Pancreatic Tissue Remodeling and Fibrosis After Irreversible Electroporation: A Histopathological and Thermal Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
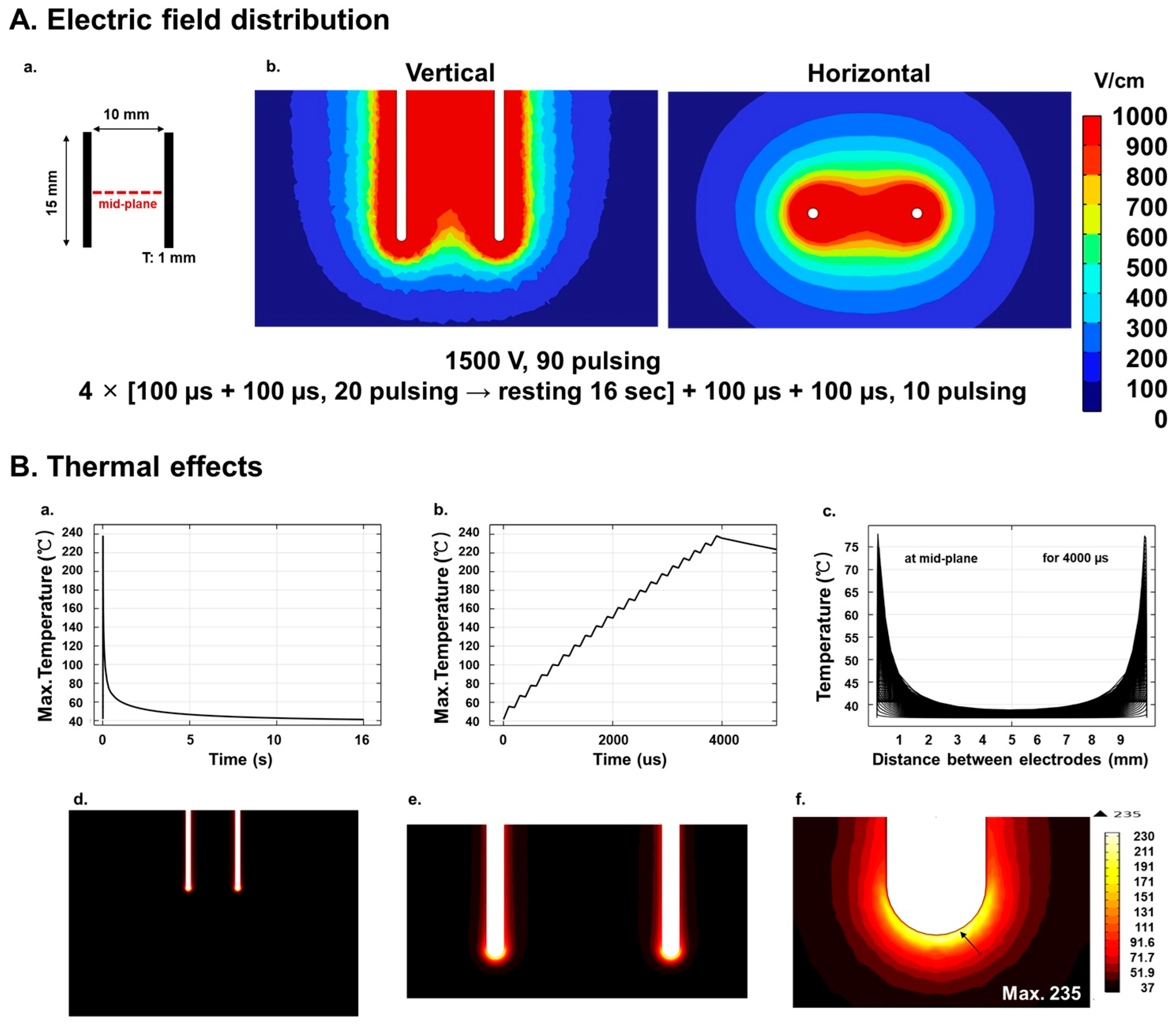
2.1. Numerical Analysis of Electric Field Distribution
2.2. Numerical Analysis of Temperature Distribution
2.3. Animals
2.4. IRE Procedure
2.5. Hematoxylin–Eosin Staining
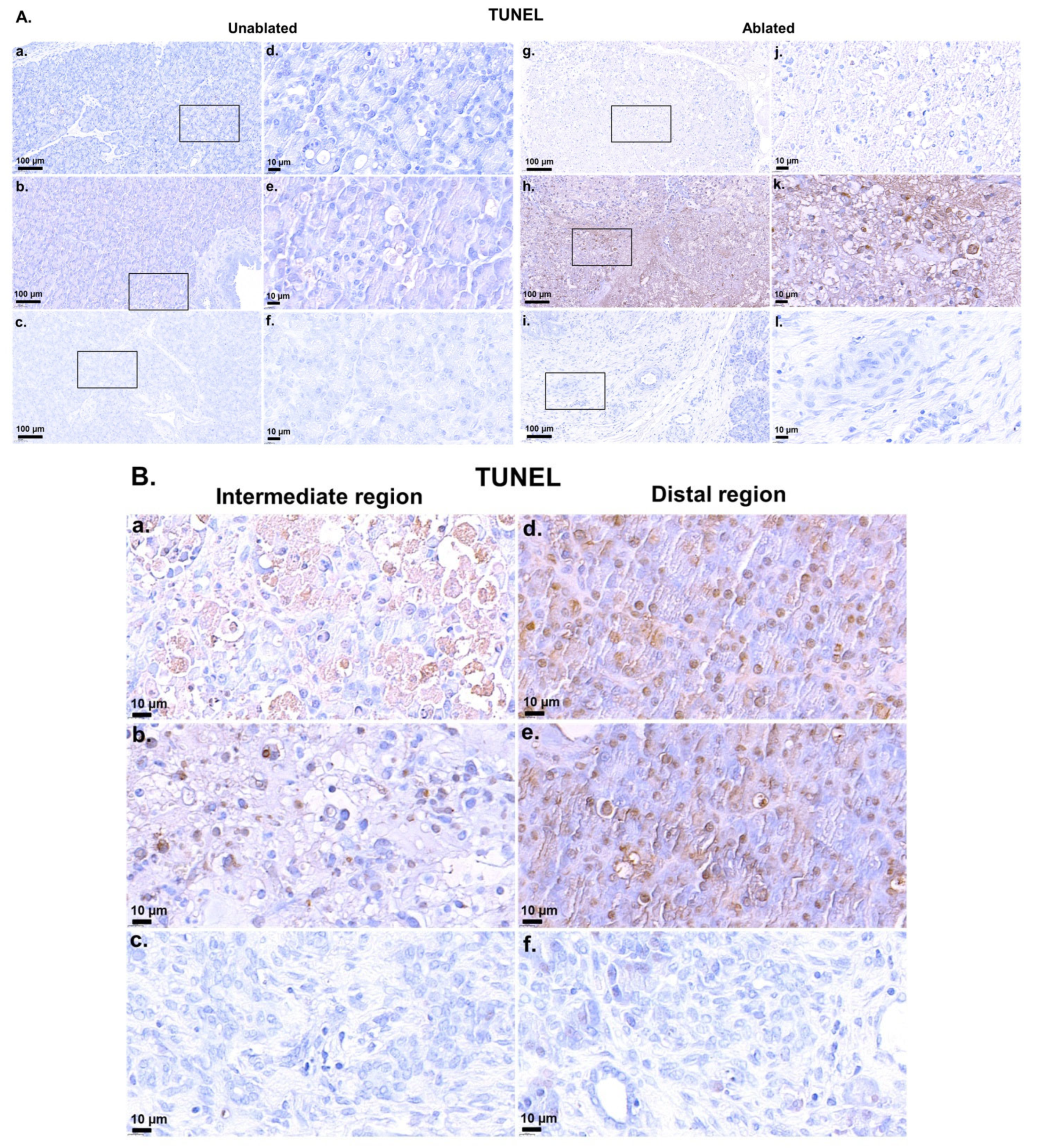
2.6. TdT-Mediated dUTP-Biotin Nick End-Labeling Staining
2.7. Masson’s Trichrome Staining
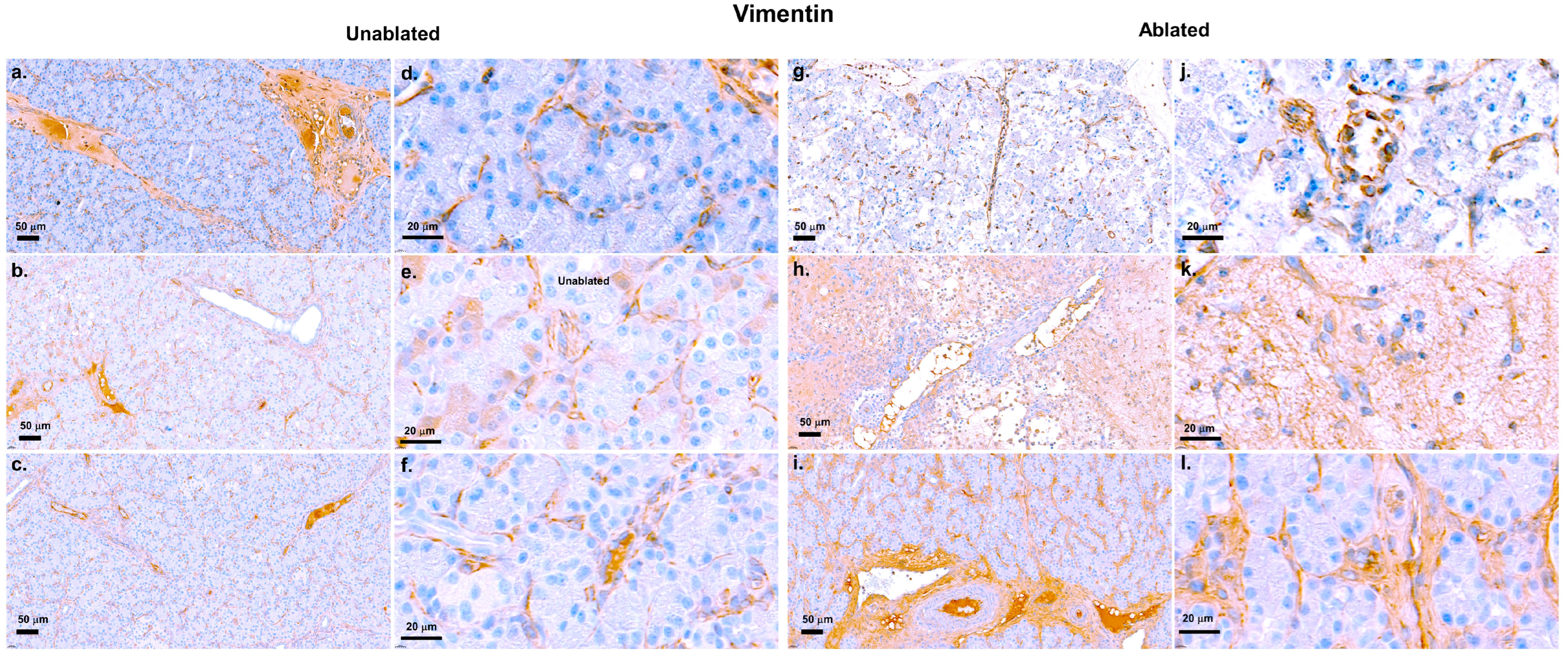
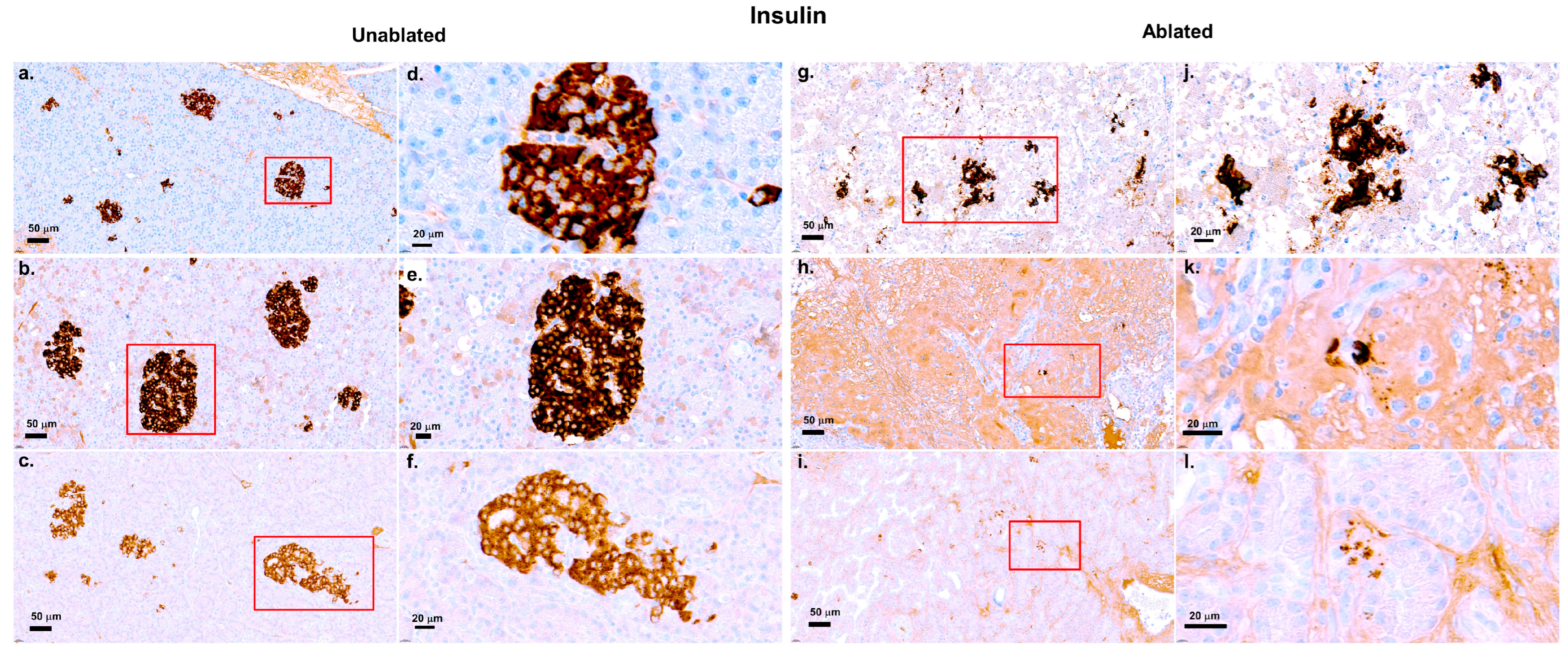
2.8. Immunohistochemistry Staining for Vimentin and Insulin
2.9. Immunofluorescence Staining for Ki-67
3. Results
3.1. Simulations, TUNEL Assay, and H&E Staining
3.2. Fibrosis Evaluation
3.3. Insulin Evaluation
3.4. Evaluation of Regeneration Using Ki-67 Staining
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IRE | Irreversible Electroporation |
| H&E | Hematoxylin–eosin |
| TUNEL | TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin Nick End-labeling |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered Saline |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry Staining |
References
- American Cancer Society. American Cancer Society annual cancer statistics 2024 shows drop in cancer mortality but increasing incidence for six of the top ten cancers. Dela J. Public Health 2024, 10, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pishvaian, M.J.; Brody, J.R. Therapeutic implications of molecular subtyping for pancreatic cancer. Oncology 2017, 31, 159–166, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S. World cancer report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfgang, C.L.; Herman, J.M.; Laheru, D.A.; Klein, A.P.; Erdek, M.A.; Fishman, E.K.; Hruban, R.H. Recent progress in pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 318–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, H.J.; Stam, A.G.; Geboers, B.; Vroomen, L.G.; Ruarus, A.; de Bruijn, B.; Tol, M.P.v.D.; Kazemier, G.; Meijerink, M.R.; de Gruijl, T.D. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer transiently alleviates immune suppression and creates a window for antitumor T cell activation. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1652532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzilli, R.; Serra, C.; Ricci, C.; Casadei, R.; Monari, F.; D’Ambra, M.; Minni, F. Radiofrequency ablation for advanced ductal pancreatic carcinoma: Is this approach beneficial for our patients? A systematic review. Pancreas 2011, 40, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsky, B.; Onik, G.; Mikus, P. Irreversible electroporation: A new ablation modality—Clinical implications. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, F.E.F.; Geboers, B.; Ruarus, A.H.; Schouten, E.A.C.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Puijk, R.S.; de Vries, J.J.; Meijerink, M.R.; Scheffer, H.J. Irreversible electroporation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 23, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Moris, D.; Pawlik, T.M. ASO author reflections: Irreversible electroporation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26 (Suppl. S3), 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Thomas, A.; Kluger, M.D. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2021, 48, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, A.; Bruinsma, B.G.; Jaramillo, M.; Yarmush, M.L.; Uygun, B.E. Rat liver regeneration following ablation with irreversible electroporation. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Maor, E.; Rubinsky, B. Nonthermal irreversible electroporation for tissue decellularization. J. Biomech. Eng. 2010, 132, 091003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.T.; Zhou, V.X.; Rubinsky, B. Using non-thermal irreversible electroporation to create an in vivo niche for exogenous cell engraftment. BioTechniques 2017, 62, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, L.; Nasto, A.; Busto, G.; Iovino, V.; Fristachi, R.; Bortone, S. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced solid pseudopapillary carcinoma of the pancreas: A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2018, 28, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, J.; White, S.A.; French, J.J.; Littler, P.; Manas, D.M. Systematic review of irreversible electroporation in the treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 40, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moris, D.; Machairas, N.