Pharmaco-Epigenetics and Epigenetic Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: Can Epigenetics Predict Drug Efficiency?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epigenetic Variation in T2DM, Drug Treatment, and Drug Response
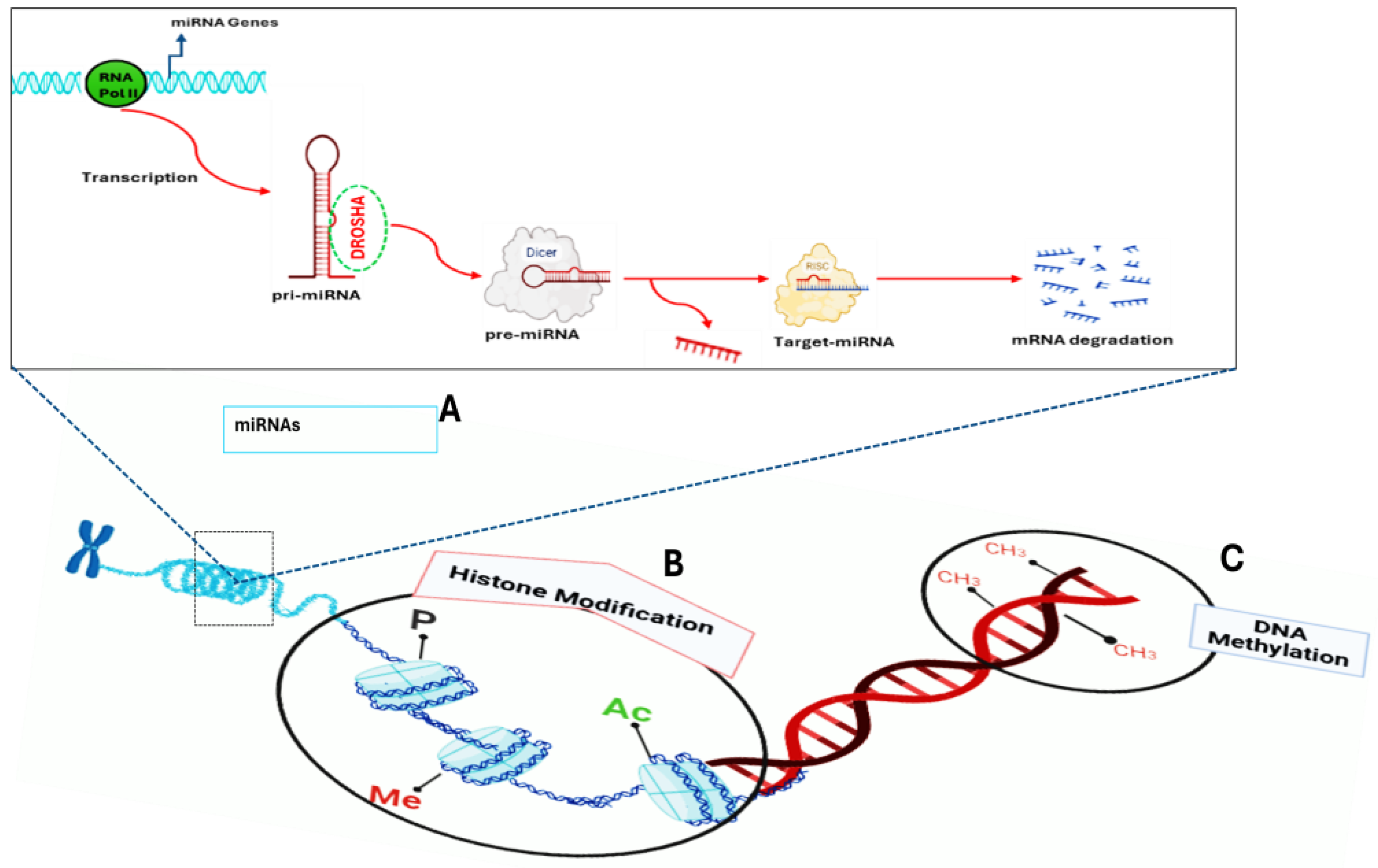
2.1. Epigenetic Variation in T2DM
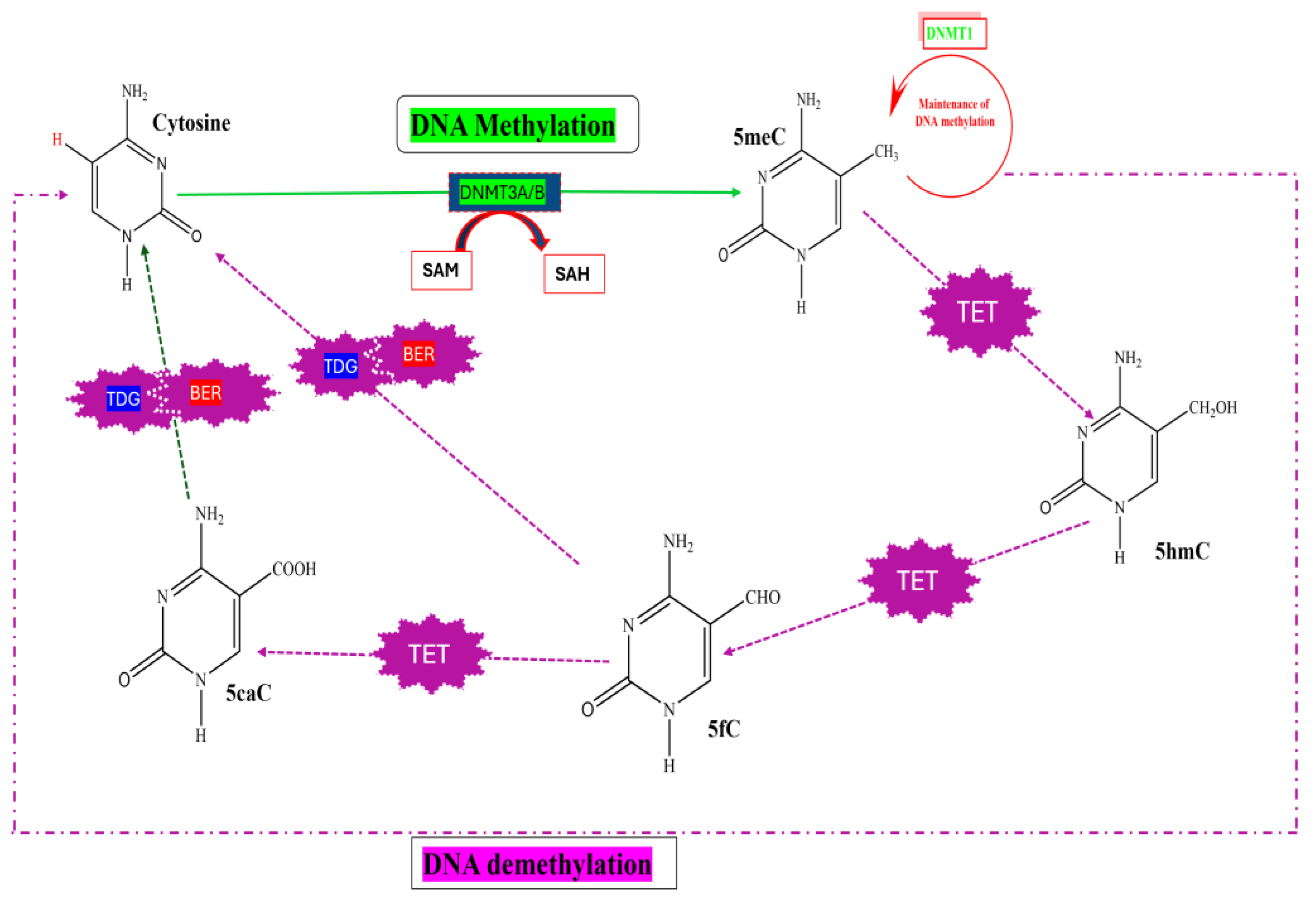
2.1.1. DNA Methylation
2.1.2. Histone Modifications
| Type of Modification | Histone Proteins | Amino Acid Residues | Associated Biological Effect | Writers | Erasers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ac | H2A | K5, k9, k13, k15, k36, k74, k95, k118, k127, k129 | Activation of a gene | p300/KAT3B, Tip60/KAT5, MYST2/KAT7 | HDAC5, SIRTs (SirT1, SirT2, SirT6) | [79,81] |
| H2B | K5, k11, k12, k15, k16, k20 | Activation of a gene | CBP/KAT3, Ap300/KAT3B | - | [82,83] | |
| H3 | K4, K14, K18, K23, K36 | Activation of a gene | - | - | [79] | |
| K9, K27 | Activation of a gene | MOF, p300, PCAF, TIP60 | HDAC | [79] | ||
| H4 | K5, K8, K16 | Activation of a gene | p300/KAT3B, Tip60/KAT5, MYST2/KAT7, ELP3 | - | [79] | |
| H3 | K4 | Activation of a gene | ASH1L, MLL1-4, SET7/9, SETD2A-B, SMYD | JARID2, KDM1A-B, KDM2B, KDM5A-D, NO66 | [79,84] | |
| K9 | Repression of a gene | GLP, G9a, SETDB1-2, SUV39H1-2 | JHDM1D, KDM1A, KDM3A-B, KDM4A-E, KDM7, PHF8 | [79] | ||
| Me | K27 | Repression of a gene | EZH 1-2, PRC2 | UTX, UTY, JMJD3, KDM7, PHF8 | [79] | |
| K36 | Activation of a gene | ASH1L, NSD1-3, SMYD, SET2 | KDM2A-B, KDM4A-E, NO66 | [85] | ||
| K79 | Activation of a gene | DOT1L | PHF8 | [79] | ||
| H4 | K2O | Repression of a gene | SET8, SUV4-20H1 | PHF8, PHF2 | [79,84] | |
| R3 | Activation of a gene | PRMT1, PRMT3, PRMT5 | JHDM1D/KDM7A, PHF8 | [79] | ||
| P | H2A | S1 | Mitosis | MSK1, PKC | - | [79] |
| S16 | eGF signaling | rSK2 | - | [86] | ||
| T120 | Mitosis, gene activation | BUB1, NHK1, VprBP | - | [86] | ||
| H2B | S32 | eGF signaling | rSK2 | - | [86] | |
| S14 | Apoptosis | MST1 | - | [79] | ||
| S36 | Transcription | AMPK | - | [86] | ||
| H3 | S14 | Apoptosis | MST1 | - | [79] | |
| S10 | Mitosis, DNA repair | MSK1&2, AuroraA | PP1 | [87] | ||
| T6 | Activation | PKCβ | - | [88] | ||
| H4 | T11 | Mitosis, DNA repair | DLK/ZIP, PRK1 | - | [88] | |
| S1 | Mitosis, gene activation | CKII, ScCK1 | - | [88] | ||
| Ub | H2A | K119 | Repression of a gene | BMI/RING1A | - | [89] |
| H2B | K120 | Activation of a gene | RNF20-RNF40 | - | [90] | |
| H3 | K23 | Maintenance of DNA methylation | UHRF1 | - | [79] | |
| Ser | H3 | Q5 | Activation of a gene | TGM2 | - | [79] |
| La | H3 | K18 | Activation of a gene | p300 | - | [91] |
| H4 | K12 | Activation of a gene | p300 | - | [91] | |
| Cr | H3 | K9 | DNA repair | p300, GCN5, MOF | HDAC1 | [79] |
| K18 | Activation of a gene | p300, GCN5, MOF | - | [79] | ||
| K27 | Gene activation | GCN5 | - | [79] |
2.2. Non-Epigenetic Drug Responsiveness Is Affected by Epigenetic Variation
2.3. Key Epigenetic Biomarkers Predict Diagnosis and Prognosis
2.4. Epigenetic Strategies for Diabetes
3. Combining Existing Pharmaco-Epigenetic Data to Explore Pharmaco-Epigenetic Correlations
| Drug Name/Type | Conditions | Status | NCT Number | Phase | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAC Resveratrol | T2DM | Completed | NCT01354977 | Phase 2 | [24] |
| T2DM | Completed | NCT02549924 | Phase 2 | [24] | |
| Gestational Diabetes | Recruiting | NCT01997762 | Phase 4 | [161] | |
| T2DM | Completed | NCT01677611 | Phase 1 | [161] | |
| T2DM | Active, | NCT03762096 | Phase 2 | [162] | |
| T2DM | Recruiting | NCT01302639 | N/A | [161] | |
| Obesity, insulin sensitivity, T2DM | Completed | NCT01412645 | N/A | [135] | |
| HATi Curcumin | T2DM; Dyslipidemias; | Recruiting | NCT05753436 | Phase 2 | [162] |
| Hypertension | |||||
| T1DM | Completed | NCT01646047 | N/A | [163] | |
| Pre-diabetes; T2DM | Unknown | NCT01052025 | Phase 4 | [162] | |
| T2D, obesity | Unknown | NCT03542240 | N/A | [24] | |
| HDACi | |||||
| ValproicAcid | Diabetes | Completed | NCT00287352 | Phase 1 | [134] |
| ValproicAcid | Obesity | Unknown | NCT00298857 | Phase 4 | [24] |
| Sodium phenylbutyrate | Obese with insulin resistance | Completed | NCT00771901 | N/A | [161] |
| DNMTi | T2DM | Completed | NCT00000620 | Phase 3 | [134] |
| Hydralazine | T2DM Hypertension | Recruiting | NCT02046395 | Phase 4 | [161] |
4. Combining Existing Pharmaco-Epigenetic Data to Explore the DNA Methylation Profile of CYP Genes
5. Challenges in Pharmaco-Epigenetics
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| T1DM | Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus |
| HMTs | Histone Methyltransferases |
| HDMs | Histone Demethylases |
| TET | Ten-Eleven Translocation |
| SAM | S-Adenosyl-L-methionine |
| 5meC | 5-Methylcytosine |
| 5hmC | 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine |
| 5fC | 5-Formylcytosine |
| 5caC | 5-Carboxylcytosine |
| DNMT | DNA Methyltransferase |
| Ac | Acetylation |
| Me | Methylation |
| P | Phosphorylation |
| NAFLD | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease |
| Ub | Ubiquitination |
| Ser | Serotonylation |
| Cr | Crotonylation |
| IR | Insulin Resistance |
| HFD | High-Fat Diet |
| VPA | Valproic Acid |
| STAC | Sirtuin-Activating Compounds |
References
