Abstract
Before the advent of modern medicine, natural resources were widely used by indigenous populations for the prevention and treatment of diseases. The associated knowledge, collectively described as folk medicine or traditional medicine, was largely based on trial-and-error testing of plant extracts (herbal remedies) and the use of invertebrates, particularly medicinal maggots of the blowfly Lucilia sericata and blood-sucking leeches. The widespread use of traditional medicine in the West declined as scientific advances allowed reproducible testing under controlled conditions and gave rise to the modern fields of biomedical research and pharmacology. However, many drugs are still derived from natural resources, and interest in traditional medicine has been renewed by the ability of researchers to investigate the medical potential of diverse species by high-throughput screening. Likewise, researchers are starting to look again at the benefits of maggot and leech therapy, based on the hypothesis that the use of such animals in traditional medicine is likely to reflect the presence of specific bioactive molecules that can be developed as drug leads. In this review, we consider the modern medical benefits of European medicinal leeches based on the systematic screening of their salivary proteins.
1. The Biology of Medicinal Leeches
European medicinal leeches of the genus Hirudo are blood-feeding annelids. The most relevant species are H. orientalis (Asian leech), H. medicinalis (European leech) and H. verbana (Hungarian leech). All three species are ectoparasites that live in freshwater ponds and slowly flowing streams, where they locate their vertebrate hosts by sensing heat, chemicals or movement [1,2]. Leeches attach to the host body surface and cut the skin using hundreds of calcified teeth [3]. They can then draw blood for up to one hour while secreting saliva into the wound. The secreted salivary proteins and peptides reach the vascular system of the host via thousands of tiny salivary gland cell ducts [4]. After ingestion by the leech, the host blood is compressed in the crop by the excretion of water and salts [5,6]. The remaining highly viscous blood comprises plasma proteins and blood cells and can be stored in the crop for up to one year [7]. It is thought that the morphology of the concentrated erythrocytes remains stable during storage [8], which means that proteolysis induced by host proteases released from leukocytes is inhibited [5]. Furthermore, leeches inevitably make contact with (and thus ingest) some bacteria on the surface of the host’s skin during feeding, but the stored blood does not become overrun with pathogens. Indeed, foremost symbiotic core bacteria such as Aeromonas veronii, A. hydrophila and Rikinella-like species survive in the alimentary tract of the leech [9,10,11]. It is supposed that symbionts like A. veronii support the digestion of host blood by facilitating hemolysis [10,12,13] and may also help to suppress the growth of other bacteria in the crop of the leech [9]. In most parasitic leeches the host blood is stored in the crop, while food digestion and the absorption of nutrients occur predominantly in the intestine. It can be assumed that medicinal leech enzymes (e.g., endopeptidases, aminopeptidases, phosphatases) promote digestion processes [14].
2. The Pharmacological Potential of Medicinal Leeches
Medicinal leeches were used by Egyptian, Indian, Greek and Arab physicians thousands of years ago. The main application was bloodletting, but leeches were also recommended for the treatment of systemic ailments such as inflammation, skin diseases, rheumatic pain or problems with the reproductive system [15]. As an advocate of leech therapy, the Greek physician Galen of Pergamon (130–201 AD) described leeches as an effective treatment for numerous diseases. Later, in the Middle Ages, leech therapy was popular because it was less painful than conventional treatments and was recommended even for diseases of the nervous system and eyes. The use of leeches declined in the age of modern medicine, but medical interest was rekindled when one of the strongest natural anticoagulants—hirudin—was discovered in leech saliva by John Berry Haycraft in 1884, further characterized by Fritz Markwardt in the 1950s [15].
In the 1960s, physicians rediscovered the pharmacological potential of leech saliva. For example, medicinal leeches were used to prevent vascular disorders after reconstructive surgery [16], to re-establish disrupted blood vessel networks and as an alternative to anti-inflammatory drugs. Most reports concerning medicinal leech therapy focus on cosmetic and reconstructive surgery. However, leech therapy has been tested for many conditions over the past two decades, including migraine [17,18], knee osteoarthritis [19,20,21,22,23,24,25], cardiovascular disease [26,27,28], skin disorders [29], diabetic foot ulcers [30,31,32], priapism [33], macroglossia [34,35], cancer [36,37] and skin wounds [38,39]. For most of these conditions only individual case studies were published [39], but migraine and knee osteoarthritis are exceptions. Migraine is a primary neurological disorder and, for most patients, a lifelong illness associated with headaches, vomiting, nausea, photophobia and phonophobia. In a case series of seven patients who were unresponsive to conventional drugs, post-auricular leech therapy was shown to significantly reduce the frequency of migraine headaches, which the authors attributed to the presence of potent anesthetic, anti-inflammatory and vasodilator substances in the leech saliva [17]. Osteoarthritis is a disorder of the joints that is prevalent in older people (>65 years) and causes pain after activity and stiffness after rest [40]. A meta-analysis of seven articles published between 2000 and 2017 showed that leech therapy could improve the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis and reduce pain [39]. Importantly, leeches placed on the knee often achieved comparable or even better pain relief than conventional drugs, and patients reported that mobility was restored and the benefits of leech therapy were sometimes still evident after six months [41]. Although the benefits of leech therapy were evident from these studies, the salivary compounds responsible for these effects and the underlying molecular mechanisms were not characterized in detail.
