Unraveling the Functional Impact of Splicing Variants in Inherited Hearing Disorders Through Minigene Splicing Assays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Study Participants and Clinical Evaluation
2.3. WES Analysis and Interpretation
2.4. In Silico Prediction
2.5. Minigene Splicing Assay
2.6. Cell Culture, Transfection, and RNA Extraction
2.7. Reverse Transcription and RT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description
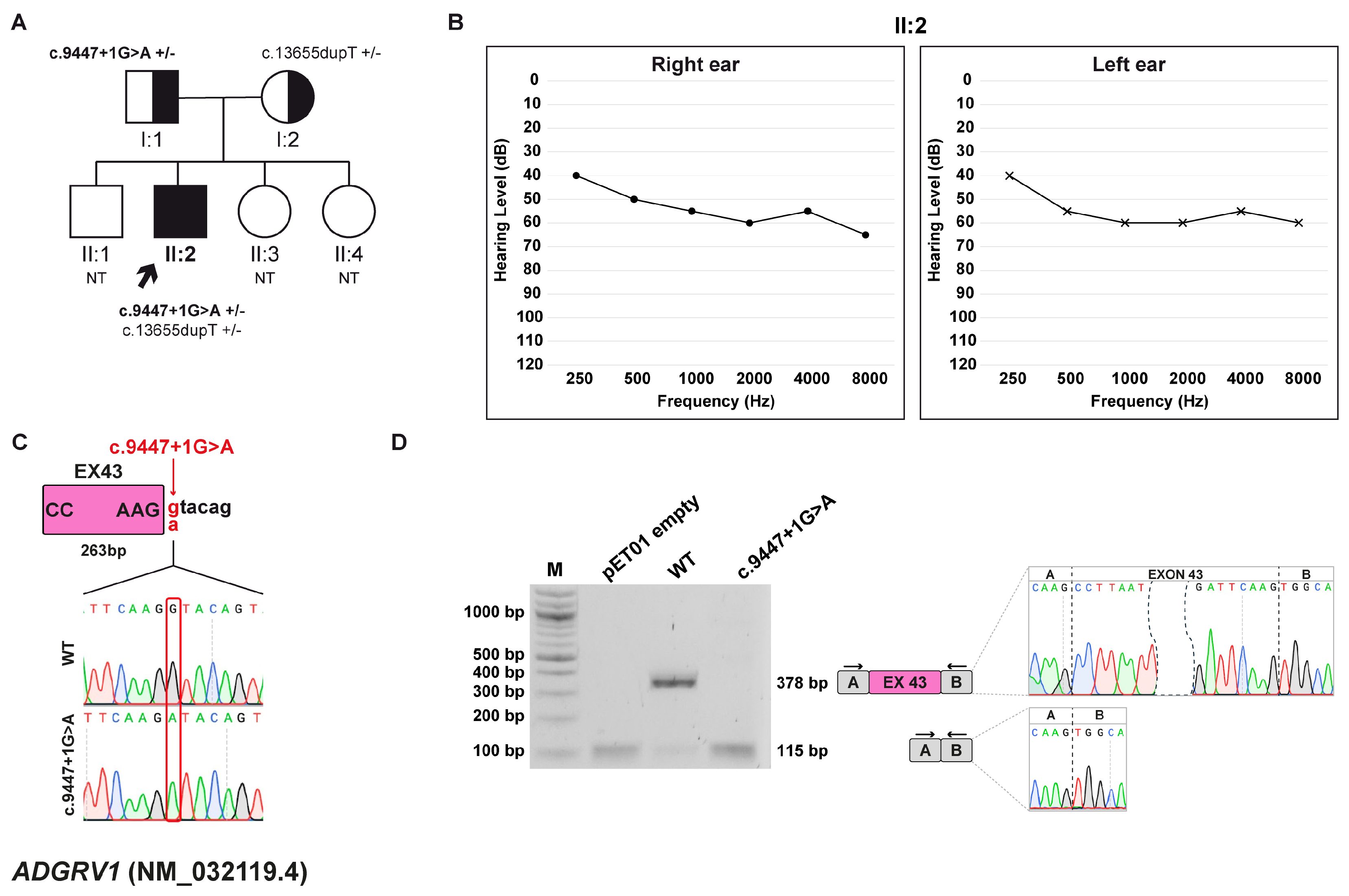
3.2. Family A: ADGRV1 (NM_032119.4) c.9447+1G>A Variant
3.2.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
3.2.2. Minigene Splicing Assay
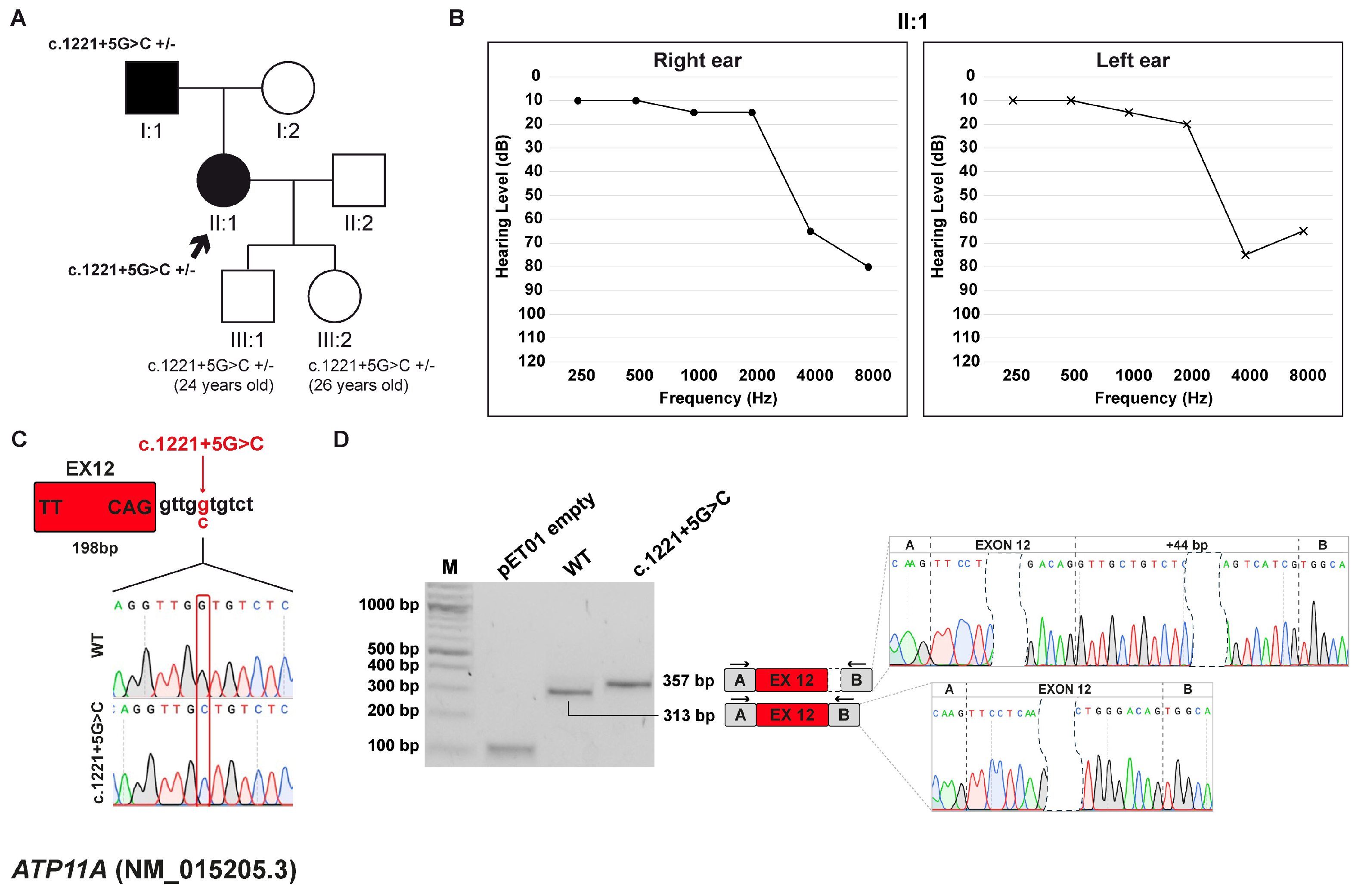
3.3. Family B: ATP11A (NM_015205.3) c.1221+5G>C Variant
3.3.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
3.3.2. Minigene Splicing Assay
3.4. Family C: GSDME (NM_004403.3) c.1183+1G>A Variant
3.4.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
3.4.2. Minigene Splicing Assay
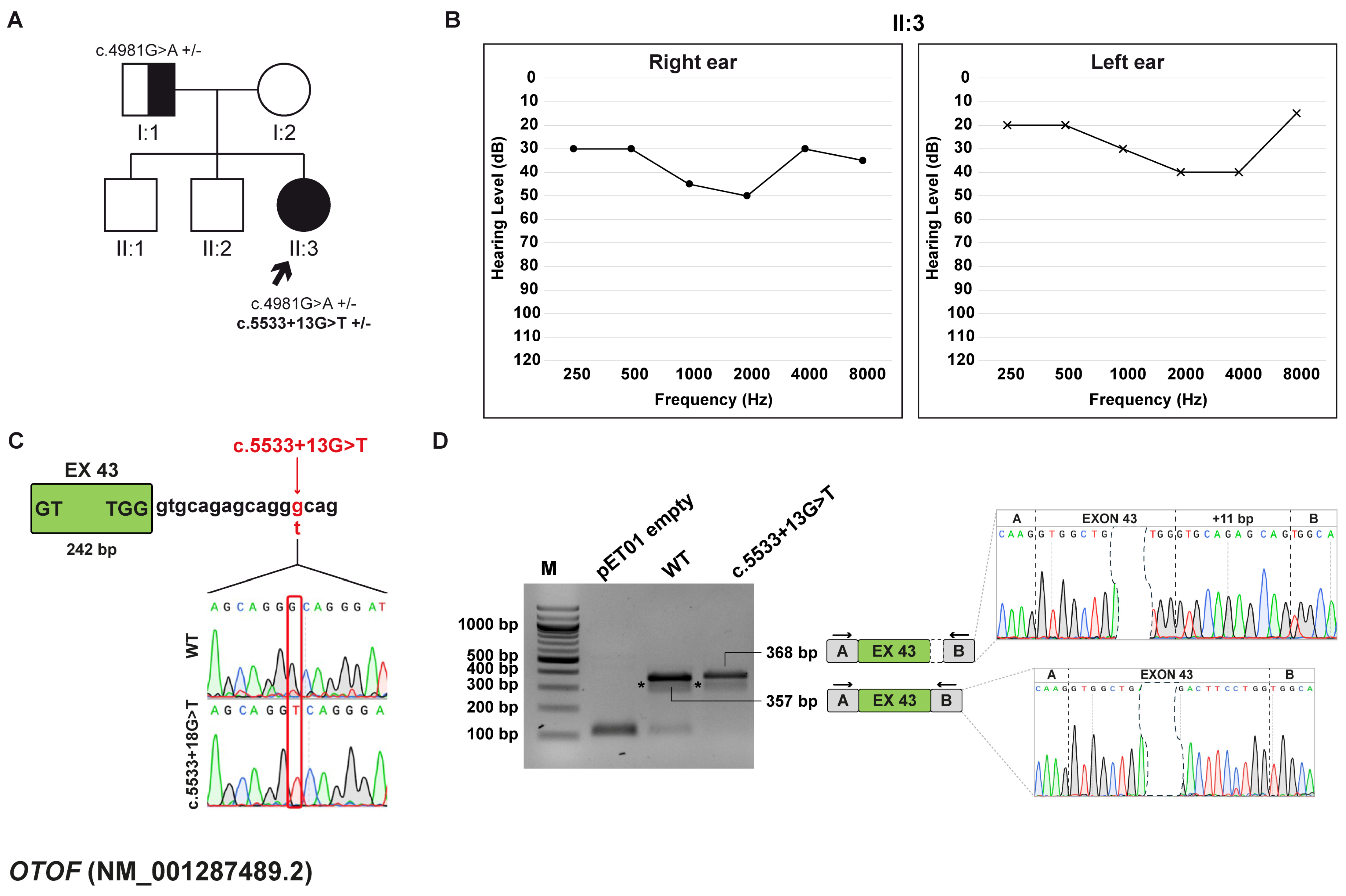
3.5. Family D: OTOF (NM_001287489.2) c.5533+13G>T Variant
3.5.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
3.5.2. Minigene Splicing Assay
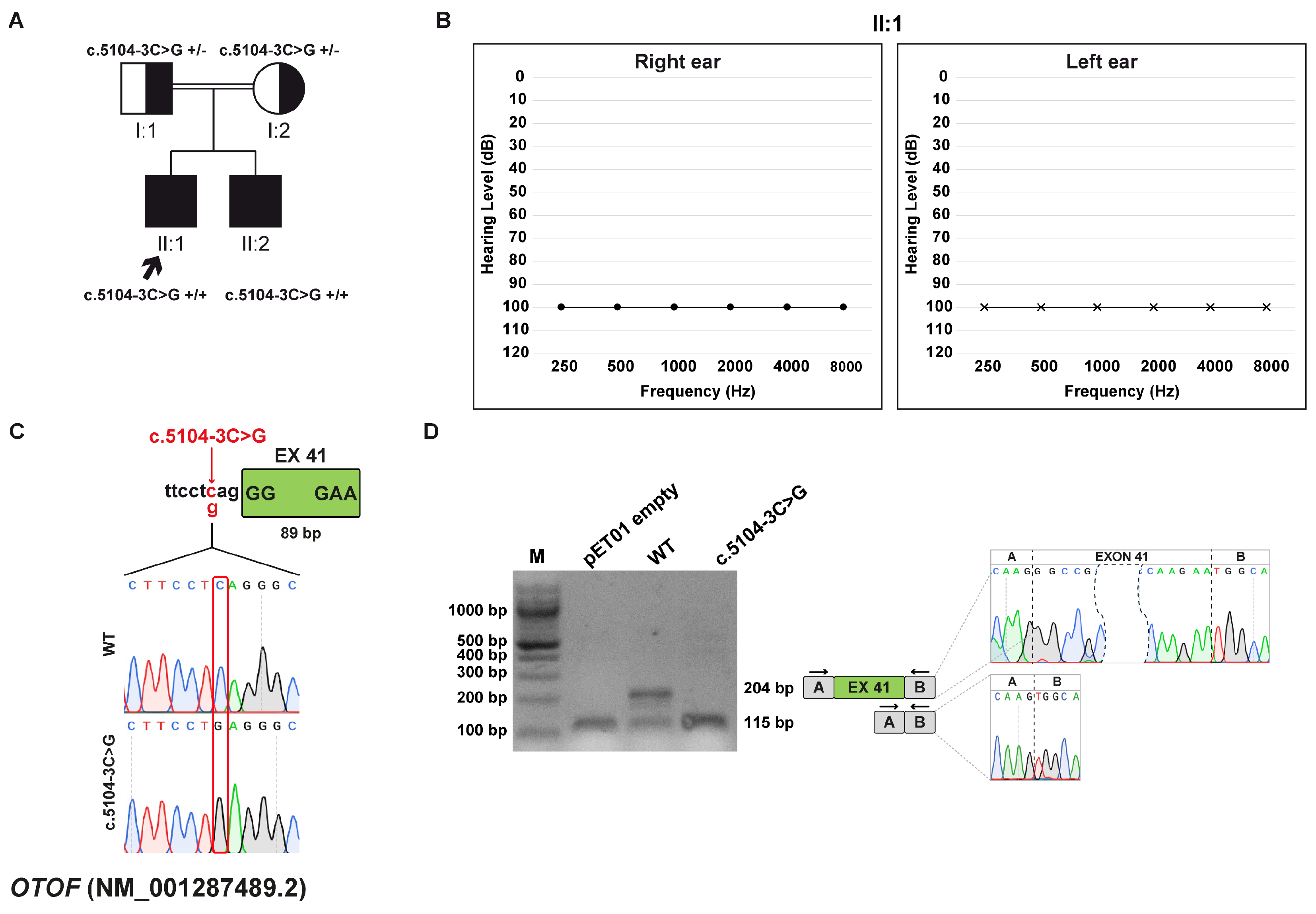
3.6. Family E: OTOF (NM_001287489.2) c.5104-3C>G Variant
3.6.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
3.6.2. Minigene Splicing Assay
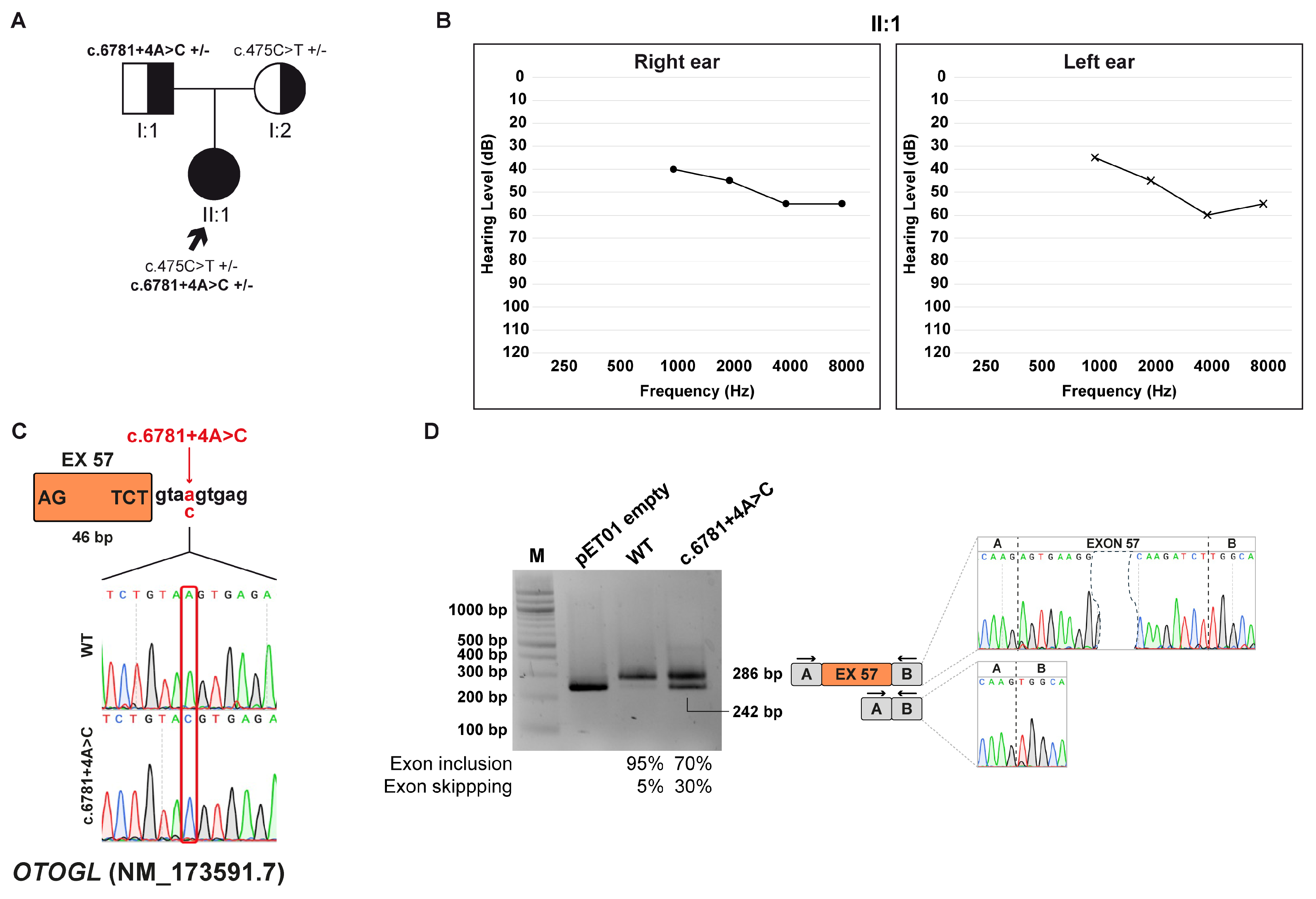
3.7. Family F: OTOGL (NM_173591.7) c.6781+4A>C Variant
3.7.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
3.7.2. Minigene Splicing Assay
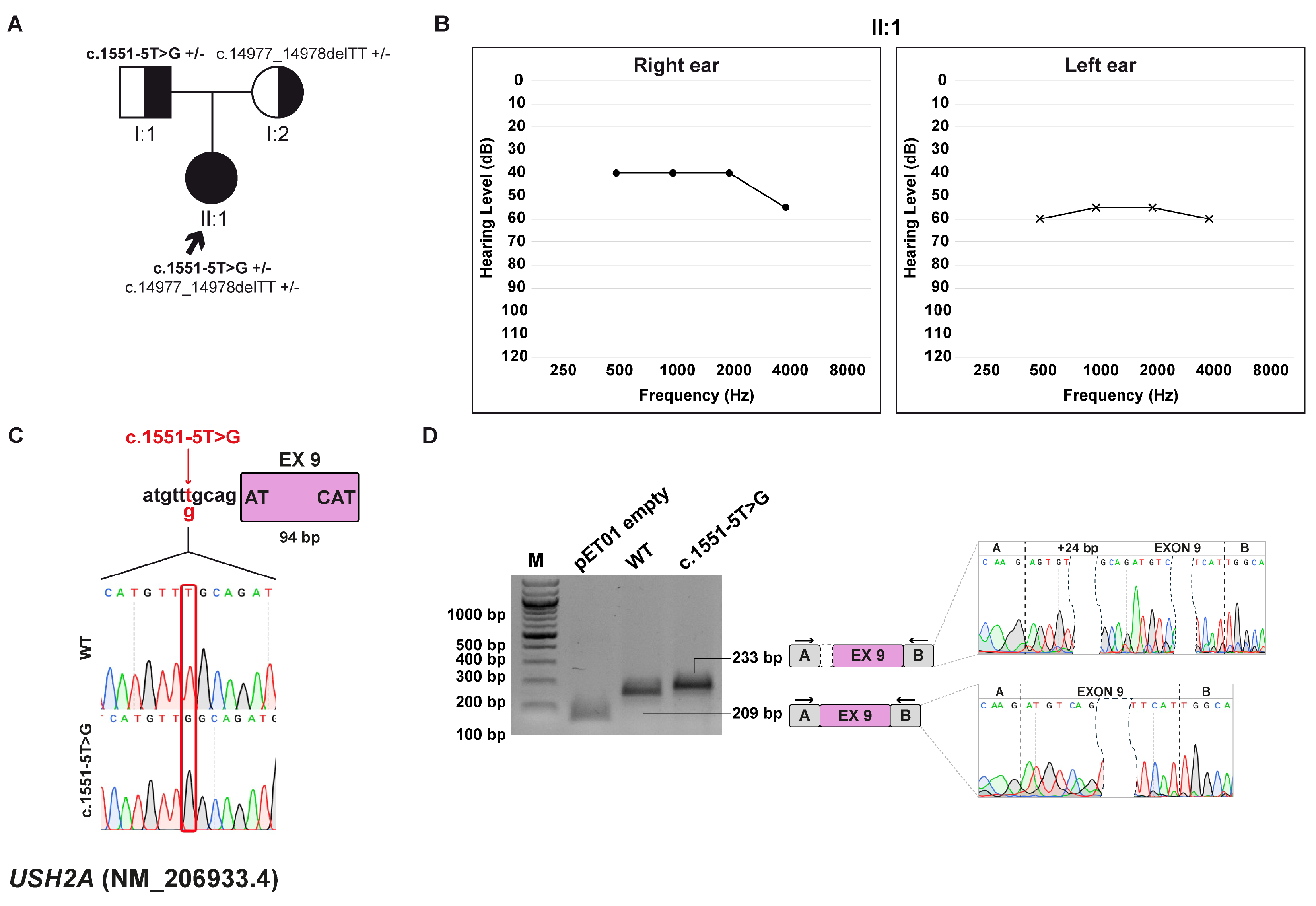
3.8. Family G: USH2A (NM_206933.4) c.1551-5T>G variant
3.8.1. Clinical and Genetic Evaluation
3.8.2. Minigene Splicing Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HL | Hearing loss |
| HHL | Hereditary hearing loss |
| WES | Whole-exome sequencing |
| SHL | Syndromic hearing loss |
| NSHL | Non-syndromic hearing loss |
| AD | Autosomal dominant |
| AR | Autosomal recessive |
| XL | X-linked |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| VUS | Variant of unknown significance |
| HGMD | Human Gene Mutation Database |
| CADD | Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion |
| gDNA | Genomic DNA |