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Prodromidou, A.; Ejaz, A.; Weiss, M.; Hasemaki, N.; Felekouras, E.; Pawlik, T.M. Systematic review of surgical and percutaneous irreversible electroporation in the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. Treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer with irreversible electroporation and intraoperative radiotherapy. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2024, 13, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.S.; Mendiratta-Lala, M.; Neal, J.; Hammad, H.; Hechtman, J.F.; Shlapak, D. Long-term follow-up experience with adjuvant therapy after irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 126, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, Z.L.; Jiang, C.; Gleim, T.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C.; Roderburg, C. Irreversible electroporation (IRE) in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A review of current clinical outcomes, mechanism of action and opportunities for synergistic therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bos, W.; de Bruin, D.M.; van Randen, A.; Dijkshoorn, M.L.; Wagstaff, P.G.; Scheffer, H.J. Thermal energy during irreversible electroporation and the influence of different ablation parameters. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardhana, G.; Wahab, R.A.; Gani, R.A.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Sadiq, A.; Rinaldi, I. Development of a thermal model for irreversible electroporation: An approach to estimate and optimize the IRE protocols. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2021, 16, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Kim, H.B.; Yim, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, E.S.; Seo, Y.S.; Jeen, Y.T.; Lee, H.S.; Chun, H.J.; et al. Effect of near-infrared pre-irradiation on irreversible electroporation treatment of rat gastric tissues. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Baik, K.Y.; Sung, C.K. Histological response to 5 kHz irreversible electroporation in a porcine liver model. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231171767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T.J.; Passeri, M.; Lorenzo, M.F.; Sulzer, J.K.; Lyman, W.B.; Swet, J.H.; Vrochides, D.; Baker, E.H.; Iannitti, D.A.; Davalos, R.V.; et al. Experimental high-frequency irreversible electroporation using a single-needle delivery approach for nonthermal pancreatic ablation in vivo. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 854–862.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, H.B.; Chung, J.; Kim, H.S.; Yi, J.H.; Park, J.K. Preclinical analysis of irreversible electroporation on rat liver tissues using a microfabricated electroporator. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2010, 16, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpentier, K.P.; Wolf, F.; Noble, L.; Winn, B.; Resnick, M.; Dupuy, D.E. Irreversible electroporation of the pancreas in swine: A pilot study. HPB 2010, 12, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, P.H.; Boyd, K.L.; Fickle, E.K.; Locuson, C.W. Subcutaneous meloxicam suspension pharmacokinetics in mice and dose considerations for postoperative analgesia. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 39, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur Clark, J. The 3Rs in research: A contemporary approach to replacement, reduction and refinement. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannitti, T.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Coacci, A.; Palmieri, B. Experimental and clinical efficacy of two hyaluronic acid-based compounds of different cross-linkage and composition in the rejuvenation of the skin. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2879–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liang, B.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chang, H.S.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.-L. Safety and feasibility of irreversible electroporation for the pancreatic head in a porcine model. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaoui, M.; Bauchet, A.L.; Fiette, L. Tissue sampling and processing for histopathology evaluation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1641, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parigiani, M.A.; Ketscher, A.; Timme, S.; Bronsert, P.; Schlimpert, M.; Kammerer, B.; Jacquel, A.; Chaintreuil, P.; Reinheckel, T. Conditional gene targeting reveals cell type-specific roles of the lysosomal protease cathepsin L in mammary tumor progression. Cancers 2020, 12, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Vlekkert, D.; Machado, E.; d’Azzo, A. Analysis of generalized fibrosis in mouse tissue sections with Masson’s trichrome staining. Bio Protoc. 2020, 10, e3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivova, Y.S.; Proshchina, A.E.; Barabanov, V.M.; Barinova, I.V.; Saveliev, S.V. Immunohistochemical detection of vimentin in pancreatic islet beta- and alpha-cells of macrosomic infants of diabetic and nondiabetic mothers. Early Hum. Dev. 2018, 117, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graefe, C.; Eichhorn, L.; Wurst, P.; Kleiner, J.; Heine, A.; Panetas, I.; Abdulla, Z.; Hoeft, A.; Frede, S.; Kurts, C.; et al. Optimized Ki-67 staining in murine cells: A tool to determine cell proliferation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 4631–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, R.V.; Bhonsle, S.; Neal, R.E., 2nd. Implications and considerations of thermal effects when applying irreversible electroporation tissue ablation therapy. Prostate 2015, 75, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Rubinsky, B. Molecular and histological study on the effects of electrolytic electroporation on the liver. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 125, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, K.M.; Brock, R.M.; Beitel-White, N.; Powar, M.; Orr, K.; Aycock, K.N.; Alinezhadbalalami, N.; Salameh, Z.S.; Eversole, P.; Tintera, B.; et al. Irreversible electroporation promotes a pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment and anti-tumor immunity in a mouse pancreatic cancer model. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnass, P.; van Veldhuisen, E.; Vogel, J.A.; Kok, H.P.; de Keijzer, M.J.; Schooneveldt, G.; de Haan, L.R.; Klaessens, J.H.; Scheffer, H.J.; Meijerink, M.R.; et al. Thermodynamic profiling during irreversible electroporation in porcine liver and pancreas: A case study series. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2020, 5, 109–132. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, R.M.; Beitel-White, N.; Davalos, R.V.; Allen, I.C. Starting a fire without flame: The induction of cell death and inflammation in electroporation-based tumor ablation strategies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Dipietro, S.A. Apoptosis and angiogenesis: An evolving mechanism for fibrosis. FASEB J. 2013, 10, 3893–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, H.; Ahn, H.K.; Han, B.; Lee, K.-C.; Song, Y.K.; Lim, S.; Yim, J.; Koh, J.; Jeon, Y.K. Increased CCL2/CCR2 axis promotes tumor progression by increasing M2 macrophages in MYC/BCL2 double-expressor DLBCL. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 5773–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Hong, W.; Guo, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B. Molecular Mechanism of Pancreatic Stellate Cells Activation in Chronic Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, C.J.; Siebeke, I.; Clements, D.; Miller, S.; Habgood, A.; John, A.E.; Navaratnam, V.; Hubbard, R.B.; Jenkins, G.; Johnson, S.R. Extracellular Matrix Cross-Linking Enhances Fibroblast Growth and Protects against Matrix Proteolysis in Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, C.H.; Victor, J.T. Mechanisms for the resolution of organ fibrosis. Physiology 2018, 34, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, A.V.; Lu, W.; Dey, S.; Bhattarai, P.; Haug, G.; Larby, J.; Chia, C.; Jaffar, J.; Westall, G.; Singhera, G.K.; et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: A precursor to pulmonary arterial remodelling in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00487–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Espinoza, L.; Huch, M. The balancing act of the liver: Tissue regeneration versus fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, S.A.; Ashour, N.A.; Marawan, M.E.