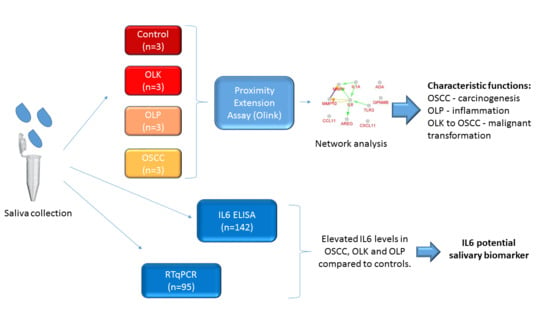
Examination of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Precancerous Lesions Using Proximity Extension Assay and Salivary RNA Quantification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Salivary Sample Collection
2.2. Relative Quantification of 186 Proteins in Saliva by Proximity Extension Assay
2.3. Statistical Analysis
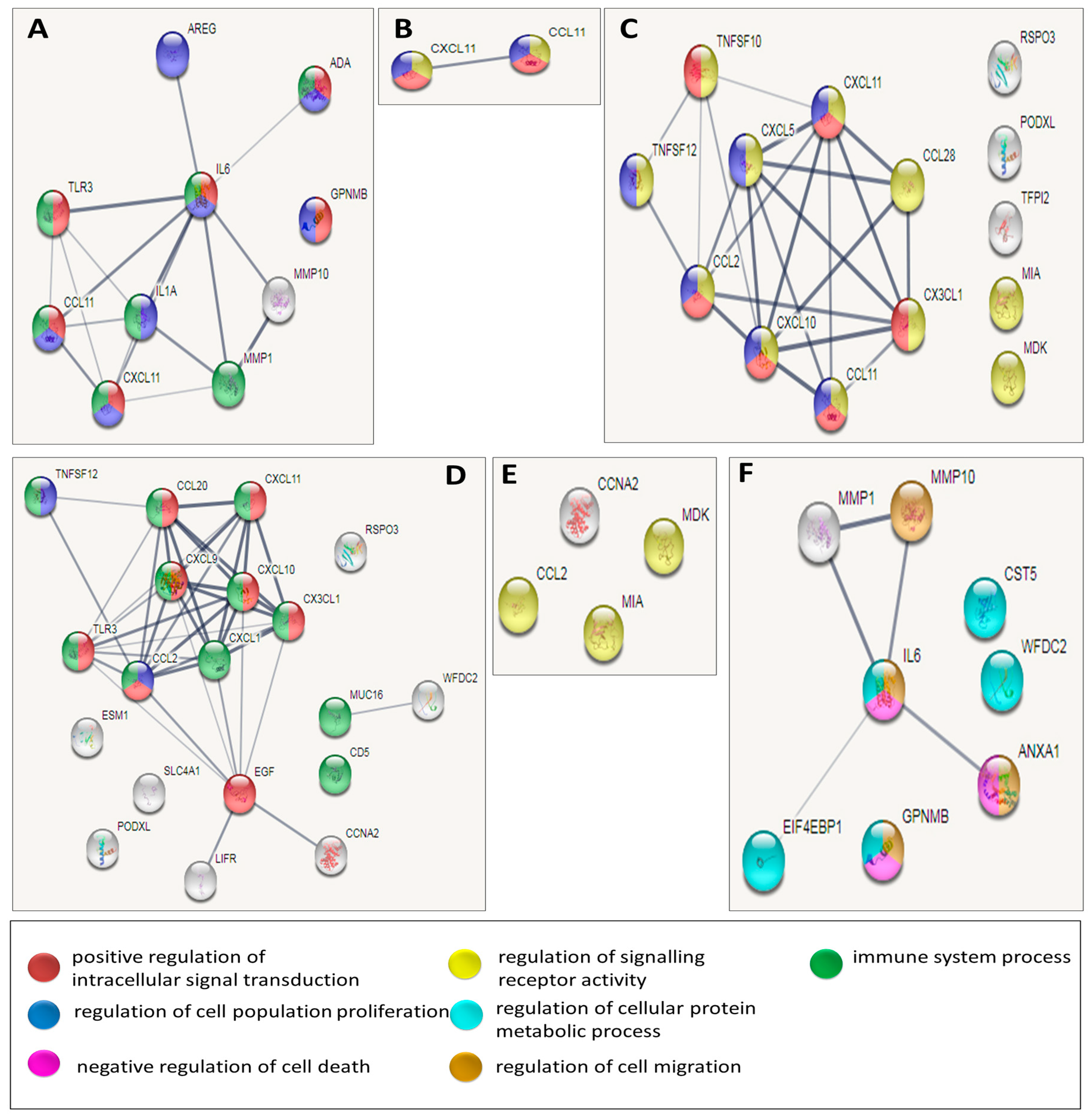
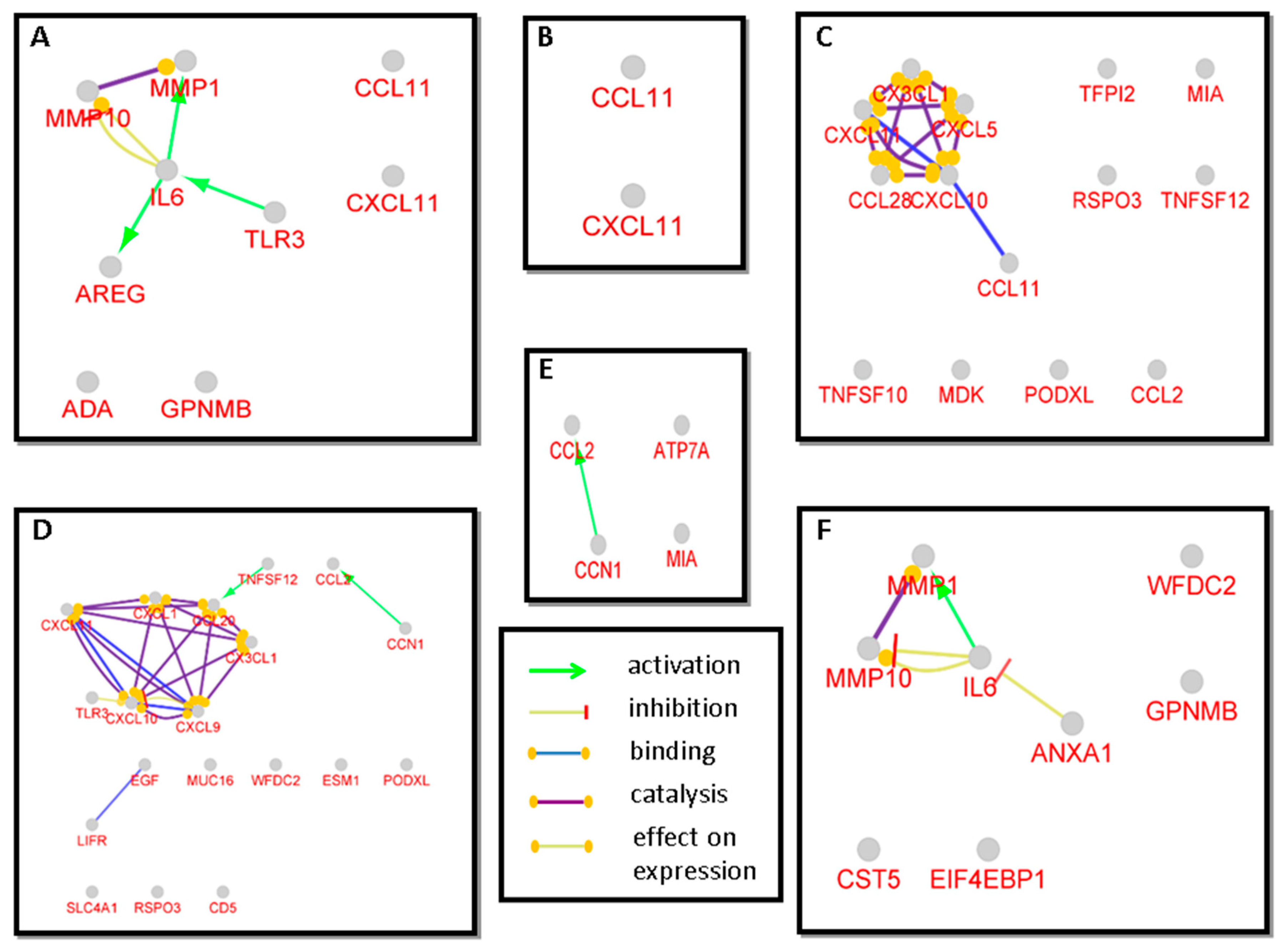
2.4. Network Analysis
2.5. ELISA Analysis
2.6. Quantification of Salivary IL6 mRNA by Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
3. Results and Discussion
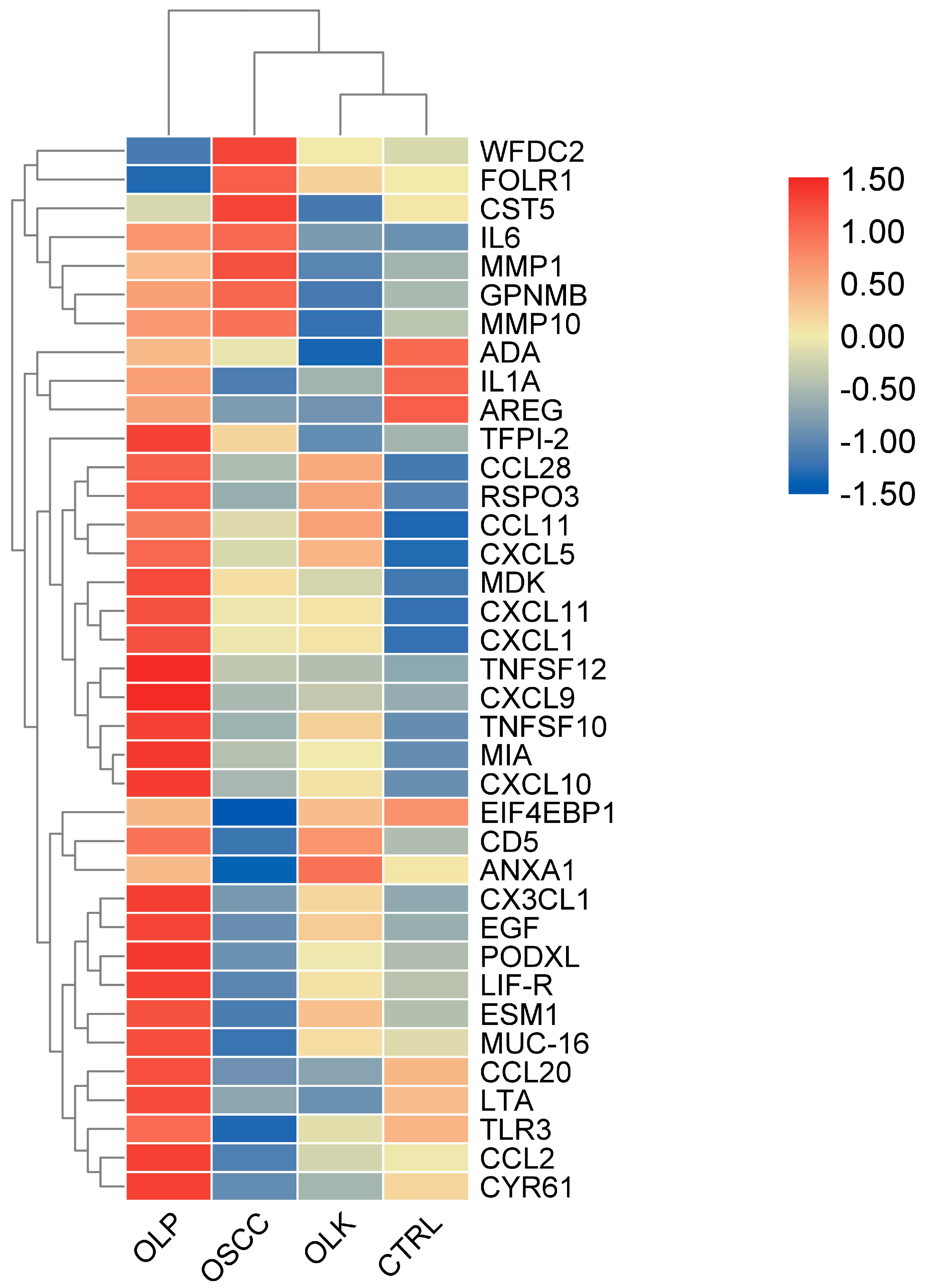
3.1. Saliva Analysis by Proximity Extension Assay (PEA)
3.2. Examination of Protein-Level Changes in Saliva Originating from Patients with Oral Cancer or Different Forms of Precancerous Lesions
3.3. Network Analysis of Proteins with Statistically Significant Changes among the Disease Groups
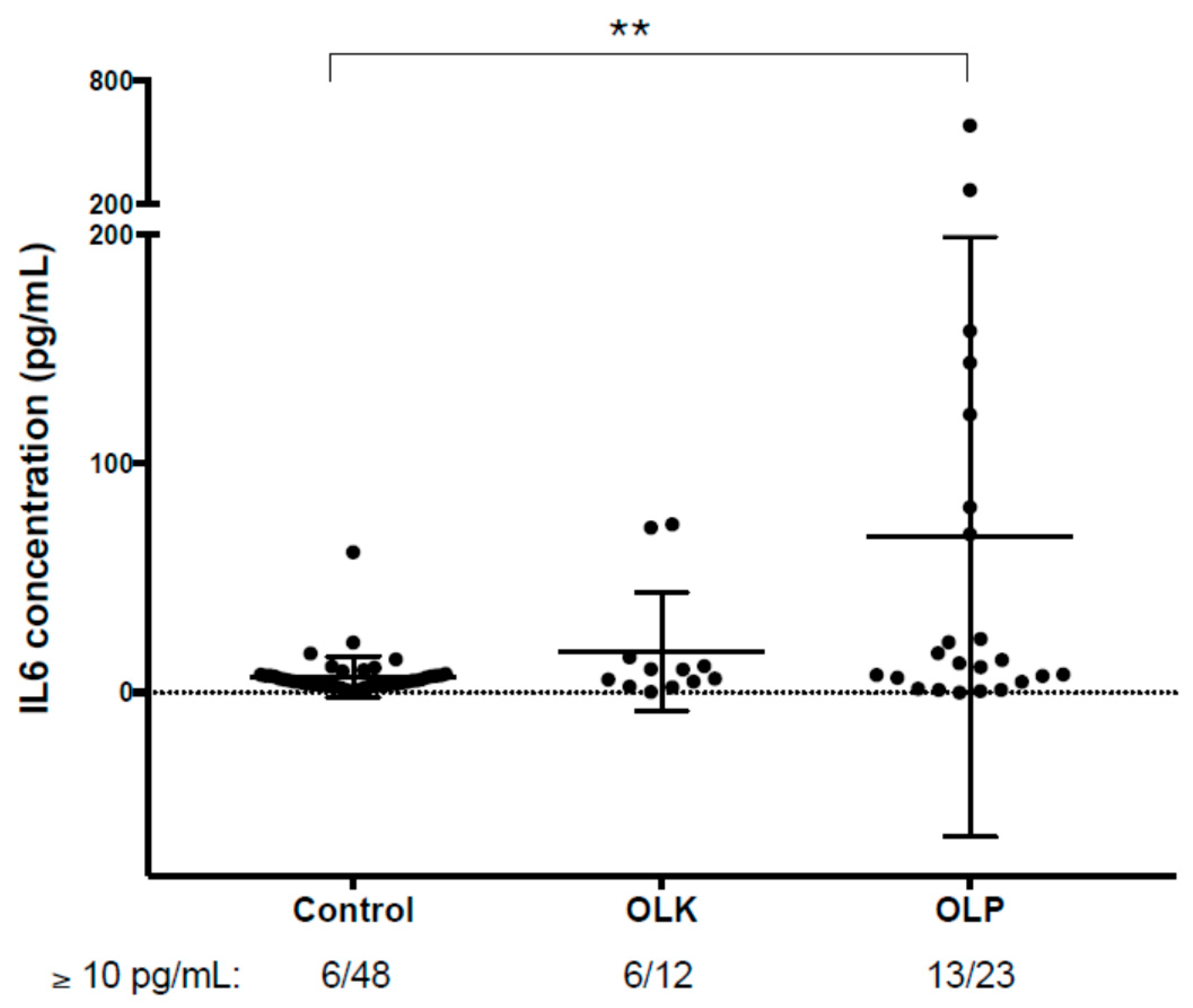
3.4. Verification of the Results Obtained by PEA-Examination of Salivary IL6 Levels Using ELISA
3.5. Examination of Salivary IL6 mRNA Levels in Patients with Precancerous Oral Lesions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganesh, D.; Sreenivasan, P.; Öhman, J.; Wallström, M.; Braz-Silva, P.; Giglio, D.; Kjeller, G.; Hasséus, B. Potentially Malignant Oral Disorders and Cancer Transformation. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz, P.; Meleti, M.; Diniz-Freitas, M.; Vescovi, P.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Johnson, N.W.; Kerr, A.R. Oral and pharyngeal cancer in Europe. Transl. Res. Oral Oncol. 2017, 2, 2057178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, C. Essentials of oral cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 11884–11894. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Dong, Y. Human papillomavirus and oral squamous cell carcinoma: A review of HPV-positive oral squamous cell carcinoma and possible strategies for future. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2017, 41, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Muthumala, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Uehara, O.; Kuramitsu, Y.; Chiba, I.; Abiko, Y. How Each Component of Betel Quid Is Involved in Oral Carcinogenesis: Mutual Interactions and Synergistic Effects with Other Carcinogens—A Review Article. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T.; Wang, H.-M.; Chang, K.-W.; Chen, W.-H.; Wen, M.-C.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Yung, B.Y.M.; Chen, I.-H.; Liao, C.-T.; Hsieh, L.-L.; et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC): Overexpression of NPM, CDK1 and NDRG1 and underexpression of CHES1. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, A.; Takahashi, H.; Patel, A.; Osman, A.; Myers, J.N. Targeting the DNA Damage Response in OSCC with TP53 Mutations. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, P.M.; Khurram, S.A.; Kujan, O. Oral potentially malignant disorders: Risk of progression to malignancy. Oral Surgery, Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 125, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waal, I.; Schepman, K.P.; Van der Meij, E.H.; Smeele, L.E. Oral leukoplakia: A clinicopathological review. Oral Oncol. 1997, 33, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Sonis, S. Oral leukoplakia remains a challenging condition. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, C.S.; Fox, S.A. Dysplastic oral leukoplakia is molecularly distinct from leukoplakia without dysplasia. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurago, Z.B. Etiology and pathogenesis of oral lichen planus: An overview. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 122, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, E.M.O.; Yáñez-Busto, A.; Henriques, I.F.R.; Lopez-Lopez, J.; Blanco-Carrión, A. Lichen planus and diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2018, 25, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratzehi, T. Oral Lichen Planus: An Overview of Potential Risk Factors, Biomarkers and Treatments. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payeras, M.R.; Cherubini, K.; Figueiredo, M.A.; Salum, F.G. Oral lichen planus: Focus on etiopathogenesis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Sugerman, P.; Walsh, L.J.; Savage, N.W. Mast cell degranulation and the role of T cell RANTES in oral lichen planus. Oral Dis. 2001, 7, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, D.K.; Montero, P.H.; Migliacci, J.C.; Shah, J.P.; Wong, R.J.; Ganly, I.; Patel, S.G. Survival outcomes after treatment of cancer of the oral cavity (1985–2015). Oral Oncol. 