3. Salivary Proteins: Natural Drugs from Medicinal Leeches
Antagonistic interactions between parasites and their hosts have led to an evolutionary “arms race”, during which ectoparasites adapted to feed on host body fluids [42,43]. To ingest and digest host blood, medicinal leeches synthesize more than 100 salivary proteins and peptides [44,45,46,47]. The molecules are secreted during feeding and target physiological pathways involved in host defense, working as analgesics (kininases), anticoagulants (hirudin, calin, saratin and apyrase), anti-inflammatories (eglins, bdellins and tryptase inhibitor), cell matrix-degrading proteins (hyaluronidase) or antimicrobials [7,45,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58]. Salivary transcriptome data from Macrobdella decora [59] and Hirudo nipponia [60], as well as expressed sequence tag libraries constructed from the salivary glands of H. verbana, M. decora and Aliolimnatis fenestrata [61], provided insight into the spectrum proteins found in leech saliva. For European medicinal leeches, the combined transcriptomic analysis of salivary gland cells and proteomic analysis of saliva in H. medicinalis, H. orientalis and H. verbana revealed a much wider repertoire of components than previously known [44], indicating that only ~15% of the salivary proteins in these species were identified and characterized (Table 1).
Analysis of the salivary transcriptomes of H. medicinalis, H. orientalis and H. verbana revealed the presence of transcripts representing 189, 86 and 344 salivary proteins, respectively [44]. The three closely related species were found to share 39 orthologous clusters, whereas 50 orthologous clusters were shared by any two of the three species [44]. Many of these newly discovered leech salivary proteins are either associated with blood feeding or related to proteins found in animal venoms [44]. The salivary proteins predicted from transcriptomic and proteomic data can be assigned to various functional groups based on their structural similarities, including metalloproteases representing the M12, M13 and M28 families, hyaluronidases, apyrases, adenosine deaminases, antistasins, cysteine-rich secretory proteins (CRISPs), eglins, cystatins, PAN/apple domain proteins, α2-macroglobulins, low-density lipoprotein receptors, R-type lectins, and salivary proteins containing a von Willebrand factor type A (vWA) domain. These proteins are likely to be involved in the regulation of blood coagulation, the temporary adjustment of blood pressure, the regulation of inflammation, the suppression of microbial growth or the digestion of blood in the crop [44]. Interestingly, differential gene expression analysis indicated that genes encoding salivary proteins, such as hirudin, eglins, saratins and destabilases, were also expressed in other leech tissues, showing that at least some leech “salivary proteins” are not restricted to the saliva and may have additional physiological functions [44]. Some leech-specific anticoagulants were also found in leeches that do not feed on blood, such as Whitmania pigra [62]. Interestingly, these anticoagulants were upregulated after feeding [62] just as they are in blood-feeding leeches [63].
The identified metalloprotease families in leech salivary encompass astacins (M12), neprilysins (M13) and aminopeptidase S (M28). Members of these metalloprotease families were also determined in the salivary secretion of medicinal maggots of Lucilia sericata [64]. Astacin-like metalloproteases are endopeptidases, which were originally identified in the crayfish Astacus astacus, which contribute to digestion. A homologues were found in the venom of the brown spiders Loxosceles, with the recombinant form able to induce morphological changes, such as loss of adhesion of muscular aorta cells in vitro and hydrolyzed purified fibrinogen and fibronectin [65]. Mammalian neprilysin is involved in reproduction and the modulation of neuronal activity and blood pressure [66]. Interestingly, the transcriptomic analysis of the salivary glands from medicinal maggots L. sericata elucidated a diversification of proteolytic enzymes [64], whereas the most diverse groups of molecules in the saliva of leeches represented protease inhibitors.

Table 1.
Leech salivary proteins from H. medicinalis, H. verbana or H. orientalis. Isoforms of individual proteins are not shown.
Table 1.
Leech salivary proteins from H. medicinalis, H. verbana or H. orientalis. Isoforms of individual proteins are not shown.