| wt | Wild-type |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| AMP | Association for Molecular Pathology |
| DVD | Deafness Variation Database |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| PTC | Premature termination codon |
| ss | Splice site |
| OAEs | Otoacoustic emissions |
| ABR | Auditory brainstem response |
| CI | Cochlear implantation |
References
- Deafness and Hearing Loss. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Sutton, A.E.; Goldman, J. Syndromic Sensorineural Hearing Loss; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, C.; Bonnet, C.; Safieddine, S. Deafness: From Genetic Architecture to Gene Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 665–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spedicati, B.; Santin, A.; Nardone, G.G.; Rubinato, E.; Lenarduzzi, S.; Graziano, C.; Garavelli, L.; Miccoli, S.; Bigoni, S.; Morgan, A.; et al. The Enigmatic Genetic Landscape of Hereditary Hearing Loss: A Diagnostic Strategy in the Italian Population. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideura, M.; Nishio, S.-Y.; Moteki, H.; Takumi, Y.; Miyagawa, M.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohyama, K.; Oda, K.; Matsui, T.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Syndromic Hearing Loss Patients in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcome to the Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage|Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage. Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- del Castillo, I.; Morín, M.; Domínguez-Ruiz, M.; Moreno-Pelayo, M.A. Genetic Etiology of Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss in Europe. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.; Azaiez, H.; Booth, K. GJB2-Related Autosomal Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Snoeckx, R.L.; Huygen, P.L.M.; Feldmann, D.; Marlin, S.; Denoyelle, F.; Waligora, J.; Mueller-Malesinska, M.; Pollak, A.; Ploski, R.; Murgia, A.; et al. GJB2 Mutations and Degree of Hearing Loss: A Multicenter Study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, B.; Hofrichter, M.A.H.; Neuner, C.; Schröder, J.; Gehrig, A.; Hennermann, J.B.; Kraus, F.; Shehata-Dieler, W.; Klopocki, E.; Nanda, I.; et al. DFNB16 Is a Frequent Cause of Congenital Hearing Impairment: Implementation of STRC Mutation Analysis in Routine Diagnostics. Clin. Genet. 