2019, 90, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, C.; Yang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y. Non-coding RNAs deregulation in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Advances and challenges. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2015, 18, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, T.; Jeddy, N.; Nithya, S.; Muthumeenakshi, R. Salivary biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma—An insight. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2016, 6, S51–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csősz, É; Kalló, G.; Márkus, B.; Deák, E.; Csutak, A.; Tőzsér, J. Quantitative body fluid proteomics in medicine — A focus on minimal invasiveness. J. Proteom. 2017, 153, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csősz, É.; Márkus, B.; Darula, Z.; Medzihradszky, K.F.K.F.; Nemes, J.; Szabo, E.; Tőzsér, J.; Kiss, C.; Márton, I. Salivary proteome profiling of oral squamous cell carcinoma in a Hungarian population. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csősz, É.; Lábiscsák, P.; Kalló, G.; Márkus, B.; Emri, M.; Szabó, A.; Tar, I.; Tőzsér, J.; Kiss, C.; Márton, I. Proteomics investigation of OSCC-specific salivary biomarkers in a Hungarian population highlights the importance of identification of population-tailored biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombeccari, G.P.; Guzzi, G.; Tettamanti, M.; Giannì, A.B.; Baj, A.; Pallotti, F.; Spadari, F. Oral lichen planus and malignant transformation: A longitudinal cohort study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2011, 112, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Ariyawardana, A. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: A systematic review of observational studies. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomens, M.A.E.M. Potentially malignant disorders of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa; terminology, classification and present concepts of management. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, Z.; Zohaib, K.; Najeeb, S.; Zafar, M.S.; Slowey, P.D.; Almas, K. Human Saliva Collection Devices for Proteomics: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márton, I.J.; Horváth, J.; Lábiscsák, P.; Márkus, B.; Dezső, B.; Szabó, A.; Tar, I.; Piffkó, J.; Jakus, P.; Barabás, J.; et al. Salivary IL-6 mRNA is a Robust Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitzhaki, S.; Schechtman, E. The Gini Methodology. Elem. Stat. Learn. 