Conjugates of Small Molecule Drugs with Antibodies and Other Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antibodies and Targets
| ADC name | Target | Cytotoxic drug | Therapeutic area | Current status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linked to cysteines via maleimidocaproyl-VC dipeptide-PAB-MMAE and cleavage by cathepsin B | ||||
| Brentuximab vedotin | CD30 | MMAE | HL, ALCL | Approved (2011) |
| CDX-011 (Glembatumumab vedotin) | GPNMB | MMAE | Breast cancer melanoma | Phase 2 |
| RG-7593 (Pinatuzuumab vedotin) DCDT2980S | CD22 | MMAE | DLBL, follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma | Phase 2 |
| PSMA-ADC | PSMA | MMAE | Prostate cancer | Phase 2 |
| Linked to lysines via SMCC thioether and released by proteolytic degradation of antibody | ||||
| Trastuzumab emtansine | Her2 | Maytansinoid DM1 | Metastatic breast cancer | Approved (2013) |
| Milatuzumab-dox | CD74 | doxorubicin | Multiple myeloma | Phase 2 |
| Linked to lysines via acetyl butyrate hydrazone and released by hydrolysis at low pH | ||||
| Gemtuzumab ozogamicin | CD33 | N-acetyl- γ calicheamicin | AML | withdrawn |
| Inotuzumab ozogamincin | CD22 | N-acetyl- γ calicheamicin | NHL, ALL | Phase 3 |
| Linked to lysines via hindered disulfide bond in SPDB and released by reductive cleavage | ||||
| BT062 | CD138 | maytansinoid | Multiple myeloma | Phase 2 |
| SAR3419 | CD19 | maytanisinoid | DLBL, ALL | Phase 2 |
| Lorvotuzumab mertansine (IMGN-901) | CD56 | maytanisinoid | Small-cell lung cancer | Phase 2 * |
3. Cytotoxic Drugs and Mechanisms of Action
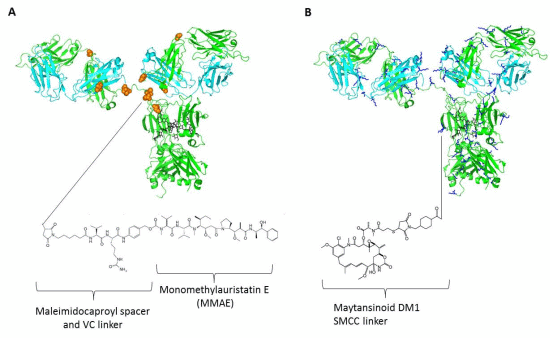
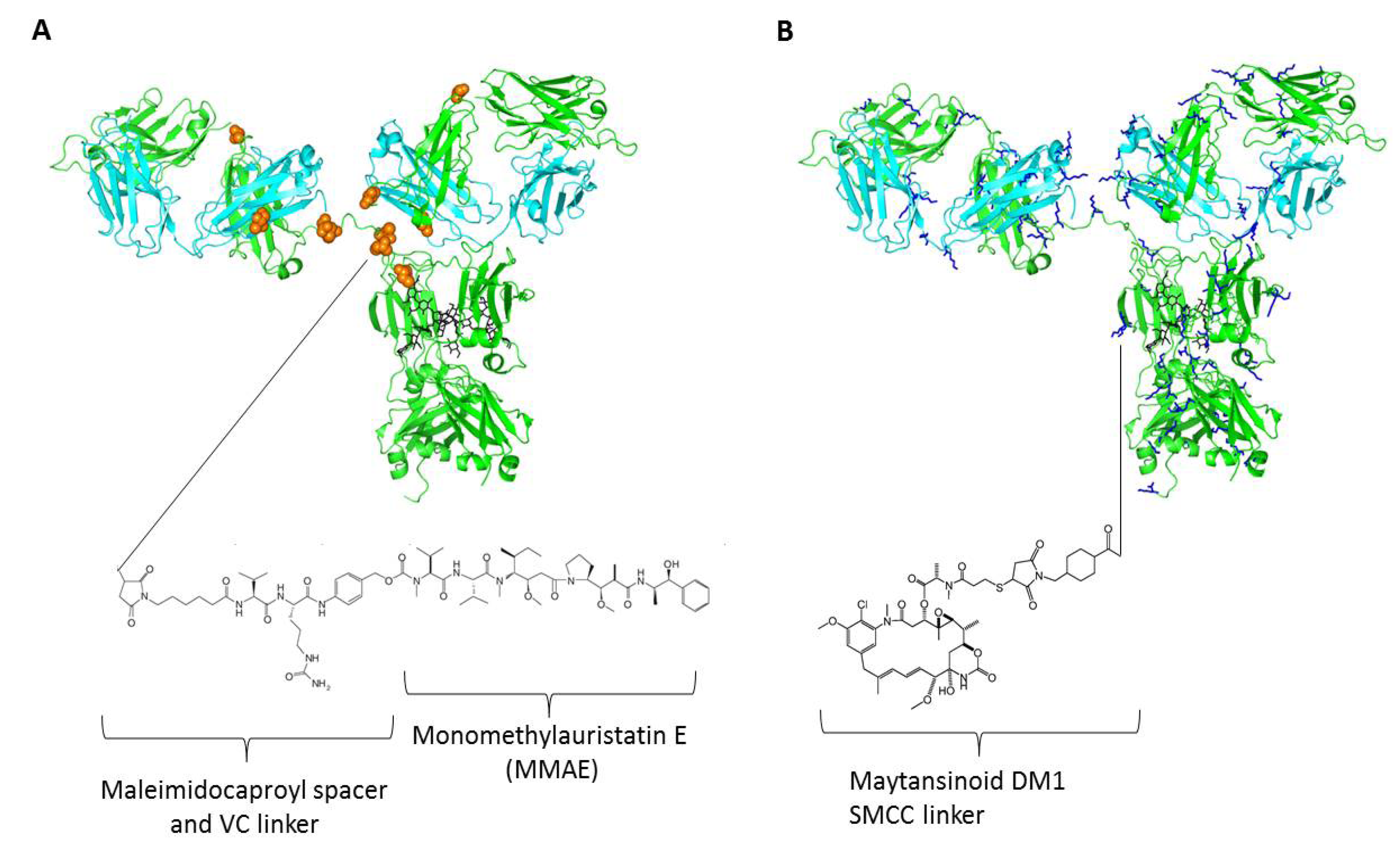
4. Linkers and Conjugation Chemistry
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sievers, E.L.; Senter, P.D. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2013, 64, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.M. Drug-conjugated antibodies for the treatment of cancer. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, J.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Meyer, D.L.; Mixan, B.J.; Klussman, K.; Chace, D.F.; Rejniak, S.X.; Gordon, K.A.; DeBlanc, R.; Toki, B.E.; et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood 2003, 102, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis Phillips, G.D.; Li, G.; Dugger, D.L.; Crocker, L.M.; Parsons, K.L.; Mai, E.; Blattler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Chari, R.V.; Lutz, R.J.; et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9280–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. Maturing antibody-drug conjugate pipeline hits 30. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvak-Greenfeld, D.; Benhar, I. Risks and untoward toxicities of antibody-based immunoconjugates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1782–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, M.; Thomas, S.; Chen, R. Management of relapsed or refractory hodgkin lymphoma with second-generation antibody-drug conjugates: Focus on brentuximab vedotin. BioDrugs 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, H.L.; Cardarelli, P.M.; Deshpande, S.; Gangwar, S.; Schroeder, G.M.; Vite, G.D.; Borzilleri, R.M. Antibody-drug conjugates: Current status and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.C.; Tredan, O. Trends in cancer-targeted antibody-drug conjugates. Target Oncol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.J.; Chien, J. Trends in translational medicine and drug targeting and delivery: New insights on an old concept-targeted drug delivery with antibody-drug conjugates for cancers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 103, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Presta, L.G.; Chen, H.; O’Connor, S.J.; Chisholm, V.; Meng, Y.G.; Krummen, L.; Winkler, M.; Ferrara, N. Humanization of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody for the therapy of solid tumors and other disorders. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4593–4599. [Google Scholar]