2015, 87, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, Y.; Moteki, H.; Nishio, S.Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Wakui, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohyama, K.; Miyazaki, H.; Matsuoka, R.; Abe, S.; et al. Frequency and Clinical Features of Hearing Loss Caused by STRC Deletions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francey, L.J.; Conlin, L.K.; Kadesch, H.E.; Clark, D.; Berrodin, D.; Sun, Y.; Glessner, J.; Hakonarson, H.; Jalas, C.; Landau, C.; et al. Genome-Wide SNP Genotyping Identifies the Stereocilin (STRC) Gene as a Major Contributor to Pediatric Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Impairment. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2012, 158, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooch, C.; Rudy, N.; Smith, R.J.H.; Robin, N.H. Genetic Testing Hearing Loss: The Challenge of Non Syndromic. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 150, 110872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, A.; Faletra, F.; Severi, G.; La Bianca, M.; Licchetta, L.; Gasparini, P.; Graziano, C.; Girotto, G. There Is More than Meets the Eye: Identification of Dual Diagnosis in Patients Affected by Hearing Loss. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Facilitates Genetic Diagnosis and improves the Management of Patients with Hearing Loss in clinical Practice. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 161, 111258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heurck, R.; Carminho-rodrigues, M.T.; Ranza, E.; Stafuzza, C.; Quteineh, L.; Gehrig, C.; Hammar, E.; Guipponi, M.; Abramowicz, M.; Senn, P.; et al. Benefits of Exome Sequencing in Children with Suspected Isolated Hearing Loss. Genes 2021, 12, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elander, J.; Ullmark, T.; Ehrencrona, H.; Jonson, T.; Piccinelli, P.; Samuelsson, S.; Löwgren, K.; Falkenius-Schmidt, K.; Ehinger, J.; Stenfeldt, K.; et al. Extended Genetic Diagnostics for Children with Profound Sensorineural Hearing Loss by Implementing Massive Parallel Sequencing. Diagnostic Outcome, Family Experience and Clinical Implementation. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 159, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergant, G.; Maver, A.; Lovrecic, L.; Čuturilo, G.; Hodzic, A.; Peterlin, B. Comprehensive Use of Extended Exome Analysis Improves Diagnostic Yield in Rare Disease: A Retrospective Survey in 1059 Cases. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, L.S.; Bader, D.M.; Mertes, C.; Kopajtich, R.; Pichler, G.; Iuso, A.; Haack, T.B.; Graf, E.; Schwarzmayr, T.; Terrile, C.; et al. Genetic Diagnosis of Mendelian Disorders via RNA Sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, P.J.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Wu, W.; Pinese, M.; Cowley, M.J. SpliceVarDB: A Comprehensive Database of Experimentally Validated Human Splicing Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HGMD® Home Page. Available online: https://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Ahmed, A.; Wang, M.; Khan, R.; Shah, A.A.; Guo, H.; Malik, S.; Xia, K.; Hu, Z. A Splice-Site Variant (c.3289-1G>T) in OTOF Underlies Hearing Loss in a Pakistani Kindred. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavaf, M.; Soveizi, M.; Maleki, M.; Mahdieh, N. MYO15A Splicing Mutations in Hearing Loss: A Review Literature and Report of a Novel Mutation. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 96, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Long, Y.; Shi, T.; Ma, X.; Lian, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Yu, L.; Zhao, X. Validating the Splicing Effect of Rare Variants in the SLC26A4 Gene Using Minigene Assay. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the Deleteriousness of Variants Throughout the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Boerwinkle, E.; Liu, X. In Silico Prediction of Splice-Altering Single Nucleotide in the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 13534–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riepe, T.V.; Khan, M.; Roosing, S.; Cremers, F.P.M.; ’t Hoen, P.A.C. Benchmarking Deep Learning Splice Prediction Tools Using Splice Assays. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, K.; Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou, S.