2013, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Galon, J.; Mlecnik, B. CluePedia Cytoscape plugin: Pathway insights using integrated experimental and in silico data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Velden, V.H.J.; on behalf of the European Study Group on MRD detection in ALL (ESG-MRD-ALL); Cazzaniga, G.; Schrauder, A.; Hancock, J.F.; Bader, P.; Panzer-Grumayer, E.R.; Flohr, T.R.; Sutton, R.S.; Cave, H.; et al. Analysis of minimal residual disease by Ig/TCR gene rearrangements: Guidelines for interpretation of real-time quantitative PCR data. Leukemia 2007, 21, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csősz, É.; Tóth, N.; Deák, E.; Csutak, A.; Tőzsér, J. Wound-Healing Markers Revealed by Proximity Extension Assay in Tears of Patients following Glaucoma Surgery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, V.; Porto, E.; Ragusa, M.; Barbagallo, C.; Davies, D.; Forcione, M.; Logan, A.; Di Pietro, C.; Purrello, M.; Grey, M.; et al. Salivary MicroRNAs: Diagnostic Markers of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Contact-Sport. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, P.M.; Rose, A.A.; Annis, M.G.; Maric, G. Glycoprotein non-metastatic b (GPNMB): A metastatic mediator and emerging therapeutic target in cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, L.; Puri, N.; Rastogi, V.; Satpute, P.; Ahmad, R.; Kaur, G. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Cancer-Roles in Threat and Therapy. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Xu, X.; Hereld, D. Chemotaxis, chemokine receptors and human disease. Cytokine 2008, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.-L.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, T. WFDC2 contributes to epithelial–Mesenchymal transition (EMT) by activating AKT signaling pathway and regulating MMP-2 expression. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Tian, J.; Qi, L.; Liu, L.; Xu, N. ANXA1 affects cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5214–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, D.P.; Thiesse, M.; Hicks, M.J. Expression of Type 2 Cystatin Genes CST1-CST5 in Adult Human Tissues and the Developing Submandibular Gland. DNA Cell Biol. 2002, 21, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, H.; Ambikan, A.T.; Gabriel, E.E.; Akusjärvi, S.S.; Palaniappan, A.N.; Sundaraj, V.; Mupanni, N.R.; Sperk, M.; Cheedarla, N.; Sridhar, R.; et al. Systemic Inflammation and the Increased Risk of Inflamm-Aging and Age-Associated Diseases in People Living With HIV on Long Term Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proost, P.; Struyf, S.; Van Damme, J.; Fiten, P.; Ugarte-Berzal, E.; Opdenakker, G. Chemokine isoforms and processing in inflammation and immunity. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 85, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, D.E.; Castro, R.; Loscalzo, J. Epigenetic Modifications. Circulation 2011, 123, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, A.; Bhatt, A.N. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11553–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodus, N.L.; Ho, V.; Miller, C.S.; Myers, S.; Ondrey, F. NF-κB dependent cytokine levels in saliva of patients with oral preneoplastic lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2005, 29, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailo, V.; Vucicevic-Boras, V.; Lukac, J.; Biocina-Lukenda, D.; Alajbeg-Zilic, I.; Milenovic, A.; Balija, M. Salivary and serum interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with leukoplakia and oral cancer. Medicina Oral Patología Oral Cirugia Bucal 2012, 17, e10–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, N.P.; Sadaksharam, J. Salivary interleukin-6 in the detection of oral cancer and precancer. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 11, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juretic, M.; Cerovic, R.; Belusic-Gobic, M.; Prso, I.B.; Kqiku, L.; Spalj, S.; Pezelj-Ribaric, S. Salivary levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in patients with oral premalignant and malignant lesions. Folia Biol. (Czech Repub.) 2013, 59, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Dikova, V.R.; Principe, S.; Bagan, J.V. Salivary inflammatory proteins in patients with oral potentially malignant disorders. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, e659–e664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, Y.; Shingu, M.; Torisu, T.; Itonaga, I.; Masumi, S. Synovial fluid and serum levels of soluble interleukin-6 receptor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Jpn. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 8, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Real, J.M.; Vayreda, M.; Richart, C.; Gutierrez, C.; Broch, M.; Vendrell, J.; Ricart, W. Circulating Interleukin 6 Levels, Blood Pressure, and Insulin Sensitivity in Apparently Healthy Men and Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Rifai, N.; Stampfer, M.J.; Hennekens, C.H. Plasma Concentration of Interleukin-6 and the Risk of Future Myocardial Infarction among Apparently Healthy Men. Circulation 2000, 101, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, T.; Thomas, A.; Webb, R.; Hughes, M. The relationship between interleukin-6 in saliva, venous and capillary plasma, at rest and in response to exercise. Cytokine 2015, 71, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Fratta, I.; Tatangelo, R.; Campagna, G.; Rizzuto, A.; Franceschelli, S.; Ferrone, A.; Patruno, A.; Speranza, L.; De Lutiis, M.A.; Felaco, M.; et al. The plasmatic and salivary levels of IL-1β, IL-18 and IL-6 are associated to emotional difference during stress in young male. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, H.; Nadeem, A.; Kashif, M.; Shahzad, F.; Tahir, R.; Afzal, N. Salivary Levels of IL-6 and IL-17 Could Be an Indicator of Disease Severity in Patients with Calculus Associated Chronic Periodontitis. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Äyräväinen, L.; Heikkinen, A.M.; Kuuliala, A.; Ahola, K.; Koivuniemi, R.; Laasonen, L.; Moilanen, E.; Hämäläinen, M.; Tervahartiala, T.; Meurman, J.H.; et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in saliva and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis with respect to periodontal status. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, S.M.S.; Corrêa, J.D.; Souza, A.F.; Travassos, D.V.; Calderaro, D.C.; Rocha, N.P.; Vieira, É.L.M.; Teixeira, A.L.; Ferreira, G.A.; Silva, T. Immunological signatures in saliva of systemic lupus erythematosus patients: Influence of periodontal condition. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Y.; Xiong, X.; Li, K.; Yao, Z.; Dong, H.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, D.