- Camidge, D.R.; Herbst, R.S.; Gordon, M.S.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Kurzrock, R.; Durbin, B.; Ing, J.; Tohnya, T.M.; Sager, J.; Ashkenazi, A.; et al. A phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of the death receptor 5 agonistic antibody PRO95780 in patients with advanced malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindon, C.I.; Hale, G.; Bruggemann, M.; Waldmann, H. Human monoclonal IgG isotypes differ in complement activating function at the level of C4 as well as C1q. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 168, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandler, R.; Kobayashi, H.; Hinson, E.R.; Brechbiel, M.W.; Waldmann, T.A. Herceptin-geldanamycin immunoconjugates: Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and enhanced antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokai, Y.; Cohen, J.A.; Drebin, J.A.; Greene, M.I. Stage- and tissue-specific expression of the neu oncogene in rat development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 8498–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.; Tchistiakova, L.; Scott, N. Implications of receptor-mediated endocytosis and intracellular trafficking dynamics in the development of antibody drug conjugates. mAbs 2013, 5, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.D. Antibody-drug conjugates of calicheamicin derivative: Gemtuzumab ozogamicin and inotuzumab ozogamicin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6417–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, A.G.; Calemine-Fenaux, J.; Chan, P.; Chang, W.; Christensen, E.; Clark, S.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Eaton, D.; Elkins, K.; Elliott, J.M.; et al. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Target and linker-drug selection. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2358–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, S.C.; Okeley, N.M.; Senter, P.D. Antibody-drug conjugates: Targeted drug delivery for cancer. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.A.; Edwardson, J.M. Endocytosis and recycling of G protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1997, 18, 276–287. [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon, I.; Blanc, V. Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) clinical pipeline: A review. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1045, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kast, J.; Boyd, R.; Ackroyd, J.; Allen, J.; Anderson, A.; Barnes, M.; Bozhenok, L.; Dusanjh, P.; Hudson, L.; Yu, X.; et al. Proteomics highlights which G-protein coupled receptors are candidates for ADC development. In Proceedings of the 103rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, American Association for Cancer Research, Chicago, IL, USA; 2012; Volume 72, p. Abstract nr 3869. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Ying, T.; Dimitrov, D.S. Antibody-based candidate therapeutics against HIV-1: Implications for virus eradication and vaccine design. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, Y.; Gong, R.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Dimitrov, D.S. Engineered single human CD4 domains as potent HIV-1 inhibitors and components of vaccine immunogens. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9395–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, Y.; Prabakaran, P.; Ying, T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Macedod, C.D.; Zhu, Z.; He, Y.; Polonis, V.R.; et al. Highly potent and broad bispecific multivalent HIV-1 inhibitors based on human CD4 and antibody domains. J. Virol. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S. Human domain antibodies to conserved sterically restricted regions on gp120 as exceptionally potent cross-reactive HIV-1 neutralizers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17121–17126. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Dimitrov, D.S. Bifunctional fusion proteins of the human engineered antibody domain m36 with human soluble CD4 are potent inhibitors of diverse HIV-1 isolates. Antivir. Res. 2010, 88, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.; Del Castillo, C.S.; Berger, E.A. Neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by sCD4–17b, a single-chain chimeric protein, based on sequential interaction of gp120 with CD4 and coreceptor. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, I.; Kunz, A.; Hamann, P.R. Selection of reaction additives used in the preparation of monomeric antibody-calicheamicin conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblett, K.J.; Senter, P.D.; Chace, D.F.; Sun, M.M.; Lenox, J.; Cerveny, C.G.; Kissler, K.M.; Bernhardt, S.X.; Kopcha, A.K.; Zabinski, R.F.; et al. Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7063–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.C.; Griffin, J.D.; Belvin, M.; Blattler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Ritz, J. Anti-MY9-blocked-ricin: An immunotoxin for selective targeting of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 1991, 77, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar]
- Aboud-Pirak, E.; Hurwitz, E.; Bellot, F.; Schlessinger, J.; Sela, M. Inhibition of human tumor growth in nude mice by a conjugate of doxorubicin with monoclonal antibodies to epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 3778–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapra, P.; Stein, R.; Pickett, J.; Qu, Z.; Govindan, S.V.; Cardillo, T.M.; Hansen, H.J.; Horak, I.D.; Griffiths, G.L.; Goldenberg, D.M. Anti-CD74 antibody-doxorubicin conjugate, IMMU-110, in a human multiple myeloma xenograft and in monkeys. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5257–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.N.; Blair, A.H.; Ghose, T.; Mammen, M. Conjugation of methotrexate to IgG antibodies and their F(ab)2 fragments and the effect of conjugated methotrexate on tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1985, 19, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Laguzza, B.C.; Nichols, C.L.; Briggs, S.L.; Cullinan, G.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Starling, J.J.; Baker, A.L.; Bumol, T.F.; Corvalan, J.R. New antitumor monoclonal antibody-vinca conjugates LY203725 and related compounds: Design, preparation, and representative in vivo activity. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumontet, C.; Jordan, M.A. Microtubule-binding agents: A dynamic field of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Schmuck, K.; Tietze, L.F.; Sieber, S.A. Duocarmycin analogues target aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 in lung cancer cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 2874–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevanayagam, L.; Bell, A.; Chakraborty, I.; Sufi, B.; Gangwar, S.; Zang, A.; Rangan, V.; Rao, C.; Wang, Z.; Pan, C.; et al. Novel detection of DNA-alkylated adducts of antibody-drug conjugates with potentially unique preclinical and biomarker applications. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, N.; Sinha, A.M.; McGahren, W.J.; Ellestad, G.A. Calicheamicin gamma 1I: An antitumor antibiotic that cleaves double-stranded DNA site specifically. Science 1988, 240, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Castaigne, S. Why is it so difficult to use gemtuzumab ozogamicin? Blood 2013, 121, 4813–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R. The Dolastatins; Herz, W., Kirby, G.W., Moore, R.E., Steglich, W., Tamm, Ch., Eds.; Fortschritte der Chemie Organischer Naturstoffe/Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Springer Vienna: Vienna, Austria, 1997; Volume 70. [Google Scholar]
