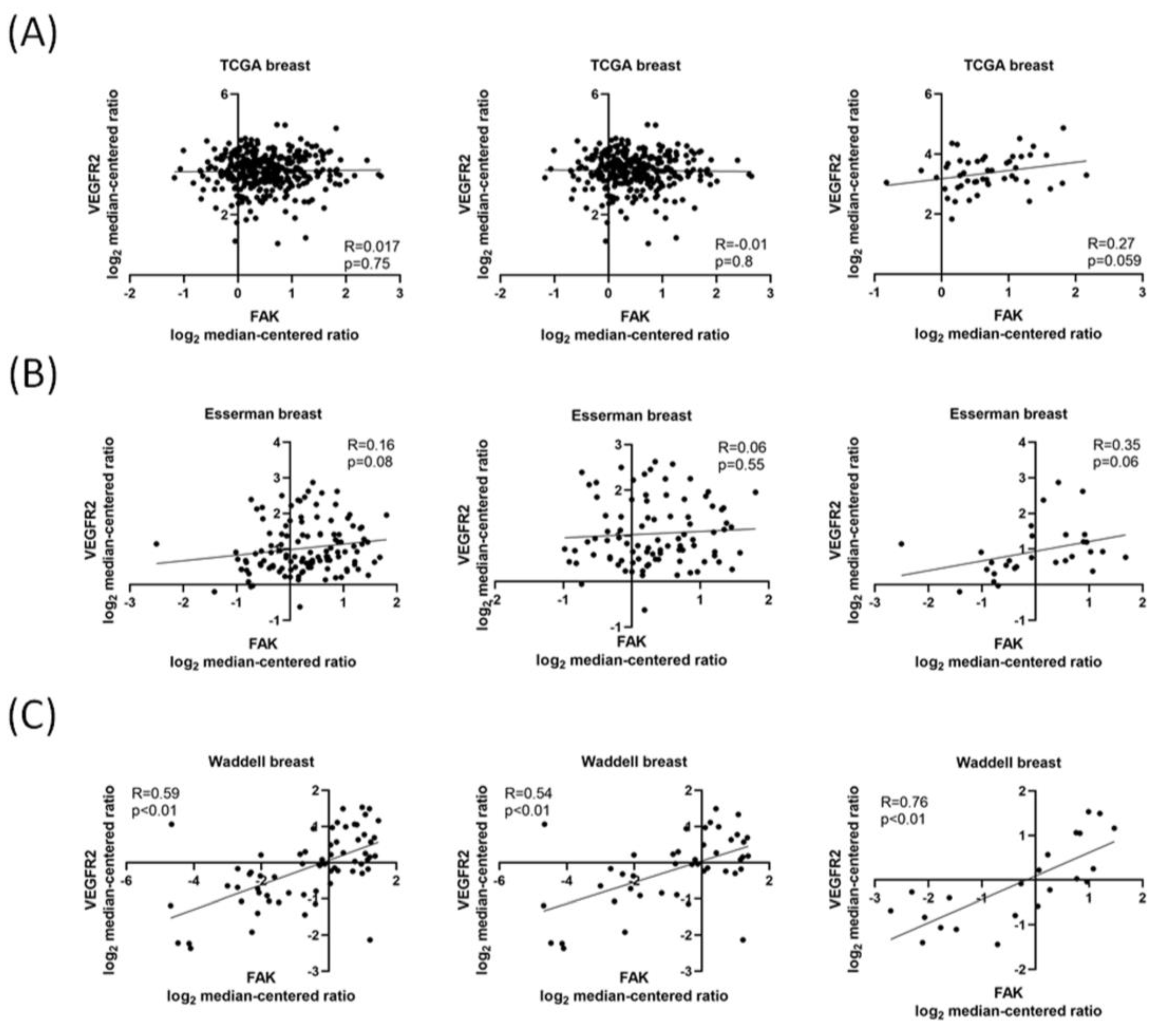
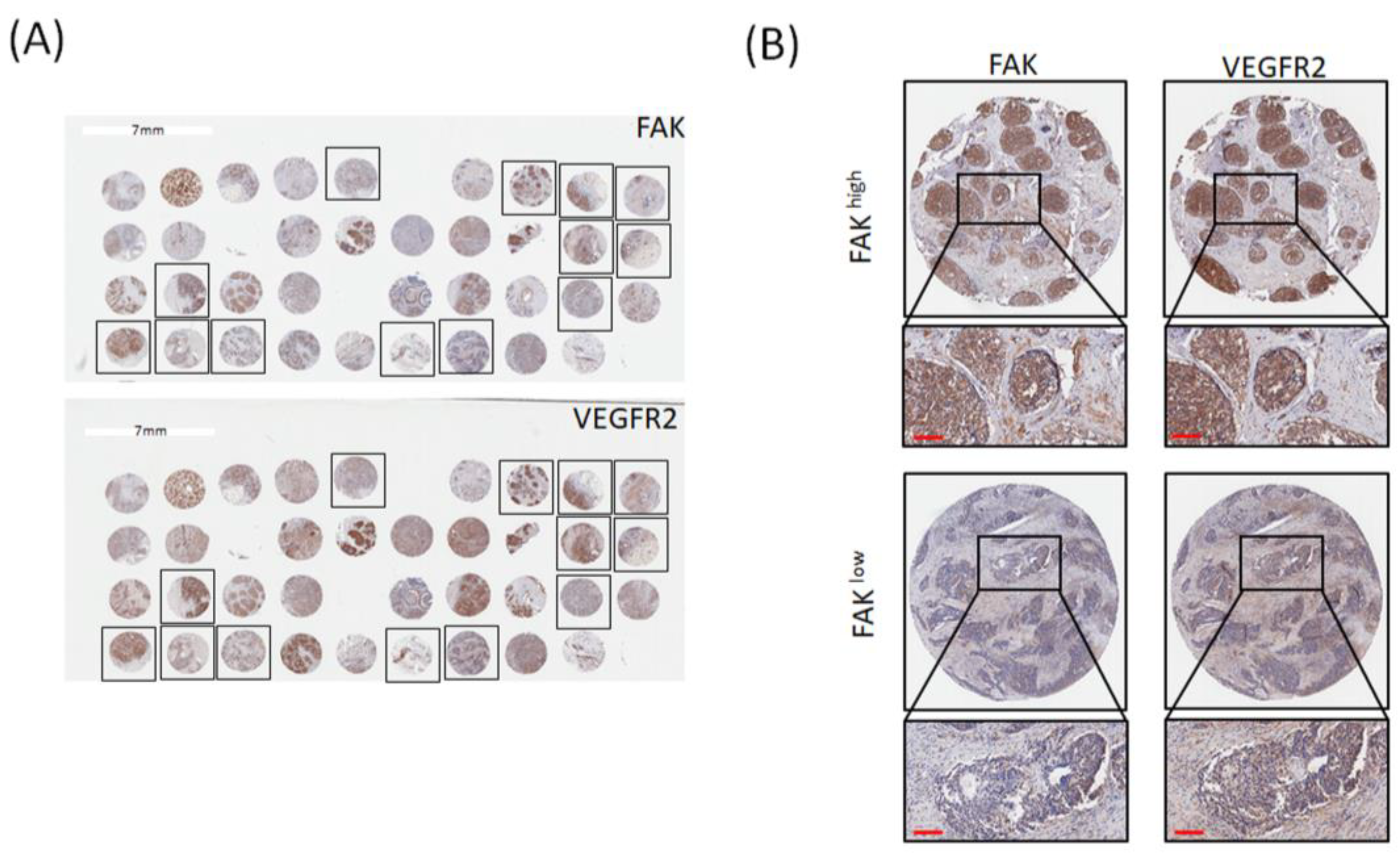
3.1. FAK Expression Is Positively Correlated with VEGFR2 Expression in Patients with TNBC
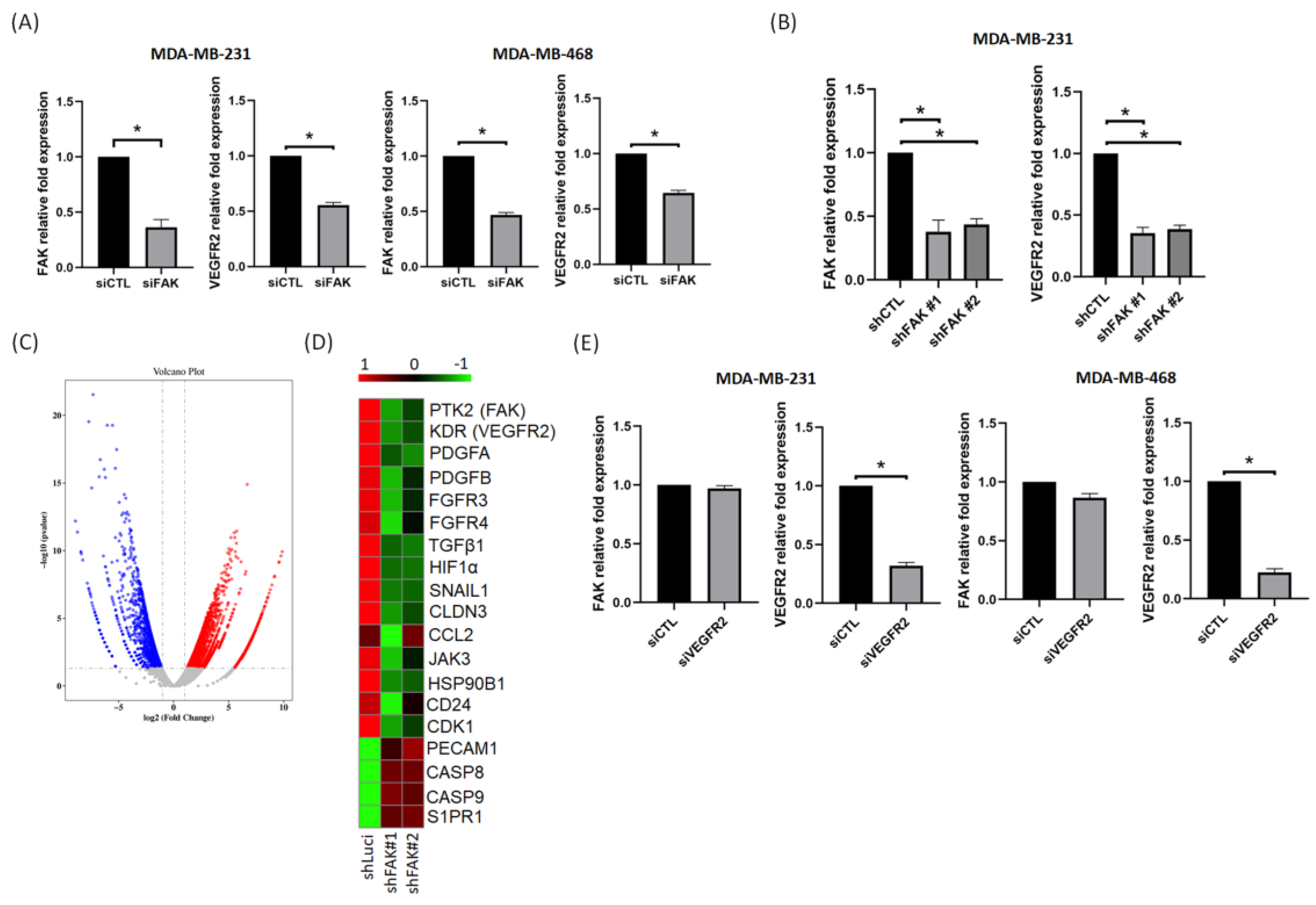
3.2. FAK Plays a Role in Regulating VEGFR2 Gene Expression in TNBC Cells
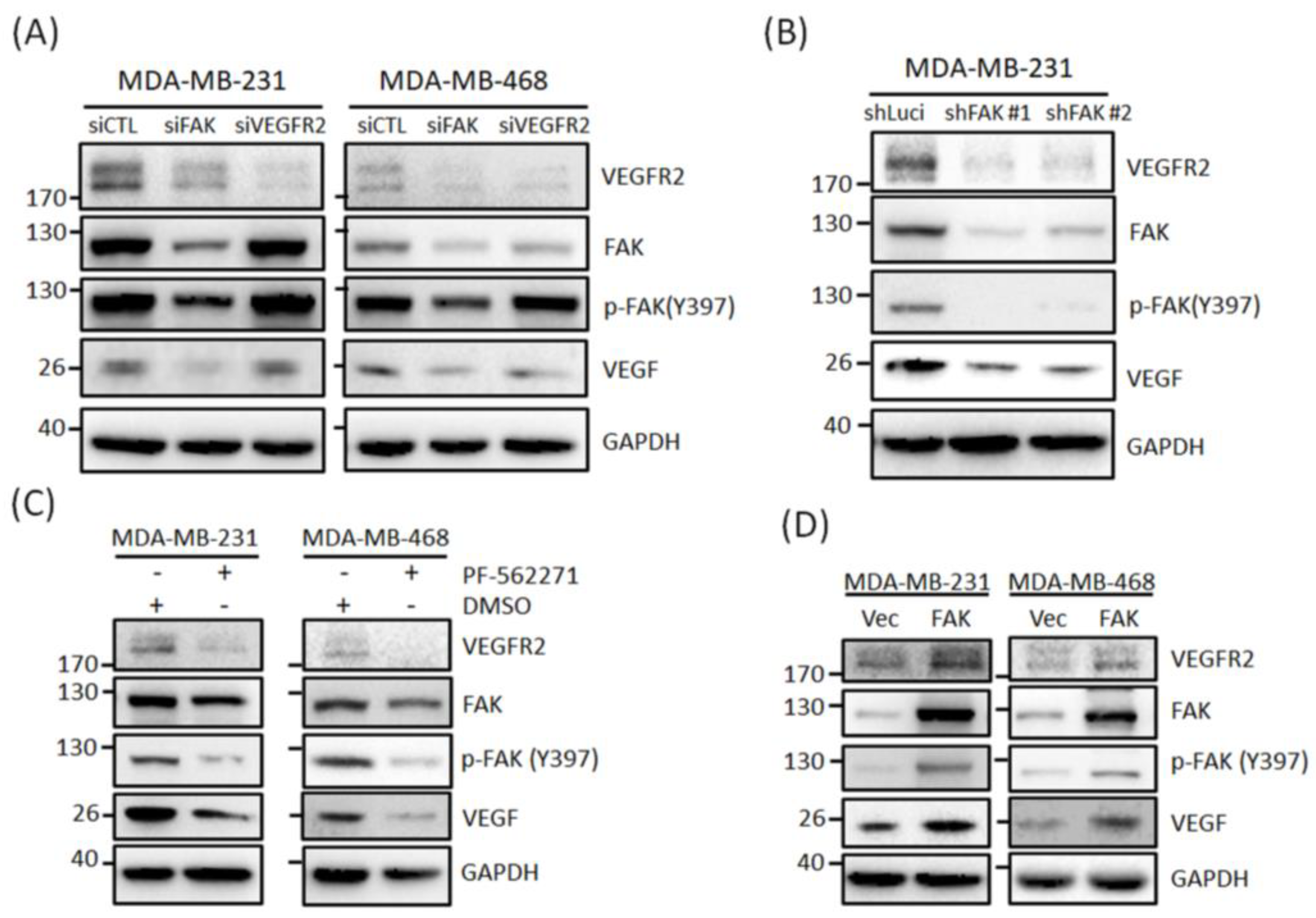
3.3. FAK Plays Roles in Regulating VEGFR2 Protein Expressions in TNBC Cells
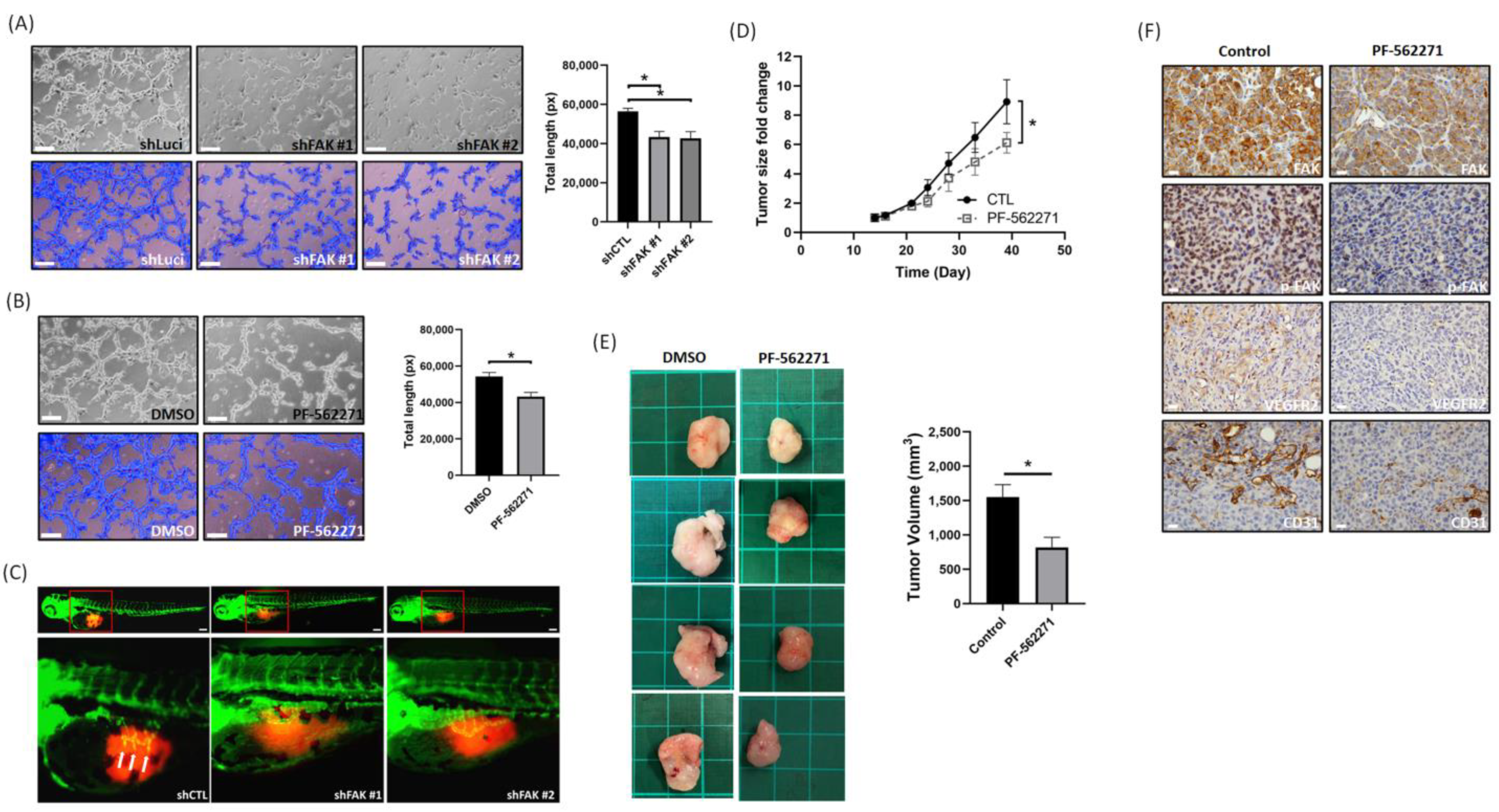
3.4. Suppression of FAK Affects the Tumor Angiogenesis and Growth In Vitro and In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigiracciolo, D.C.; Santolla, M.F.; Lappano, R.; Vivacqua, A.; Cirillo, F.; Galli, G.R.; Talia, M.; Muglia, L.; Pellegrino, M.; Nohata, N.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation by estrogens involves GPER in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deepak, K.; Vempati, R.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Dasari, V.R.; Nagini, S.; Rao, D.; Malla, R.R. Tumor microenvironment: Challenges and opportunities in targeting metastasis of triple negative breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 153, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielenberg, D.R.; Zetter, B.R. The Contribution of Angiogenesis to the Process of Metastasis. Cancer J. 2015, 21, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Ruggieri, S.; Tamma, R.; Simone, G.; Mangia, A. Angiogenesis and Antiangiogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Folkman, J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behelgardi, M.F.; Zahri, S.; Shahvir, Z.G.; Mashayekhi, F.; Mirzanejad, L.; Asghari, S.M. Targeting signaling pathways of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 as a potential target in the treatment of breast cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Shibuya, M. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor system and its role under physiological and pathological conditions. Clin. Sci. 2005, 109, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bridges, E.M.; Harris, A.L. The angiogenic process as a therapeutic target in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, A.S.; Lee, J.; Ferrara, N. Targeting the tumour vasculature: Insights from physiological angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot-Applanat, M.; Di Benedetto, M. Autocrine functions of VEGF in breast tumor cells. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2012, 6, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Bove, A.M.; Simone, G.; Ma, B. Molecular Bases of VEGFR-2-Mediated Physiological Function and Pathological Role. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 599281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, W. The Emerging Regulation of VEGFR-2 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.-D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Liu, G.-Y.; Xu, J.-H.; Liu, L.-Y.; Hu, Y.-M. Expression and prognostic significance of VEGFR-2 in breast cancer. Pathol.—Res. Pr. 2015, 211, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linderholm, B.K.; Hellborg, H.; Johansson, U.; Elmberger, G.; Skoog, L.; Lehtiö, J.; Lewensohn, R. Significantly higher levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and shorter survival times for patients with primary operable triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.M.; Rodriguez, Y.A.R.; Jeong, K.; Ahn, E.-Y.E.; Lim, S.-T.S. Targeting focal adhesion kinase in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.-R.; Hou, M.-F.; Ou-Yang, F.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, S.-J.; Hung, W.-C.; Yip, H.-K.; Luo, C.-W. FAK is Required for Tumor Metastasis-Related Fluid Microenvironment in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabrita, M.A.; Jones, L.M.; Quizi, J.L.; Sabourin, L.A.; McKay, B.C.; Addison, C.L. Focal adhesion kinase inhibitors are potent anti-angiogenic agents. Mol. Oncol. 2011, 5, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Yi, Q.; Tang, L. The roles of nuclear focal adhesion kinase (FAK) on Cancer: A focused review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, C.-W.; Wu, C.-C.; Ch’Ang, H.-J. Radiation sensitization of tumor cells induced by shear stress: The roles of integrins and FAK. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Bioenerg. 2014, 1843, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, M.-R.; Wu, C.-C.; Kan, J.-Y.; Li, Q.-L.; Chang, S.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Li, C.-L.; Ou-Yang, F.; Hou, M.-F.; Yip, H.-K.; et al. Impact of FAK Expression on the Cytotoxic Effects of CIK Therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2019, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohan, N.; Hosain, S.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, J.; Endo, Y.; Wu, W.J. Atezolizumab potentiates Tcell-mediated cytotoxicity and coordinates with FAK to suppress cell invasion and motility in PD-L1+ triple negative breast cancer cells. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, e1624128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohanty, A.; Pharaon, R.R.; Nam, A.; Salgia, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Massarelli, E. FAK-targeted and combination therapies for the treatment of cancer: An overview of phase I and II clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lechertier, T.; Hodivala-Dilke, K. Focal adhesion kinase and tumour angiogenesis. J. Pathol. 2011, 226, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Wu, M.; Li, Z. Rutacecarpine Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting the VEGFR2 and VEGFR2-Mediated Akt/mTOR/p70s6k Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Wu, H.-J.; Guan, J.-L. Nuclear FAK and its kinase activity regulate VEGFR2 transcription in angiogenesis of adult mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedrosa, A.R.; Bodrug, N.; Gomez-Escudero, J.; Carter, E.; Reynolds, L.E.; Georgiou, P.N.; Fernandez, I.; Lees, D.M.; Kostourou, V.; Alexopoulou, A.N.; et al. Tumor Angiogenesis Is Differentially Regulated by Phosphorylation of Endothelial Cell Focal Adhesion Kinase Tyrosines-397 and -861. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4371–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-L.; Huang, C.-R.; Chang, S.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Luo, C.-W.; Yip, H.-K. CHD4 as an important mediator in regulating the malignant behaviors of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou-Yang, F.; Pan, M.-R.; Chang, S.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Fang, S.-Y.; Li, C.-L.; Hou, M.-F.; Luo, C.