Placental Morphology and Metabolomic Profile in Uncomplicated Metabolically Healthy Obese Pregnancy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Placental Tissue Collection
2.3. Placental Histology
2.4. Untargeted Metabolomics Using Chemical Isotope Labeling (CIL) GC-MS
2.5. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
2.6. Antioxidant Marker Assays
2.7. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation Markers
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pregnancy and Placental Characteristics
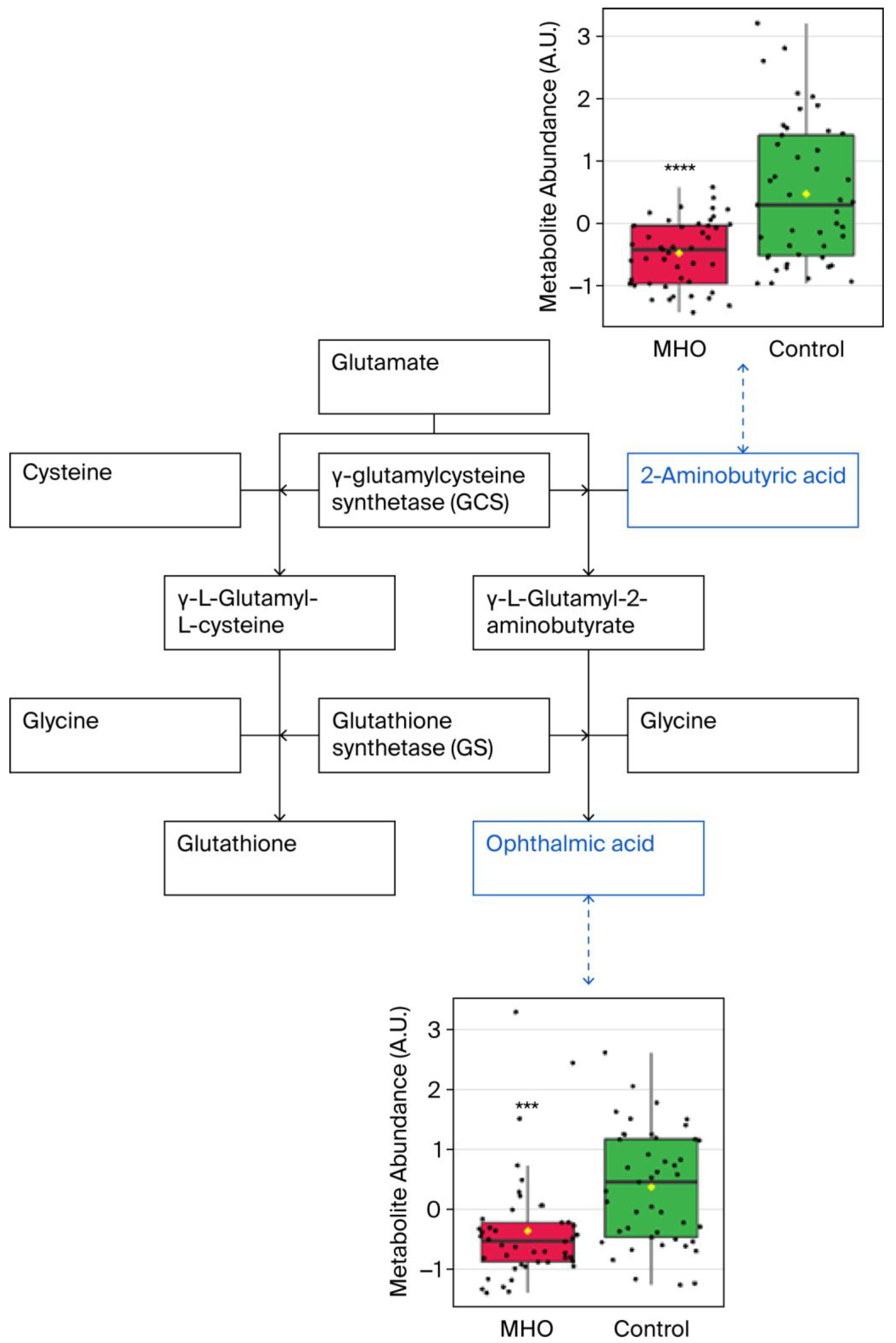
3.2. Changes in the Metabolome in MHO
3.3. Relationship Between Metabolite Changes and Placental Measurements
3.4. Placental Antioxidant Defense and Proinflammatory Markers
3.5. Lipid Peroxidation Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BPV | Birth Weight/Placental Volume Ratio |
| BPW | Birth Weight/Placental Weight Ratio |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| GDM | Gestational Diabetes Mellitus |
| LC–MS | Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| MHO | Metabolically Healthy Obesity |
| MUO | Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| VIP | Variable Importance in Projection |
| CIL GC-MS | Chemical Isotope Labeling Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| QTOF | Quadrupole Time-of-Flight |
References
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsoulis, A.; Paschou, S.A. Metabolically Healthy Obesity: Criteria, Epidemiology, Controversies, and Consequences. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeland, I.J.; Ross, R.; Després, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; et al. Visceral and Ectopic Fat, Atherosclerosis, and Cardiometabolic Disease: A Position Statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karelis, A.D.; Brochu, M.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. Can We Identify Metabolically Healthy but Obese Individuals (MHO)? Diabetes Metab. 2004, 30, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, L.; Wertz, M.; McDowell, I. Obesity in Pregnancy: Risks and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 97, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poston, L.; Caleyachetty, R.; Cnattingius, S.; Corvalán, C.; Uauy, R.; Herring, S.; Gillman, M.W. Preconceptional and Maternal Obesity: Epidemiology and Health Consequences. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, K.R.; Powell, T.L. Effects of Maternal Obesity on Placental Function and Fetal Development. Reproduction 2017, 153, R97–R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, E.W.; Most, J.; Altazan, A.D.; Boyle, K.E.; Redman, L.M. A Role for the Early Pregnancy Maternal Milieu in the Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity. Obesity 2021, 29, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizli, M.; Capitano, M.L.; Kua, K.L. Maternal Obesity and the Impact of Associated Early-Life Inflammation on Long-Term Health of Offspring. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, U.; Knorr, S.; Fuglsang, J.; Ovesen, P. Determinants of Maternal Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy: An Updated Overview. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 5320156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelstrup, L.; Damm, P.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Hansen, T.; Vaag, A.A.; Pedersen, O.; Clausen, T.D. Insulin Resistance and Impaired Pancreatic β-Cell Function in Adult Offspring of Women with Diabetes in Pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3793–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétursdóttir Maack, H.; Larsson, A.; Axelsson, O.; Olovsson, M.; Wikström, A.K.; Sundström Poromaa, I. Pregnancy in Metabolic Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Women. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, S.L.; Chan, D.W.K.; Ku, C.W.; Cheung, Y.B.; Godfrey, K.M.; Tan, K.M.L.; Chong, Y.S.; Shek, L.P.C.; Tan, K.H.; Chan, S.Y.; et al. Metabolic Health Status and Fecundability in a Singapore Preconception Cohort Study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 714.e1–714.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Rosendo, C.; Bugatto, F.; González-Domínguez, A.; Lechuga-Sancho, A.M.; Mateos, R.M.; Visiedo, F. Placental Adaptive Changes to Protect Function and Decrease Oxidative Damage in Metabolically Healthy Maternal Obesity. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.; Guo, E.; Pucchio, A.; Vrijer, B.; Shepherd, T.G.; Eastabrook, G. Maternal Obesity Reduces Placental Autophagy Marker Expression in Uncomplicated Pregnancies. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2020, 46, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneventi, F.; Bellingeri, C.; De Maggio, I.; Cavagnoli, C.; Fumanelli, S.; Ligari, E.; Fiandrino, G.; Cesari, S.; Spinillo, A. Placental Pathologic Features in Obesity. Placenta 2023, 144, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, B. Placental Origins of Preeclampsia: Challenging the Current Hypothesis. Hypertension 2008, 51, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, K.M. The Role of the Placenta in Fetal Programming—A Review. Placenta 2002, 23, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ph, D. The Value of Fetal Placental Ratio and Placental Efficiency in Term Human Pregnancy and Complications. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowden, A.L.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N.; Coan, P.M.; Constancia, M.; Burton, G.J. Placental Efficiency and Adaptation: Endocrine Regulation. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 3459–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Cho, S.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Sohn, I.S.; Hwang, H.S. The Significance of Placental Ratios in Pregnancies Complicated by Small for Gestational Age, Preeclampsia, and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2014, 57, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, C.; Taricco, E.; Cardellicchio, M.; Mandò, C.; Massari, M.; Savasi, V.; Cetin, I. The Role of Obesity and Gestational Diabetes on Placental Size and Fetal Oxygenation. Placenta 2021, 103, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Fowden, A.L.; Thornburg, K.L. Placental Origins of Chronic Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1509–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, L. Insights into the Role of Placenta Thickness as a Predictive Marker of Perinatal Outcome. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 0300060521990969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitierno, R.; Imparato, A.; Iavazzo, N.; Salzillo, C.; Marzullo, A.; Laganà, A.S.; Etrusco, A.; Agrifoglio, V.; D’amato, A.; Renata, E.; et al. Microscopic Changes and Gross Morphology of Placenta in Women Affected by Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Dietary Treatment: A Systematic Review. Open Med. 2025, 20, 20251142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.M.; Ali, L.E.; eed, E.M.; Siniyeh, A.A. Histomorphometric Study of Placental Blood Vessels of Chorion and Chorionic Villi Vascular Area among Women with Preeclampsia. Placenta 2022, 124, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwasel, S.H.; Abotalib, Z.; Aljarallah, J.S.; Osmond, C.; Al Omar, S.Y.; Harrath, A.; Thornburg, K.; Barker, D.J.P. The Breadth of the Placental Surface but Not the Length Is Associated with Body Size at Birth. Placenta 2012, 33, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benirschke, K.; Burton, G.J.; Baergen, R.N. Placental Shape Aberrations. In Pathology of the Human Placenta; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 80, pp. 377–393. ISBN 9783642239403. [Google Scholar]
- Nascente, L.M.d.P.; Grandi, C.; Aragon, D.C.; Cardoso, V.C. Placental Measurements and Their Association with Birth Weight in a Brazilian Cohort. Rev. Bras. De Epidemiol. 2020, 23, e200004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, T.; Subramaniam, R.K.; Johnson, W.M.S.; Prabhu, K. Placental Thickness & Its Correlation to Gestational Age & Foetal Growth Parameters—A Cross Sectional Ultrasonographic Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2012, 6, 1732–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.; Hernández, M.H.; Sérazin, V.; Vialard, F.; Dieudonné, M.N. Human Placental Adaptive Changes in Response to Maternal Obesity: Sex Specificities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda-Rivera, A.K.; Cruz-Gregorio, A.; Arancibia-Hernández, Y.L.; Hernández-Cruz, E.Y.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. RONS and Oxidative Stress: An Overview of Basic Concepts. Oxygen 2022, 2, 437–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, T.; Tian, K.; Li, Z.; Luo, F. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Scavenging Biomaterials for Anti-Inflammatory Diseases: From Mechanism to Therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics for Investigating Physiological and Pathophysiological Processes. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1819–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, A. Small Molecule Metabolites: Discovery of Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, O.; Demmelmair, H.; Segura, M.T.; Florido, J.; Rueda, R.; Campoy, C.; Koletzko, B. Effects of Obesity and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Placental Phospholipids. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 109, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattuoni, C.; Mandò, C.; Palmas, F.; Anelli, G.M.; Novielli, C.; Parejo Laudicina, E.; Savasi, V.M.; Barberini, L.; Dessì, A.; Pintus, R.; et al. Preliminary Metabolomics Analysis of Placenta in Maternal Obesity. Placenta 2018, 61, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthi, D.; Malik, P.; Mohamed, A.; Kousar, A.; Subramanian, R.A.; Manikyam, U.K. An Objective Histopathological Scoring System for Placental Pathology in Pre-Eclampsia and Eclampsia. Cureus 2020, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Han, W.; Chan, W.; Li, L. Metabolomic Coverage of Chemical-Group-Submetabolome Analysis: Group Classification and Four-Channel Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12108–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, W.; Yang, J.; Westaway, D.; Li, L. Development of Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Tissue Metabolomics and Its Application for Brain and Liver Metabolome Profiling in Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L. Determination of Total Concentration of Chemically Labeled Metabolites as a Means of Metabolome Sample Normalization and Sample Loading Optimization in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10723–10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L. Sample Normalization Methods in Quantitative Metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1430, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, L. Differential 12C-/13C-Isotope Dansylation Labeling and Fast Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry for Absolute and Relative Quantification of the Metabolome. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3919–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Tseng, C.L.; Huan, T.; Li, L. IsoMS: Automated Processing of LC-MS Data Generated by a Chemical Isotope Labeling Metabolomics Platform. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4675–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Zuniga, A.; Stanislaus, A.E.; Wu, Y.; Huan, T.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. MyCompoundID: Using an Evidence-Based Metabolome Library for Metabolite Identification. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, K.S.M.; Oliveira, G.M.; Beltrame, M.; Coelho, J.M.F.; Pimentel, R.F.W.; Das Merces, M.C. Effectiveness of Auriculotherapy on Stress Reduction in Health Workers: A Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2022, 30, e3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K. Alternatives to P Value: Confidence Interval and Effect Size. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2016, 69, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, M.; Kadam, L.; Kim, J.; Zemaitis, K.J.; Veličković, D.; Gao, Y.; Wu, R.; Fillmore, T.L.; Orton, D.; Williams, S.M.; et al. Advanced Multi-Modal Mass Spectrometry Imaging Reveals Functional Differences of Placental Villous Compartments at Microscale Resolution. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mierlo, K.M.C.; Dello, S.A.W.G.; De Jong, M.C.; Van Eijk, H.M.H.; De Kok, T.M. Ophthalmic Acid as a Read-out for Hepatic Glutathione Metabolism in Humans. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2017, 3, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.D.; Danielski, L.G.; Novochadlo, M.M.; Goldim, M.P.S.; Joaquim, L.; Metzker, K.L.L.; De Carli, R.J.; Denicol, T.; Cidreira, T.; Vieira, T.; et al. Vitamin B6 Reduces Oxidative Stress in Lungs and Liver in Experimental Sepsis. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019, 91, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, M.M.; Zhou, S.Q.; Kummerow, F.A. Vitamin B 6 Compounds Are Capable of Reducing the Superoxide Radical and Lipid Peroxide Levels Induced by H 2 O 2 in Vascular Endothelial Cells in Culture. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2009, 79, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibley, C.P.; Turner, M.A.; Cetin, I.; Ayuk, P.; Boyd, C.A.R.; D’Souza, S.W.; Glazier, J.D.; Greenwood, S.L.; Jansson, T.; Powell, T. Placental Phenotypes of Intrauterine Growth. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 58, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, I.; Nalinakumari, S.D.; Ponniraivan, K. Effect of Increased Prepregnancy Body Mass Index on Placental Morphologic Features in Gestational Diabetes. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2018, 12, AC13–AC17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.C.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Placental Function in Maternal Obesity. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanianskii, D.A.; Jarzebska, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; O’sullivan, J.F.; Rodionov, R.N. Beta-Aminoisobutyric Acid as a Novel Regulator of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2019, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, M.; Yao, T.; Hu, G.; Wan, G.; Chang, B. Signaling Metabolite β-Aminoisobutyric Acid as a Metabolic Regulator, Biomarker, and Potential Exercise Pill. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Salihovic, S.; Sundström, J.; Elmståhl, S.; Hammar, U.; Dekkers, K.; Ärnlöv, J.; Smith, J.G.; Engström, G.; Fall, T. Metabolic Profiling of Obesity With and Without the Metabolic Syndrome: A Multisample Evaluation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Chen, W.Y.; Tsai, P.J.; Cheng, F.C.; Kuo, J.S. Effect of Diethylmaleate on Liver Extracellular Glutathione Levels before and after Global Liver Ischemia in Anesthetized Rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 53, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, T.; Baran, R.; Suematsu, M.; Ueno, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Sakurakawa, T.; Kakazu, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Robert, M.; Nishioka, T.; et al. Differential Metabolomics Reveals Ophthalmic Acid as an Oxidative Stress Biomarker Indicating Hepatic Glutathione Consumption. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16768–16776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dello, S.A.W.G.; Neis, E.P.J.G.; de Jong, M.C.; van Eijk, H.M.H.; Kicken, C.H.; Olde Damink, S.W.M.; Dejong, C.H.C. Systematic Review of Ophthalmate as a Novel Biomarker of Hepatic Glutathione Depletion. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, S.; Pramadhani, A. Vitamin B, Role of Gut Microbiota and Gut Health. In Vitamin B and Vitamin E—Pleiotropic and Nutritional Benefits; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024; Volume 11, p. 13. ISBN 0000957720. [Google Scholar]