- Madden, T.; Tran, H.T.; Beck, D.; Huie, R.; Newman, R.A.; Pusztai, L.; Wright, J.J.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Novel marine-derived anticancer agents: A phase I clinical, pharmacological, and pharmacodynamic study of dolastatin 10 (NSC 376128) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, G.R.; Singh, S.B.; Hogan, F.; Lloyd-Williams, P.; Herald, D.L.; Burkett, D.D.; Clewlow, P.J. The absolute configuration and synthesis of natural (−)-dolastatin 10. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 5463–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronina, S.O.; Mendelsohn, B.A.; Bovee, T.D.; Cerveny, C.G.; Alley, S.C.; Meyer, D.L.; Oflazoglu, E.; Toki, B.E.; Sanderson, R.J.; Zabinski, R.F.; et al. Enhanced activity of monomethylauristatin F through monoclonal antibody delivery: Effects of linker technology on efficacy and toxicity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2006, 17, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski, L.; Junutula, J.R. Glembatumumab vedotin, a conjugate of an anti-glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B mAb and monomethyl auristatin E for the treatment of melanoma and breast cancer. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2010, 12, 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Poon, K.A.; Yu, S.F.; Dere, R.; Go, M.; Lau, J.; Zheng, B.; Elkins, K.; Danilenko, D.; Kozak, K.R.; et al. DCDT2980S, an anti-CD22-monomethyl auristatin E antibody-drug conjugate, is a potential treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Hopf, C.E.; Malewicz, A.D.; Donovan, G.P.; Senter, P.D.; Goeckeler, W.F.; Maddon, P.J.; Olson, W.C. Potent antitumor activity of an auristatin-conjugated, fully human monoclonal antibody to prostate-specific membrane antigen. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 2591–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, J.P.; Chan, P.; Lee, C.; Nelson, C.; Elliott, J.M.; Bechtel, C.; Raab, H.; Xie, D.; Akutagawa, J.; Baudys, J.; et al. Anti-CD22-MCC-DM1 and MC-MMAF conjugates: Impact of assay format on pharmacokinetic parameters determination. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, B.; Boeggeman, E.; Qasba, P.K. Novel method for in vitro O-glycosylation of proteins: Application for bioconjugation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, B.; Boeggeman, E.; Manzoni, M.; Zhu, Z.; Loomis, K.; Puri, A.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Qasba, P.K. Multiple site-specific in vitro labeling of single-chain antibody. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, T.; Skeffington, L.R.; Chapman, C.M.; Rader, C. Molecularly defined antibody conjugation through a selenocysteine interface. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 12047–12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.P.; Meyer, D.L.; Setter, J.R.; Senter, P.D. Conjugation of anticancer drugs through endogenous monoclonal antibody cysteine residues. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 502, 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Doronina, S.O.; Bovee, T.D.; Meyer, D.W.; Miyamoto, J.B.; Anderson, M.E.; Morris-Tilden, C.A.; Senter, P.D. Novel peptide linkers for highly potent antibody-auristatin conjugate. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1960–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valliere-Douglass, J.F.; McFee, W.A.; Salas-Solano, O. Native intact mass determination of antibodies conjugated with monomethyl Auristatin E and F at interchain cysteine residues. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junutula, J.R.; Bhakta, S.; Raab, H.; Ervin, K.E.; Eigenbrot, C.; Vandlen, R.; Scheller, R.H.; Lowman, H.B. Rapid identification of reactive cysteine residues for site-specific labeling of antibody-Fabs. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 332, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.Q.; Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Raab, H.; Bhakta, S.; Kenrick, M.; Parsons-Reponte, K.L.; Tien, J.; Yu, S.F.; Mai, E.; et al. Conjugation site modulates the in vivo stability and therapeutic activity of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Amphlett, G.; Blattler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Zhang, W. Structural characterization of the maytansinoid-monoclonal antibody immunoconjugate, huN901-DM1, by mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flygare, J.A.; Pillow, T.H.; Aristoff, P. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of cancer. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remillard, S.; Rebhun, L.I.; Howie, G.A.; Kupchan, S.M. Antimitotic activity of the potent tumor inhibitor maytansine. Science 1975, 189, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, H.K.; Park, P.U.; Widdison, W.C.; Kovtun, Y.V.; Garrett, L.M.; Hoffman, K.; Lutz, R.J.; Goldmacher, V.S.; Blattler, W.A. Antibody-maytansinoid conjugates are activated in targeted cancer cells by lysosomal degradation and linker-dependent intracellular processing. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4426–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, L.; Offner, F.; Smith, M.R.; Verhoef, G.; Johnson, P.; Kaufman, J.L.; Rohatiner, A.; Advani, A.; Foran, J.; Hess, G.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of a combination therapy comprising two antibody-based targeting agents for the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Results of a phase I/II study evaluating the immunoconjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin with rituximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, N.K.; Frost, P. Antibody-targeted chemotherapy with immunoconjugates of calicheamicin. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, M.P.; Gauzy-Lazo, L. Protocols for lysine conjugation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1045, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ducry, L.; Stump, B. Antibody-drug conjugates: Linking cytotoxic payloads to monoclonal antibodies. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, H.K.; Widdison, W.C.; Mayo, M.F.; Whiteman, K.; Audette, C.; Wilhelm, S.D.; Singh, R. Tumor delivery and in vivo processing of disulfide-linked and thioether-linked antibody-maytansinoid conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acchione, M.; Kwon, H.; Jochheim, C.M.; Atkins, W.M. Impact of linker and conjugation chemistry on antigen binding, Fc receptor binding and thermal stability of model antibody-drug conjugates. mAbs 2012, 4, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, W.; Prabakaran, P.; Lin, K.; Dimitrov, D.S. Conjugates of Small Molecule Drugs with Antibodies and Other Proteins. Biomedicines 2014, 2, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2010001
Feng Y, Zhu Z, Chen W, Prabakaran P, Lin K, Dimitrov DS. Conjugates of Small Molecule Drugs with Antibodies and Other Proteins. Biomedicines. 2014; 2(1):1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yang, Zhongyu Zhu, Weizao Chen, Ponraj Prabakaran, Kedan Lin, and Dimiter S. Dimitrov. 2014. "Conjugates of Small Molecule Drugs with Antibodies and Other Proteins" Biomedicines 2, no. 1: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2010001
APA StyleFeng, Y., Zhu, Z., Chen, W., Prabakaran, P., Lin, K., & Dimitrov, D. S. (2014). Conjugates of Small Molecule Drugs with Antibodies and Other Proteins. Biomedicines, 2(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines2010001