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soens, Z.T.; Branch, J.; Wu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Xu, M.; Rajan, L.; Motta, F.L.; et al. Leveraging Splice-Affecting Variant Predictors and a Minigene Validation System to Identify Mendelian Disease-Causing Variants Among Exon-Captured Variants of Uncertain Significance. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SpliceAI Lookup. Available online: https://spliceailookup.broadinstitute.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VarSome the Human Genomics Community. Available online: https://varsome.com/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick David and Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; Voelkerding, K.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, A.M.; DiStefano, M.T.; Hemphill, S.E.; Cushman, B.J.; Grant, A.R.; Siegert Rebecca, K.; Shen, J.; Chapin, A.; Boczek, N.J.; Schimmenti, L.A.; et al. Expert Specification of the ACMG/AMP Variant Interpretation for Genetic Hearing Loss. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1593–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deafness Variation Database. Available online: https://deafnessvariationdatabase.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Morgan, A.; Lenarduzzi, S.; Spedicati, B.; Cattaruzzi, E.; Murru, F.M.; Pelliccione, G.; Mazzà, D.; Zollino, M.; Graziano, C.; Ambrosetti, U.; et al. Lights and Shadows in the Genetics of Syndromic And-Syndromic Hearing Loss in the Italian Population. Genes 2020, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanany, M.; Rivolta, C.; Sharon, D. Worldwide Carrier Frequency and Genetic Prevalence of Autosomal Recessive Inherited Retinal Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2710–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Liang, P.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, B.; Yang, Y.; An, X.; Chen, J.; Zha, D. A Novel Splice Site Variant c.1183 + 1 G > C in DFNA5 Autosomal Dominant Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss in a Chinese Family. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guan, J.; Guan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, K.; Lin, Q.; Xiong, W.; Lan, L.; Zhao, C.; Xie, L.; et al. Further Evidence for “Gain-of-Function” Mechanism of DFNA5 Related Hearing Loss. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, B.; Rad, A.; Reisinger, E. The Many Faces of DFNB9: Relating OTOF Variants to Hearing. Genes 2020, 11, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodi, A.; Mariottini, A.; Passerini, I.; Murro, V.; Tachyla, I.; Bianchi, B.; Menchini, U.; Torricelli, F. MYO7A and USH2A Gene Sequence Variants in Italian patients with Usher Syndrome. Mol. Vis. 2014, 20, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, L.; Maltese, P.E.; Castori, M.; El Shamieh, S.; Zeitz, C.; Audo, I.; Zulian, A.; Marinelli, C.; Benedetti, S.; Costantini, A.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology in 591 Italian Probands with Nonsyndromic Pigmentosa and Usher Syndrome. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baux, D.; Vaché, C.; Blanchet, C.; Willems, M.; Baudoin, C.; Moclyn, M.; Faugère, V.; Touraine, R.; Isidor, B.; Dupin-Deguine, D.; et al. Combined Genetic Approaches Yield a 48% Diagnostic Rate in a Large Cohort of French Hearing-Impaired Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Increased Diagnostic Yield by Reanalysis of Data from a Hearing Gene Panel. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosaki, T.; Popp, M.W.; Maquat, L.E. Quality and Quantity Control of Gene Expression by Nonsense-Mediated MRNA Decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Yang, M.-N.; Shen, X.-F.; Wei, Q.-J.; Yao, J.; Lu, Y.-J.; Cao, X.; Xing, G.-Q. IVS8+1 DelG, a Novel Splice Site Mutation Causing DFNA5 Deafness in a Chinese Family. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 2510–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benefits and Risks of Cochlear Implants|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/cochlear-implants/benefits-and-risks-cochlear-implants (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Jafari, Z.; Fitzpatrick, E.M.; Schramm David, R.; Rouillon, I.; Koravand, A. Predictors of Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Pediatric Auditory: A Matched Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotto, D.; Greggio, M.; De Filippis, C.; Trevisi, P. Autosomal Recessive Non-Syndromic Deafness: Is AAV Gene Therapy a Real Chance? Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, A.E.; Eppsteiner, R.W.; Frees, K.; Tejani, V.; Sloan-Heggen, C.M.; Brown, C.; Abbas, P.; Dunn, C.; Hansen, M.R.; Gantz, B.J.; et al. Genetic Variants in the Peripheral Auditory System Significantly Adult Cochlear Implant Performance. Hear. Res. 2017, 348, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Sequence 5′- -3′ | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ADGRV1-gDNA_F | CGGGCCCCCCCTCGACATCAGGTTAAGGAAGCTGCCT | Amplification for cloning |
| ADGRV1-gDNA_R | ACCGCGGTGGCGGCCCCAGTTGCGCTTTATACAGAGT | |
| ATP11A-gDNA_F | CGGGCCCCCCCTCGACCGCCCATAGTCCTTGTC | Amplification for cloning |
| ATP11A-gDNA_R | ACCGCGGTGGCGGCCTGTAAATGTAACAGCACGGC | |
| GSDME-gDNA-F | CGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGCCAGGTTCAGCTTACTGTCCC | Amplification for cloning |
| GSDME-gDNA-R | ACCGCGGTGGCGGCCCCGAAGGGGGGTTTCCCATC | |
| OTOF (c.5533+13G>T)-gDNA-F | CGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGCCCACAGACAAGCATGTGGC | Amplification for cloning |
| OTOF (c.5533+13G>T)-gDNA-R | ACCGCGGTGGCGGCCGCCACATGCTTGTCTGTGGGC | |
| OTOF (c.5104-3C>G)-gDNA-F | CGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGCTCAGGCAGAGACCTGGG | Amplification for cloning |
| OTOF (c.5104-3C>G)-gDNA-R | ACCGCGGTGGCGGCCCTCTCCAGGGCAGGCCCTAAAC | |
| OTOGL-gDNA-F | CGGGCCCCCCCTCGATAATGTAATTTTAAACAAAATATCTACTCC | Amplification for cloning |
| OTOGL-gDNA-R | ACCGCGGTGGCGGCCATACAAAAACCTTTAAGTTAAAGAC | |
| USH2A-gDNA-F | CGGGCCCCCCCTCGACCACACGATTAAGGAGAAACTG | Amplification for cloning |
| USH2A-gDNA-R | ACCGCGGTGGCGGCCTCAGTTGTAATTTCTCTGGCTG | |
| pET01-EX1_RT-PCR_F | GATCGATCCGCTTCCTGCCCC | pET01 cDNA amplification |
| pET01-EX2_RT-PCR_R | CTGCCGGGCCACCTCCAGTGCC | |
| pET01-EX1_SEQ_F | GGATTCTTCTACACACCC | pET01 sequencing primers |
| pET01-EX2_SEQ_R | TCCACCCAGCTCCAGTTG |
| Family ID | Gene (Transcript) | Inheritance | Zigosity | Variant | ACMG/AMP | DVD | CADD | dbscSNV Score (ADA/RF) | SpliceAI Delta Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ADGRV1 (NM_032119.4) | AR | Compound Heterozygous | c.9447+1G>A | Path (PVS1, PM2_Supp, PM3) | NA | 33 | 0.999/0.938 | DL 0.98, DG 0.53 |