-W. Identification of CHD4-β1 integrin axis as a prognostic marker in triple-negative breast cancer using next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics. Life Sci. 2019, 238, 116963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Li, N.; Qiu, X.; Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Hua, J.; Yin, P.; Zhuang, G. TIPE regulates VEGFR2 expression and promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenbach, M.; Stoll, S.J.; Jörgens, K.; Seufferlein, T.; Kroll, J. Different Regulation of Physiological and Tumor Angiogenesis in Zebrafish by Protein Kinase D1 (PKD1). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Heukamp, L.C.; Siobal, M.; Schöttle, J.; Wieczorek, C.; Peifer, M.; Frasca, D.; Koker, M.; König, K.; Meder, L.; et al. Tumor VEGF:VEGFR2 autocrine feed-forward loop triggers angiogenesis in lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeLisser, H.M.; Christofidou-Solomidou, M.; Strieter, R.M.; Burdick, M.D.; Robinson, C.S.; Wexler, R.S.; Kerr, J.S.; Garlanda, C.; Merwin, J.R.; Madri, J.A.; et al. Involvement of endothelial PECAM-1/CD31 in angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol 1997, 151, 671–677. [Google Scholar]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saharinen, P.; Eklund, L.; Pulkki, K.; Bono, P.; Alitalo, K. VEGF and angiopoietin signaling in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Liang, C.; Zhou, X.; Ge, M.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Yin, J.; Xu, H.; Xie, C.; et al. Apatinib suppresses lung cancer stem-like cells by complex interplay between β-catenin signaling and mitochondrial ROS accumulation. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeny, M.; Sabourinejad, Z.; Zarrinrad, G.; Moghaddaskho, F.; Eyvani, H.; Yousefi, H.; Mirshahvaladi, S.; Poursani, E.M.; Barghi, F.; Poursheikhani, A.; et al. Anti-tumour activity of tivozanib, a pan-inhibitor of VEGF receptors, in