| Salivary Protein | Mechanism of Action | Biological Significance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hirustasin (Mass: 5.866 kDa) | Tissue kallikrein inhibitor and inhibitor of trypsin, chymotrypsin and neutrophil cathepsin G | Anti-inflammatory | [55] |
| Apyrase (Mass: 45 kDa) | Cleavage of adenosine 5′-diphosphate | Inhibitor of platelet aggregation | [67] |
| Bdellin B-3 (Mass: 6.141 kDa) | Inhibitor of plasmin, trypsin and sperm acrosin | Anti-inflammatory | [68] |
| Calin (Mass: 65 kDa) | Prevents the binding of von Willebrand factor to collagen | Inhibitor of platelet aggregation | [50,69] |
| Collagenase (Mass: 50 kDa) | Cleavage of collagen | Collagen digestion | [70] |
| Destabilase (Mass: 12.6–12.9 kDa) | Cleavage of fibrin clots, cleavage of peptidoglycans in bacterial walls | Anticoagulant/antimicrobial | [71,72,73] |
| Eglin C (Mass: 8.1 kDa) | Neutrophil elastase inhibitor, cathepsin G inhibitor | Anti-inflammatory | [74,75] |
| Hirudin (Mass: 7.1 kDa) | Thrombin inhibitor | Anticoagulant | [48,76] |
| Hirudin-like factors (Mass: 4.27–6.67; isoforms HLF1-HLF3) | Unknown for the three European species | [77,78] | |
| Hyaluronidase (Mass: 27.5 kDa) | Cleavage of hyaluronic acid | Extracellular matrix digestion | [79] |
| Leech-derived tryptase inhibitor (Mass: 4.7 kDa) | Mast cell tryptase inhibitor | Anti-inflammatory | [56,57] |
| Leech carboxypeptidase inhibitor (Mass: 7.2 kDa) | Carboxypeptidase B inhibitor | Unclear | [80] |
| Saratin (Mass: 12 kDa) | Inhibits the binding of von Willebrand factor to collagen | Inhibitor of platelet aggregation | [51,81] |
| Yagin (Mass: 15.4 kDa) | Factor Xa inhibitor | Anticoagulant | [82] |
Many leech salivary proteins, including antistasin-like inhibitors, hirudins, hirudin-like factors and Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitors, show remarkable diversity [44,78], possibly reflecting target-oriented evolution [83] promoted by gene duplication events [84]. Gene duplication events are likely to have promoted the acquisition of two major salivary protein families—salivary blood coagulation inhibitors and platelet aggregation inhibitors—in blood-feeding ticks [85]. Gene recruitment also supports the diversification of salivary protein isoforms, based on the hypothesis that regulatory evolution is fundamental for adaptive evolution [86]. Accordingly, at least some venom and salivary proteins were recruited from other tissues, where they fulfilled distinct biological functions. The recruitment of alternative splice variants and 5′ exon evolution might explain the adaptation of vampire bats to hematophagy and may be a more common source of genomic complexity in sanguivorous animals than the evolution of new genes [86]. This led to the identification of novel and convergently recruited venom proteins in blood-feeding leeches and vampire bats [86].
Evolutionary models explaining the adaptation of leech salivary proteins to specific hosts are still a matter of debate. Current challenges include the lack of well-characterized proteins in terms of mode of action and target. The isoproteins in leech saliva may have more than one target in the host, or their activity may be dependent on pH, temperature, the season or the developmental phase. Both the redundancy of salivary proteins (multiple proteins directed against the same target) and the potential cooperative interactions among multiple salivary proteins should be considered. The interplay of several salivary proteins can be seen in the bloodsucking arthropod Rhodnius prolixus, which produces four isoforms of salivary nitrophorin. All of them are vasodilators (working in cooperation) and histamine suppressors, but one is a strong inhibitor of factor IXa, another is a weaker anticoagulant and the remaining two isoforms appear to have lost their anticoagulant activity [87].
4. Antistasins as a Representative Leech Salivary Protein Family
Several antistasins were identified in leech species, including (1) the prototype antistasin, isolated from the salivary glands of the Mexican leech, Haementeria officials; (2) hirustasin and bdellastasin, identified in H. medicinalis; (3) ghilanten, identified in Haementeria ghilianii; (4) piguamerin, identified in H. nipponia; and (5) guamerin I (H. nipponia) and guamerin II, isolated from Whitmania edentula [88,89,90,91,92,93]. All of these cysteine-rich proteins contain several repeated motifs, each consisting of six conserved cysteine and two conserved glycine residues [94], but differ widely in terms of structure and function [89].
The prototype antistasin is a polypeptide of 119 amino acids that includes 10 disulfide bridges and a twofold internal repeat, suggesting that it arose following a gene duplication event [54,95]. This protein is a potent competitive inhibitor of coagulation factor Xa, a serine protease which cleaves antistasin at position Arg34 to yield a 10-kDa fragment [91]. The presence of antistasin therefore maintains host blood in a liquid state [54]. The medical applications of antistasin are not restricted to its role as an anticoagulant because its ability to inhibit serine proteases was also shown to prevent the spread of tumors, probably by reducing the likelihood of metastasis [96].
Additional antistasin-type proteins known to inhibit factor Xa include ghilanten [93] and yagin [82]. In contrast, guamerin I [97] and guamerin II [88] are specific inhibitors of neutrophil and pancreas elastases, whereas hirustasin is a potent inhibitor of trypsin, chymotrypsin, cathepsin G and tissue kallikrein [55]. In contrast to hirustasin, piguamerin does not inhibit tissue kallikrein, but does inhibit plasma kallikrein and trypsin [89]. The P1 residue of the reactive site determines the specificity of serine protease inhibitors [98]. If it is lysine or arginine, the inhibitor targets trypsin and trypsin-like enzymes. However, if it is tyrosine, phenylalanine, leucine or methionine, then chymotrypsin or chymotrypsin-like enzymes are more likely targets [99]. If it is alanine or serine, the inhibitor will tend to target elastase-like enzymes [98,99]. This was confirmed for a serine protease inhibitor containing antistasin and whey acidic protein (WAP) domains (StmAW-SPI) isolated from the tropical sea cucumber Stichopus monotuberculatus [98].
