Interferon Regulator Factor 5: A Novel Inflammatory Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target in Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Immunostaining Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
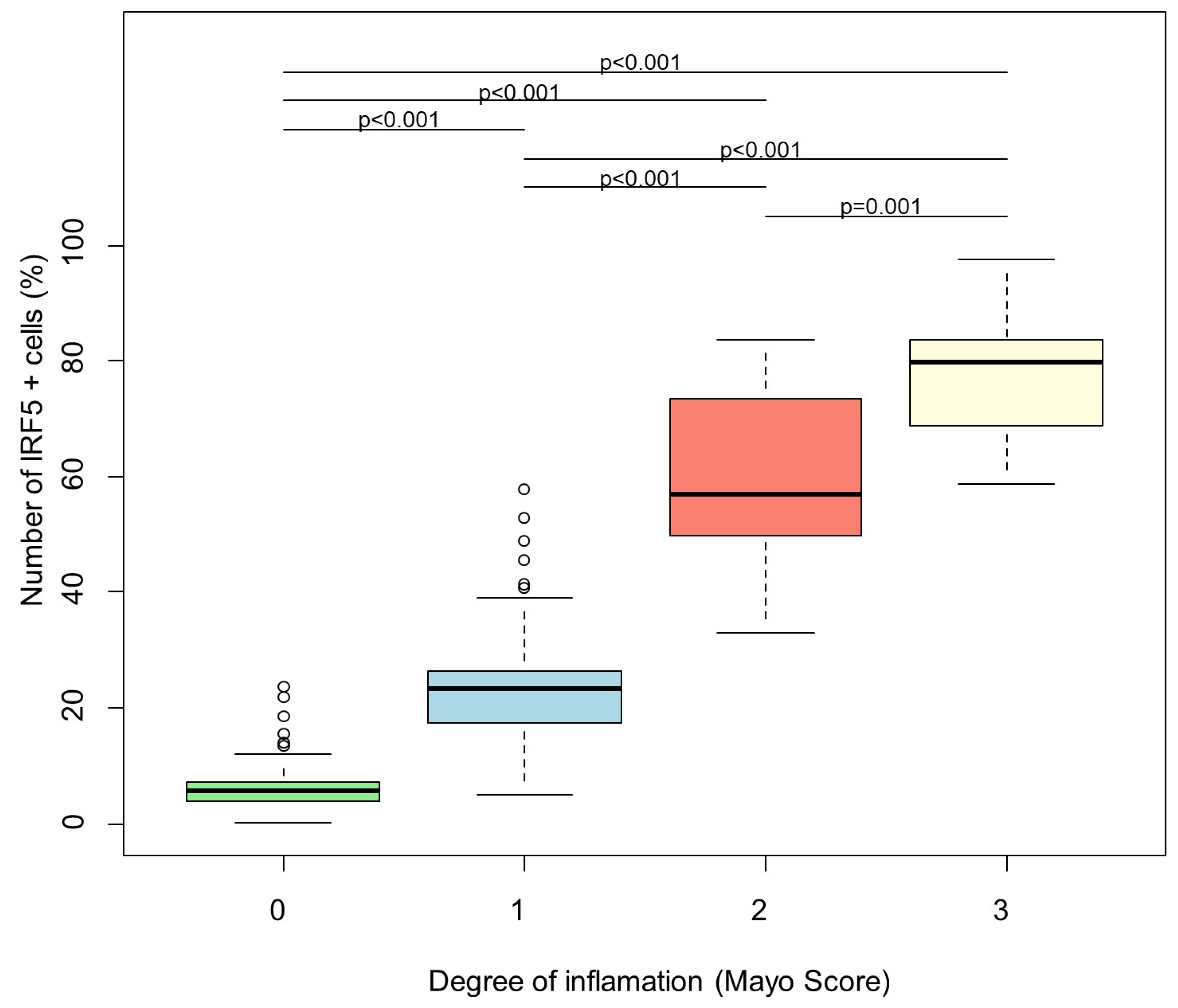
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ordas, I.; Eckmann, L.; Talamini, M.; Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2012, 380, 1606–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2012, 380, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.P.; Driscoll, R.; Pounder, R.E.; Wakefield, A.J. Genetics versus environment in inflammatory bowel disease: Results of a British twin study. BMJ 1996, 312, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larabi, A.; Barnich, N.; Nguyen, H.T.T. New insights into the interplay between autophagy, gut microbiota and inflammatory responses in IBD. Autophagy 2020, 16, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.A.; Boucher, G.; Lees, C.W.; Franke, A.; D’Amato, M.; Taylor, K.D.; Lee, J.C.; Goyette, P.; Imielinski, M.; Latiano, A.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies 29 additional ulcerative colitis risk loci, increasing the number of confirmed associations to 47. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 2007, 447, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elding, H.; Lau, W.; Swallow, D.M.; Maniatis, N. Refinement in localization and identification of gene regions associated with Crohn disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathungu, G.; Zhang, C.K.; Zhang, W.; Cho, J.H. A two-marker haplotype in the IRF5 gene is associated with inflammatory bowel disease in a North American cohort. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesage, S.; Zouali, H.; Cezard, J.P.; Colombel, J.F.; Belaiche, J.; Almer, S.; Tysk, C.; O’Morain, C.; Gassull, M.; Binder, V.; et al. CARD15/NOD2 mutational analysis and genotype-phenotype correlation in 612 patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dideberg, V.; Kristjansdottir, G.; Milani, L.; Libioulle, C.; Sigurdsson, S.; Louis, E.; Wiman, A.C.; Vermeire, S.; Rutgeerts, P.; Belaiche, J.; et al. An insertion-deletion polymorphism in the interferon regulatory Factor 5 (IRF5) gene confers risk of inflammatory bowel diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 3008–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Sato, G.R.; Tamura, T. Regulation and role of the transcription factor IRF5 in innate immune responses and systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idborg, H.; Zandian, A.; Ossipova, E.; Wigren, E.; Preger, C.; Mobarrez, F.; Checa, A.; Sohrabian, A.; Pucholt, P.; Sandling, J.K.; et al. Circulating Levels of Interferon Regulatory Factor-5 Associates With Subgroups of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Chen, H.M.; Inuzuka, T.; Kondo, S.; Mak, T.W.; Takaoka, A.; Honda, K.; Taniguchi, T. Role of IFN regulatory factor 5 transcription factor in antiviral immunity and tumor suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3402–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eames, H.L.; Corbin, A.L.; Udalova, I.A. Interferon regulatory factor 5 in human autoimmunity and murine models of autoimmune disease. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronnblom, L. The importance of the type I interferon system in autoimmunity. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34 (Suppl. S98), 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom, J.; Lagutkin, D.; Sherina, N.; Idborg, H.; Beretta, L.; Borghi, M.O.; PRECISESADS Clinical Consortium; Peyper, J.M.; Barturen, G.; Jakobsson, P.J.; et al. Novel IgG and IgA autoantibodies validated in two independent cohorts are associated with disease activity and determine organ manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: Implications for anti-LIN28A, anti-HMGN5, anti-IRF5, and anti-TGIF1. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2025, 84, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhakov, G.; Eames, H.L.; Udalova, I.A. Activation and function of interferon regulatory factor 5. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaoka, A.; Yanai, H.; Kondo, S.; Duncan, G.; Negishi, H.; Mizutani, T.; Kano, S.; Honda, K.; Ohba, Y.; Mak, T.W.; et al. Integral role of IRF-5 in the gene induction programme activated by Toll-like receptors. Nature 2005, 434, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Taniguchi, T. IRFs: Master regulators of signalling by Toll-like receptors and cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoyratty, T.E.; Udalova, I.A. Diverse mechanisms of IRF5 action in inflammatory responses. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 99, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Byrne, A.J.; Blazek, K.; Saliba, D.G.; Pease, J.E.; Perocheau, D.; Feldmann, M.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 controls both acute and chronic inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Blazek, K.; Byrne, A.J.; Perocheau, D.P.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 Is a Specific Marker of Inflammatory Macrophages In Vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.J.; Field, A.E.; Pitha-Rowe, P.M. Virus-induced heterodimer formation between IRF-5 and IRF-7 modulates assembly of the IFNA enhanceosome in vivo and transcriptional activity of IFNA genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16630–16641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Mancl, M.E.; Barnes, B.J. Signaling through IFN regulatory factor-5 sensitizes p53-deficient tumors to DNA damage-induced apoptosis and cell death. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7403–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.J.; Moore, P.A.; Pitha, P.M. Virus-specific activation of a novel interferon regulatory factor, IRF-5, results in the induction of distinct interferon alpha genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 23382–23390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Sato, G.R.; Nishiyama, A.; Akiyama, A.; Takasuna, M.; Umehara, M.; Suzuki, S.; Ichino, M.; Matsunaga, S.; Kimura, A.; et al. Lyn Kinase Suppresses the Transcriptional Activity of IRF5 in the TLR-MyD88 Pathway to Restrain the Development of Autoimmunity. Immunity 2016, 45, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang Foreman, H.C.; Van Scoy, S.; Cheng, T.F.; Reich, N.C. Activation of interferon regulatory factor 5 by site specific phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuttaqi, H.; Udalova, I.A. Advances and challenges in targeting IRF5, a key regulator of inflammation. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhakov, G.; Almuttaqi, H.; Corbin, A.L.; Khoyratty, T.E.; Berthold, D.L.; Bullers, S.J.; Eames, H.L.; Ai, Z.; Bonham, S.; Fischer, R.; et al. PYK2 controls intestinal inflammation via activation of IRF5 in macrophages. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, L.; Winkler, A.; Jelinsky, S.A.; Lee, K.; Korver, W.; Hawtin, R.; Rao, V.R.; Fleming, M.; Lin, L.L. IRAK4 kinase activity controls Toll-like receptor-induced inflammation through the transcription factor IRF5 in primary human monocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 18689–18698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausgruber, T.; Blazek, K.; Smallie, T.; Alzabin, S.; Lockstone, H.; Sahgal, N.; Hussell, T.; Feldmann, M.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globig, A.M.; Hennecke, N.; Martin, B.; Seidl, M.; Ruf, G.; Hasselblatt, P.; Thimme, R.; Bengsch, B. Comprehensive intestinal T helper cell profiling reveals specific accumulation of IFN-gamma+IL-17+coproducing CD4+ T cells in active inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncone, E.; Laudisi, F.; Di Fusco, V.; Dinallo, V.; De Simone, E.; Monteleone, I.; Franzè, E.; Monteleone, G. Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 Expressing Cells infiltrate Lamina Propria of IBD Patients and produce inflammatory Cytokines. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, e73–e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhakov, G.; Almuttaqi, H.; Corbin, A.L.; Berthold, D.L.; Khoyratty, T.; Eames, H.L.; Bullers, S.; Pearson, C.; Ai, Z.; Zec, K.; et al. Defactinib inhibits PYK2 phosphorylation of IRF5 and reduces intestinal inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, T.; Niederreiter, L.; Tilg, H.; Blumberg, R.S.; Kaser, A. Controversy over NOD2, inflammation, and defensins. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1996–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Lee, L.H.; Chow, S.C.; Fang, C.M. IRF5-mediated immune responses and its implications in immunological disorders. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 37, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jing, D.; He, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, G. IRF5 Acts as a Potential Therapeutic Marker in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayling, R.M.; Kok, K. Fecal Calprotectin. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 87, 161–190. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; De, S.; Nelson, V.; Chopra, S.; LaPan, M.; Kampta, K.; Sun, S.; He, M.; Thompson, C.D.; Li, D.; et al. Inhibition of IRF5 hyperactivation protects from lupus onset and severity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6700–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, D.E.; Camidge, D.R.; Morgensztern, D.; Cetnar, J.; Kelly, R.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Spigel, D.R.; Jeong, W.; Scaglioni, P.P.; Zhang, S.; et al. Phase 2 study of the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor defactinib (VS-6063) in previously treated advanced KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 139, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, J.R.; Camidge, D.R.; Mileshkin, L.R.; Chen, E.X.; Hicks, R.J.; Rischin, D.; Fingert, H.; Pierce, K.J.; Xu, H.; Roberts, W.G.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic phase I dose-escalation trial of PF-00562271, an inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase, in advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Fukuoka, K.; Takeda, M.; Iwasa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Horobin, J.; Keegan, M.; Vaickus, L.; Chavan, A.; Padval, M.; et al. A first-in-Asian phase 1 study to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics and clinical activity of VS-6063, a focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitor in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Liu, K. Integrins in cancer: Emerging mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 247, 108458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ulcerative Colitis | |
|---|---|
| N (female) | 30 (19) |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 42.7 ± 13.0 |
| Disease localization | |
| Ulcerative Colitis, n (%) | |
| E1 proctitis | 3 (10) |
| E2 left-sided colitis | 9 (30) |
| E3 pancolitis | 9 (30) |
| Remission | 9 (30) |
| Medication, n (%) | |
| No treatment | 0 (0) |
| 5-ASA | 8 (26.6) |
| Corticosteroids | 2 (6.6) |
| Azathioprin | 1 (3.3) |
| Sulfasalazine | 1 (3.3) |
| Vedolizumab | 9 (30) |
| TNF-alpha inhibitors | 8 (26.6) |
| JAK inhibitors | 1 (3.3) |
| Laboratory markers, median (min–max) | |
| Calprotectin [µg/mg] | 252.76 (50–1122) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farrag, K.; Aksan, A.; Korotkova, M.; Idborg, H.; Jakobsson, P.-J.; Weigert, A.; Vieth, M.; Zeuzem, S.; Blumenstein, I.; Stein, J. Interferon Regulator Factor 5: A Novel Inflammatory Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target in Ulcerative Colitis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092251
Farrag K, Aksan A, Korotkova M, Idborg H, Jakobsson P-J, Weigert A, Vieth M, Zeuzem S, Blumenstein I, Stein J. Interferon Regulator Factor 5: A Novel Inflammatory Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target in Ulcerative Colitis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092251
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarrag, Karima, Aysegül Aksan, Marina Korotkova, Helena Idborg, Per-Johan Jakobsson, Andreas Weigert, Michael Vieth, Stefan Zeuzem, Irina Blumenstein, and Jürgen Stein. 2025. "Interferon Regulator Factor 5: A Novel Inflammatory Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target in Ulcerative Colitis" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092251
APA StyleFarrag, K., Aksan, A., Korotkova, M., Idborg, H., Jakobsson, P.-J., Weigert, A., Vieth, M., Zeuzem, S., Blumenstein, I., & Stein, J. (2025). Interferon Regulator Factor 5: A Novel Inflammatory Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target in Ulcerative Colitis. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092251