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Fibrosis: Types, effects, markers, mechanisms for disease progression, and its relation with oxidative stress, immunity, and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Lopez-Ichikawa, M.; Rubinsky, B.; Chang, T.T. Normal and fibrotic liver parenchyma respond differently to irreversible electroporation. HPB 2019, 21, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.A.; van Veldhuisen, E.; Agnass, P.; Crezee, J.; Dijk, F.; Verheij, J.; van Gulik, T.M.; Meijerink, M.R.; Vroomen, L.G.; van Lienden, K.P.; et al. Time-dependent impact of irreversible electroporation on pancreas, liver, blood vessels and nerves: A systematic review of experimental studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.C.G., 2nd; White, R.R.; Bilimoria, M.M.; Kluger, M.D.; Iannitti, D.A.; Polanco, P.M.; Hammil, C.W.; Cleary, S.P.; Heithaus, R.E.; Welling, T.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of irreversible electroporation when used for the ablation of stage 3 pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Initial results from the DIRECT registry study. Cancers 2024, 16, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, A.; Gloor, B.; Kappeler, A.; Uhl, W.; Friess, H.; Büchler, M.W. Pancreatic stellate cells contribute to regeneration early after acute necrotising pancreatitis in humans. Gut 2002, 51, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.B.; Youm, J.Y.; Yang, J.-M.; Sim, S.B. Pancreatic Tissue Remodeling and Fibrosis After Irreversible Electroporation: A Histopathological and Thermal Perspective. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092222
Kim HB, Youm JY, Yang J-M, Sim SB. Pancreatic Tissue Remodeling and Fibrosis After Irreversible Electroporation: A Histopathological and Thermal Perspective. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092222
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hong Bae, Jin Young Youm, Joon-Mo Yang, and Sung Bo Sim. 2025. "Pancreatic Tissue Remodeling and Fibrosis After Irreversible Electroporation: A Histopathological and Thermal Perspective" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092222
APA StyleKim, H. B., Youm, J. Y., Yang, J.-M., & Sim, S. B. (2025). Pancreatic Tissue Remodeling and Fibrosis After Irreversible Electroporation: A Histopathological and Thermal Perspective. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092222