5. Leech Salivary Proteins as Drug Leads
Natural products from plants and animals provide an astonishingly diverse source of active compounds for drug development and clinical trials [100] and can be used as tools for pharmacological or biotechnological applications [101]. Medicinal leeches are promising for the treatment of diseases associated with pain, inflammation or blood disorders. However, the use of living animals poses a risk of infection. Leeches carry bacteria in their digestive tract [10,11] and on their skin, and these bacteria could infect patients undergoing treatment. The use of antibiotic prophylaxis to minimize post-operative leech-borne infections only partially addresses this issue and encourages the emergence of multidrug-resistant pathogens in a clinical setting [102]. One strategy to avoid contact with leeches altogether is the extraction and purification of individual salivary components and their production as recombinant proteins to be administered using sterile equipment. Linked sets of proteomic and transcriptomic data are needed to explore bioactive proteins and peptides derived from natural animal sources such as leech saliva [101]. Such combined analysis (e.g., RNA-Seq + MALDI-TOF-MS or NanoLC-ESI-MS) allows researchers to compare salivary gland transcripts containing signal peptides with salivary proteins secreted into the host wound. Because European medical leeches have thousands of single salivary glands cells and their saliva secretion mechanisms are still unknown, it is necessary to prepare salivary gland cell tissues for proteomics. Comparative proteomic analysis of unfed leeches and fed leeches enabled researchers to separate proteins and to distinguish between secretory and nonsecretory proteins [63]. The combination of proteomics and transcriptomics followed by a conserved domain search made it possible to predict the functional domains of salivary proteins that may be responsible for the observed therapeutic effects of leeches, leading to the identification of new anti-inflammatory, analgesic or pro-coagulant leads (Figure 1). The pharmacological potential of a protein can only be established if its target is known, and this is best achieved by expressing the drug lead as a recombinant protein so that ample amounts are available for testing in vitro, in cells, in tissue-based assays and in animal models. Multiple assays are available for the detection of targets related to blood coagulation, pain pathways, antimicrobial activity, cytotoxicity and inflammation. Recombinant leech proteins can be expressed in bacteria [77,103], yeast [104,105,106], insect cells [107] or a cell-free expression system, or leech peptides can be prepared by chemical synthesis. Correct folding is important but difficult to control, because leech salivary proteins often contain numerous cysteine residues that form disulfide bonds and these structures must be replicated to ensure that synthetic and recombinant proteins remain stable and functional. Eglins are an identified leech salivary protein family without cysteine residues [74,75], while other described salivary proteins possess six cysteine residues (hirudin, hirudin-like factors, leech-derived tryptase inhibitor, bdellin-B3; saratin; [48,51,56,57,68,76,77,81]), eight cysteine residues (leech carboxypeptidase inhibitor; [80]), 10 cysteine residues (hirustasin; [55]) or 14 cysteine residues (destabilase; [71,72,73]). The formation of disulfide bonds is one of the most important post-translational modifications, ensuring the bioactivity of the protein and underpinnig the assignment of the protein to a given class or family [101]. Correct folding can be confirmed by X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, but large quantities of protein are required. In contrast, preliminary structural analysis with limited sample quantities is possible using approaches such as electron capture dissociation (ECD) or electron transfer dissociation (ETD) coupled with liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) using a triple quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer [108].
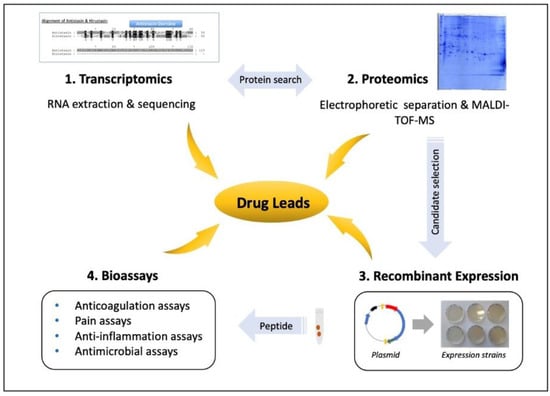
Figure 1.
Workflow for the analysis of leech salivary proteins as drug leads. To analyze individual leech salivary proteins, a combination of transcriptomics and proteomics provides the protein sequences. Recombinant proteins are expressed to test their activities in cells, tissues and animal models, for example, to determine whether they possess anticoagulation, analgesic, anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial effects.