therapy-resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep45954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Pan, C.; Sun, J.; Gilbert, C.A.; Drews-Elger, K.; Azzam, D.; Ruiz, M.P.; Kim, M.; Ullmer, W.; Elashry, D.; et al. VEGF drives cancer-initiating stem cells through VEGFR-2/Stat3 signaling to upregulate Myc and Sox2. Oncogene 2014, 34, 3107–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinand, C.S.; Raju, R.; Soumya, S.J.; Arya, P.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R. VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling network in endothelial cells relevant to angiogenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 10, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veikkola, T.; Karkkainen, M.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Alitalo, K. Regulation of angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.; Yu, K.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Q.; et al. Discovery of a highly selective VEGFR2 kinase inhibitor CHMFL-VEGFR2-002 as a novel anti-angiogenesis agent. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 10, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terman, B.I.; Dougher-Vermazen, M.; Carrion, M.E.; Dimitrov, D.; Armellino, D.C.; Gospodarowicz, D.; Böhlen, P. Identification of the KDR tyrosine kinase as a receptor for vascular endothelial cell growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 187, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor: Basic Science and Clinical Progress. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, A.-K.; Dimberg, A.; Kreuger, J.; Claesson-Welsh, L. VEGF receptor signalling? in control of vascular function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, H.; et al. A novel humanized Frizzled-7-targeting antibody enhances antitumor effects of Bevacizumab against triple-negative breast cancer via blocking Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekian, S.; Rahmati, M.; Sari, S.; Kazemimanesh, M.; Kheirbakhsh, R.; Muhammadnejad, A.; Amanpour, S. Expression of Diverse Angiogenesis Factor in Different Stages of the 4T1 Tumor as a Mouse Model of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.G.; Ung, E.; Whalen, P.; Cooper, B.; Hulford, C.; Autry, C.; Richter, D.; Emerson, E.; Lin, J.; Kath, J.; et al. Antitumor Activity and Pharmacology of a Selective Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor, PF-562,271. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, H.; Dehart, J.P.; Murphy, J.M.; Lim, S.-T.S. Understanding the Roles of FAK in Cancer. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 63, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domingues, I.; Rino, J.; Demmers, J.A.A.; De Lanerolle, P.; Santos, S.C.R. VEGFR2 Translocates to the Nucleus to Regulate Its Own Transcription. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Xing, X.; Wu, S.; Dong, Y.; You, Y.; Chen, R.; Ren, Z.; Guo, W.; et al. Integrin αVβ5/Akt/Sp1 pathway participates in matrix stiffness-mediated effects on VEGFR2 upregulation in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2635–2648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; et al. Programmed death ligand-1 regulates angiogenesis and metastasis by participating in the c-JUN/VEGFR2 signaling axis in ovarian cancer. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Breast Cancer | VEGFR2, n (%) | p-value | |