| B | ATP11A (NM_015205.3) | AD | Heterozygous | c.1221+5G>C | VUS (PM2_Supp, PP3, PP1) | NA | 23.3 | 0.999/0.982 | DL 0.97, DG 0.62 |
| C | GSDME (NM_004403.3) | AD | Heterozygous | c.1183+1G>A | Path (PVS1, PM2_Supp, PP1_Supp) | Likely Path | 33 | 0.999/0.814 | DL 1.00, DG 0.78 |
| D | OTOF (NM_001287489.2) | AR | Compound Heterozygous | c.5533+13G>T | VUS (PM2_Supp) | VUS | 4.6 | NA | DL 0.84, DG 1.00 |
| E | OTOF (NM_001287489.2) | AR | Homozygous | c.5104-3C>G | VUS (PM2_Supp, PP3, PM3_Supp) | NA | 24.4 | 0.999/0.96 | AL 0.96, AG 0.32 |
| F | OTOGL (NM_173591.7) | AR | Compound Heterozygous | c.6781+4A>C | VUS (PM2_Supp, PP3) | VUS | 22.7 | 0.999/0.916 | DL 0.21 |
| G | USH2A (NM_206933.4) | AR | Compound Heterozygous | c.1551-5T>G | VUS (PM2_Supp, PM3) | VUS | 17.5 | 0.358/0.486 | AL 0.50, AG 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosso, L.E.; Pianigiani, G.; Morgan, A.; Rubinato, E.; Paccagnella, E.; Lenarduzzi, S.; Wischmeijer, A.; Spedicati, B.; Girotto, G. Unraveling the Functional Impact of Splicing Variants in Inherited Hearing Disorders Through Minigene Splicing Assays. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092245
Rosso LE, Pianigiani G, Morgan A, Rubinato E, Paccagnella E, Lenarduzzi S, Wischmeijer A, Spedicati B, Girotto G. Unraveling the Functional Impact of Splicing Variants in Inherited Hearing Disorders Through Minigene Splicing Assays. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092245
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosso, Lara Emily, Giulia Pianigiani, Anna Morgan, Elisa Rubinato, Elisa Paccagnella, Stefania Lenarduzzi, Anita Wischmeijer, Beatrice Spedicati, and Giorgia Girotto. 2025. "Unraveling the Functional Impact of Splicing Variants in Inherited Hearing Disorders Through Minigene Splicing Assays" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092245
APA StyleRosso, L. E., Pianigiani, G., Morgan, A., Rubinato, E., Paccagnella, E., Lenarduzzi, S., Wischmeijer, A., Spedicati, B., & Girotto, G. (2025). Unraveling the Functional Impact of Splicing Variants in Inherited Hearing Disorders Through Minigene Splicing Assays. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092245