- Vrolijk, M.F.; Opperhuizen, A.; Jansen, E.H.J.M.; Hageman, G.J.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. The Vitamin B6 Paradox: Supplementation with High Concentrations of Pyridoxine Leads to Decreased Vitamin B6 Function. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 44, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albersen, M.; Bosma, M.; Jans, J.J.M.; Hofstede, F.C.; Van Hasselt, P.M.; De Sain-van Der Velden, M.G.M.; Visser, G.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M. Vitamin B6 in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Children. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørke-Monsen, A.L.; Ulvik, A.; Nilsen, R.M.; Midttun, Ø.; Roth, C.; Magnus, P.; Stoltenberg, C.; Vollset, S.E.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; Ueland, P.M. Impact of Pre-Pregnancy BMI on B Vitamin and Inflammatory Status in Early Pregnancy: An Observational Cohort Study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsaperla, R.; Saporito, M.A.N.; Di Stefano, V.; Mauceri, L.; Quattrocchi, E.; Musolino, A.; Corsello, G. Pyridoxine Supplementation during Pregnancy, Lactation and the First Months of Life: A Review of the Literature. Curr. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 21, 613–619. [Google Scholar]
- Drejza, M.A.; Rylewicz, K.; Majcherek, E.; Gross-Tyrkin, K.; Mizgier, M.; Plagens-Rotman, K.; Wójcik, M.; Panecka-Mysza, K.; Pisarska-Krawczyk, M.; Kędzia, W.; et al. Markers of Oxidative Stress in Obstetrics and Gynaecology—A Systematic Literature Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalto, D.B.; Matte, J.J. Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) and the Glutathione Peroxidase System; a Link between One-Carbon Metabolism and Antioxidation. Nutrients 2017, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, Y.; O’Rourke, B.; Gilbert, L.R.; Keeling, C.; Matthews, D.E.; Stacpoole, P.W.; Gregory, J.F. Vitamin B-6 Restriction Tends to Reduce the Red Blood Cell Glutathione Synthesis Rate without Affecting Red Blood Cell or Plasma Glutathione Concentrations in Healthy Men and Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.P.; Davis, S.R.; Mackey, A.D.; Scheer, J.B.; Williamson, J.; Iii, J.F.G. Vitamin B-6 Deficiency Suppresses the Hepatic Transsulfuration Pathway but Increases Glutathione Concentration in Rats Fed AIN-76A or AIN-93G Diets 1. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.-Y.; Cho, Y.-O. Effect of Vitamin B6 Deficiency on Antioxidative Status in Rats with Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2009, 3, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrini, L.; Bergami, R.; Fiorentini, D.; Marchetti, M.; Landi, L.; Tolomelli, B. Vitamin B6 Deficiency Affects Antioxidant Defences in Rat Liver and Heart. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1998, 46, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Ha, S.K. Uric Acid Puzzle: Dual Role as Anti-Oxidantand pro-Oxidant. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2014, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knöfler, M.; Haider, S.; Saleh, L.; Pollheimer, J.; Gamage, T.K.J.B.; James, J. Human Placenta and Trophoblast Development: Key Molecular Mechanisms and Model Systems. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3479–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, B.J.; Hanson, M.A.; Casanello, P. Role of Nitric Oxide in Placental Vascular Development and Function. Placenta 2011, 32, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantape, T.; Kongwattanakul, K.; Arribas, S.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Iampanichakul, M.; Settheetham-Ishida, W.; Phuthong, S. Maternal Obesity Alters Placental and Umbilical Cord Plasma Oxidative Stress, a Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, M.E.; Baker, B.; Duval, C.; Gaudreault, V.; Jones, R.L.; Girard, S. Alarmins at the Maternal–Fetal Interface: Involvement of Inflammation in Placental Dysfunction and Pregnancy Complications1. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brombach, C.; Tong, W.; Giussani, D.A. Maternal Obesity: New Placental Paradigms Unfolded. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.H.; O’Malley, A.J.; Mauri, L. Receiver-Operating Characteristic Analysis for Evaluating Diagnostic Tests and Predictive Models. Circulation 2007, 115, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Smith, G.I.; Palacios, H.H.; Farabi, S.S.; Yoshino, M.; Yoshino, J.; Cho, K.; Davila-Roman, V.G.; Shankaran, M.; Barve, R.A.; et al. Cardiometabolic Characteristics of People with Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obesity. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 745–761.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Bhattacharjee, J.; Vasanthan, T.; Harris, C.S.; Bainbridge, S.A.; Adamo, K.B. Metabolomics to Understand Placental Biology: Where Are We Now? Tissue Cell 2021, 73, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
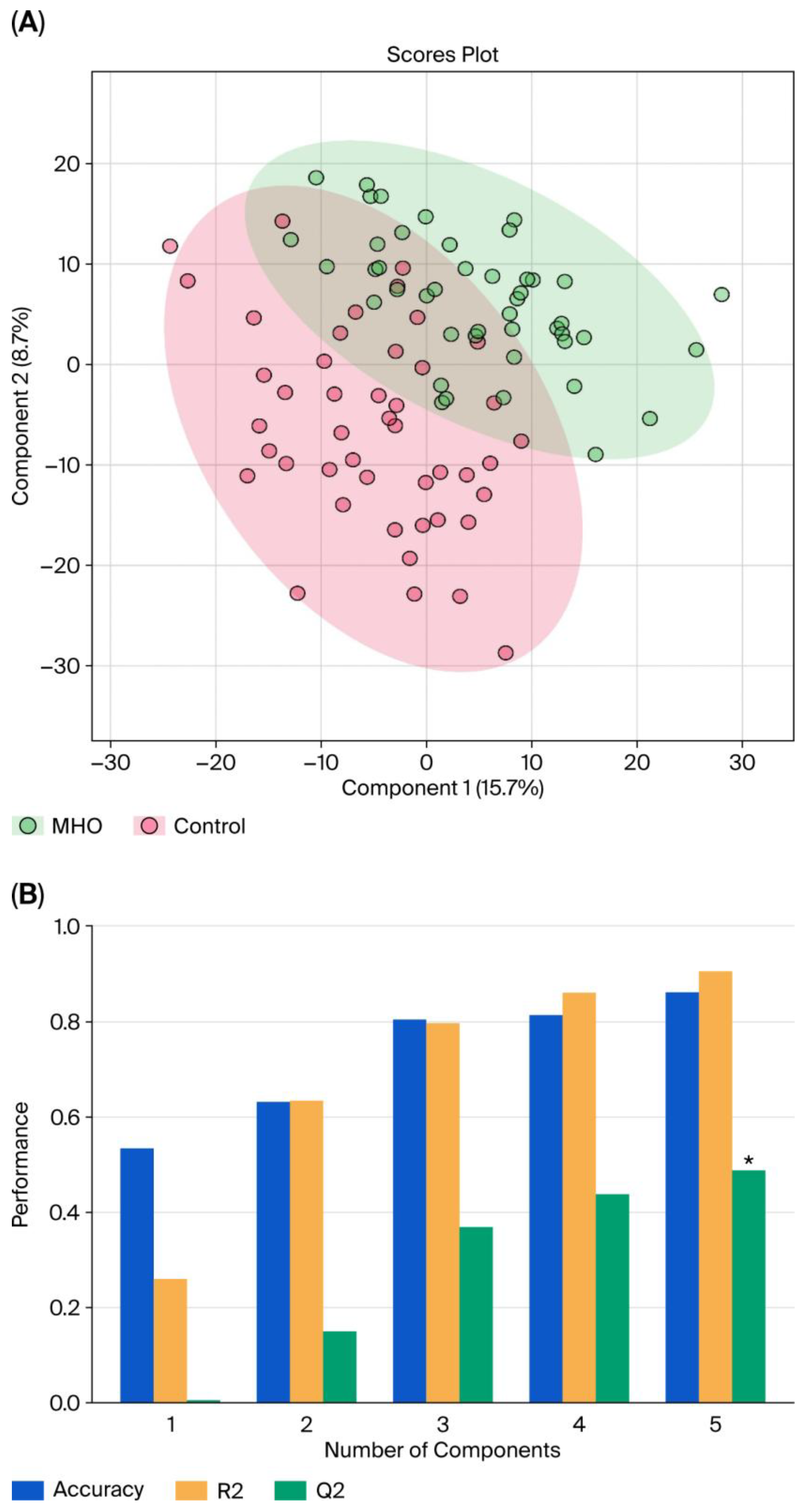

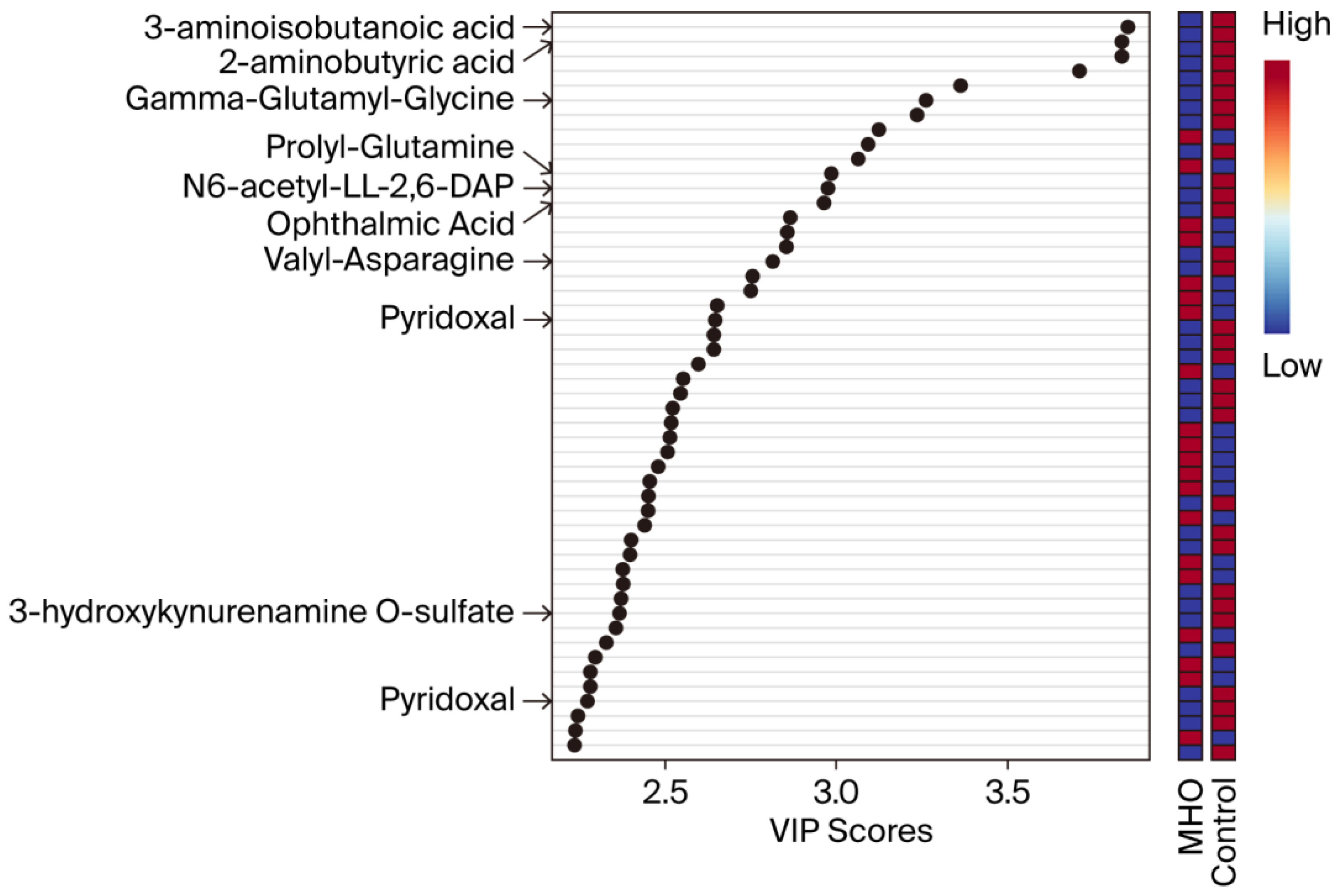
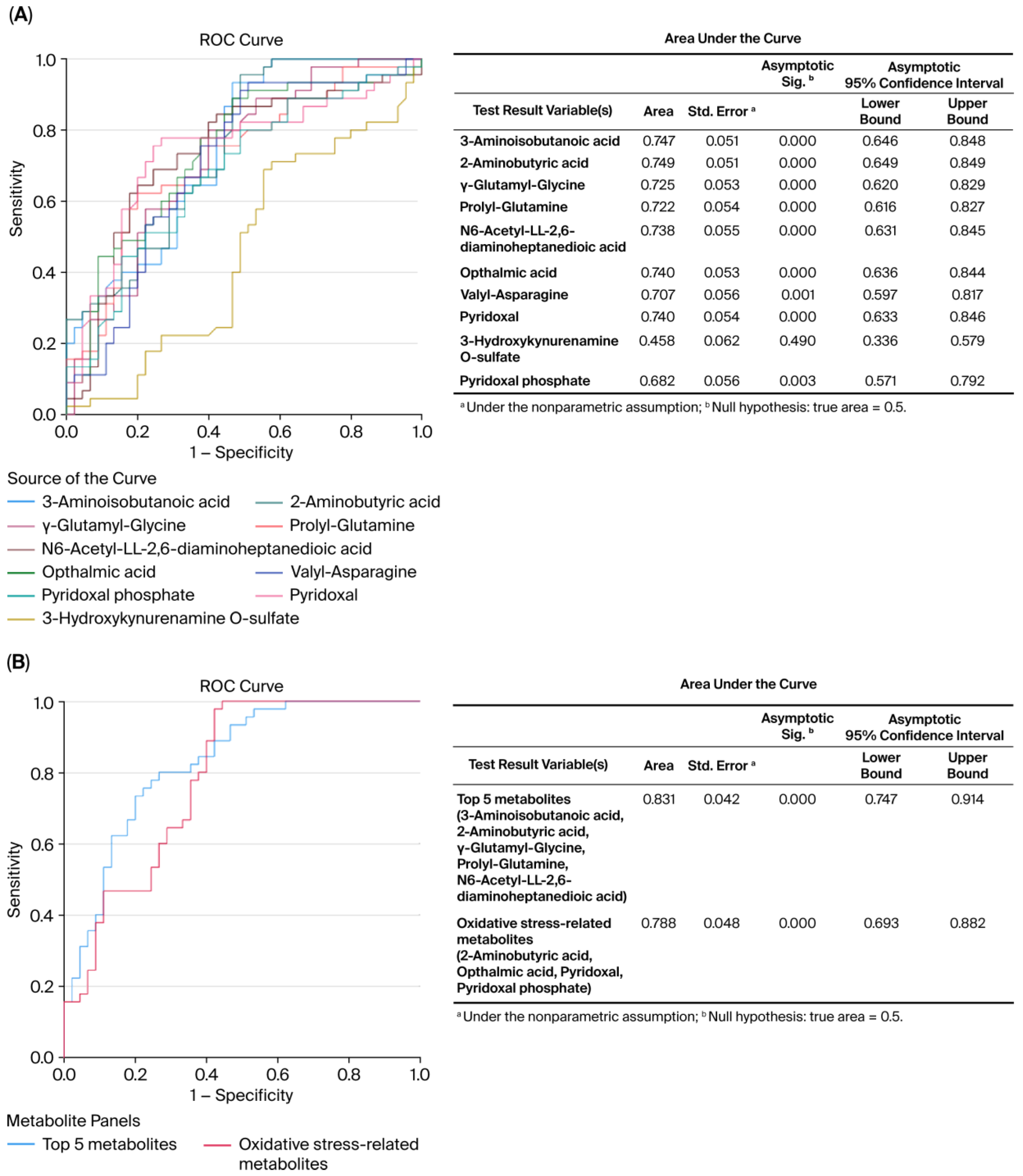
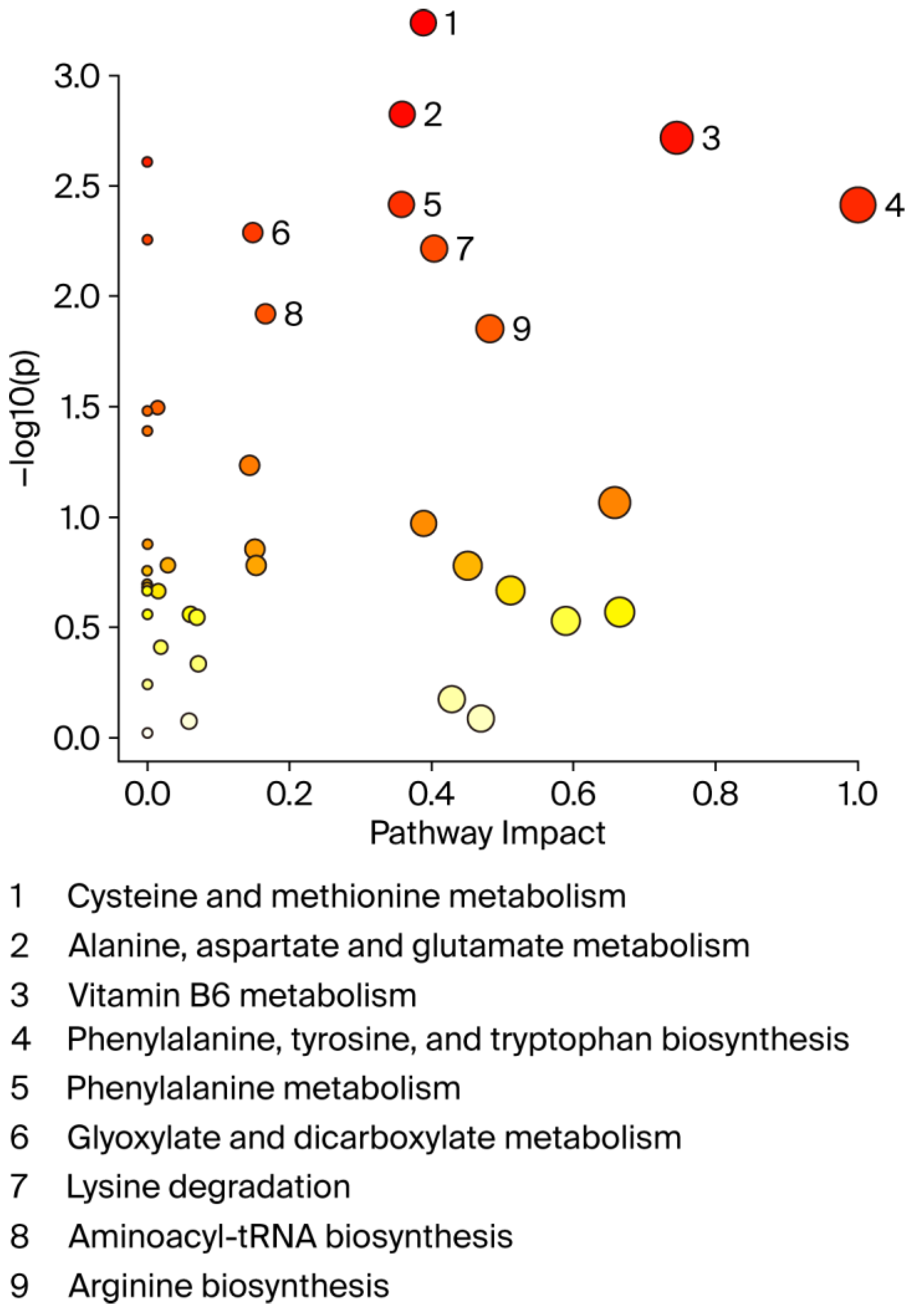


| C | MHO | p-Value | d/V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placental weight 1 (g) | 592.3 ± 111.0 | 762.0 ± 164.3 | 0.0026 | 1.2 |
| Placental length (cm) | 16.7 ± 2.1 | 18.1 ± 2.0 | 0.0685 | 0.7 |
| Placental breadth (cm) | 15.1 ± 1.5 | 16.9 ± 2.0 | 0.0091 | 1.0 |
| Placental thickness (cm) | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 0.0049 | 1.2 |
| Placental surface area (cm2) | 199.6 ± 34.9 | 243.7 ± 52.7 | 0.0116 | 1.0 |
| Distal villous hypoplasia (focal or diffuse) 2 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NS | ND |
| Syncytial knots | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NS | ND |
| Chorangiosis | 0 (0) | 2 (13) | NS | 0.3 |
| Delayed villous maturation (focal or diffuse) | 1 (7) | 5 (33) | NS | 0.3 |
| Avascular fibrotic villi | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NS | ND |
| Increased focal perivillous fibrin deposition | 1 (7) | 1 (7) | NS | 0.0 |
| Massive perivillous fibrin deposition | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NS | ND |
| Maternal floor infarct pattern | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NS | ND |
| Intervillous thrombi | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NS | ND |