- Jiang, H.; Xia, C.; Lin, J.; Garalleh, H.A.; Alalawi, A.; Pugazhendhi, A. Carbon Nanomaterials: A Growing Tool for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sifunda, S.; Mbewu, A.D.; Mabaso, M.; Manyaapelo, T.; Sewpaul, R.; Morgan, J.W.; Harriman, N.W.; Williams, D.R.; Reddy, S.P. Prevalence and Psychosocial Correlates of Diabetes Mellitus in South Africa: Results from the South African National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (SANHANES-1). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Gopalan, H.; Jayawardena, R.; Hills, A.P.; Soares, M.; Reza-Albarrán, A.A.; Ramaiya, K.L. Diabetes in Developing Countries. J. Diabetes 2019, 11, 522–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.; Mei Wong, J.L.; Sim, Y.J.; Wong, S.S.; Mohamed Elhassan, S.A.; Tan, S.H.; Ling Lim, G.P.; Rong Tay, N.W.; Annan, N.C.; Bhattamisra, S.K.; et al. Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review on Current Treatment Approach and Gene Therapy as Potential Intervention. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharravi, A.M.; Jafar, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Mahmodi, A.; Pourhashemi, E.; Haseli, N.; Talaie, N.; Hajiasgarli, P. Current Status of Stem Cell Therapy, Scaffolds for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Hasan, M.K.; Neaz, S.; Hussain, N.; Hossain, M.F.; Rahman, T. Diabetes Mellitus: Insights from Epidemiology, Biochemistry, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Complications and Comprehensive Management. Diabetology 2021, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.M.; Cusi, K. Prediabetes: A worldwide epidemic. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. 2016, 45, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiglie, J.A.; Marcus, M.E.; Ebert, C.; Prodromidis, N.; Geldsetzer, P.; Theilmann, M.; Agoudavi, K.; Andall-Brereton, G.; Aryal, K.K.; Bicaba, B.W.; et al. Diabetes Prevalence and Its Relationship with Education, Wealth, and BMI in 29 Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosibo, A.M.; Mzimela, N.C.; Ngubane, P.S.; Khathi, A. Prevalence and Correlates of Pre-Diabetes in Adults of Mixed Ethnicities in the South African Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocol. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzy, J.; Campos, M.R.; Emmerick, I.; da Silva, R.S.; Schramm, J.M.d.A. Prevalência de Diabetes Mellitus E Suas Complicações E Caracterização Das Lacunas Na Atenção à Saúde a Partir Da Triangulação de Pesquisas. Cad. Saúde Pública 2021, 37, e00076120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why Does Obesity Cause Diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Yin, R.X. Recent Progress in Epigenetics of Obesity. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.I.M. Epigenetic Regulation of Obesity-Associated Type 2 Diabetes. Medicina 2022, 58, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiderio, A.; Spinelli, R.; Ciccarelli, M.; Nigro, C.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F.; Raciti, G.A. Epigenetics: Spotlight on Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, S.; Drong, A.; Lehne, B.; Loh, M.; Scott, W.R.; Kunze, S.; Tsai, P.-C.; Ried, J.S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Body Mass Index, and the Adverse Outcomes of Adiposity. Nature 2017, 541, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, M.C.; Johnstone, A.; Eccles, D.; Harmon, B.; Hayes, M.T.; Lea, R.A.; Griffiths, L.; Hoffman, E.P.; Stubbs, R.S.; Macartney-Coxson, D. An Analysis of DNA Methylation in Human Adipose Tissue Reveals Differential Modification of Obesity Genes before and after Gastric Bypass and Weight Loss. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrinli, S.; Maihofer, A.X.; Wani, A.H.; Pfeiffer, J.R.; Ketema, E.; Ratanatharathorn, A.; Baker, D.G.; Boks, M.P.; Geuze, E.; Kessler, R.C.; et al. Epigenome-Wide Meta-Analysis of PTSD Symptom Severity in Three Military Cohorts Implicates DNA Methylation Changes in Genes Involved in Immune System and Oxidative Stress. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, K. Targeting Epigenetic Enzymes for Drug Discovery and Development. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. News 2019, 39, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehley, T.; O’Donnell, C.W.; Mendlein, J.; Karande, M.; McCauley, T. Drugging the Epigenome in the Age of Precision Medicine. Clin. Epigenetics 2023, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, S. The Advances in the Development of Epigenetic Modifications Therapeutic Drugs Delivery Systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 10623–10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einav Nili, G.Y.; Saito, Y.; Egger, G.; Jones, P.A. Cancer Epigenetics: Modifications, Screening, and Therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2008, 59, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsetti, A.; Illi, B.; Gaetano, C. How Epigenetics Impacts on Human Diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 114, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lin, Z.J.; Li, C.C.; Lin, X.; Shan, S.K.; Guo, B.; Zheng, M.H.; Li, F.; Yuan, L.Q.; Li, Z. Epigenetic Regulation in Metabolic Diseases: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Lee, Y.-T.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y. Targeting Epigenetic Regulatory Machinery to Overcome Cancer Therapy Resistance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 83, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Bacos, K.; Rönn, T. Epigenetics of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Weight Change—A Tool for Precision Medicine? Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkin, I.; Barrès, R. Sperm Epigenetics and Influence of Environmental Factors. Mol. Metab. 2018, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredy, T.W.; Sun, Y.E.; Kobor, M.S. How the Epigenome Contributes to the Development of Psychiatric Disorders. Dev. Psychobiol. 2010, 52, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Modern Epigenetics Methods in Biological Research. Methods 2020, 187, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, A.; Motevalizadeh Ardekani, A. Role of Epigenetics in Biology and Human Diseases. Iran. Biomed. J. 2016, 20, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendup, T.; Feng, X.; Clingan, S.; Astell-Burt, T. Environmental Risk Factors for Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I.; Claycombe, K.J.; Schalinske, K.L. Epigenetics in Adipose Tissue, Obesity, Weight Loss, and Diabetes. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, K.; Keller, M.; la Cour Poulsen, L.; Blüher, M.; Kovacs, P.; Böttcher, Y. Genetics and Epigenetics in Obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Rönn, T. Epigenetics in Human Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, M.; Rajagopal, P.; Devarajan, N.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Palanisamy, C.P.; Cui, B.; Patil, S.; Jayaraman, S. A Comprehensive Review on High -Fat Diet-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: An Epigenetic View. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 107, 109037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Epigenetic Mechanisms Link Maternal Diets and Gut Microbiome to Obesity in the Offspring. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kutateladze, T.G. Diet and the Epigenome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrillo, L.; Costa, V.; Raciti, G.A.; Longo, M.; Spinelli, R.; Esposito, R.; Nigro, C.; Vastolo, V.; Desiderio, A.; Zatterale, F.; et al. Hoxa5 Undergoes Dynamic DNA Methylation and Transcriptional Repression in the Adipose Tissue of Mice Exposed to High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamka, G.F.; Harder, A.M.; Sundaram, M.; Schwartz, T.S.; Christie, M.R.; DeWoody, J.A.; Willoughby, J.R. Epigenetics in Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 871791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diels, S.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Van Hul, W. Insights into the Multifactorial Causation of Obesity by Integrated Genetic and Epigenetic Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.; Matte, A.; Perfilyev, A.; de Mello, V.D.; Käkelä, P.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Ling, C. Epigenetic Alterations in Human Liver from Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes in Parallel with Reduced Folate Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1491–E1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, T.; Sehar, U.; Selman, A.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H. Support provided by caregivers for community-dwelling obesity individuals: Focus on elderly and Hispanics. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Barbosa, T.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Alm, P.S.; Versteyhe, S.; Massart, J.; Rasmussen, M.; Donkin, I.; Sjögren, R.; Mudry, J.M.; Vetterli, L.; et al. High-Fat Diet Reprograms the Epigenome of Rat Spermatozoa and Transgenerationally Affects Metabolism of the Offspring. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, S.J.; Tellam, R.L.; Morrison, J.L.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; Molloy, P.L. Recent Developments on the Role of Epigenetics in Obesity and Metabolic Disease. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrillo, L.; Spinelli, R.; Nicolò, A.; Longo, M.; Mirra, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Nutritional Factors, DNA Methylation, and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: Perspectives and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, A.L.; Bailly, N.; Meissner, A. DNA Methylation: A Historical Perspective. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 676–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Pinney, S.E. DNA Methylation and Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakierska-Chudy, A.; Kostrzewa, R.M.; Filip, M. A Comprehensive View of the Epigenetic Landscape Part I: DNA Methylation, Passive and Active DNA Demethylation Pathways and Histone Variants. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 27, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, M.; Bell, D.W.; Haber, D.A.; Li, E. DNA Methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b Are Essential for de Novo Methylation and Mammalian Development. Cell 1999, 99, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unoki, M. Recent Insights into the Mechanisms of de Novo and Maintenance of DNA Methylation in Mammals. In DNA Methylation Mechanism; Intechopen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, J.; Muto, M.; Takebayashi, S.; Suetake, I.; Iwamatsu, A.; Endo, T.A.; Shinga, J.; Mizutani-Koseki, Y.; Toyoda, T.; Okamura, K.; et al. The SRA Protein Np95 Mediates Epigenetic Inheritance by Recruiting Dnmt1 to Methylated DNA. Nature 2007, 450, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostick, M.; Kim, J.K.; Esteve, P.O.; Clark, A.; Pradhan, S.; Jacobsen, S.E. UHRF1 Plays a Role in Maintaining DNA Methylation in Mammalian Cells. Science 2007, 317, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, A.; Bollepalli, S.; Ollikainen, M. The Potential of DNA Methylation as a Biomarker for Obesity and Smoking. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, H.J.; Esteller, M. CpG Islands in Cancer: Heads, Tails, and Sides. In CpG Islands: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1766, pp. 49–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Riggs, A.D. DNA Methylation and Demethylation in Mammals. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 18347–18353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zane, A.; Fulton, C.; Philipoom, J. Statistical and Bioinformatic Analysis of Hemimethylation Patterns in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Shen, L.; Dai, Q.; Wu, S.C.; Collins, L.B.; Swenberg, J.A.; He, C.; Zhang, Y. Tet Proteins Can Convert 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine. Science 2011, 333, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, W.A.; Aravind, L.; Rao, A. TETonic Shift: Biological Roles of TET Proteins in DNA Demethylation and Transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Riso, G.; Fiorillo, D.F.G.; Fierro, A.; Cuomo, M.; Chiariotti, L.; Miele, G.; Cocozza, S. Modeling DNA Methylation Profiles through a Dynamic Equilibrium between Methylation and Demethylation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; He, W.J.; Liao, X.; Tang, M.; Nie, X.Q. Targeting DNA Methylation and Demethylation in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 54, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.V.C.; Bourc’his, D. The Diverse Roles of DNA Methylation in Mammalian Development and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 590–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayeh, T.A.; Olsson, A.H.; Volkov, P.; Almgren, P.; Rönn, T.; Ling, C. Identification of CpG-SNPs Associated with Type 2 Diabetes and Differential DNA Methylation in Human Pancreatic Islets. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneera, J.; Lang, S.; Sharma, A.; Fadista, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ahlqvist, E.; Jonsson, A.; Lyssenko, V.; Vikman, P.; Hansson, O.; et al. A Systems Genetics Approach Identifies Genes and Pathways for Type 2 Diabetes in Human Islets. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.; Dayeh, T.; Kirkpatrick, C.L.; Wollheim, C.B.; Dekker Nitert, M.; Ling, C. DNA Methylation of the Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor (GLP1R) in Human Pancreatic Islets. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, M.; Reinherz, E.L.; Reche, P.A. Recognition and Classification of Histones Using Support Vector Machine. J. Comput. Biol. 2006, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, G. Diversification of the Histone Fold Motif in Plants: Evolution of New Functional Roles. Def. Life Sci. J. 2016, 1, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Höllmüller, E.; Geigges, S.; Niedermeier, M.L.; Kammer, K.-M.; Kienle, S.M.; Rösner, D.; Scheffner, M.; Marx, A.; Stengel, F. Site-Specific Ubiquitylation Acts as a Regulator of Linker Histone H1. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.R.; Habib, S.; Uddin, M. Recent Advances in Histone Glycation: Emerging Role in Diabetes and Cancer. Glycobiology 2021, 31, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Cao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Lian, Y.; Liu, P.; Zeng, Y.; Lyu, W.; Chen, Q. Histone Deacetylases and Inhibitors in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 117010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, A.J.; Kouzarides, T. Regulation of Chromatin by Histone Modifications. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahl, B.D.; Allis, C.D. The Language of Covalent Histone Modifications. Nature 2000, 403, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Chen, R. Pathological Implication of Protein Post-Translational Modifications in Cancer. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 86, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Zhou, T.; Cheng, X.; Huang, W.; Xu, Y. Novel Histone Post-Translational Modifications in Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes: The Underlying Mechanisms and Implications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Chandel, S.; Dey, D.; Ghosh, A.; Roy, S.; Ravichandiran, V.; Ghosh, D. Epigenetic Modification and Therapeutic Targets of Diabetes Mellitus. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20202160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deussing, J.M.; Jakovcevski, M. Histone Modifications in Major Depressive Disorder and Related Rodent Models. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 978, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čugalj Kern, B.; Trebušak Podkrajšek, K.; Kovač, J.; Šket, R.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Tesovnik, T.; Debeljak, M.; Battelino, T.; Bratina, N. The Role of Epigenetic Modifications in Late Complications in Type 1 Diabetes. Genes 2022, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Oh, S.; Ro, D.H.; Yoo, H.; Kwon, Y.W. The Key Role of DNA Methylation and Histone Acetylation in Epigenetics of Atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2020, 9, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziato, A. DNA packaging: Nucleosomes and chromatin. Nat. Educ. 2008, 1, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Yi, S.J. The Role of Histone Modifications: From Neurodevelopment to Neurodiseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmallah, M.I.Y.; Micheau, O. Epigenetic Regulation of TRAIL Signaling: Implication for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Conrad, R.J.; Verdin, E.; Ott, M. Lysine Acetylation Goes Global: From Epigenetics to Metabolism and Therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1216–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wu, M.; Ma, X.; Huang, W.; Xu, Y. Function and Mechanism of Novel Histone Posttranslational Modifications in Health and Disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6635225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Beyond Histone Acetylation—Writing and Erasing Histone Acylations. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2018, 53, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.; Jeon, J.; Park, K.; Kim, J. Writing, Erasing and Reading Histone Lysine Methylations. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiroli, F.; Penengo, L. Histone Ubiquitination: An Integrative Signaling Platform in Genome Stability. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, D.; Avvakumov, N.; Côté, J. Histone Phosphorylation. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, C. Phosphorylation of Serine 10 in Histone H3, What For? J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaf, R.R.; Ramadan, W.S.; El-Awady, R. Deciphering the Interplay of Histone Post-Translational Modifications in Cancer: Co-Targeting Histone Modulators for Precision Therapy. Life Sci. 2024, 346, 122639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, C.; Pei, Y.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Kong, J.; Lu, K.; Ma, L.; Dou, S.-X.; Wang, P.-Y.; Li, G.; et al. Histone H2A Ubiquitination Reinforces Mechanical Stability and Asymmetry at the Single-Nucleosome Level. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3340–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyal, L.; Lerenthal, Y.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Mass, G.; So, S.; Wang, S.-Y.; Eppink, B.; Chung, Y.; Shalev, G.; Shema, E.; et al. Requirement of ATM-Dependent Monoubiquitylation of Histone H2B for Timely Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Mol. Cell. 2011, 41, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Luo, H.; Lee, S.; Jin, F.; Yang, J.S.; Montellier, E.; Buchou, T.; Cheng, Z.; Rousseaux, S.; Rajagopal, N.; et al. Identification of 67 Histone Marks and Histone Lysine Crotonylation as a New Type of Histone Modification. Cell 2011, 146, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.E.; English, D.M.; Cowley, S.M.; Gilbert, N.; Allan, J. Acetylation & Co: An Expanding Repertoire of Histone Acylations Regulates Chromatin and Transcription. Essays Biochem. 2019, 63, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, V. The Expanding Constellation of Histone Post-Translational Modifications in the Epigenetic Landscape. Genes 2021, 12, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghubeer, S. The Influence of Epigenetics and Inflammation on Cardiometabolic Risks. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 154, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbroek, B.; Youn, J. Chapter 5. Environment Challenges and the Brain. In Gene Environ. Interact. Psychiatry; Farra, N., Padilla, K., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 107–139. [Google Scholar]
- Albini, S.; Zakharova, V.; Ait-Si-Ali, S. Chapter 3—Histone Modifications. In Epigenetics and Regeneration; Palacios, D., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Camacho, C.V.; Setlem, R.; Ryu, K.W.; Parameswaran, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Kraus, W.L. Functional Interplay between Histone H2B ADP-Ribosylation and Phosphorylation Controls Adipogenesis. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 934–949.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, T.A.; Batchu, S.N.; Hadden, M.J.; Yerra, V.G.; Liu, Y.; Bowskill, B.B.; Advani, S.L.; Geldenhuys, L.; Siddiqi, F.S.; Majumder, S.; et al. Histone H3 Serine 10 Phosphorylation Facilitates Endothelial Activation in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2668–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, E.L.; Shi, Y. Histone Methylation: A Dynamic Mark in Health, Disease and Inheritance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, R.J.; Zhang, Y. Regulation of Histone Methylation by Demethylimination and Demethylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.S.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.I.; Baek, S.H. Epigenetic Regulation of Autophagy by Histone-Modifying Enzymes under Nutrient Stress. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Chen, X.; Qin, B.; Ren, K.-D.; Luan, Y. Epigenetics and Beyond: Targeting Histone Methylation to Treat Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 807413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Miller, K.M. Preserving Genome Integrity and Function: The DNA Damage Response and Histone Modifications. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 54, 208–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A.; Hitz, B.C.; Sloan, C.A.; Chan, E.T.; Davidson, J.M.; Gabdank, I.; Hilton, J.A.; Jain, K.; Baymuradov, U.K.; Narayanan, A.K.; et al. The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE): Data Portal Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D794–D801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco, C.; Sgarra, L.; Potenza, M.A.; Nacci, C.; Pasculli, B.; Barbano, R.; Parrella, P.; Montagnani, M. Can Epigenetics of Endothelial Dysfunction Represent the Key to Precision Medicine in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, P.; Li, X.; Ma, B.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Ni, Z.; Jiang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; et al. Liver Histone H3 Methylation and Acetylation May Associate with Type 2 Diabetes Development. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Li, M.; Song, C.; Xu, Q.; Huo, R.; Shen, L.; Xing, Q.; Cui, D.; Li, W.; Zhao, J.; et al. Combined Study of Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarker Risperidone Treatment Efficacy in Chinese Han Schizophrenia Patients. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.A.; Sadler, M.C.; Altman, R.B. Promises and Challenges in Pharmacoepigenetics. Camb. Prism. Precis. Med. 2023, 1, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodoridis, J.; Strathdee, G.; Brown, R. Epigenetic Silencing Mediated by CpG Island Methylation: Potential as a Therapeutic Target and as a Biomarker. Drug Resist. Updat. 2004, 7, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemont, S.; Curie, A.; des Portes, V.; Torrioli, M.G.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Hagerman, R.J.; Ramos, F.J.; Cornish, K.; He, Y.; Paulding, C.; et al. Epigenetic Modification of the FMR1 Gene in Fragile X Syndrome Is Associated with Differential Response to the MGluR5 Antagonist AFQ056. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 64ra1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascorbi, I.; Schwab, M. Epigenetics in Drug Response. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 99, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M. Effects of Histone Deacetylation and DNA Methylation on the Constitutive and TCDD-Inducible Expressions of the Human CYP1 Family in MCF-7 and HeLa Cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 144, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Hart, S.N.; Klaassen, C.D.; Zhong, X.-B. Dynamic Patterns of Histone Methylation Are Associated with Ontogenic Expression of the Cyp3a Genes during Mouse Liver Maturation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.D. Epigenetics Primer: Why the Clinician Should Care about Epigenetics. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2013, 33, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, R.; Wang, S.Z.; Sargent, T.; Zhu, S.Z.; Ginder, G.D. Methylation of Promoter Proximal-Transcribed Sequences of an Embryonic Globin Gene Inhibits Transcription in Primary Erythroid Cells and Promotes Formation of a Cell Type-Specific Methyl Cytosine Binding Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dolan, M.E.; Huang, R.S. Integrating Epigenomics into Pharmacogenomic Studies. Pharmacogenom. Pers. Med. 2008, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Calzón, S.; Perfilyev, A.; Martinell, M.; Ustinova, M.; Kalamajski, S.; Franks, P.W.; Bacos, K.; Elbere, I.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Volkov, P.; et al. Epigenetic Markers Associated with Metformin Response and Intolerance in Drug-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Church, G.; Dombkowski, A.; Ecker, J.R.; Gil, E.; Giresi, P.G.; Greely, H.; Greenleaf, W.J.; Hacohen, N.; et al. Challenges and Recommendations for Epigenomics in Precision Health. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raciti, G.A.; Nigro, C.; Longo, M.; Parrillo, L.; Miele, C.; Formisano, P.; Béguinot, F. Personalized Medicine and Type 2 Diabetes: Lesson from Epigenetics. Epigenomics 2014, 6, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, H.R.; Sharp, G.C.; Relton, C.L.; Lawlor, D.A. Epigenetics and Gestational Diabetes: A Review of Epigenetic Epidemiology Studies and Their Use to Explore Epigenetic Mediation and Improve Prediction. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Longo, M.; Leone, A.; Zatterale, F.; Prevenzano, I.; Miele, C.; Napoli, R.; Beguinot, F. DNA Methylation and Type 2 Diabetes: Novel Biomarkers for Risk Assessment? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillberg, L.; Ling, C. The Potential Use of DNA Methylation Biomarkers to Identify Risk and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayeh, T.; Volkov, P.; Salö, S.; Hall, E.; Nilsson, E.; Olsson, A.H.; Kirkpatrick, C.L.; Wollheim, C.B.; Eliasson, L.; Rönn, T.; et al. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Human Pancreatic Islets from Type 2 Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Donors Identifies Candidate Genes That Influence Insulin Secretion. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.T.; Dayeh, T.A.; Volkov, P.A.; Kirkpatrick, C.L.; Malmgren, S.; Jing, X.; Renström, E.; Wollheim, C.B.; Nitert, M.D.; Ling, C. Increased DNA Methylation and Decreased Expression of PDX-1 in Pancreatic Islets from Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthikumar, S.; Neeland, M.R.; Maksimovic, J.; Ranganathan, S.C.; Saffery, R. DNA Methylation Biomarkers of Future Health Outcomes in Children. Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- María Martín-Núñez, G.; Rubio-Martín, E.; Cabrera-Mulero, R.; Rojo-Martínez, G.; Olveira, G.; Valdés, S.; Soriguer, F.; Castaño, L.; Morcillo, S. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Relation to Global LINE-1 DNA Methylation in Peripheral Blood: A Cohort Study. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Martinez, F.; Wojciechowska, G.; Szczerbinski, L.; Kretowski, A. Circulating Nucleic Acid-Based Biomarkers of Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toperoff, G.; Aran, D.; Kark, J.D.; Rosenberg, M.; Dubnikov, T.; Nissan, B.; Wainstein, J.; Friedlander, Y.; Levy-Lahad, E.; Glaser, B.; et al. Genome-Wide Survey Reveals Predisposing Diabetes Type 2-Related DNA Methylation Variations in Human Peripheral Blood. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 21, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.; Jansson, P.A.; Perfilyev, A.; Volkov, P.; Pedersen, M.; Svensson, M.K.; Poulsen, P.; Ribel-Madsen, R.; Pedersen, N.L.; Almgren, P.; et al. Altered DNA Methylation and Differential Expression of Genes Influencing Metabolism and Inflammation in Adipose Tissue from Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2962–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinge, C.; Clauss, S.; Boddum, K.; Jabbari, R.; Jabbari, J.; Risgaard, B.; Tomsits, P.; Hildebrand, B.; Kääb, S.; Wakili, R.; et al. Stability of Circulating Blood-Based MicroRNAs—Pre-Analytic Methodological Considerations. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0167969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiró-Chova, L.; Peña-Chilet, M.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; García-Giménez, J.L.; Alonso-Yuste, E.; Burgues, O.; Lluch, A.; Ferrer-Lozano, J.; Ribas, G. High Stability of MicroRNAs in Tissue Samples of Compromised Quality. Virchows Arch. 2013, 463, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, B. Personalized Medicine: A Review with Regard to Biomarkers. J. Bioequiv. Availab. 2015, 7, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Giménez, J.L.; Seco-Cervera, M.; Tollefsbol, T.O.; Romá-Mateo, C.; Peiró-Chova, L.; Lapunzina, P.; Pallardó, F.V. Epigenetic Biomarkers: Current Strategies and Future Challenges for Their Use in the Clinical Laboratory. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2017, 54, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Dey, M.K.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Biomarkers in Cancer Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis. Sensors 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arguelles, A.O.; Meruvu, S.; Bowman, J.D.; Choudhury, M. Are Epigenetic Drugs for Diabetes and Obesity at Our Door Step? Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altucci, L.; Rots, M.G. Epigenetic Drugs: From Chemistry via Biology to Medicine and Back. Clin. Epigenetics 2016, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Giacca, A.; Lewis, G.F. Sodium Phenylbutyrate, a Drug with Known Capacity to Reduce Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Partially Alleviates Lipid-Induced Insulin Resistance and β-Cell Dysfunction in Humans. Diabetes 2011, 60, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.C.; Blaabjerg, L.; Størling, J.; Ronn, S.G.; Mascagni, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. The Oral Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor ITF2357 Reduces Cytokines and Protects Islet β Cells in Vivo and in Vitro. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Feng, Q.; Nie, C.; Li, T. Clinical Perspectives and Concerns of Metformin as an Anti-Aging Drug. Aging Med. 2020, 3, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, F.R.; Lecis, D.; Illuminato, F.; Milite, M.; Celotto, R.; Lerakis, S.; Romeo, F.; Barillà, F. Epigenetic Modifications and Non-Coding RNA in Diabetes-Mellitus-Induced Coronary Artery Disease: Pathophysiological Link and New Therapeutic Frontiers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scisciola, L.; Rizzo, M.R.; Cataldo, V.; Fontanella, R.A.; Balestrieri, M.L.; D’Onofrio, N.; Marfella, R.; Paolisso, G.; Barbieri, M. Incretin Drugs Effect on Epigenetic Machinery: New Potential Therapeutic Implications in Preventing Vascular Diabetic Complications. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 16489–16503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Habener, J.F.; Holst, J.J. Discovery, Characterization, and Clinical Development of the Glucagon-like Peptides. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 4217–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentza, V.; Pavlidis, G.; Ikonomidis, I.; Pililis, S.; Lampsas, S.; Kountouri, A.; Pliouta, L.; Korakas, E.; Thymis, J.; Palaiodimou, L.; et al. Antidiabetic Treatment and Prevention of Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtara, M.; Syeda, Y.; Mozgała, N.; Mazumder, A. Examining Off-Label Prescribing of Ozempic for Weight-Loss. Qeios, 2023; Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odimegwu, C.; Uwaezuoke, S.; Chikani, U.; Mbanefo, N.; Adiele, K.; Nwolisa, C.; Eneh, C.; Ndiokwelu, C.; Okpala, S.; Ogbuka, F.; et al. Targeting the Epigenetic Marks in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Will Epigenetic Therapy Be a Valuable Adjunct to Pharmacotherapy? Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 3557–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer-Dubowska, W.; Majchrzak-Celińska, A.; Cichocki, M. Pharmocoepigenetics: A New Approach to Predicting Individual Drug Responses and Targeting New Drugs. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauschke, V.M.; Barragan, I.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Pharmacoepigenetics and Toxicoepigenetics: Novel Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 58, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Pharmacoepigenetics: Its Role in Interindividual Differences in Drug Response. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 85, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, S.L.; Morrissey, K.M.; Yee, S.W.; Castro, R.A.; Xu, L.; Dahlin, A.; Ramirez, A.H.; Roden, D.M.; Wilke, R.A.; McCarty, C.A.; et al. The Effect of Novel Promoter Variants in MATE1 and MATE2 on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Metformin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 93, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-T.; Chiang, C.-H.; Chen, C.; Lin, S.-C.; Lee, H.-J.; Chen, J.-W. Antioxidation and Nrf2-Mediated Heme Oxygenase-1 Activation Contribute to Renal Protective Effects of Hydralazine in Diabetic Nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, B.P.; Nguyen, L.T.; Hou, M.; Glastras, S.J.; Chen, H.; Faiz, A.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Pollock, C.A.; Saad, S. Low-Dose Hydralazine Reduces Albuminuria and Glomerulosclerosis in a Mouse Model of Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, H.; Teijeiro, A.; Chaves-Pérez, A.; Perna, C.; Satish, B.; Novials, A.; Wang, J.P.; Djouder, N. Coxsackievirus B Type 4 Infection in β Cells Downregulates the Chaperone Prefoldin URI to Induce a MODY4-like Diabetes via Pdx1 Silencing. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, S.; Rieneck, K.; Bovin, L.F.; Skak, K.; Tomra, S.; Michelsen, B.K.; Ødum, N. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: A New Class of Immunosuppressors Targeting a Novel Signal Pathway Essential for CD154 Expression. Blood 2003, 101, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Jena, G. Valproic Acid Improves Glucose Homeostasis by Increasing Beta-Cell Proliferation, Function, and Reducing Its Apoptosis through HDAC Inhibition in Juvenile Diabetic Rat. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-R.; Huang, S.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-W.; Hong, Z.-J.; Cheng, C.-P.; Sytwu, H.-K.; Lin, G.-J. Valproic Acid Suppresses Autoimmune Recurrence and Allograft Rejection in Islet Transplantation through Induction of the Differentiation of Regulatory T Cells and Can Be Used in Cell Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, K.; Meena, R.L.; Kabra, D.G.; Gaikwad, A.B. Change in Post-Translational Modifications of Histone H3, Heat-Shock Protein-27 and MAP Kinase P38 Expression by Curcumin in Streptozotocin-Induced Type I Diabetic Nephropathy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Han, S.W.; Bang, Y.J. Epigenetic-Based Therapies in Cancer. Drugs 2011, 71, 2391–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griazeva, E.D.; Fedoseeva, D.M.; Radion, E.I.; Ershov, P.V.; Meshkov, I.O.; Semyanihina, A.V.; Makarova, A.S.; Makarov, V.V.; Yudin, V.S.; Keskinov, A.A.; et al. Current Approaches to Epigenetic Therapy. Epigenomes 2023, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, W.; Dismuke, A.D.; Turker, M.S. Epigenetic Patents: A Stressful Environment for an Emerging Science. Biotechnol. Law Rep. 2013, 32, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biosystems, C.; Smith, K.D.; Yazvenko, N.; Smit, M. Recent Patents in Epigenetic Targeting. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommese, L.; Zullo, A.; Mancini, F.P.; Fabbricini, R.; Soricelli, A.; Napoli, C. Clinical Relevance of Epigenetics in the Onset and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwell, L.R.; Ahiarah, C.; Rasheed, S.; Rahman, S.M.; Choudhury, M. Traditional Therapeutics and Potential Epidrugs for CVD: Why Not Both? Life 2023, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chous, A.P.; Richer, S.P.; Gerson, J.D.; Kowluru, R.A. The Diabetes Visual Function Supplement Study (DiVFuSS). Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 100, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Meng, C.; He, S.; Gu, C.; Lhamo, T.; Draga, D.; Luo, D.; Qiu, Q. DNA Methylation in Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathogenetic Role and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peedicayil, J. Pharmacoepigenetics and Pharmacoepigenomics. Pharmacogenomics 2008, 9, 1785–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacabelos, R.; Naidoo, V.; Corzo, L.; Cacabelos, N.; Carril, J.C. Genophenotypic Factors and Pharmacogenomics in Adverse Drug Reactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhong, X. Epigenetic Mechanisms Contribute to Intraindividual Variations of Drug Metabolism Mediated by Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2023, 51, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habano, W.; Gamo, T.; Terashima, J.; Sugai, T.; Otsuka, K.; Wakabayashi, G.; Ozawa, S. Involvement of Promoter Methylation in the Regulation of Pregnane X Receptor in Colon Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habano, W.; Kawamura, K.; Iizuka, N.; Terashima, J.; Sugai, T.; Ozawa, S. Analysis of DNA Methylation Landscape Reveals the Roles of DNA Methylation in the Regulation of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.; Kals, M.; Kacevska, M.; Barragan, I.; Kasuga, K.; Rane, A.; Metspalu, A.; Milani, L.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Ontogeny, Distribution and Potential Roles of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Human Liver Function. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokizane, T.; Shiina, H.; Igawa, M.; Enokida, H.; Urakami, S.; Kawakami, T.; Ogishima, T.; Okino, S.T.; Li, L.-C.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Cytochrome P450 1B1 Is Overexpressed and Regulated by Hypomethylation in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5793–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rountree, M.R.; Bachman, K.E.; Baylin, S.B. DNMT1 Binds HDAC2 and a New Co-Repressor, DMAP1, to Form a Complex at Replication Foci. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, S.T.; Pookot, D.; Li, L.C.; Zhao, H.; Urakami, S.; Shiina, H.; Igawa, M.; Dahiya, R. Epigenetic Inactivation of the Dioxin-Responsive Cytochrome P4501A1 Gene in Human Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7420–7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, S.; Hakkola, J.; Tuominen, P.; Elovaara, E.; Husgafvel-Pursiainen, K.; Karjalainen, A.; Hirvonen, A.; Nurminen, T. Methylation of Cytochrome P4501A1 Promoter in the Lung Is Associated with Tobacco Smoking. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8623–8628. [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha, S.; Singh, N. Review: Association between Dna Methylation of Cyp Gene Family in Vitamin D Signalling Pathway and Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Recent Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 24246–24252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.; Chappell, G.; Guyton, K.Z.; Pogribny, I.P.; Rusyn, I. Epigenetic Alterations Induced by Genotoxic Occupational and Environmental Human Chemical Carcinogens: An Update of a Systematic Literature Review. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2022, 789, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjan, D.R.; Flavahan, W.A.; Bernstein, B.E. Epigenome Editing Strategies for the Functional Annotation of CTCF Insulators. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.K.; Cascorbi, I. Opportunities and Limitations: The Value of Pharmacogenetics in Clinical Practice. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 77, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjaltema, R.A.F.; Rots, M.G. Advances of Epigenetic Editing. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 57, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.P.; Sato, F.; Greenwald, B.D.; Suntharalingam, M.; Krasna, M.J.; Edelman, M.J.; Doyle, A.; Berki, A.T.; Abraham, J.M.; Mori, Y.; et al. Promoter Methylation and Response to Chemotherapy and Radiation in Esophageal Cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C. Pharmacoepigenetics in Type 2 Diabetes: Is It Clinically Relevant? Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1849–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mkhize, S.S.; Chuturgoon, A.A.; Ghazi, T.; Machaba, K.E. Pharmaco-Epigenetics and Epigenetic Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: Can Epigenetics Predict Drug Efficiency? Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092278
Mkhize SS, Chuturgoon AA, Ghazi T, Machaba KE. Pharmaco-Epigenetics and Epigenetic Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: Can Epigenetics Predict Drug Efficiency? Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092278
Chicago/Turabian StyleMkhize, Senzosenkosi Surprise, Anil Amichund Chuturgoon, Terisha Ghazi, and Kgothatso Eugene Machaba. 2025. "Pharmaco-Epigenetics and Epigenetic Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: Can Epigenetics Predict Drug Efficiency?" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092278
APA StyleMkhize, S. S., Chuturgoon, A. A., Ghazi, T., & Machaba, K. E. (2025). Pharmaco-Epigenetics and Epigenetic Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: Can Epigenetics Predict Drug Efficiency? Biomedicines, 13(9), 2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092278