Author Contributions
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the generous funding by the Hessen State Ministry of Higher Education, Research and the Arts (HMWK) for the project “Animal Venomics” via the LOEWE Center “Translational Biodiversity Genomics”.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Richard M. Twyman for editing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dickinson, M.H.; Lent, C.M. Feeding behavior of the medicinal leech, Hirudo medicinalis L. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1984, 154, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M.; Tullett, P.A. The effects of temperature, atmospheric pressure and season on the swimming activity of the medicinal leech, Hirudo medicinalis (Hirudinea; Hirudinidae), in a Lake District tarn. Freshwater Biol. 1986, 16, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammersen, F. The muscle structure in the pharyngeal wall of Hirudo medicinalis and Haemopsis sanguisuga. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 1963, 60, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, C.G.; Lent, C.M. Excitability and secretory activity in the salivary gland cells of jawed leeches (Hirudinea: Gnathobdellida). J. Exp. Biol. 1988, 137, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lent, C.M.; Fliegner, K.H.; Freedman, E.; Dickinson, M.H. Ingestive behaviour and physiology of the medicinal leech. J. Exp. Biol. 1988, 137, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zerbst-Boroffka, I. Ion transport mechanism in basal and diuretic nephridia of the leech, Hirudo medicinalis L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1973, 86, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roters, F.J.; Zebe, E. Protease inhibitors in the alimentary tract of the medicinal leech Hirudo medicinalis: In vivo and in vitro studies. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1992, 162, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roters, F.J. Untersuchungen über Die Verdauungsphysiologie des Blutegels Hirudo medicinalis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Münster, Münster, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Indergand, S.; Graf, J. Ingested blood contributes to the specificity of the symbiosis of Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria and Hirudo medicinalis, the medicinal leech. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4735–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltz, M.A.; Bomar, L.; Lapierre, P.; Morrison, H.G.; McClure, E.A.; Sogin, M.L.; Graf, J. Metagenomic analysis of the medicinal leech gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, M.E.; Min, G.S.; Fontanella, F.M.; Phillips, A.J.; Watson, S.C. Bacterial symbiont and salivary peptide evolution in the context of leech phylogeny. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomar, L.; Maltz, M.; Colston, S.; Graf, J. Directed culturing of microorganisms using metatranscriptomics. Mbio 2011, 2, e00012-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltz, M.A.; Graf, J. The Type II Secretion System Is Essential for Erythrocyte Lysis and Gut Colonization by the Leech Digestive Tract Symbiont Aeromonas veronii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziekońska-Rynko, J.; Bielecki, A.; Palińska, K. Activity of selected hydrolytic enzymes from leeches (Clitellata: Hirudinida) with different feeding strategies. Biologia 2009, 64, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualkader, A.M.; Ghawi, A.M.; Alaama, M.; Awang, M.; Merzouk, A. Leech therapeutic applications. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deganc, M.; Zdravic, F. Venous congestion of flaps treated by application of leeches. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1960, 13, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Fasihuzzaman, N.; Jabeen, A.; Sultana, A.; Khan, A.Q. Post-auricular leech therapy reduced headache & migraine days in chronic migraine. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi, M.; Jalalian, B.; Valian, M.; Shariati, S.; Saeidi, T.; Ranjbar, H. Can leech therapy be used as an alternative treatment for controlling migraine headache? A Pilot Study. Acta Fac. Med. Naissensis 2015, 32, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Andereya, S.; Stanzel, S.; Maus, U.; Mueller-Rath, R.; Mumme, T.; Siebert, C.H.; Stock, F.; Schneider, U. Assessment of leech therapy for knee osteoarthritis: A randomized study. Acta Orthop. 2008, 79, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalsen, A.; Moebus, S.; Spahn, G.; Esch, T.; Langhorst, J.; Dobos, G.J. Leech therapy for symptomatic treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Results and implications of a pilot study. Leech 2002, 84, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Michalsen, A.; Klotz, S.; Lüdtke, R.; Moebus, S.; Spahn, G.; Dobos, G.J. Effectiveness of leech therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee: A randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, O.P.; Rai, N.P.; Dwivedi, A.K. Efficacy of leech therapy in the management of osteoarthritis (Sandhivata). Ayu 2011, 32, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiffa, M.; Siddiquib, M.A.; Sultana, A.; Zaman, F.; Fahamiya, N.; Akhtarc, M.U. Comparative clinical evaluation of leech therapy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Eur. J. Integr. 2013, 5, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, R.; Moser, C.; Hopfenmueller, W.; Mansmann, U.; Buehring, M.; Uehleke, B. Randomised controlled trial with medical leeches for osteoarthritis of the knee. Complement. Ther. Med. 2012, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.M.; Abbas Jamil, S.S.; Sultana, A.; Zaman, F.; Fuzail, M. Safety and efficacy of leeching therapy for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis using Indian medicinal leech. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2009, 8, 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, H.; Nouri, M.; Amirjamshidi, A. Medicinal leech therapy in neurosurgical practice. J. Inj. Violence Res. 2012, 4, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Kusnetsova, L.P.; Lusov, V.A.; Volov, N.A.; Smirnova, N.A.; Bogdanova, L.S. Hirudotherapy in complex treatment of chronic heart failure. Russ. J. Cardiol. 2008, 2, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nargiza, E.; Mirdjuraev, E.; Ergasheva, N. Leech therapy to prevent ischemic stroke: p1231. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, K.P.; Rao, S.D.; Umar, S.N.; Gopalakrishnaiah, V. A clinical trial for evaluation of leech application in the management of Vicarcikā (Eczema). Anc. Sci. Life 2014, 33, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarprakash, P.D. Case study of leech application in diabetic foot ulcer. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 2012, 3, 748–751. [Google Scholar]