| Chronic inflammation | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NS | ND |
| Compound 1 | Fold Change | p Adjusted | p-Value |
| 3-Aminoisobutanoic acid (BAIBA) | 0.6804 | 0.0011 | <0.0001 |
| 2-Aminobutyric acid (2AB) | 0.7071 | 0.0011 | <0.0001 |
| Gamma-glutamyl-glycine (γ-Glu-Gly) | 0.8057 | 0.0198 | 0.0001 |
| Ophthalmic acid (OPT) | 0.6763 | 0.0448 | 0.0004 |
| Prolyl-glutamine (Pro-Gln) | 0.7571 | 0.0448 | 0.0003 |
| N6-acetyl-LL-2,6-diaminoheptanedioic acid (N6-acetyl-LL-2,6-DAP) | 0.8121 | 0.0448 | 0.0003 |
| Valyl-asparagine (Val-Asn) | 0.7438 | 0.0698 | 0.0007 |
| Pyridoxal | 0.6582 | 0.1130 | 0.0015 |
| 3-Hydroxykynurenamine O-sulfate (C05636) | 0.7918 | 0.1967 | 0.0049 |
| Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) | 0.8017 | 0.2440 | 0.0069 |
| Metabolite | Placental Weight | Placental Thickness | Placental Breadth | Placental Surface Area | ||||
| r | p | r | p | r | p | |||
| BAIBA | −0.2961 | 0.0046 * | −0.5406 | <0.0001 * | −0.2792 | 0.0077 * | 0.1339 | 0.2083 |
| 2-aminobutyric acid | −0.2927 | 0.0051 * | −0.5379 | <0.0010 * | −0.2754 | 0.0086 * | −0.1359 | 0.2014 |
| γ-Glu-Gly | −0.0939 | 0.3787 | −0.3125 | 0.0075 * | −0.2448 | 0.0200 * | −0.1715 | 0.1060 |
| Ophthalmic acid | −0.1531 | 0.1497 | −0.2563 | 0.0298 * | −0.2283 | 0.0304 * | −0.1709 | 0.1073 |
| Prolyl-glutamine | −0.1345 | 0.2061 | −0.2930 | 0.0125 * | −0.1086 | 0.2061 | −0.0696 | 0.5144 |
| N6-acetyl-LL-2,6-DAP | −0.3018 | 0.0038 * | −0.4134 | 0.0003 * | −0.1559 | 0.1423 | −0.0959 | 0.3688 |
| Valyl-asparagine | −0.2324 | 0.0540 * | −0.3960 | 0.1569 | −0.1282 | 0.0164 * | −0.1098 | 0.3030 |
| Pyridoxal | −03432 | 0.0009 * | −0.2125 | 0.0731 | −0.2640 | 0.0119 * | −0.1826 | 0.0849 |
| C05636 | −0.0625 | 0.5583 | −0.0768 | 0.5211 | −0.0168 | 0.8752 | −0.0701 | 0.5115 |
| Pyridoxal phosphate | −0.2298 | 0.0293 * | −0.2265 | 0.5580 | −0.0720 | 0.4998 | 0.0406 | 0.7041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarr, O.; Rajagopaul, A.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Grynspan, D.; Eastabrook, G.; Li, L.; Regnault, T.R.H.; de Vrijer, B. Placental Morphology and Metabolomic Profile in Uncomplicated Metabolically Healthy Obese Pregnancy. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092149
Sarr O, Rajagopaul A, Zhao S, Wang X, Grynspan D, Eastabrook G, Li L, Regnault TRH, de Vrijer B. Placental Morphology and Metabolomic Profile in Uncomplicated Metabolically Healthy Obese Pregnancy. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092149
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarr, Ousseynou, Akasham Rajagopaul, Shuang Zhao, Xiaohang Wang, David Grynspan, Genevieve Eastabrook, Liang Li, Timothy R. H. Regnault, and Barbra de Vrijer. 2025. "Placental Morphology and Metabolomic Profile in Uncomplicated Metabolically Healthy Obese Pregnancy" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092149
APA StyleSarr, O., Rajagopaul, A., Zhao, S., Wang, X., Grynspan, D., Eastabrook, G., Li, L., Regnault, T. R. H., & de Vrijer, B. (2025). Placental Morphology and Metabolomic Profile in Uncomplicated Metabolically Healthy Obese Pregnancy. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092149