| Positive | Negative | ||
| High | 15 (41.7) | 8 (22.2) | |
| FAK | |||
| Low | 4 (11.1) | 9 (25.0) | p > 0.05 |
| Non-TNBC | VEGFR2, n (%) | p-value | |
| Positive | Negative | ||
| High | 8 (34.8) | 7 (30.4) | |
| FAK | |||
| Low | 3 (13.0) | 5 (21.7) | p > 0.05 |
| TNBC | VEGFR2, n (%) | p-value | |
| Positive | Negative | ||
| High | 7 (53.8) | 1 (7.7) | |
| FAK | |||
| Low | 1 (7.7) | 4 (30.8) | p < 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiau, J.-P.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, S.-J.; Pan, M.-R.; Liu, W.; Ou-Yang, F.; Chen, F.-M.; Hou, M.-F.; Shih, S.-L.; Luo, C.-W. FAK Regulates VEGFR2 Expression and Promotes Angiogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121789
Shiau J-P, Wu C-C, Chang S-J, Pan M-R, Liu W, Ou-Yang F, Chen F-M, Hou M-F, Shih S-L, Luo C-W. FAK Regulates VEGFR2 Expression and Promotes Angiogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(12):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121789
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiau, Jun-Ping, Cheng-Che Wu, Shu-Jyuan Chang, Mei-Ren Pan, Wangta Liu, Fu Ou-Yang, Fang-Ming Chen, Ming-Feng Hou, Shen-Liang Shih, and Chi-Wen Luo. 2021. "FAK Regulates VEGFR2 Expression and Promotes Angiogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Biomedicines 9, no. 12: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121789
APA StyleShiau, J.-P., Wu, C.-C., Chang, S.-J., Pan, M.-R., Liu, W., Ou-Yang, F., Chen, F.-M., Hou, M.-F., Shih, S.-L., & Luo, C.-W. (2021). FAK Regulates VEGFR2 Expression and Promotes Angiogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Biomedicines, 9(12), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121789