- Na, H.J. The Effects of live leech (Hirudo Medicinalis) therapy on diabetic foot: A clinical case report. Korean J. Orient. Med. 2003, 24, 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi, S.A. Unani treatment and leech therapy saved the diabetic foot of a patient from amputation. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, S.A.; Rostami, S.; Teimoori, M. Leech therapy for treating priapism: Case report. Iran. J. Public Health 2017, 46, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bumpous, J.M.; Byrne, P.J.; Bernstein, P.E. The use of medicinal leeches to treat macroglossia secondary to blunt trauma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2001, 125, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramzan, M.; Droog, W.; Sleeswijk Visser, S.; van Roessel, E.W.; Meynaar, I.A. Leech got your tongue? Haematoma of the tongue treated with medicinal leeches: A case report. Neth. J. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 268–270. [Google Scholar]
- Kalender, M.E.; Comez, G.; Sevinc, A.; Dirier, A.; Camci, C. Leech therapy for symptomatic relief of cancer pain. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, J.; Armitage, D.W.; Phillips, K.R.; Parr, N.J. Leech therapy for penoscrotal oedema in patients with hormone-refractory prostate carcinoma. BJU Int. 2003, 91, 579–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darestani, K.D.; Mirghazanfari, S.M.; Moghaddam, K.G.; Hejazi, S. Leech therapy for linear incisional skin-wound healing in rats. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2014, 7, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, R.; Abdi, M.; Pourrahimi, M.; Dabaghian, F.H. Leech therapy indications: A scoping review. Tradit. Med. Res. 2019, 4, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan, F.; Wibowo, Y.R.; Bunawan, N.C.; Turner, J.H. Controversy: Hirudotherapy (leech therapy) as an alternative treatment for osteoarthritis. Acta Med. Indones. 2015, 47, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pilcher, H. Medicinal leeches: Stuck on you. Nature 2004, 432, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, B.; Balvín, O.; Vonhof, M.J.; Broders, H.G.; Fenton, B.; Keyghobadi, N. Host association and selection on salivary protein genes in bed bugs and related blood-feeding ectoparasites. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Valen, L. A new evolutionary law. In Evolutionary Theory; Band 1; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1973; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Babenko, V.V.; Podgorny, O.V.; Manuvera, V.A.; Kasianov, A.S.; Manolov, A.I.; Grafskaia, E.N.; Shirokov, D.A.; Kurdyumov, A.S.; Vinogradov, D.V.; Nikitina, A.S.; et al. Draft genome sequences of Hirudo medicinalis and salivary transcriptome of three closely related medicinal leeches. BioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskova, I.P.; Zavalova, L.L. Proteinase inhibitors from the medicinal leech Hirudo medicinalis. Biochemistry 2001, 66, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baskova, I.P.; Zavalova, L.L.; Basanova, A.V.; Moshkovskii, S.A.; Zgoda, V.G. Protein profiling of the medicinal leech salivary gland secretion by proteomic analytical methods. Biochemistry 2004, 69, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, J.-P.; Lemke, S. Small bite, large impact—Saliva and salivary molecules in the medical leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Naturwissenschaften 2011, 98, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Amiconi, G.; Bode, W.; Bolognesi, M.; Coletta, M.; Menegatti, E. Proteinase inhibitors from the European medicinal leech Hirudo medicinalis: Structural, functional and biomedical aspects. Mol. Asp. Med. 1995, 16, 215–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskova, I.P.; Khalil, S.; Nartikova, V.F.; Paskhina, T.S. Inhibition of plasma kallikrein. Kininase and kinin-like activities of preparations from the medicinal leeches. Thromb. Res. 1992, 67, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckmyn, H.; Stassen, J.M.; Vreys, I.; Van Houtte, E.; Sawyer, R.T.; Vermylen, J. Calin from Hirudo medicinalis, an inhibitor of platelet adhesion to collagen, prevents platelet-rich thrombosis in hamsters. Blood 1995, 85, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronwald, W.; Bomke, J.; Maurer, T.; Domogalla, B.; Huber, F.; Schumann, F.; Kremer, W.; Fink, F.; Rysiok, T.; Frech, M.; et al. Structure of the leech protein saratin and characterization of its binding to collagen. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 381, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haycraft, J.B. On the action of a secretion obtained from the medicinal leech on the coagulation of the blood. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1884, 36, 478–487. [Google Scholar]
- Linker, A.; Meyer, K.; Hoffman, P. The production of hyaluronate oligosaccharides by leech hyaluronidase and alkali. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mittl, P.R.; Di Marco, S.; Fendrich, G.; Pohlig, G.; Heim, J.; Sommerhoff, C.; Fritz, H.; Priestle, J.P.; Grütter, M.G. A new structural class of serine protease inhibitors revealed by the structure of the hirustasin-kallikrein complex. Structure 1997, 5, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söllner, C.; Mentele, R.; Eckerskorn, C.; Fritz, H.; Sommerhoff, C.P. Isolation and characterization of hirustasin, an antistasin-type serine-proteinase inhibitor from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 219, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerhoff, C.P.; Söllner, C.; Mentele, R.; Piechottka, G.P.; Auerswald, E.A.; Fritz, H. A Kazal-type inhibitor of human mast cell tryptase: Isolation from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis, characterization, and sequence analysis. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1994, 375, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, M.T.; Morenweiser, R.; Stürzebecher, J.; Bauer, M.; Bode, W.; Huber, R.; Piechottka, G.P.; Matschiner, G.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Fritz, H.; et al. The three-dimensional structure of recombinant leech-derived tryptase inhibitor in complex with trypsin. Implications for the structure of human mast cell tryptase and its inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 19931–19937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilahur, G.; Duran, X.; Juan-Babot, O.; Casani, L.; Badimon, L. Antithrombotic effects of saratin on human atherosclerotic plaques. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 191–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.-S.; Sarkar, I.N.; Siddall, M.E. Salivary Transcriptome of the North American Medicinal Leech, Macrobdella decora. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shi, P.; You, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Transcriptomic analysis of the salivary gland of medicinal leech Hirudo nipponia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvist, S.; Min, G.-S.; Siddall, M.E. Diversity and selective pressures of anticoagulants in three medicinal leeches (Hirudinida: Hirudinidae, Macrobdellidae). Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Guan, D.-L.; Kvist, S.; Ma, L.B.; Xie, J.X.; Xu, S.Q. Transcriptomics and differential gene expression in Whitmania pigra (Annelida: Clitellata: Hirudinida: Hirudinidae): Contrasting feeding and fasting modes. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 4706–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, S.; Müller, C.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. Be ready at any time: Postprandial synthesis of salivary proteins in salivary gland cells of the haematophagous leech Hirudo verbana. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franta, Z.; Vogel, H.; Lehmann, R.; Rupp, O.; Goesmann, A.; Vilcinskas, A. Next generation sequencing identifies five major classes of potentially therapeutic enzymes secreted by Lucilia sericata medical maggots. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8285428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Moreira, D.; Matsubara, F.; Schemczssen-Graeff, Z.; De Bona, E.; Heidemann, V.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Gremski, L.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Chaim, O.; et al. Brown Spider (Loxosceles) venom toxins as potential biotools for the development of novel therapeutics. Toxins 2019, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feygina, E.; Katrukha, G.; Semenov, G. Neutral Endopeptidase (Neprilysin) in Therapy and Diagnostics: Yin and Yang. Biochemistry 2019, 84, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigbi, M.; Orevi, M.; Eldor, A. Platelet aggregation and coagulation inhibitors in leech saliva and their roles in leech therapy. In Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis; Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 22, pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, E.; Rehm, H.; Gippner, C.; Bode, W.; Eulitz, M.; Machleidt, W.; Fritz, H. The primary structure of bdellin B-3 from the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Bdellin B-3 is a compact proteinase inhibitor of a “non-classical” Kazal type. It is present in the leech in a high molecular mass form. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1986, 367, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, R.; Jones, C.P.; Sawyer, R.T. Calin—A platelet adhesion inhibitor from the saliva of the medicinal leech. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1991, 2, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigbi, M.; Levy, H.; Iraqi, F.; Teitelbaum, M.; Orevi, M.; Alajoutsijarvi, A.; Horovitz, A.; Galun, R. The saliva of the medicinal leech Hirudo medicinalis—I. Biochemical characterization of the high molecular weight fraction. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1987, 87, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskova, I.P.; Zavalova, L.L. Polyfunctionality of lysozyme destabilase from the medicinal leech. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2008, 34, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalova, L.L.; Baskova, I.P.; Lukyanov, S.A.; Sass, A.V.; Snezhkov, E.V.; Akopov, S.B.; Artamonova, I.I.; Archipova, V.S.; Nesmeyanov, V.A.; Kozlov, D.G.; et al. Destabilase from the medicinal leech is a representative of a novel family of lysozymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2000, 1478, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalova, L.L.; Yudina, T.G.; Artamonova, I.I.; Baskova, I.P. Antibacterial non-glycosidase activity of invertebrate destabilase-lysozyme and of its helical amphipathic peptides. Chemotherapy 2006, 52, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, N.J.; Bodmer, J.L.; Virca, G.D.; Metz-Virca, G.; Maschler, R.; Bieth, J.G.; Schnebli, H.P. Kinetic studies on the interaction of eglin c with human leukocyte elastase and cathepsin G. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1987, 368, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junger, W.G.; Hallstrom, S.; Redl, H.; Schlag, G. Inhibition of human, ovine, and baboon neutrophil elastase with eglin c and secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1992, 373, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwardt, F. Untersuchungen über hirudin. Naturwiss 1955, 42, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Mescke, K.; Liebig, S.; Mahfoud, H.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. More than just one: Multiplicity of Hirudins and Hirudin-like Factors in the Medicinal Leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Haase, M.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. Hirudins and hirudin-like factors in Hirudinidae: Implications for function and phylogenetic relationships. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovingh, P.; Linker, A. Hyaluronidase activity in leeches (Hirudinea). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 124, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, D.; Vendrell, J.; Canals, F.; Horstmann, J.; Aviles, F.X.; Fritz, H.; Sommerhoff, C.P. A carboxypeptidase inhibitor from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis. Isolation, sequence analysis, cDNA cloning, recombinant expression, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32927–32933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domogalla, B. NMR-Lösungsstruktur des Proteins Saratin, Strukturelle Charakterisierung der Saratin-Kollagen-Interaktion und des Carausius Morosus-hyperthrehalosämischen Hormons (Cam-HrTH-I). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kornowski, R.; Eldor, A.; Werber, M.M.; Ezov, N.; Zwang, E.; Nimrod, A.; Chernine, A.; Finkelstein, A.; Panet, A.; Laniado, S.; et al. Enhancement of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator thrombolysis with a selective factor Xa inhibitor derived from the leech Hirudo medicinalis: Comparison with heparin and hirudin in a rabbit thrombosis model. Coron. Artery Dis. 1996, 7, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Kopecký, J.; Valdés, J.J. Understanding the evolutionary structural variability and target specificity of tick salivary Kunitz peptides using next generation transcriptome data. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.F. Structure and mechanism in salivary proteins from blood-feeding arthropods. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, B.J.; Neitz, A.W.H. Adaptation of ticks to a blood-feeding environment: Evolution from a functional perspective. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.D.; Baker, R.J. Secretory gene recruitments in vampire bat salivary adaptation and potential convergences with sanguivorous leeches. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, D.E. Antihemostatic molecules from saliva of blood-feeding arthropods. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.R.; Hong, S.J.; Ha, K.S.; Joe, C.O.; Kang, K.W. A cysteine-rich serine protease inhibitor (Guamerin II) from the non-blood sucking leech Whitmania edentula: Biochemical characterization and amino acid sequence analysis. J. Enzym. Inhib. 1996, 10, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R.; Kang, K.W. Amino acid sequence of piguamerin, an antistasin-type protease inhibitor from the blood sucking leech Hirudo nipponia. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 254, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chu, T.T.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, D.R.; Nguyen, C.M.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.R.; Hahn, M.J.; Kim, K.K. The crystal structure of guamerin in complex with chymotrypsin and the development of an elastase-specific inhibitor. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 376, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, E.M.; Jain, D.; Lenny, A.B.; Schaffer, L.; Siegl, P.K.; Dunwiddie, C.T. Purification and characterization of recombinant antistasin: A leech-derived inhibitor of coagulation factor Xa. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 285, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rester, U.; Bode, W.; Moser, M.; Parry, M.A.; Huber, R.; Auerswald, E. Structure of the complex of the antistasin-type inhibitor bdellastasin with trypsin and modelling of the bdellastasin-microplasmin system. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 293, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rester, U.; Bode, W.; Sampaio, C.A.M.; Auerswald, E.; Lopes, A.P.Y. Cloning, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the antistasin-type inhibitor ghilanten (domain I) from Haementeria ghilianii in complex with porcine beta-trypsin. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2001, 57, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.S.; Won, T.J.; Kim, J.S.; Yoo, Y.M.; Tak, E.S.; Park, S.Y.; Park, H.Y.; Hwang, K.W.; Park, S.C.; Lee, D.I. Inhibition of Coagulation Activation and Inflammation by a Novel Factor Xa Inhibitor Synthesized from the Earthworm Eisenia andrei. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstein, T.W.; Mala, C.; Kurz, E.; Bauer, K.; Greber, M.; David, C.N. The primitive metazoan Hydra expresses antistasin, a serine protease inhibitor of vertebrate blood coagulation: cDNA cloning, cellular localization and developmental regulation. FEBS Lett. 1992, 309, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Law, S.W.; Keller, P.M.; Kniskern, P.J.; Silberklang, M.; Tung, J.-S.; Gasic, T.B.; Gasic, G.J.; Friedman, P.A.; Ellis, R.W. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding antistasin, a leech-derived protein having anti-coagulant and anti-metastatic properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 83, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.I.; Kim, S.I.; Ha, K.S.; Joe, C.O.; Kang, K.W. Isolation and characterization of guamerin, a new human leukocyte elastase inhibitor from Hirudo nipponia. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 13879–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A.; Ren, C.; Chen, T.; Jiang, X.; Sun, H.; Hu, C. Identification and functional characterization of a novel antistasin/WAP-like serine protease inhibitor from the tropical sea cucumber, Stichopus monotuberculatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 59, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, M., Jr.; Kato, I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 49, 593–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J. Bioinformatics-Aided Venomics. Toxins 2015, 7, 2159–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verriere, B.; Sabatier, B.; Carbonnelle, E.; Mainardi, J.L.; Prognon, P.; Whitaker, I.; Lantieri, L.; Hivelin, M. Medicinal leech therapy and Aeromonas spp. infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strube, K.H.; Kröger, B.; Bialojan, S.; Otte, M.; Dodt, J. Isolation, sequence analysis, and cloning of haemadin. An anticoagulant peptide from the Indian leech. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8590–8595. [Google Scholar]
- Marco, S.D.; Fendrich, G.; Knecht, R.; Strauss, A.; Pohlig, G.; Heim, J.; Priestle, J.-P.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Grütter, M.G. Recombinant hirustasin: Production in yeast, crystallization, and interaction with serine proteases. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlig, G.; Fendrich, G.; Knecht, R.; Eder, B.; Piechottka, G.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Heim, J. Purification, characterization and biological evaluation of recombinant leech-derived tryptase inhibitor (rLDTI) expressed at high level in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 241, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, S.A.; Nadeau, D.; Tirado, J.; Hollis, G.F.; Knabb, R.M.; Jia, S. Production and purification of recombinant hirudin expressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 1996, 8, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollewe, C.; Vilcinskas, A. Production of recombinant proteins in insect cells. Am. J. Bioch. Biotech. 2013, 9, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-L.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Q.; Dai, S.; Hancock, W.S.; Karger, B.L. Mass Spectrometric Determination of Disulfide Linkages in Recombinant Therapeutic Proteins Using On-line LC-MS with Electron Transfer Dissociation (ETD). Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).