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; Zhang, H. Detection of Exosomal PD-L1 RNA in Saliva of Patients With Periodontitis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jia, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, W. Salivary Exosomes: Emerging Roles in Systemic Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, W.; Cui, Q.; Zhou, Y. Computational screening of potential regulators for mRNA-protein expression level discrepancy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, D.; Colangelo, C.; Williams, K.R.; Gerstein, M.B. Comparing protein abundance and mRNA expression levels on a genomic scale. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| OLP | OLK | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 23) | (N = 12) | ||
| Sex | Male (N, %) | 9 (40%) | 11 (33%) |
| Female (N, %) | 14 (60%) | 22 (66%) | |
| Age | (years; mean ± SD) | 62 ± 3.5 | 62 ± 5 |
| Gingival index (Loe–Silness index) | (mean ± SD) | 0.56 ± 0.35 | 0.13 ± 0.06 |
| Regular ethanol consumption | Number of regular alcohol consumers, % | 4 (17%) | 5 (41%) |
| Smoking | Number of smokers, % | 5 (22%) | 2 (16%) |
Publisher's Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scholtz, B.; Vo Minh, D.; Kiss, C.; Tar, I.; Kumar, A.; Tőzsér, J.; Csősz, É.; Márton, I. Examination of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Precancerous Lesions Using Proximity Extension Assay and Salivary RNA Quantification. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120610
Scholtz B, Vo Minh D, Kiss C, Tar I, Kumar A, Tőzsér J, Csősz É, Márton I. Examination of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Precancerous Lesions Using Proximity Extension Assay and Salivary RNA Quantification. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(12):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120610
Chicago/Turabian StyleScholtz, Beáta, Doan Vo Minh, Csongor Kiss, Ildikó Tar, Ajneesh Kumar, József Tőzsér, Éva Csősz, and Ildikó Márton. 2020. "Examination of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Precancerous Lesions Using Proximity Extension Assay and Salivary RNA Quantification" Biomedicines 8, no. 12: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120610
APA StyleScholtz, B., Vo Minh, D., Kiss, C., Tar, I., Kumar, A., Tőzsér, J., Csősz, É., & Márton, I. (2020). Examination of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Precancerous Lesions Using Proximity Extension Assay and Salivary RNA Quantification. Biomedicines, 8(12), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8120610